Neuromuscular Physiology
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
How do signals travel along the axon?
A signal (binding of neurotransmitter to dendrite) is received on one end, relayed over the axon, and upon reaching the other end, releases a signal (neurotransmitter) that communicates with other neurons
How do we establish a signal over the length of the cell?
Establish a charge across the plasma membrane (create polarized membranes) then trigger depolarization on one end of the cell; depolarization will spread as a wave over the length of the axon and trigger the release of neurotransmitters upon reaching the end of the axon
As the depolarization wave moves down a nerve, it maintains the same ___________
strength
Frequency modulation
a more intense contraction of muscle occurs with a higher firing frequency
The strength of a muscle contraction depends on (2):
the number of motor units activated AND the frequency of nerve firing
Electric potenial
ability of electrons to due work based on a concentration gradient
Name of two equations used to determine electrical potential
Nernst equation and Goldman equation
Membrane potential
difference in electrical charge across a cell's plasma membrane; the voltage difference between the inside and outside of the cell
The membrane potential is the charge _______ the cell minus the charge _______ the cell
inside; outside
If the inside of the cell is negative compared to the outside (as it usually is), the membrane potential is ________
negative
If the inside becomes positive compared to the outside (like during an action potential), the membrane potential becomes _________
positive
Threshold potential
miniumum potential that will elicit excitation; will not reestablish resting potential past this point
Depolarization
Increase in the membrane potential
Polarization
Decrease in the membrane potential
Repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell
What is the threshold potential?
-55mV
What happens when a stimulus is powerful enough to reach the threshold potential?
membrane will rapidly depolarize and cause an action potential
action potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell
The difference between the threshold value and resting membrane potential is called ___________
excitability
If there is low extracellular potassium, there will be a _______ concentration gradient
higher
If there is a higher concentration gradient between intra and extracellular concentration of K, a ___________ stimulus is required for depolarization
higher
A higher concentration gradient will cause a __________ membrane potential
decreased (further from threshold)
Hyperpolarization
membrane potential becomes more negative due to higher extracellular potassium
If there is high extracellular potassium, there will be a _______ concentration gradient
lower
A lower concentration gradient will cause a __________ membrane potential
higher (closer to the threshold value)
If there is a lower concentration gradient between intra and extracellular concentration of K, a ___________ stimulus is required for depolarization
smaller
Calcium will __________ a nerve
stabilize
What effect does calcium have on the threshold value?
it raises the threshold value
If there is high extracellular Ca, the threshold value will ___________
increase
If there is higher extracellular Ca, a ________ stimulus will be required to reach the threshold value
greater
______ potassium or _______ calcium will cause a lower excitability
low; high
______ potassium or _______ calcium will cause a higher excitability
high; low
Excitability
ease with which a stimulus can initiate an action potential
Excitable cells have a ___________ resting membrane potential
higher
Resting membrane potential
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active (-90mV)
What ion is the main contributor to the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
Potassium
Why is potassium the main contributor to the resting membrane potential?
it has the ability to travel across the membrane very readily when the membrane is resting; it is very permeable
There are high concentrations of __________ inside the cell and high concentrations of _________ outside the cell
Potassium; sodium
The longer a cell is in a resting the state, it loses its charge. Why?
1.) the cell loses potassium since it is highly permeable
2.) some sodium cells will leak into the cell
Potassium Leak channels
allow a small amount of potassium to leak out of the cell down the concentration gradient
What establishes the resting membrane potential?
sodium potassium pump
Na/K exchange pump
pumps potassium into the cell and sodium out of the cell
The Na/K exchange pump requires _____. Why?
ATP; potassium and sodium are being pumped against their concentration gradients
The sodium-potassium pump moves ________ sodium molecules ________ the cell and _________ potassium molecules __________ the cell
Three; out
Two; into
Action potential
Change in the membrane potential that reverses the polarity of the cell (such as going from a negative to a positive membrane potential)
How is depolarization accomplished?
Since it is an increase in the membrane potential, an influx of positive ions into the neuron
Depolarization is initiated by allowing extracellular _________ to flow back into the cell
Sodium
Voltage gated Na channel
Channel with a gate that is closed between -90 and -50 mV, but opens above -50 mV, allowing Na to flow back into the cell along its concentration gradient
As the membrane potential becomes closer to the ________ value, more Voltage gated Na channels will __________
threshold; open
The opening of the voltage gated Na channel is a __________ feedback loop
positive
Two channels that help to reestablish the resting potential after depolarization
1.) potassium leak channels
2.) Na/K pump
How do the Na-K pump and K leak channels work to establish the resting potential?
-Na/K pump moves 3 NA out the cell and 2 K in of the cell using ATP
-this creates a high intracellular concentration of K and low intracellular concentration of Na inside the cell
-then, the K leak channel allows only K to move out of the cell, which creates the resting potential of -90mV
Refractory period
a period of inactivity after an action potential occurs where the cell membrane is unable to mount another action potential
Why does the refractory period take place?
once Na channels close, they cannot be opened again for a period of time
Absolute refractory period
no impulse can cause an action potential
When does the absolute refractory period occur?
during the action potential
Relative refractory period
maximal (subthreshold) impulse can cause an action potential, but threshold stimulus will not elicit action potential
When does the relative refractory period occur?
during repolarization
Total refractory period
absolute refractory period + relative refractory period
Positions of the gates of Na gated channel at rest
outside gate is closed
inside gate is opened
Positions of the gates of Na gated channel during depolarization
outside gate is opened
inside gate is opened
Positions of the gates of Na gated channel during refractory period
outside gate is opened
inside gate is closed
switch terms and definitions
switch terms and definitions
total refractory period
black arrow

relative refractory period
blue box
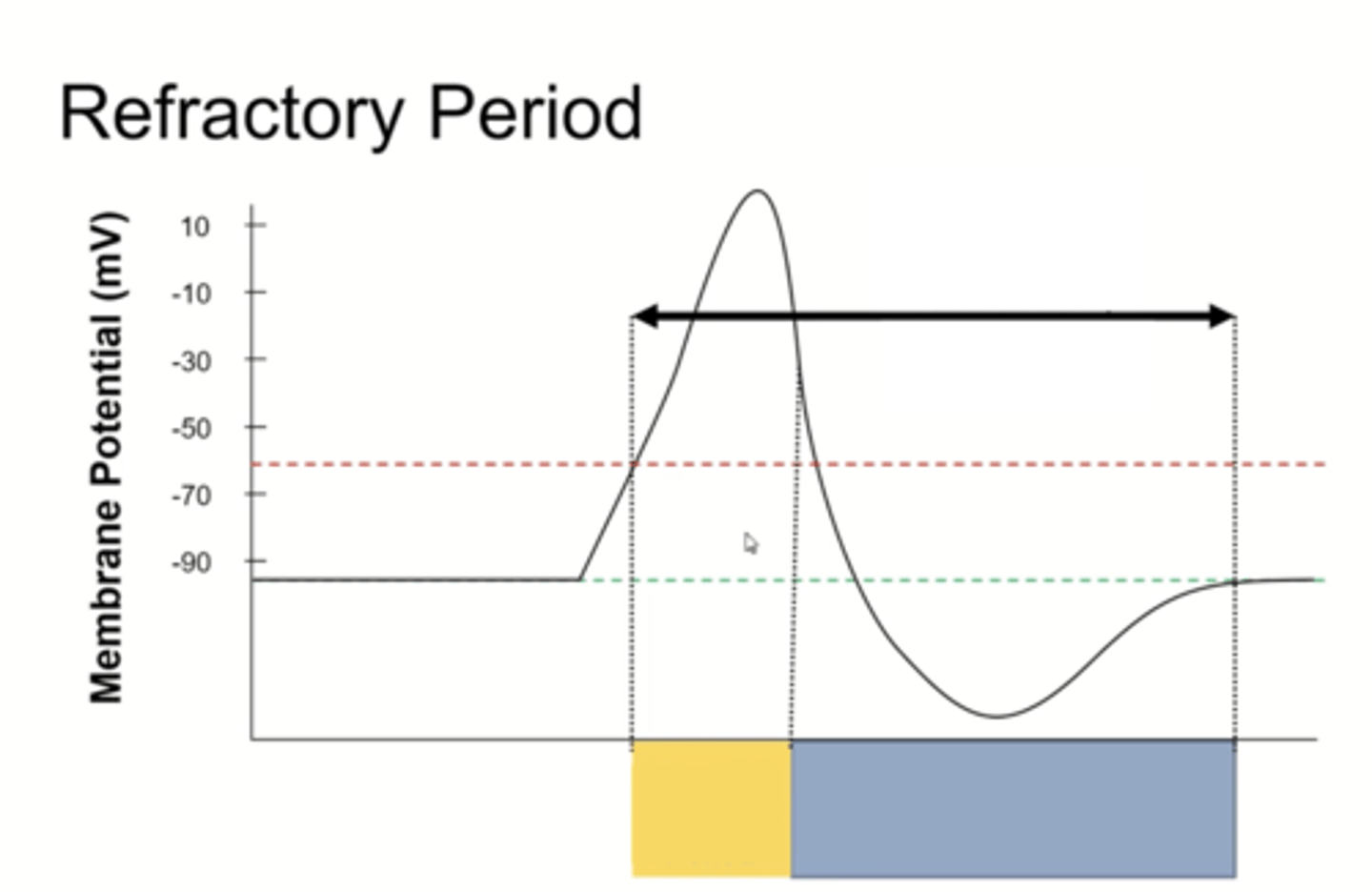
absolute refractory period
yellow box
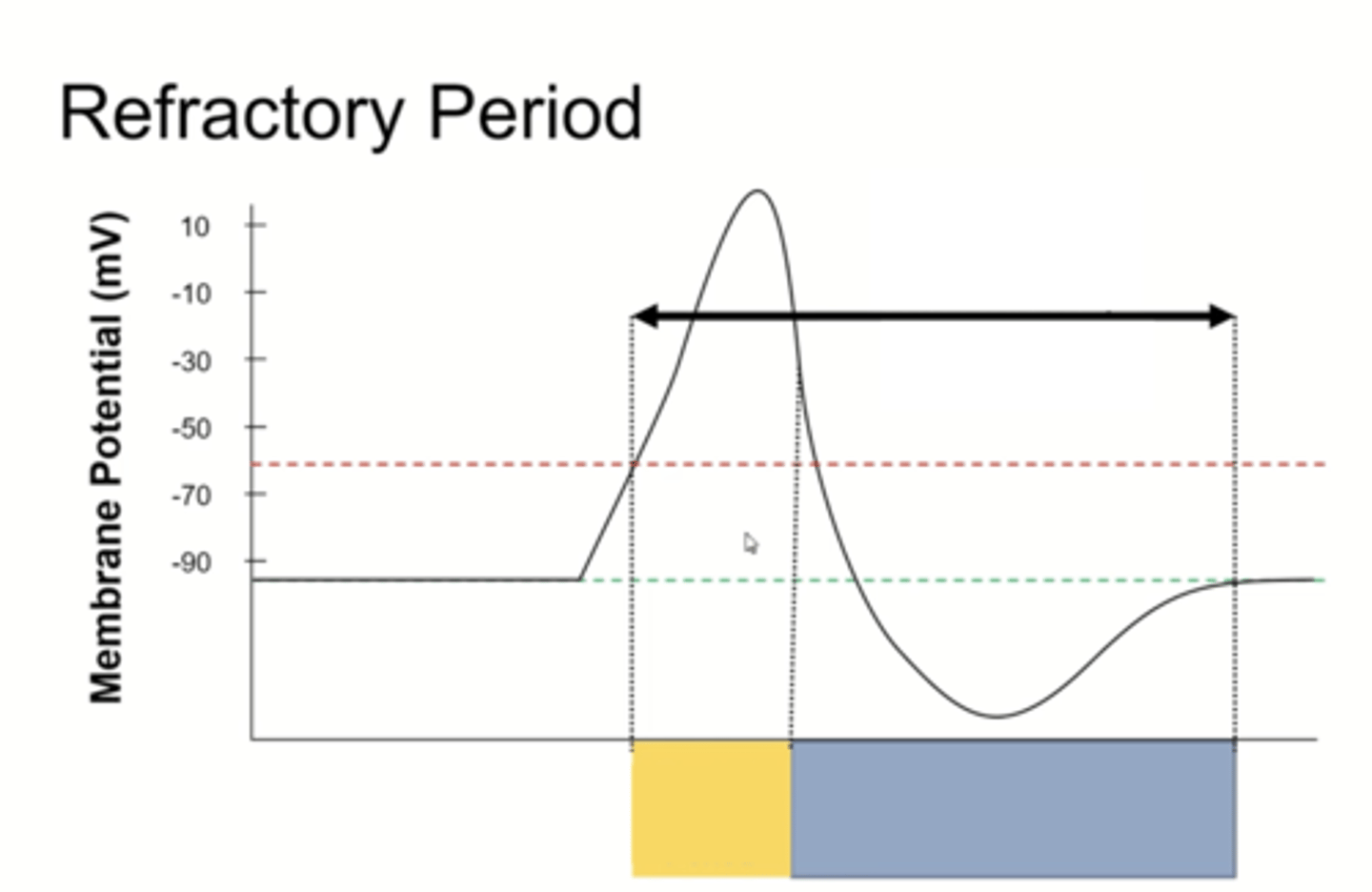
During the relative refractory period, another action potential can be fired if...
the stimulus is large enough; has to be above the threshold value
How do signals travel along the axon?
A signal (binding of neurotransmitter to dendrite) is received on one end, relayed over the axon through several different action potentials, and upon reaching the other end, releases a signal (neurotransmitter) that communicates with other neurons
Action potentials travel in what direction?
unidirectional
What keeps the action potential from heading in the opposite direction?
the refractory period
As one part of a neuron is depolarized...
it triggers depolarization in the adjacent part of the cell
Myelinated nerves
nerves that are wrapped in myelin sheaths that act as an insulator
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath to which voltage-gated sodium channels are confined
Why are action potentials transported down the nerve faster in a myelinated neuron?
1.) the action potential jumps from one node of ranvier to the next without having to travel across the entire nerve fiber
2.) insulation prevents ions from leaking out
saltatory conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane
Neuromuscular junction
Synapse between motor neuron and muscle fiber
Neurotransmitter
chemical used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to a muscle cell
Most common neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
Terminal nerve fiber
end of the nerve that synapses with a muscle fiber
Motor end plate
specialized part of a muscle fiber membrane at a neuromuscular junction
Where is acetylcholine found?
in vesicles at the end of a nerve fiber
What causes acetylcholine to be released?
-the action potential reaches the end of the nerve
-this opens voltage gated calcium channels to open
-as calcium rushes into the terminal nerve fiber, acetylene vesicles are released through exocytosis
What space is acetylcholine released into?
synaptic cleft
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell
After being released into the synaptic cleft, acetylcholine will...
bind to receptors on the motor end plate
When acetylchoine binds to receptors on the motor end plate, this causes...
voltage gated sodium channels to open
voltage gated sodium channels on motor end plate
when opened cause sodium to rush into the muscle cell
What happens when sodium rushes into the muscle cell?
end plate potential; analogous to action potential in neuron
Two things that can happen to acetylcholine after it binds:
1.) it can bind to the neurotransmitter again
2.) it is degraded by acetylcholinesterase
Muscle fibers are arranged into bundles called _____________
Myofibrils
Fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
Each muscle fiber is made up of __________
Myofibrils
Myofibrils
Individual sarcomeres joined together in a chain; made up of myofilaments
Myofilaments
The contractile proteins, actin and myosin, of muscle cells
Arrangement of muscle components from small to large
Myofilaments —> myofibrils —> muscle fiber —> fascicle —> muscle
Three levels of connective tissue of skeletal muscle
1.) Epimysium 2.) Perimysium 3.) Endomysium
Epimysium
Wrap the entire muscle in a sheath of connective tissue, holding the fasciles in a group
Perimysium
Connective tissue that surrounds each individual fascicle
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding an individual muscle fiber
Sarcomere
a structural unit of a myofibril in striated muscle; contractile unit of a muscle cell that contains actin and myosin myofilaments