Chap 11 performance appraisal (part 2)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
performance appraisal
Process of identifying, measuring, and managing human performance in organizations
one of the least favorite activities of managers
Purposes of PA
administrative
developmental
legal
strategic
Administrative purpose
•Provide information for day-to-day HR decisions about people (raise, promote, train, discipline, etc.)
Developmental purpose
•Developing employees’ knowledge and skills. Let employees know how they’re doing, how to improve.
Legal Purpose
•Provide legal basis for company to defend admin HR decisions
Strategic Purpose
•Align interests and direct / motivate specific behavior. Helps organization achieve business objectives
Common Problems with PA
Poorly defined performance metrics
Lack of standards; Irrelevant, subjective, or unrealistic standards
Poor Measurement
Not accurate and / or measure wrong things
Rater errors
Poor Feedback
Content and Frequency
What to Do
Improve appraisal formats: Appropriate for purpose.
Select the right raters
Train raters: Understand why raters make errors
Improve communication / feedback process
Choosing Appropriate Performance Appraisal Methods
Relative Judgements
Trait Approach
Behavioral Approach
Outcomes Approach
Relative Judgements
ranking
forced distribution
only one that isn’t absolute
Purpose: admin
ex. if you want to give a raise to one person you would use relative
Trait Approach
(e.g. leadership)
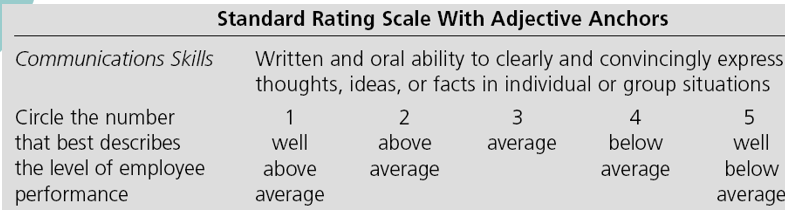
standards rating scale
Absolute
Purpose: Small d, s, a, l
Does a lot of things, inexpensive, but doesn’t necessarily maximize any purposes
several people can have the same rating
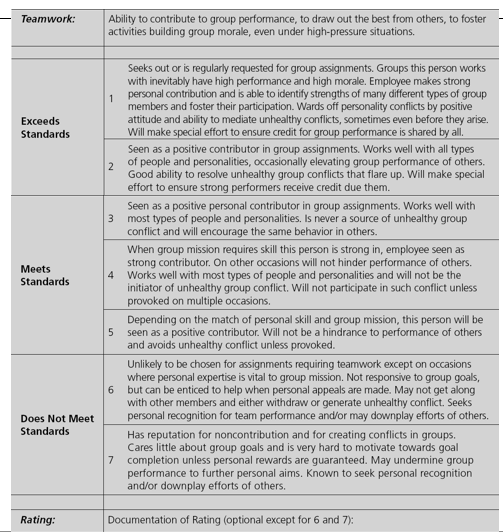
Behavioral Approach
BARS
Purpose: Heavily development
ex. this explains why the employee isn’t meeting standards. Whats wrong with the outcome? This actually tells you what you should do differently to improve
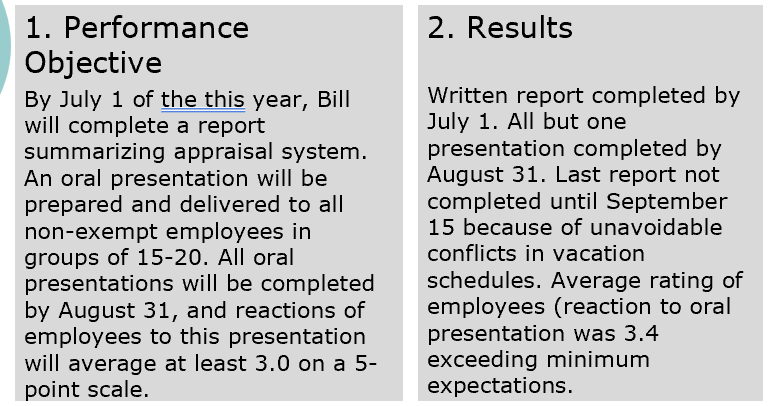
Outcomes Approach
Management by objectives (MBO)
Absolute
Purpose: Big S- strategic
Getting company goals and telling them what you need them to do to reach company outcome. Aligning individual performance with what the company is trying to do. could suggest actions that people could make to change but it doesn’t do so explicitly
Little d development
Addressing rating errors
“Idiosyncratic rater errors”—rating reflects beliefs (bias) of individual raters, not actual employee performance
Gets in the way of achieving PA purposes
Rating Errors
halo/horn
first impression error
recency error
personal bias - “clone error”
restriction of range
leniency, severity, central tendency
halo/horn error
a cognitive bias that causes people to make unfair judgments based on a single positive or negative trait
first impression error
a cognitive bias that occurs when someone forms an initial judgment of a person or situation based on superficial factors. This judgment can be positive or negative, and can lead to inaccurate decisions.
examples:
Forming a positive impression of a job candidate based on their appearance or charisma
Ignoring information that doesn't support an initial judgment
recency error
a cognitive bias that occurs when people give more weight to recent events when making judgments or decisions
ex. Performance appraisals
When an employee's most recent behavior is the main focus of their evaluation, even if it's at odds with their overall performance
personal bias - “clone error”
learned beliefs, opinions, or attitudes that people are unaware of and often reinforce stereotypes
Performance reviews
When a manager's personal bias affects how they evaluate an employee's performance.
restriction of range
leniency, severity, central tendency…
(insert photo)
Training raters to rate more accurately
rater-error training
performance-dimension training
performance-standard trianing
rater-error trianing
reduces psychometric errors by familiarizing raters with their existence
performance-dimension training
exposes supervisors to the performance dimensions to be used in rating
Performance-standard training
provides raters with a standard or frame of reference for making appraisals
Addressing restriction of range errors
leniency errors are generally the most difficult to overcome. Why?
the effect on employees is less if we default with saying everyone is a top performer
Is forced distribution the answer? Is it fair to employees
ex. being required to rate one person at a 5
Not fair, not based on the person
Choosing who should do PA
insert photo
supervisors
peers
self
customers
subordinates
Provide effective performance feedback
frequent
focus on behavior and not the person
praise as well as criticize
problem solving and participative
Performance appraisal summary
Know:
1.Goals / purposes of P.A.
2.Measurement issues and types of performance
3.Common problems with P.A.
4.Strengths and weaknesses of P.A. methods
5.Rating errors and what to do (Training raters)
6.Who should do P.A. (360 degree feedback)
7.Effective performance feedback techniques