2550 - Hamilton G5
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
Ventilator function overview
- microprocessor controlled
- electronically controlled pneumatic ventilation system
- AC power + internal battery backup (extended battery backup optional)
- internal gas mixer for air-O2, option for heliox
- electronically controlled pneumatic ventilation system
- AC power + internal battery backup (extended battery backup optional)
- internal gas mixer for air-O2, option for heliox
2
New cards
What's the purpose of heliox as an adjunct therapy?
Mixture of helium + oxygen --> used in pts w high resistance
- He less dense than air --> so lighter --> higher R not as impactful (wouldn't prevent gas from reaching alveoli)
- dec tendency for flow to be turbulent w high R
Still setting flow RATE, but now flow PATTERN is dif (turbulent vs laminar)
- He less dense than air --> so lighter --> higher R not as impactful (wouldn't prevent gas from reaching alveoli)
- dec tendency for flow to be turbulent w high R
Still setting flow RATE, but now flow PATTERN is dif (turbulent vs laminar)
3
New cards
Limitation to heliox/ when it's not beneficial
If FiO2 greater than 40% --> heliox ineffective
If FiO2 is higher --> less useful
- bc delivering more gas --> gas mixture heavier
If FiO2 is higher --> less useful
- bc delivering more gas --> gas mixture heavier
4
New cards
What is special about the flow sensor?
1. Uses propriety proximal flow sensor @ pt wye
2. Flow sensor has variable bidirectional flow
2. Flow sensor has variable bidirectional flow
5
New cards
Why is flow sensor proximal to pt?
Hoping that bc flow sensor is closer to pt --> it can sense changes in flow faster (vs if it was internal like 840 or 980)
- so potentially more synchronous w pt
- v sensitive to water + secretion build-up in circuit --> often get high priority alarm saying flow sensor needs to be changed
- so potentially more synchronous w pt
- v sensitive to water + secretion build-up in circuit --> often get high priority alarm saying flow sensor needs to be changed
6
New cards
Ventilator tests (3)
1. Start up test
- occurs when ventilator power is on (~15sec)
2. Pre-operational test
- sensor calibration + tightness test
3. Oxygen cell calibration
- ensures delivery of desired FiO2
- occurs when ventilator power is on (~15sec)
2. Pre-operational test
- sensor calibration + tightness test
3. Oxygen cell calibration
- ensures delivery of desired FiO2
7
New cards
How does vent trigger? (3)
1. Pressure
2. Flow
3. Manual
2. Flow
3. Manual
8
New cards
If pt were to trigger, how would you know it was pt triggered vs time? (3)
1. Colour of waveform changes
2. Top L corner C if controlled, A if pt triggered
3. Any triangle under time axis means it was pt triggered
2. Top L corner C if controlled, A if pt triggered
3. Any triangle under time axis means it was pt triggered
9
New cards
Dif colour triangles under time axis
Yellow triangle --> flow triggered
Pink triangle --> pressure triggered
^^signifies diaphragm
Pink triangle --> pressure triggered
^^signifies diaphragm
10
New cards
Pressure trigger
Vent is triggered when P drops below baseline sensitivity setting
11
New cards
Flow trigger --> what is bias flow?
Bias flow is 4LPM if sensitivity is equal or less than 2LPM
Bias flow becomes 2x sensitivity if greater than 2LPM
Bias flow becomes 2x sensitivity if greater than 2LPM
12
New cards
If sensitivity was 3, what would the bias flow through the system be?
6LPM
13
New cards
Patient set-up
- input gender + height
- IBW determined from these
- option of selecting last pt
- IBW determined from these
- option of selecting last pt
14
New cards
What is S(CMV)
(Spontaneous) controlled mandatory ventilation
- under AC mode --> allowing pt to trigger
- VC
- under AC mode --> allowing pt to trigger
- VC
15
New cards
Set parameters on S(CMV)
VT, RR, flow, PEEP, FiO2
16
New cards
Flow waveforms on S(CMV)
1. Square
2. Decelerating
- option to set decelerating to 0 or to half
3. Sinusoidal (would never use)
2. Decelerating
- option to set decelerating to 0 or to half
3. Sinusoidal (would never use)
17
New cards
How can you measure Pplat on (S)CMV?
Input an insp pause on every breath
- activate TIP button --> will tell you your Pplat every breath
*but don't do bc uncomfy for pt
Instead do manual insp pause under "tools" function
- activate TIP button --> will tell you your Pplat every breath
*but don't do bc uncomfy for pt
Instead do manual insp pause under "tools" function
18
New cards
What is P-CMV
PC
19
New cards
Set parameters in P-CMV
PC (above PEEP) --> relative, not absolute
Ti is set by RR and %Ti
P-ramp
Ti is set by RR and %Ti
P-ramp
20
New cards
What is RCT
Resp cycle time, same as TCT
21
New cards
How is Ti set in P-CMV?
Ti is a % under PC (not setting absolute time for Ti)
- so dependent on RR and TCT (aka RCT)
- so dependent on RR and TCT (aka RCT)
22
New cards
If RCT = 5sec and Ti is set to 50%, Ti = ?
2.5sec
23
New cards
What is P-ramp?
Analogous to rise time
- measured in milliseconds (ms), not % or 1-9
- measured in milliseconds (ms), not % or 1-9
24
New cards
What is SIMV? What is P-SIMV?
Combo of mandatory + spontaneous breaths
SIMV = VC breaths
P-SIMV = PC breaths
SIMV = VC breaths
P-SIMV = PC breaths
25
New cards
How does SIMV work?
Each SIMV interval includes Tmand + Tspont portions
- cycle time set by SIMV control
- mandatory breaths set similar to its corresponding control mode (VC vs PC)
- cycle time set by SIMV control
- mandatory breaths set similar to its corresponding control mode (VC vs PC)
26
New cards
What's different about SIMV in Hamilton compared to PB and LTV?
Nothing different besides what's set
??
??
27
New cards
What is APV?
Adaptive pressure ventilation
- volume guarantee w PC breath
- Hamilton's version of PC+
- volume guarantee w PC breath
- Hamilton's version of PC+
28
New cards
2 APV options (+ what they're similar to)
1. APVcmv
- like AC-VC+ on PB
2. APVsimv
- like SIMV-VC+ on PB
- Option for AC mode u want + spont mode u want (so it means you've set APV as AC mode u want)
- like AC-VC+ on PB
2. APVsimv
- like SIMV-VC+ on PB
- Option for AC mode u want + spont mode u want (so it means you've set APV as AC mode u want)
29
New cards
What do you set for APV?
VTarget, RR, PEEP, high P limit
30
New cards
How does APV work?
Vent delivers 3 test breaths to determine pt's vol/ pressure response
- sees what vol is coming back --> adjusts P to deliver the set vol
- sees what vol is coming back --> adjusts P to deliver the set vol
31
New cards
What is the min P delivered by APV?
3cm/H2O --> but adjusted by +/- 2cmH2O to achieve set VT
32
New cards
APV limitations + how to mitigate
Same as VC+
- runaway P due to air leak
- air hungry pts --> vent dec P to dec vol --> pt has to work harder for more support --> pt-vent asynchrony
So make sure to set safe limits/ alarms
- runaway P due to air leak
- air hungry pts --> vent dec P to dec vol --> pt has to work harder for more support --> pt-vent asynchrony
So make sure to set safe limits/ alarms
33
New cards
What are the spontaneous modalities of the Hamilton?
1. DuoPAP
2. APRV
3. Spont
2. APRV
3. Spont
34
New cards
What are DuoPAP + APRV (+ what are they similar to?)
Two related modes to support spontaneous breathing on 2 alternating levels of CPAP (combo of mandatory + spontaneous breaths)
DuoPAP = duo positive airway pressure
APRV = airway pressure release ventilation
^^same thing basically
Similar to bilevel
DuoPAP = duo positive airway pressure
APRV = airway pressure release ventilation
^^same thing basically
Similar to bilevel
35
New cards
DuoPAP set variables
Phigh, PEEP, PS
36
New cards
APRV set variables
Phigh, Plow, PS
37
New cards
How is cycling defined on DuoPAP?
By P setting + time settings: Thigh + rate
- rate is like release breath --> responsible for CO2 clearance
- rate is like release breath --> responsible for CO2 clearance
38
New cards
How is cycling defined on APRV?
By P settings Phigh and Plow, and time settings Thigh and Tlow
(rate not set)
- not setting breaths directly --> they're a function of TH and TL
(rate not set)
- not setting breaths directly --> they're a function of TH and TL
39
New cards
APRV: If TH is 5.5 and TL is 0.5, release breaths = ?
TCT = TH + TL = 5.5 + 0.5 = 6sec
Release breaths = 60/TCT = 60/6 = 10
Release breaths = 60/TCT = 60/6 = 10
40
New cards
What is PS in duoPAP/ APRV and when is it given?
PS is above PEEP (duo) or Plow (APRV)
41
New cards
Is PS given at Phigh? (DuoPAP/APRV)
Only if PS is less that target P
42
New cards
Why use APRV?
For pts w ARDS to spend more time at higher PEEP --> inc MAP --> recruit alveoli --> improve lung compliance + gas exchange
Pt can and should breathe spontaneously @ higher P
Pt can and should breathe spontaneously @ higher P
43
New cards
What is SPONT + what is it
PS (labelled SPONT on Hamilton)
Set PS + demand flow system
Set PS + demand flow system
44
New cards
Set parameters on SPONT
PS set above PEEP (relative), P-ramp, ETS (expiratory trigger sensitivity), FiO2, sensitivity
45
New cards
What does "demand flow system" mean?
Flow is variable to meet pt demands
46
New cards
What is P-ramp? Units?
Similar to rise time % --> how fast P changes from PEEP to PS u set
- milliseconds
- milliseconds
47
New cards
What's ETS?
Expiratory trigger sensitivity
- similar to Esens --> when it'll cycle to exp
- similar to Esens --> when it'll cycle to exp
48
New cards
If PS is set to 0, what is that?
CPAP
?
?
49
New cards
What should you always ensure to set on SPONT?
Apnea ventilation --> chooses the mode for when pt is in apnea
50
New cards
What apnea ventilation mode is available for PS (SPONT)?
P-CMV
(so basically PS defaults to PC?)
(so basically PS defaults to PC?)
51
New cards
What apnea ventilation mode is available for SIMV?
(S) - CMV
- spont
(so basically SIMV defaults to VC?)
- spont
(so basically SIMV defaults to VC?)
52
New cards
What apnea ventilation mode is available for APVsimv?
APVcmv
(so basically VC+ w SIMV defaults to VC+ AC)
(so basically VC+ w SIMV defaults to VC+ AC)
53
New cards
How can apnea ventilation be reset if activated?
By pt triggering 2 consecutive breaths
54
New cards
What is TRC?
Tube resistance compensation (similar to TC in PB)
- designed to offset the flow resistance imposed by the ETT or tracheostomy tube
- active for use w spontaneously breathing pts
- designed to offset the flow resistance imposed by the ETT or tracheostomy tube
- active for use w spontaneously breathing pts
55
New cards
What do you set for TRC?
Artificial airway size + type, % compensation
- so if u set 100% compensation --> vent overcomes entire R of tube + pt just has to overcome their own airway resistance
- so if u set 100% compensation --> vent overcomes entire R of tube + pt just has to overcome their own airway resistance
56
New cards
How could a kink impact TRC?
Kink could cause inc R --> TRC (or TC) wouldn't compensate for that
- so any changes in R to tube (kink or buildup of secretions) --> machine won't compensate
- only knows R of tube w/o additional effects
- so any changes in R to tube (kink or buildup of secretions) --> machine won't compensate
- only knows R of tube w/o additional effects
57
New cards
What is NIV?
Non-invasive ventilation
- ventilator functions as demand flow system
- spontaneous breaths can be supported w PS level set (so like PS but giving breath non-invasively)
- ventilator functions as demand flow system
- spontaneous breaths can be supported w PS level set (so like PS but giving breath non-invasively)
58
New cards
In NIV, is PS is set to 0, what does it function as?
CPAP
59
New cards
What's NIV-ST?
Mandatory breaths: PC, time-cycled
Spontaneous breaths: PS, flow-cycled
Automatic leak compensation
(similar to V60 STE?)
Spontaneous breaths: PS, flow-cycled
Automatic leak compensation
(similar to V60 STE?)
60
New cards
Why is NIV-ST like SIMV?
- set rate + mandatory-type breath, and pt can breathe spontaneously btwn those mandatory-type breaths
- mandatory breaths are PS-like --> cycle off to Ti
- the rest of the period is spontaneous --> PS but flow-cycled
- mandatory breaths are PS-like --> cycle off to Ti
- the rest of the period is spontaneous --> PS but flow-cycled
61
New cards
Why do you set RR in NIV-ST?
Used as a semi-backup for pt so if they happen to go apneic --> can get some backup breaths
62
New cards
If under NIV-ST + BGA shows v high CO2 (hypercapnic), what could you do?
1. Could inc RR --> but this could be a band-aid soln for something that's a bigger problem --> pt clearly not tolerating NIV
2. So escalate care --> intubate --> so strict control of their CO2 clearance (e.g. w VC)
2. So escalate care --> intubate --> so strict control of their CO2 clearance (e.g. w VC)
63
New cards
Does NIV-ST have leak sync?
No. But it automatically compensates for leak
- gives idea of how well mask is fitting pt face
- gives idea of how well mask is fitting pt face
64
New cards
How much leak can NIV-ST compensate for?
If P sensitivity --> can compensate for 1L/min
If flow sensitivity --> can compensate up to 30L/min
If flow sensitivity --> can compensate up to 30L/min
65
New cards
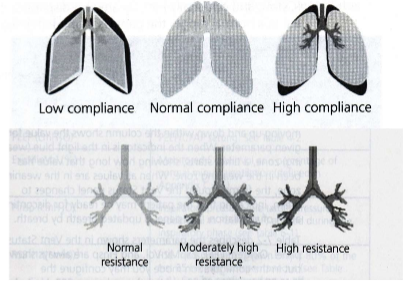
What's special about the Hamilton graphic display?
Shows lung C + R with a lung graphic
- low C --> rounder lungs
- high C --> more angular lungs
- low R --> airways less shaded (grey)
- high R --> darker airways (black)
Don't make therapeutic decisions based on this graphic.
- low C --> rounder lungs
- high C --> more angular lungs
- low R --> airways less shaded (grey)
- high R --> darker airways (black)
Don't make therapeutic decisions based on this graphic.
66
New cards
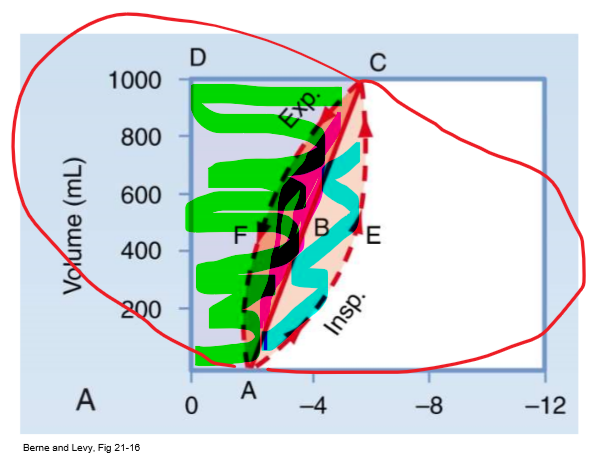
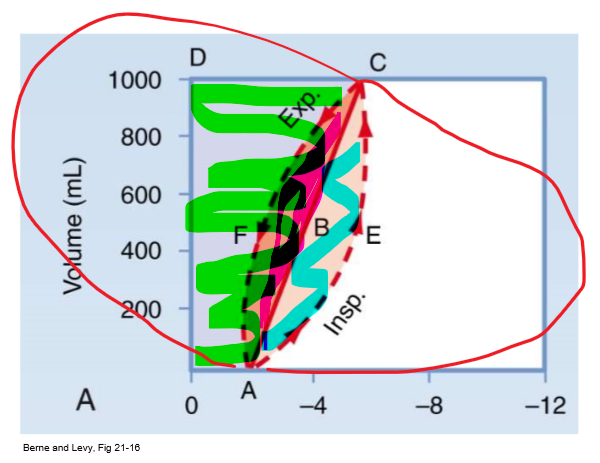
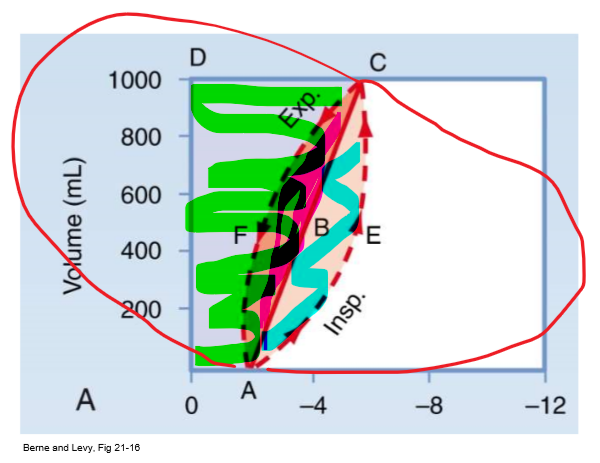
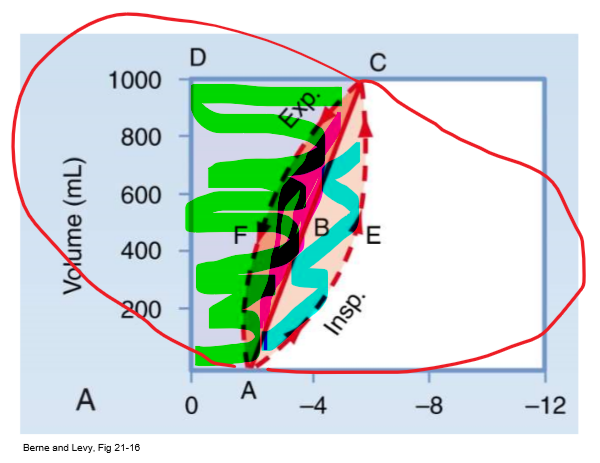
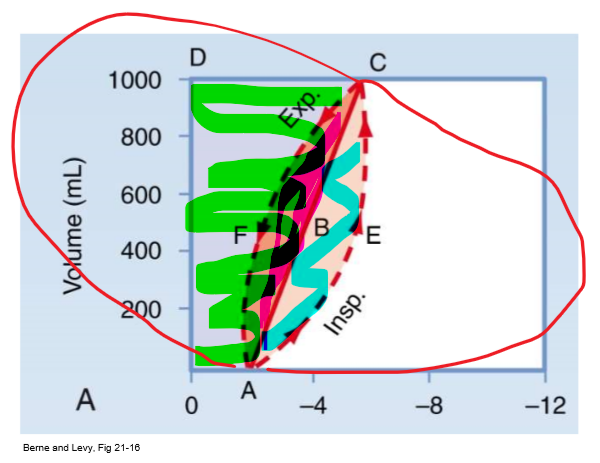
PV curve 0AECD (everything shaded)
Total mechanical work of insp
67
New cards
PV curve straight line
Static compliance (C = vol/P)
68
New cards
PV curve 0ABCD (green/ everything above straight line)
Inspiratory WOB to overcome elastic resistance (potential energy available for PASSIVE exp)
- expand lung against natural elastance
- expand lung against natural elastance
69
New cards
PV curve AECB (blue/ bottom half of almond)
Insp WOB to overcome non-elastic resistance (e.g. airway resistance)
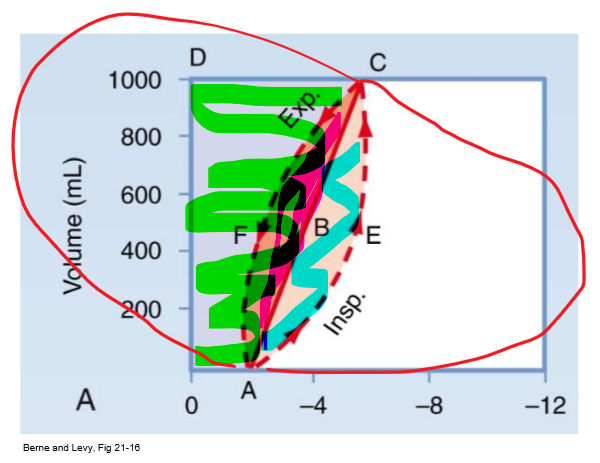
70
New cards
PV curve ABCF (pink/ top half of almond)
Energy required to overcome resistance to airflow DURING expansion
- energy to overcome R from exhalation (R exists on airway on way out too)
- energy to overcome R from exhalation (R exists on airway on way out too)
71
New cards
Why do you need less effort on exhalation?
If lungs not diseased --> passive exhalation
- as u inspire --> build up potential energy in lungs --> converted to kinetic energy when u exhale (so no extra effort needed)
- lungs, diaphragms, etc go back to resting state
- as u inspire --> build up potential energy in lungs --> converted to kinetic energy when u exhale (so no extra effort needed)
- lungs, diaphragms, etc go back to resting state
72
New cards
How would PV curve look for a pt w COPD?
Would be way larger
- way larger P and V
- EPP occurs closer to alveoli --> pinching --> air-trapping --> inc RV --> so FRC in
- way larger P and V
- EPP occurs closer to alveoli --> pinching --> air-trapping --> inc RV --> so FRC in
73
New cards
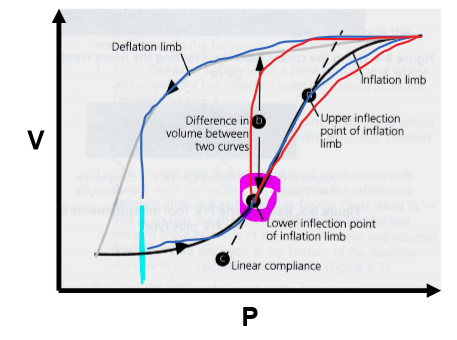
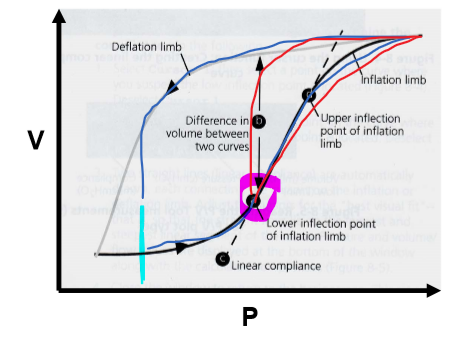
What happens at the Lower Inflection Point (LIP) on the PV curve?
Marks shift from low to high C (slope inc)
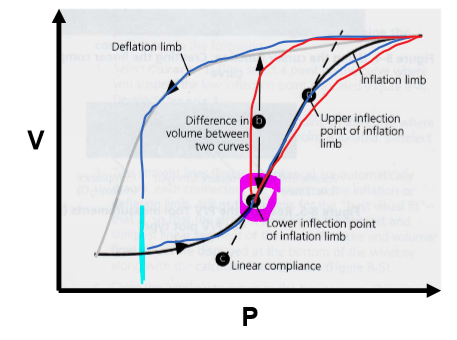
74
New cards
What happens at the Upper Inflection Point (UIP) on the PV curve?
C shifts from high to low (slope dec)
- lungs nearing TLC --> already inflated --> dec C as elastance wants to take over bc lungs wanna recoil back to resting vol
- lungs nearing TLC --> already inflated --> dec C as elastance wants to take over bc lungs wanna recoil back to resting vol
75
New cards
Why is too low of a PEEP sub-optimal? (e.g. blue line in this pic)
Breathing back to this low P every breath --> constantly opening + closing alveoli bc putting pt back to low C @ end of every breath
- atelectrauma --> VILI
- atelectrauma --> VILI
76
New cards
What is an optimal PEEP? (pink circle on pic)
@ P of LIP --> point of highest compliance (steepest slope on PV curve)
- keeps pt in higher C state --> don't have to re-recruit alveoli each breath
- wanna keep pt in high C part of curve
- keeps pt in higher C state --> don't have to re-recruit alveoli each breath
- wanna keep pt in high C part of curve
77
New cards
PV tool requirements (3)
1. Pt has to be intubated + paralyzed (can't make effort/ movement)
- can't do w NIV
- if they take breath @ high P --> can cause pt-induced lung injury
2. Minimum C = 5 mL/cmH2O
- pretty low
3. No gas leak
- bc using higher P so don't want any leaks to occur
- can't do w NIV
- if they take breath @ high P --> can cause pt-induced lung injury
2. Minimum C = 5 mL/cmH2O
- pretty low
3. No gas leak
- bc using higher P so don't want any leaks to occur
78
New cards
Can you re-paralyze a pt to use PV tool?
Risky to re-paralyze pt bc paralytics have risks --> like they drive muscle atrophy
- could do it once or twice but risky
- also they need to be sedated (don't paralyze w/o sedation!!!)
- could do it once or twice but risky
- also they need to be sedated (don't paralyze w/o sedation!!!)
79
New cards
What are PV tool indications? (3)
1. Determining optimal pt PEEP
2. Decreased C (ARDS)
3. Recruitment maneuver (RM)
- use this tool to create high P to recruit alveoli
2. Decreased C (ARDS)
3. Recruitment maneuver (RM)
- use this tool to create high P to recruit alveoli
80
New cards
What are PV tool contraindications? (5)
1. Spontaneous breathing
- don't want pt overriding
2. Unstable CV status
- if hyper-perfused --> don't wanna do this bc delivering high P --> offset CV elements (preload, afterload, etc.)
3. Inc ICP
- high P in lungs --> backflow of blood to R-heart --> SVC --> feeds back to head --> inc ICP
4. Leaks
5. Vulnerability to barotrauma + volutrauma (e.g. BP fistula)
- don't want pt overriding
2. Unstable CV status
- if hyper-perfused --> don't wanna do this bc delivering high P --> offset CV elements (preload, afterload, etc.)
3. Inc ICP
- high P in lungs --> backflow of blood to R-heart --> SVC --> feeds back to head --> inc ICP
4. Leaks
5. Vulnerability to barotrauma + volutrauma (e.g. BP fistula)
81
New cards
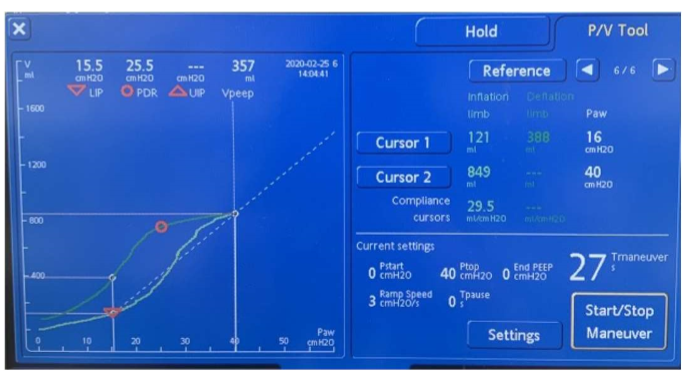
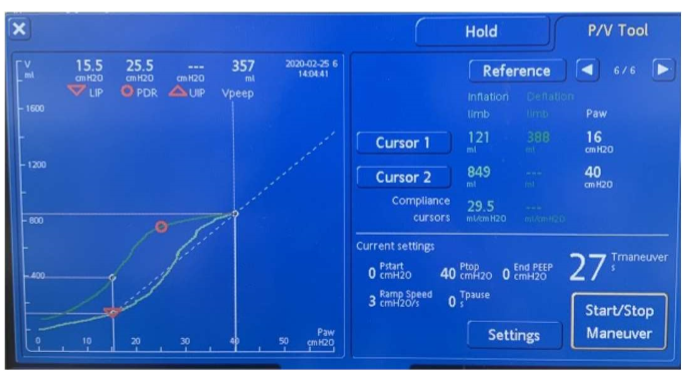
How to access/use PV tool + what is set
Under "TOOLS" button
- info window pops up (read + acknowledge)
- set: Pstart, Ptop, EndPEEP, Ramp speed, Tpause (Tmaneuver is a function of Tpause)
- when ready --> hit "START/STOP Maneuver"
- info window pops up (read + acknowledge)
- set: Pstart, Ptop, EndPEEP, Ramp speed, Tpause (Tmaneuver is a function of Tpause)
- when ready --> hit "START/STOP Maneuver"
82
New cards
What's a good Ptop?
Ptop = max P
- good to put ~40
- good to put ~40
83
New cards
What's the optimal EndPEEP value?
P at LIP (16 in pic)
e.g. Pstart = 0, EndPEEP = 16
e.g. Pstart = 0, EndPEEP = 16
84
New cards
What is "40 for 40" on PV tool?
40 for 40 sec --> standard of time u want pts to undergo maneuver
- 27sec on this slide example --> to reach 40sec --> set Tpause to 13sec
- so P will reach 40 @ 27sec --> then hold 40 for 13sec --> til 40sec reached (27 + 13 = 40)
Builds up to 40 over 27sec, then holds for 13 sec (ex)
- 27sec on this slide example --> to reach 40sec --> set Tpause to 13sec
- so P will reach 40 @ 27sec --> then hold 40 for 13sec --> til 40sec reached (27 + 13 = 40)
Builds up to 40 over 27sec, then holds for 13 sec (ex)
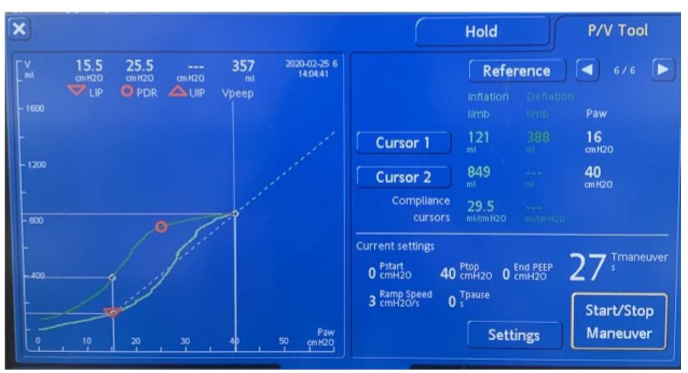
85
New cards
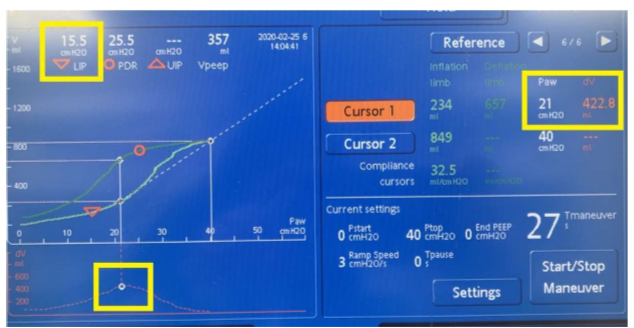
How do you find LIP/ optimal PEEP on PV tool?
DV graph shows what vol change was during maneuver --> highest C yields highest vol change --> so put cursor on highest point of graph --> correlates to LIP --> optimal PEEP
^^proof that LIP yielded highest C
^^proof that LIP yielded highest C
86
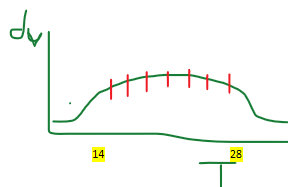
New cards
If DV graph plateaus + largest P occurs for long time period, which time would you pick for your PEEP?
Set it @ lowest time point w that P
- every incremental P change doesn't yield higher vol --> don't wanna subject pt to more time @ P w/o more reward
14 in pic
- every incremental P change doesn't yield higher vol --> don't wanna subject pt to more time @ P w/o more reward
14 in pic
87
New cards
What's ASV?
Adaptive Support Ventilation
- maintains min MV that's independent of pt's activity
- maintains min MV that's independent of pt's activity
88
New cards
Why is ASV useful?
To maintain optimal breathing pattern for pt that avoids deadspace ventilation, excess P
- optimal combo of RR + vol to be delivered to pt to target MV that doesn't cause harm
Ensure safe + ideal MV for pt
- optimal combo of RR + vol to be delivered to pt to target MV that doesn't cause harm
Ensure safe + ideal MV for pt
89
New cards
How does ASV work?
Shifts btwn passive + active mode depending on what pt is doing (w/o you changing anything)
- so it adapts
- utilizes OTIS eqn
- so it adapts
- utilizes OTIS eqn
90
New cards
Passive mode
APV
- vol-targeted, PC, time-cycled
- vol-targeted, PC, time-cycled
91
New cards
Active mode (when is this activated?)
VS-like
- vol-targeted, PS, flow-cycled
When pt makes effort --> breathing spontaneously
- vol-targeted, PS, flow-cycled
When pt makes effort --> breathing spontaneously
92
New cards
What is set on ASV?
- set % MV
--> so it'll target MV by automatically adjusting RR, VT, and Ti based on lung mechanic changes + pt effort
--> so it'll target MV by automatically adjusting RR, VT, and Ti based on lung mechanic changes + pt effort
93
New cards
Combo of active and passive?
Looks like SIMV --> grey zone --> so not just passive OR active
94
New cards
How does ASV deliver optimal MV?
Uses OTIS eqn to give pattern w lowest WOB
- vent chooses RR + VT according to R and C
- vent chooses RR + VT according to R and C
95
New cards
ASV pt set-up
- input gender
- input pt height (cm)
- vent will determine pt's IBW based on ^^
- anatomical deadspace is automatically calculated from IBW determined by pt's height
- input pt height (cm)
- vent will determine pt's IBW based on ^^
- anatomical deadspace is automatically calculated from IBW determined by pt's height
96
New cards
What's set on ASV?
% MV, P-ramp, ETS, P ASV limit, P-trigger, PEEP/CPAP, FiO2
97
New cards
What does 100% MV mean?
100mL/kg/min = normal for adults
--> so 100% is 100, over 100% is more, under 100% is less
(based on healthy adult --> may need to compensate for disease pathology of pt)
--> so 100% is 100, over 100% is more, under 100% is less
(based on healthy adult --> may need to compensate for disease pathology of pt)
98
New cards
How could HME impact MV? How to overcome?
HME can add deadspace --> add 10% to IBW to overcome + account for added deadspace
99
New cards
What's P-ramp?
How fast P rises from PEEP to max P
- in passive mode --> vol-targeted PC
- in active mode --> vol-targeted PS
- in passive mode --> vol-targeted PC
- in active mode --> vol-targeted PS
100
New cards
What is ETS?
Expiratory trigger
- applies during active
- if pt under sedation + paralytics --> purely passive --> ETS won't take effect (no pt effort)
- applies during active
- if pt under sedation + paralytics --> purely passive --> ETS won't take effect (no pt effort)