topic 15 adaptive immunity pt 1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is an antigen
any chemical compound or structure foreign to the body that elicits an adaptive immune response
structural components of bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa
toxins produces by bacteria
food, dust, pollen - allergies
an epitope is a part of an antigen that is recognized by antibodies, B cells and T cells t or f
True
which lymphocyte is involved in antibody (humoral) mediated immunity
a-b cells
b-neutrophils
c- cytotoxic t cell
B cells
which lymphocyte is involved in cell mediated immunity
a-b cells
b-monocytes
c-cytotoxic t cells
cytotoxic t cells
where would you find an endogenous antigen
a-in the bloodstream
b-inside a cell
c-in the tissues
inside of a cell
the purpose of the lymphatic system is to screen for foreign antigens t or f
true
what are the two primary lymphoid organs
thymus and bone marrow
where do b cells arise and mature
arise in bone marrow and mature in bone marrow
what does the acronym apc stand for- list three examples
antigen presenting cell
1-dendritic cells
2-monocytes
3-macrophages
what type of cell produces antibodies
b cells
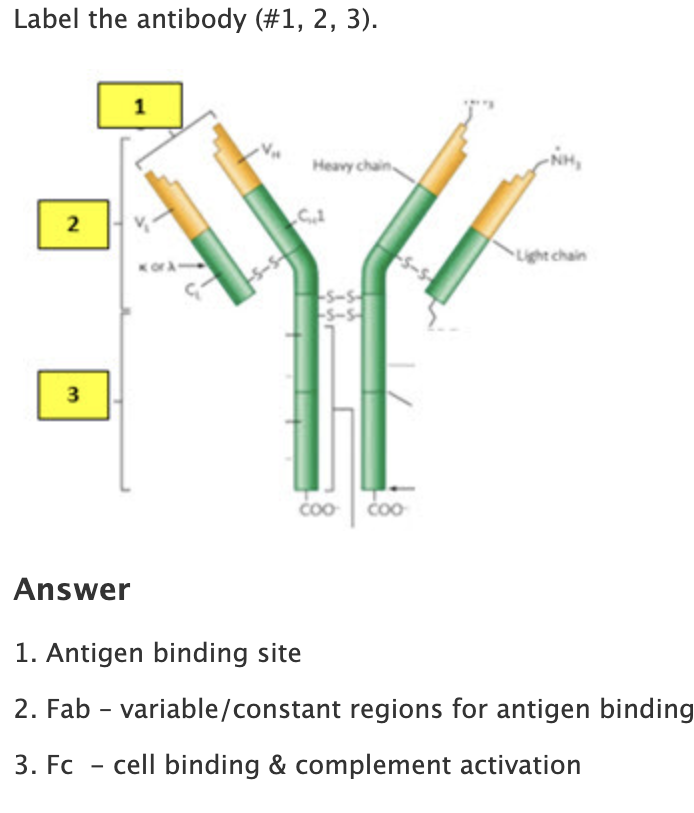
label the antibody #1,2,3
1-antigen binding site
2-Fab- variable/constant region for antigen binding
3-Fc - cell binding and complement activation
which antibody is the first antibody produced
A-IgA
b-IgD
c-IgG
d-IgM
IgM
which antibody is found in breast milk and help protect an infant
a- iga
b-igd
c-igg
d-igm
IgA
t or f- plasma produces about 10 antibodies per hour
false
in the antibody immune response, if a b cell cannot activate on its own, what can assist in the activation process
helper t cell
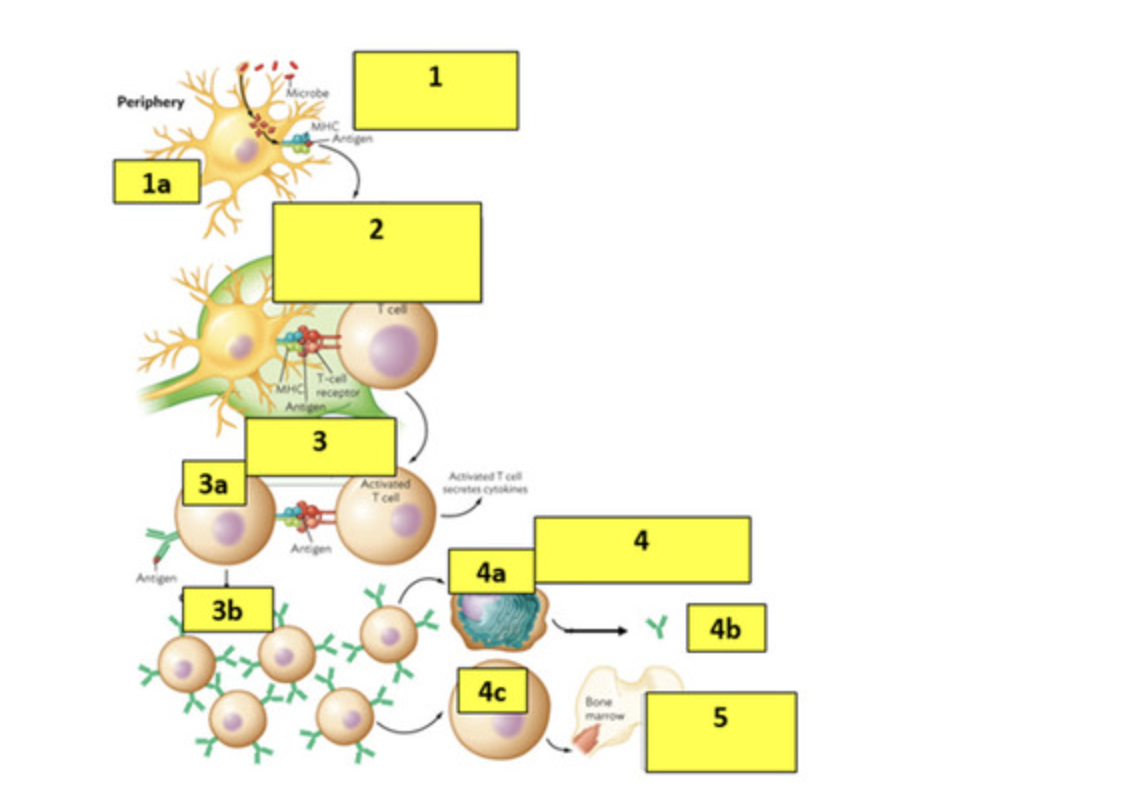
Answer the following questions on Step 1:
a. What is the cell shown in 1a?
b. What process is the cell doing to the microbe?
c. What does the term MHC stand for?
d. What is another name for part of the antigen found in the MHC receptor?
e. What does the term APC stand for?
a- dendritic cells
b- phagocytosis
c- major histocompatibility proteins
d-epitope
e-antigen presenting cell
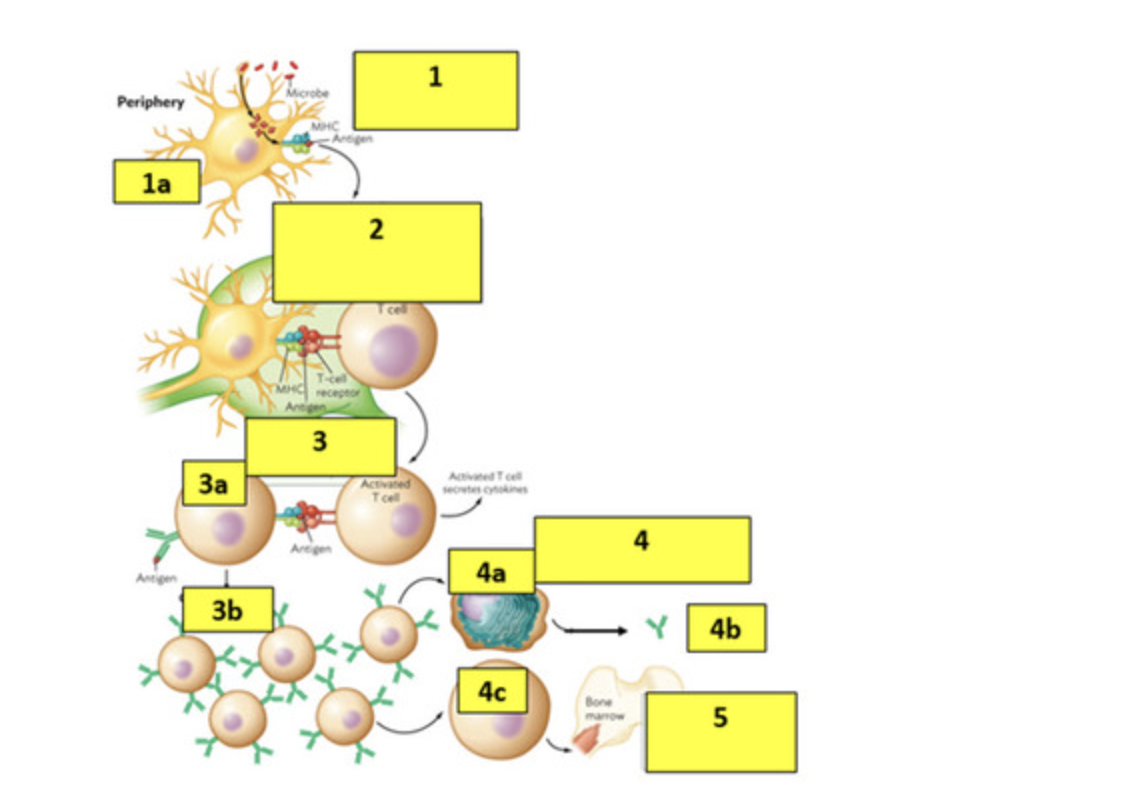
Answer the following questions on Step 2:
a. What type of T cell is shown?
b. What are the surface proteins on the T cell that helps it binds to the MHC-Antigen complex?
c. What location are the cells interacting?
a- t helper CD4 cell
b- CD4 receptor and TCR- T cell receptor
c- lymph node
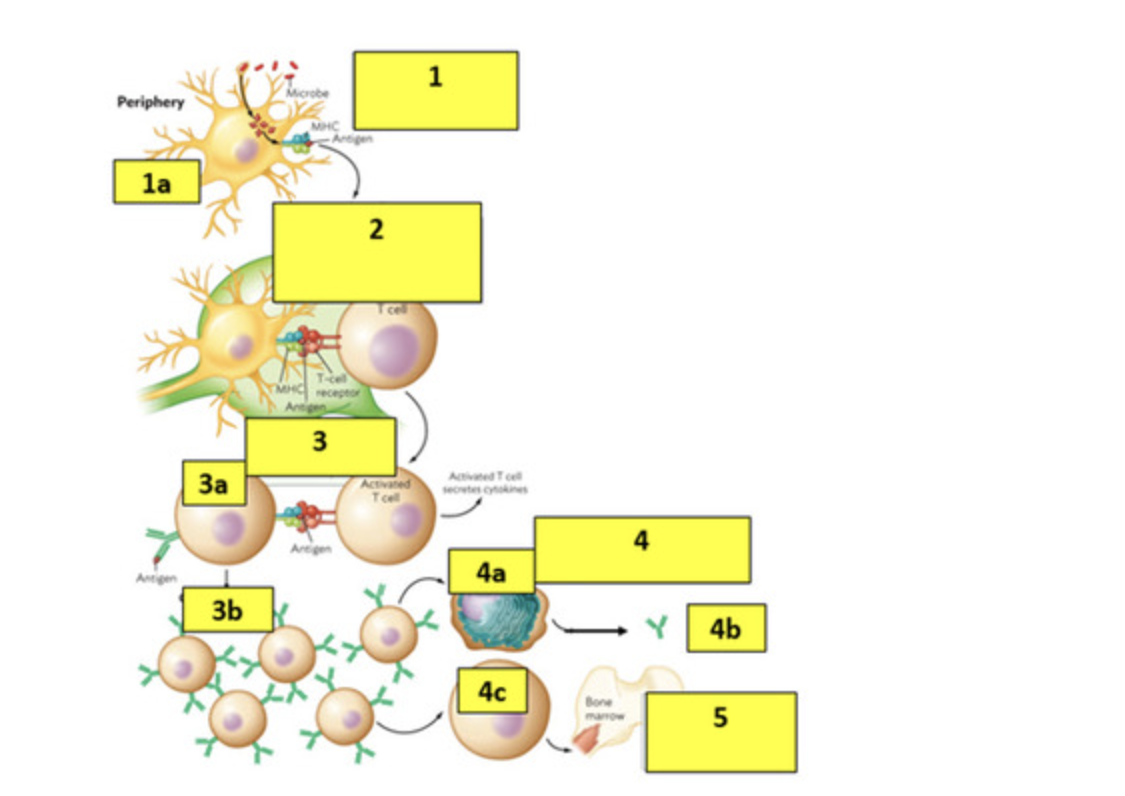
Answer the following questions on Step 3:
a. What is the cell labelled 3a?
b. What is the structure on the left of the cell (3a) and why does it contain an antigen?
c. What is the process called (3b) of making more of the cells labelled 3a?
a- B cell
b- BCR (b cell receptor) bc the b cell recognized the antigen but couldnt activate without the helper t cell binding to it
c- clonal expansion of the b cells
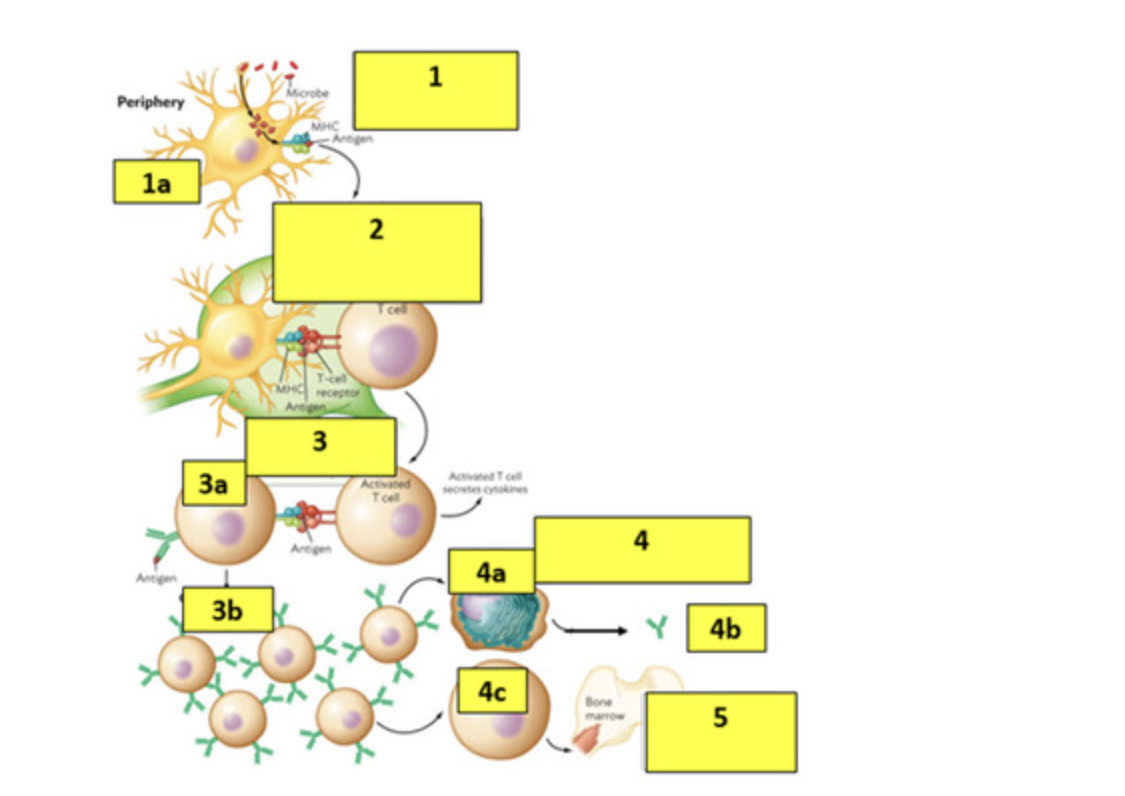
Answer the following questions on Step 4:
a. What is the cell labelled 4a?
b. What is produced (4b) by the 4a cell?
c. What is the cell labeled 4c?
a-plasma cell
b-antibodies
c-memory cell
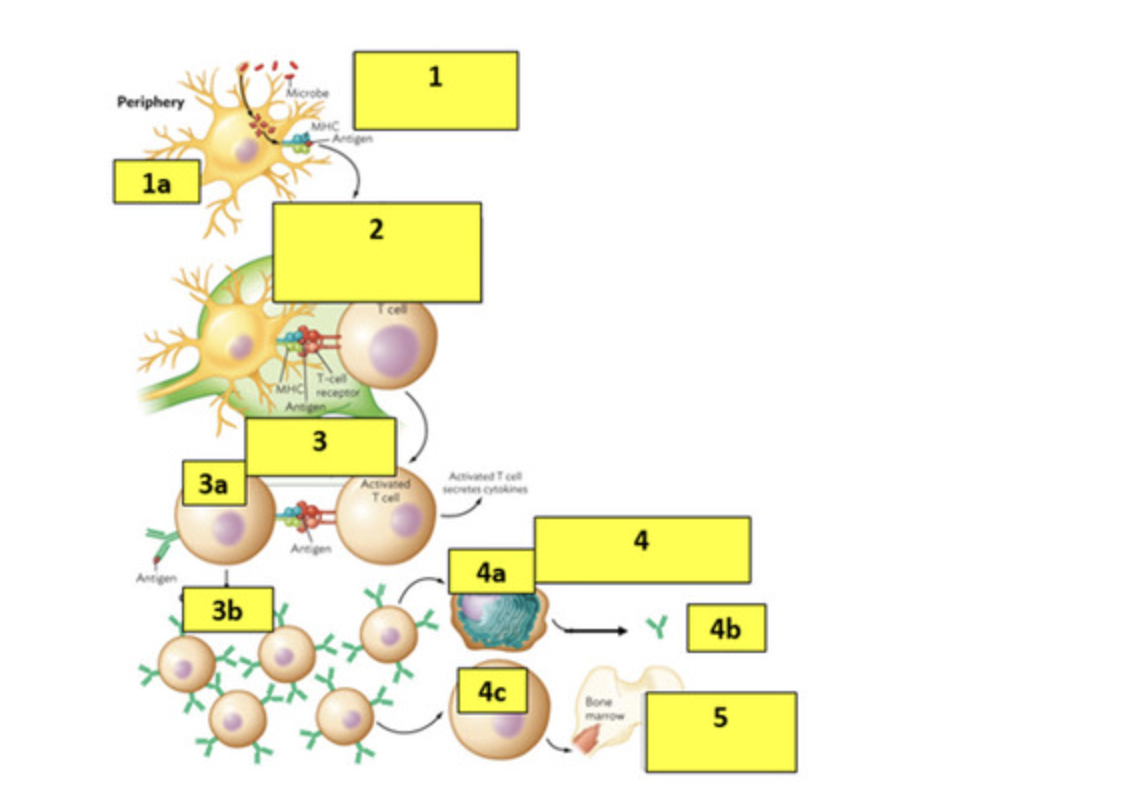
step 5
why would the cell (4c) return to the bone marrow
waits in the bone marrow to recognize new infections