all negative feedback loops & ch6.2
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
6.2 regulation of gas concentrations all negative feedback loops we need to know/in ch5-6 & recap of receptors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
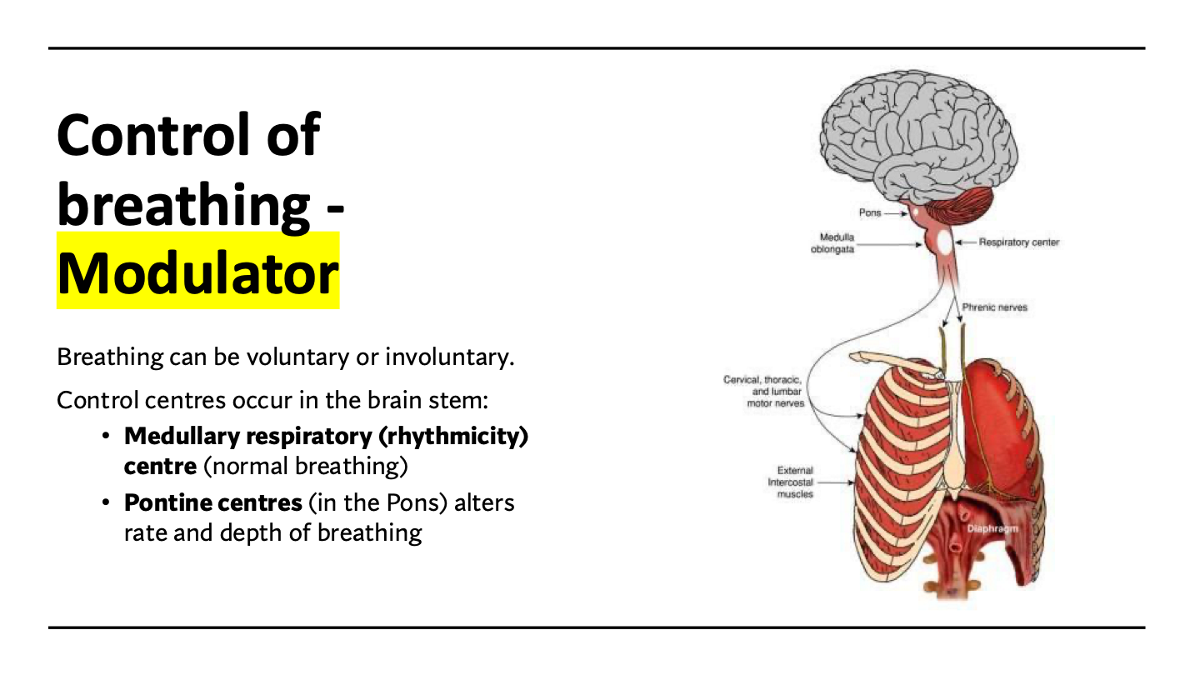
how are gas concs controlled?
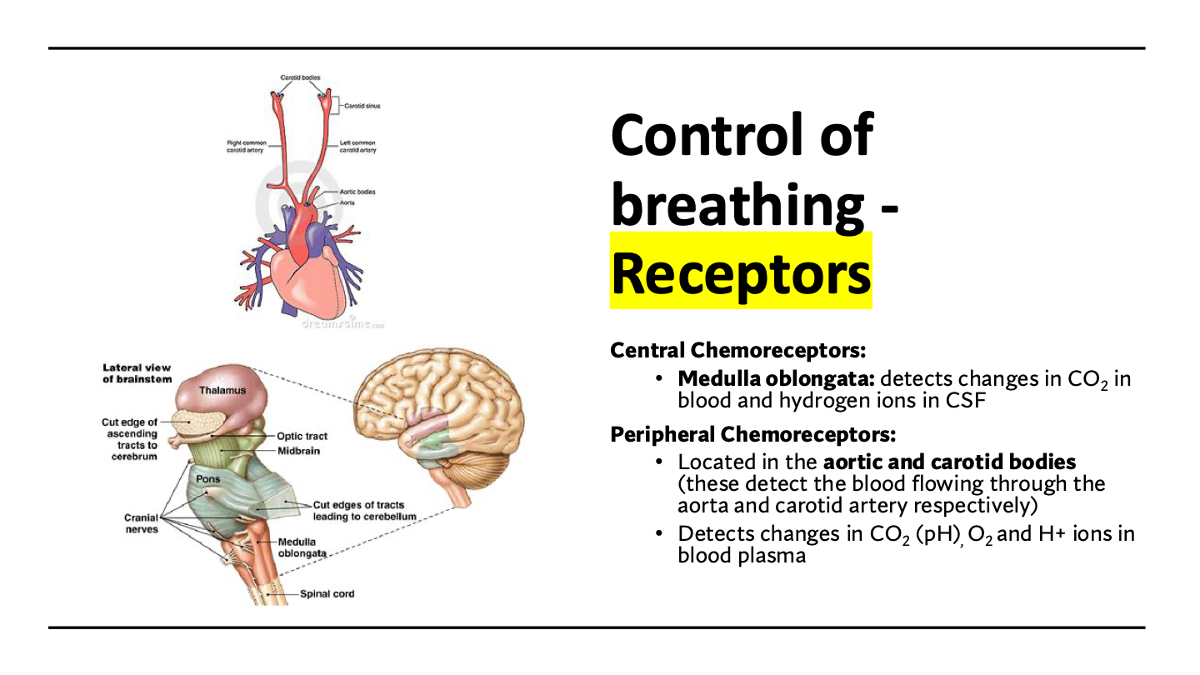
explain how chemoreceptors control breathing
idk
define & explain hyperventilation

Thermoreceptors
A) finish the following sentence: Thermoreceptors can be Peripheral (external ___) or central (internal ___)
B) state role
C) what stimulus/s does it detect?
D) what is the location/s?
E) what is its modulator?
A) temp, temp
B) maintain body temp
C) Hot = detected by heat receptors, cold = detected by cold receptors
D) external temp = skin, internal temp (temp of blood flowing through brain) = hypothalamus
E) hypothalamus
Osmoreceptors
A) state role
B) what stimulus/s does it detect?
C) what is the location/s?
D) what is its modulator?
A) maintain body’s water content
B) changes in osmotic pressure (water concs)
C) hypothalamus
D) hypothalamus
chemoreceptors
A) finish the following sentence: chemoreceptors can be Peripheral (blood ___) or central (___)
B) state role
C) what stimulus/s does it detect?
D) what is the location/s?
E) what is its modulator?
A) plasma, CSF
B) regulation of heartbeat & breathing
C) particular chemicals (odors, tastes), composition of body fluids, pH
D) nose, mouth, blood vessels - aortic & carotid bodies, medulla oblongata
E) Medulla oblongata
Touch receptors
A) what are the other names of this receptor?
B) state role
C) what stimulus/s does it detect?
D) what is the location/s?
E) what is its modulator?
A) mechanoreceptors / pressure receptors
B) perceiving diff sensations
C) light touch, bending hair, pressure & vibrations
D) skin - some close to surface, some further down
E) not involved in homeostasis so receptors are not utilized in feedback loops - only used in reflex arcs
Pain receptors
A) what is the other name of this receptor?
B) state role
C) what stimulus/s does it detect?
D) what is the location/s?
E) what is its modulator?
A) nociceptors
B) alert to damage tissue so we take action to minimise it
C) damage to tissues
D) skin, mucous membranes, and most organs except the brain
E) not involved in homeostasis so receptors are not utilized in feedback loops - only used in reflex arcs
identify 5 negative feedback loops & identify which feedback loop has a modulator that is not in the CNS
water lvls, pH: CO2 lvls / hydrogen ion lvls, temp regulation & glucose
glucose is the only case where the modulcator is not in the CNS
explain the negative feedback loop for low water levels
stimulus: Low water conc in blood
receptor: Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
modulator: hypothalamus
communication corner (side mission): Releasing factors → Nerve → posterior pituitary → ADH
effector: DCT in the kidney
response: Reduces urine, increased drinking & reuptake of water
(negative) feedback: Water conc will increase
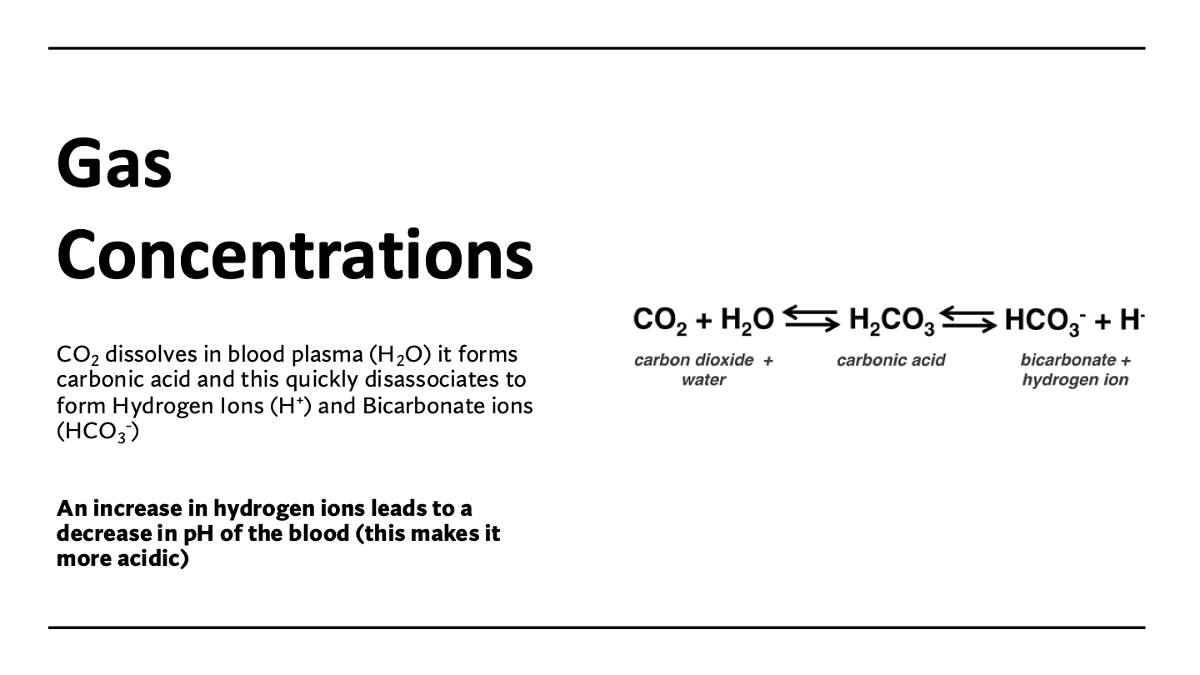
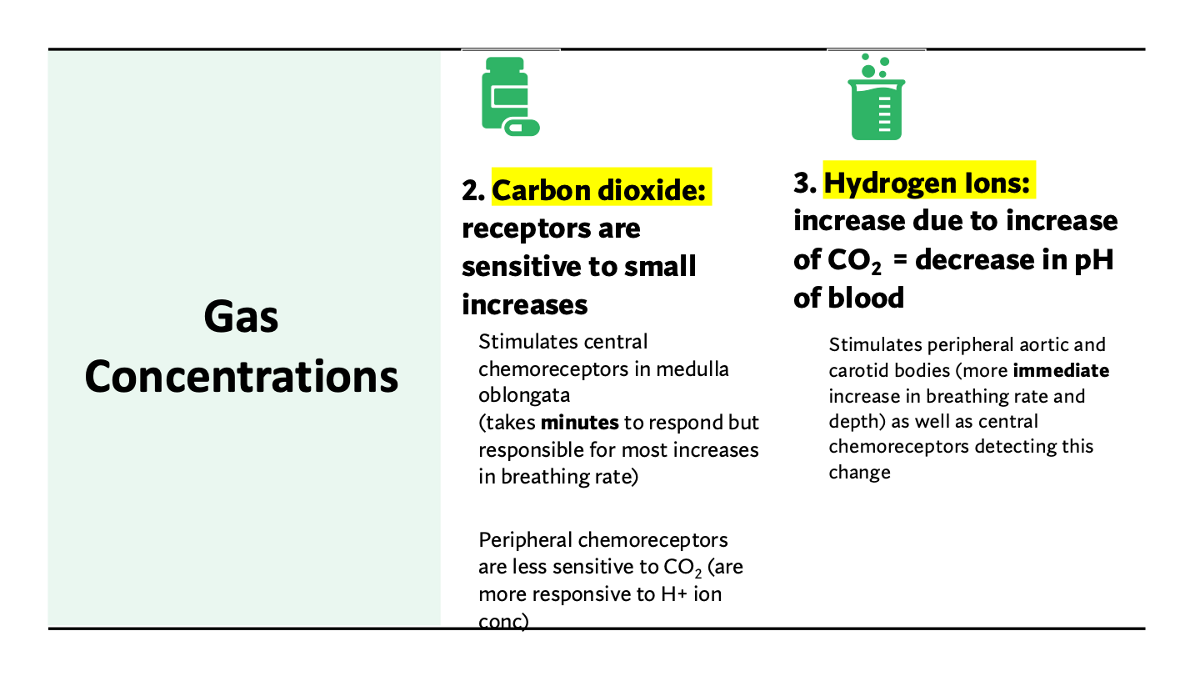
explain the negative feedback loop for high CO2 levels & hydrogen ions (low pH)
stimulus: High CO2 & hydrogen ion levels = low pH
receptor: Chemoreceptors & medulla - respiratory system
modulator: Medalla - respiratory system
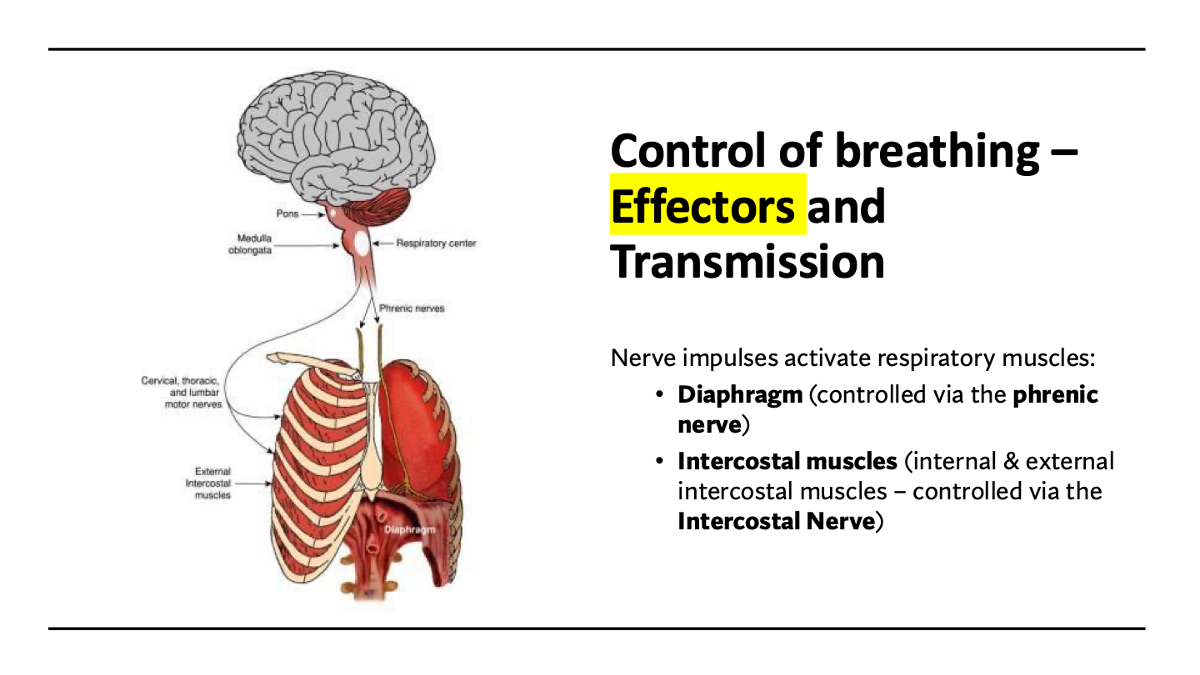
communication corner (side mission): Nervous system / autonomic / parasympathetic - Phrenic & intercostal nerves
effector: Intercoastal & diaphragm
response: Increased breathing rate
(negative) feedback: CO2 & hydrogen ions decreases & pH increase
explain the negative feedback loop for temp regulation - low temp
stimulus: Low core temp
receptor: Thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus
modulator: Hypothalamus
communication corner (side mission): Releasing factor → anterior pituitary → TSH → thyroid → T4 / thyroxine
effector: Muscles, smooth muscles in arterioles & body cells
response: Shiver, increase rate of metabolism / respiration & vasoconstriction
(negative) feedback: Increase in temp
explain the negative feedback loop for high glucose
stimulus: high blood glucose
receptor: Beta cells in islets of Langerhans
modulator: NOT in the CNS - Beta cells in islets of langerhans
communication corner (side mission): insulin
effector: Liver / muscle cells / body cells
response: Glycogenesis - increase uptake of glucose by muscle/cells
(negative) feedback: decrease blood glucose
explain the negative feedback loop for low glucose
stimulus: high blood glucose
receptor: alpha cells in islets of Langerhans
modulator: NOT in the CNS - alpha cells in islets of langerhans
communication corner (side mission): Glucagon / cortisol / adrenaline
effector: Liver / muscle cells / body cells
response: Gluconeogenesis / glycogenolysis
(negative) feedback: increased blood glucose