Anatomy/Physiology Lab Practical 2 PNS
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
–Consists of nerve fibers that carry information between the CNS and other parts of the body
–Subdivided into Afferent and Efferent divisions
Afferent Division
Carries Information TO the CNS
Efferent Division
•Carries information away from CNS to effector organs
–Muscles and glands carry out orders to bring about desired effect
Cranial Nerve 1 (I)
Olfactory
Cranial Nerve 2 (II)
Optic
Cranial Nerve 3 (III)
Oculomotor
Cranial Nerve 4 (IV)
Trochlear
Cranial Nerve 5 (V)
Trigeminal
Cranial Nerve 6 (VI)
Abducens
Cranial Nerve 7 (VII)
Facial
Cranial Nerve 8 (VIII)
Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerve 9 (IX)
Glossopharyngeal
Cranial Nerve 10 (X)
Vagus
Cranial Nerve 11 (XI)
Accessory
Cranial Nerve 12 (XII)
Hypoglossal
Olfactory
CN near nose
Major Function = Smell
Optic
CN near eyes
Major Function - vision
Oculomotor
Eyeball and Eyelid Movement, Pupil Constriction, Change of lens shape for near vision
Proprioception (awareness of the position of body parts)
Trochlear
Eyeball Movement
Proprioception
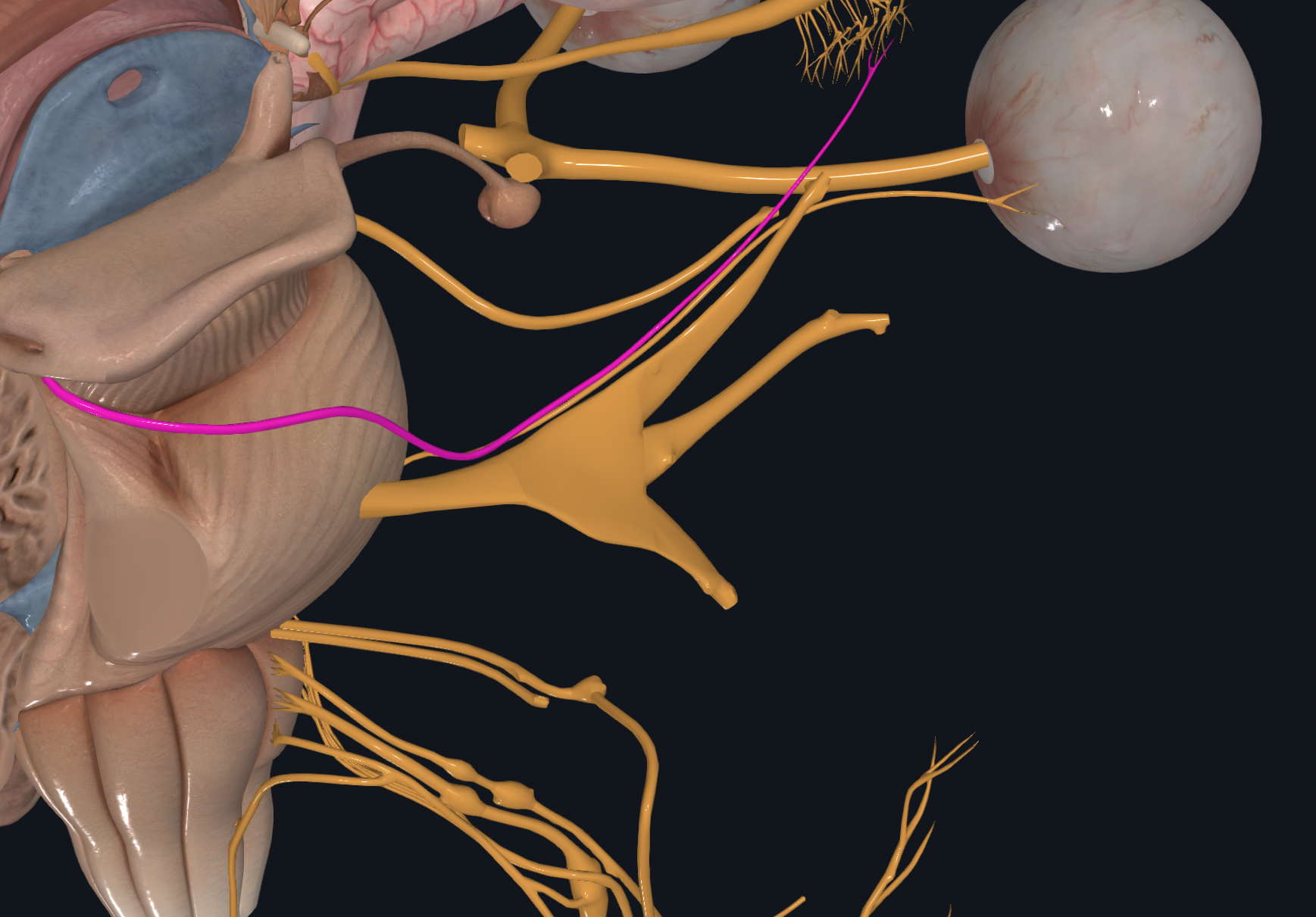
Trigeminal
Chewing
Somatic Sensations (touch, pressure, pain, and temperature) of face and mouth
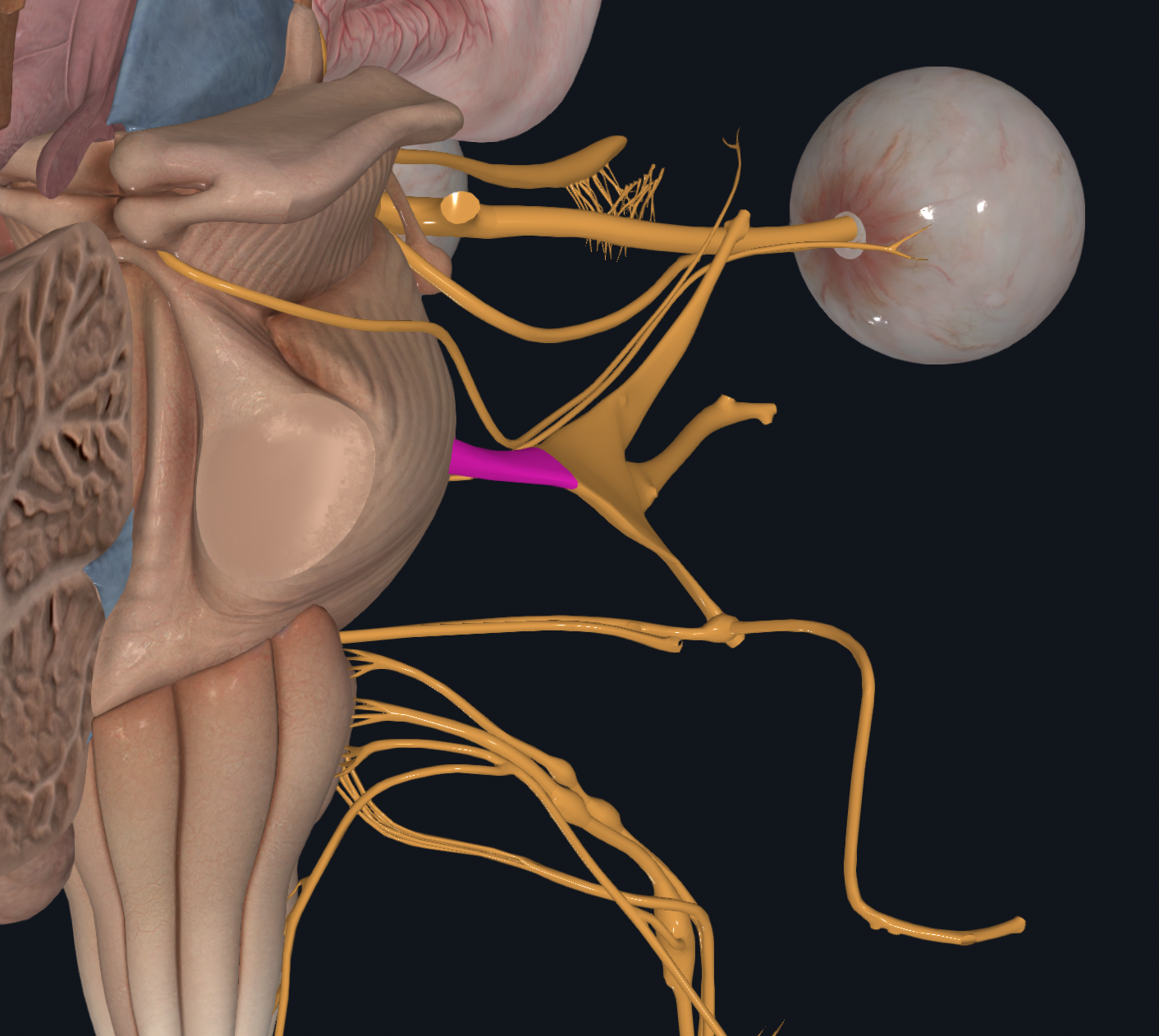
Abducens
Eyeball Movement
Proprioception
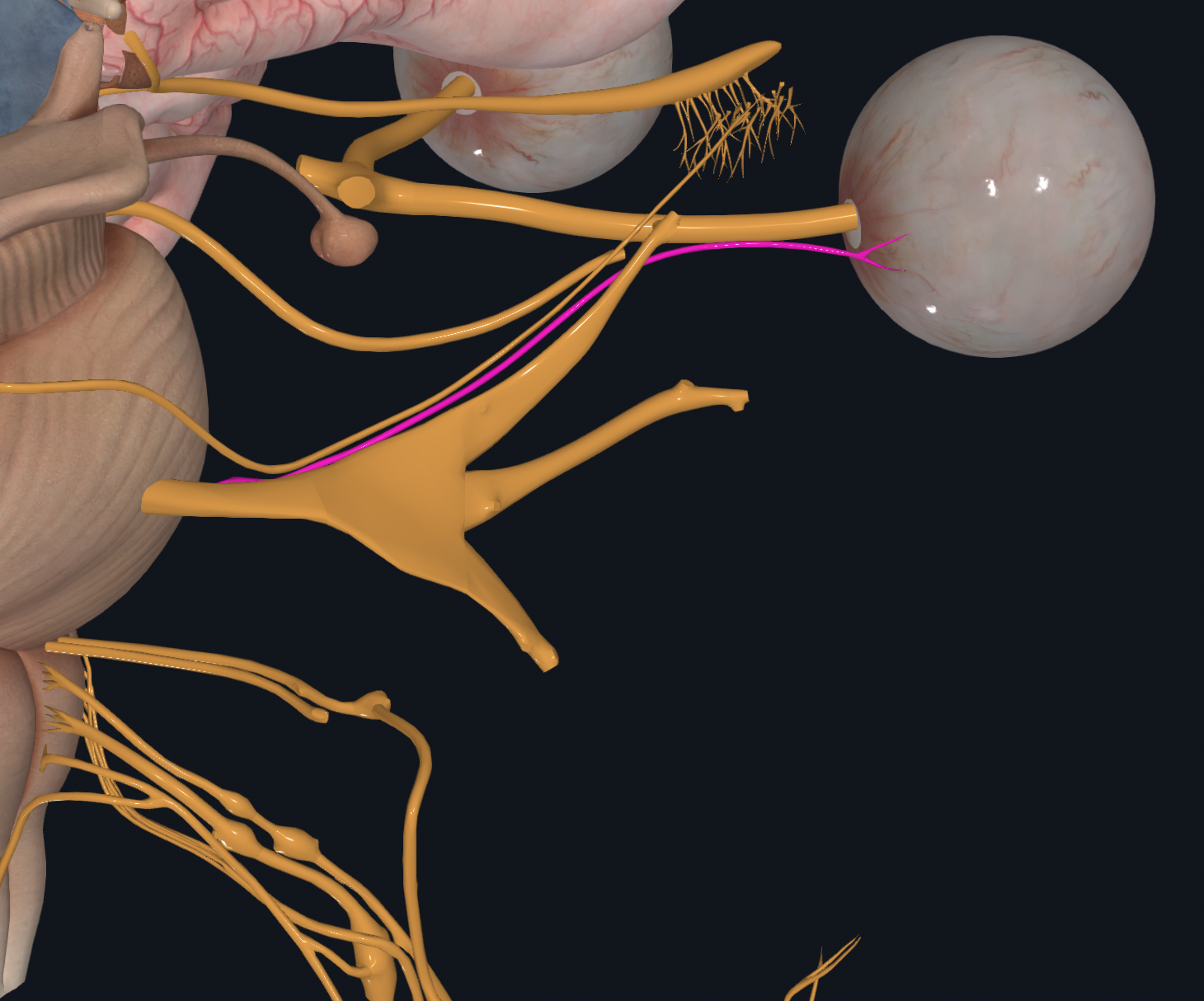
Facial
Facial expressions, secretion of saliva and tears
Taste from front of tongue
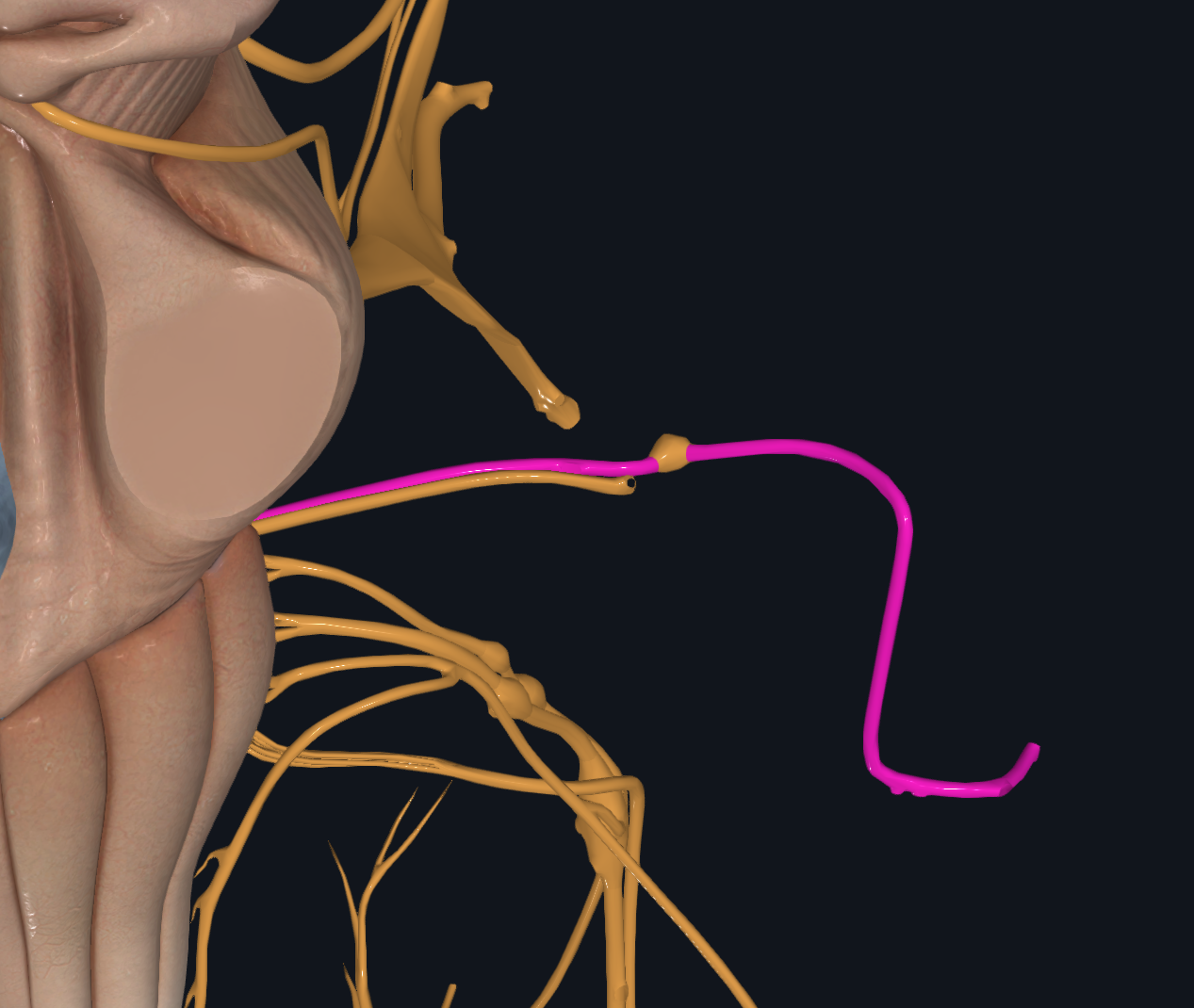
Vestibulocochlear
Hearing, sense of equilibrium
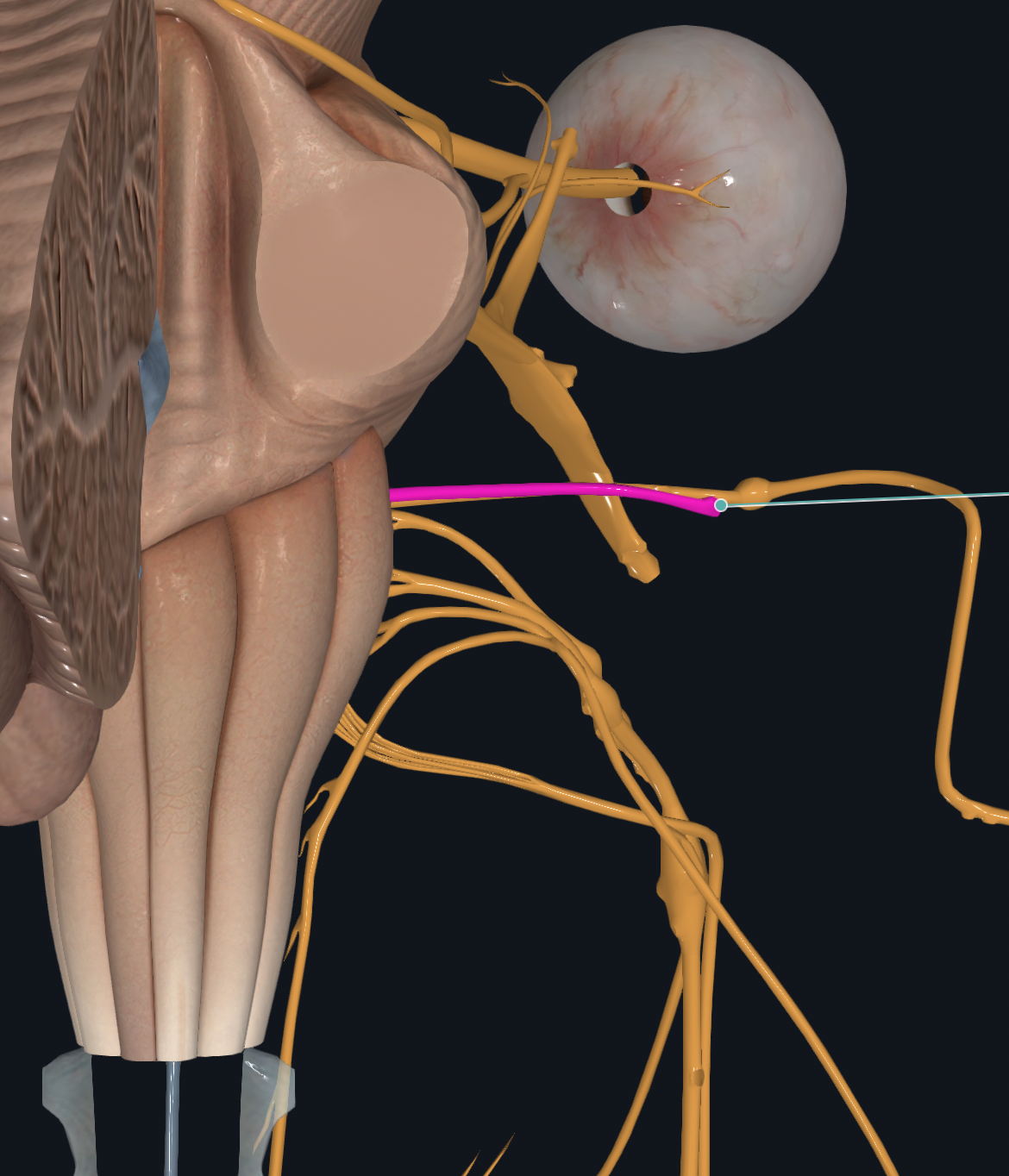
Glossopharyngeal
Swallowing, secretion of saliva
Taste from back of tongue, somatic sensation of oral cavity, blood-pressure monitoring
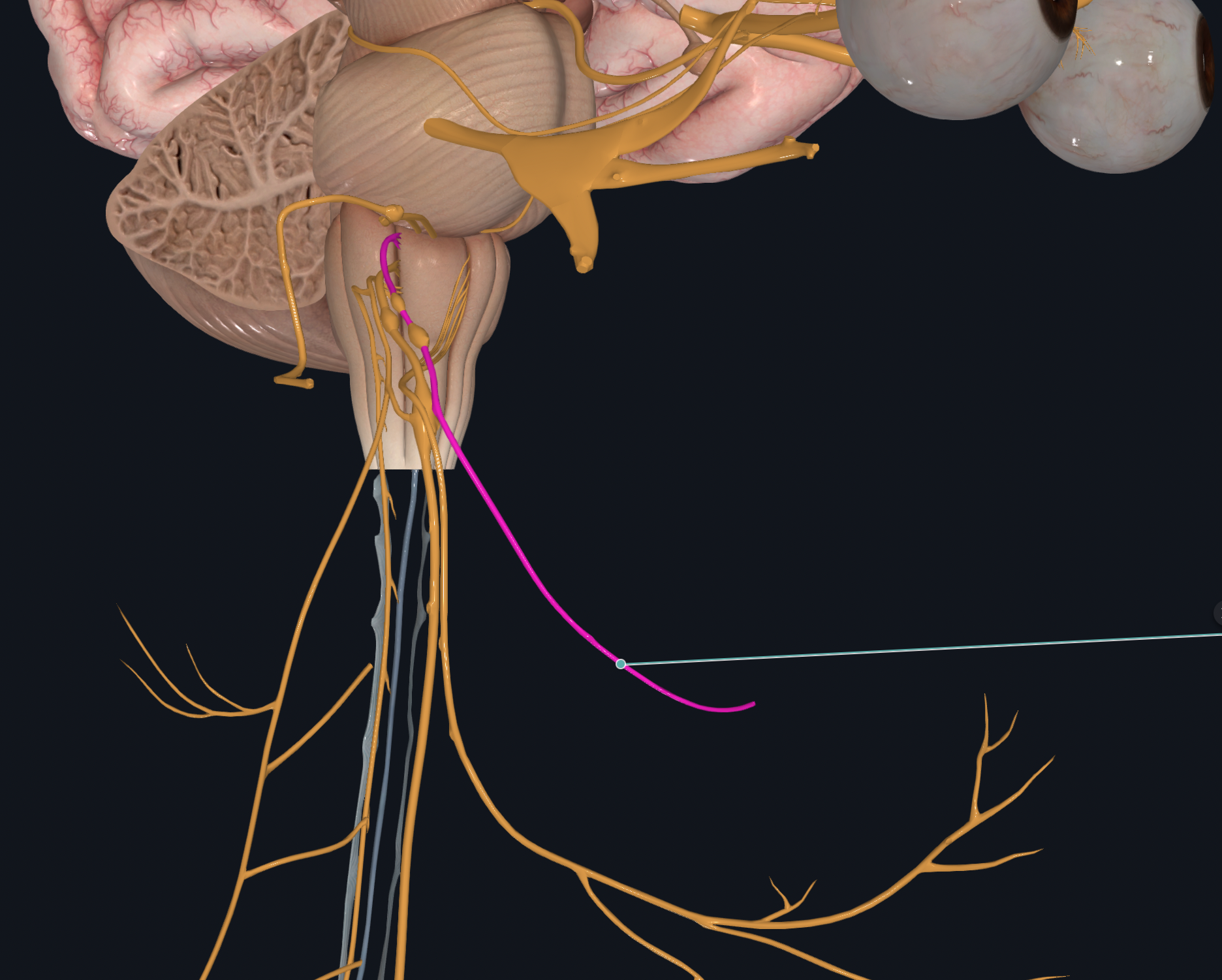
Vagus
Efferent output for skeletal muscles of pharynx (throat) and larynx (voice box) and for smooth muscle and glands of thoracic and abdominal organs and for cardiac muscle of heart
Afferent input for thoracic and abdominal organs, blood pressure monitoring
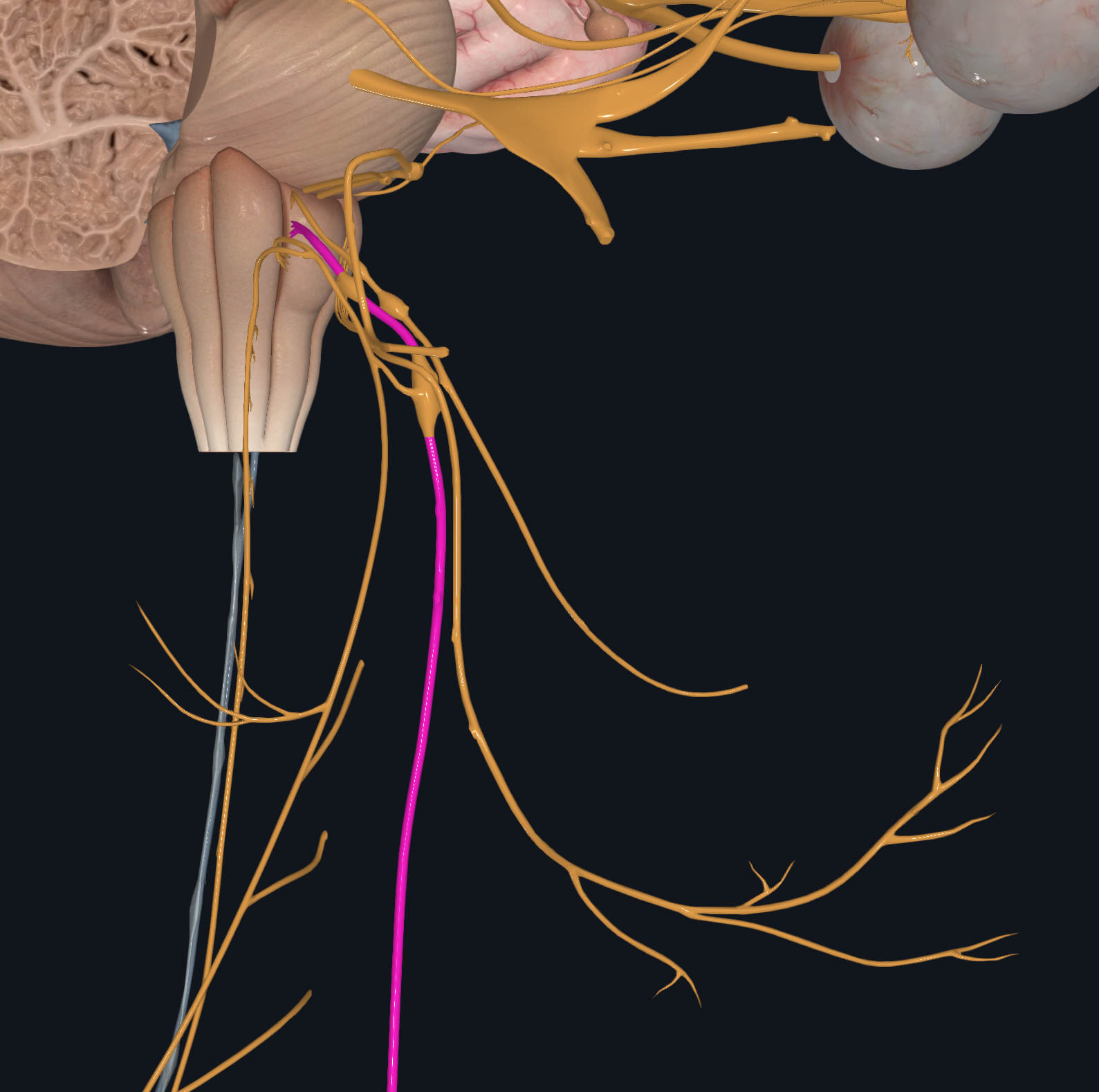
Accessory
Efferent output for skeletal muscles of pharynx, larynx, neck, and shoulder
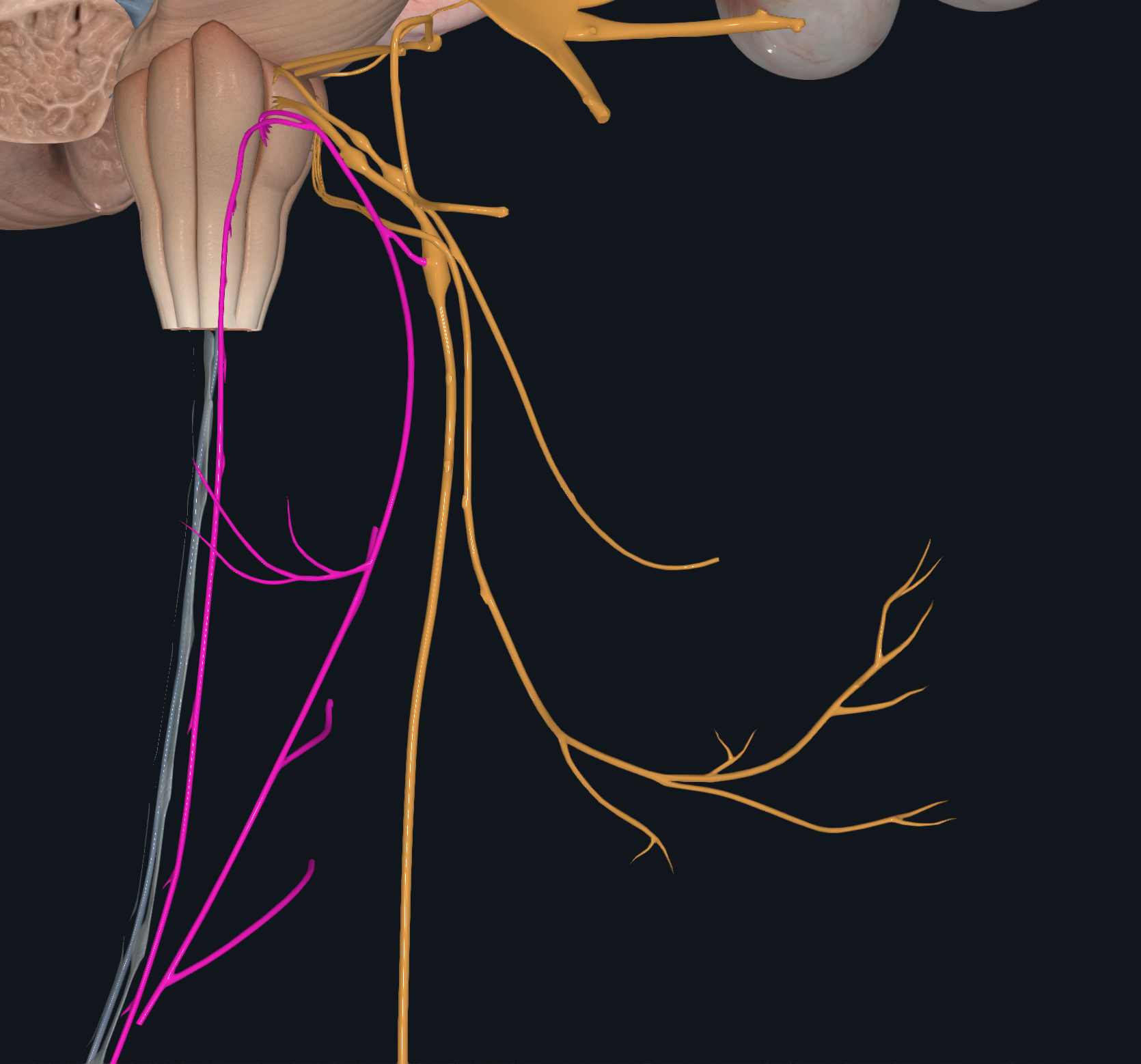
Hypoglossal
Tongue Movement
Sensory
Olfactory CN is what type of fiber?
Sensory
Optic CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed (mainly motor)
Oculomotor CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed (mainly motor)
Trochlear CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed
Trigeminal CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed (mainly motor)
Abducens CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed
Facial CN is what type of fiber?
Sensory
Vestibulocochlear CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed
Glosspharyngeal CN is what type of fiber?
Mixed
Vagus CN is what type of fiber?
Motor
Accessory CN is what type of fiber?
Motor
Hypoglossal CN is what type of fiber?
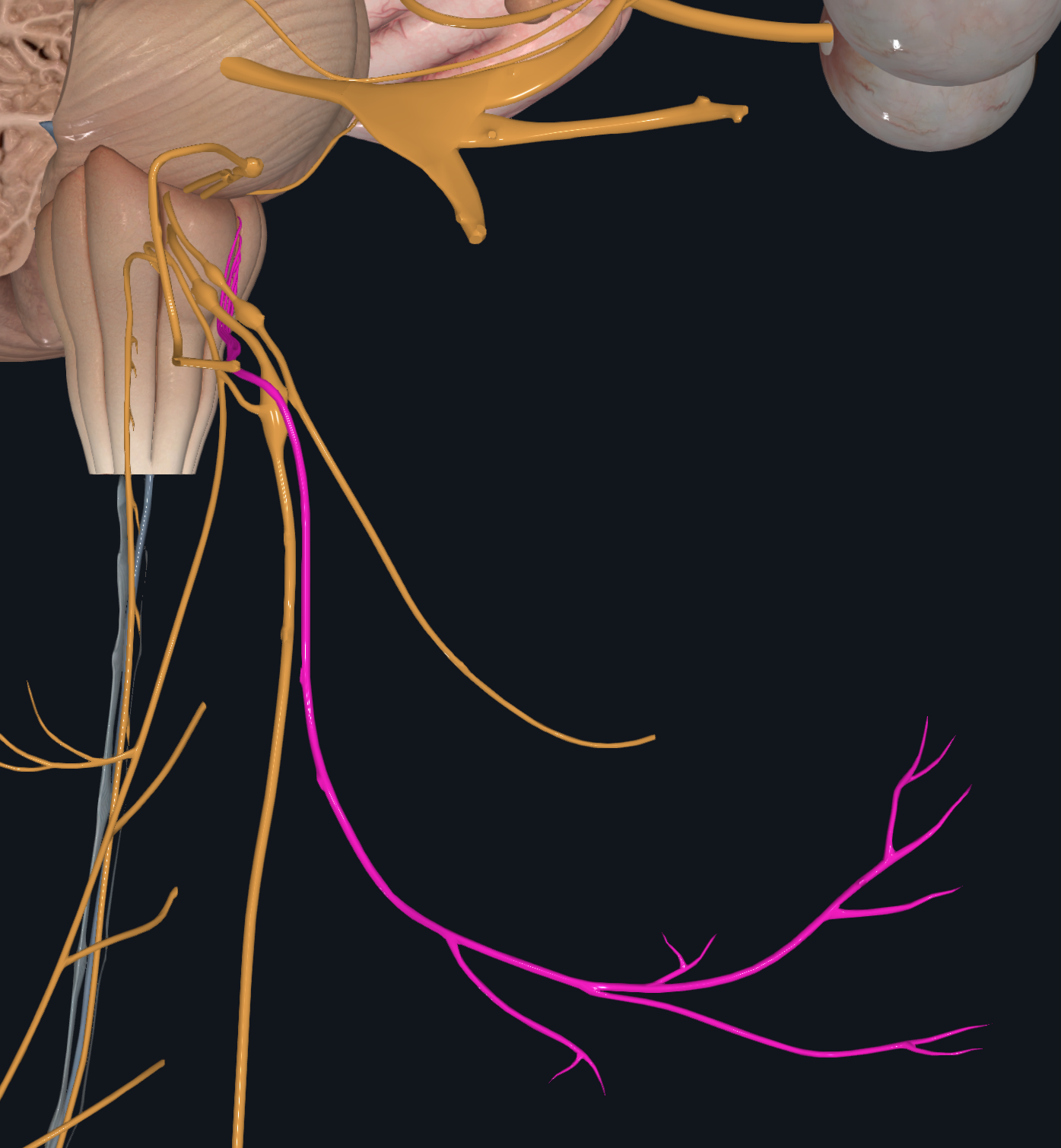
Spinal Meninges
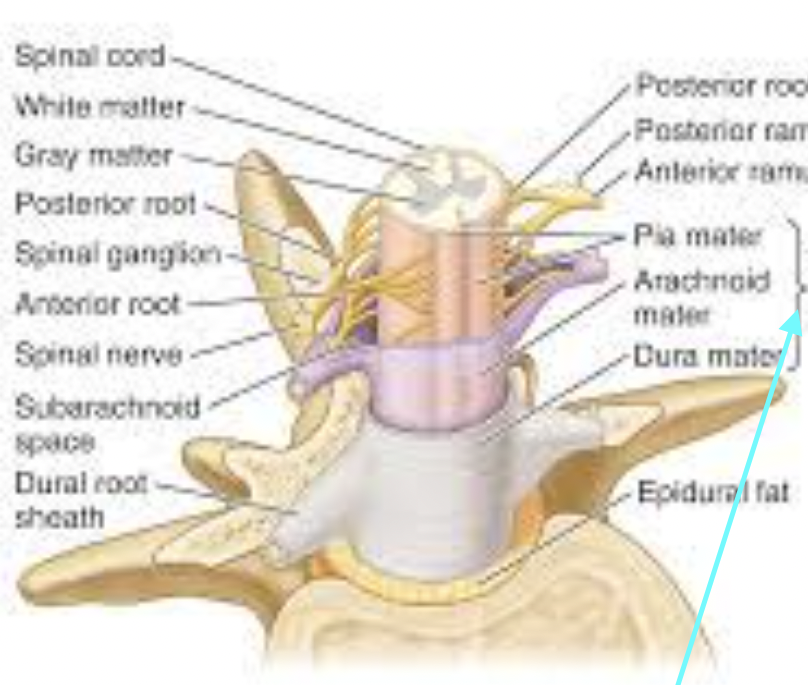
White Matter in Spinal Cord
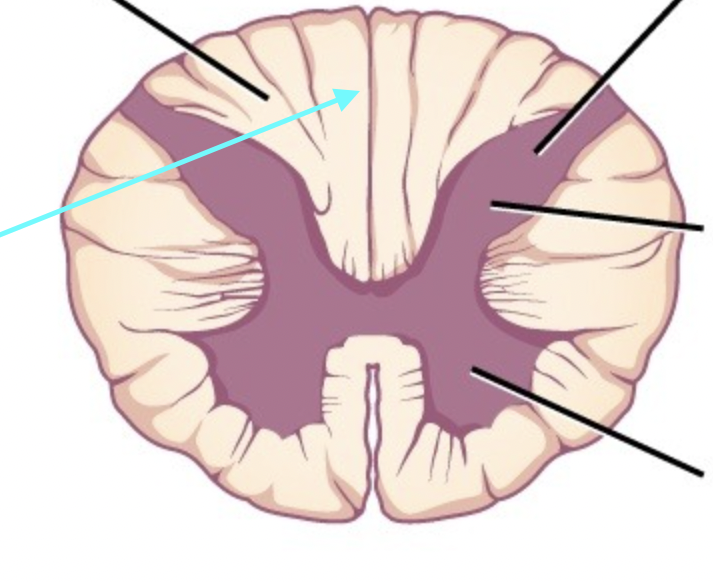
Spinal Nerve
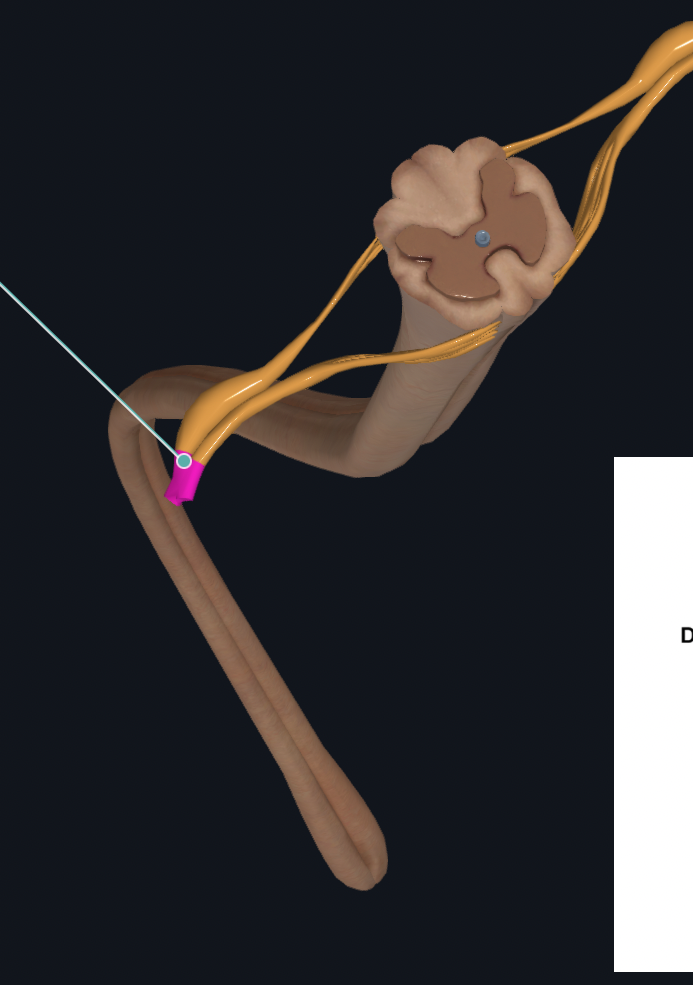
Dorsal Roots
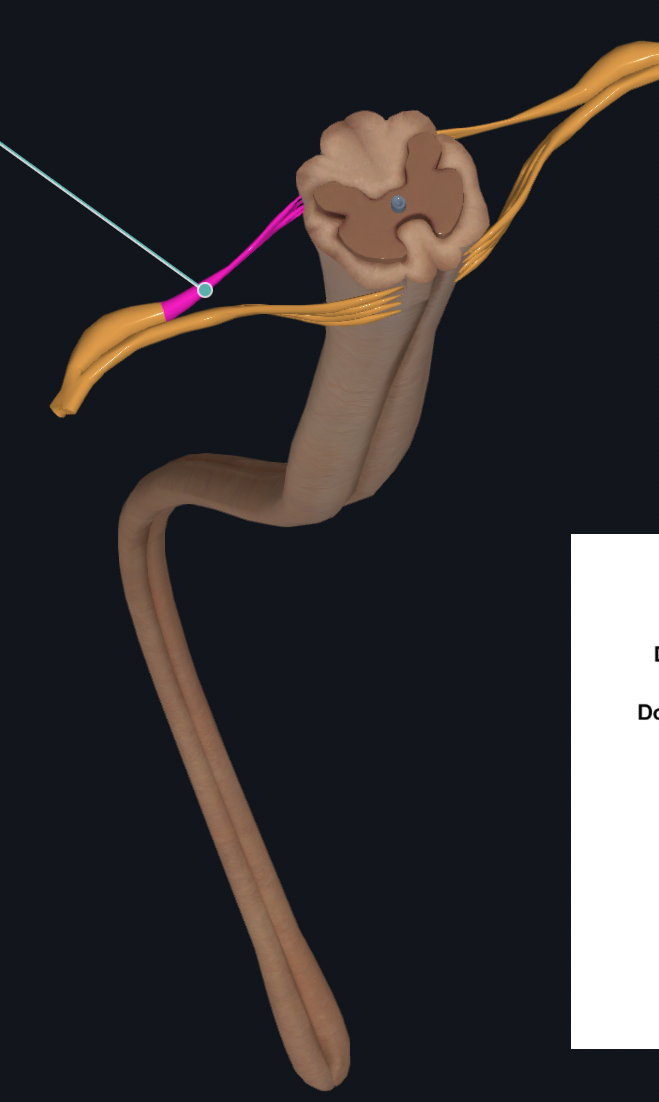
Ventral Roots
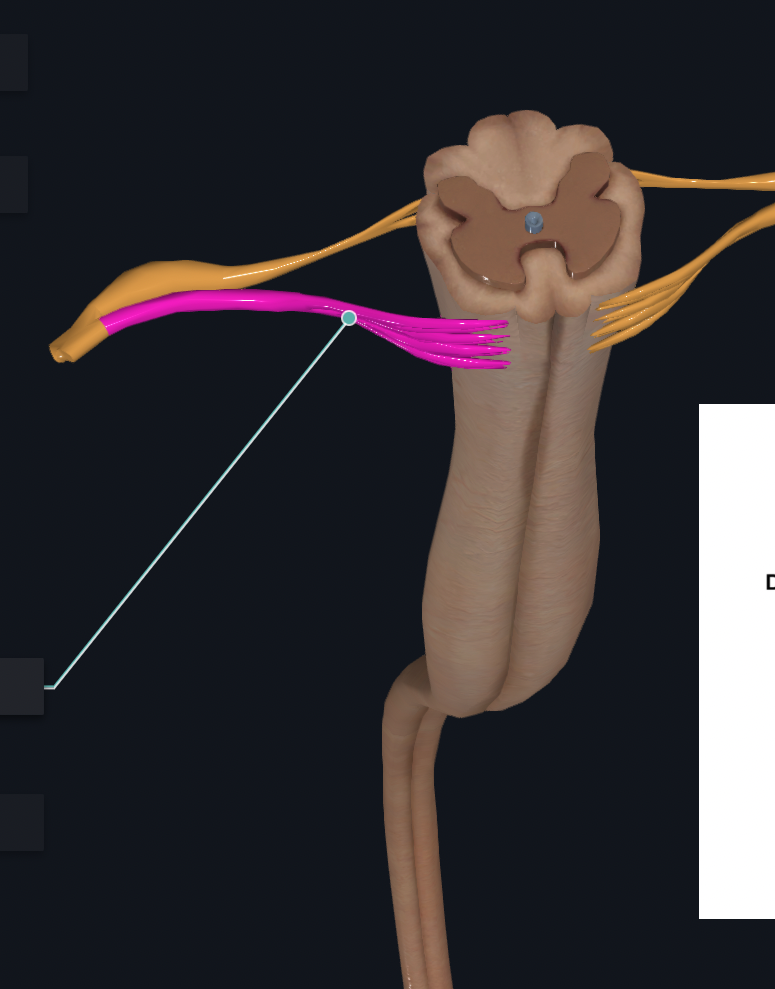
Dorsal Root Ganglia
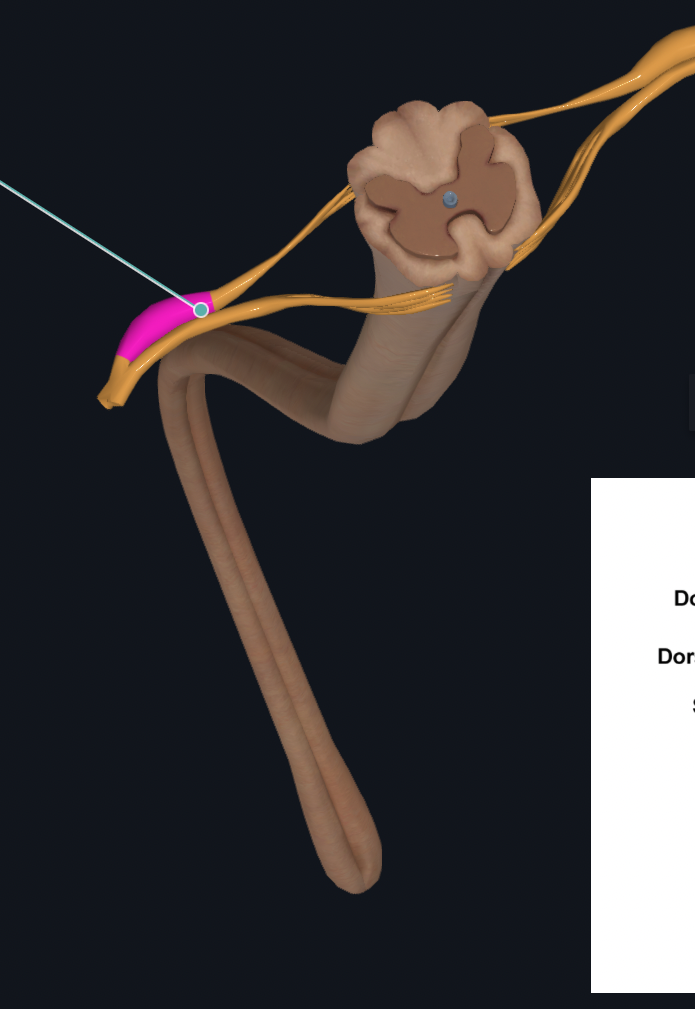
Central Canal
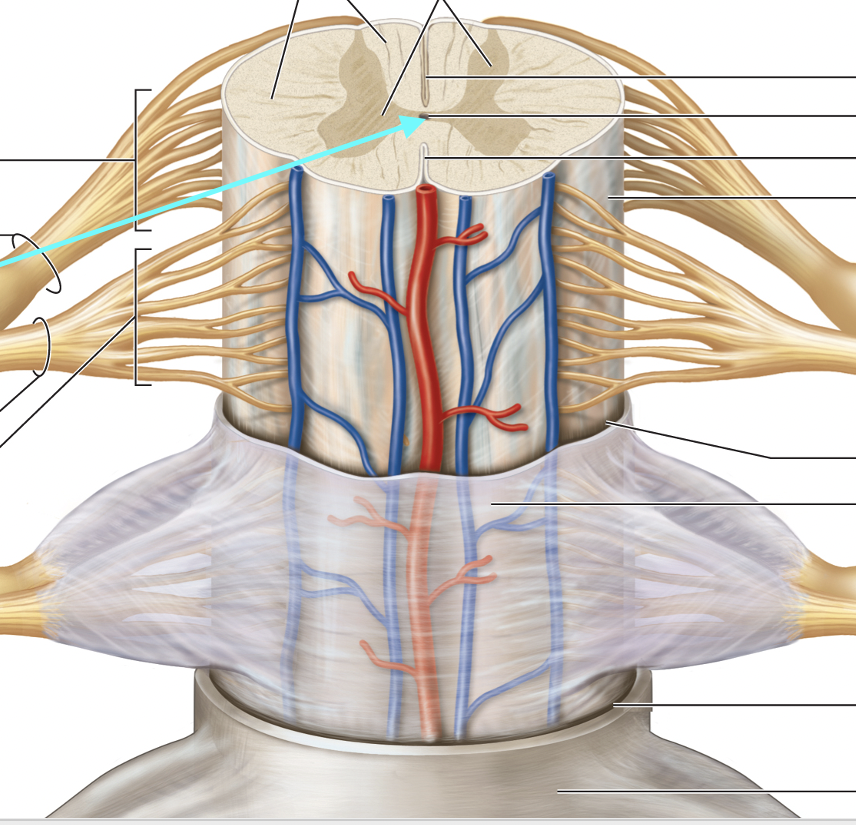
Posterior Median Sulcus
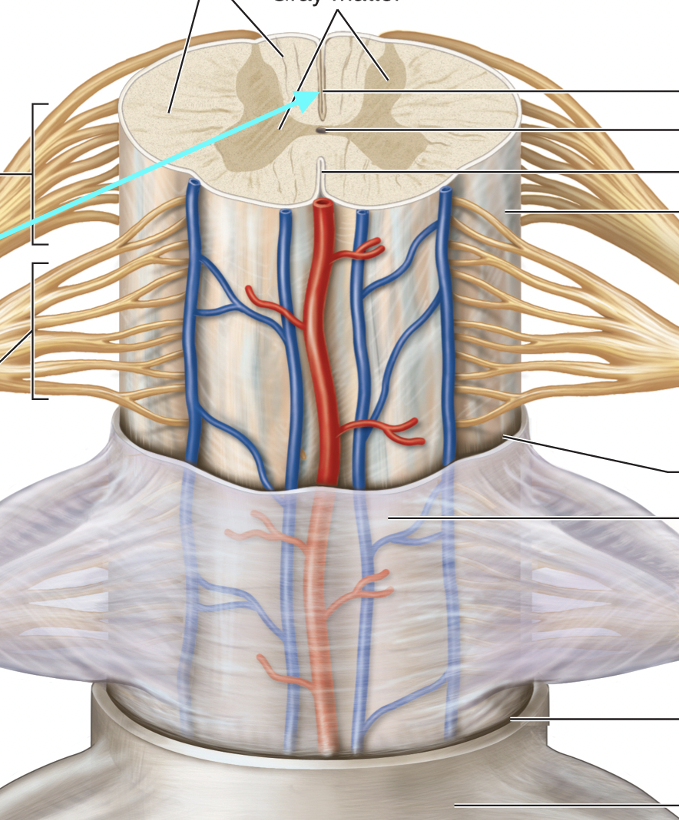
Anterior Median Fissure
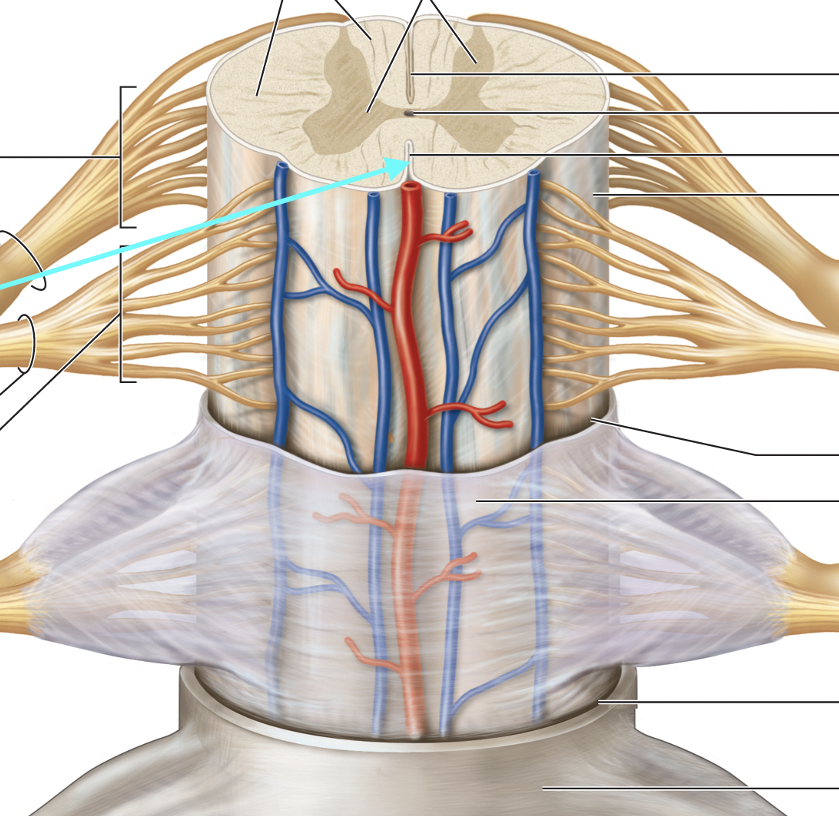
Anterior Gray Matter Horns
Posterior Gray Matter Horns
Lateral Horns Gray Matter
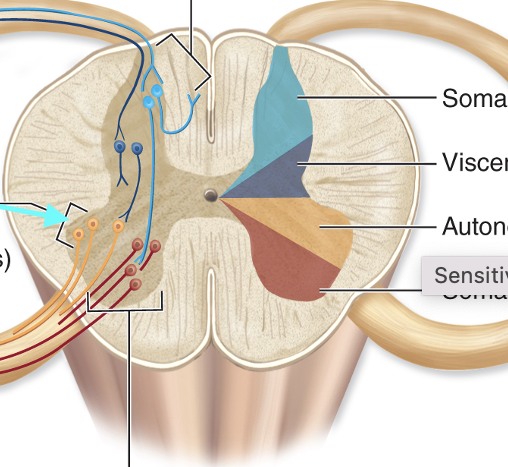
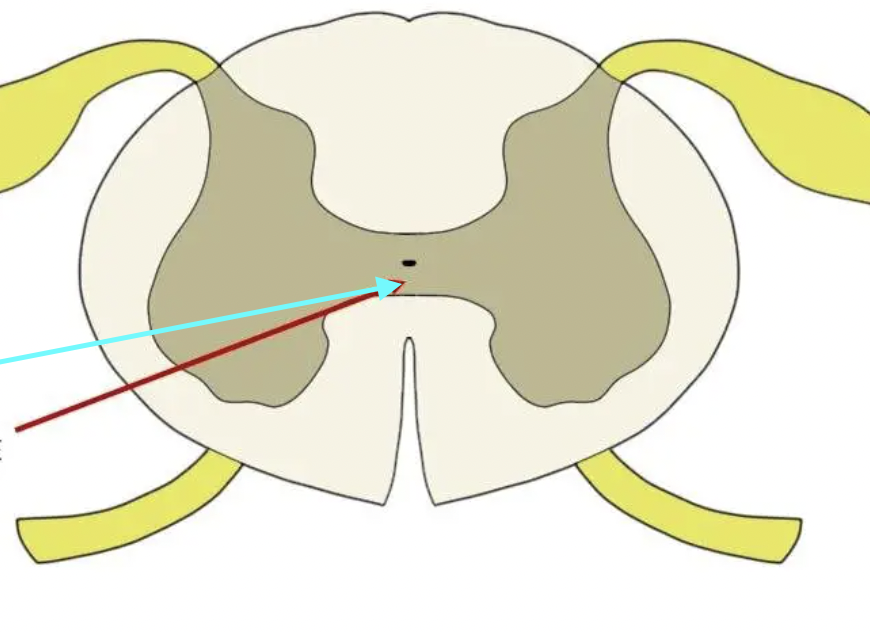
Gray Commissure
Cervical Plexus
Which plexus is formed by C1-C4 SNs?
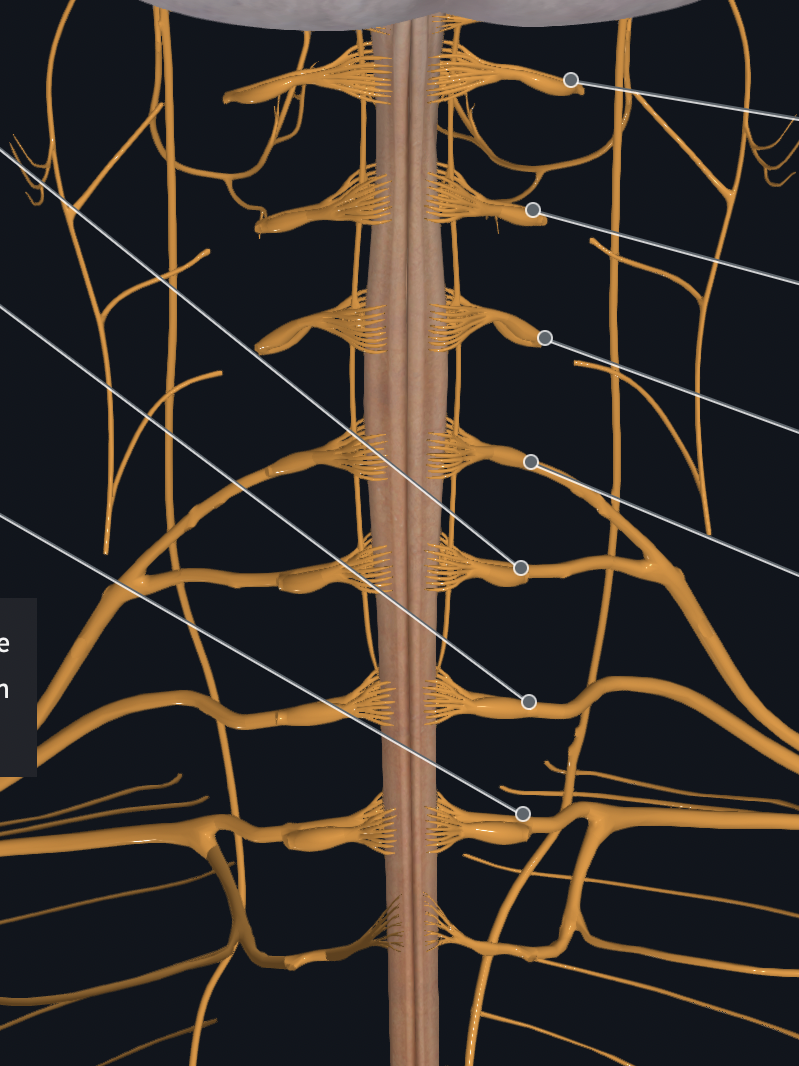
Cervical Plexus
Which plexus innervates the skin and muscles of the neck, shoulder, and arm?
Brachial Plexus
Which plexus is formed by C5-C8, T1 SNs?
Brachial Plexus
Which plexus supplies sensory and motor nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand?
Brachial Plexus
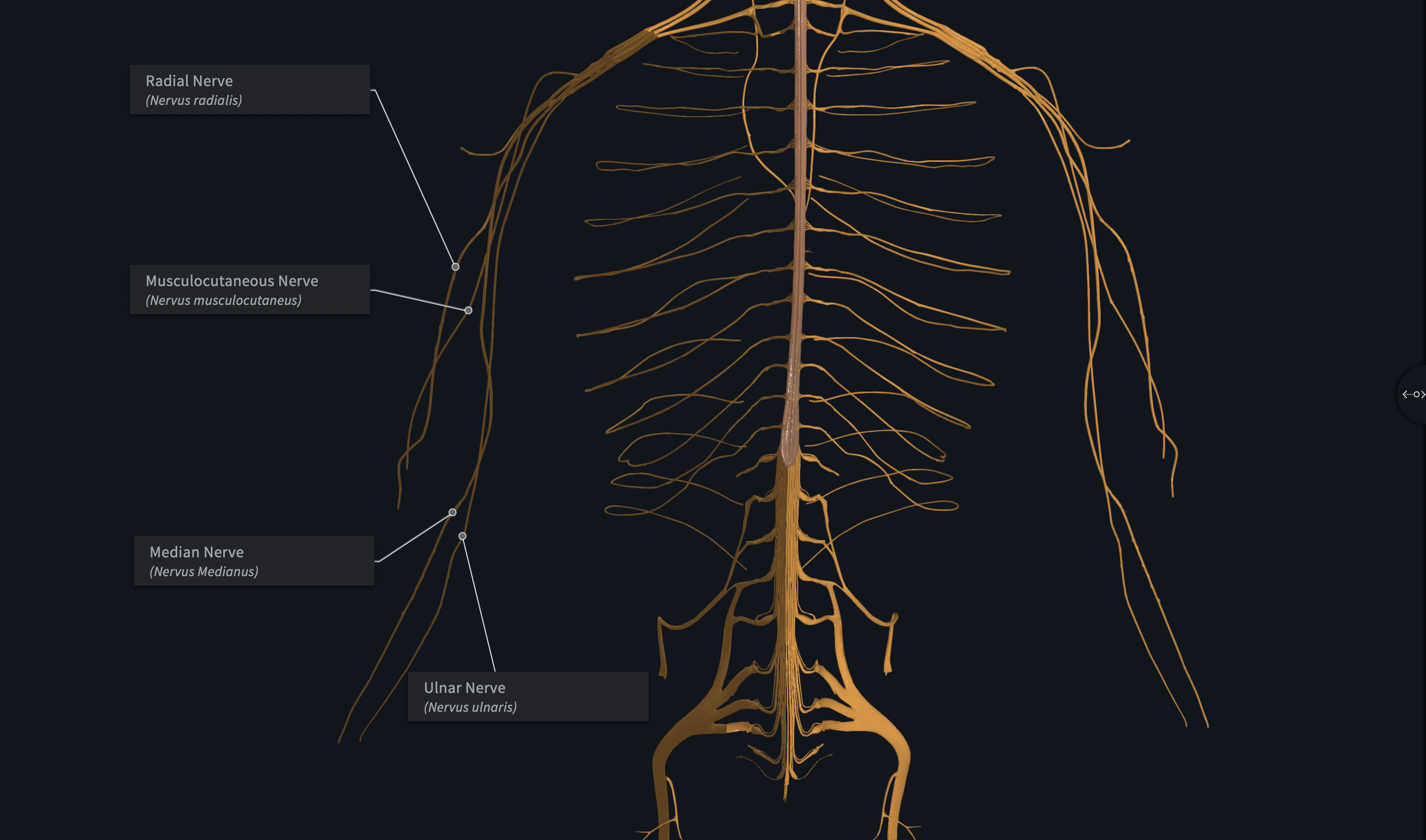
Major Branches of which Plexus?
Musculocutaneous Nerves
Median Nerves
Ulnar Nerves
Axillary Nerves
Radial Nerves
Thoracic nerves
Which Plexus/Nerves are formed by T1-T12 SNs?
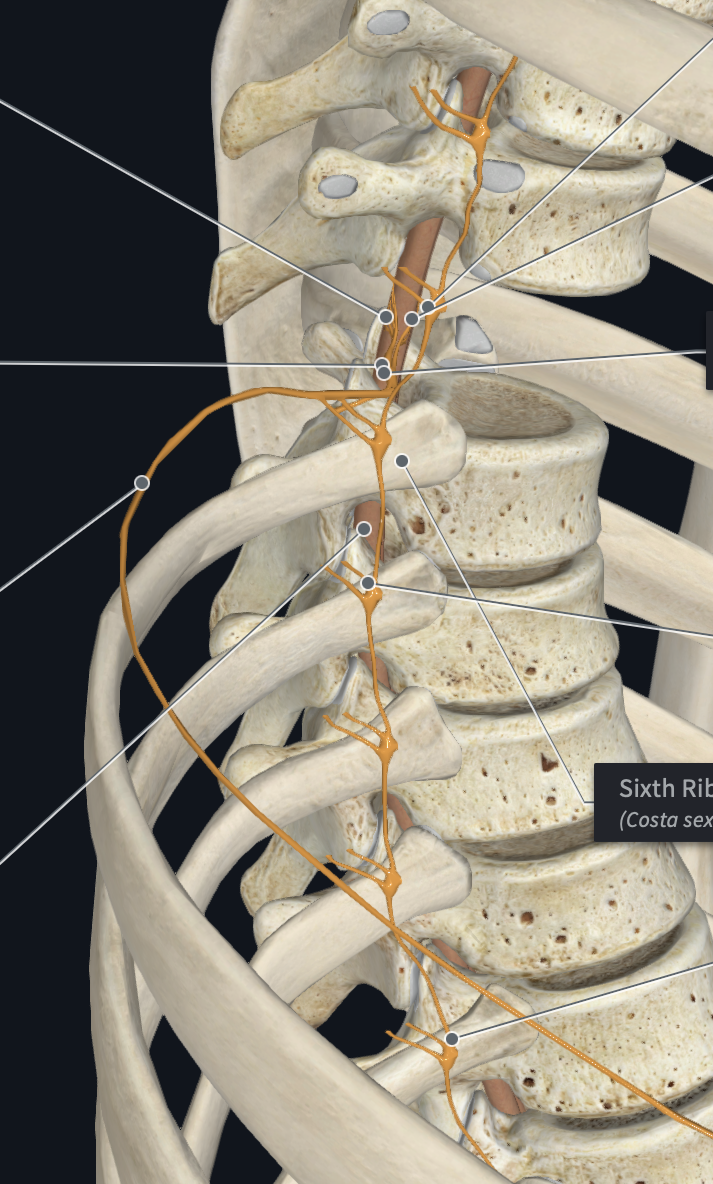
Thoracic Nerves
Which plexus/nerves provide both somatic sensory and motor innervation to their corresponding intercostal spaces and some adjacent structures. Each intercostal nerve travels the entire length of its own numerically equivalent intercostal space. In other words, the nerves run their own course after emerging from the cord, innervating a narrow strip of skin in the anterior and posterior portion of the body in line with their emergence point from the spinal cord.
Lumbar Plexus
Which plexus is formed by L1-L4
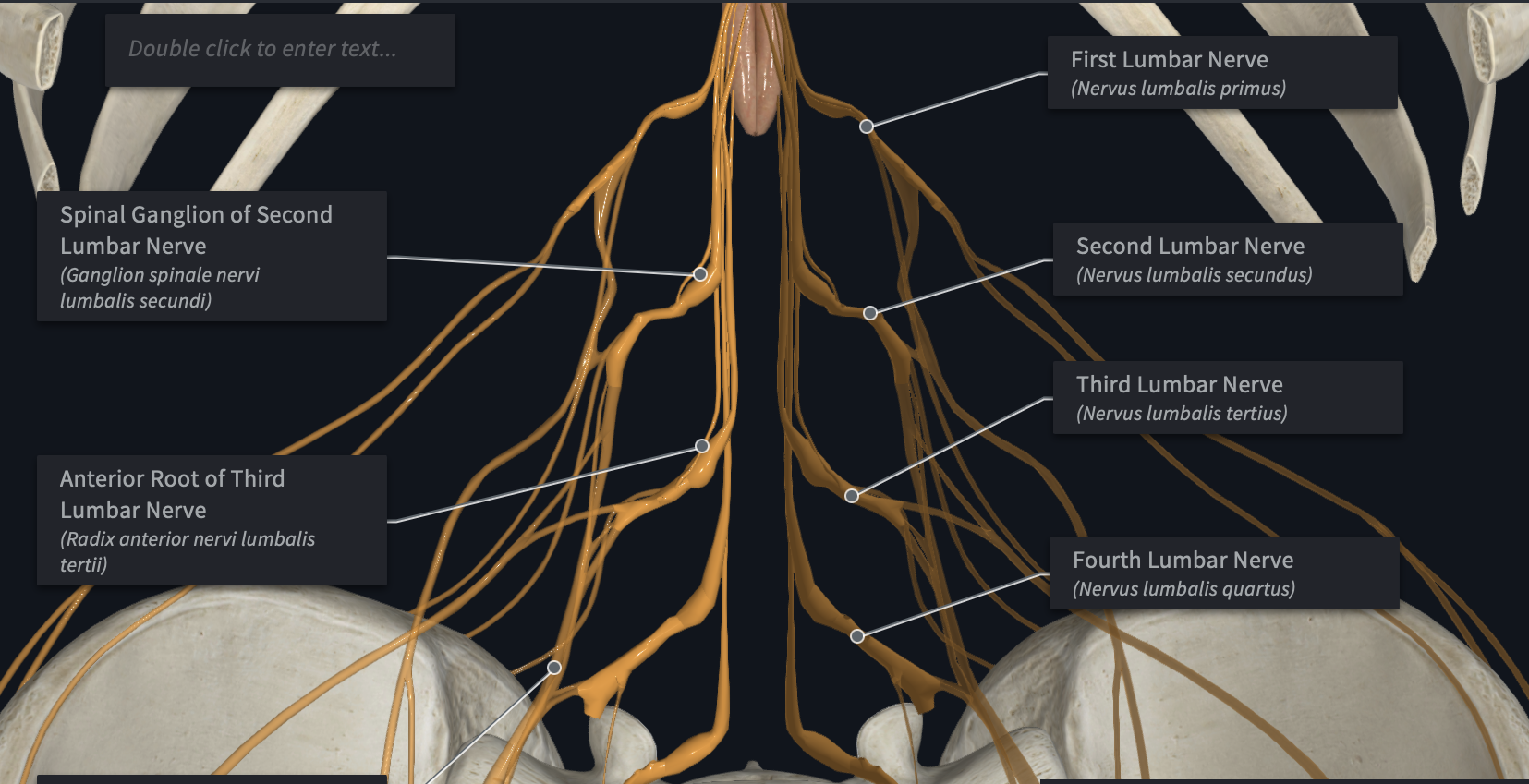
Lumbar Plexus
Which plexus innervates the lower anterior abdominal wall, groin, thighs, knees, and calves?
Lumbar Plexus
Major branches of which plexus?
Femoral Nerves
Obturator Nerves
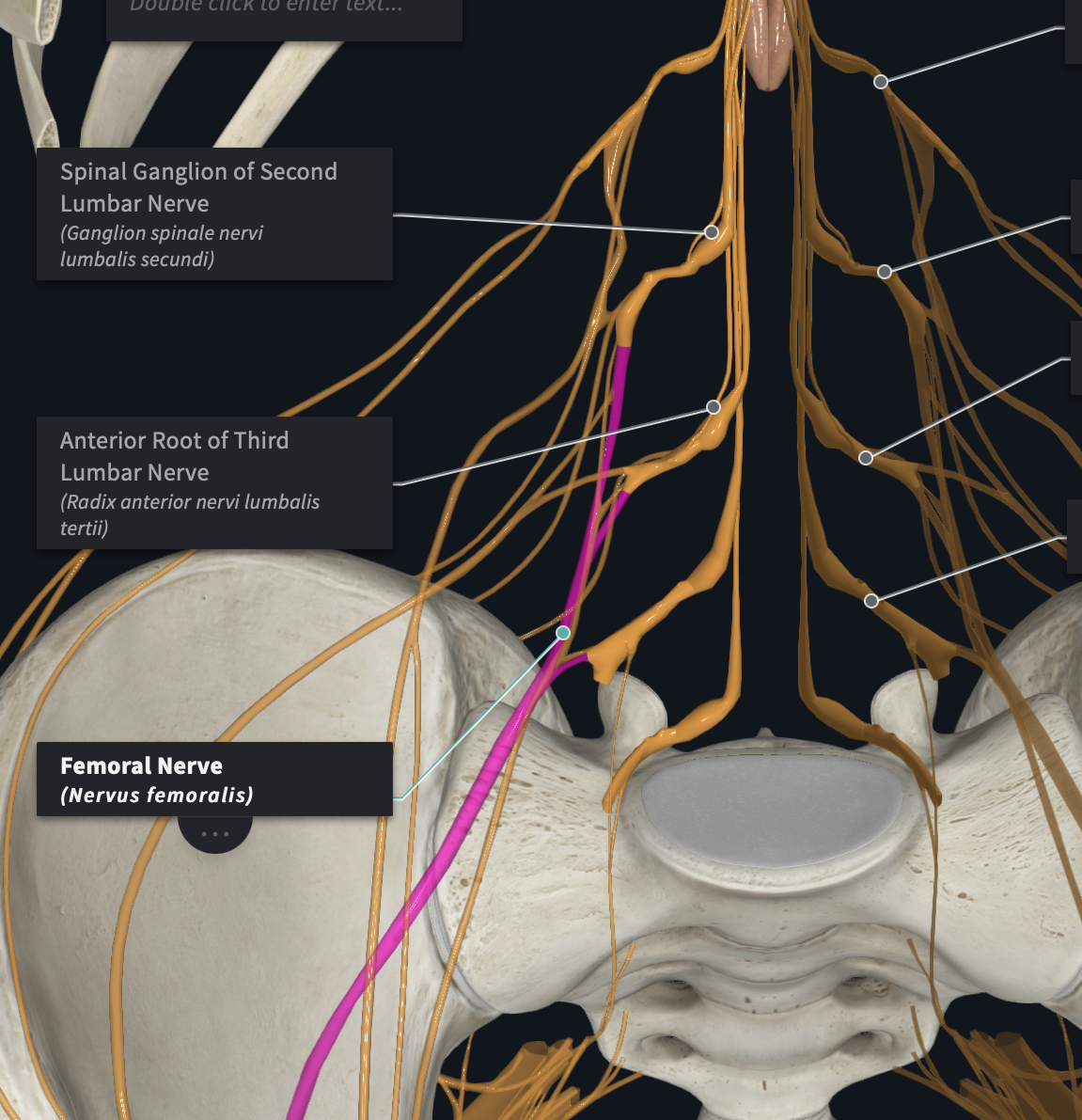
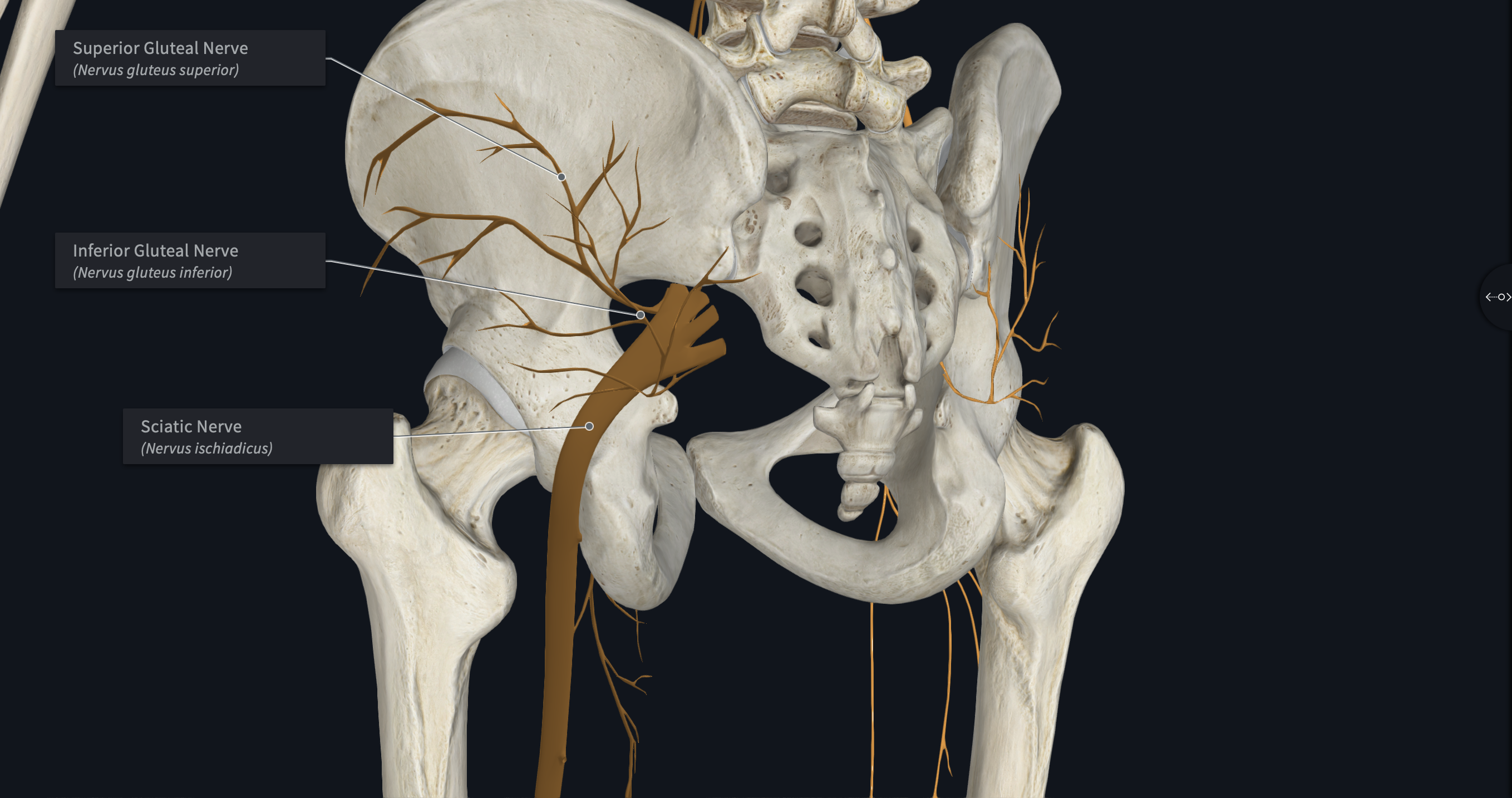
Sacral Plexus
Which plexus is formed by L4-S3 SNs?
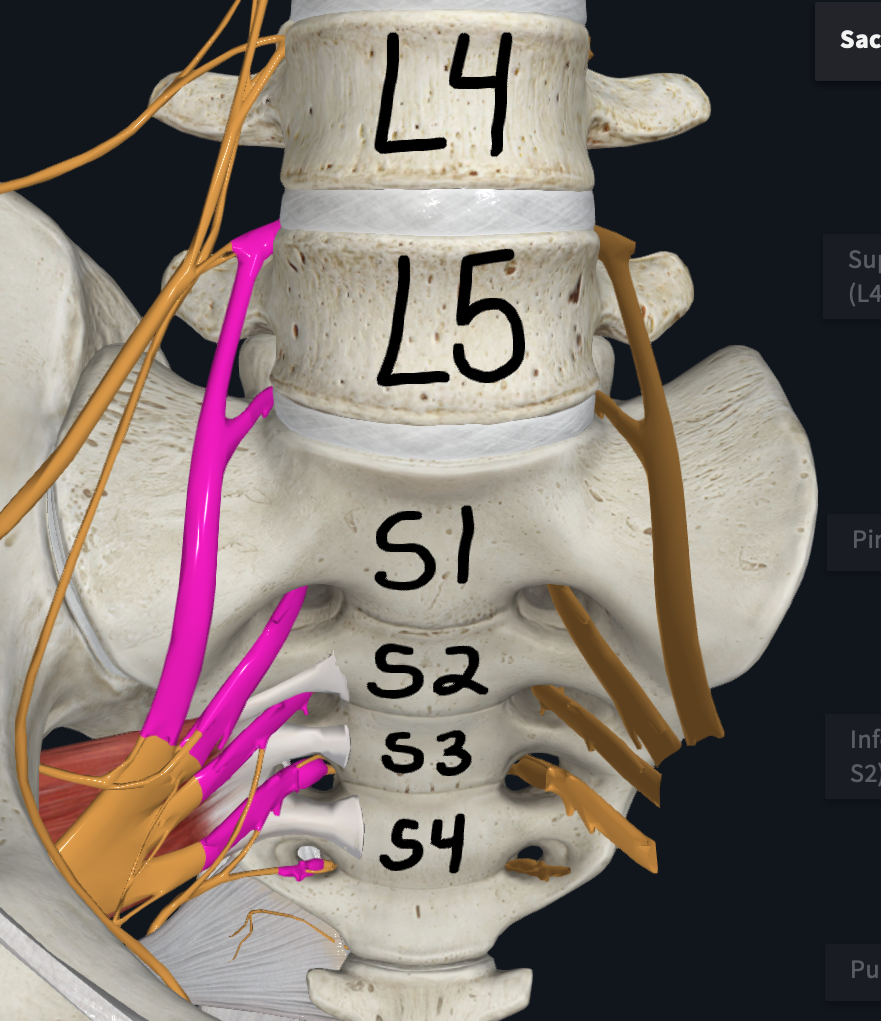
Sacral Plexus
Which plexus innervates motor control to and receives sensory information from most of the pelvis and leg (upper, lower, foot)
Sacral Plexus
Major branches of which plexus?
Sciatic Nerve
Inferior Gluteal Nerves
Superior Gluteal Nerves