Edexcel A Level Mathematics - Statistics
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
What is the northernmost UK weather station?
Leuchars
What is the northernmost English weather station?
Leeming
What is the westernmost UK weather station?
Camborne
Which weather station is closest to London?
Heathrow
Which UK weather station is closest to the Isle of Wight?
Hurn
In alphabetical order, what are the three overseas weather stations?
Beijing, Jacksonville, Perth
In what unit (and tenths) is the daily mean temperature measure in?
Degrees Celcius - average of the hourly temperature during a 24 hour period
Between which times (at GMT) is the daily mean temperature measured?
09:00 to 09:00
What would be seen if no data was available for daily mean air temperature?
n/a
Between which times (at GMT) is the daily total rainfall measured?
09:00 to 09:00
What does a tr / trace value mean for daily total rainfall?
<0.05mm
What unit is daily total rainfall measured in?
Millimetres
What would be seen if no data was available for daily total rainfall?
n/a
What is daily total sunshine measured in?
Nearest tenth of an hour (of bright sunshine)
What would be seen if no data was available for daily total sunshine?
n/a
What is daily maximum relative humidity a measure of?
How close the air is to being saturated with water vapour.
What is a relative humidity of 95% and above associated with?
Mist and fog.
What would be seen if no data was available for daily maximum relative humidity?
n/a
What are wind speeds measured in?
Knots - unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour
What is one knot approximately equal to, in mph?
1.15 (mph)
To how many degrees is the daily mean wind direction rounded?
(To the nearest) 10 (degrees)
What is the daily maximum gust direction?
The direction from which the wind was blowing during the maximum gust
What is the daily maximum gust speed?
The highest instantaneous speed which occurred during the 24 hours on the date given
What other type of direction is given for windpseeds?
Cardinal (compass) direction and bearings
What would be seen if no data was available for wind speeds?
n/a
What is the name of the unit in which cloud cover is measured in?
Oktas
How much is an Okta?
One eighth
What is cloud cover?
The fraction of the celestial dome covered by cloud
How would visibility be defined at daytime?
The greatest distance at which an object can be seen and recognised in daylight
How would visibility be defined at nighttime?
The greatest distance at which an object can be seen and recognised if the general illumination were raised to daylight level
In which direction is visibility measured?
Horizontally
What is visibility measured in?
Decametres
What would be seen if no data was available for visibility?
From what level is the mean sea level pressure calculated?
Station level
What was previously used as the unit of pressure?
Millibars
Which SI unit is currently used as the unit of pressure?
Hectopascals
What is one hectopascal equal to?
One millibar
Describe how air temperature is measured
By thermometers in a louvered screen 1.25 metres above short grass
What are the exceptions to how air temperature and humidity is measured?
At some Weather Centre's and Climate Data Logger stations from a non-standard roof top exposure
In British Summer Time, when do the 24 hour measuring periods start?
10:00
Daily Total Rainfall also includes
solid precipitation which is melted
What device measures visibility,?
Visiometer
Windspeed is measured from what time, over...?
00:00 GMT, 24 hours
What are the categories for the Beaufort scale corresponding to 0, 1-3, 4 and 5 respectively?
Calm, Light, Moderate, Fresh
Give the range of windspeeds, in knots, for calm, light, moderate and fresh speeds respectively.
<1, 1-10, 11-16, 17-21
What are the only data recorded in overseas stations?
Daily mean: rainfall, temperature, pressure, windspeed
Coastal locations are typically
windier
Northern locations are typically
colder
For 2015 the windiest month on average, for all stations, was
May
In the UK in 2015, the wettest month on average was
August
Worldwide, the wettest city in 2015 was
Jacksonville
In 2015 the wettest UK city was
Camborne
The warmest UK location on average in 2015
Heathrow
In 2015, in order of mean temperature for overseas stations
Jacksonville, Beijing, Perth
Why is Perth pretty cold during the range of months given compared to the rest of the world?
It is in the southern hemisphere whereas the rest are in the northern hemisphere. So the seasons occur at different times.
What extreme event happen in 1987, when, and where?
The Great Storm of 1987. A violent extra tropical cyclone that occurred on the night of 15-16 October in England
In 2015, what extreme event happened, when, and where?
26 August, Heathrow airport was affected by the heavy rains
Give the date of a strong heat wave which occurred across the UK, and the temperature.
30 June 2015, 30 degrees and above
Why is it important to know where measurements are taken?
For consistency and comparison
What type of data is in the data set, in terms of collection?
Secondary
Why is it important to know about windspeed and maximum wind gusts for Heathrow?
It is an airport, wind greatly affects landing and taking off.
What is the median?
The middle data value when all the data values are placed in order of size.
What is the mode?
The most frequently occurring data value.
How do you calculate the median when the total frequency is even?
The median is the average of the middle two values.
How do you calculate the median when the total frequency is odd?
The median is the middle value.
How is the standard deviation calculated?
Mean of the squares, minus the square of the mean. (MOSSOM)
How do you calculate frequency density for a histogram?
Frequency divided by class width.
How do you find the mean of grouped data?
Assume all data in class takes the midpoint.
How do you find the median of grouped data?
Use linear interpolation.
How do you find the lower quartile of data where n/4 is an integer?
The lower quartile is the average of this term and the one above it.
How do you find the lower quartile of data where n/4 is a non-integer?
Round the number up to find the position of the lower quartile.
How do you find the upper quartile of data where 3n/4 is an integer?
The upper quartile is the average of this term and the one above it.
How do you find the upper quartile of data where 3n/4 is a non-integer?
Round the number up to find the position of the upper quartile.
What is an outlier?
Outliers are extreme data values that do not fit with the general pattern of the data.
When coding data, what operations change the mean?
All of them.
When coding data, what operations change the standard deviation?
Multiplication and division.
What is the formula for conditional probability?
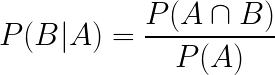
What is the formula for independent events?
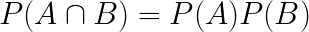
What are the conditions for a binomial distribution?
There is a fixed number of trials.
Each trial results in success or failure.
All the trials are independent.
The probability of success is the same in each trial.
The variable is the total number of successes in the n trials.
In the normal distribution, what percentage of the area is within one standard deviation of the mean?
68%
In the normal distribution, what percentage of the area is within two standard deviations of the mean?
95%
In the normal distribution, what percentage of the area is within three standard deviations of the mean?
99.7%
What is the mean and variance of the standard normal distribution?
Mean is zero. Variance is 1.
How do you convert a normally-distributed variable to the standard normal distribution?
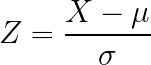
When is it suitable for a normal distribution to be approximated as a binomial distribution?
When p is approximately 0.5, and n is large.
How do you find the mean for the normal approximation?
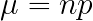
How do you find the standard deviation for the normal approximation?
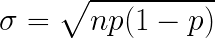
What must you always apply when using the normal approximation?
Continuity correction.
What are the conditions for the normal distribution?
The data is continuous.
The data is roughly symmetrical distributed, with a peak in the middle at the mean.
The data becomes less frequent as you move further from the mean. Almost all of the data is within three standard deviations of the mean.
What is a population?
A group of people or items you want to find information about.
What is a finite population?
A population where is is possible to know how many members there are.
What is a infinite population?
A population where it is impossible to know how many members there are.
What is a census?
A survey method where information is collected from the entire population?
What are the advantages of a census?
You get accurate information about the population, as every member has been surveyed.
It’s a true representation of the population and is unbiased.
What are the disadvantages of a census?
For large populations, it requires a large amount of time and effort.
Census’ can be expensive.
It can be difficult to make sure all all members are surveyed. If some are missed, this can result in bias.
If the tested items are used up or destroyed, a census is impractical.
What is a sample?
The selection of people or items in a population to gather data.
What are sampling units?
The individual members of a population that are selected as part of a sample.
What is the sampling frame?
The full list of all sampling units. The list must give a unique name or number to each sampling unit, as is used to represent the population when selecting a random sample.
What steps can be taken to avoid sampling bias?
Select from the collect population and make sure none of the population is excluded.
Select the sample at random.
Make sure all sample members respond to survey or interview.
What are the advantages of sampling over taking a census?
Quicker and cheaper than census, easier to get hold of all the required information.
It’s the only option when surveyed items are used up or damaged.