APAH Unit 2
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
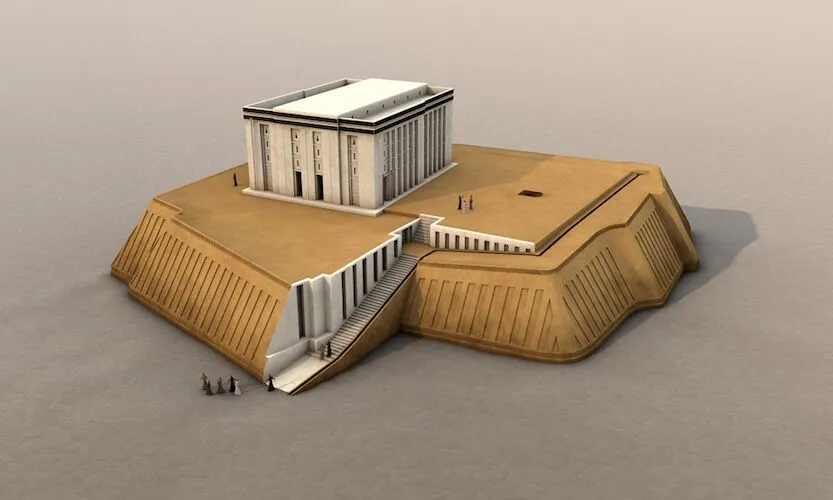
White Temple and its Ziggurat
Iraq (Sumerian)
3500-3000 BCE
Form: Mud brick, tar for waterproof ceiling, corners match cardinal directions, “bent axis approach“ (turn 90* to face altar), visitors must walk around White Temple to find door from Ziggurat stairs, rain well in middle of temple
History: where writing began, slavery/religious works, theocracy, gypsum tablets for accounting
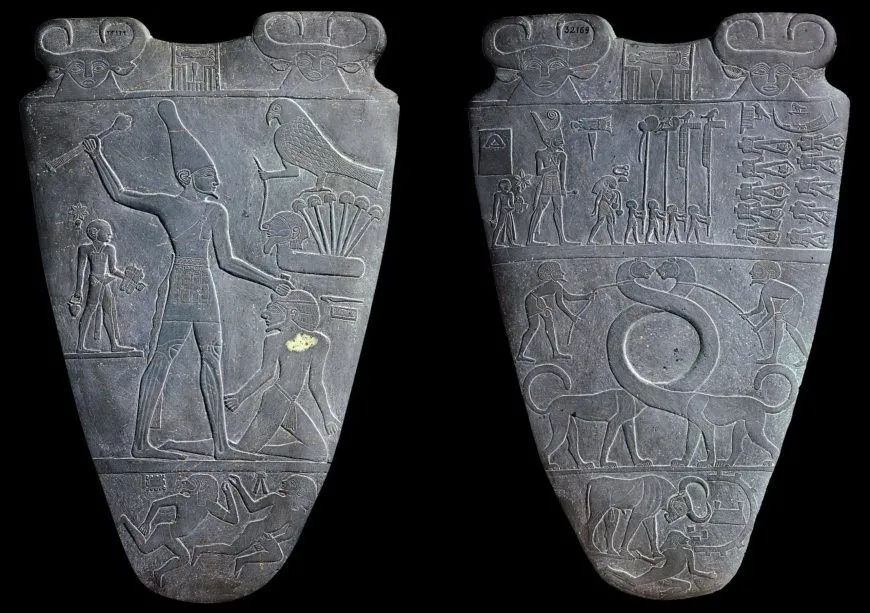

Palette of King Narmer
Egypt
3000-2920 BCE
Greywacke/siltstone
Form: 2 feet tell siltstone in relief with humans, gods, and animals
Function: temple ceremonies and mixing makeup for either gods or humans
Context: Buried after elite donation overflow in Horus’s temple, controlled excavation
Content: Tales of a unified (North and South) Egypt, hierarchical scale, powerful pose, twisted perspective, kingly regalia of North and South
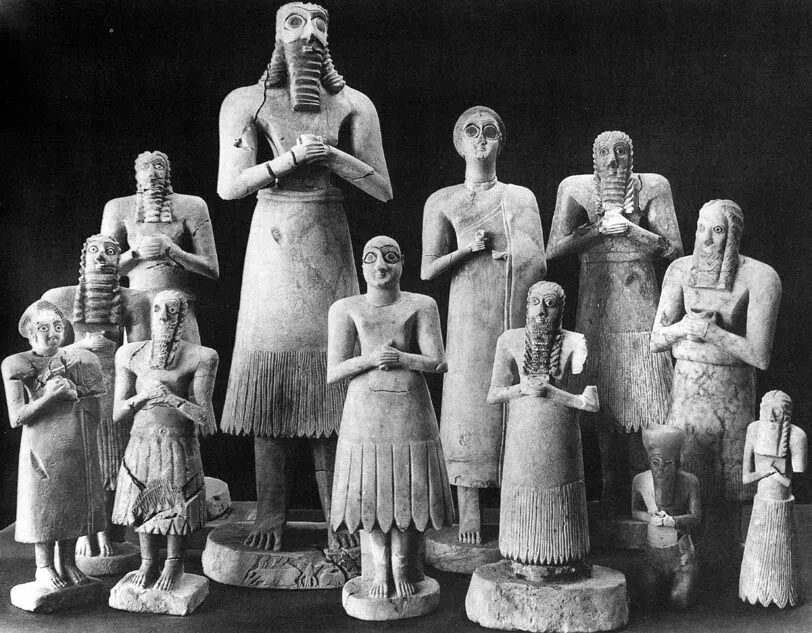

Statues of Votive Figures from the Square Temple at Eshnunna (Iraq) (Sumerian)
2700 BCE
Gypsum inlaid with shell and limestone
Form + Content: 9-28 inches, “hero“ figure the largest, 10 male, 2 female, inscribed with prayer and name, holding goblet
Function: Meant to worship Abu eternally, buried in excess donation by elites
Context: Growing class of non-religious elites
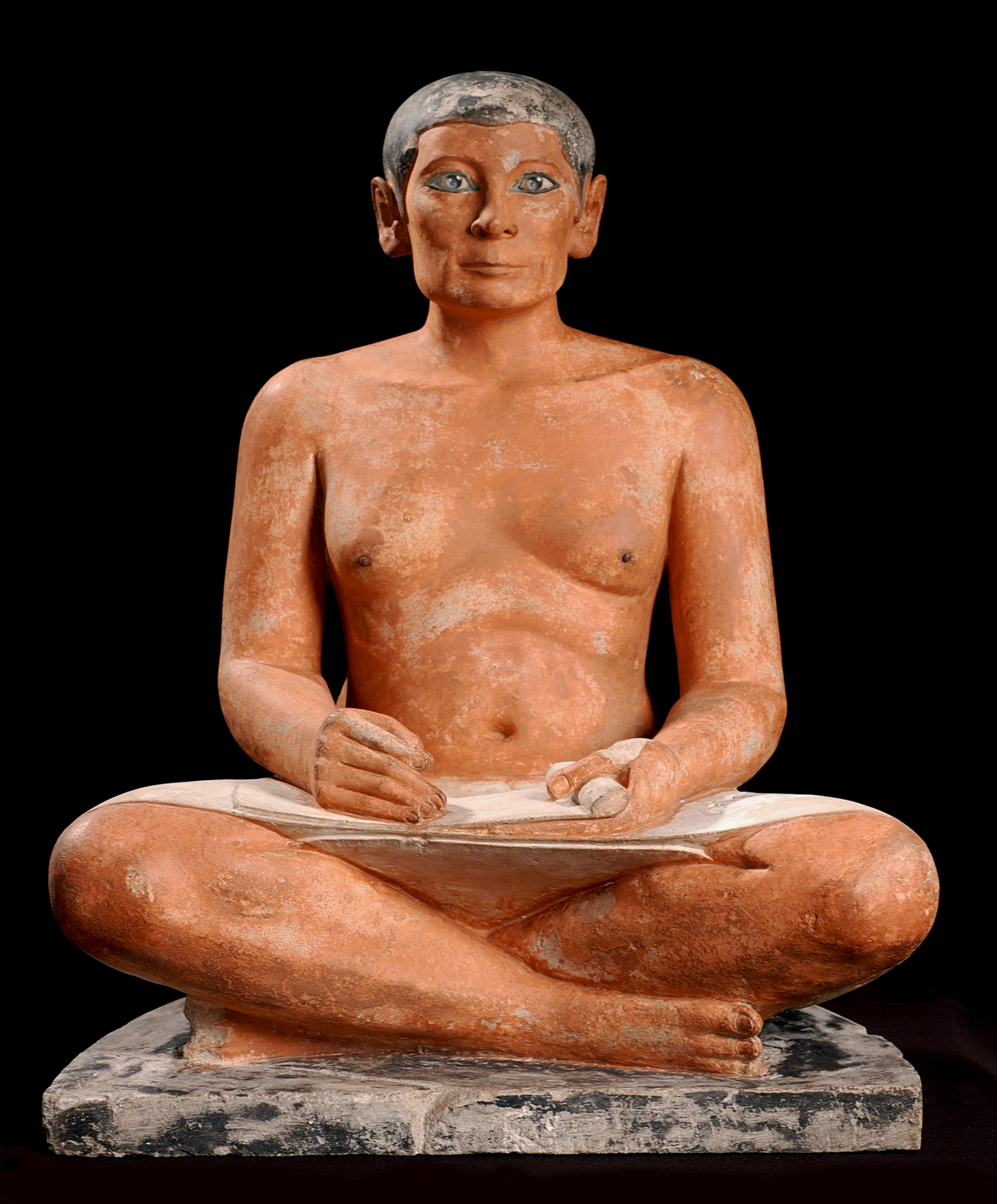

Seated Scribe
Egypt
2620-2500 BCE
Painted Limestone
Form + Content: canon divergent realism and casual momentary job, physique, and pose, wooden dowel nipples, accentuated eyes (polished and colored crystals)
Function + Context: Found in a necropolis
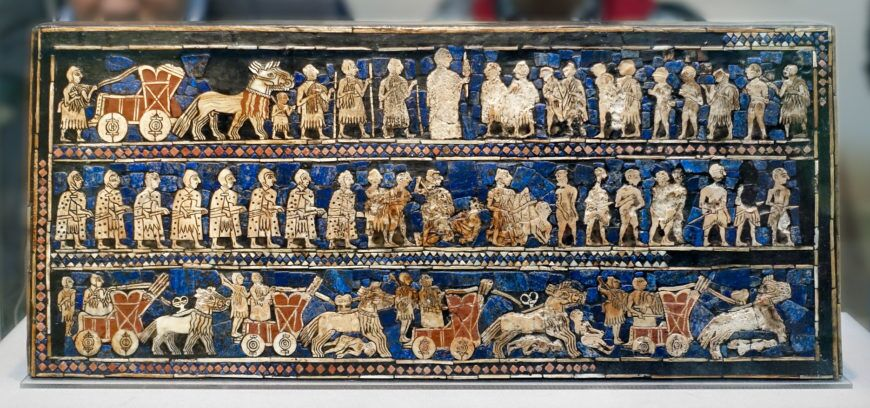

Standard of Ur from the Royal Tombs at Ur (Sumerian, Iraq)
2600-2400 BCE
Wood with shell, lapis, and red limestone
Form + Content: small enough to be carried, sides represent war and peace, 3 registers, hierarchical scale, lapis from Afghanistan, red limestone from India, and shells from Persian Gulf
Function + Context: Carried into battle and used in elaborate royal funerary rituals

Great Pyramids and Great Sphinx
Giza, Egypt
2550-2490 BCE
Cut limestone
Form + Content: 3 pyramids, sphynx representing the pharaoh, long stone causeway, temple at base of pyramids, satellite queen pyramids, elite tombs (mastabas) in grid, faces facing cardinal directions
Function + Context: Royal burial site, “steps“ to heavens, corvee labor, built over 3 generations
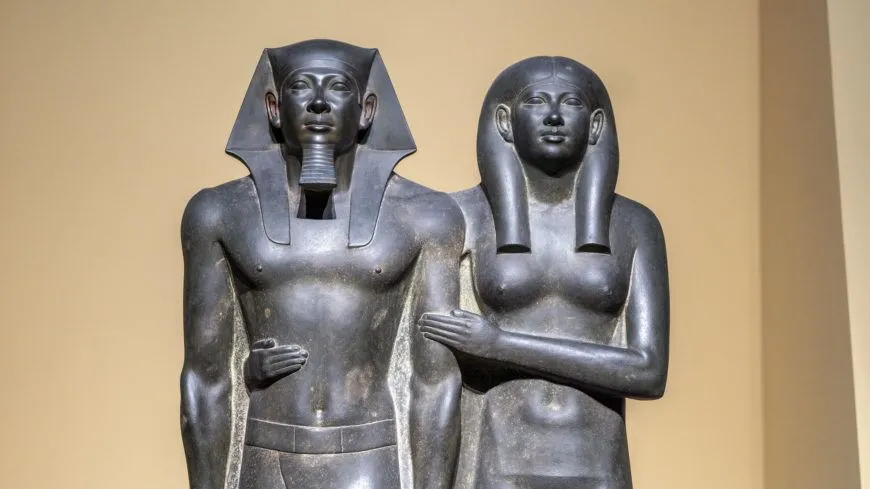

King Menkaura and Queen
Giza, Egypt
2490-2472 BCE
Greywacke
Form + Content: finished dark stone, Pharaoh Menkaure and Queen Mother (same height), canon posture and form, angled to look emerging, pharaonic cobra headpiece
Context + Function: Found in valley temple at base of pyramid, intentionally unfinished but painted and erected

The Code of Hammurabi
Babylon (Iran, Susian)
1792-1750 BCE
Tall, carved basalt rock
Form + Content: cuneiform writing, depicted scene = prologue of Hammurabi being given divine right of rule by Shamash
Context + Function: Divine law code, idea of eye for eye, issues regarding agriculture and irrigation

Temple of Amun-Re and Hypostyle Hall
Luxor, Egypt
1550 BCE and 1250 BCE
Sandstone and mud brick
Form + Content: one of largest religious complexes, Hatshepsut Obelisk, Thutmose III’s festival temple in war tent style, restrictive access halls, temple roof full of star and bird imagery whereas columns full of creation mound imagery, intentional spiritual flooding from Nile, pylons (big arch) and clerestory (above head windows)
Context + Function: Temple of Amun-Re, shrine, and priestly estate, pharaonic expansion, mound of creation (center of temple is higher than outside)
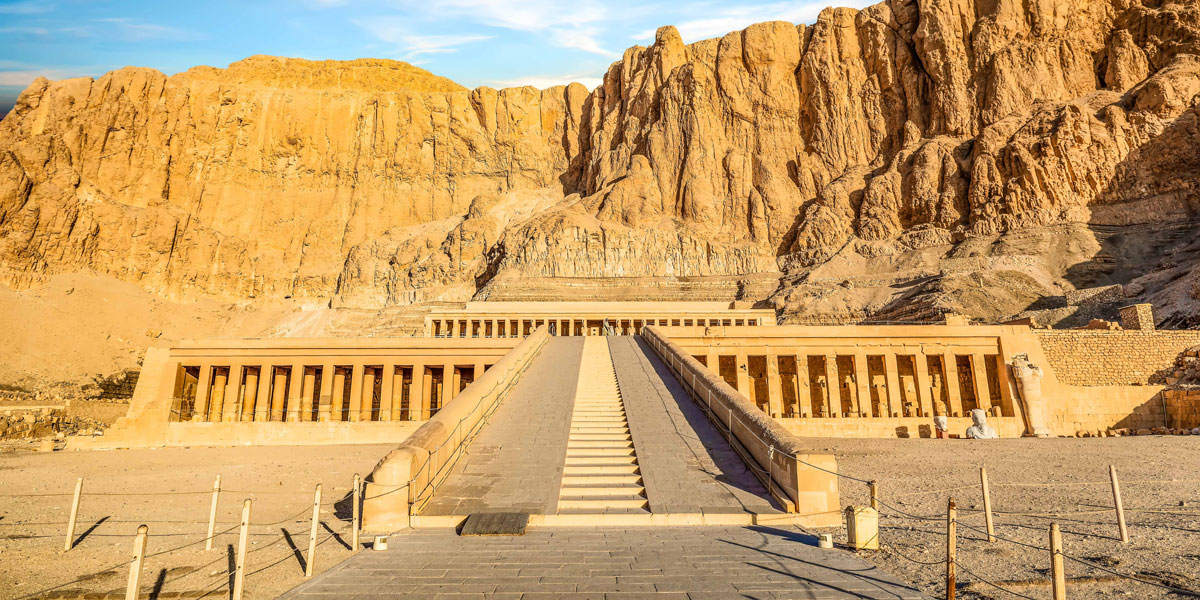

Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut
Egypt
1473-1458 BCE
Sandstone carved into cliff and red granite
Form + content: contrast between organic cliffs and geometric temple, permanence, stability, and authority, masculinized figures
Function + context: She created mythology around her kingship (divine birth and oracle), location of ritual transportation of godly statue across Nile (she knelt to only the god), destroyed with successor
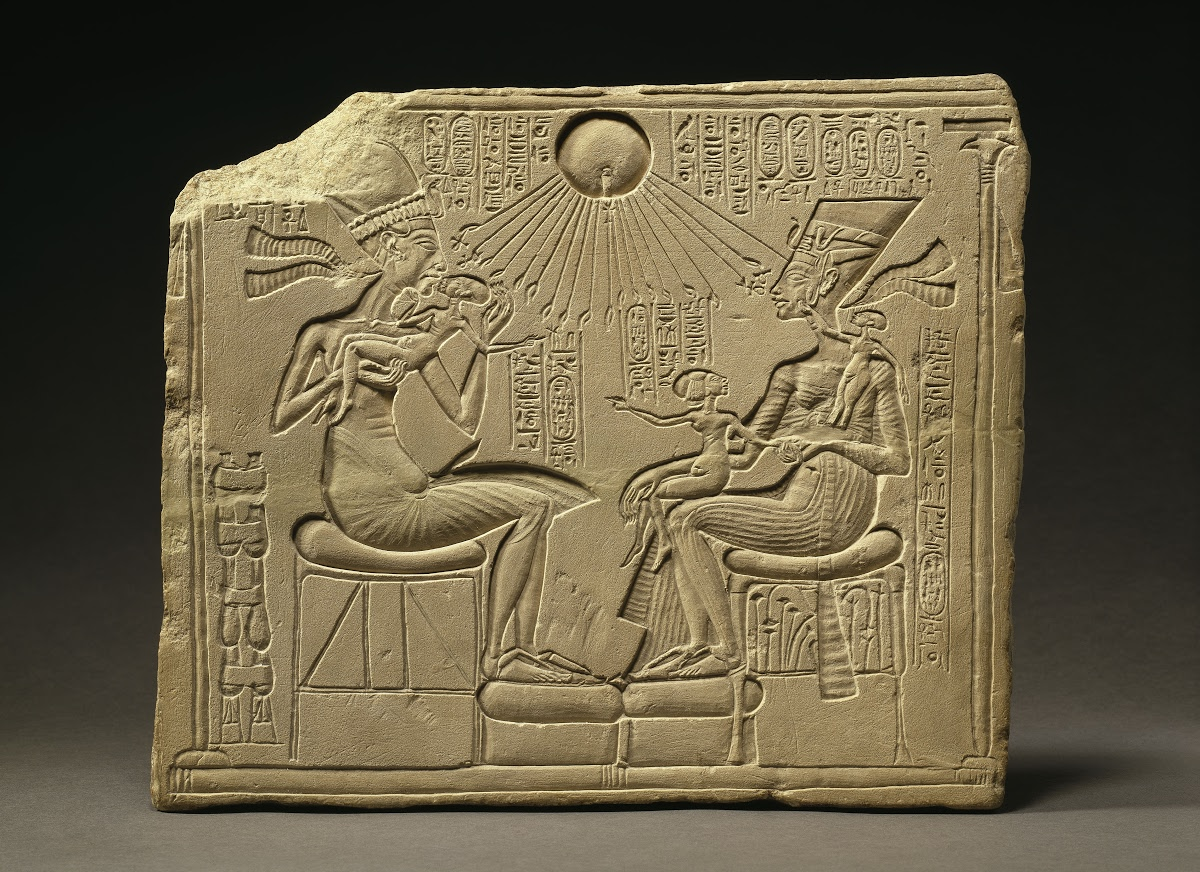

Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and 3 daughters
Egypt
1353-1335 BCE (Amarna Period)
Limestone relief carving
Form and content: Home altar, Amarna Period: informal, domestic sight, curvilinear forms, sun disk god
Function and context: Monotheist altar from religious shift (Amun - Aten), Akhenaten and Nefertiti were the only two channels to god (disrupted priest class)
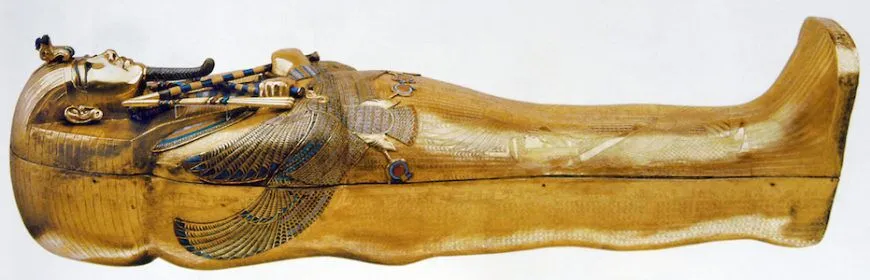
Tutenkhamun’s Tomb, innermost coffin
Valley of the Kings (Royal Burial Ground), Egypt
1323 BCE
Gold with enamel and semi-precious stones
Form + content: found with glittering gold burial objects, innermost of 3 coffin layers, covered in anointing liquid, goddesses stretch across torso, gold sheet Death Mask resting on shoulders with limb protection spell from Book of Dead and falcon imagery
Function + context: found in Tut’s tomb, son of Akhenaten, restored tradition, died young, advisor married wife and became pharaoh
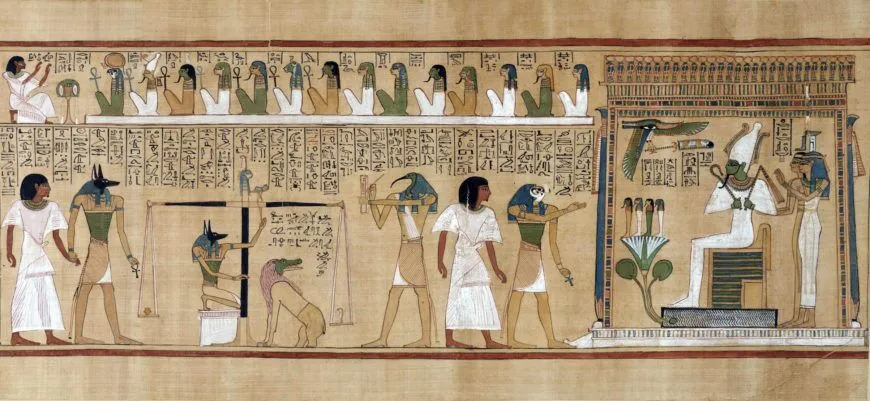
Last Judgement of Hu-Nefer from his tomb
page from Book of Dead
Egypt
1275 BCE
Painted papyrus scroll
Function + Context: found in a scribe’s tomb, traditional blending of text and art (contrasting with the Amarna Period)
Content + Form: top register depicts Hu-Nefer professing good life, then weighing heart with Anubis against Ma’at’s feather, crossing the doorway of natron to Osiris’ room with Horus (bird), 4 cardinal children of Osiris, wife Isis and her sister
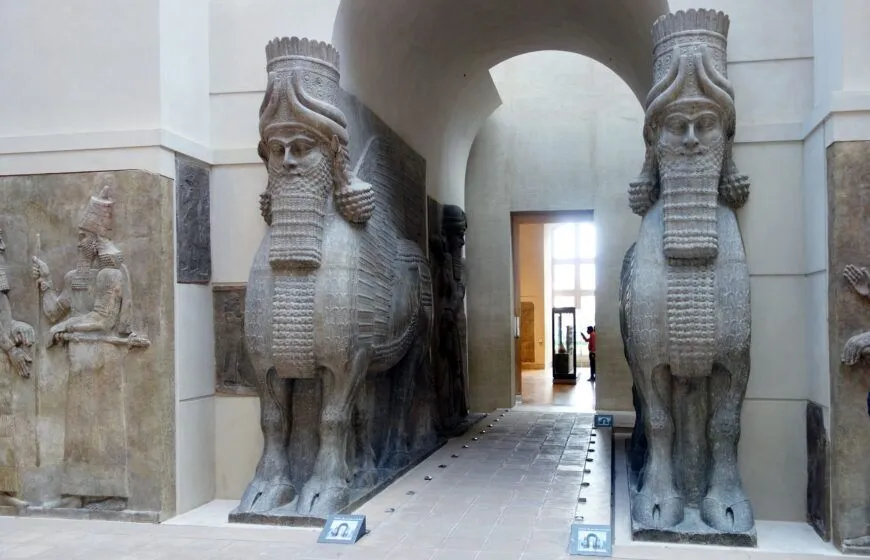

Lamassu from the Citadel of Sargon II
Iraq (Neo-Assyrian)
720-705 BCE
Alabaster, limestone, and breccia
Form + content: entrance to giant courtyards, strong features, looks over humans as if otherworldly (20 ft), mineral pigment, repetition, godly crowns, double horns, and rosettes symbolize divinity, 5 legs symbolize walking and standing, background cuneiform tablet listing victories of the king
Function + context: depicts destruction of enemies, extraction of natural resources, the king hunting lions, and spirits attending the tree of life
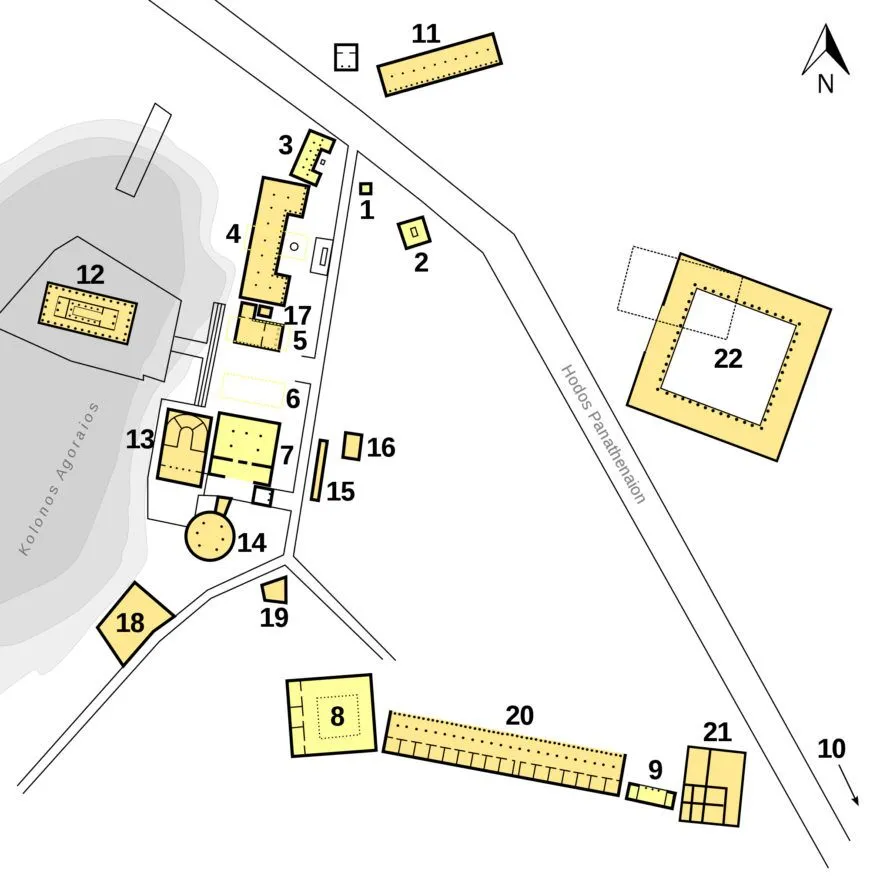
Athenian Agora
Archaic - Hellenistic Greek (600-150 CE Plan)
Content + Form: base of Acropolis, Athens. Doric order (simple capital, baseless columns, friezes)
Bouleuterion: council chamber
Tholos: Emergency area
Stoa: covered walkway with columns
Context + Function: outdoor public plaza, location of Panathenic Festival, built to support democracy
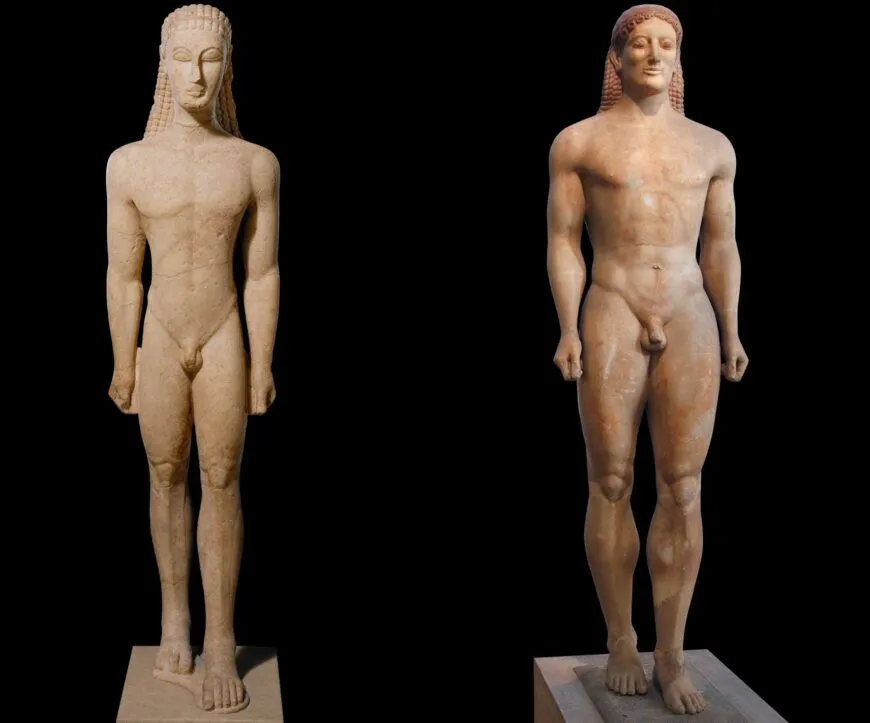

Anavysos Kouros
Archaic Greek (530 BCE)
Painted marble statue
Art: slightly larger than life sculpture of ideal young male physique, wearing nothing but a headband and braids. archaic smile. newer ones look more rounded and natural, older ones looked stiffer and geometric. hands connected to hips for structure
History: inspired by Egyptian canon. commissioned by wealthy family to mark grave of son lost in battle
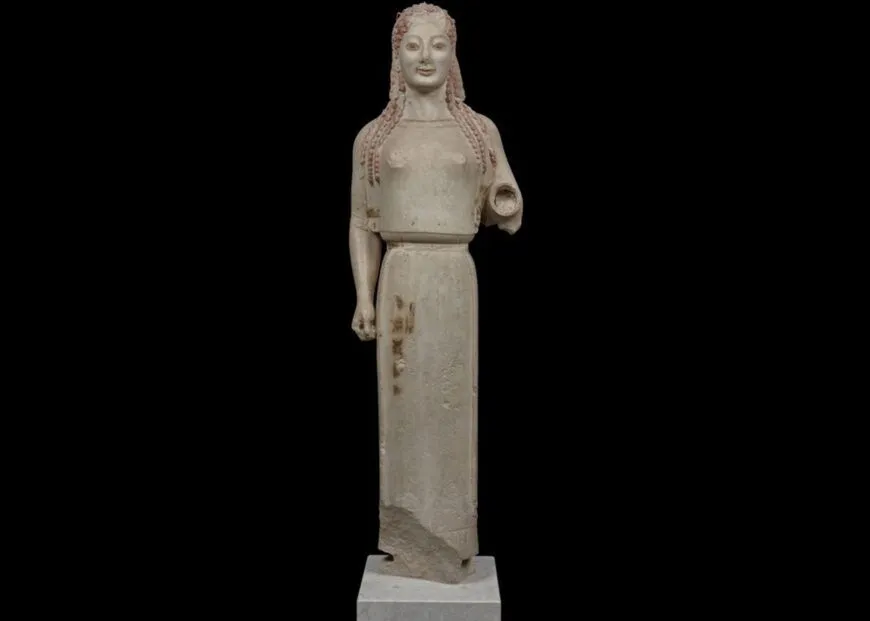

Peplos Kore
Acropolis
Archaic Greek (530 BCE)
Painted marble
Art: Gold crown, bent arm, sense of movement, painted skirt with animals, earrings, archaic smile, believed to be a depiction of either Artemis or Athena. peplos is the sheet she wears
History: Depiction or offerings brought by men to Athena
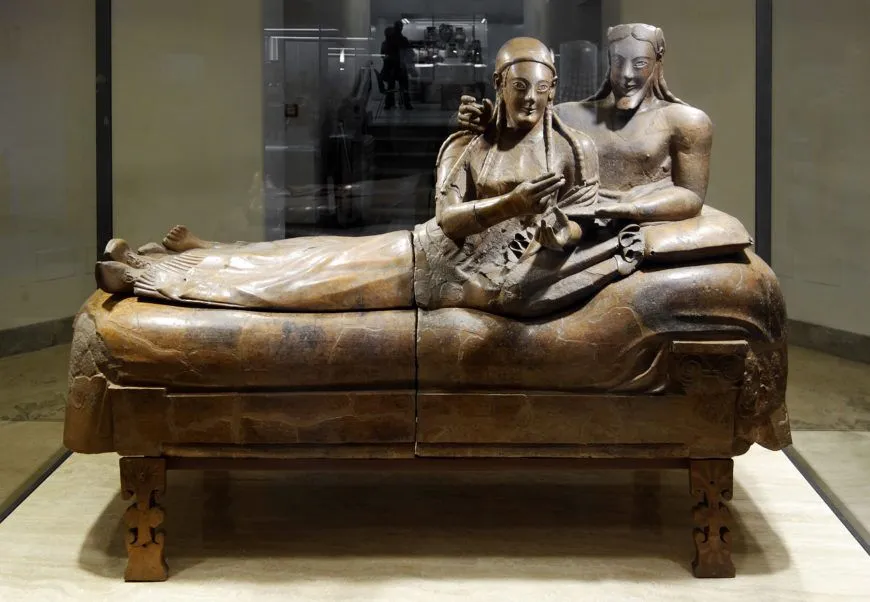

Sarcophagus of the Spouses
Etruscan
520 BCE
Terra cotta
Form + Content: burnished and smoothed ceramic spouses (lid) on chaise (container), lifelike and embracing, spouses show Etruscan equality through similar size
Function + Context: Northern Italy Etruscans left only funerary artwork with inscriptions in dirt hut tombs, they ruled Rome, found in necropolis, held banquet objects
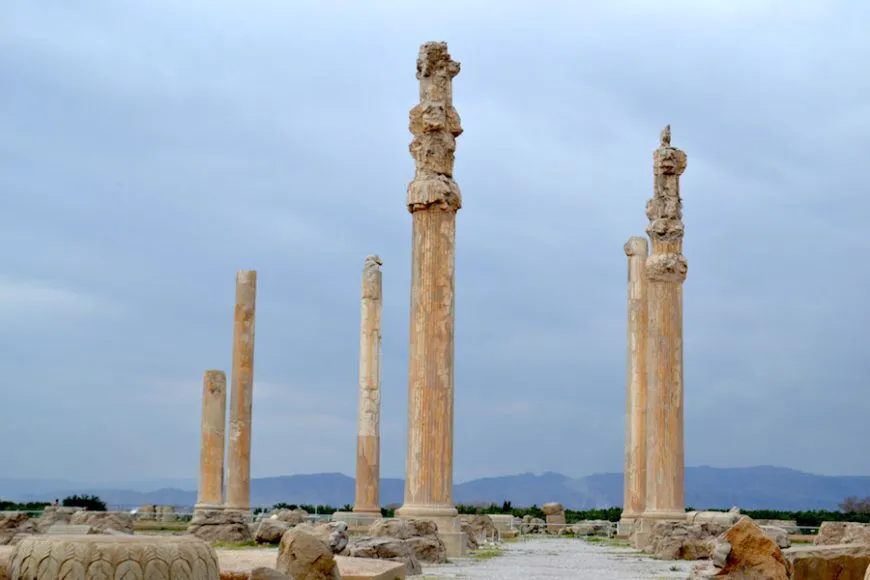

Audience Hall (apadana) of Darius and Xerxes
Persepolis, Iran (Persian)
520-465 BCE
Limestone
Art: Animals, noblemen, attendants, representatives, and vassals shown bringing eternal tribute on Persian New Year. Hypostyle (columns supporting roof).
History: Stronghold, sacred site, administrative, and economic center. Large ceremonial building for receiving tribute. Thriving Persian bureaucracy under Darius
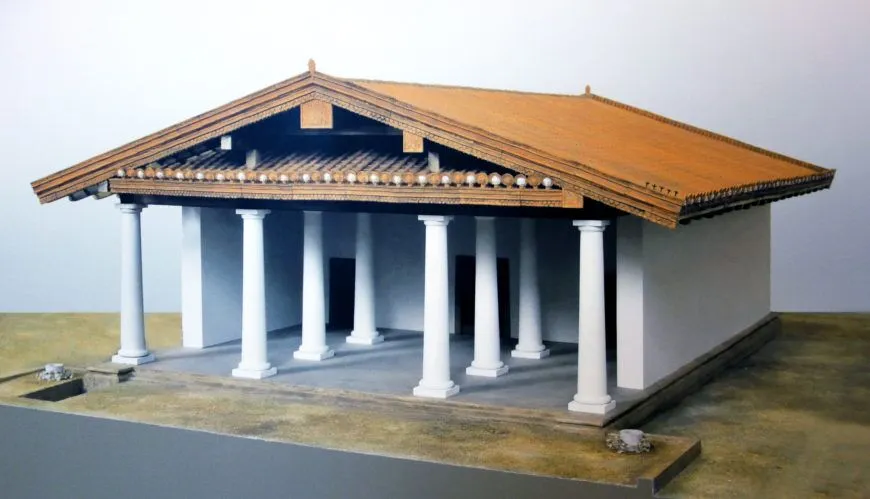

Temple of Minerva (Athena)
Veii, Italy
510-500 BCE
Wood, mud brick, or volcanic rock (tufa)
Sculpture of Apollo made of terra cotta
Form + content: Deep porch, square temple, inspired by ancient Greece, painted sculptures lined the roof, movement and liveliness, depicted the 3rd labor of Hercules: capture Apollo’s giant deer with gold horns. Apollo is depicted idealistically
Function + context: Etruscan collaboration with Greece. Place of worship of Athena, Hera, and Zeus in the triplecella structure
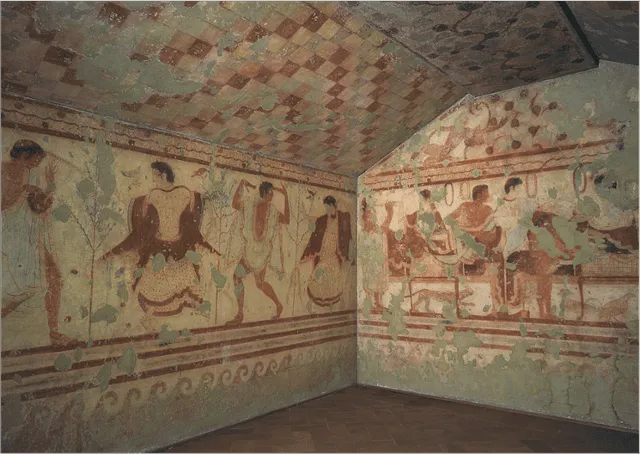

Tomb of the Triclinium
Italy (Etruscan)
480-470 BCE
Tufa (volcanic rock) and painted fresco wall decoration
Form + content: Banqueters having a dinner party and dance with a barbiton accompaniment, checkered ceilings to imitate funeral banquet tents, mixed gender festival and games (equestrian), funerary offerings
Function + context: festive Etruscan funerary rituals to flaunt status (sometimes the deceased held public office), Advanced Iron Age
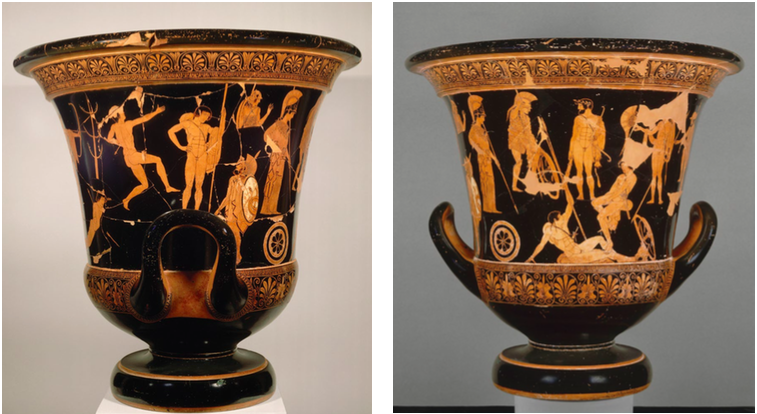

Niobides Krater by the Niobid Painter
Classical Greece
460-450 BCE
Clay, red-figure technique (dark background, red figures, and white highlights)
Form + content: Isocephalism has disappeared (everyone is now different sizes), influenced by wall painting, Niobe’s children were killed by Artemis and Apollo after she bragged to god, on other side, warriors of marathon.
Function + context: Ceremonial krater to mix wine. Would sometimes have a hold at the bottom that would spill onto graves

Doryphoros (Spear-Bearer) by Polykleitos
450-440 BCE
Roman copy of Greek original
Marble
Art: contrapposto, mathematically perfect proportions, movement, represented the canon
History: believed the human figure could be perfect, Pythagoras found harmony is based in math, found in an ancient gym
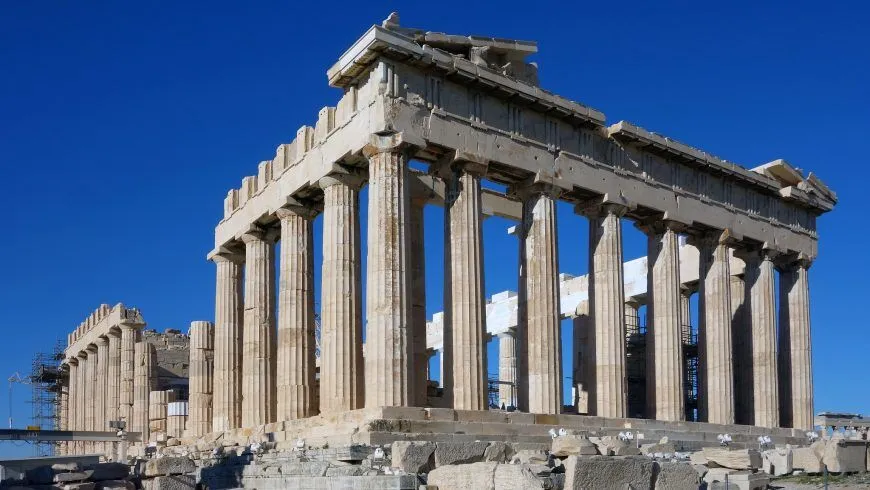

The Acropolis
Athens, Greece
447-424 BCE
Marble
Parthenon:
- Located at the top of the Agora
- Central point of city (religious center)
- Destroyed by Persians
- Never a temple, but used as a religious center by Byzantines and Roman Catholics
- Idealized proportions
- Curved stylobate (floor) to avoid water collection
- Columns and ceiling thicker in corners to create uniform look
- Doric and Ionic orders
- 40 ft gold and ivory statue of Athena
- Friezes and pediment (triangular composition) tell of Athena’s battles and birth from Zeus’s head
- wet drapery look
- cunty walk = contrapposto
Temple of Athena Nike:
- Frieze: high relief on top, low relief on bottom. Brightly depicting the Ergastines (six women who would weave Athena’s sculpture’s shawl) and the Panathenaic Festival. Isocephalism: everyone’s the same height
- ionic columns at the entrance of the Acropolis
- commemorated the Greek defeat of the Persians
- Depicts Nike (victory) adjusting her sandal while using wings to adjust movement in high relief
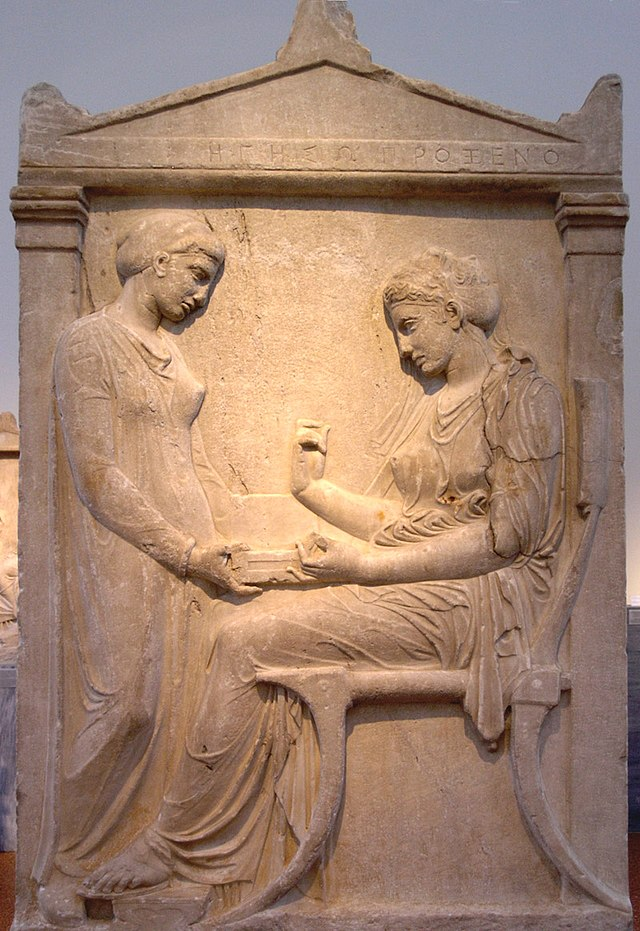

Grave Stele of Hegeso by Kallimachos
Athens, Greece
410 BCE
Painted marble relief sculpture
Art: drapery follows the form of the body, footrest, Hegeso looking at painted on jewelry with servant between pediment and plasters, inscription on pediment describes Hegeso’s fathers relation, showing how women were defined by the men in their life
History: Grave marker. End of High Classical Period (period of public works) has resurgence in private funerary sculpture
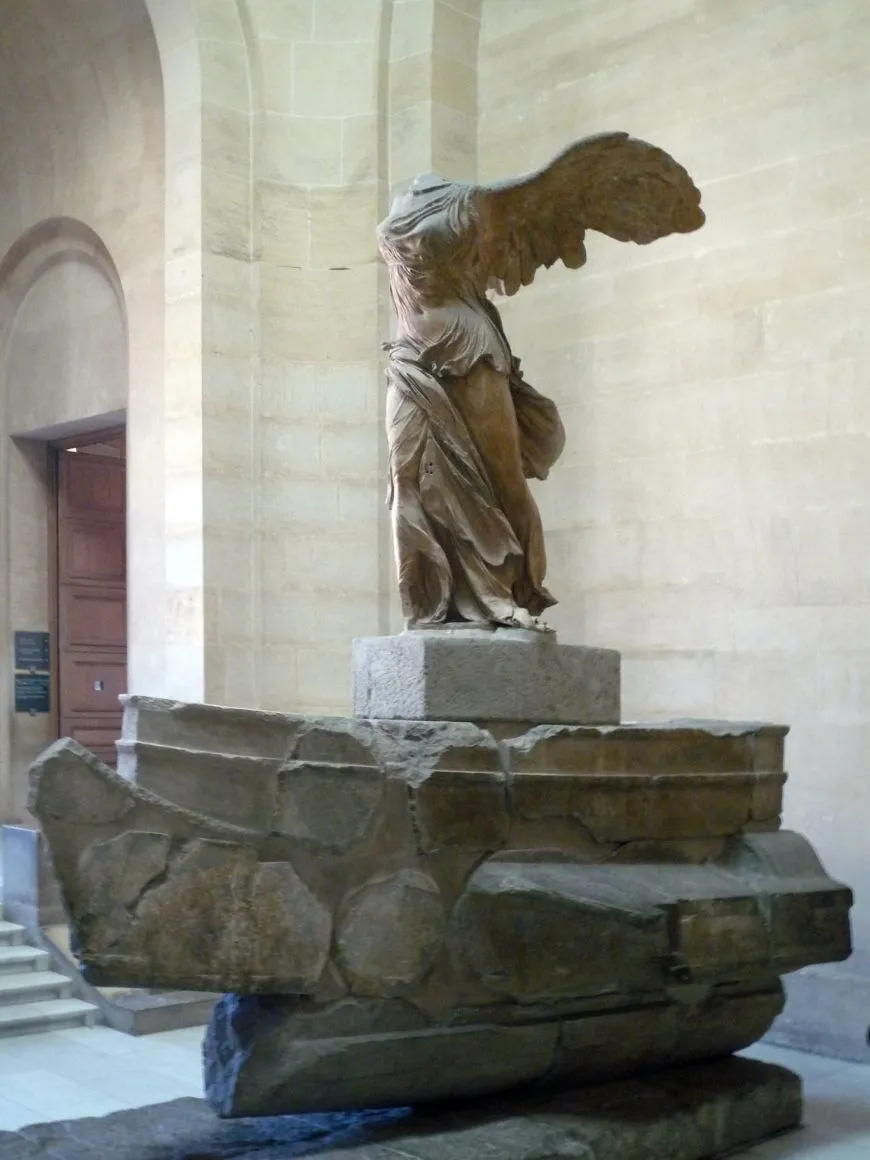

Winged Victory (Nike) of Samothrace from the Sanctuary of the Great Gods
Hellenistic Greek (190 BCE)
Marble
Art: Drama and energy of drapery in wind, facing oncoming visitors to the island of gods, figure is “alighting“/landing, juxtaposition of direction from grounded bottom half and stretching top half
History: restored after being found in pieces, post-Alex the Great, Greece was very expressive
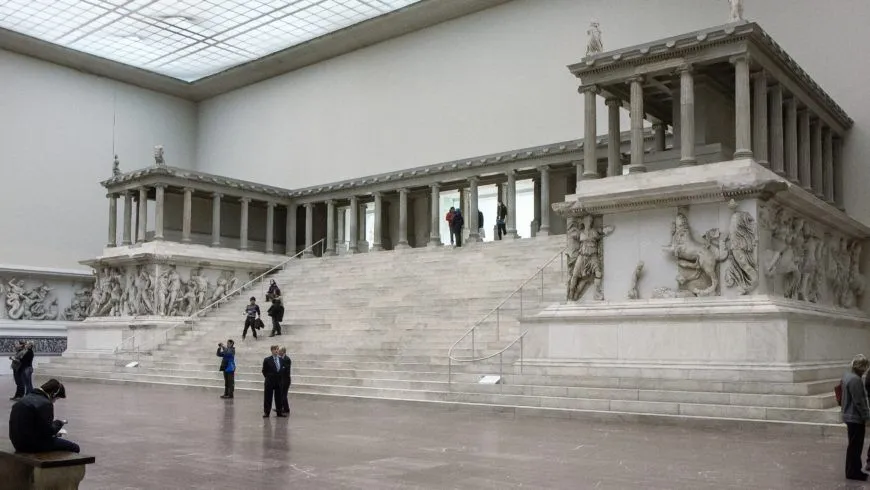

Great Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
Turkey (Hellenistic Greece)
175 BCE
Painted marble architecture and sculpture
Art: Athena and Zeus statues in the center, along with a fire pit, battle between giants and gods, motion and drama, high relief that sculptures spill out, Zeus commands eagles and thunder to battle giants
History: Hellenistic = post-Alex G. represents Greek optimism and strength in battle, found in the Acropolis
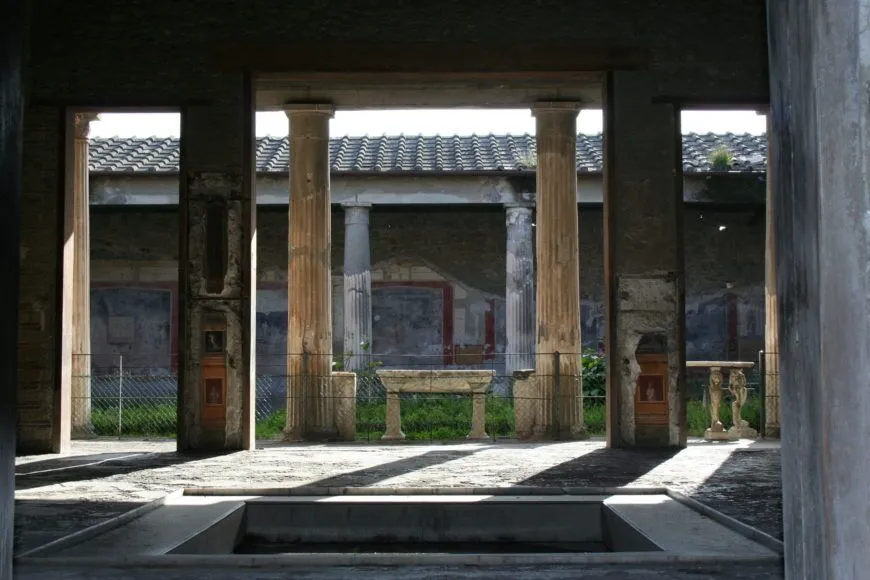

House of the Vettii
Pompeii, Italy
Imperial Rome (2nd century BCE), rebuilt in 62-79 CE
Art: Townhouse, deviated from canon by not including office but having a rainwater collection, narrow doorway, atrium, wings, courtyard, kitchen, dining, and garden. 2nd floor had storage and bedrooms. strongboxes (safes) were prominently displayed. Erotes and picture gallery decoration
History: showed the wealth of the patrician when inviting clients, buried in the explosion of Mt. Vesuvius, owned by freedmen in political power
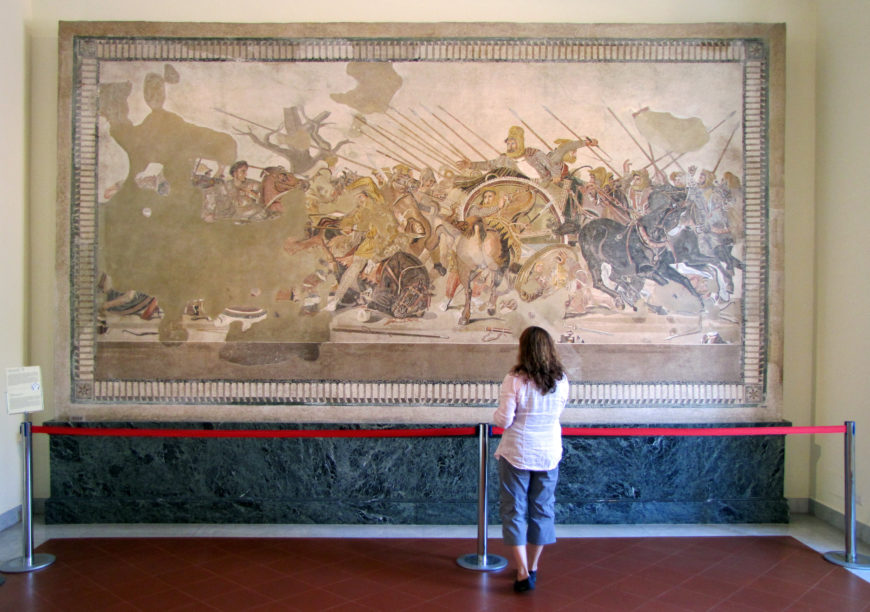

Alexander Mosaic from the House of Faun, Pompeii
100 BCE
Stone and glass mosaic
Art: high quality of materials, use of light and dark, anatomy and foreshortening, empty at top, dramatic torque of Darius’ Persian forces retreating, wounded at the bottom, based off of Ancient Greek painting
History: Turning point between momentous battle and victory from the Greeks on the Persians, Alex G. unified Europe and West Asia, preserved in eruption of Mount Vesuvius
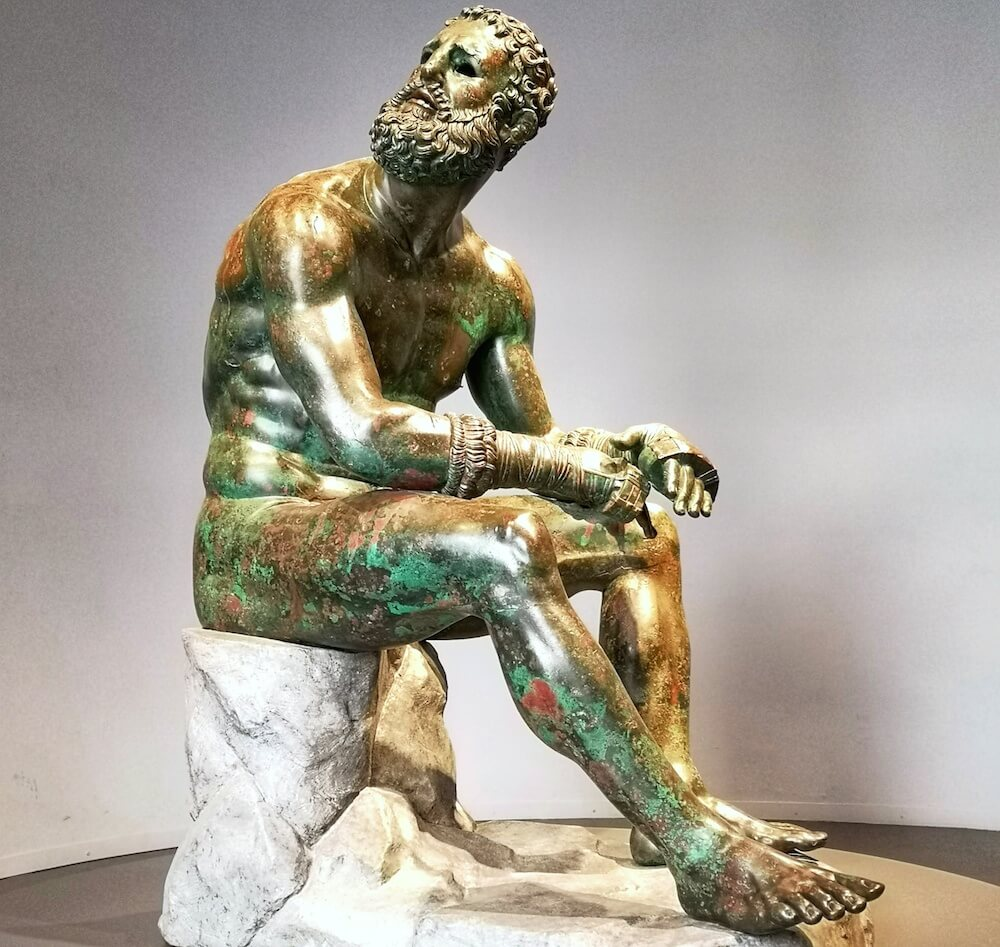

Seated Boxer
Hellenistic Greek (100 BCE)
bronze with copper wounds
Art: hollow, lost wax casting, inlaid copper wounds, missing inlaid eyes, sense of presence, different from other Greek athlete sculptures because it shows aged defeat
History: Boxing in Greece focused on blows to the head, so body remains perfect
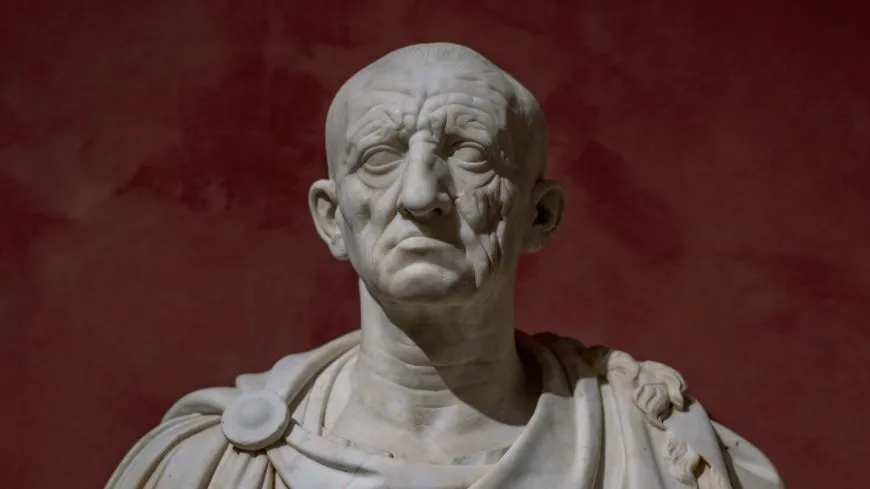

Head of a Roman patrician
Roman Republic
75-50 BCE
Marble
Art: wrinkled caricature of man serving public career, similar to death masks that were worn at subsequent funerals
History: meant to increase respect for family, Republic valued verism and wisdom
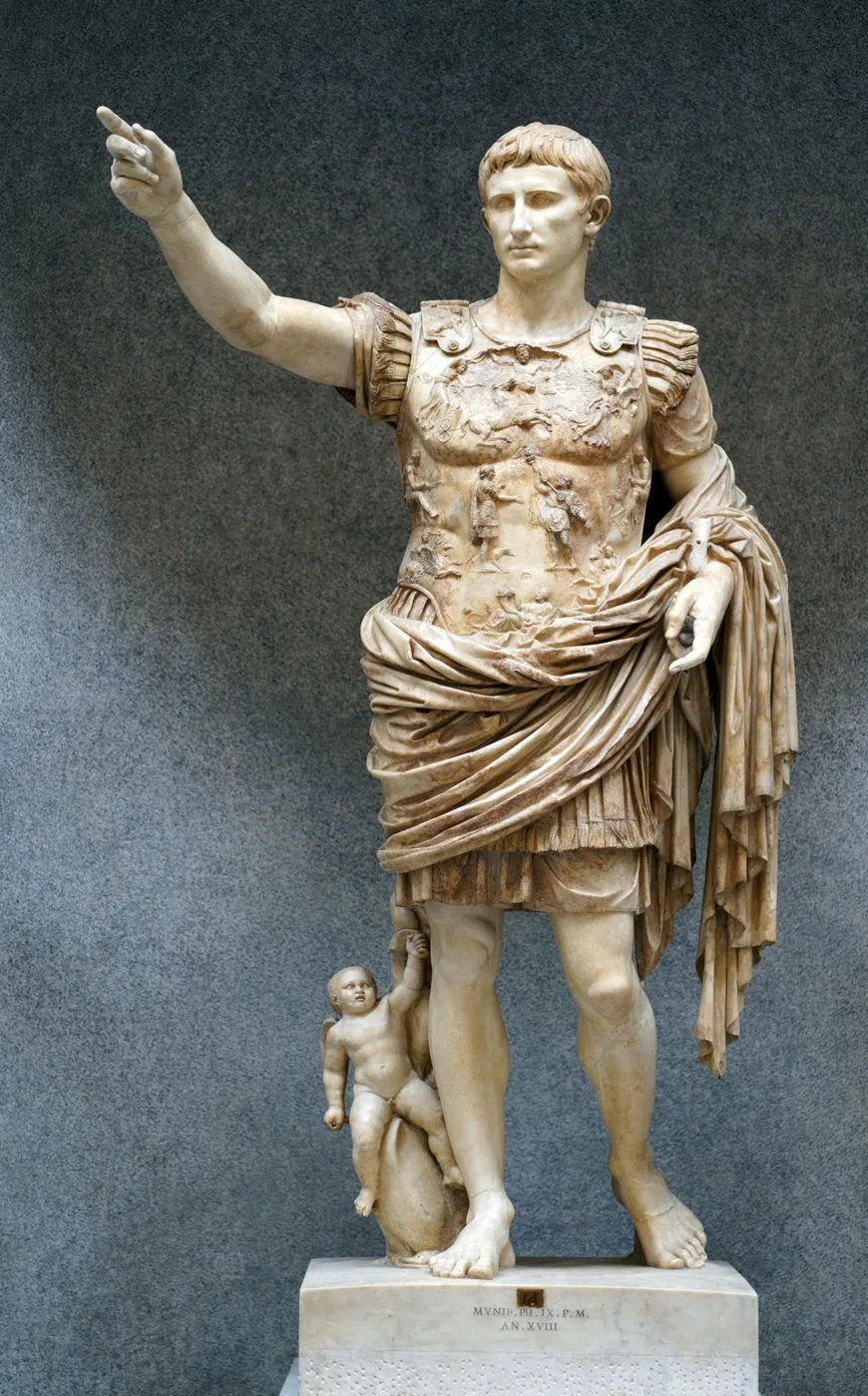

Augustus of Prima Porta (gates near Rome)
1st Century CE
Marble
Art: naturalistic, painted, Augustus’ wife’s marble copy of a public bronze copy, idealized nobility and youthfulness (contrast between the newer Roman Empire and old Roman Republic), contrapposto and addressing troops, armored breastplate has decorations of personifications of earth, sky, Rome, sun and moon, captives, barbaric depiction of Parthians returning stolen Roman standards, and cupid the son of Venus riding a dolphin at his foot
History: 1st Roman Emperor (traced his lineage to a Greek God), made after victory over Parthians after long battle,
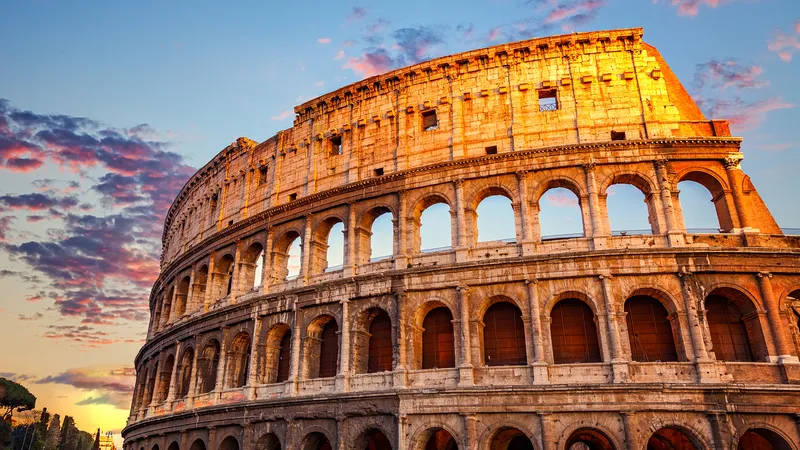

Colosseum (Flavian Amphitheater)
Rome, Italy
Imperial Rome (70-80 CE)
Stone and concrete
Art: previous colossal statue, numbered arches (concrete!), axial main entrances, complex archways, rich people sat on marble at bottom, poor people sat on wood at top, hand powered elevators pulled animals and victims to stage, Tuscan (Italian Doric), Ionic, and Corinthian columns in order from ground
History: abattoir (slaughterhouse), built as Flavian public work after death of Nero, pillaged later by Romans for housing, Animals in morning, executions at noon, gladiators in afternoon.
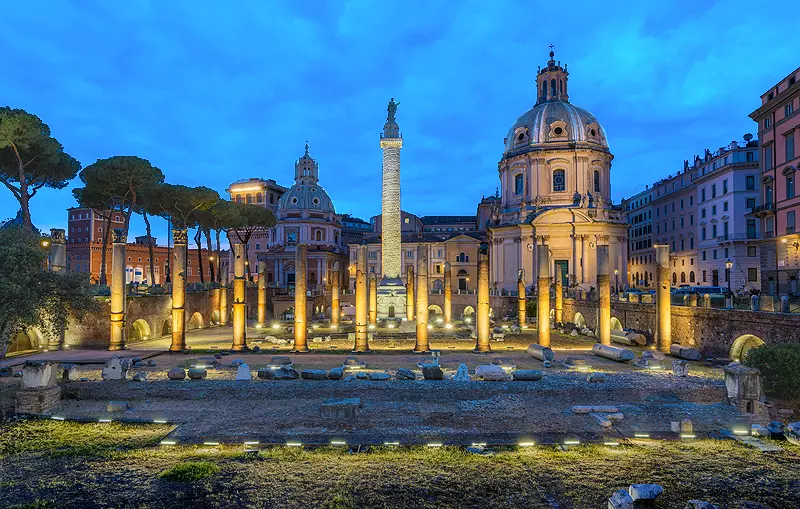

Forum of Trajan, Apollodorus of Damascus
Rome, Italy
106-113 CE
Brick and concrete (architecture) marble (column)
Art: contains ruins of houses demolished by Trajan, bigger than all other forums by emperors, extravagant statue of Trajan on horse surrounded by Dacian captures, basilica, temple, and libraries flanked the column (at the top was a statue of Trajan and the suicide of the Dacian leader, at the bottom was the crossing of the Danube) covered in mundane stories of victory, supermarket complex with groin vaults
History: social and commercial center, Trajan expanded RE to peak, column marks the height of the land before demolition to show how nature is subservient to man
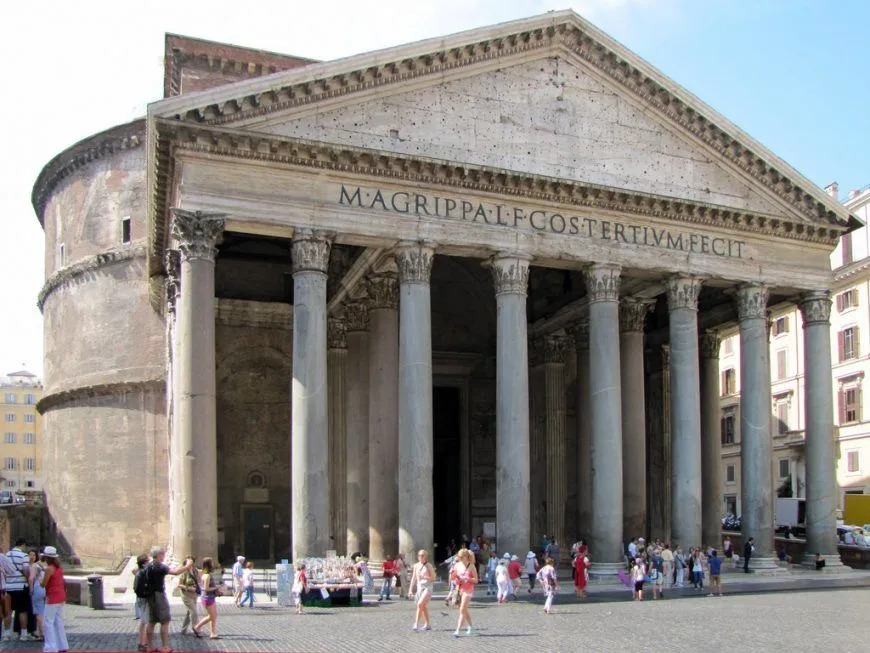

The Pantheon (Rome)
Imperial Rome (118-125 CE)
Concrete with stone facing
Art: downhill to modern street, uphill to ancient street, originally surrounded by columns that obstructed barrel, geometric dynamic design, marble from all over RE, oculus represents heavens movement, Corinthian columns imported as a single stone from Egypt. engraving on frieze honors the consul who had previously built on the land
History: temple to the gods, image of Hadrian emperor

Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus
Imperial Rome
250 CE
Marble
Art: dense carpet of heroic Roman figures in light and barbaric Goths in deep shadow and caricature in deep relief, bigger at the top and smaller at the bottom for a high vantage point of viewing. Greek idea of Barbarians, but unique use of space, veristic = realistic, as the Empire fell, less traditional art
History: Roman conflict with the Goths, Romans began to bury instead of cremate, instability of Rome = deviation from Greek tradition