Catalyst/Transition metals
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Transition metals and their compounds can act as…
heterogenrous and homogeneous catalyst
heterogeneous - catalyst in a different phase from the reactants, reaction occurs at the surface of the catalyst
homogenous - catalyst in the same phase as the reactants, catalysed reaction will proceed via an intermediate species
transitions metal ions are effective as catalyst because they have variable oxidation states and easy to gain or lose electrons
How does V2O5 acts as a catalyst in the contact process
is reduced to VO2 but regenerated so oxidised back by reacting with oxygen
Explain how a catalytic converter decrease CO and NO (use of catalyst)
adsorption of CO and NO onto the surface of catalyst at active sites
weakening of bonds, holding reactants close together on the surface in the correct orientation to react so chemical reaction takes place on the surface
then desorbs CO2 and N2 from the surface of catalyst
What is the role of Fe2+ in catalysing the reaction between I- and S2O8 2-
what is the role of Mn2+ in autocatalysing the reaction between MnO4- and C2O42-
oxidised to Fe3+ and then reacts with I- and reduced to Fe2+, so regenerated, acts as catalyst. This reaction is quite slow due to collisions between two -ve charged ions, so has repulsion
MnO4- is reduced to Mn 2+, so Mn2+ as the product is able to acts as a catalyst for the reaction
Which types of binding exist within complex ion [Cr(H2O)]?
dative covalent and covalent only
How can impurities on reactant make catalyst less effective
impurities also get adsorb onto the catalyst surface
but impurities prevent bond weakening in the reactants and less surface area available for the reaction
impurities less likely to desorb from the surface as they form strong bond to the surface
Define a transition element
An element which forms at least one stable ion with a partially full d-shell of electrons
physical properties of transition metals
metallic
good conductor of heat and electricity
hard, strong, shiny
high melting point and boiling point
low reactivity - compare with group1/2
chemical properties of transition metals
variable oxidation states
coloured compounds/ions in solution
good catalysts
form complex ions
Define complex ion
central transition metal ion surrounded by ligands that are bonded by coordinate bonds
Define ligand
an ion or molecule with at least one lone pair of electrons that donate to a transition metal ion to form a coordinate bond and a complex ion
Define mono dentate ligands
a ligand that forms one coordinate bond to the central metal ion (bidentate forms 2, multi-dentate forms multiple)
name some common mono-dentate/bidentate/multidentate ligands
water, NH3, CN-, OH-
C2O42-, H2NCH2CH2NH2
EDTA4- (hexadentate)
define coordination number
the number of coordinate bonds the metal ion has formed to the surrounding ligands
what is a chelate
name of the complex ion with multi dentate ligands
what ion is usually formed when a transition metal compound is dissolved in water? What shape?
aqua ion
6 water ligands around the central metal ion, so octahedral shape
tetrahedral, square planar complex ion and linear complex ion example
tetrahedral: [CuCl4]2-, Cl- is much bigger than water, so can only fit 4 around the central metal ion
Square planar: [Pt(NH3)2(H20)2] - cisplatin
linear:
How can complex ions display E/Z or cis/trans isomerism?
what shapes of ion does this apply to
2 ligands of the same type can be on the same/opposite sides of the metal ion, which forms E/Z or cis/trans isomers
applies to square planar and octahedral complex ions
What conditions are needed for a complex ion display optical isomerism
applies to octahedral molecules with 2 or more bidentate ligands so mirror images are non-superimposable
What is harm - its metal ion, coordination number and ligands?
a molecule which makes up protein chains
with Fe2+ central metal ion, coordination number of 6
4 bonded to haem, 1 to nitrogen of global, one to oxygen
Why is CO toxic
CO coordinately bonds to the Fe2+, acts as a ligand, ligand exchange occurs
CO can bond more strongly to the central metal ion than oxygen
Why are transition metal coloured?
they have partially filled d-orbitals with free electrons between the d-orbitals
when ligands coordinately bond to the ion, d-orbitals split into different energy levels
electrons can absorb energy in the form of photons to become excited and move to higher energy level
we see the colours that are not absorbed
why is there a lack of colour in some aqueous ions and other complex ions
ions that have completely filled 3d energy levels or with 0 are not coloured
must have a partially filled 3d energy level
vanadium colours and chromium colours
You -yellow, 6+
better - blue, 5+
get - green, 3+
violent - violet, 2+
Or - orange, 6+ (Cr2O72-)
You - yellow, 6+
Get - green, 3+
Burnt - blue, 2+
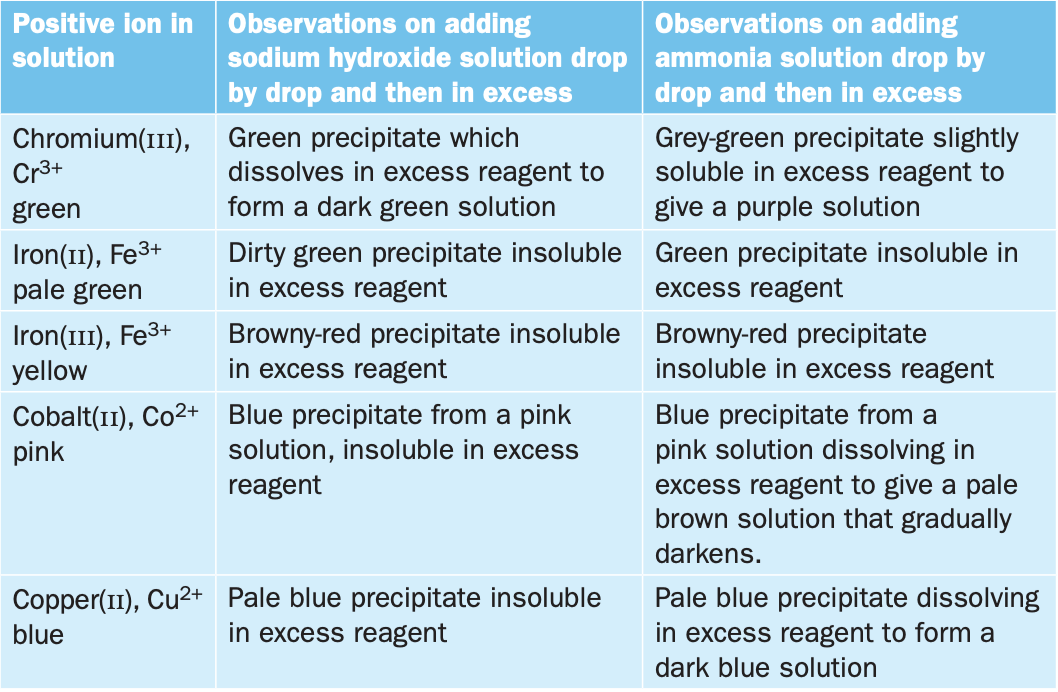
colours of complex ions!!
why can transition metals have variable oxidation states
which oxidation states do all transition metals have, why?
they have partially filled d-orbitals, can lose 4s and 3d electrons
+2 due to loss of electrons from 4s orbital
why are transition metals good catalysts
they can exist in variable oxidation states, so can provide alternate pathways easily
What is an advantage of using a heterogeneous catalyst
easy to separation of products from catalyst
What properties does the catalyst need to have to make it a good catalyst
can’t adsorb too strongly, otherwise products will not desorb
cant adsorb too weakly as reactants would not be held in place for long enough and bonds would not be sufficiently weakened
so need a good balance between adsorption and desorption
how to increase efficiency of heterogeneous catalysts
increase surface area to increase number of active sites present
spread onto an inert support medium to increase surface/mass ratio e.g. ceramic honeycomb
define autocatalysis
when the product of a reaction is also a catalyst for that reaction