Anatomy 338 Exam 3
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
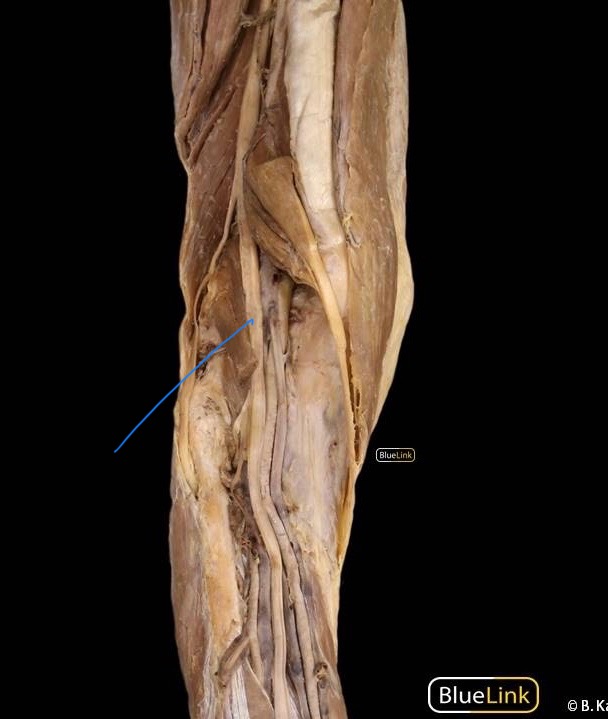
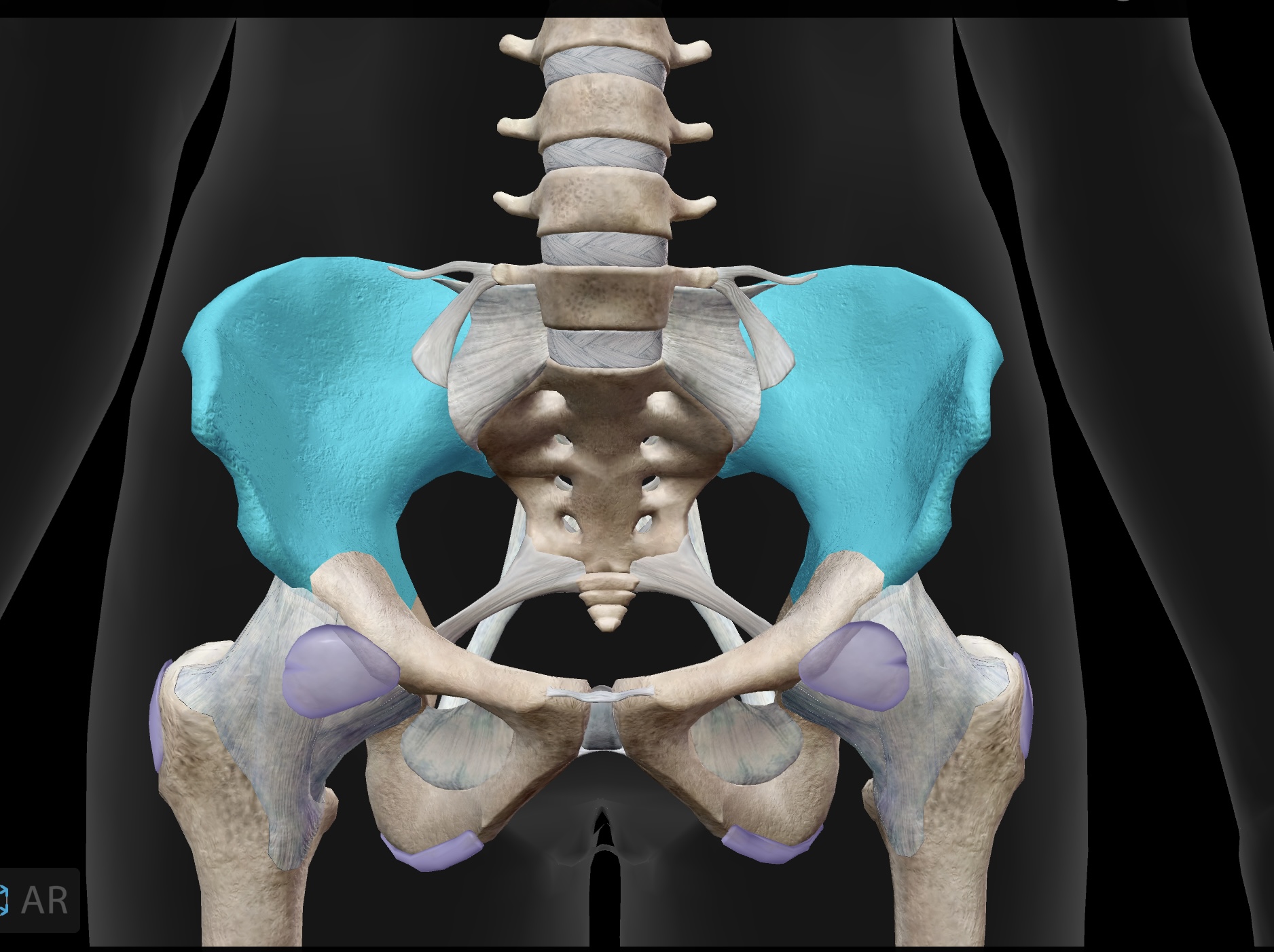
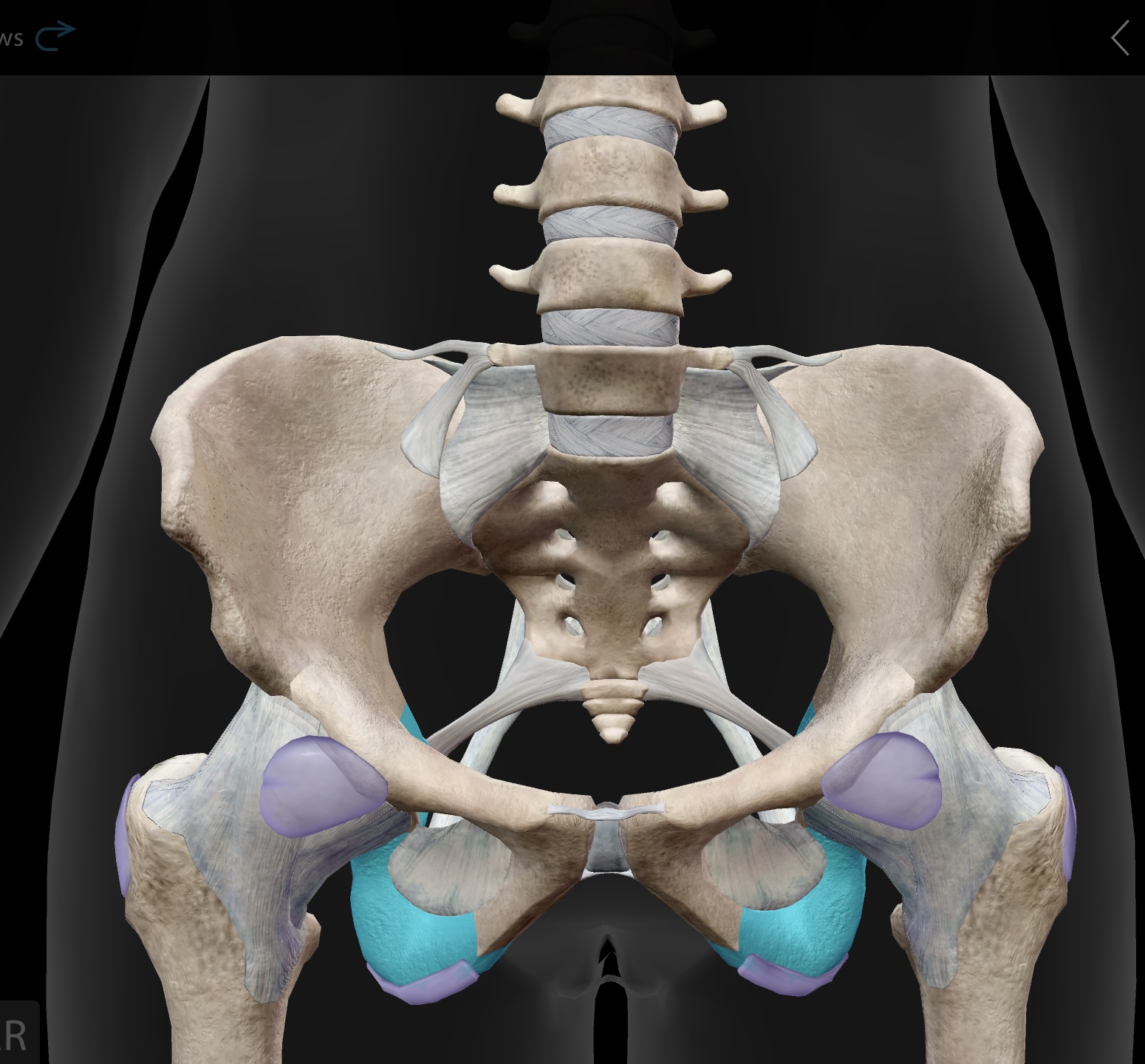
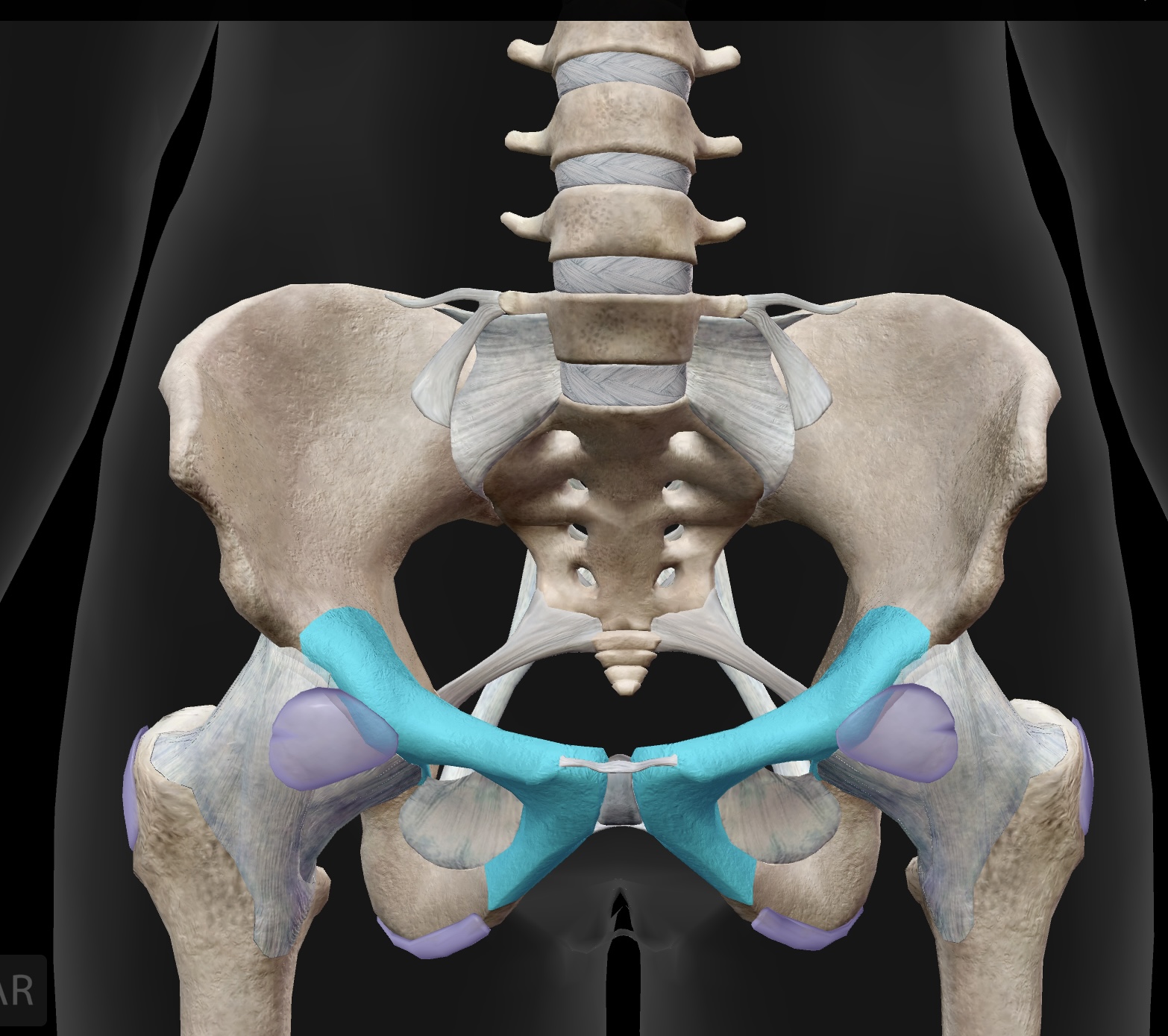
sacroiliac joint
The joint formed between the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis, providing stability and support during movement.
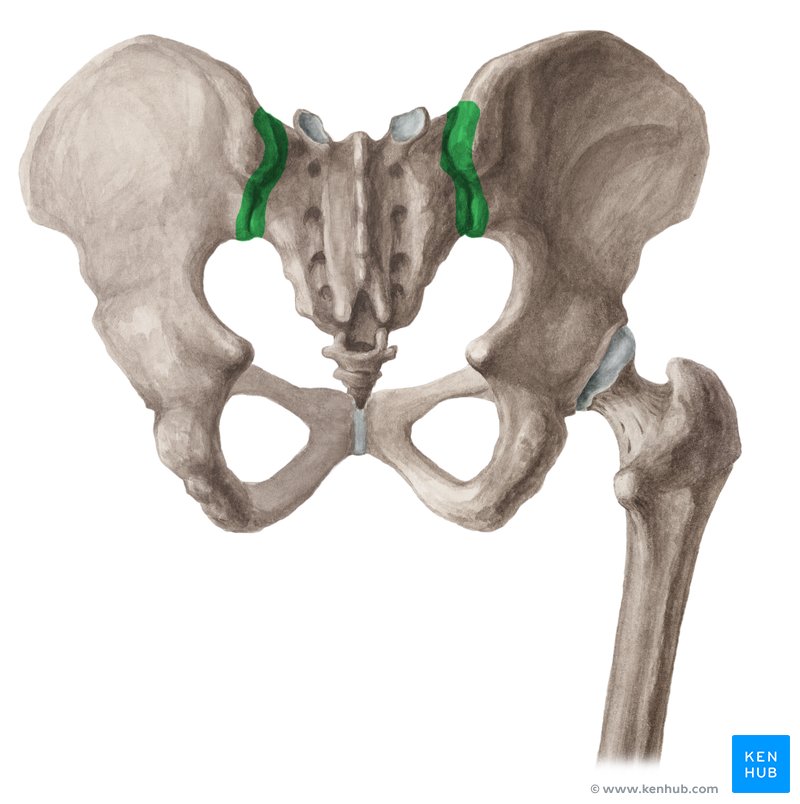
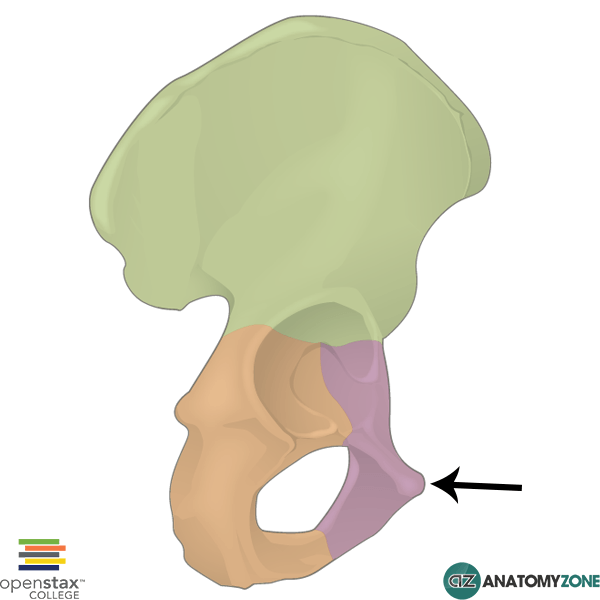
os coxae
bones of the pelvis, formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubis
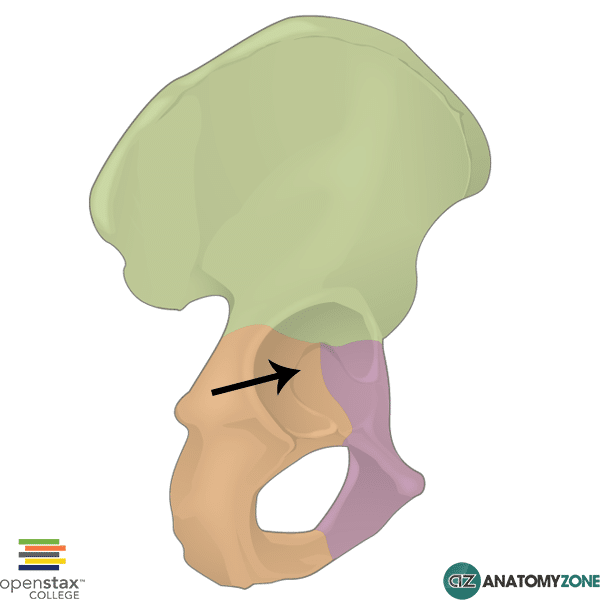
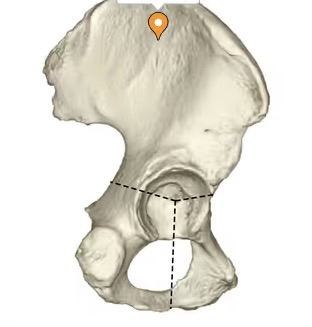
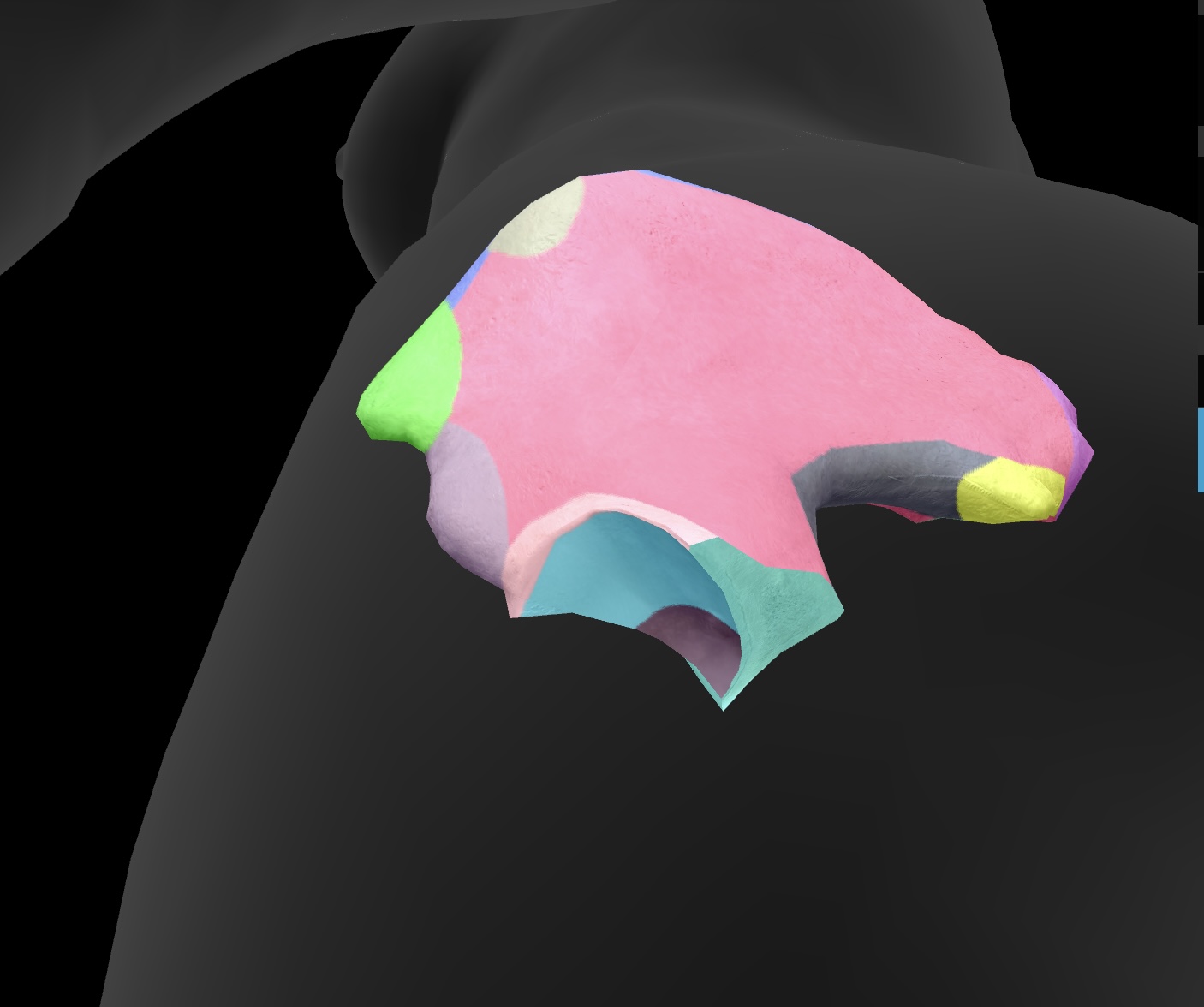
acetabulum
articular surface of the pelvis that articulates with the head of the femur and it forms the hip joint.
ilium
(large butterfly wing) — the most superior of the bones of the os coxae
arcuate line
a curved line on the ilium that defines the boundary between the pelvis and abdominal cavity.

iliac fossa
the cupped, concave area of the ilium that serves as the site for muscle attachment and supports the pelvic organs.
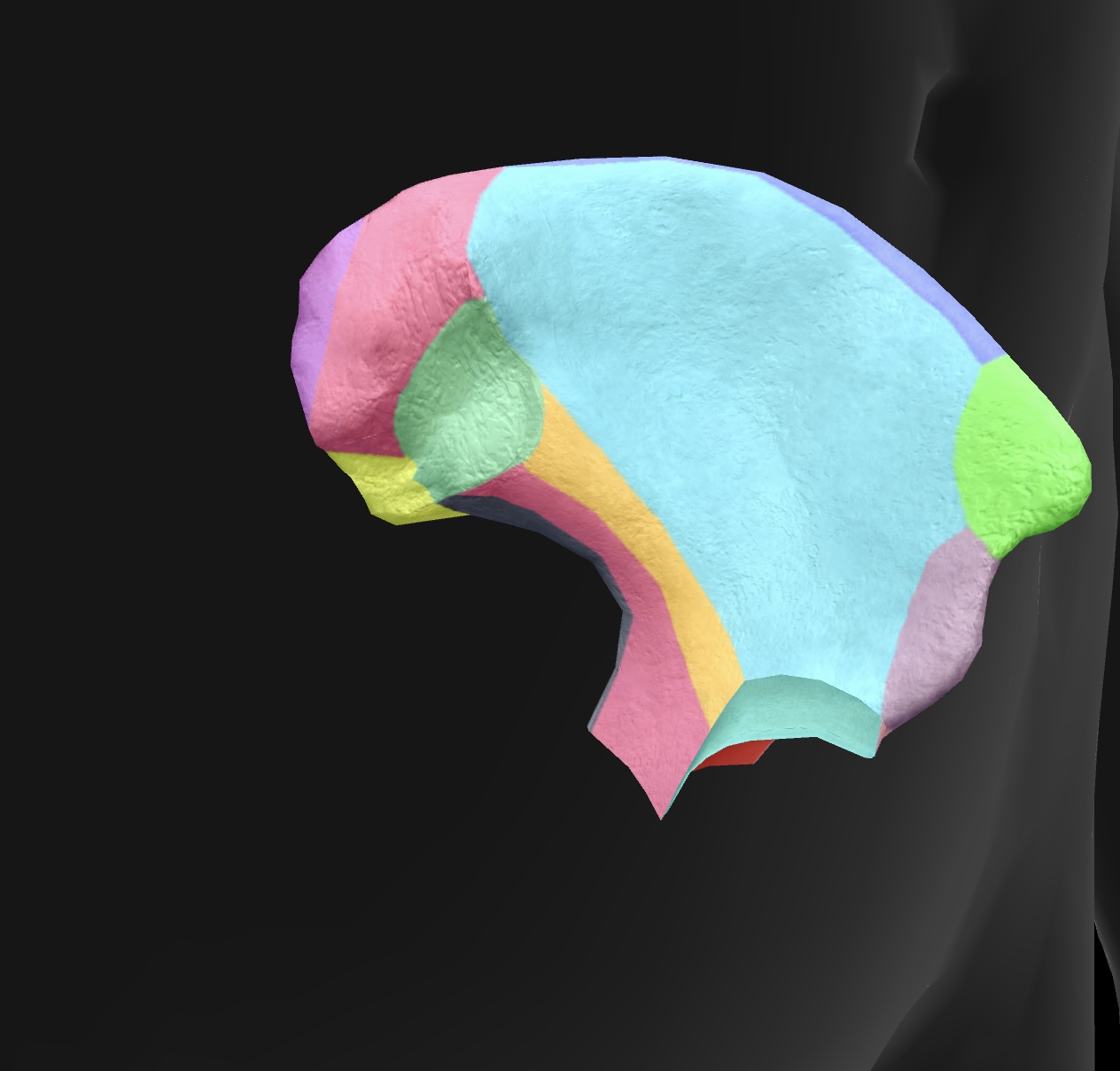
iliac crest
the superior border of the ilium, providing attachment for muscles and ligaments.
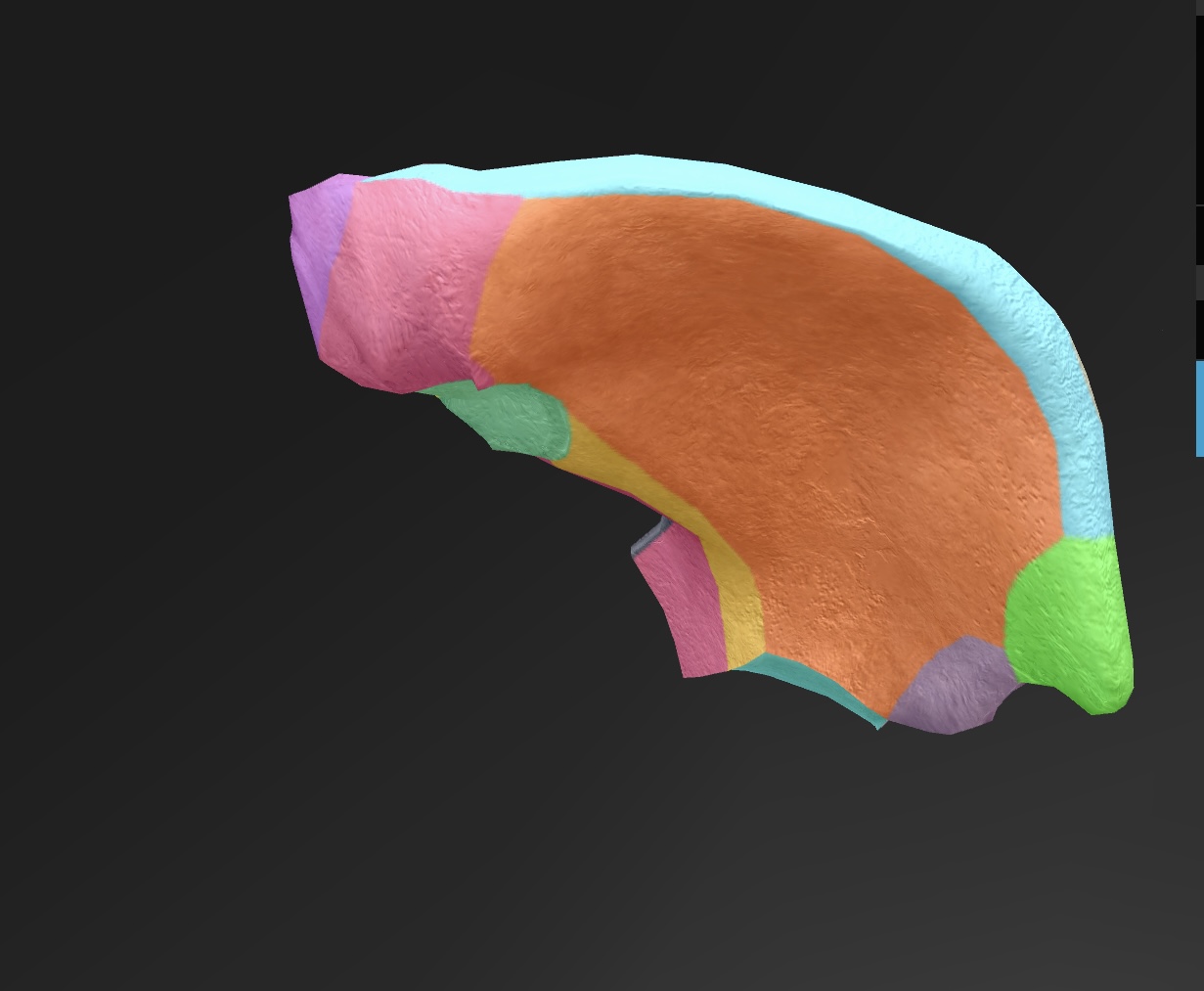
anterior superior iliac spine
lateral upper projection of the ilium, serving as an important landmark for muscle attachment and pelvic alignment.
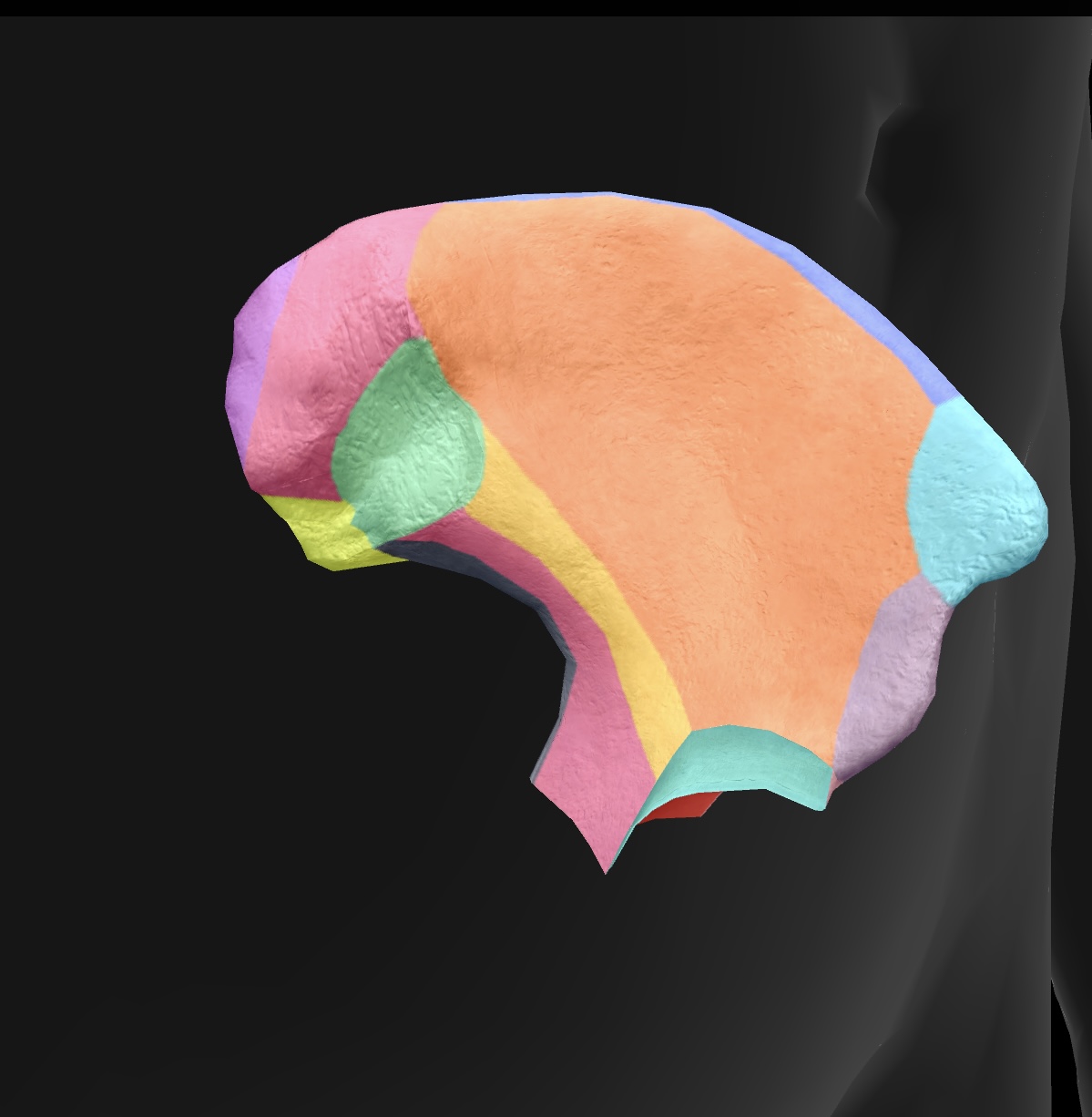
anterior inferior iliac spine
lateral lower projection of the ilium, providing attachment for the rectus femoris muscle and supporting the hip joint.
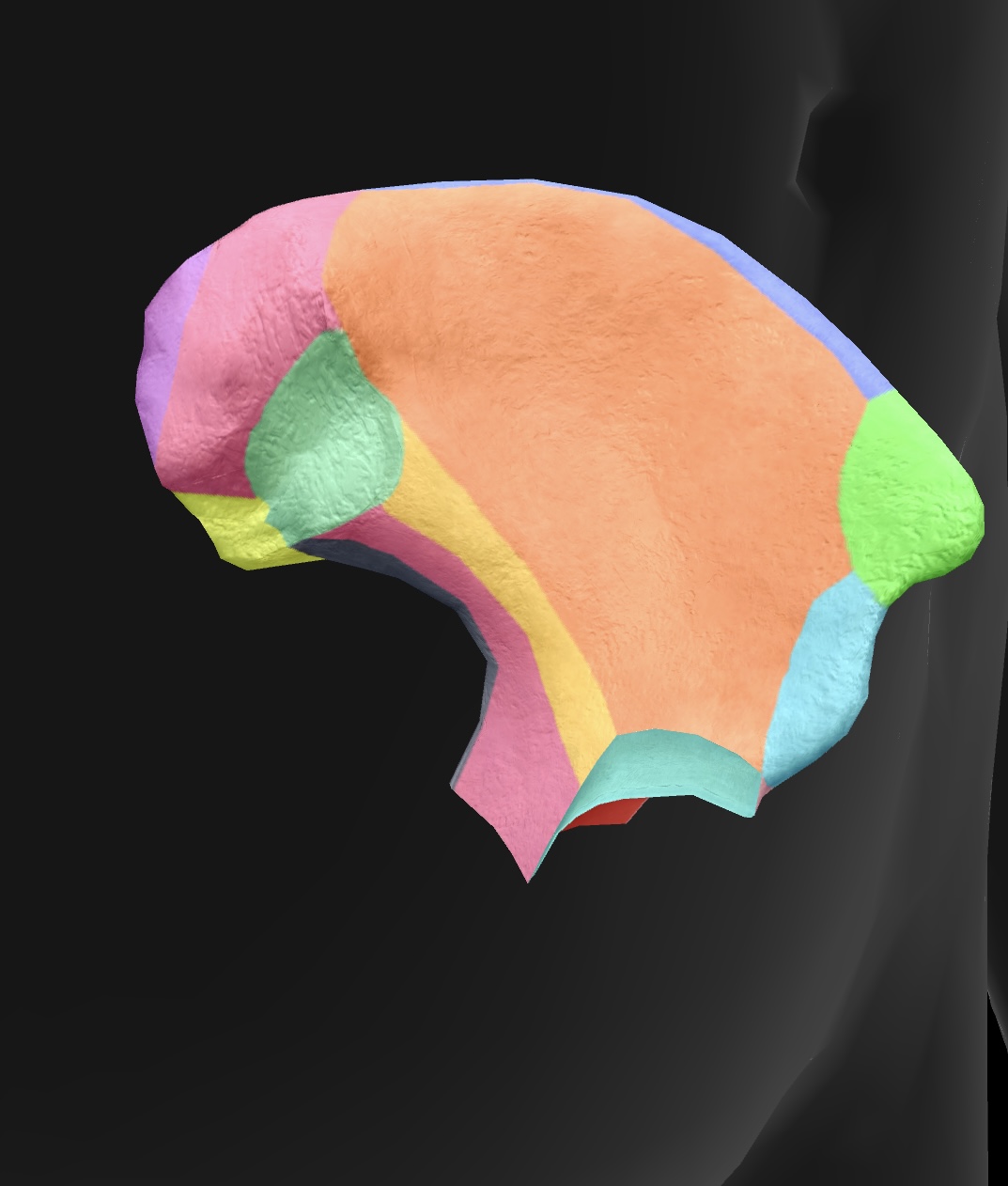
posterior superior iliac spine
medial & superior projection of the ilium, serving as a landmark for anatomical and clinical reference.
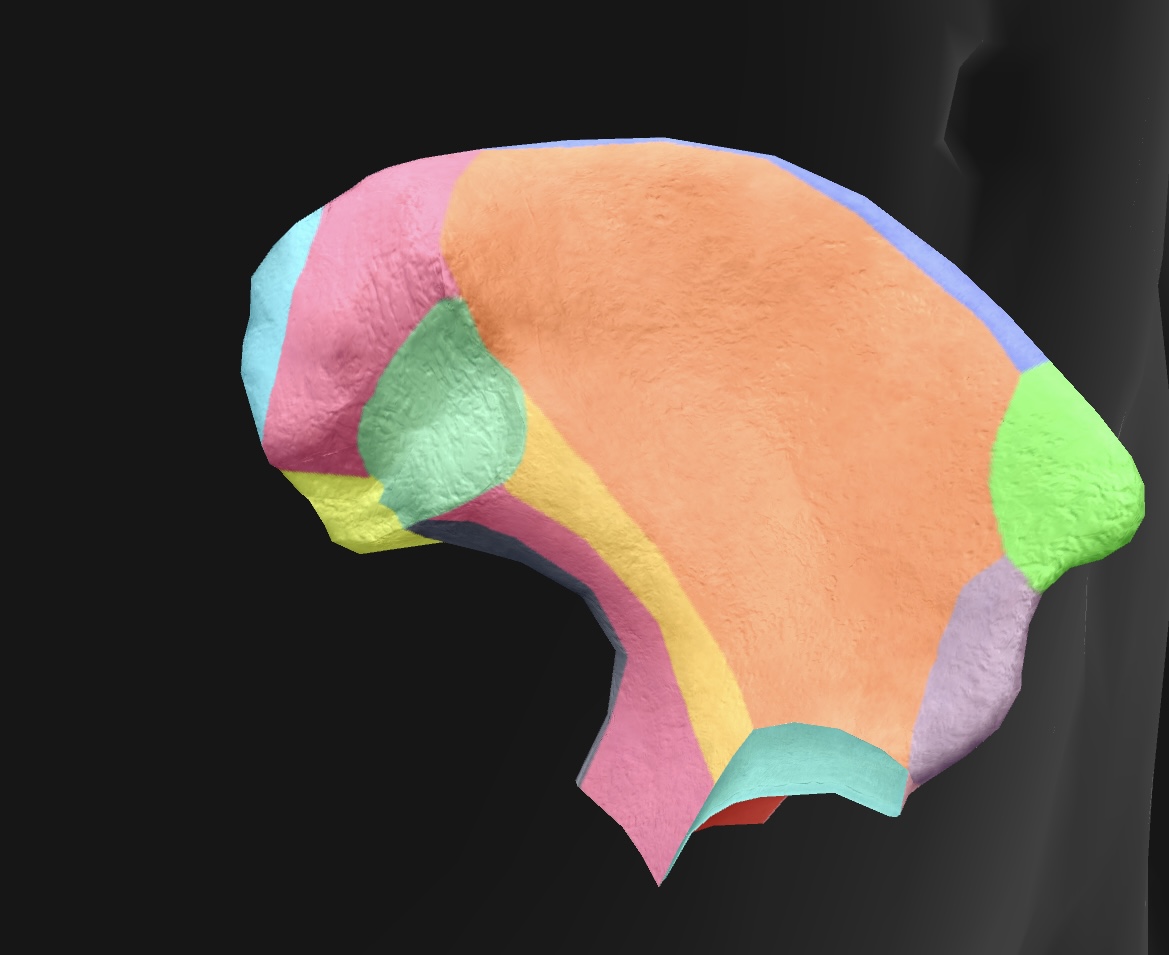
posterior inferior iliac spine
medial & inferior projection of the ilium, important for pelvic anatomy and muscle attachments.
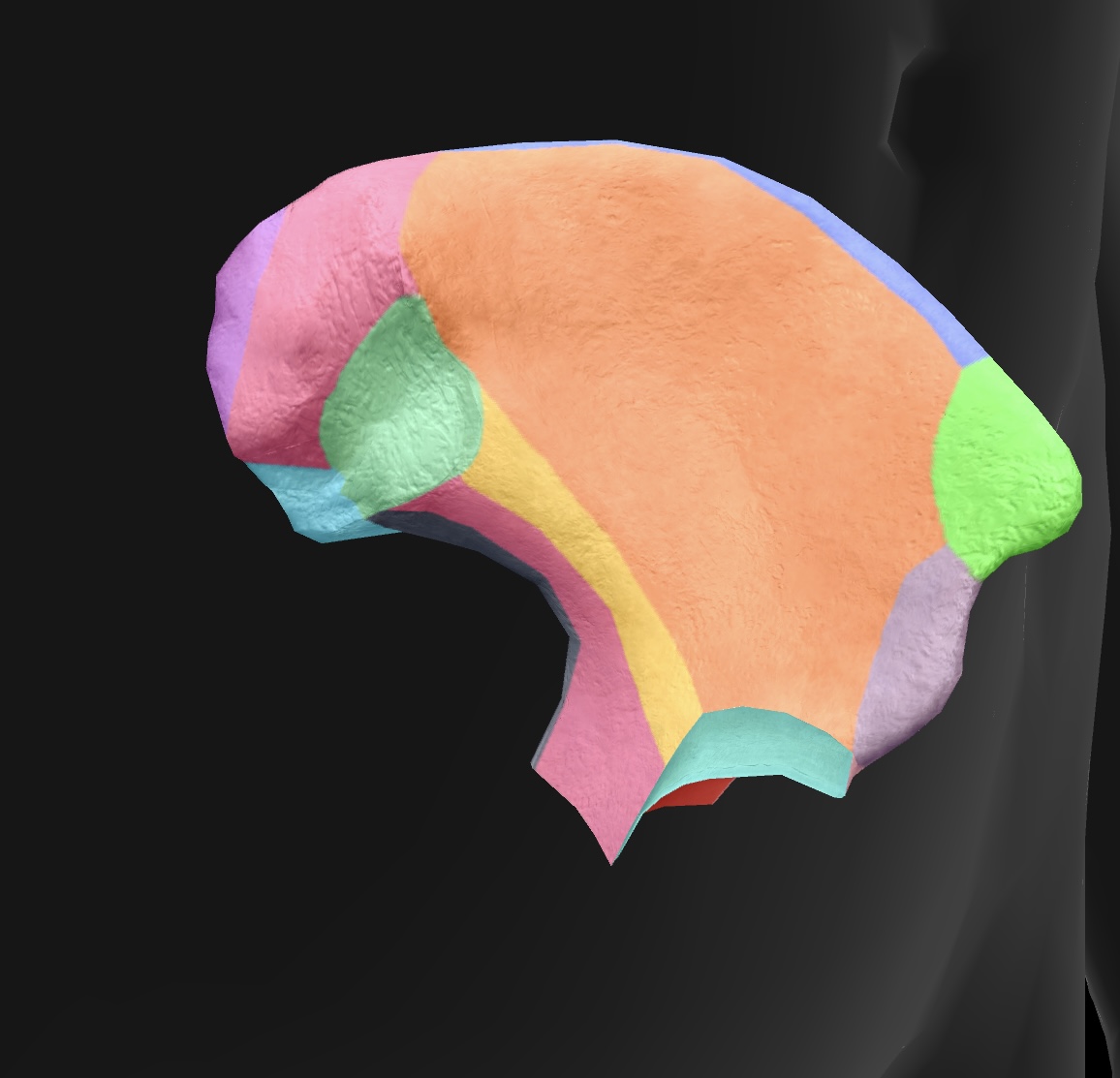
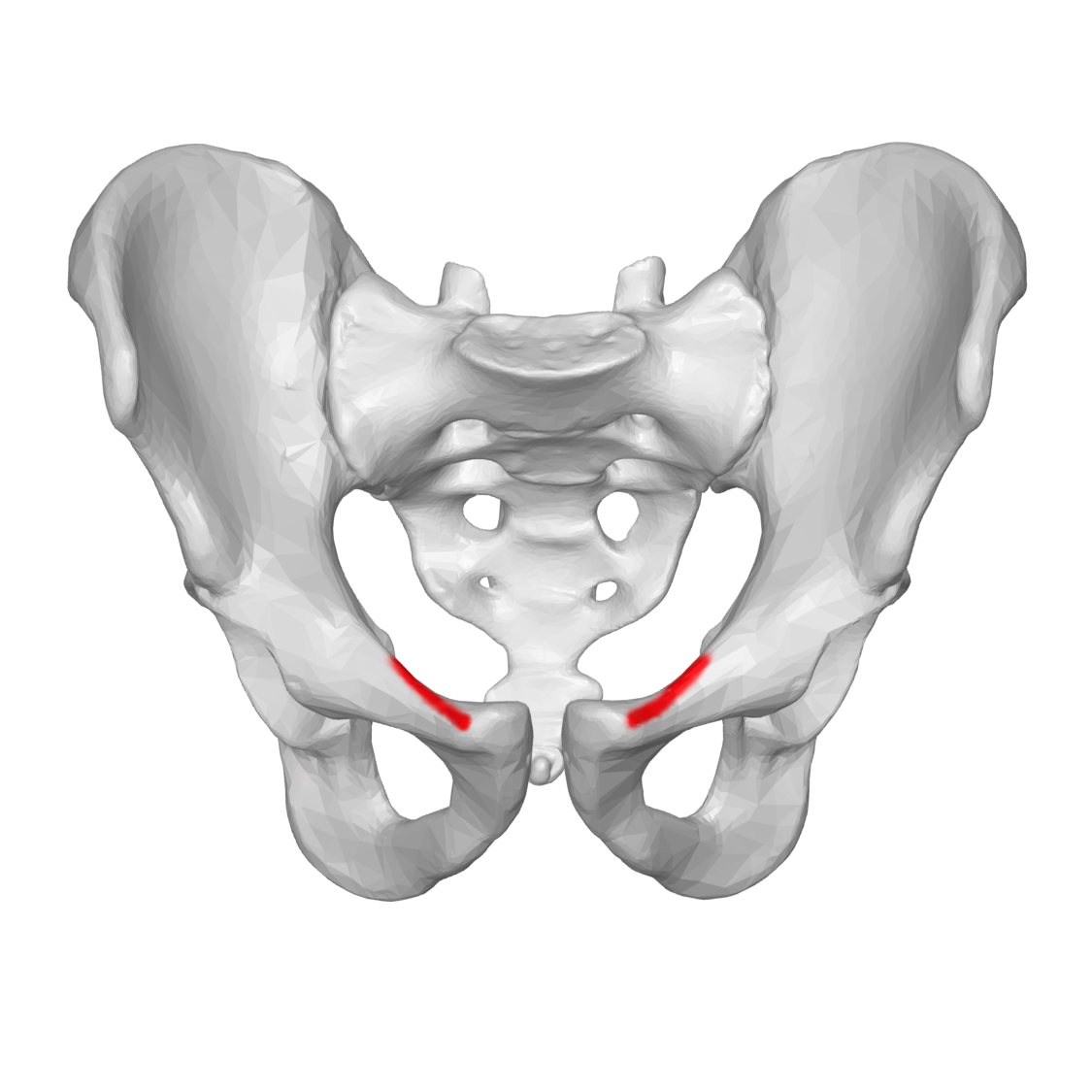
greater sciatic notch
A large indentation on the posterior border of the ilium — becomes the greater sciatic foramen as the sacrospinal ligament closes the notch, piriform passes through it. superior gluteal vessels & nerve pass above the piriformis in the foramen, & the inferior gluteal vessels & sciatic nerves pass inferior to the piriformis
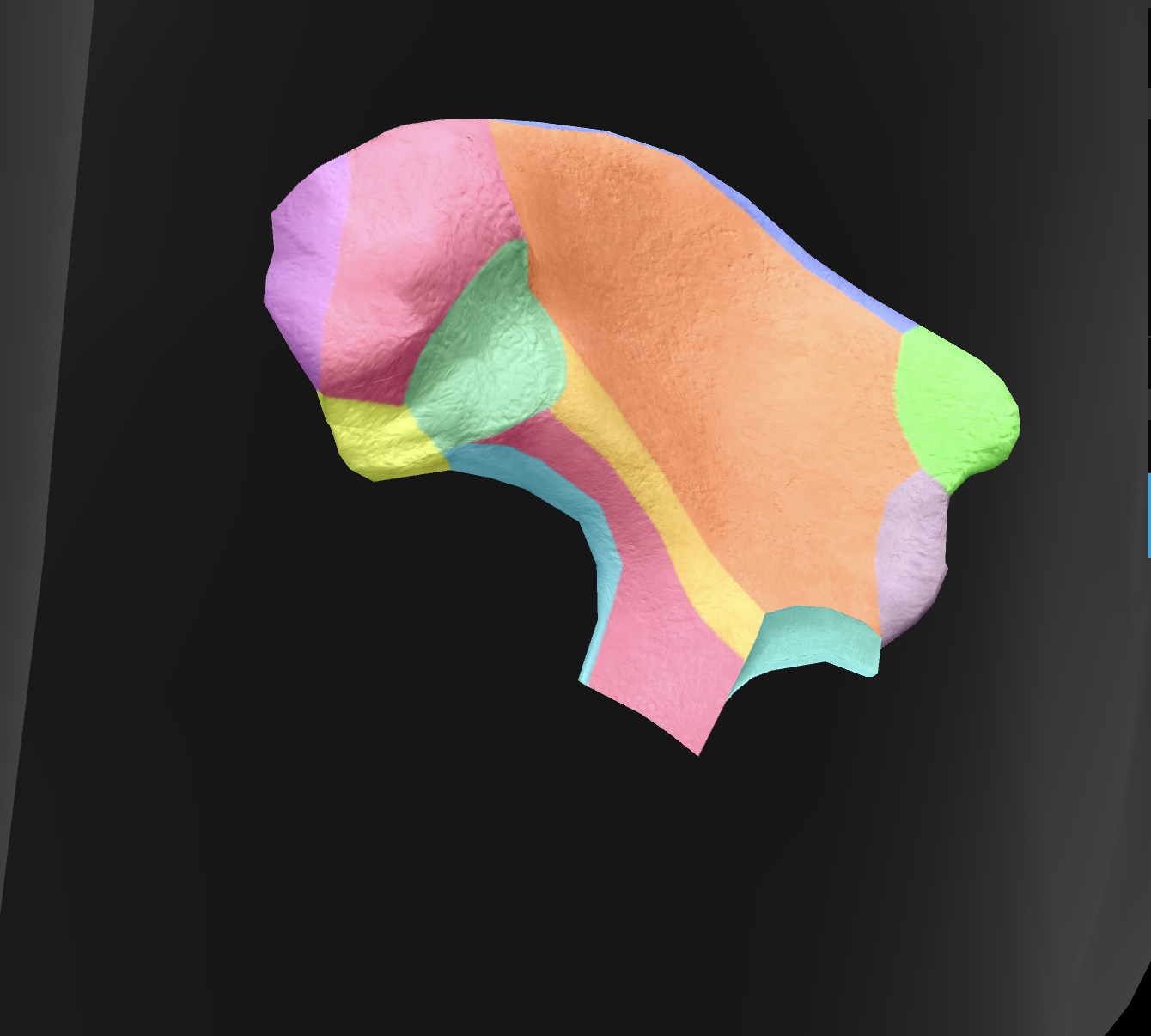
ala
posterior side of the ilium bone in the pelvis (butterfly wing)
ischium
(bottom butterfly wing) — posteroinferior bone of the os coxae
ischial spine
A bony projection on the ischium that serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles, contributing to the pelvic structure.
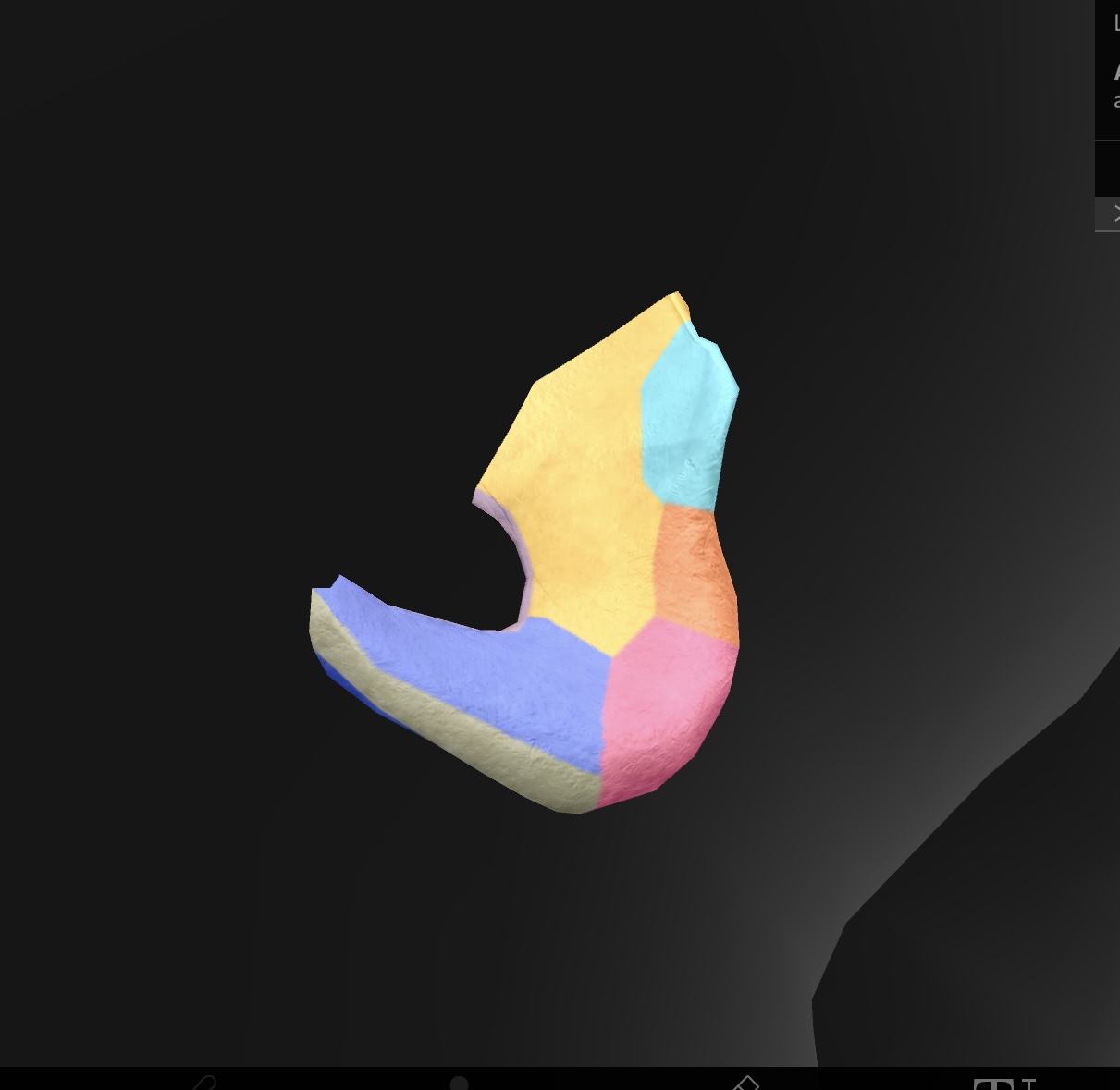
ischial tuberosity
bony prominence inferior to the ischial spine, serves as the origin for the hamstring muscles and supports the weight of the body when sitting.
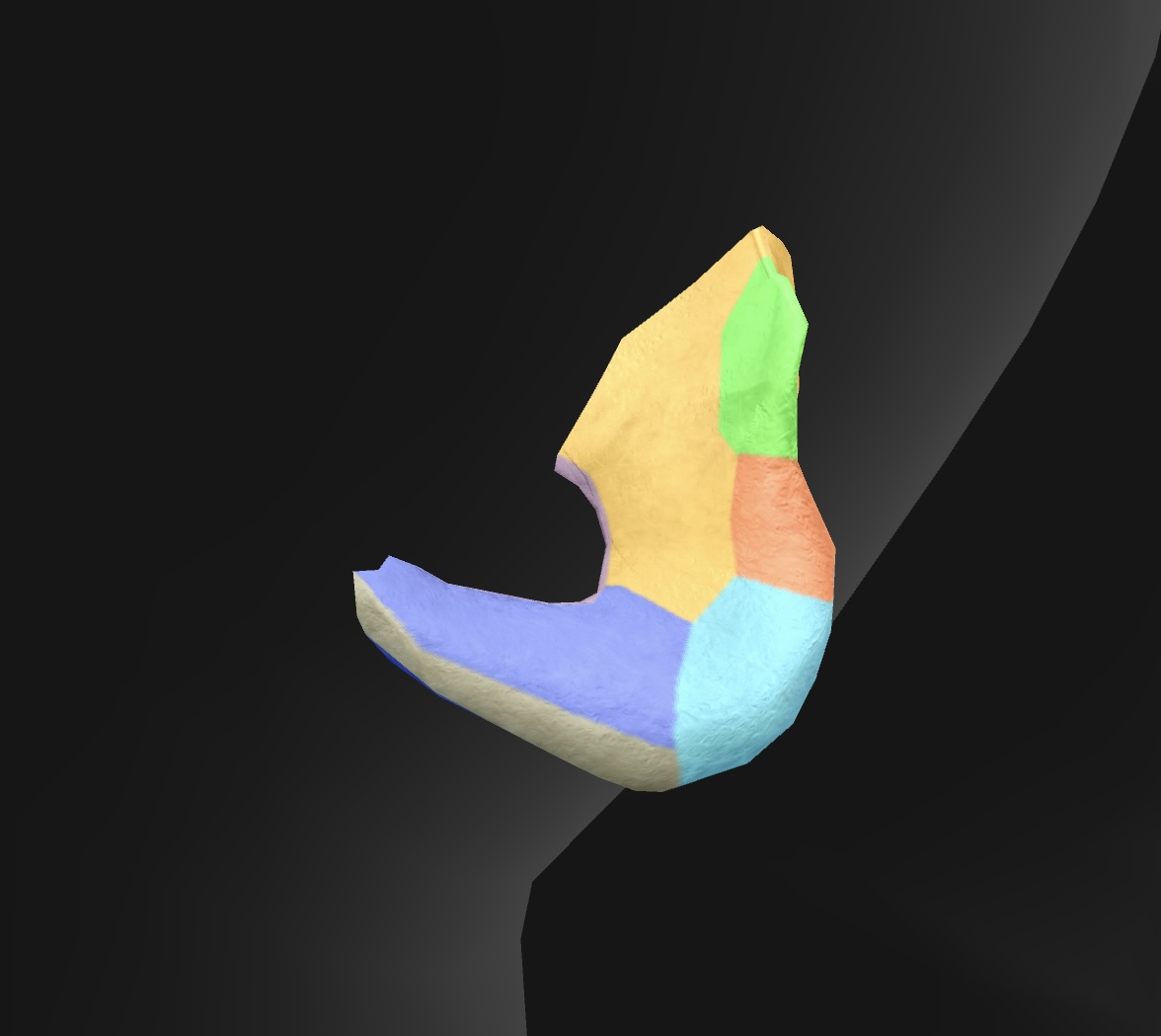
ischial ramus
a part of the ischium that connects with the pubis, contributing to the structure of the pelvic bone.
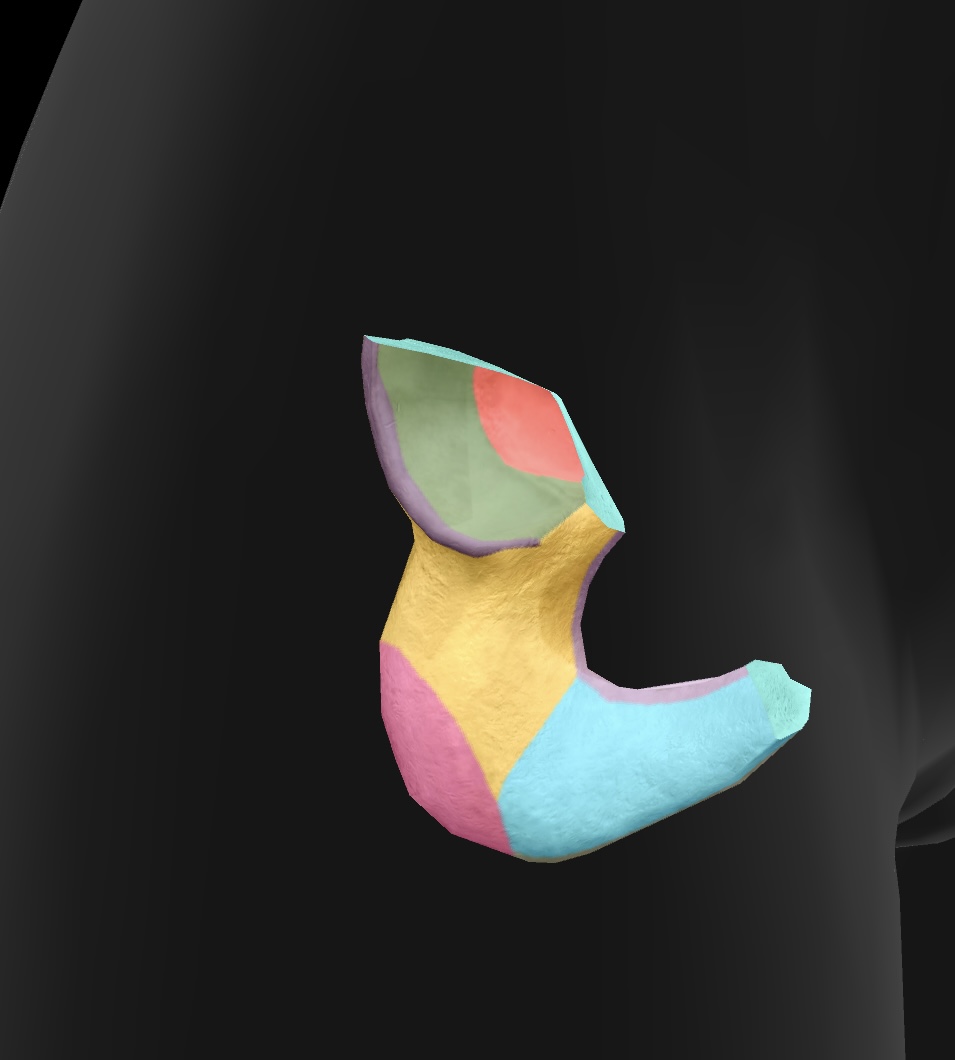
lesser sciatic notch
a notch located on the ischium—becomes the lesser sciatic foramen when the sacrotuberal ligament closes the notch. transmits the obturator internus tendon, the nerve to this tendon, and other vessels & nerves to the pelvis
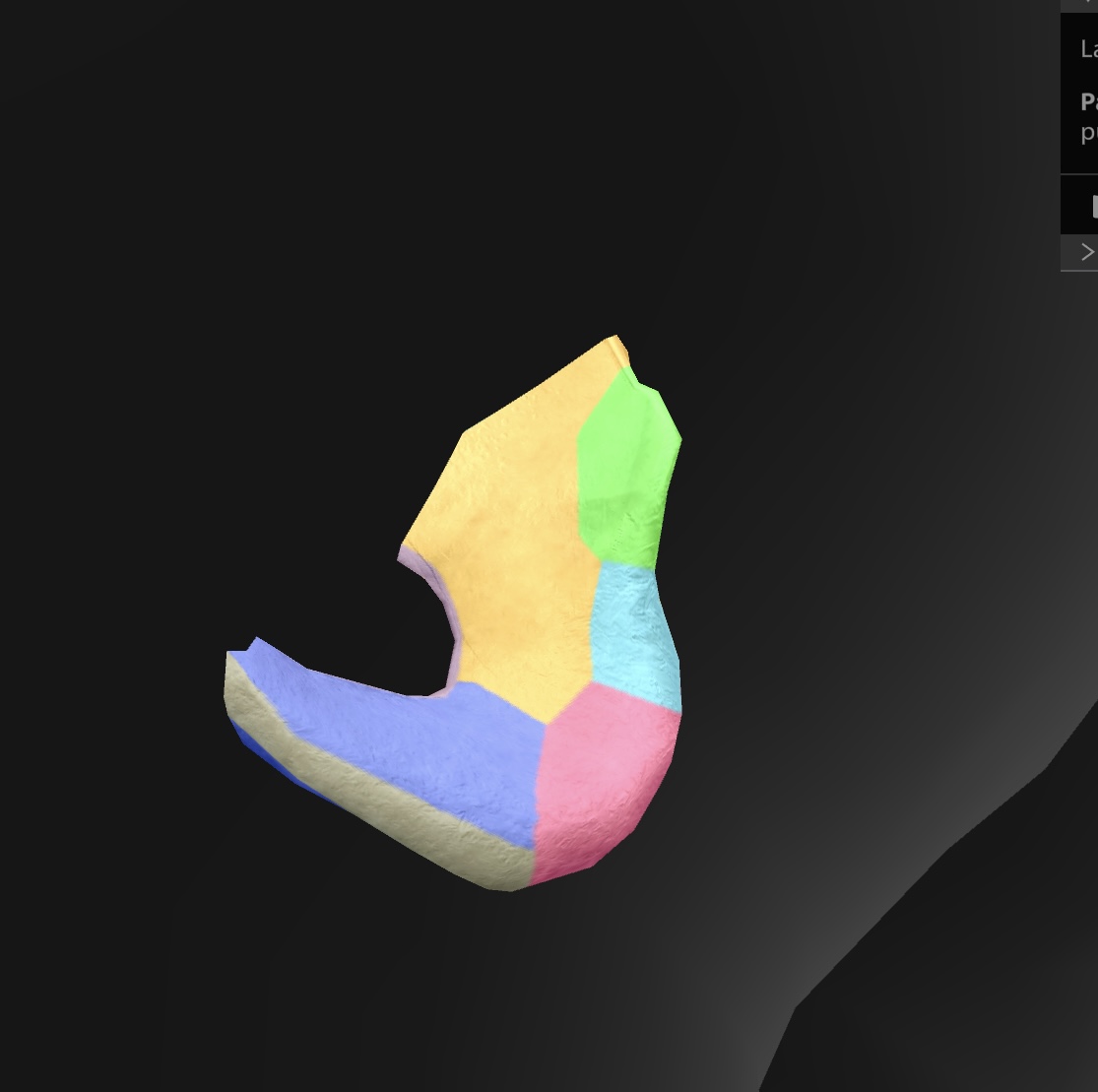
lunate surface
The smooth, curved surface of the acetabulum that articulates with the head of the femur, forming part of the hip joint.
pubis
anteroinferior bone of the os coxae
superior rami
a pair of bony extensions of the pubis that help form the pelvic arch and contribute to the acetabulum.
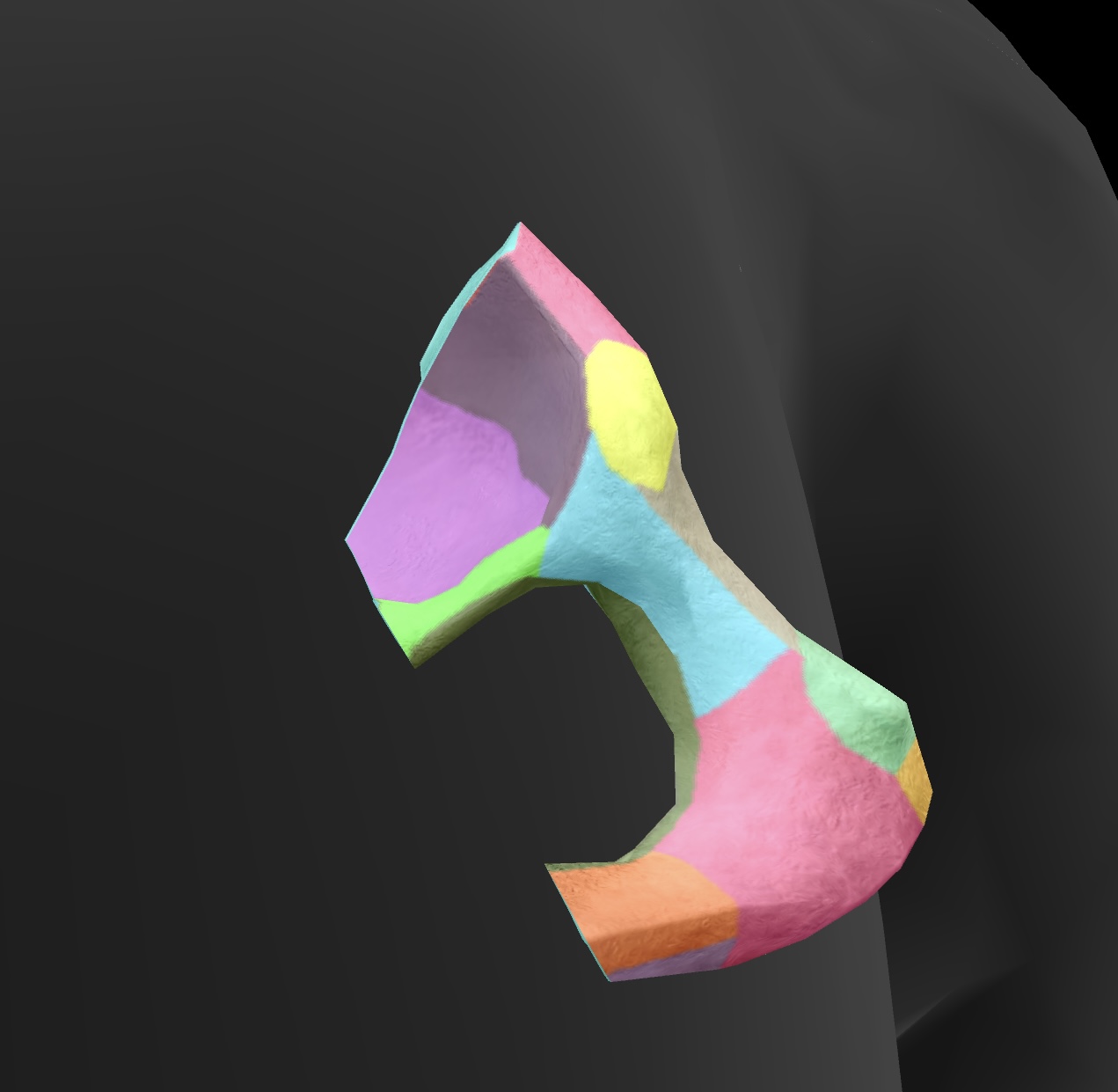
inferior rami
the projections of the pubis that extend downward and contribute to the formation of the obturator foramen.
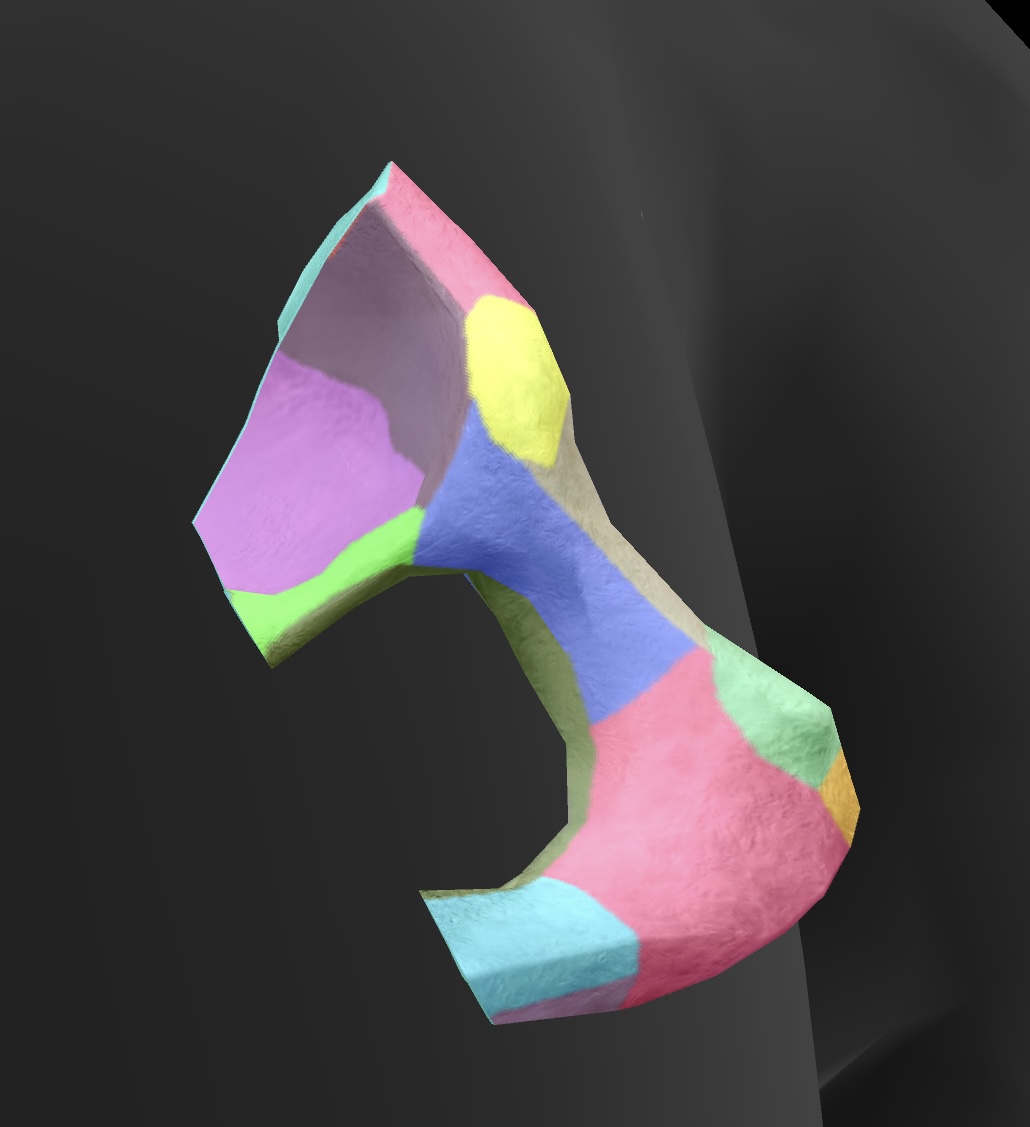
pubic crest
the ridge on the superior part of the pubis that serves as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
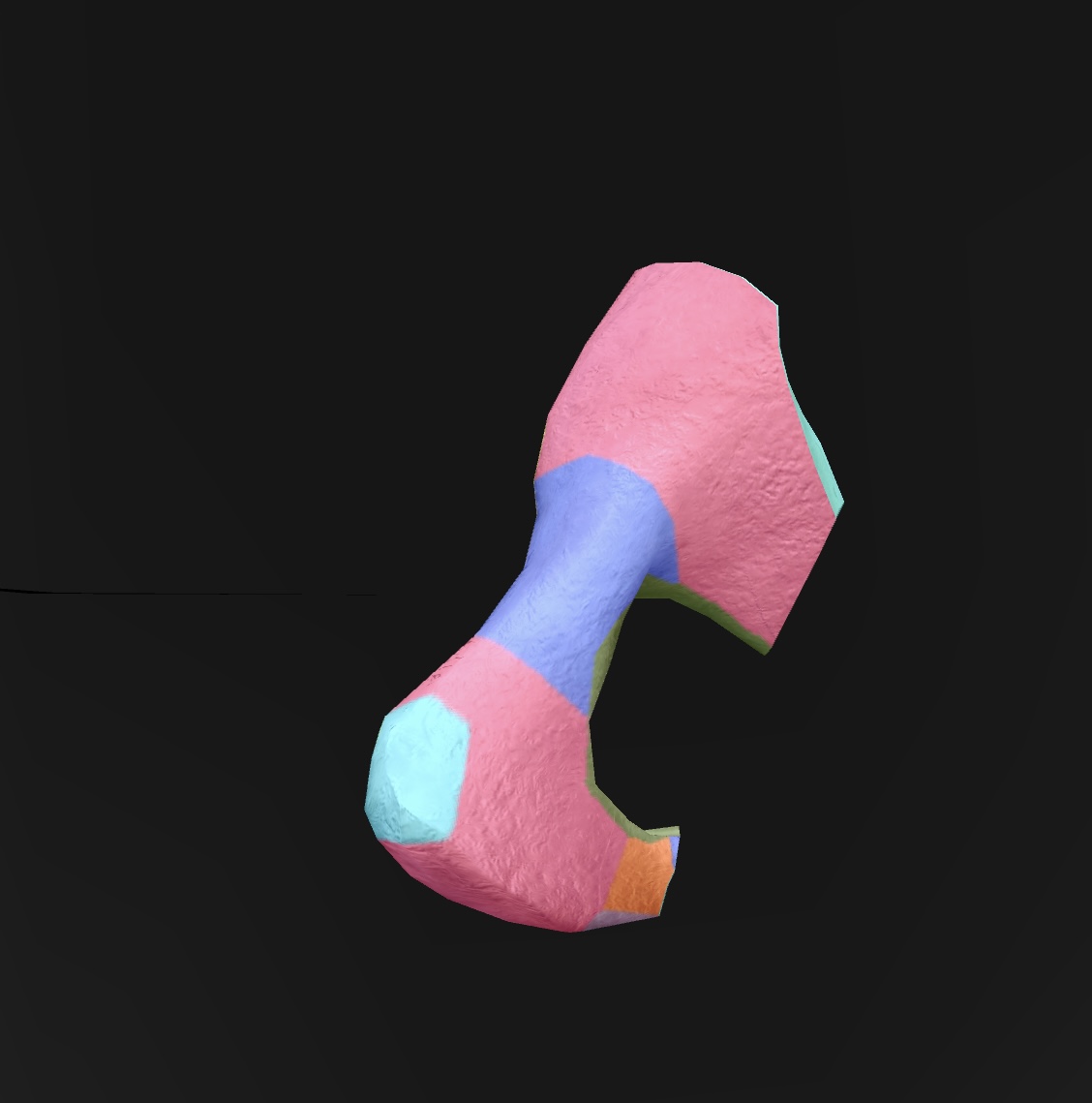
pubic tubercle
A small, bony prominence on the superior part of the pubic bone that serves as an attachment point for the inguinal ligament.
obturator foramen
A large opening in the pelvis formed by the ischium and pubis, allowing passage for nerves and blood vessels.

pectineal line
A ridge located on the superior ramus of the pubis, serving as an attachment site for muscles and as a landmark for the pelvic inlet.
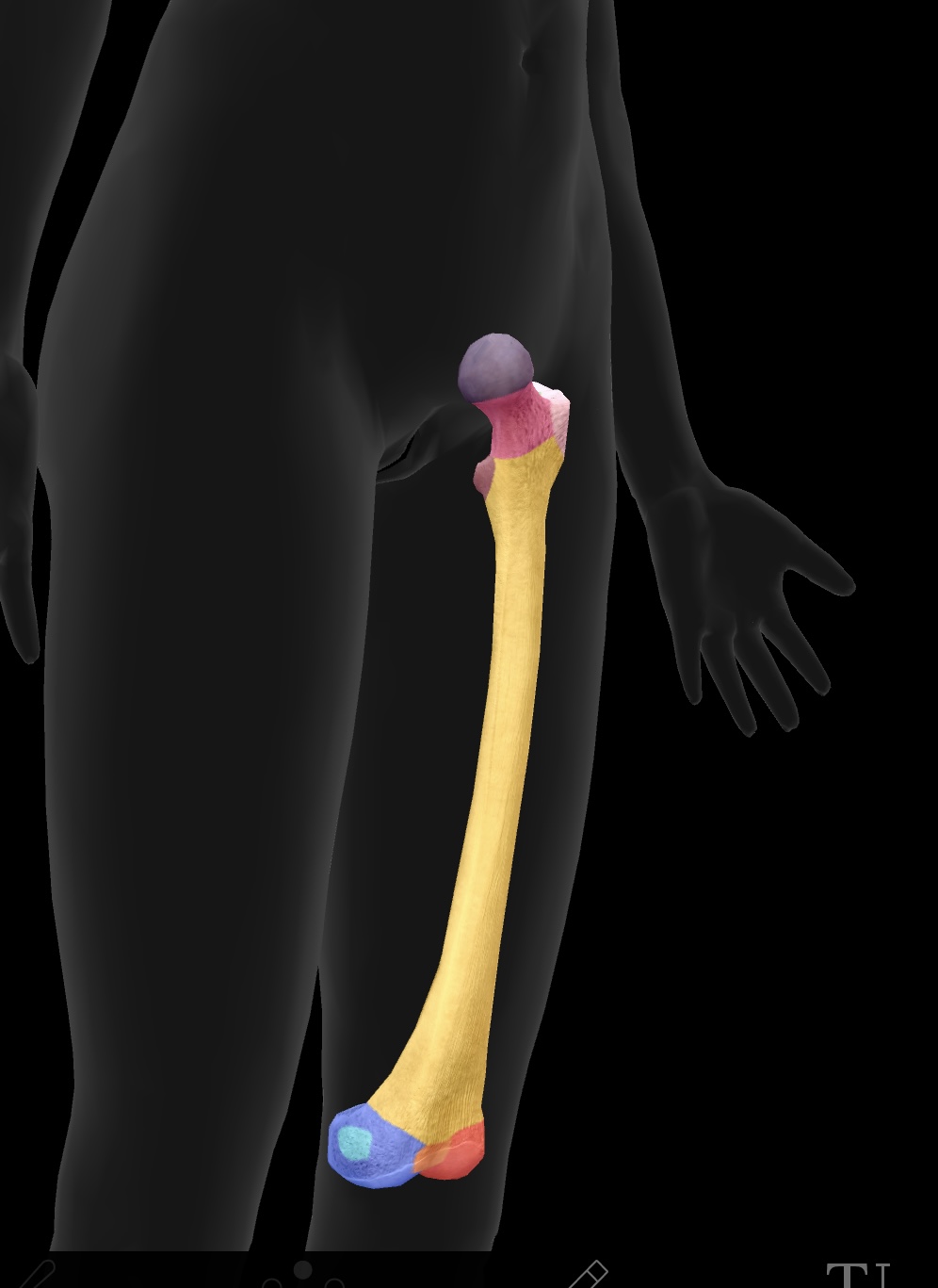
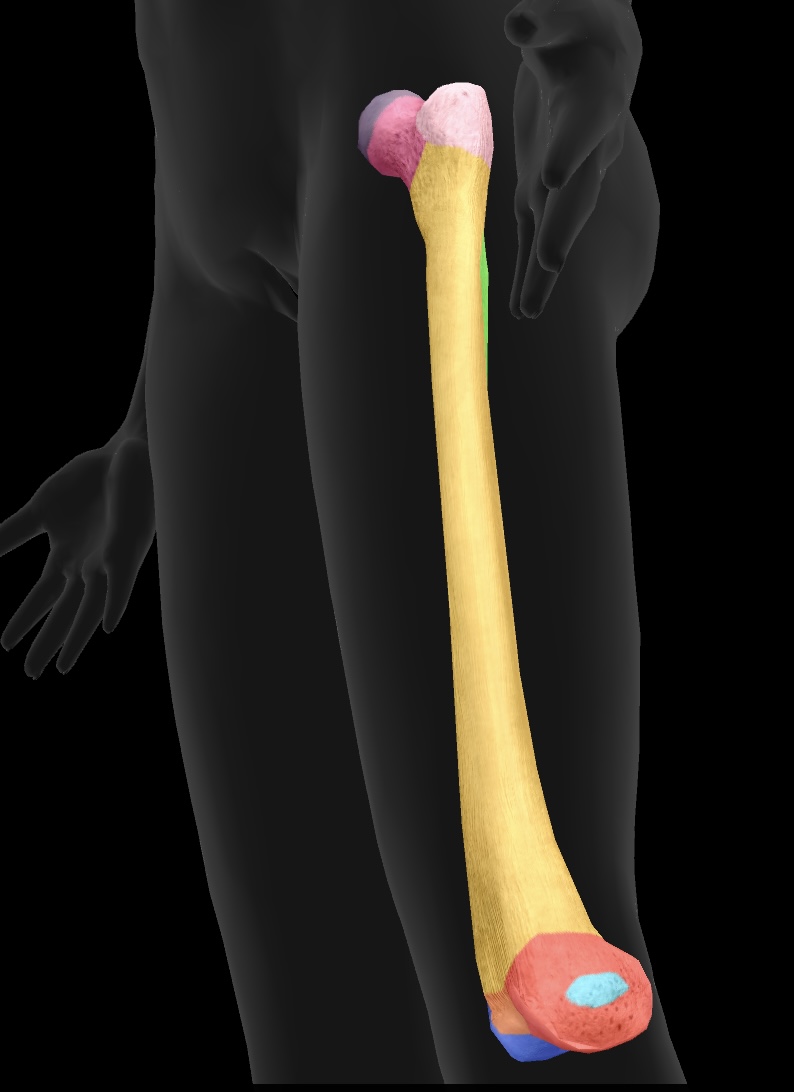
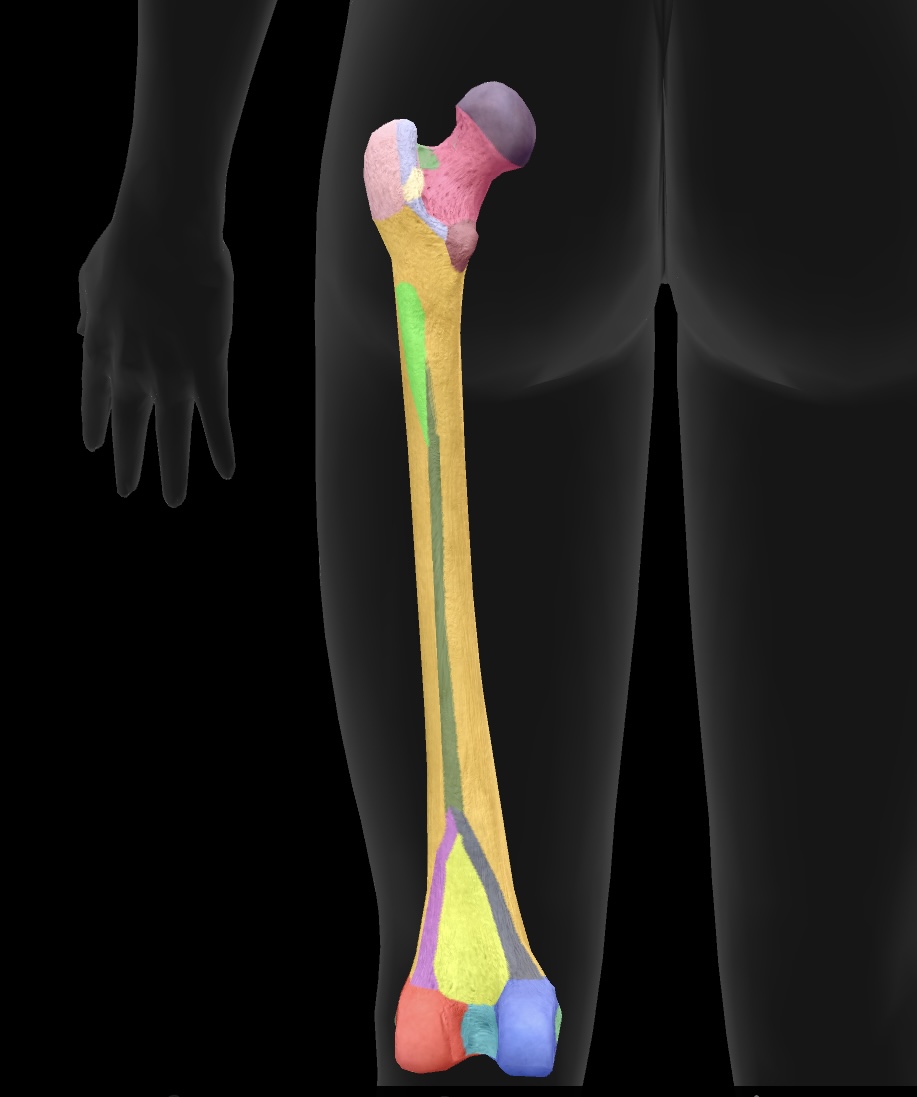
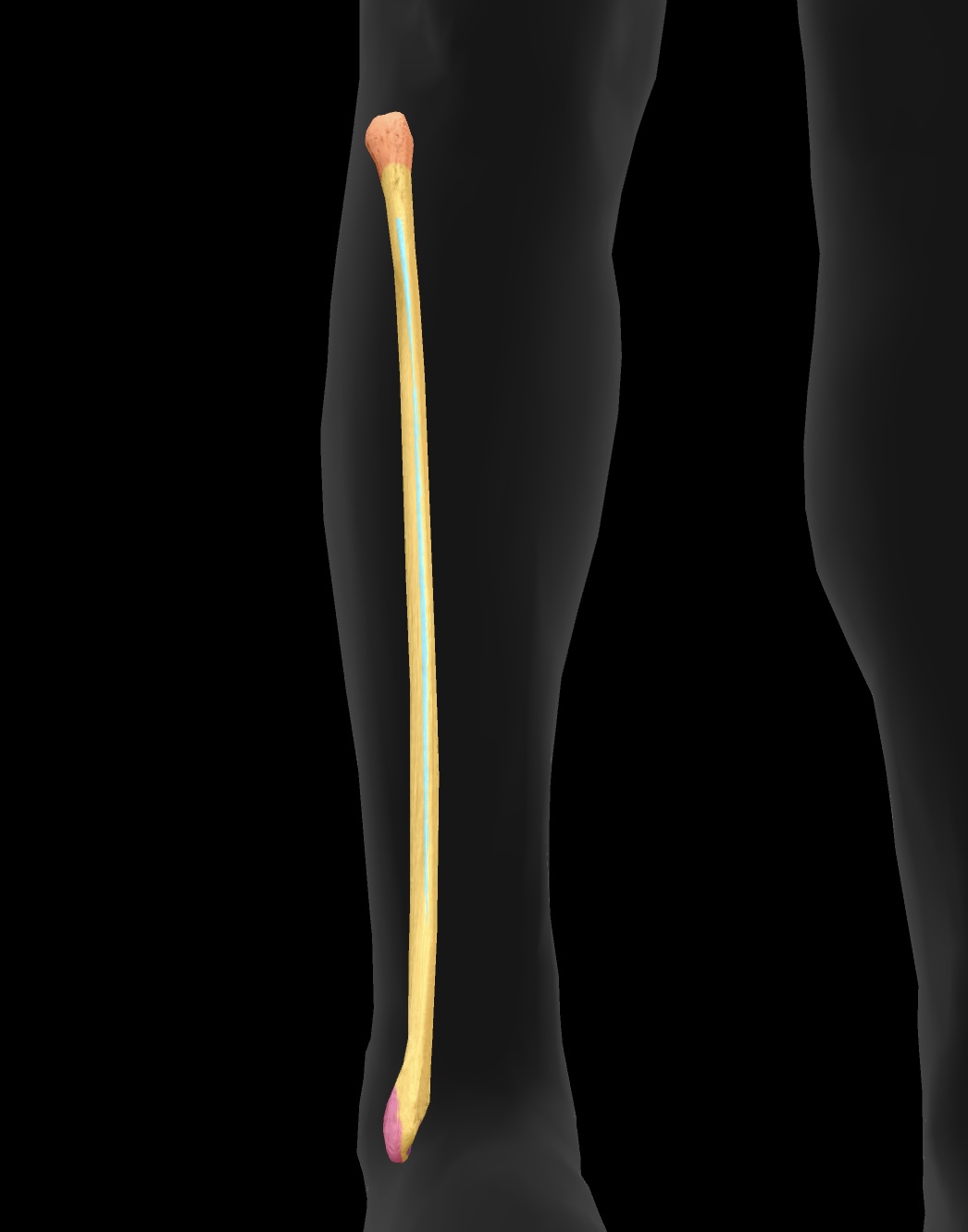
femur
longest bone of our body, located between the hip & knee
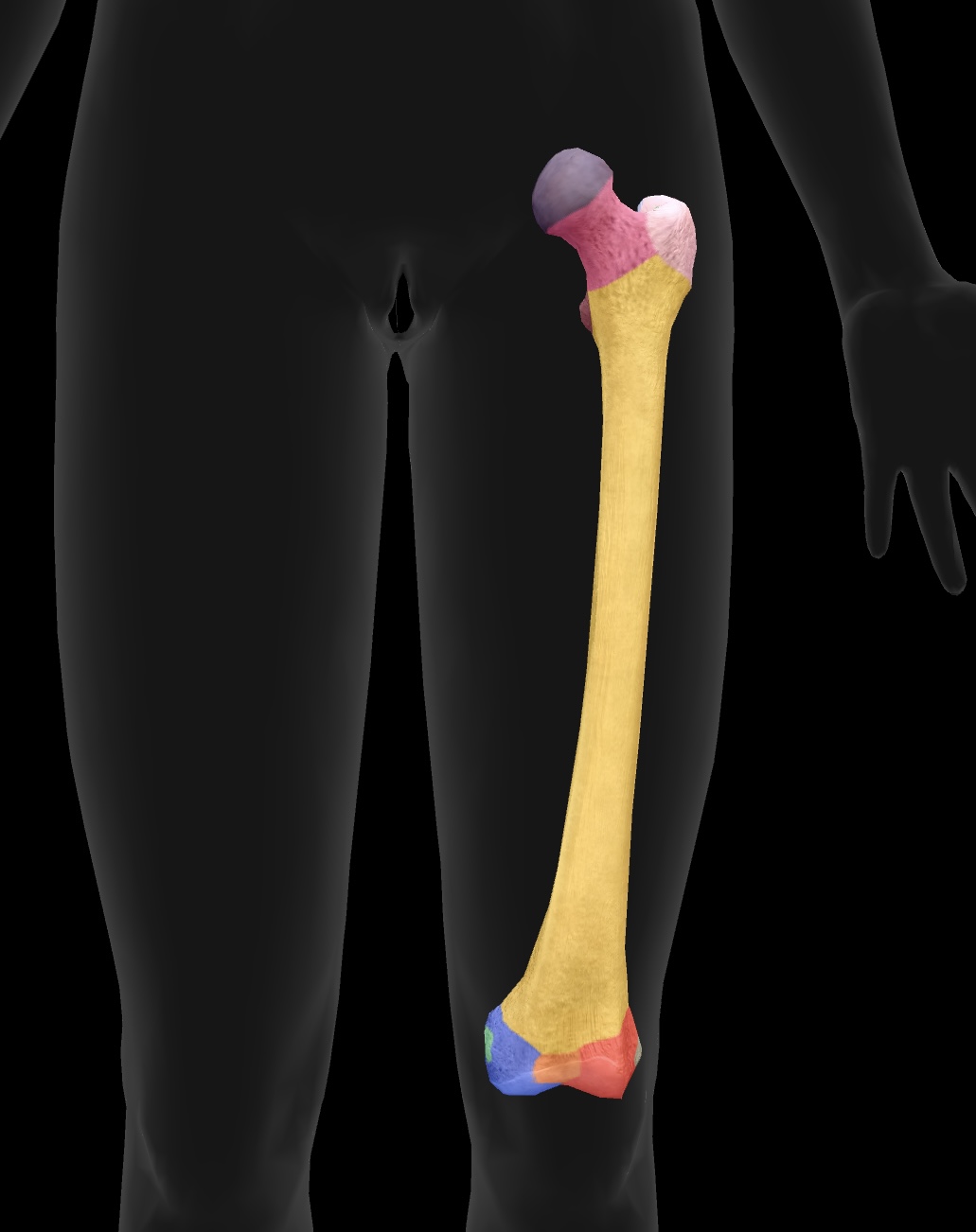
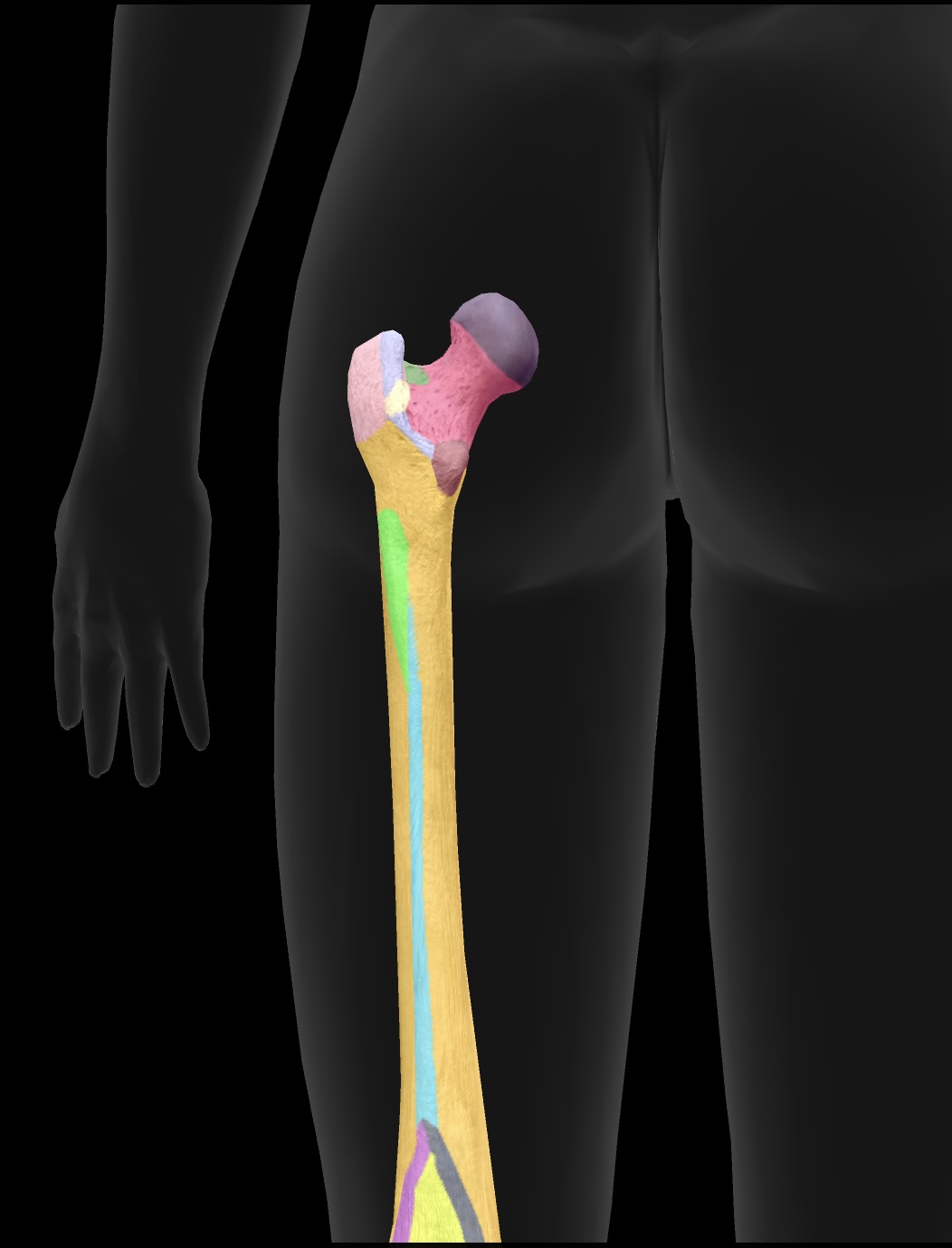
head of femur
ball on top — articulates with the acetabulum of the ox coxae to form the hip joint
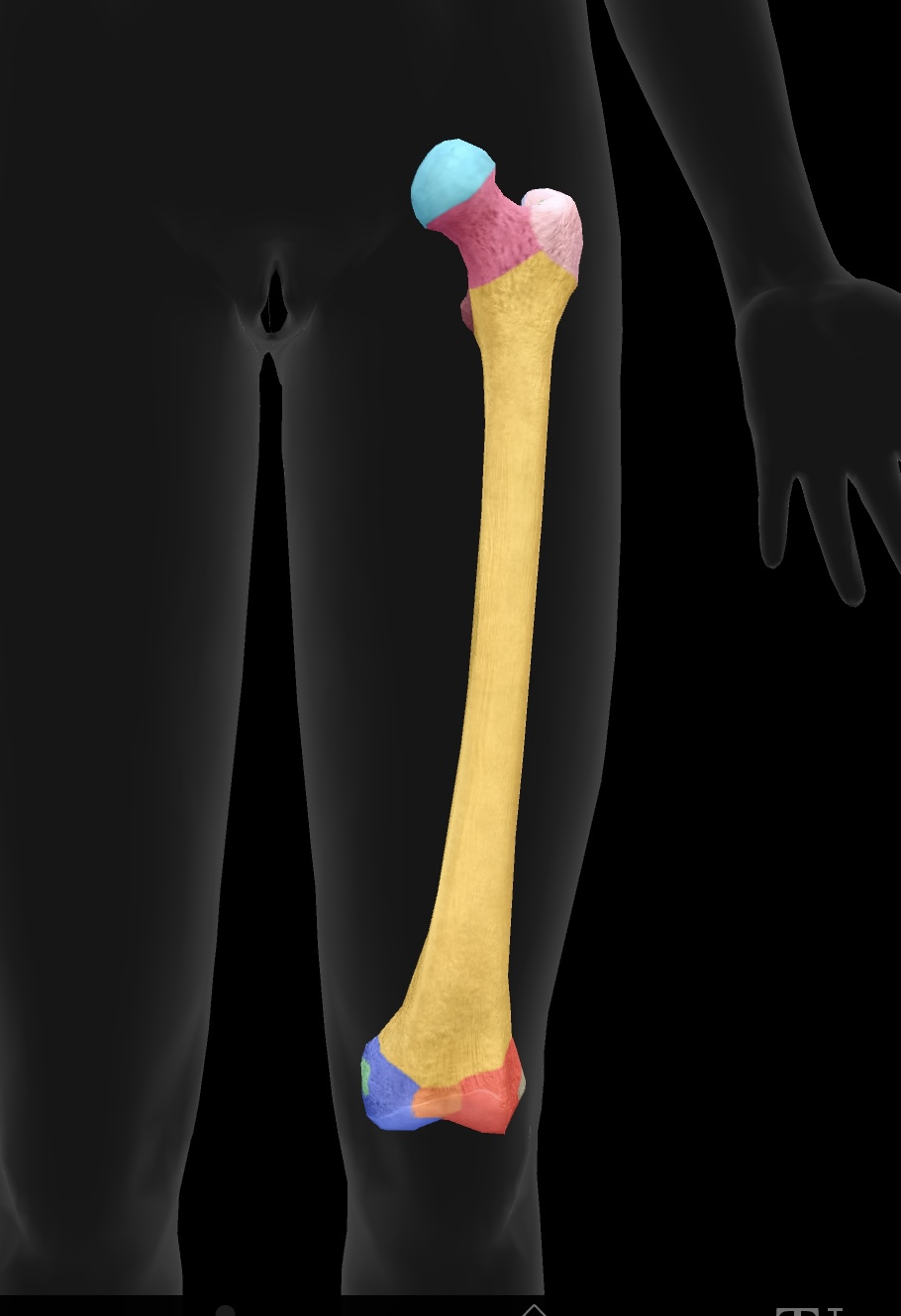
fovea
hole on the head of the femur — attachment point for the ligament of the head of head of the femur or the ligamentun teres
neck of femur
the region below the head of the femur that connects it to the shaft and is prone to fractures (weakest)
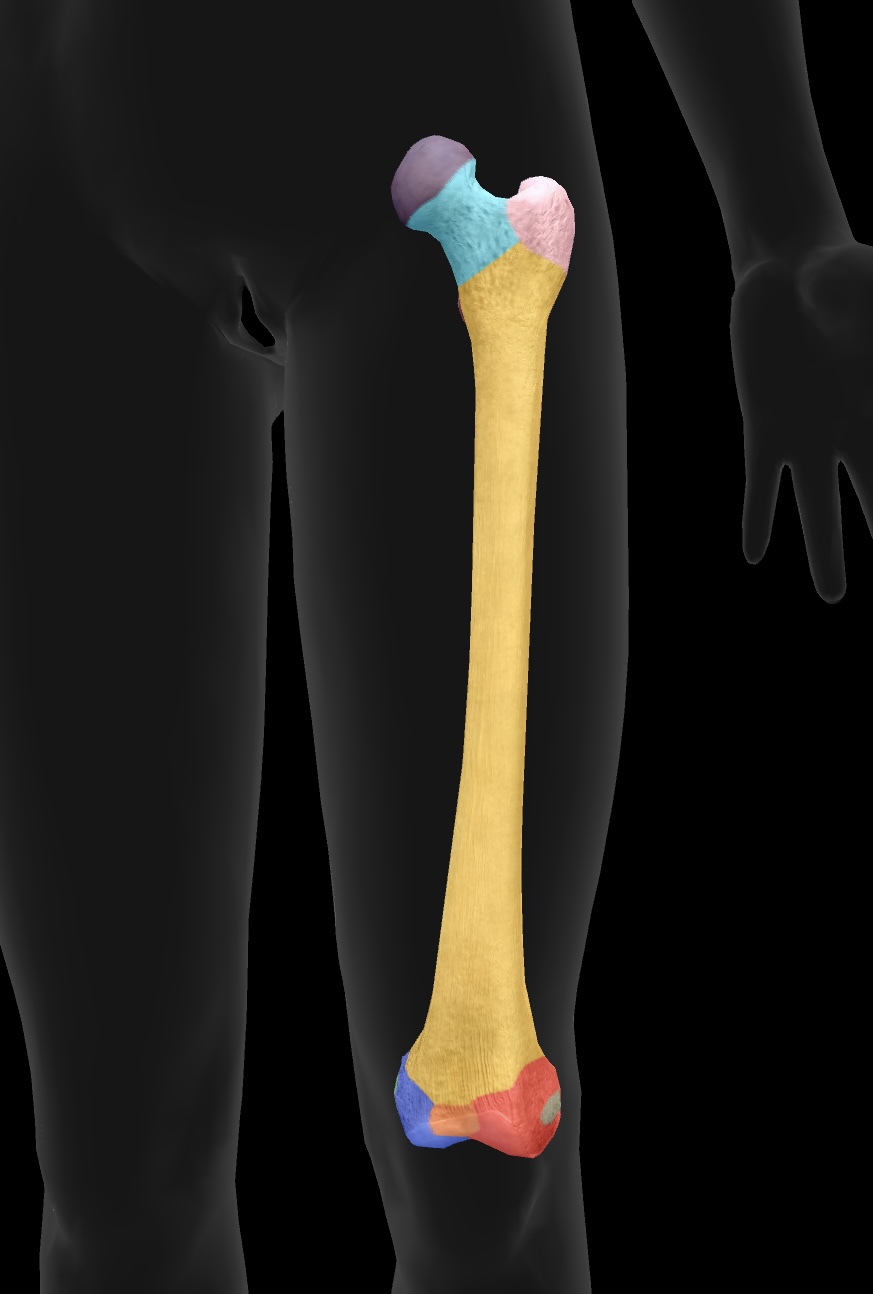
greater trochanter
higher large bony prominence — site of muscle attachment on the proximal aspect of the bone
insertion: gluteus medius & gluteus minimus
origin: vastus lateralis
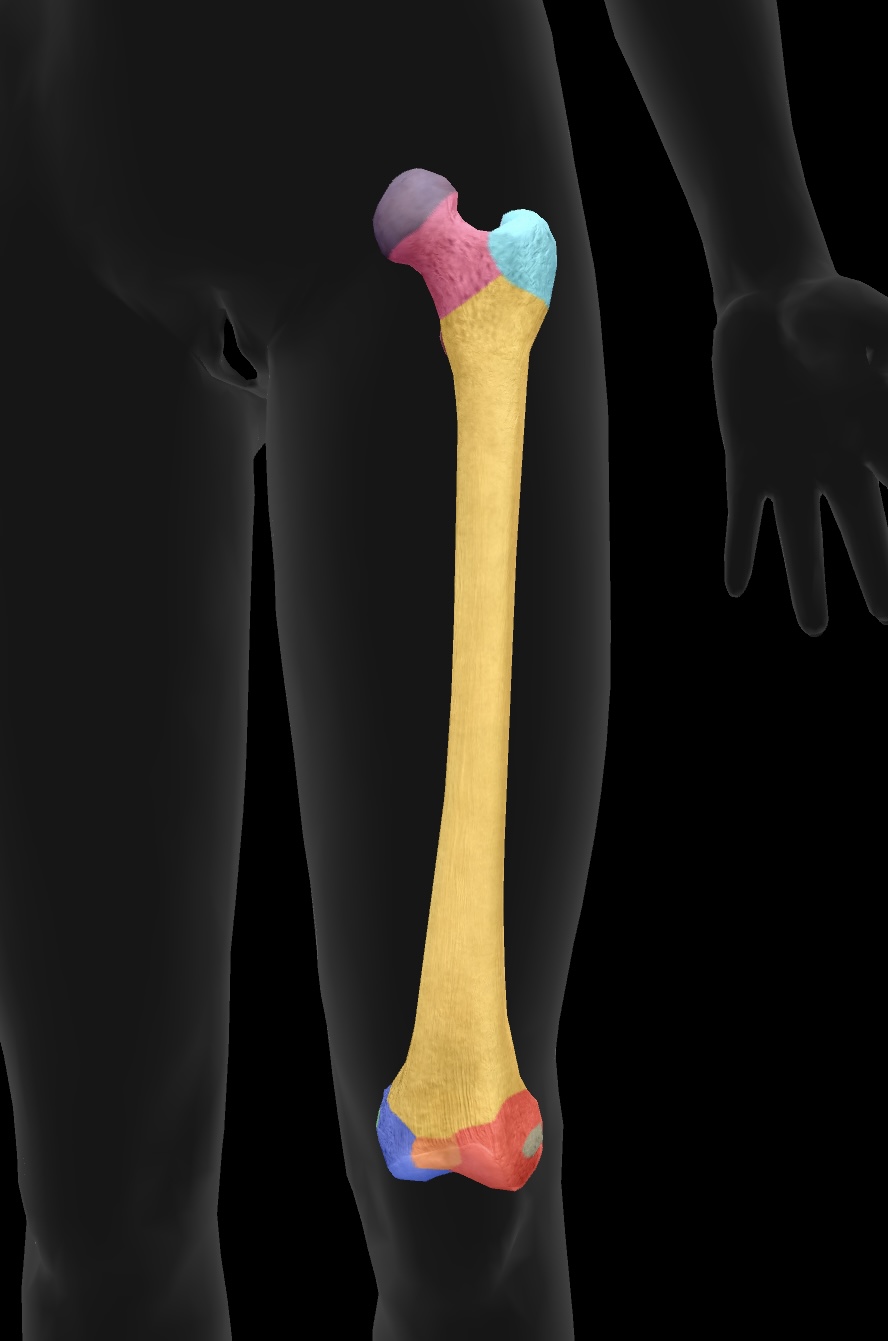
lesser trochanter
smaller lower bony prominence — site of muscle attachment on the proximal aspect of the bone
insertion: psoas major & iliacus muscles as the iliopsoas

gluteal tuberosity
ridge on the femur for gluteus maximus attachment
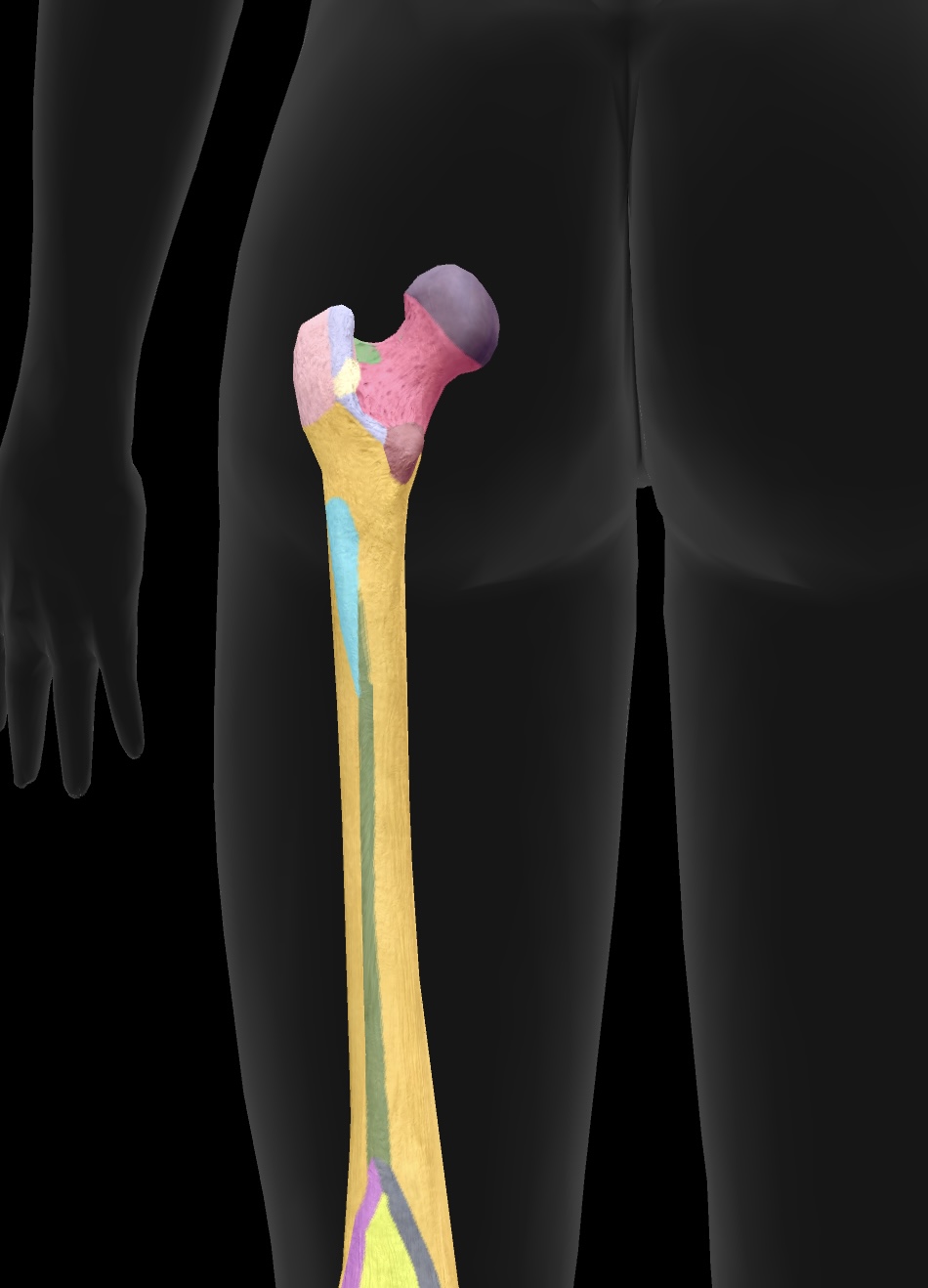
linea aspera
the ridge on the posterior aspect of the femur that serves as an attachment site for several muscles, including the adductor longus, adductor brevis, hamstring part adductor magnus
medial condyle of the femur
articulate with the tibia to form the knee joint—medial side
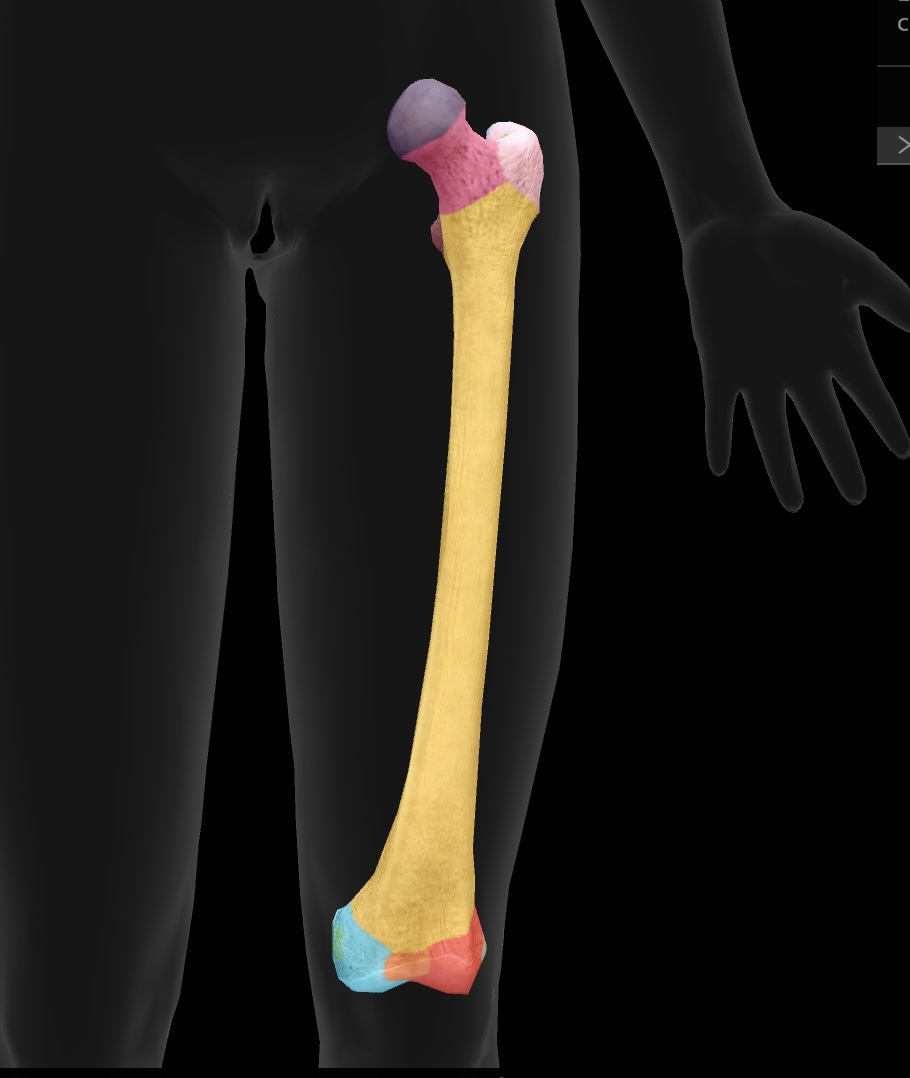
lateral condyle of the femur
articulate with the tibia to form the knee joint—similar to the medial condyle, located on the opposite side.
medial epicondyle of the femur
attachment site for the medial collateral ligament (MCL) on the distal aspect of the femur
origin: medial head of the gastrocnemius
lateral epicondyle of the femur
attachment site for the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) on the distal aspect of the femur
origin: lateral head of the gastrocnemius
intercondylar fossae
depression between the condyles of the femur, serving as an attachment point for the cruciate ligaments of the knee
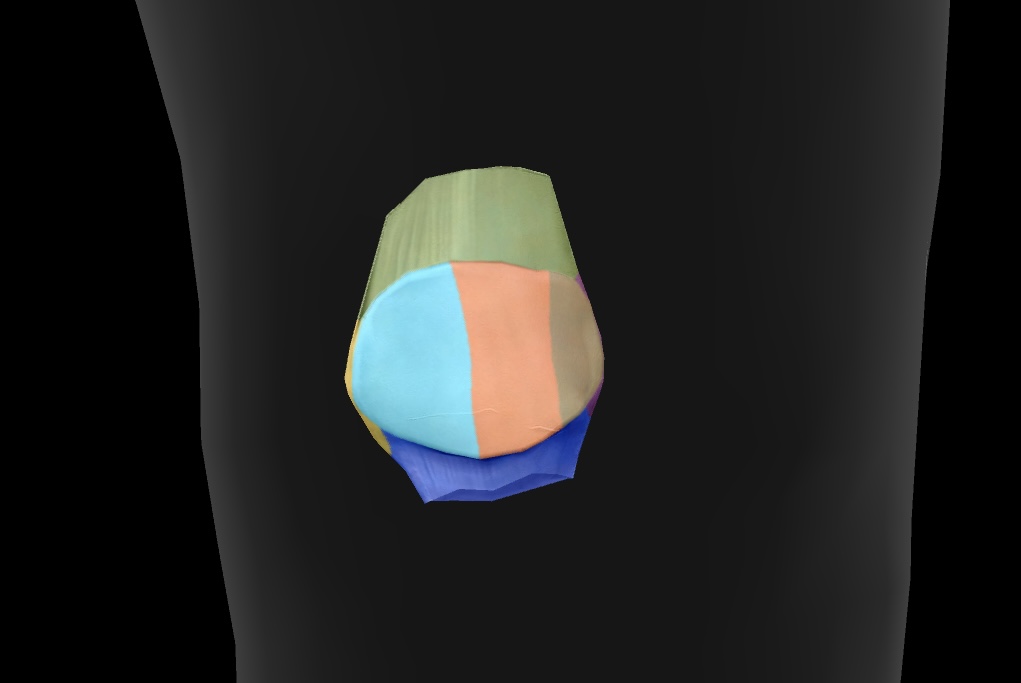
patellar surface
area on the distal femur where the patella articulates
patella
The kneecap, which articulates with the femur at the patellar surface and provides structural support to the knee joint.
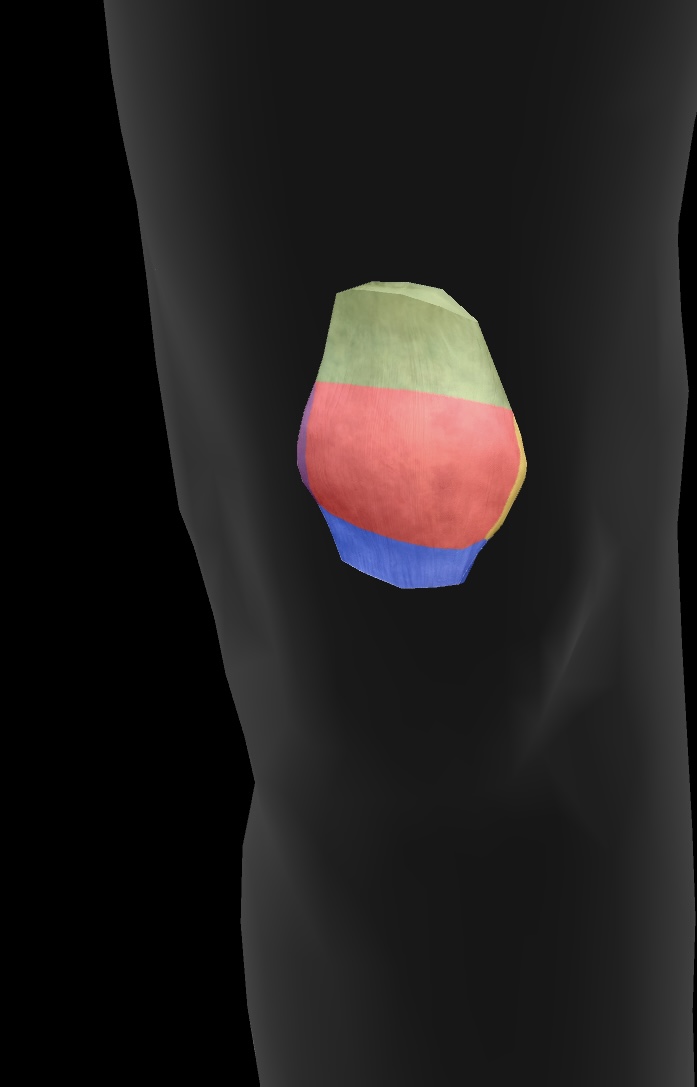
sesamoid bone
sits within the tendon of the quadriceps muscle — a bone that is located within a tendon
medial arricular facet
The surface of the femur that articulates with the medial meniscus and the tibia.
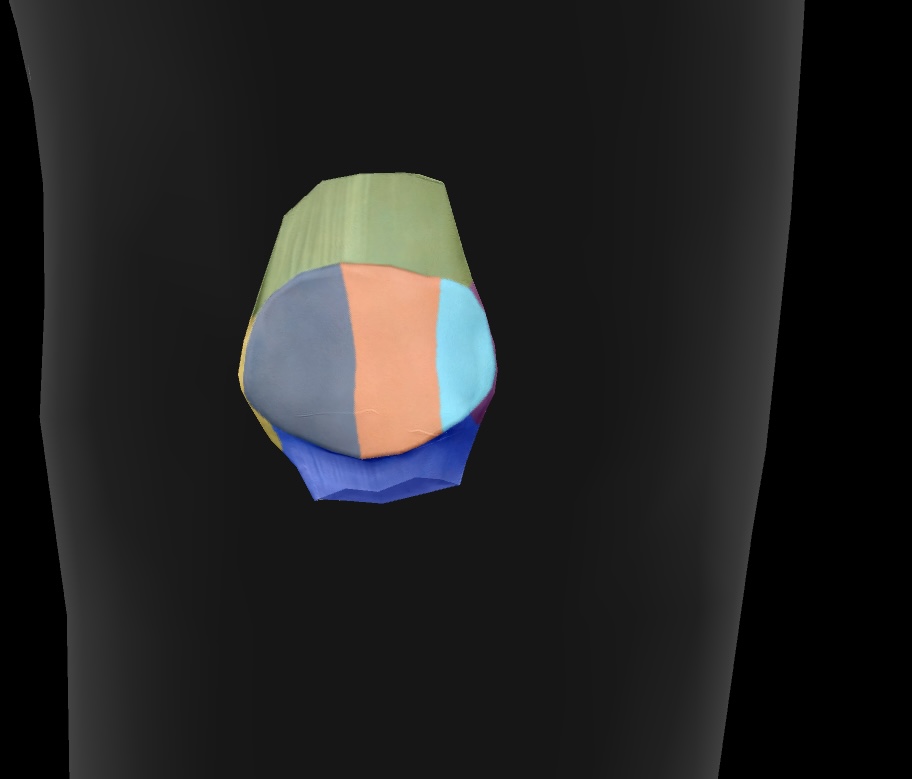
lateral articular facet
The surface of the patella that articulates with the femur on the outer side of the knee joint.
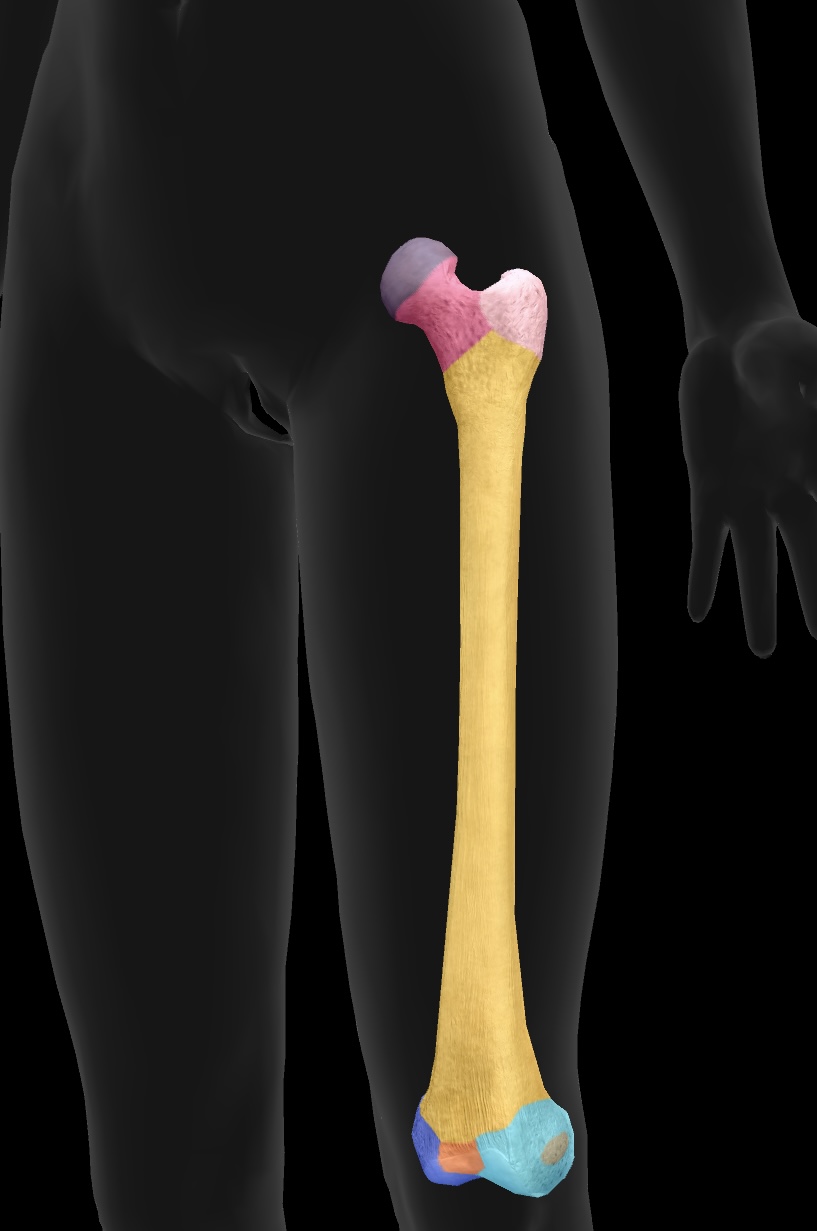
tibia
The tibia is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the lower leg, commonly known as the shinbone, and it supports most of the body's weight.
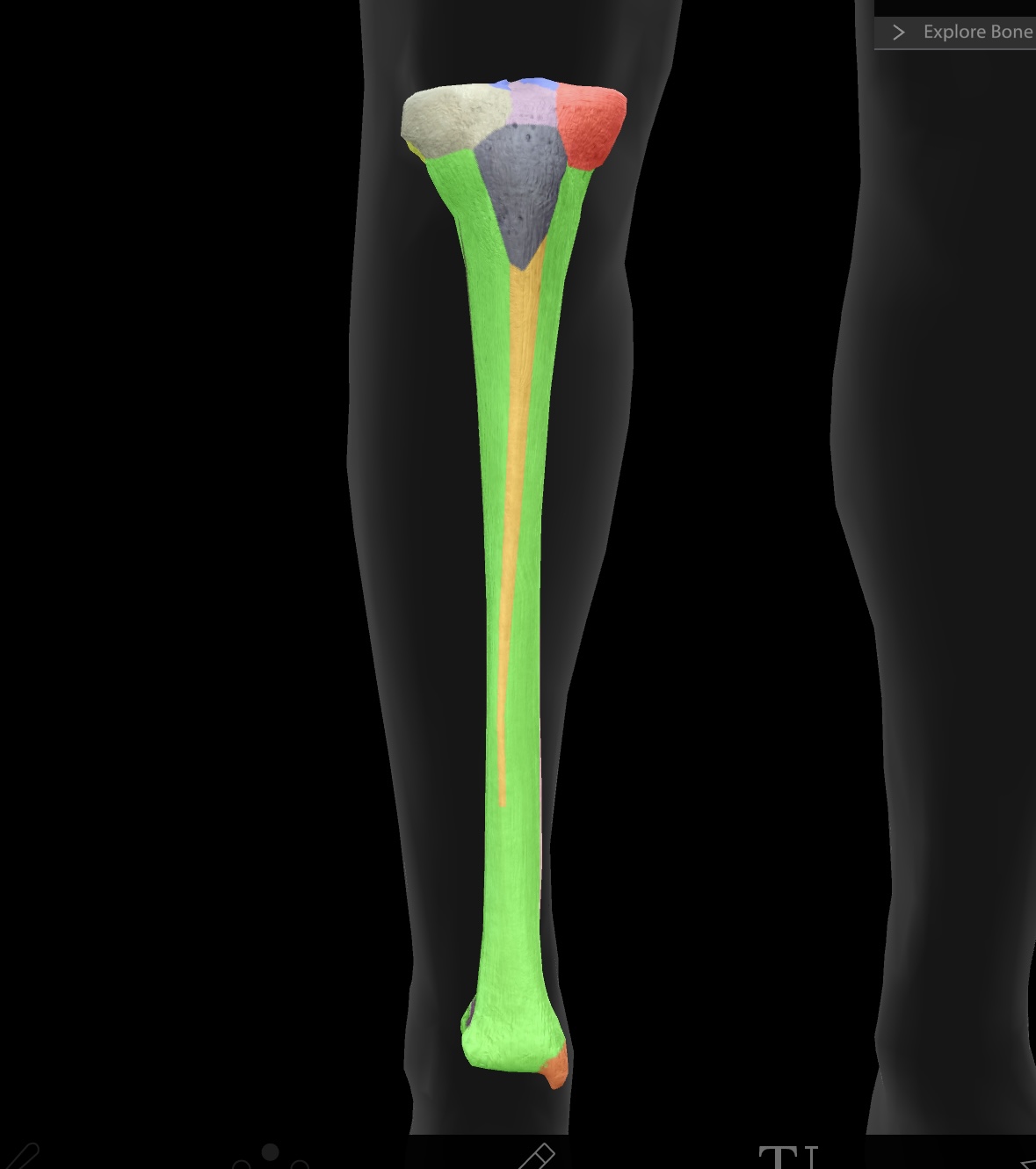
medial condyle of the tibia
The medial surface of the tibia that articulates with the femur, playing a critical role in knee joint function.
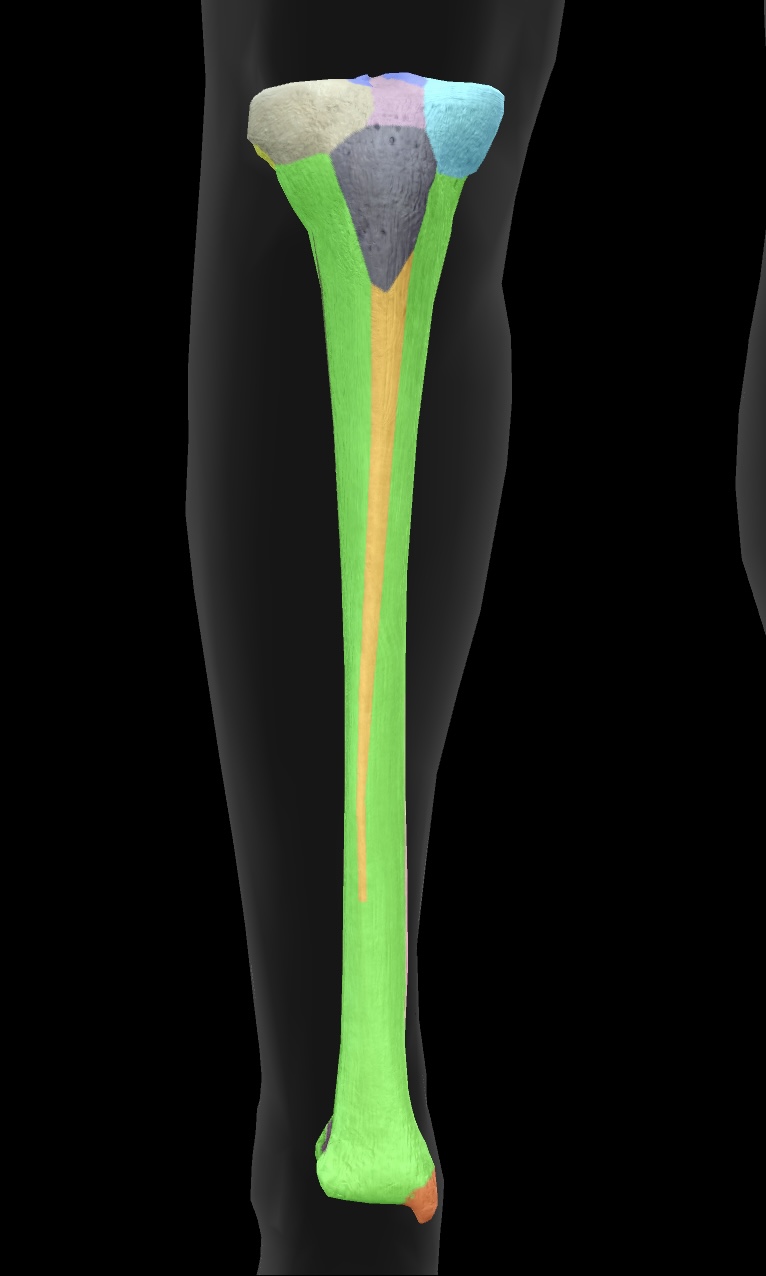
lateral condyle of the tibia
The lateral surface of the tibia that articulates with the femur, crucial for stabilizing the knee joint.
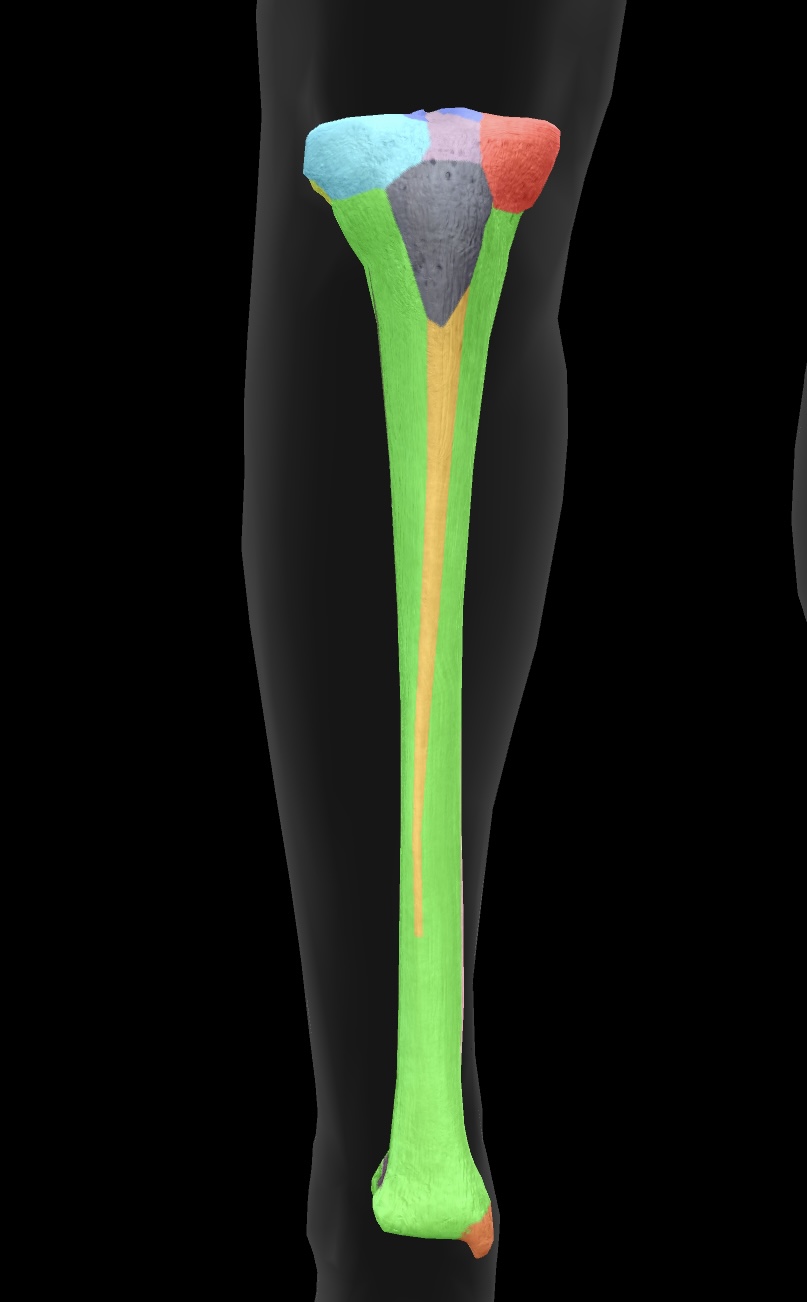
fibular articular facet
A small surface on the tibia where the fibula articulates, facilitating ankle joint movement.
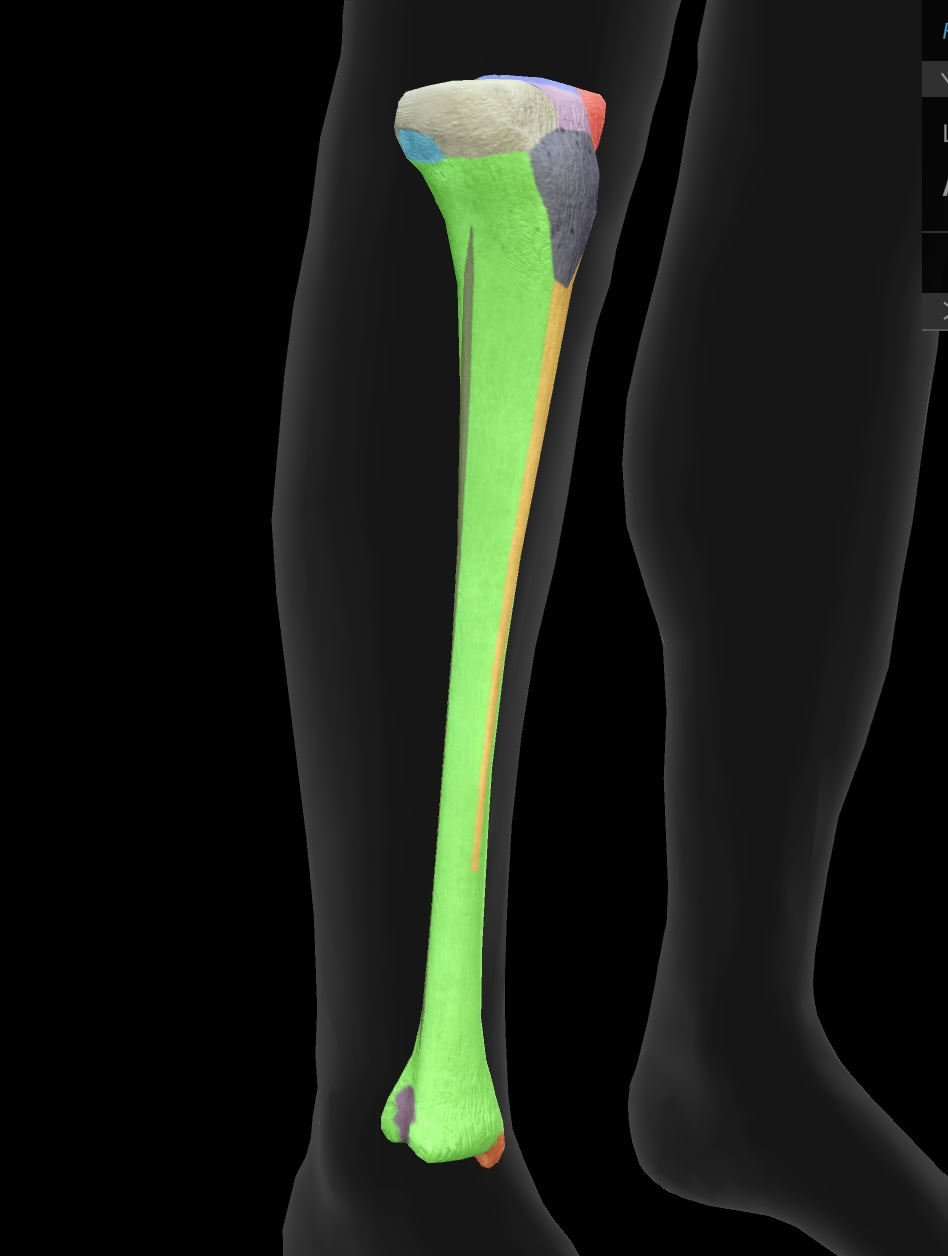
tibial tuberosity
The prominent bony projection on the anterior aspect of the tibia, serving as the attachment site for the patellar ligament.
insertion: quadriceps nuscle group
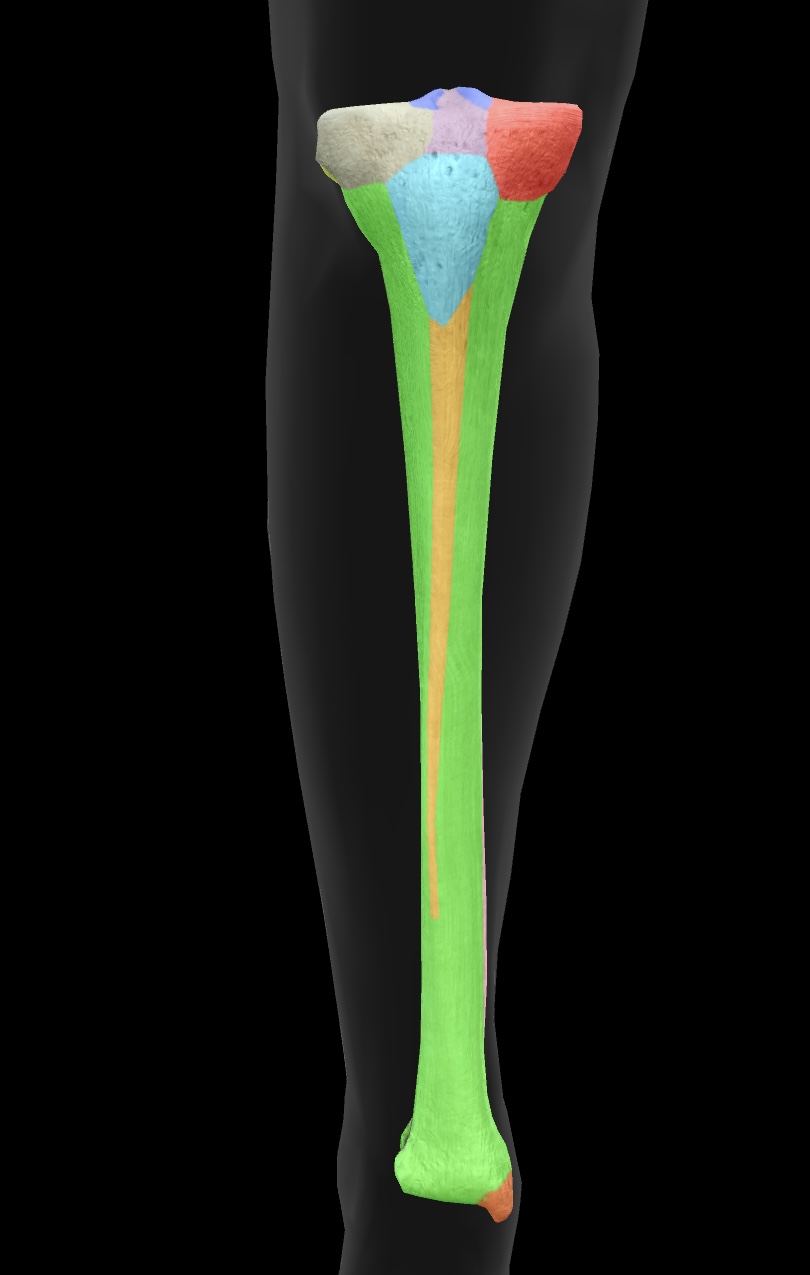
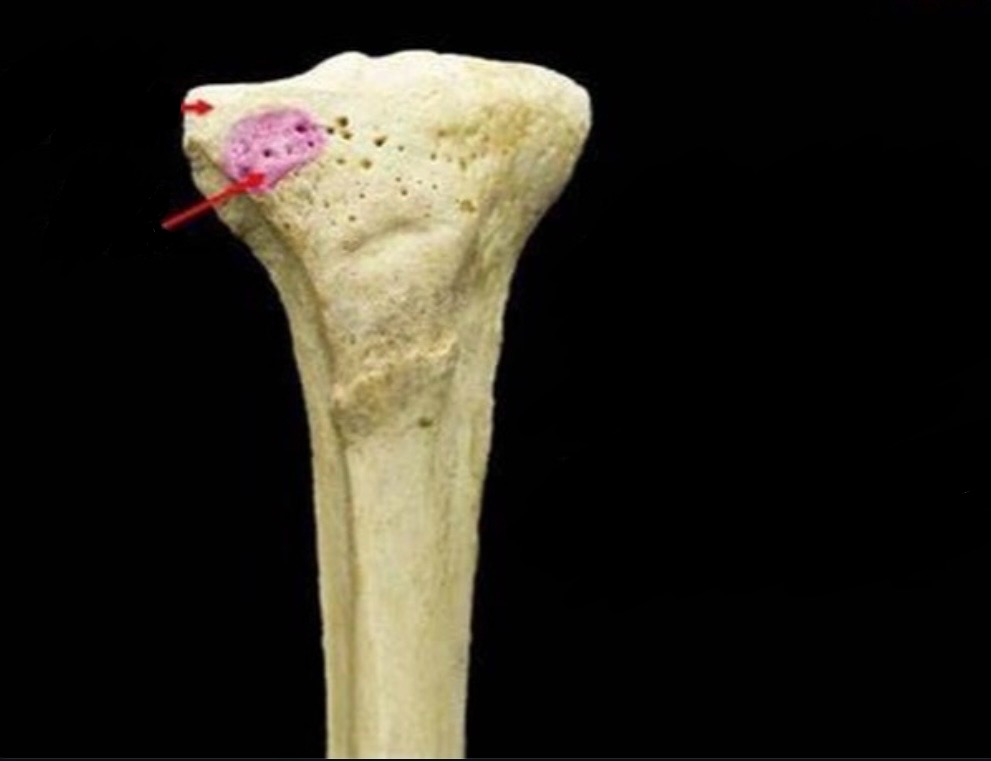
gerdy’s tubercle
A bony prominence on the lateral aspect of the tibia that serves as an attachment point for the iliotibial band.
insertion: iliotibial tract (band)
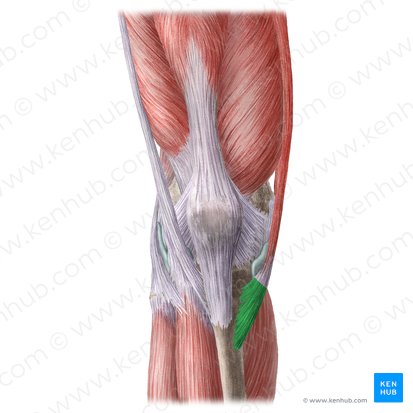
pes anserine insertion
A conjoined tendon insertion on the anteromedial aspect of the tibia for the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles.
located below the knee joint, near the tibial tuberosity.
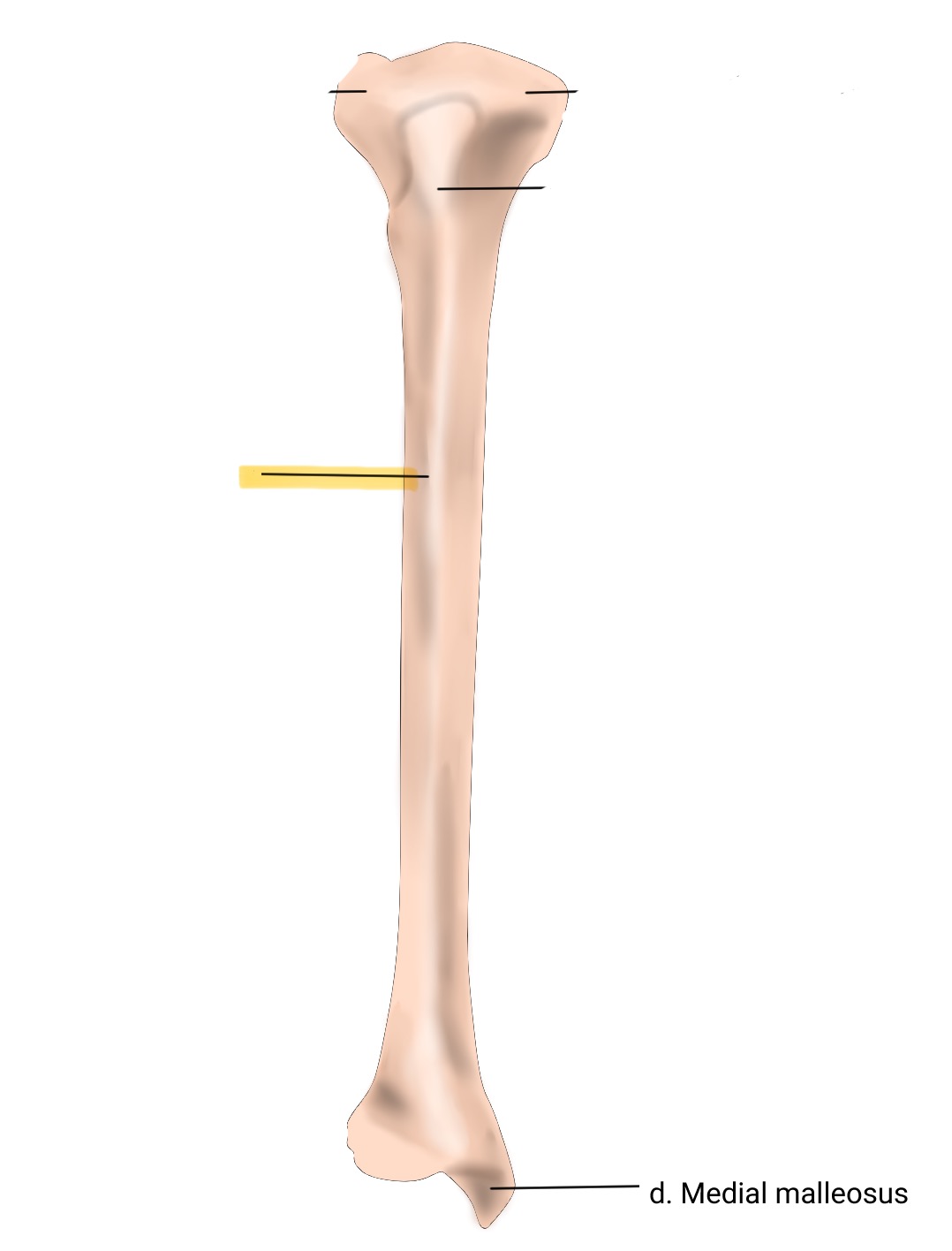
anterior border
The sharp edge along the anterior aspect of the tibia, providing attachment for muscles and enhancing stability.
medial malleolus
The bony prominence on the medial aspect of the ankle that is formed by the distal end of the tibia.
attachment site for ligaments of the talocurural (ankle) joint
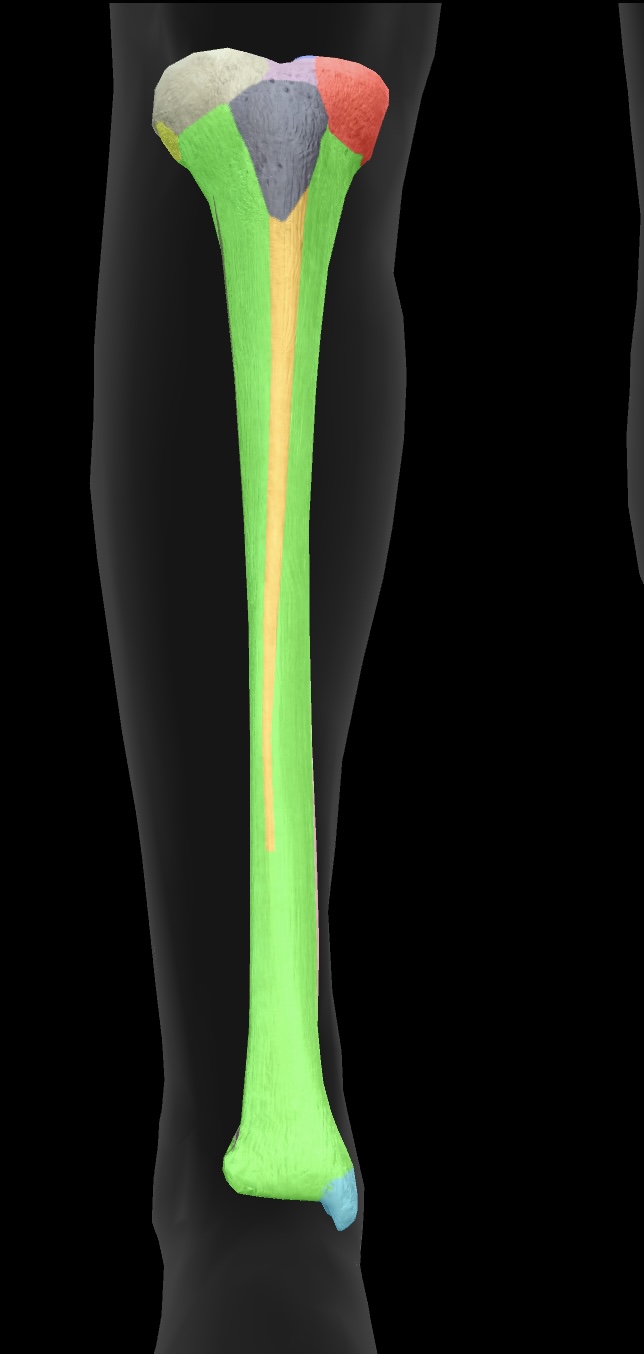
fibula
The smaller of the two bones in the lower leg, located alongside the tibia, providing support and stability to the ankle.
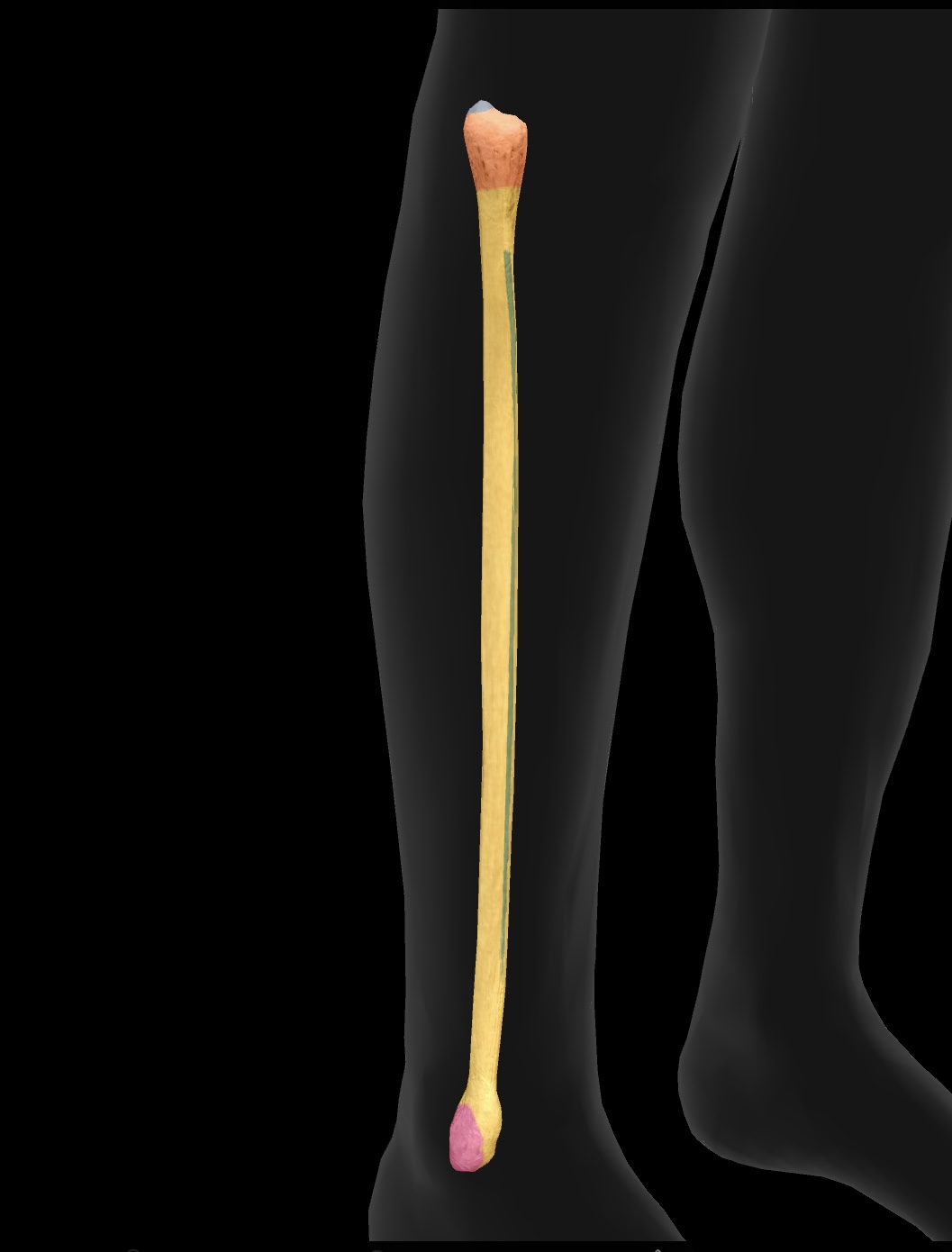
head of the fibula
The upper end of the fibula that forms a joint with the tibia, providing stability and serving as an insertion point for the biceps femoris
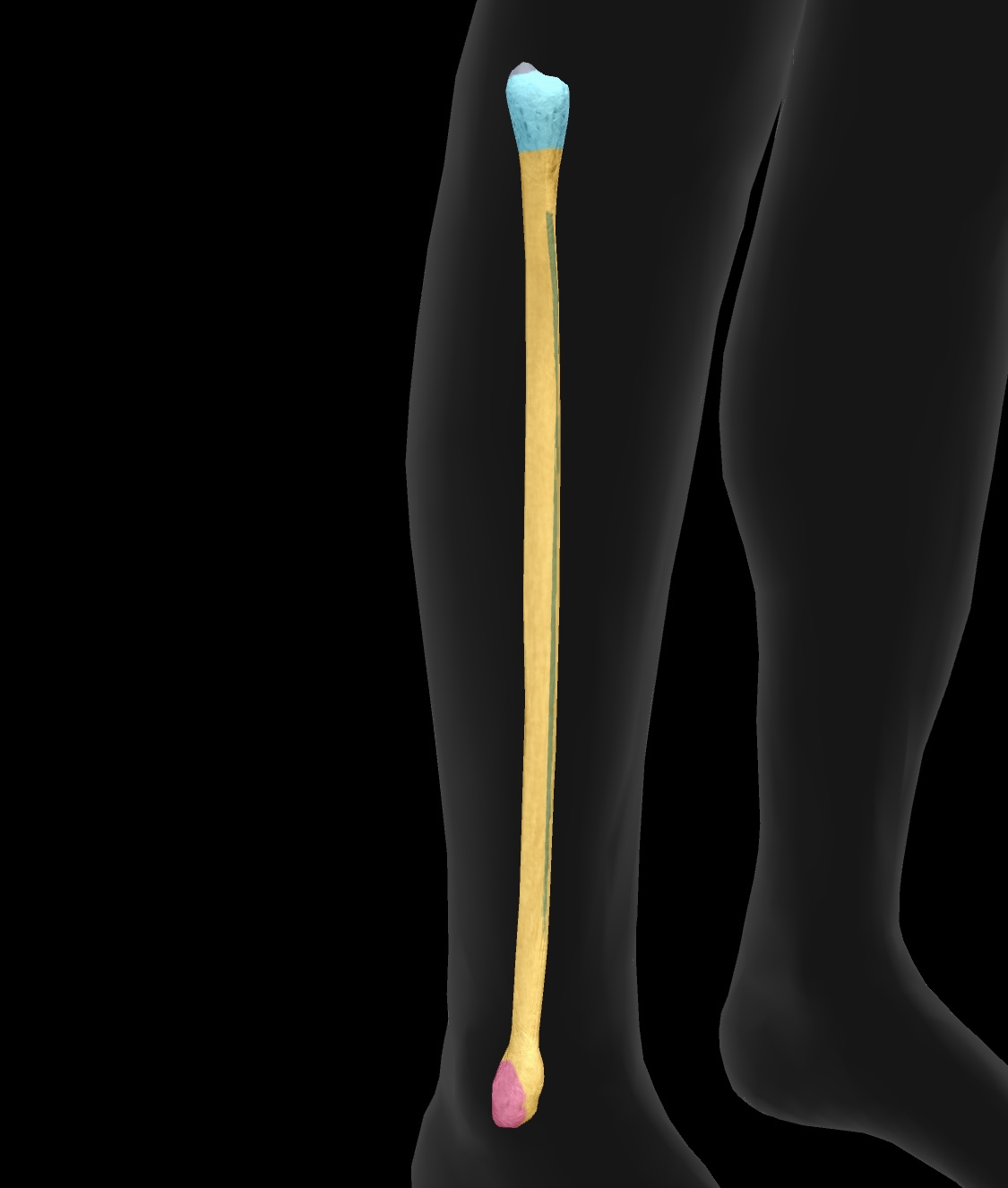
articular facet
A smooth surface on a bone that articulates with another bone, allowing for joint movement.
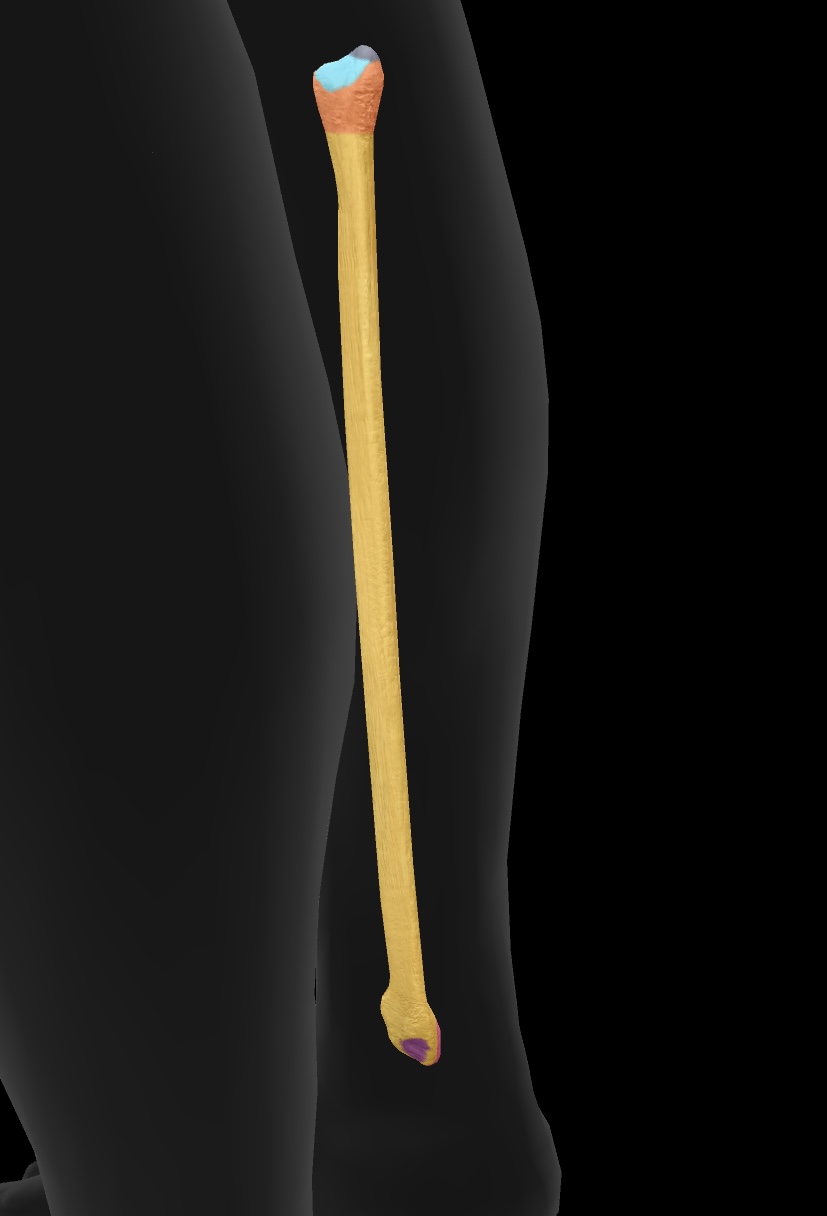
neck of the fibula
The region of the fibula between the head and the shaft, providing attachment for ligaments and muscles.

lateral mallelous
The bony prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the distal end of the fibula, that provides stability to the ankle joint.
attachment site for ligaments of the talocrural (ankle) joint

interosseous membrane
A fibrous sheet that connects the shafts of the tibia and fibula, providing stability and transmitting forces between the two bones.
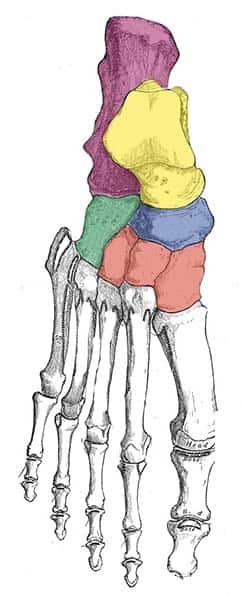
tarsals
posterior aspect of the foot consist of seven bones that form the midfoot and rearfoot, playing a crucial role in walking and balance.
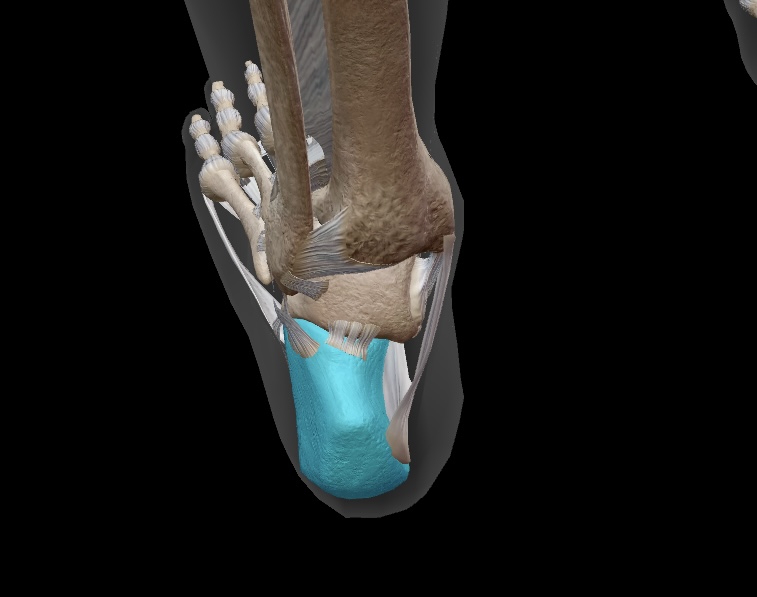
calcaneous
we bear weight on this bone when we stand as it forms our heel
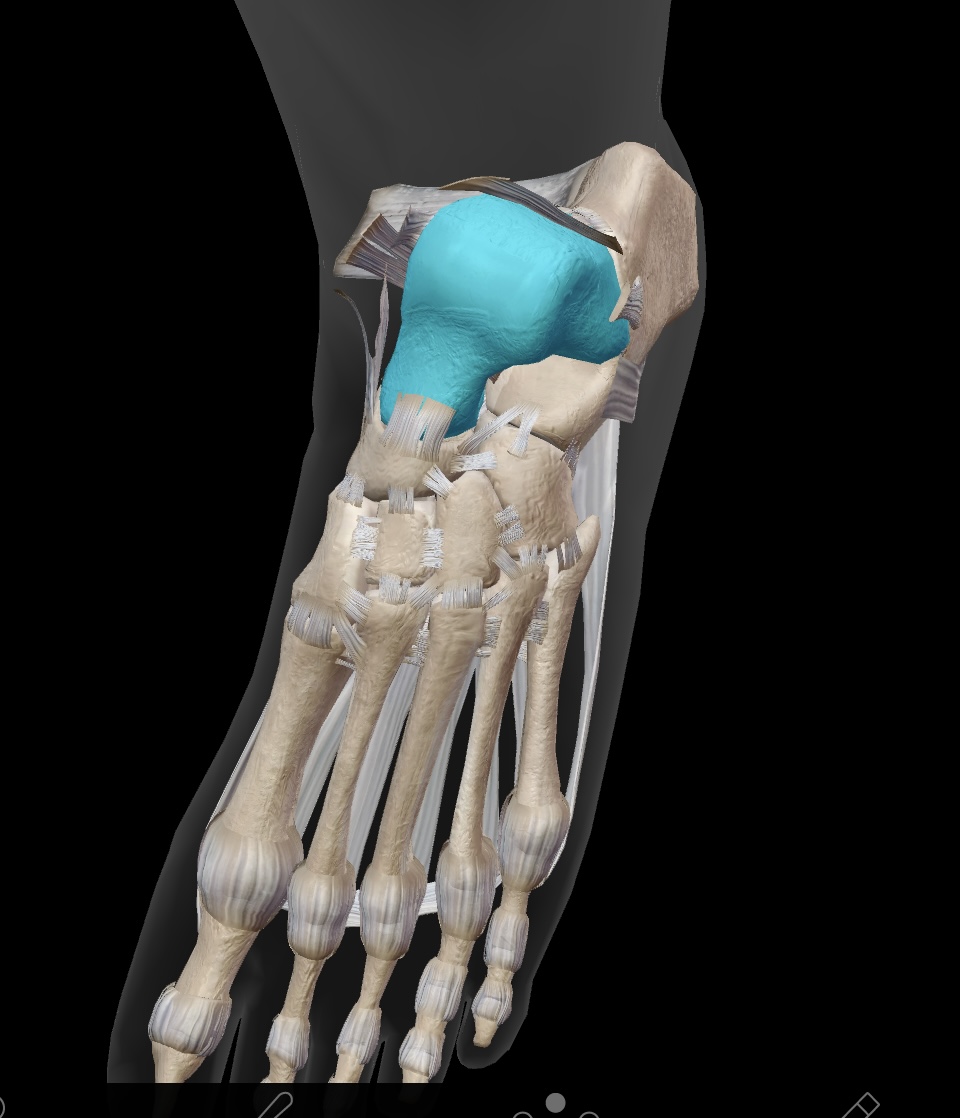
talus
the bone articulates with the tibia & fibula to form the ankle joint
navicular
this is the proximal medial bone of the mid-foot. it sits just posterior to the cuneiforms
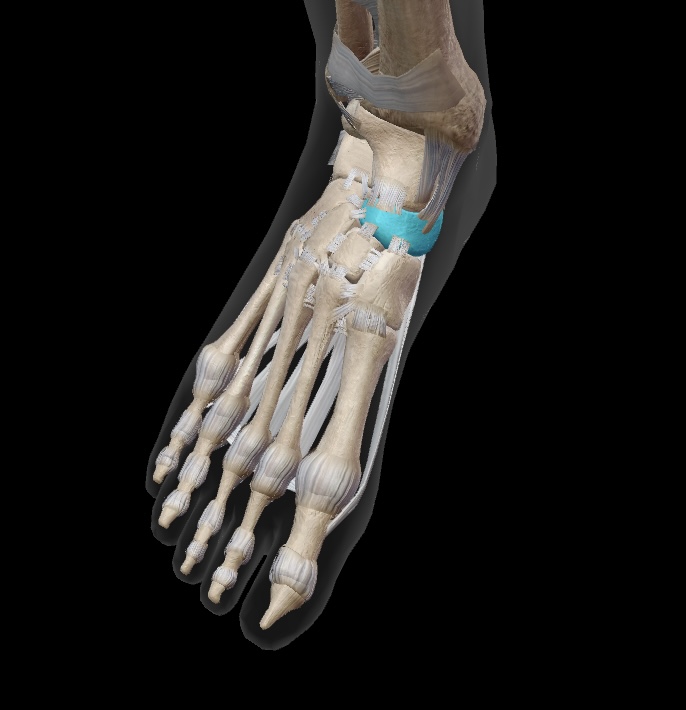
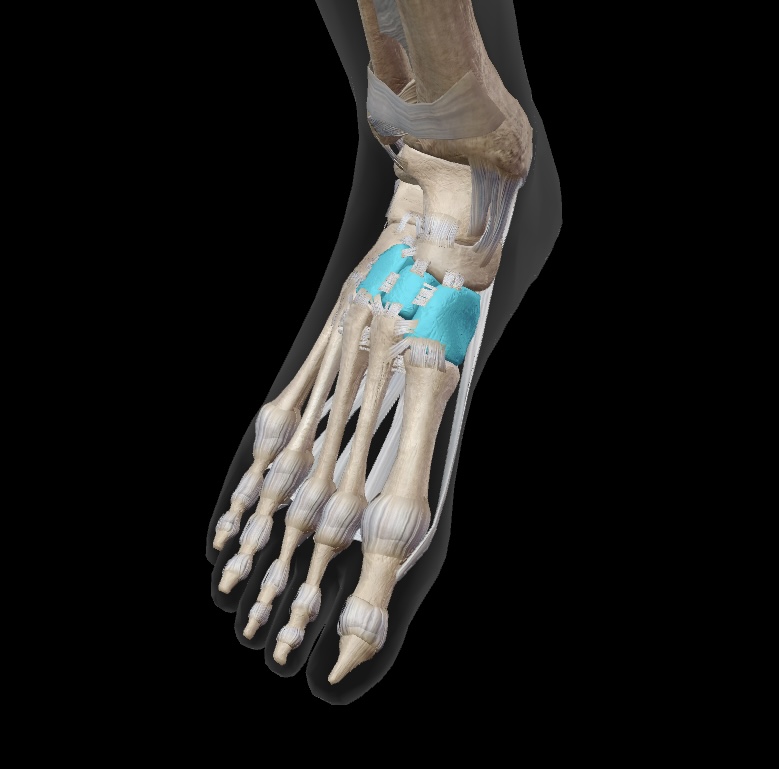
cuneiform
three bones sit anterior to navicular on the medial aspect of the mid-foot
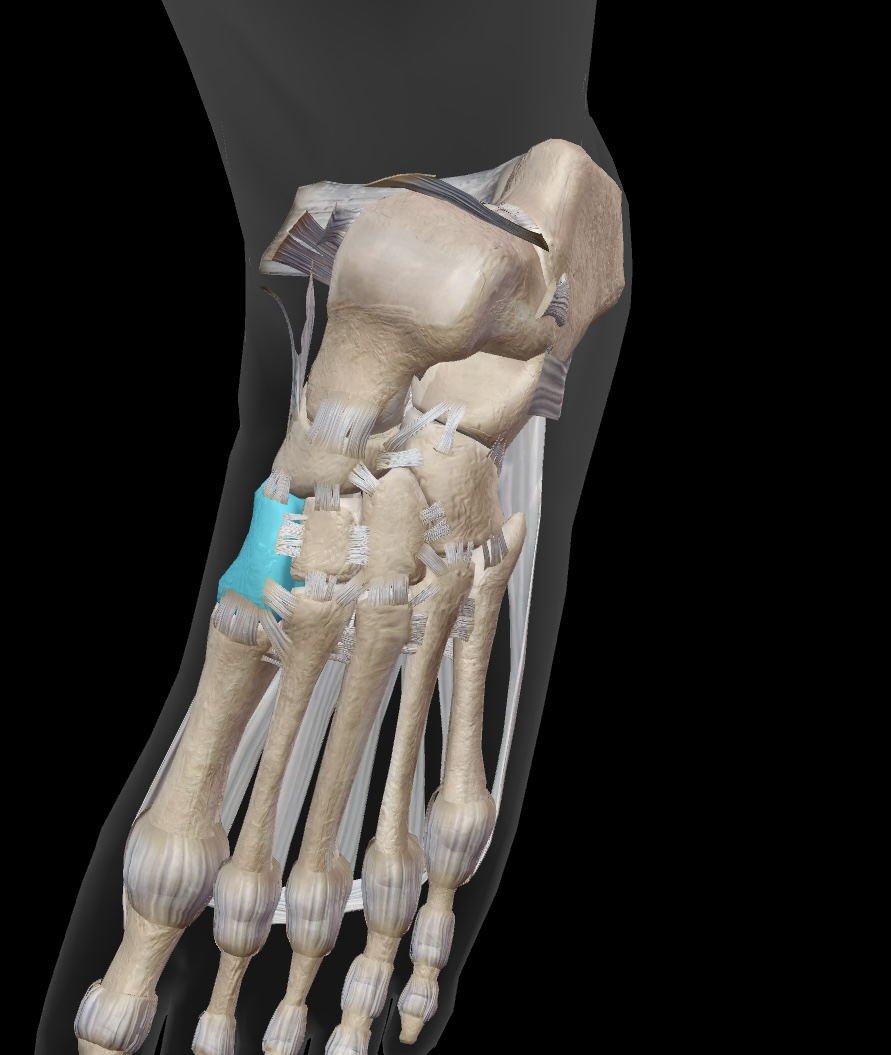
medial cuneiform
one of the three cuneiform bones that articulates with the navicular and the first metatarsal.
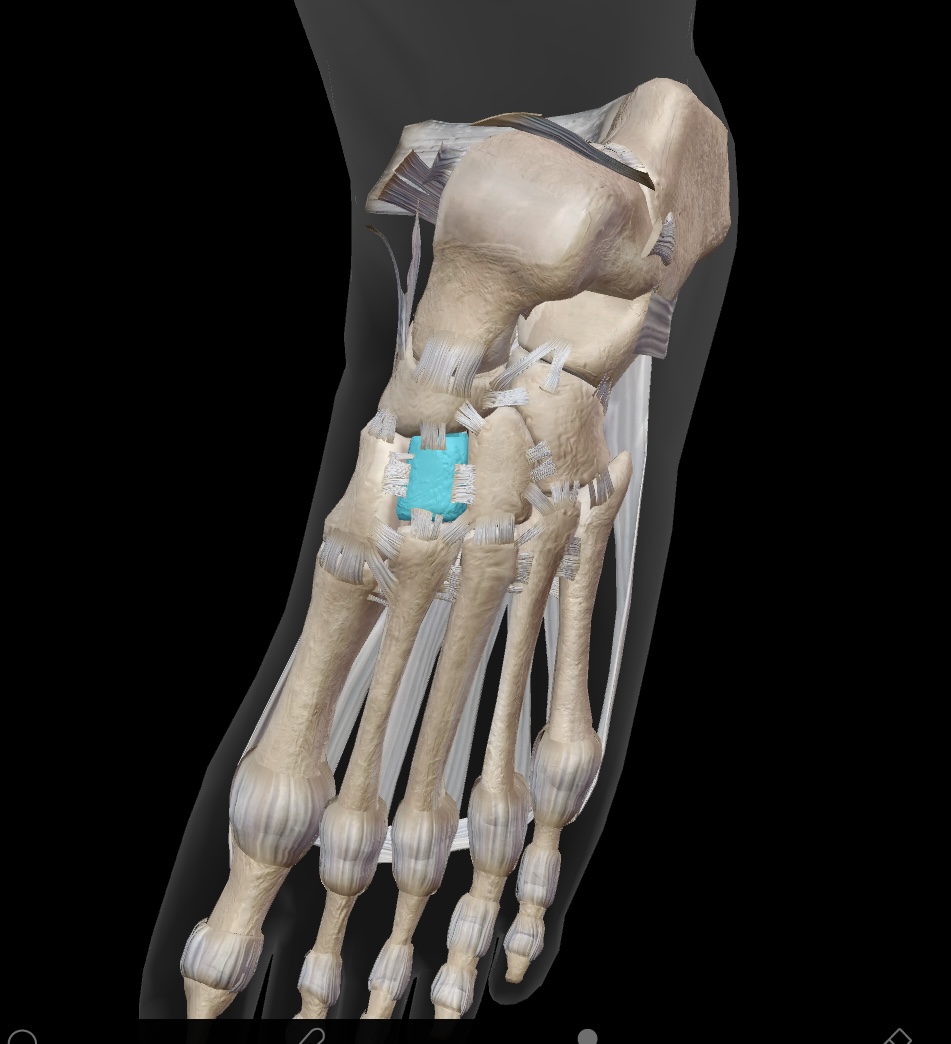
intermediate cuneiform
the bone located between the medial and lateral cuneiforms, contributing to the stability of the mid-foot.
lateral cuneiform
the bone situated laterally among the three cuneiform bones, contributing to the structure of the mid-foot.
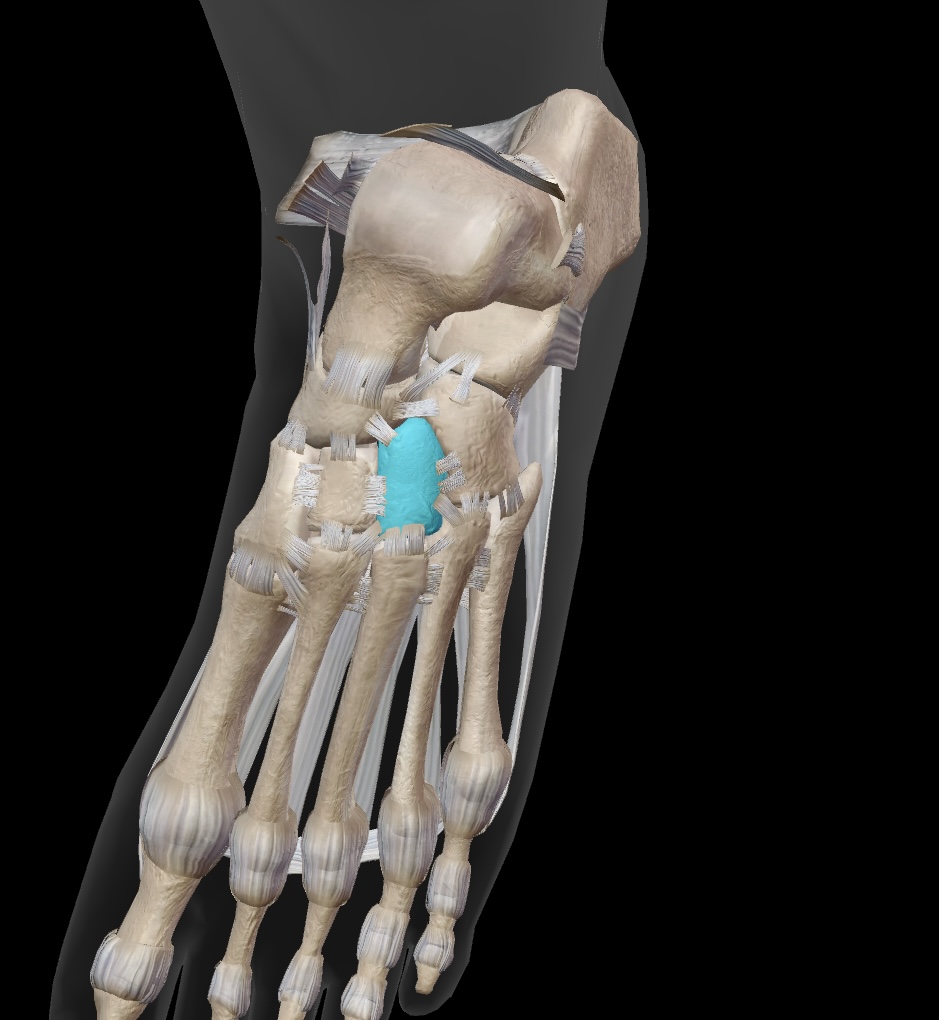
cuboid
large lateral bone of the midfoot

metatarsals
long bones of the foot (numbered I-V based, I being the “big toe”)
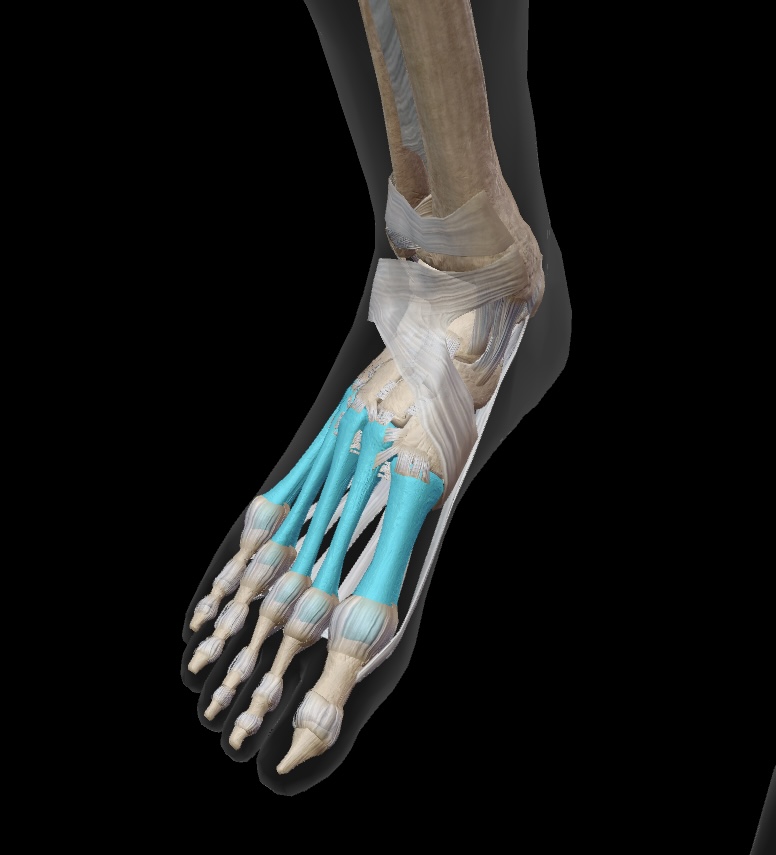
phalanges
most distal bones that form the toes
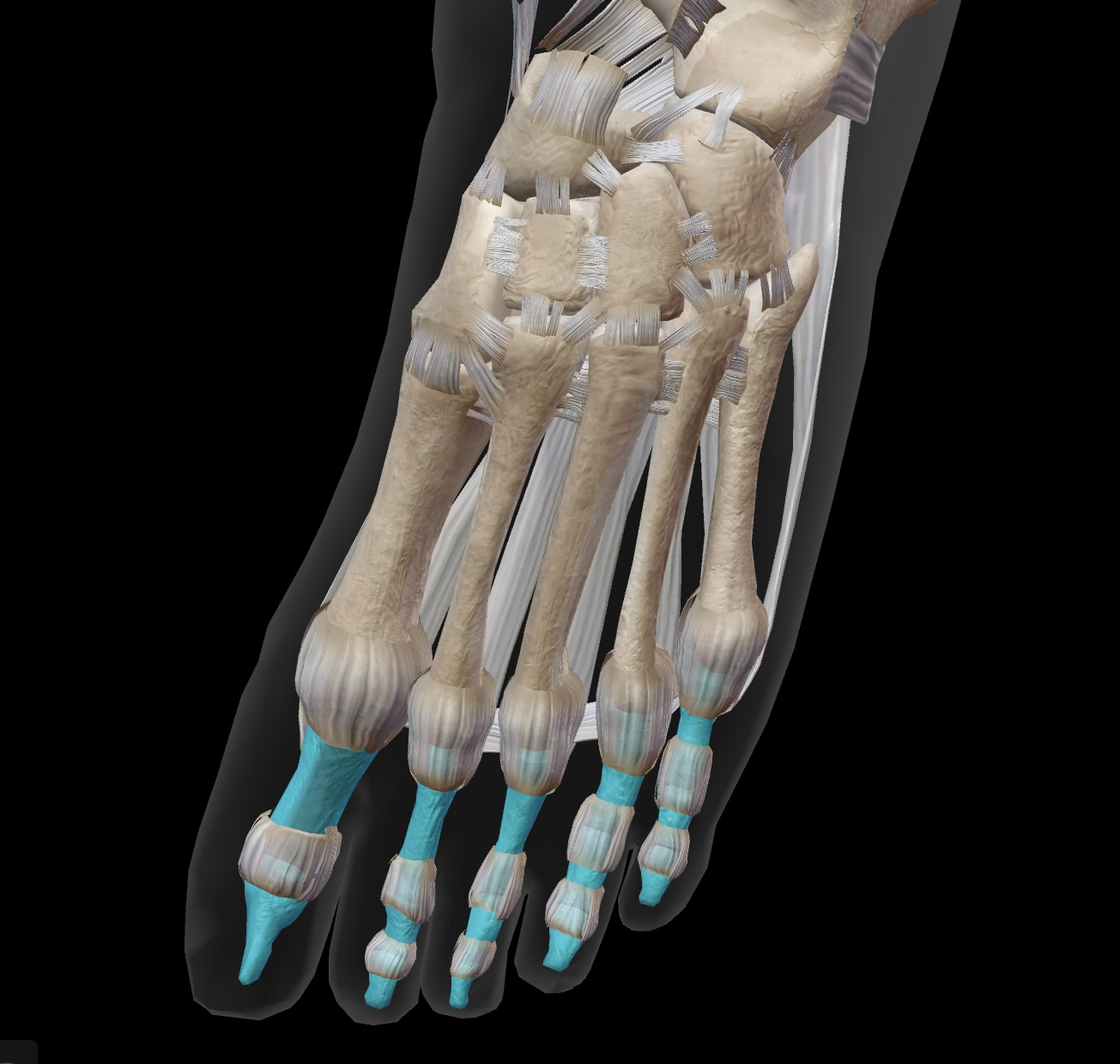
proximal phalanges
the long bones that are closest to the metatarsals, forming the base of each toe. (Toes 2-5)
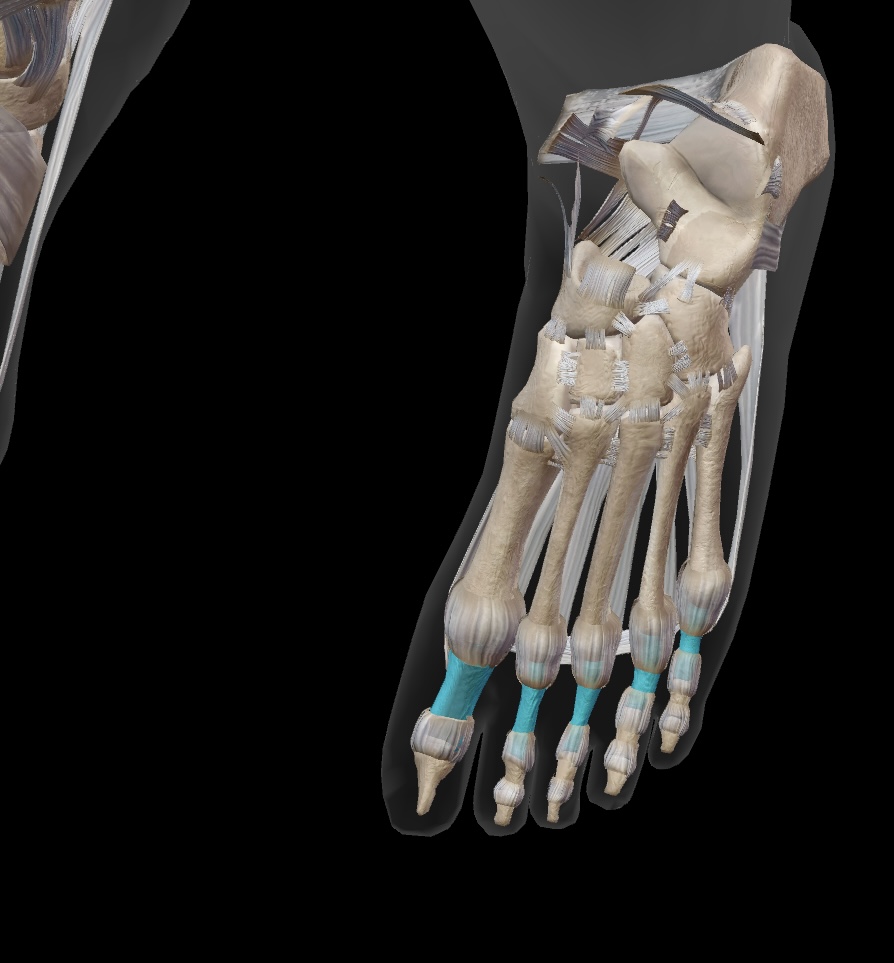
middle phalanges
the bones located between the proximal and distal phalanges in each toe, forming part of the toe structure for toes 2-5.
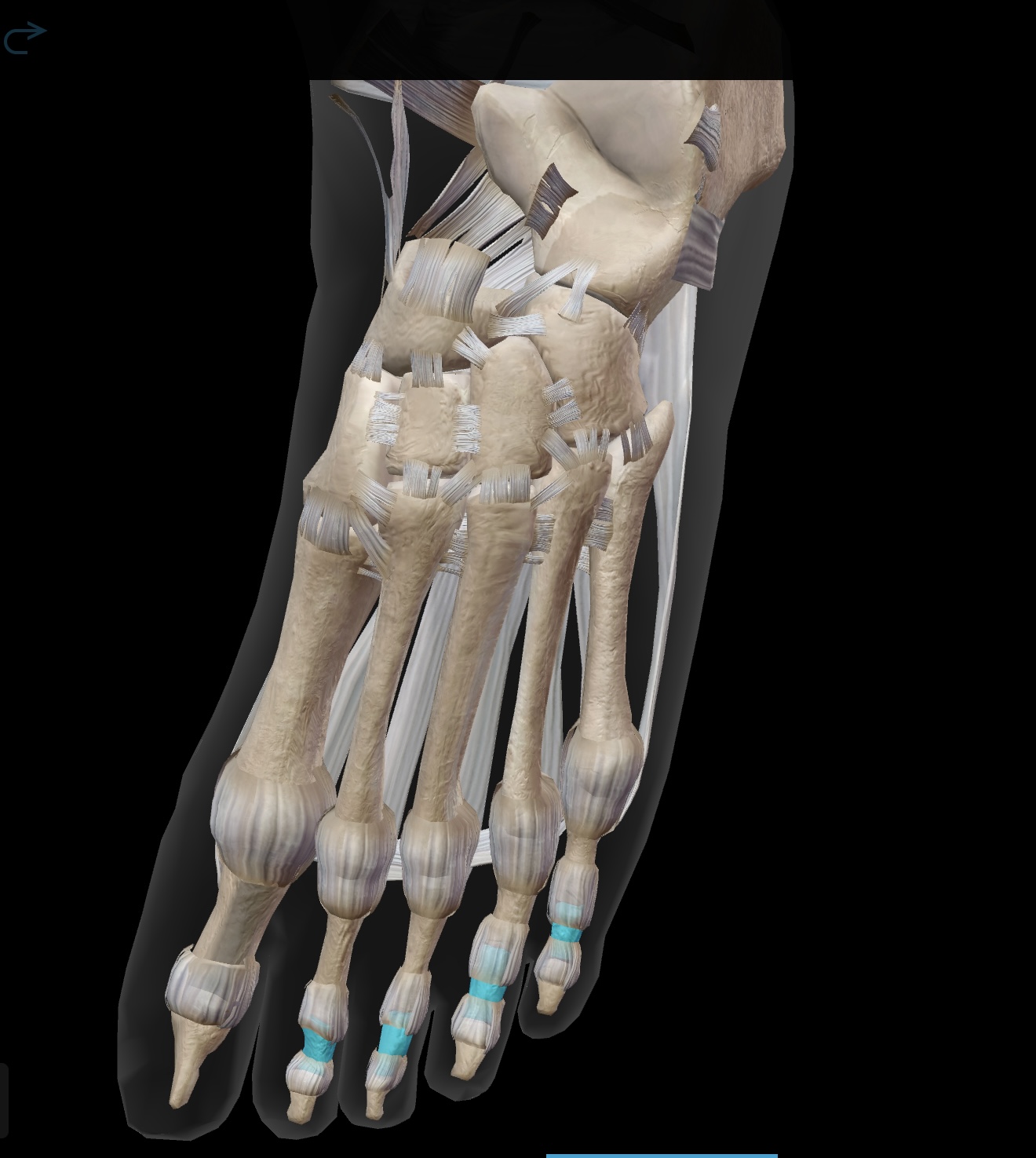
distal phalanges
the bones at the tips of the toes, providing support and balance. (Toes 2-5)
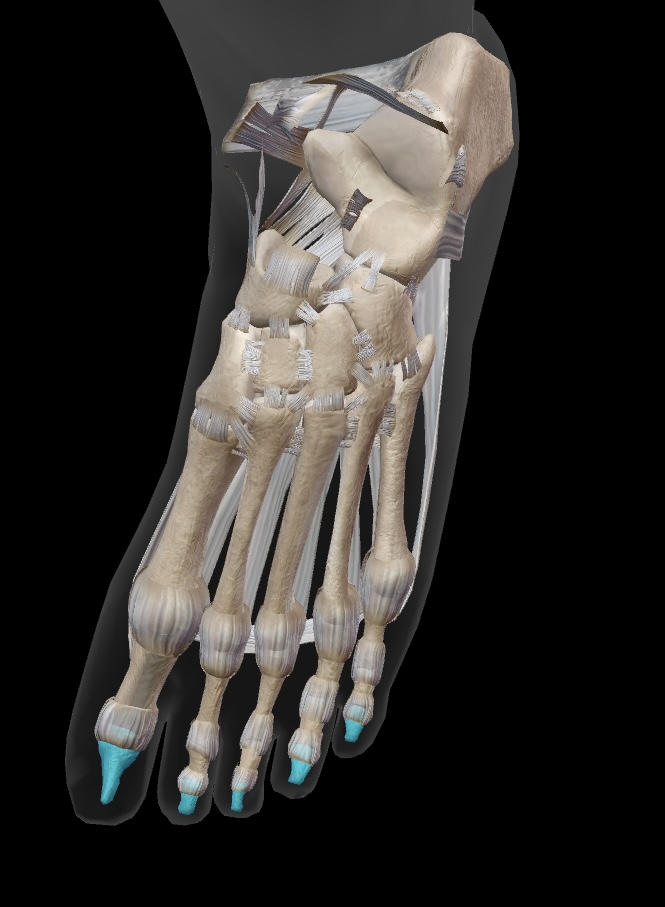
hallux phalanges
first toe with a proximal and distal phalanx
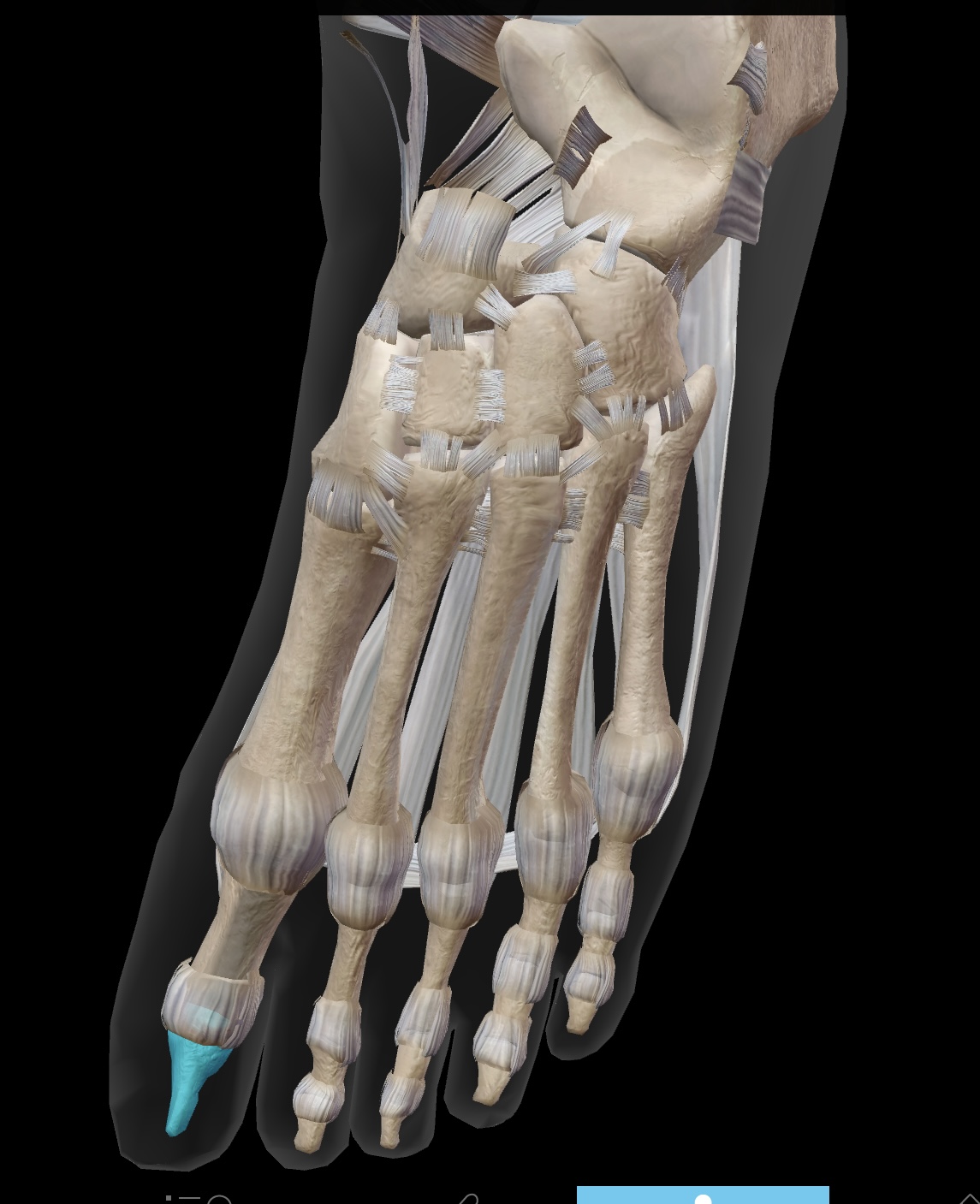
intertarsal joints
located between the tarsal bones
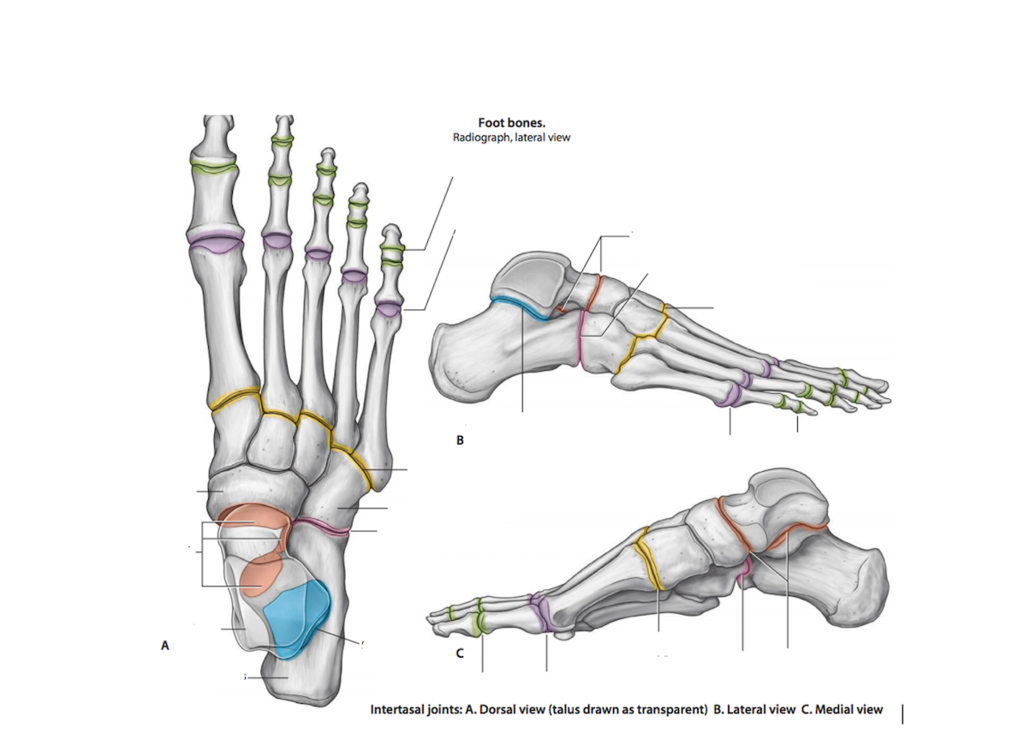
tarsometatarsal joints
located between the cuneiforms or cuboid and the metatarsal bones
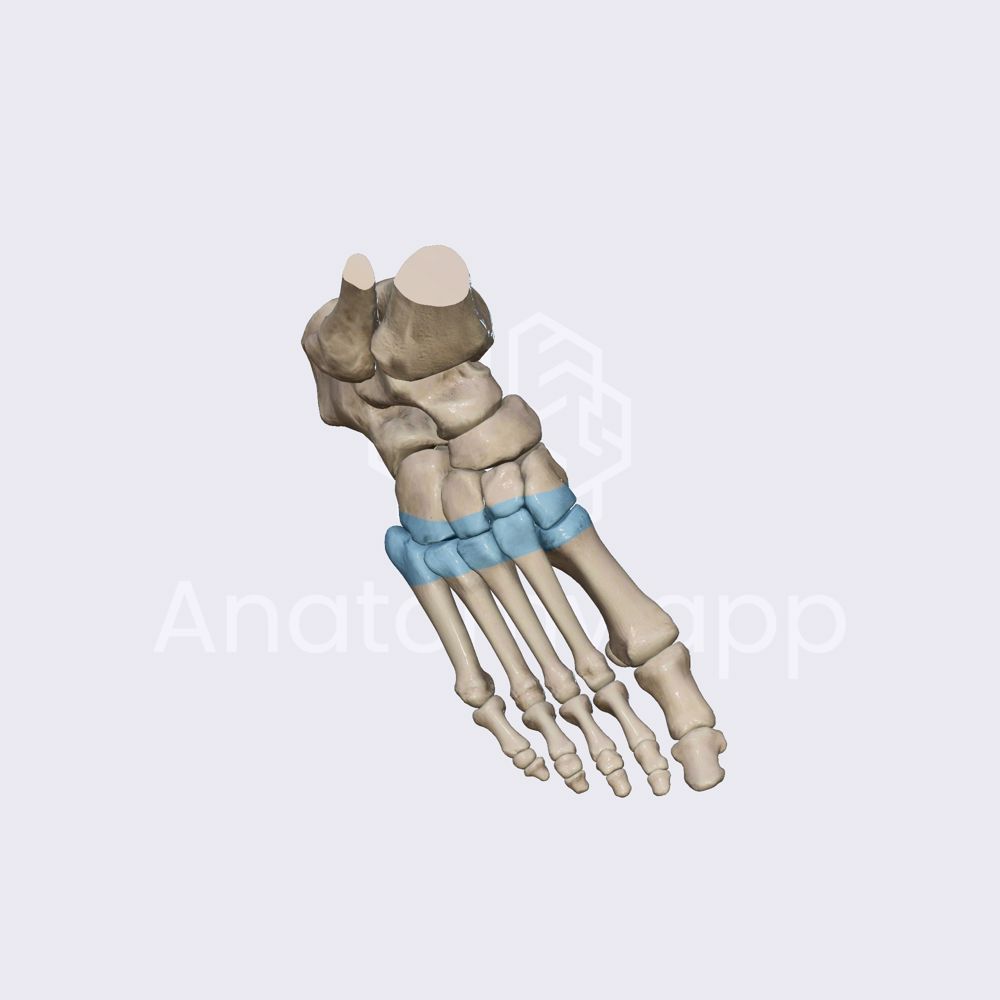
metatarsophalangeal joints
located between the metatarsals and the phalanges
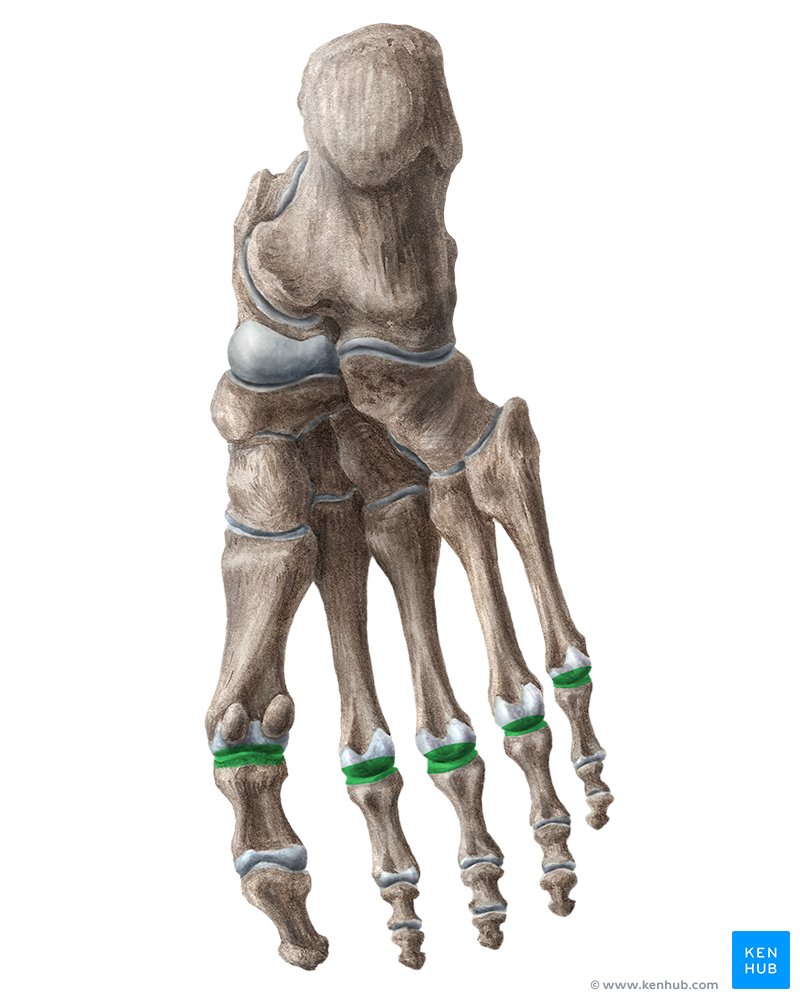
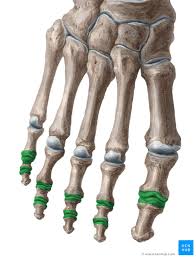
interphalangeal joints
located between the individual phalanges — in toes 2-5, proximal and distal joint
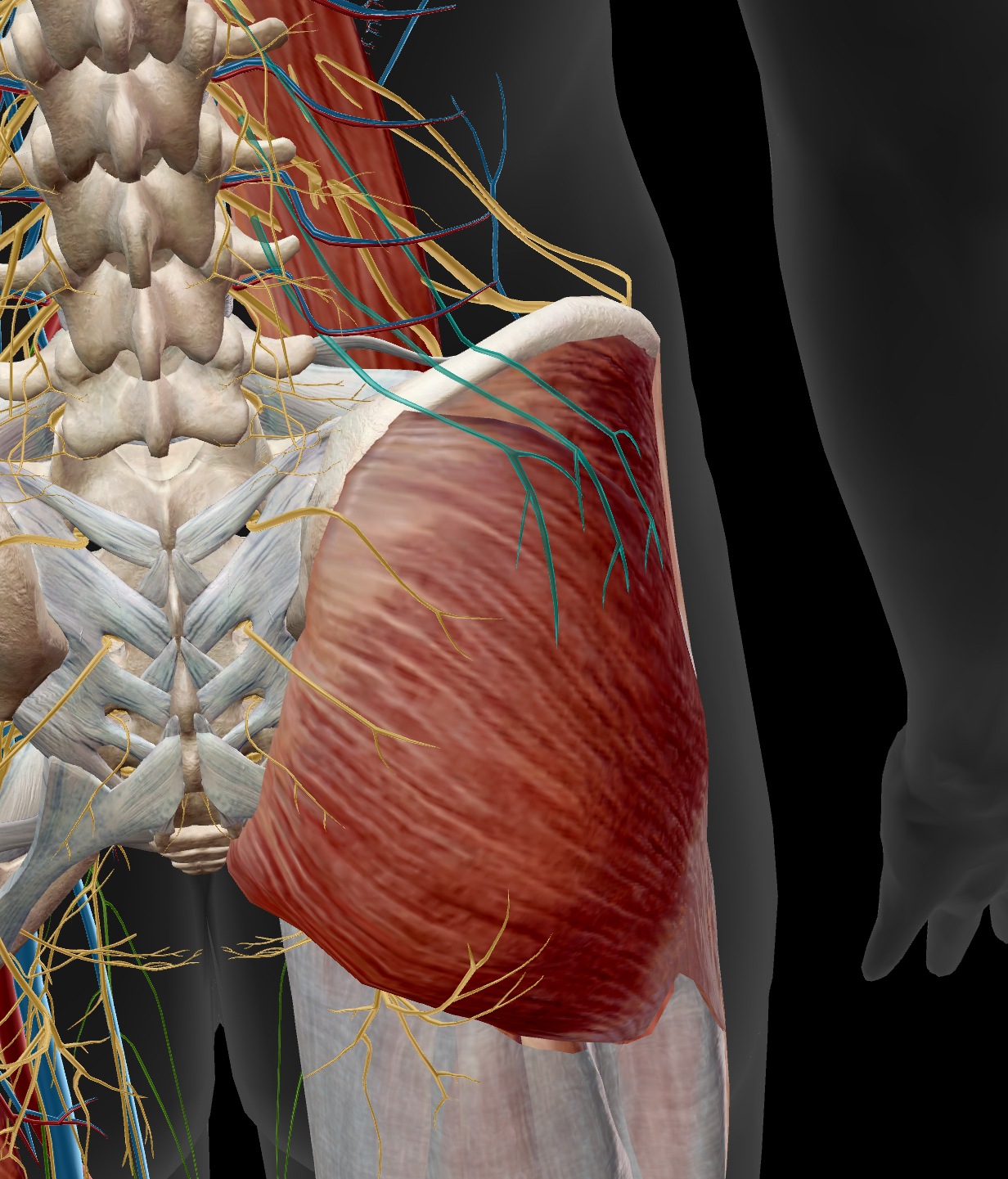
inferior gluteal neve
lower nerve in the gluteus — innervates the glutues maximus

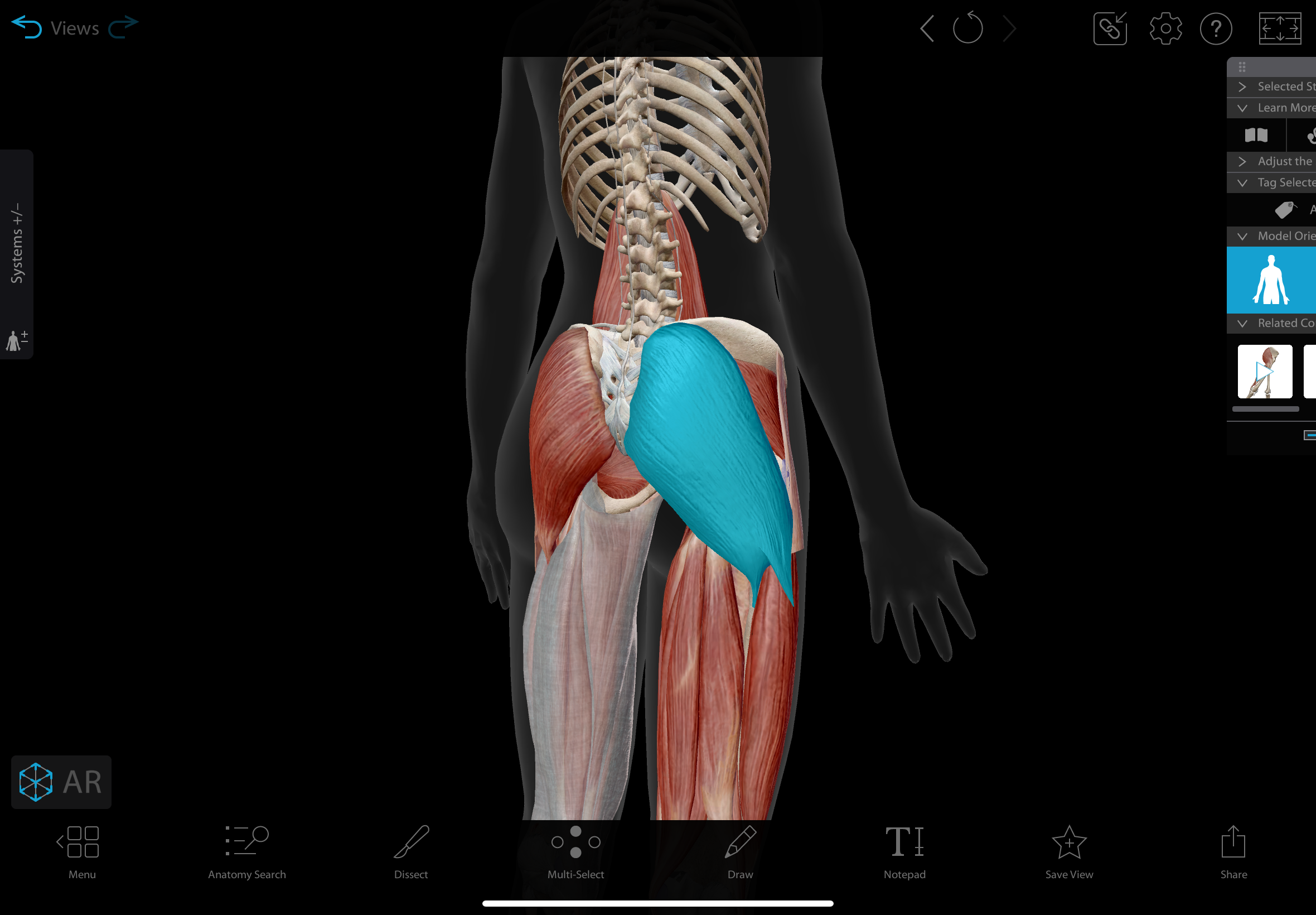
gluteus maximus
the largest muscle in the gluteal region
actions: extends, laterally rotates, & abducts the hip
insertion: iliotibial tract (gerdy’s tubercle), gluteal tuberosity of femur
innervation: inferior gluteal nerve
superior gluteal nerve
a branch of the sacral plexus — innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, & tensor fasciae latae
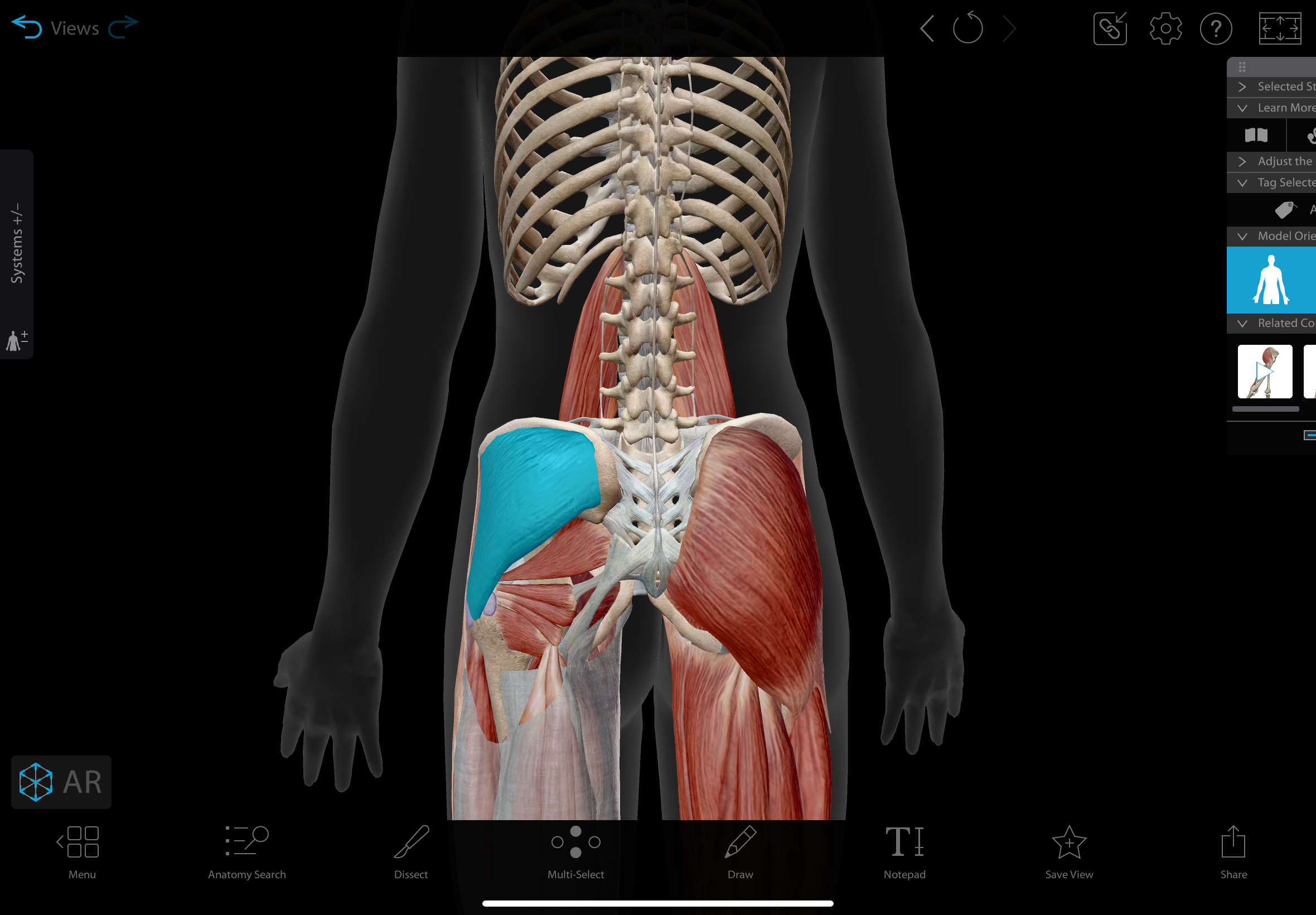
gluteus medius
A muscle located on the outer surface of the ilium
actions: abducts and medially rotates hip
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: superior gluteal nerve
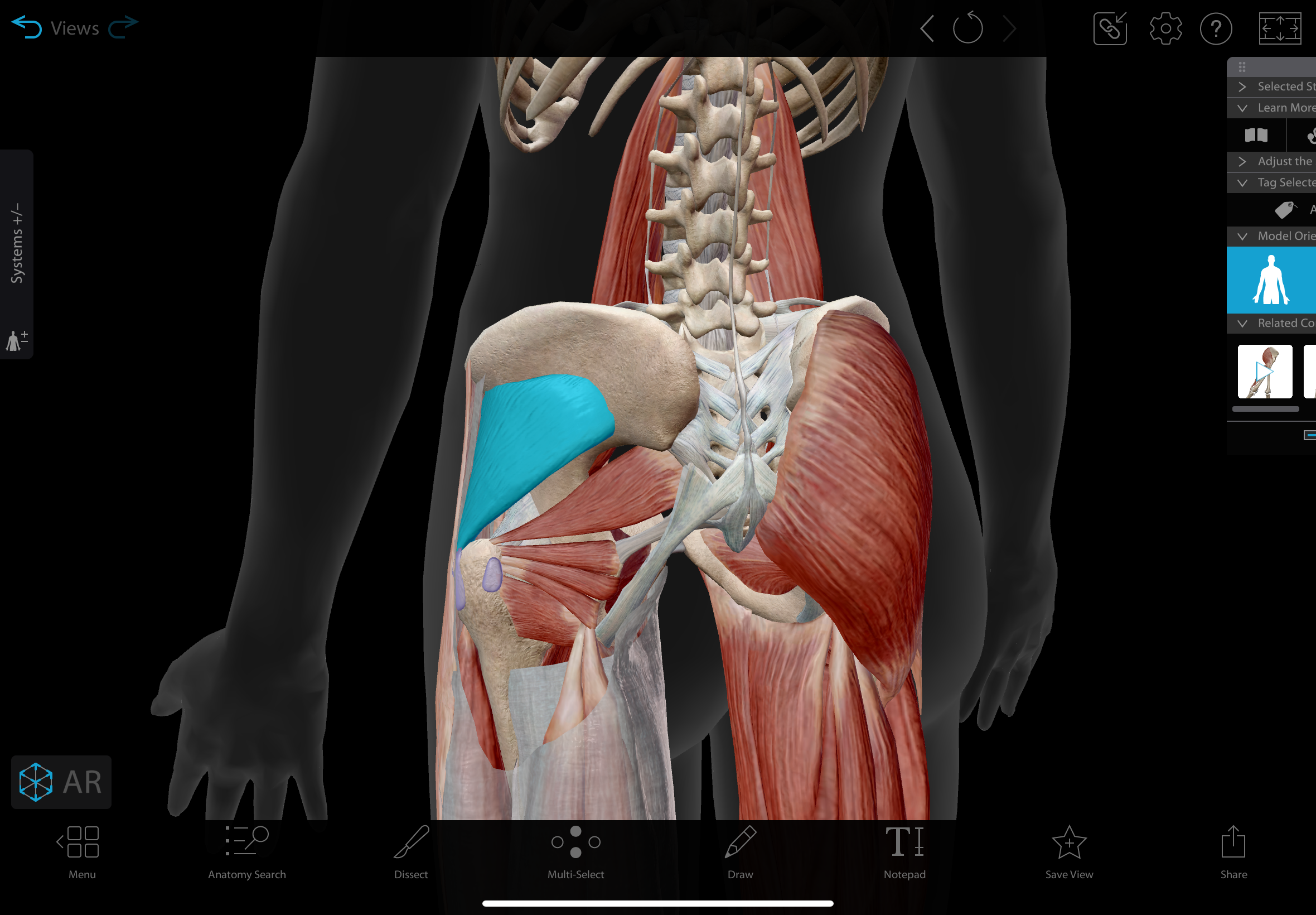
gluteus minimus
A muscle located beneath the gluteus medius
actions: abducts & medially rotates hip
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: superior gluteal nerve
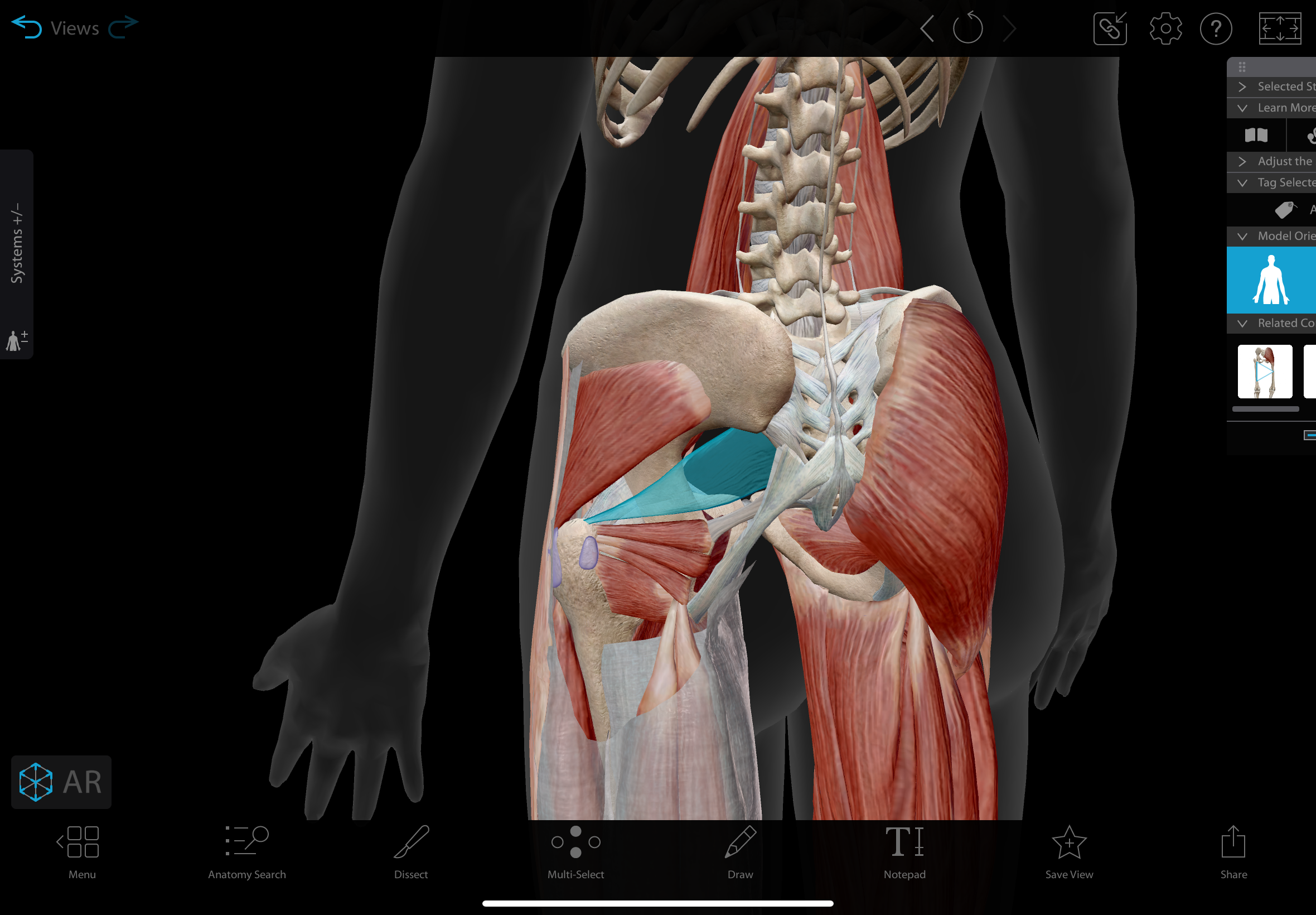
piriformis
A muscle located in the posterior pelvis, superior to the sciatic nerve as the nerve exits the pelvis
action: laterally rotates the hip
quadratus femoris
flat, quadrilateral muscle located in the posterior hip, superior to the adductor magnus
action: laterally rotates the hip
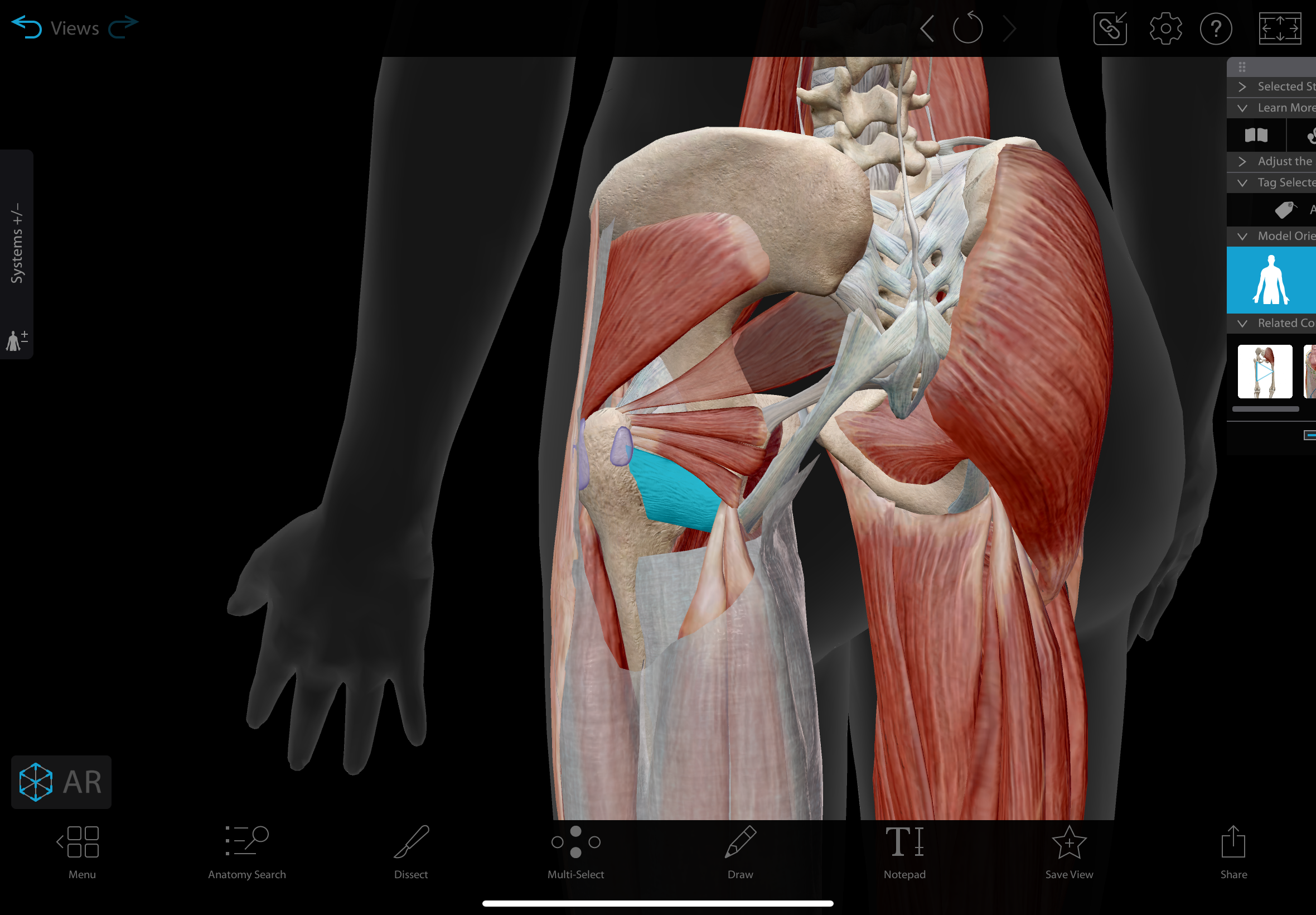
superior gemellus
A small muscle located in the posterior hip, lying above the obturator internus and below the piriformis.
action: laterally rotates the hip
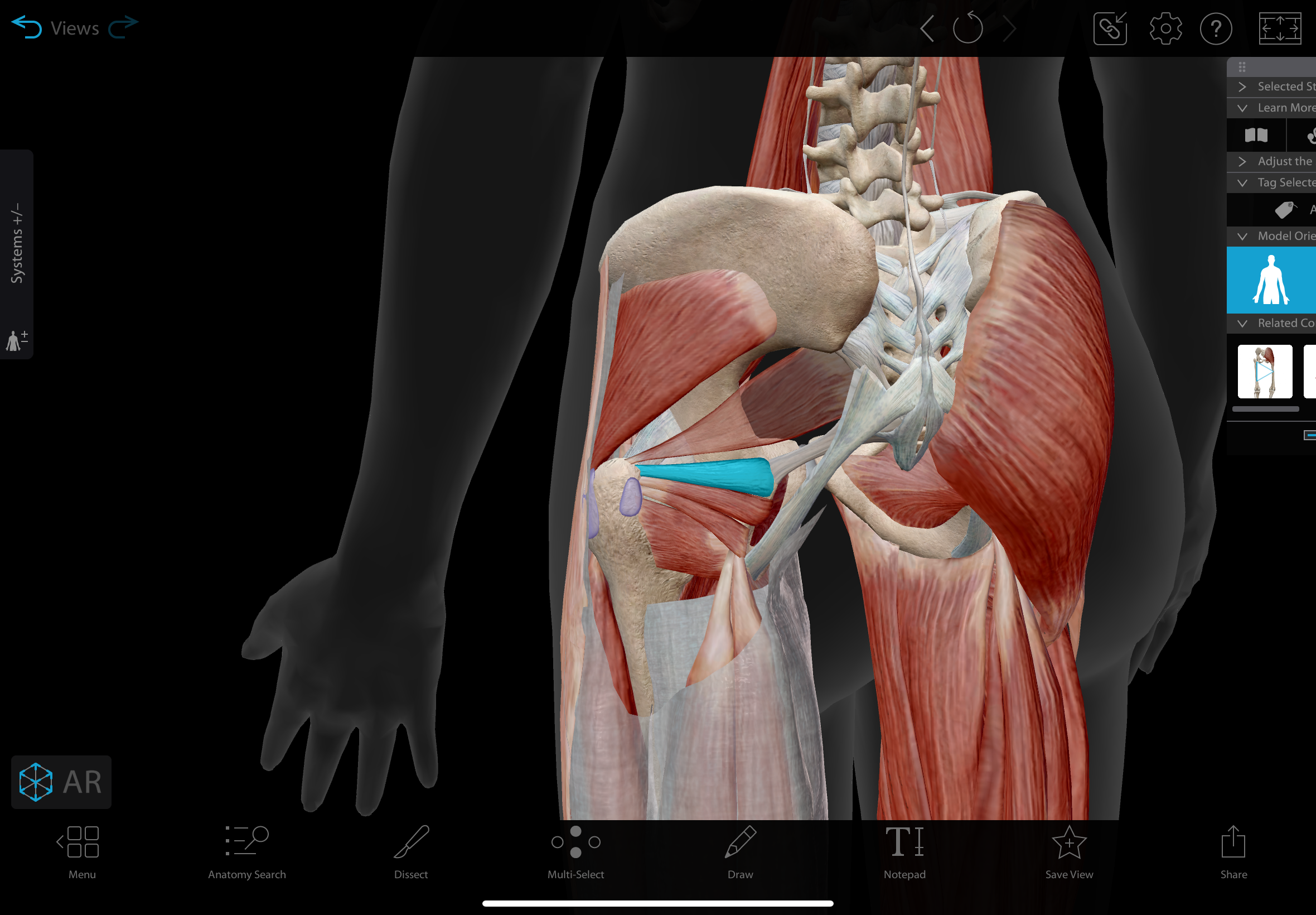
inferior gemellus
A small muscle located in the posterior hip, lying below the obturator internus and above the quadratus femoris.
action: laterally rotates the hip
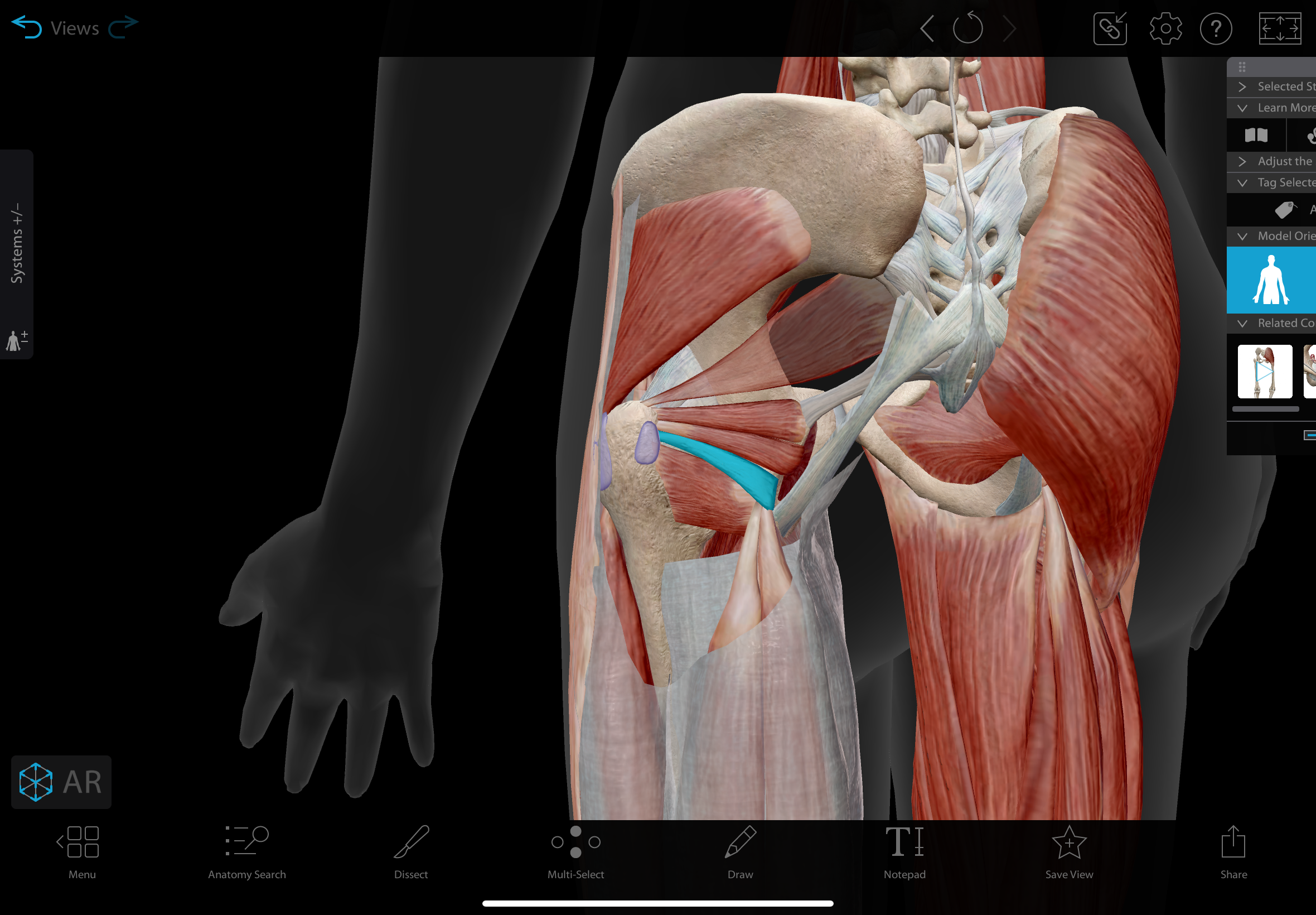
obturator internus
A flat, triangular muscle located in the posterior hip, originating from the internal surface of the obturator membrane and surrounding bone.
action: laterally rotates the hip
obturator nerve
The obturator nerve is a major nerve in the lower limb that originates from the lumbar plexus. It supplies sensation to the skin of the medial thigh
innervates: gracillis, pectineus, adductor magnust (adductor part)
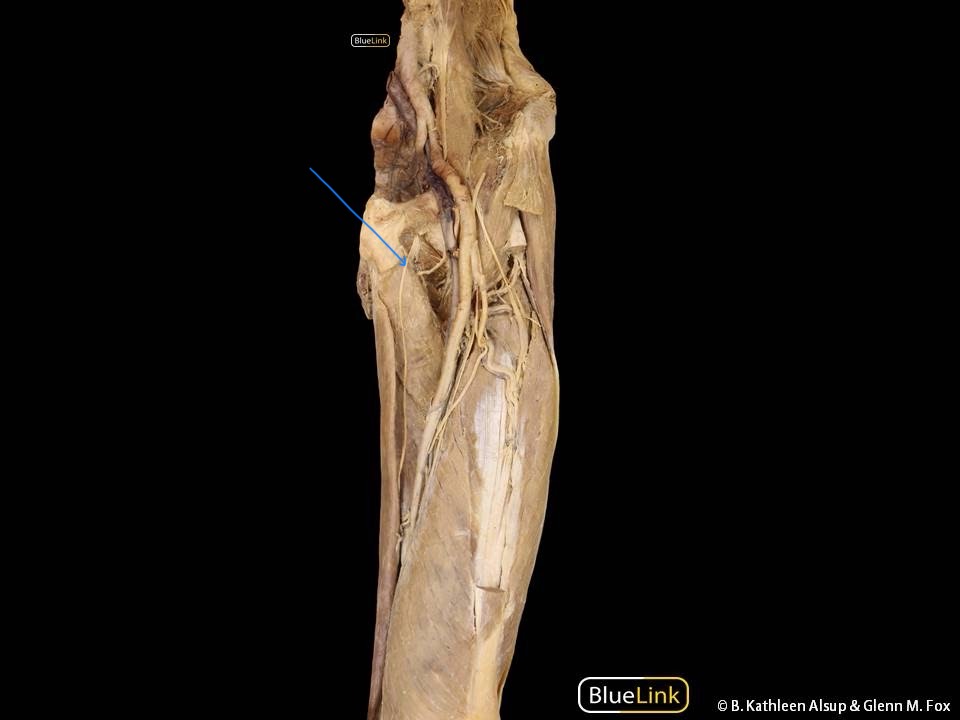
What muscles make up the medial thigh
adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, pectineus, adductor magnus
adductor longus
Long and narrow muscle in the medial thigh
actions: adducts, medially rotates, & flexes teh hip
insertion: linea aspera of the femur
innervation: obturator nerve
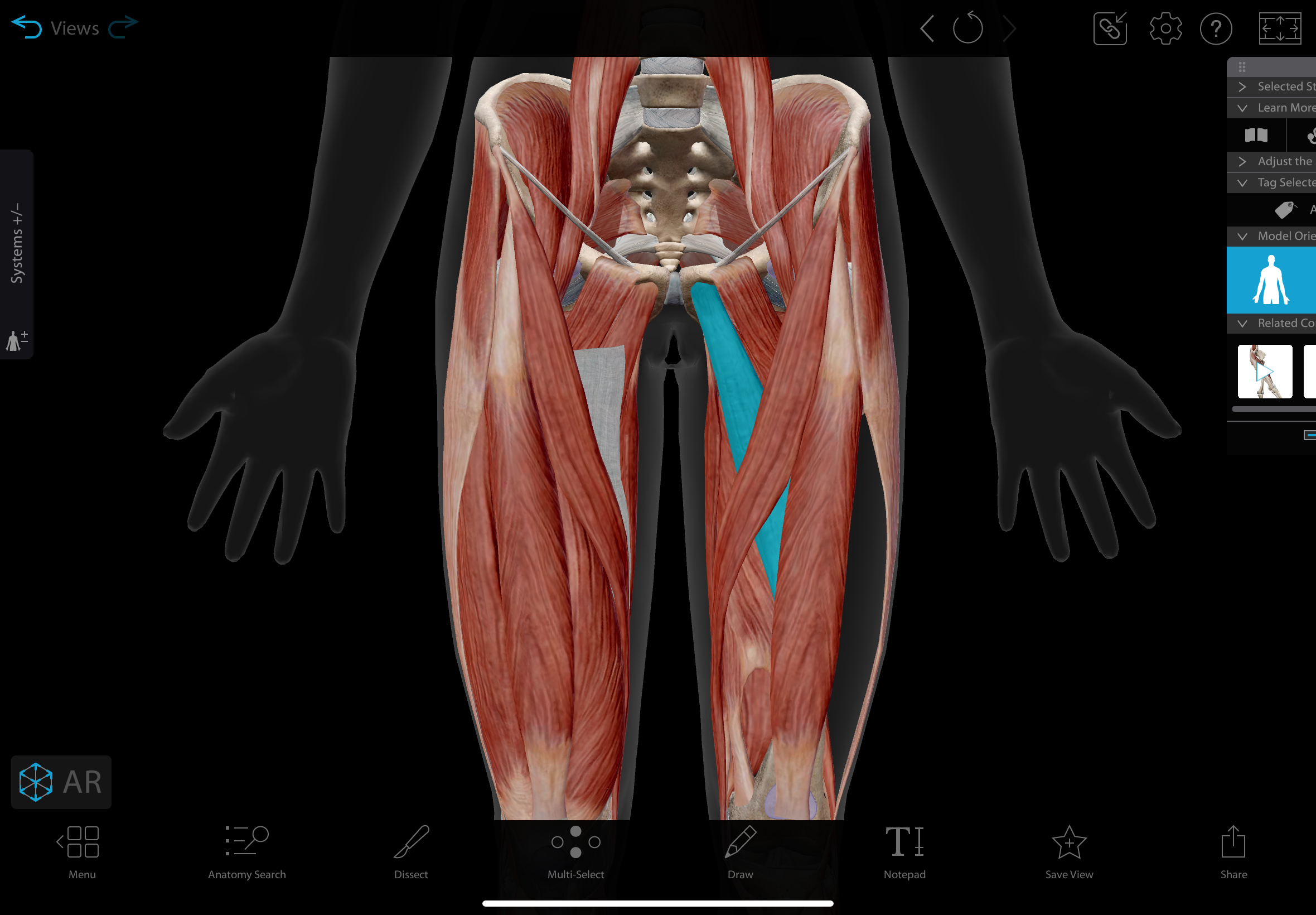
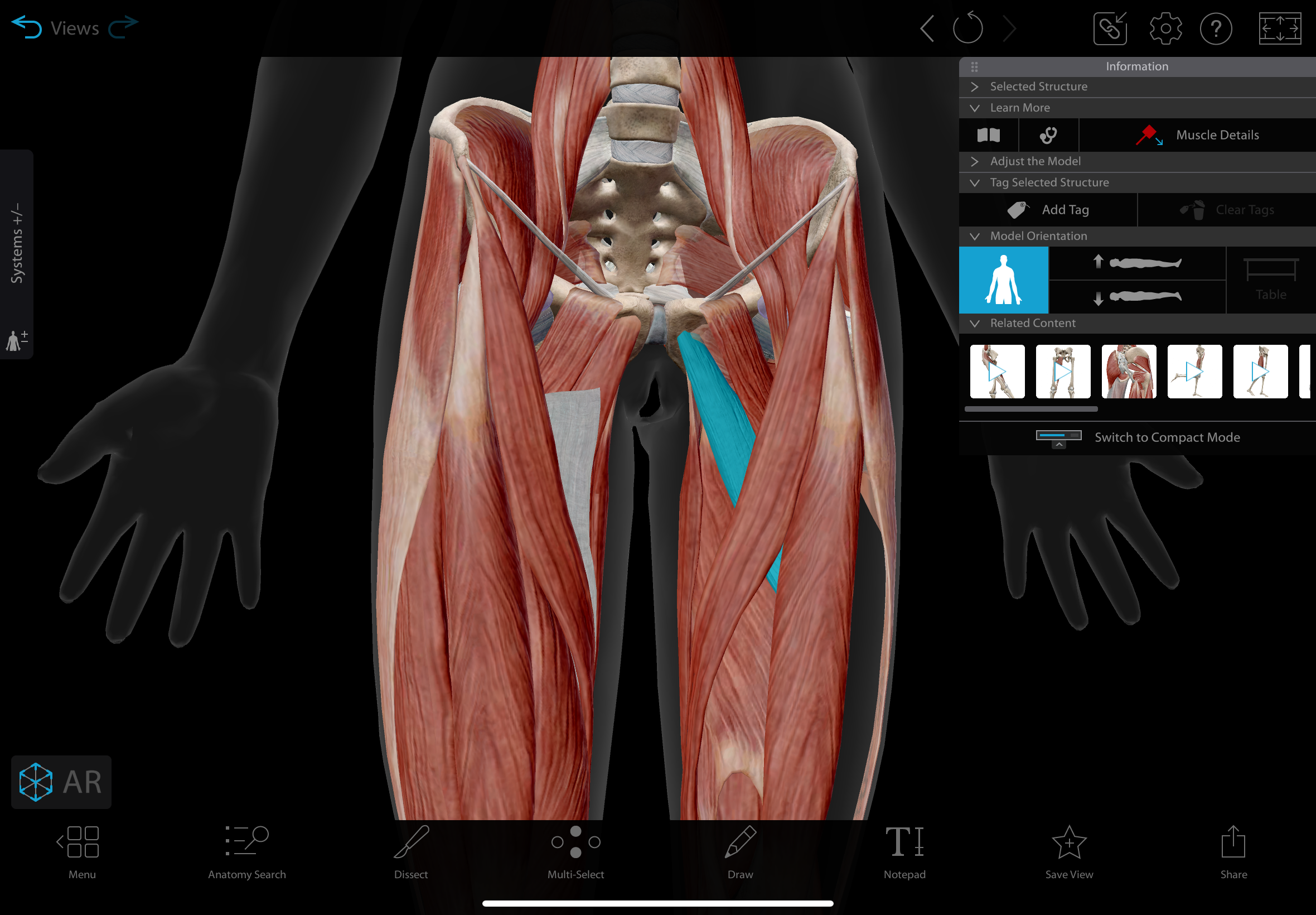
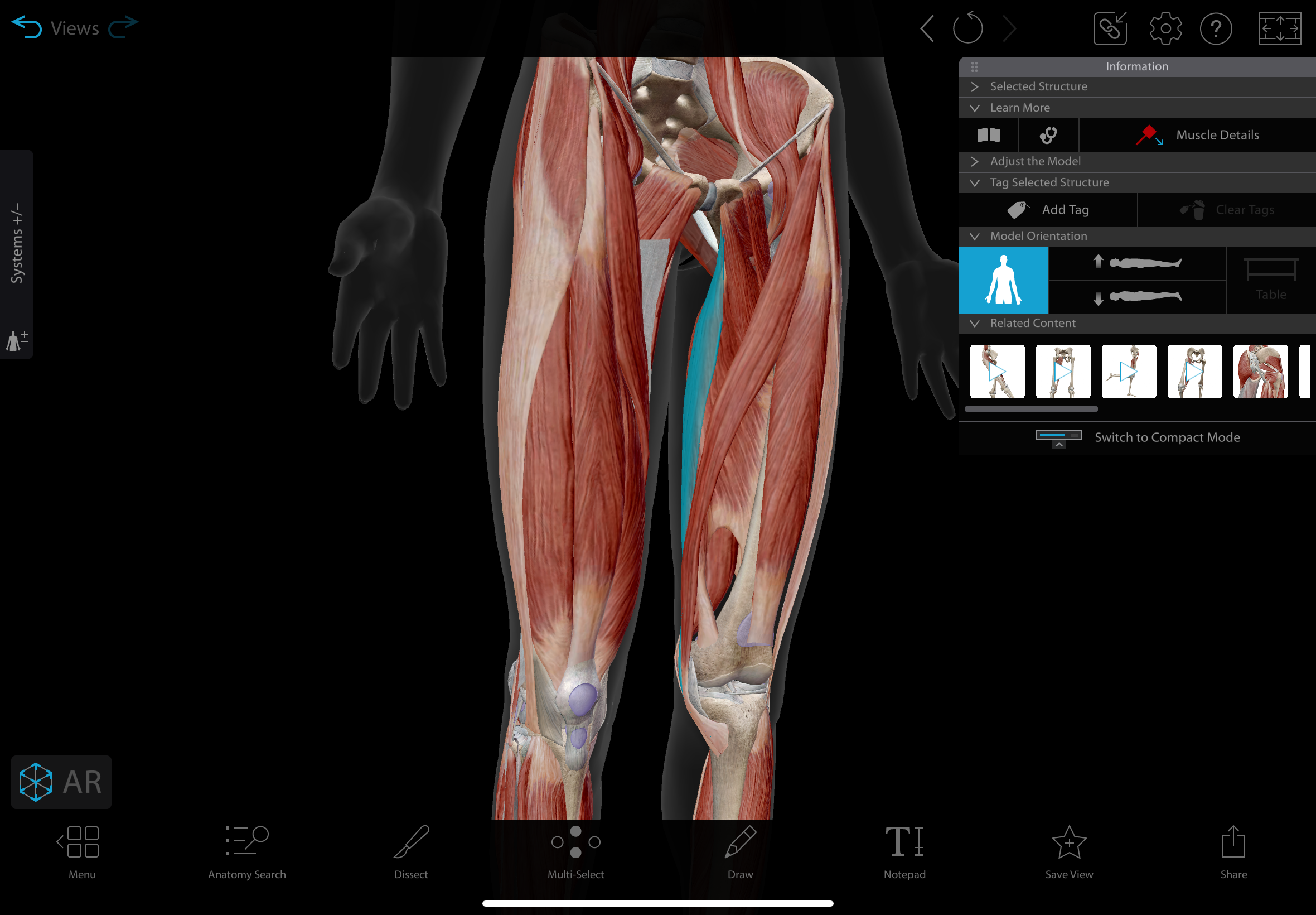
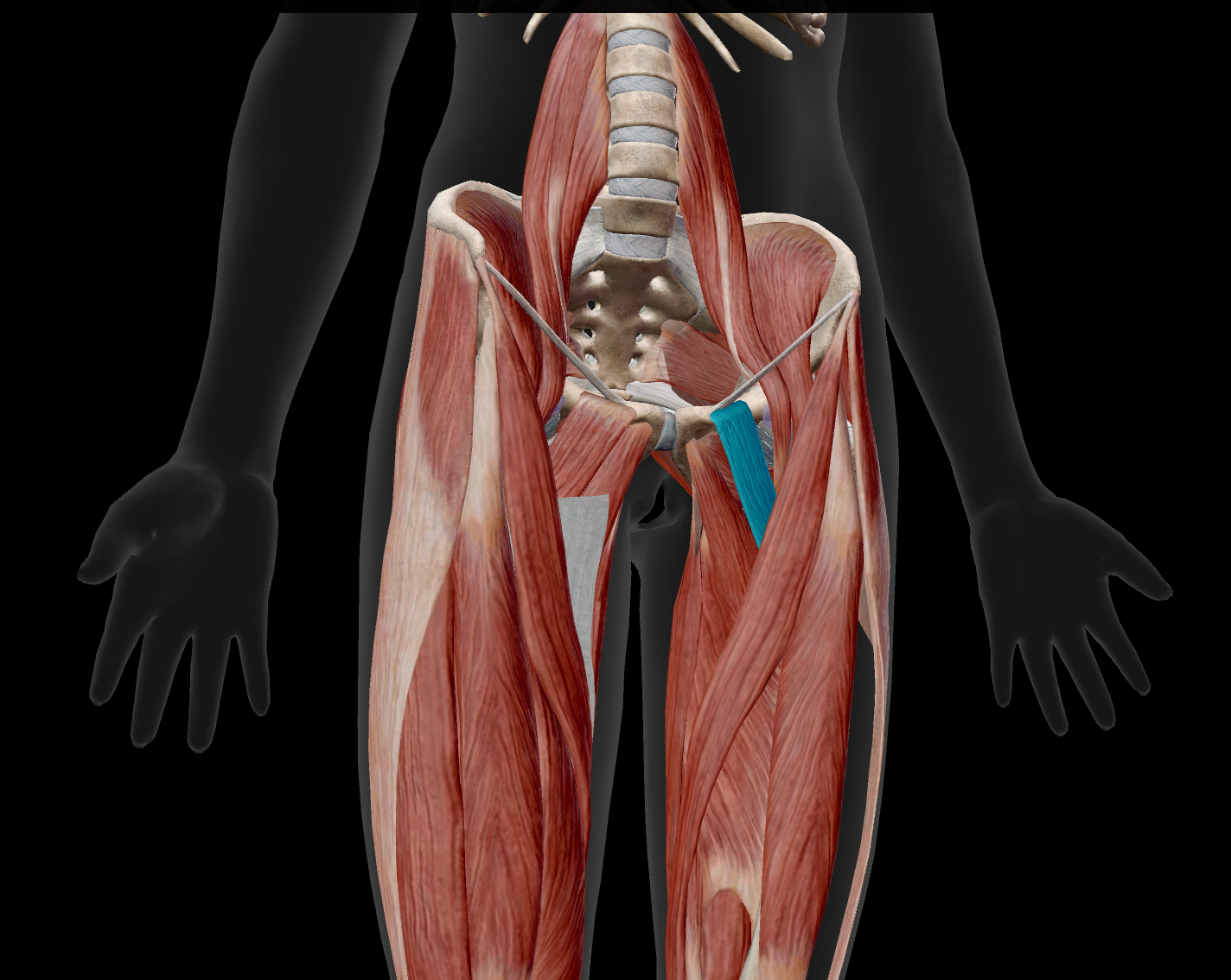
adductor brevis
A short muscle located in the medial compartment of the thigh.
actions: adducts, medially rotates, & flexes the hip
insertion: linea aspera of the femur.
innervation: obturator nerve
gracilis
A long, thin muscle in the medial thigh
actions: hip: adduction, medial rotation, knee: flexion, medial rotation
innervation: obturator nerve
pectineus
A flat, quadrangular muscle located in the anterior part of the medial thigh
actions: adducts, medially rotates & flexes the hip
insertion: pectineal line of the femur.
innervation: femoral nerve & obturator nerve
adductor magnus
A large muscle in the medial compartment of the thigh
actions: adductor part: adducts, medially rotates, & flexes hip, hamstring part: extends & laterally rotates hip
insertion: linea aspera & adductor tubercle
innervation: adductor part: obturator nerve, hamstring part: tibial division of sciatic nerve
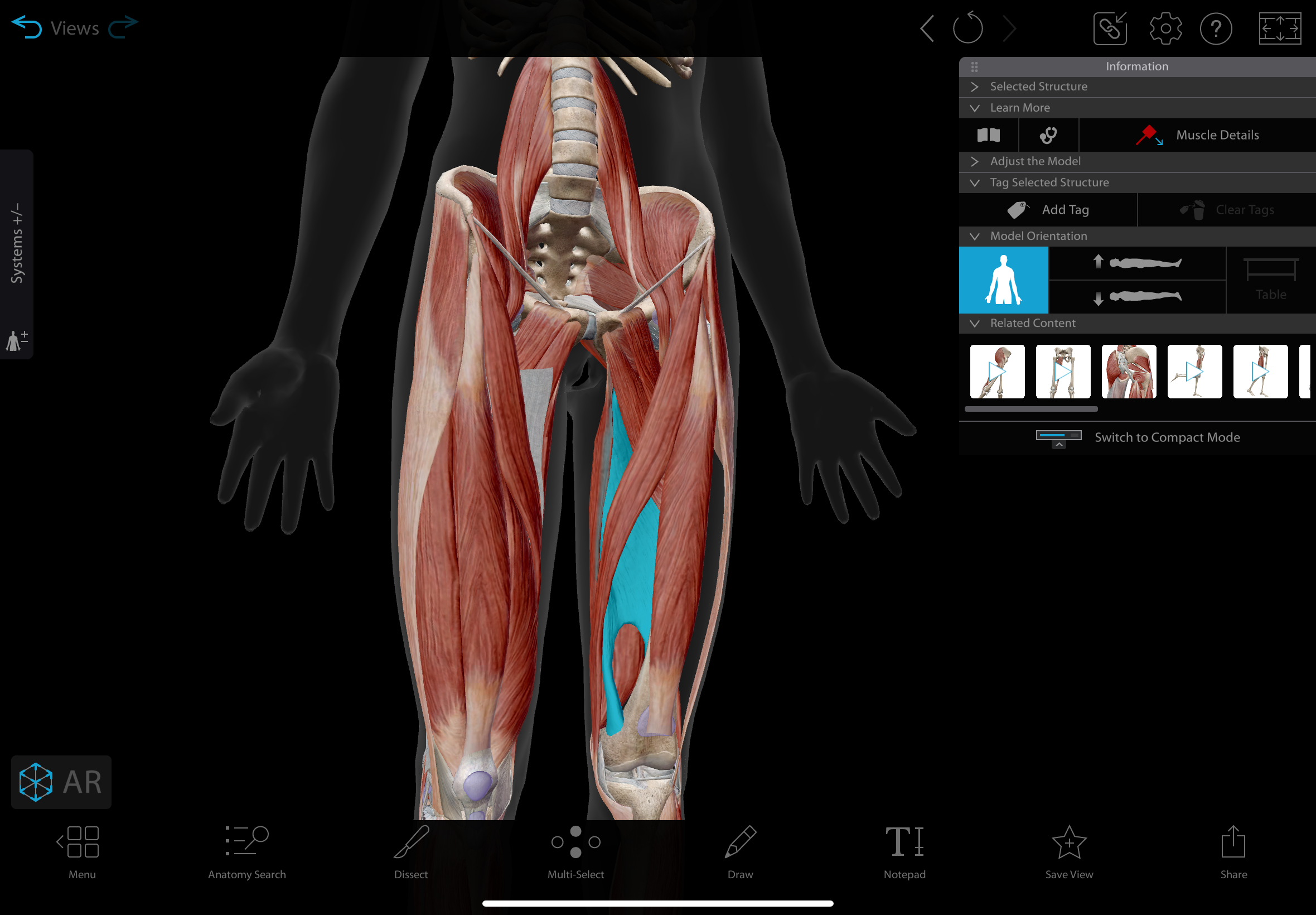
sciatic nerve
A major nerve in the lower limb that runs from the lower back down the leg, composed of fibers from the lumbar and sacral plexuses.
innervates: nothing
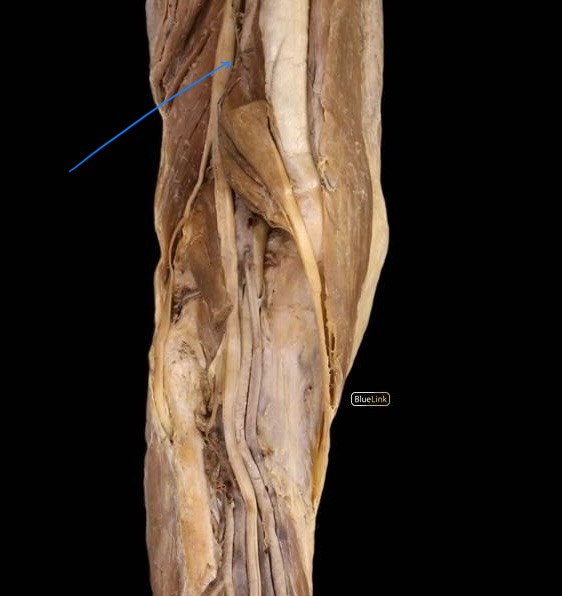
common fibular nerve
The lateral split of the sciatic nerve, divides into the superficial and deep fibular nerves.
innervates: short head of the biceps femoris
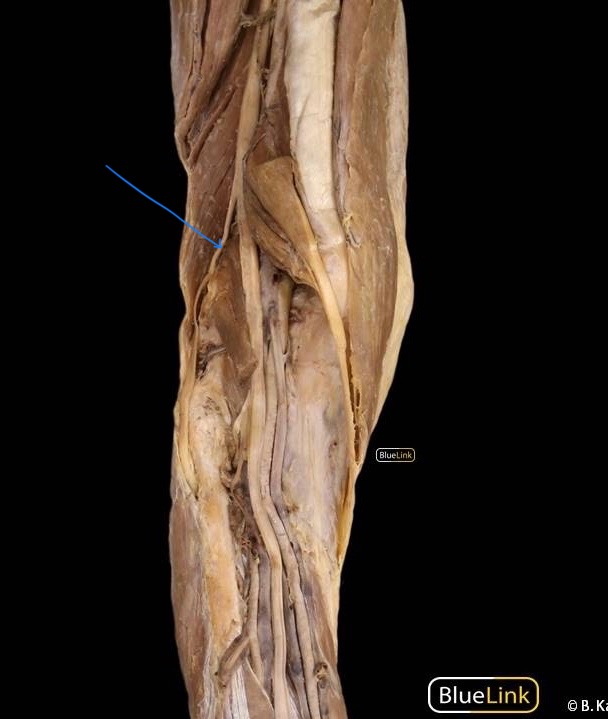
deep fibular (peroneal) nerve
terminal branch of the common fibular nerve. It descends in the anterior compartment of the leg with the anterior tibial artery
innervates: extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, fibularis (peroneus) tertius, tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis brevis, extensor digitorum brevis
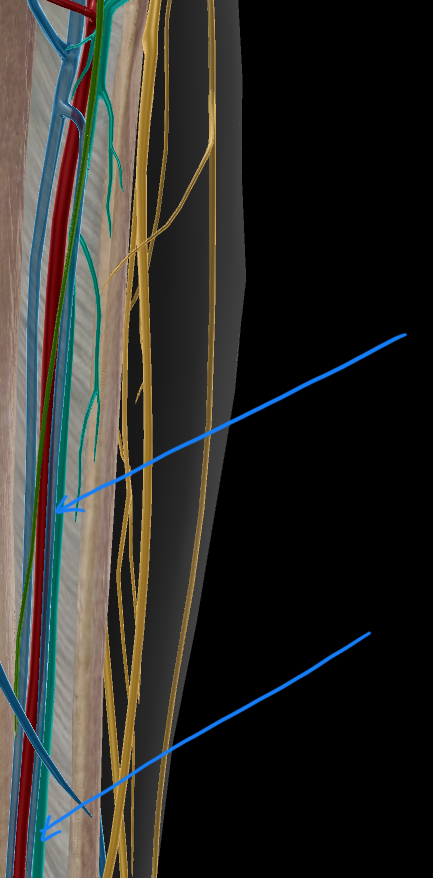
superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve
terminal branch of the common fibuilar nerve, descends in the lateral compartment of the leg with the tibial artery
innervates: fibularis (peroneus) longus & fibularis (peroneus) brevis
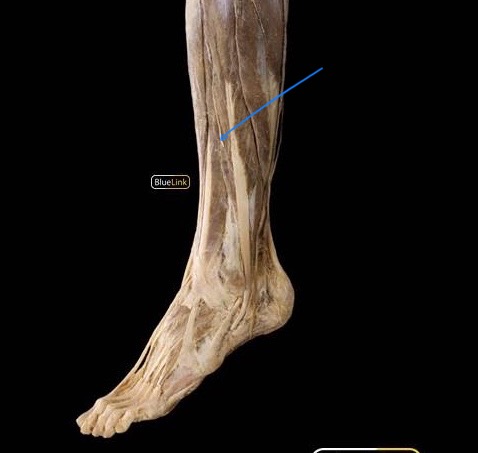
tibial nerve
The medial split of the sciatic nerve. It descends through the popliteal fossa and then in the posterior compartment of the leg,
innervates: semimembranosus, semitendinosus, hamstring part of adductor magnus, gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, tibialis posterior, popliteus