World War 1, Interwar Period, World War 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country

Alliances
agreements between nations to aid and protect one another
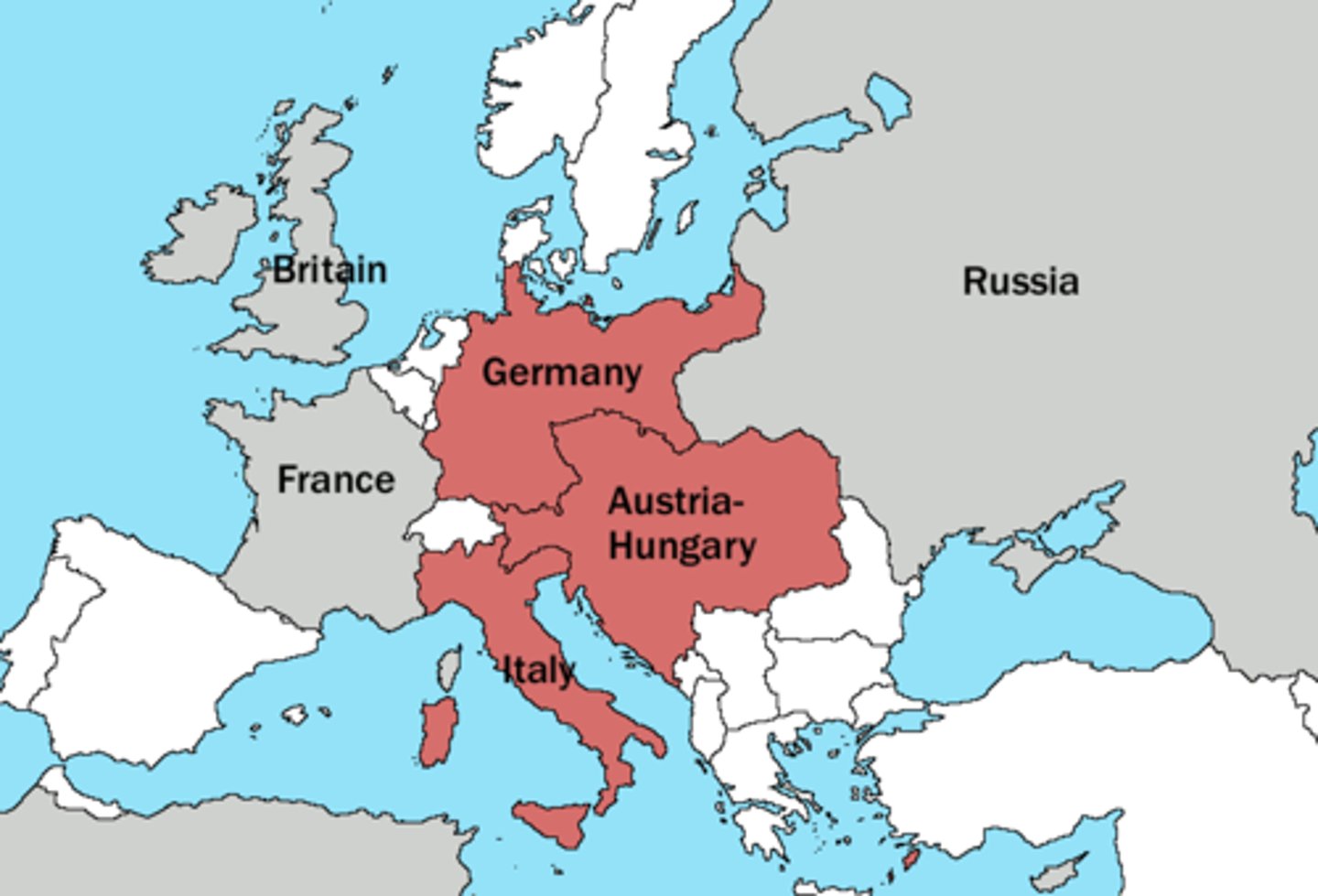
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

Militarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war

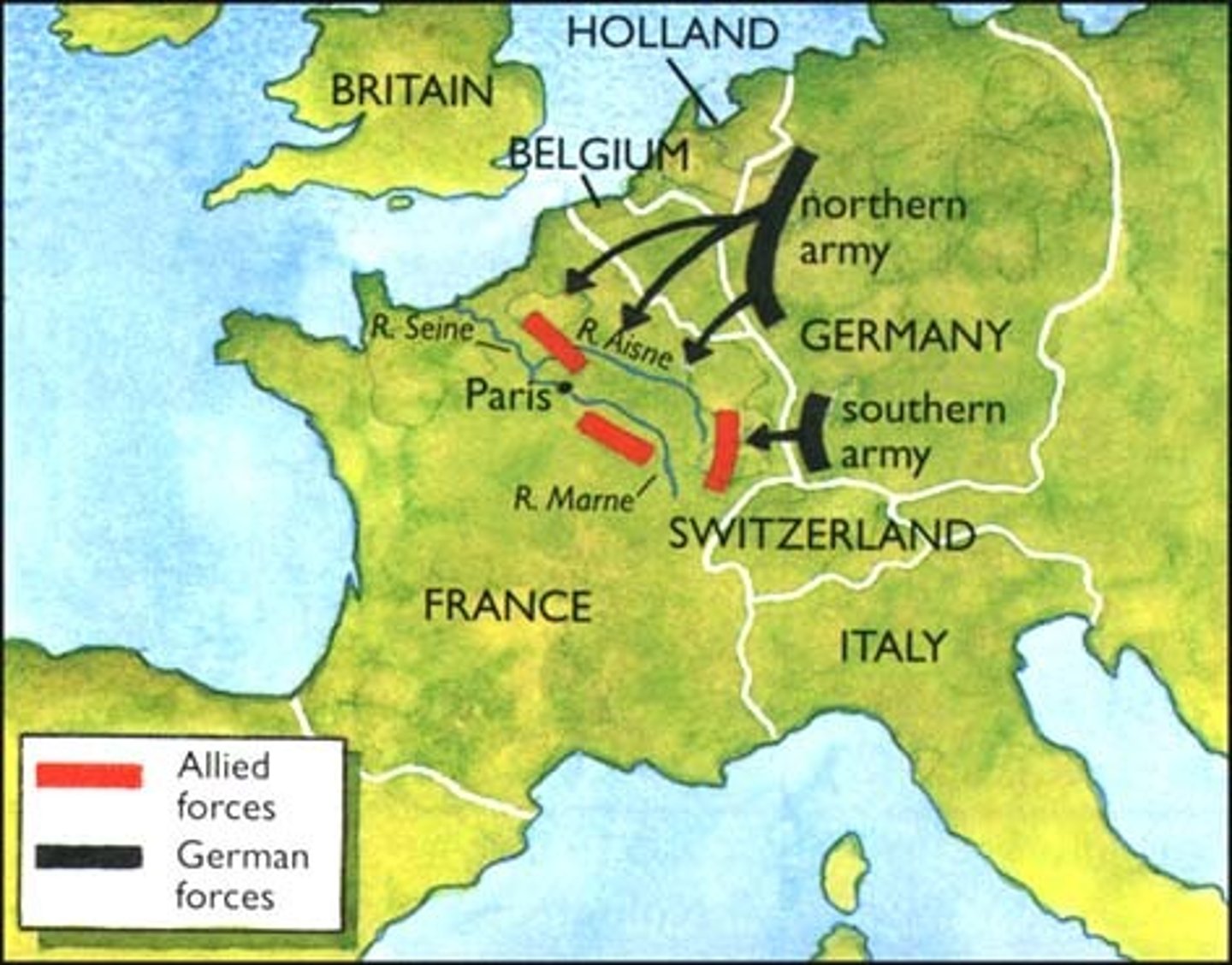
The Schlieffen Plan
A plan given by a German General in which the Germans invaded France through Belgium while the Russians mobilized.
Battle of Ypres
The first battle in Belgium, where Canadians faced poison gas for the first time.

Battle of Vimy Ridge
Canada's first independent battle against Germany; claimed victory in a matter of days, where other Allied forces had tried for months. Created first real sense of nationalism in Canadian citizens.

Battle of Passchendaele
One of the worst slaughters of World War I. During the summer and fall of 1917, Allied troops fought through endless rains across fields of deep mud, to capture the small town of Passchendaele in Belgium.
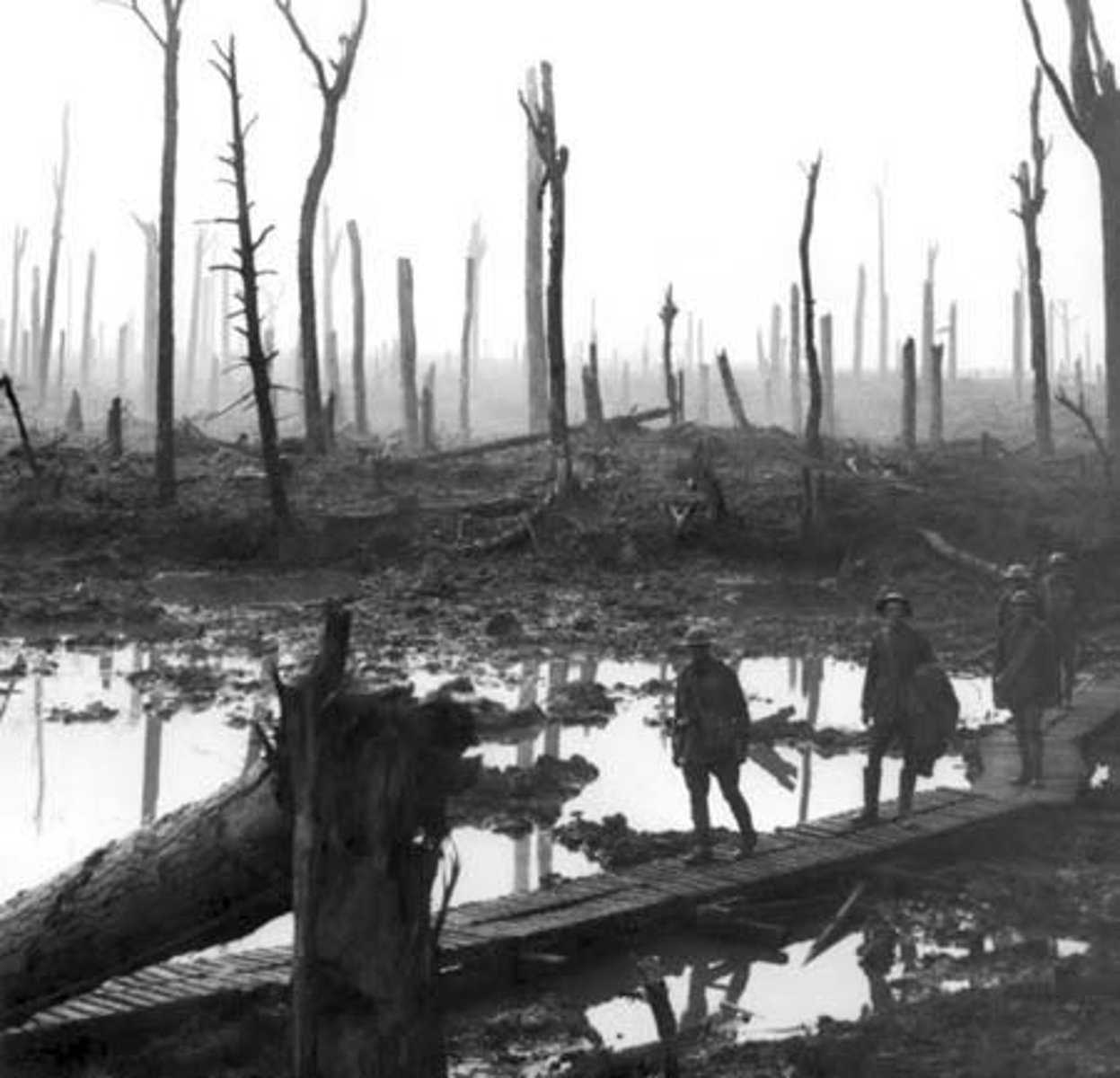

Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.

Trench Foot
Foot rot caused by long periods of time in wet boots

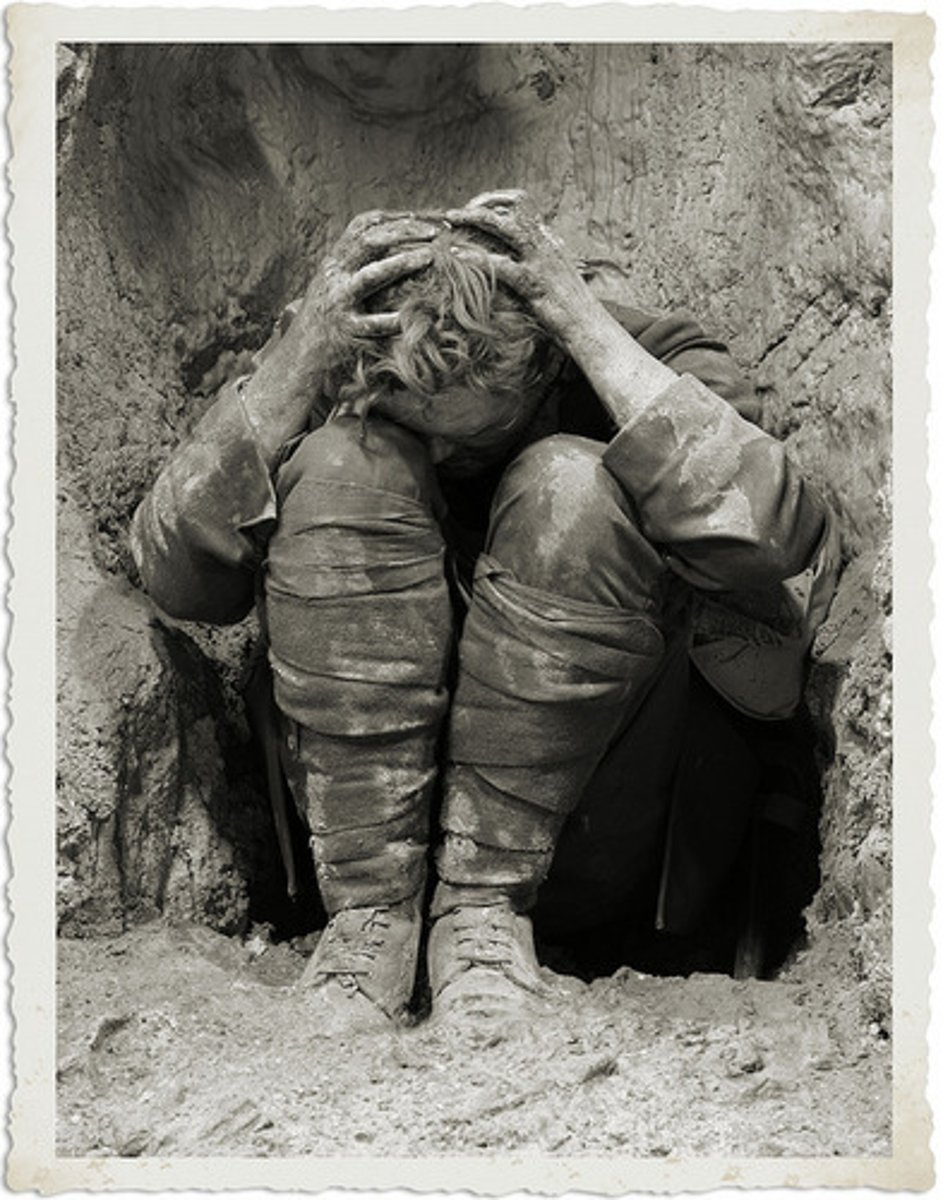
Shell Shock
Medical condition caused by prolonged exposure to the distressing experiences of trench warfare.

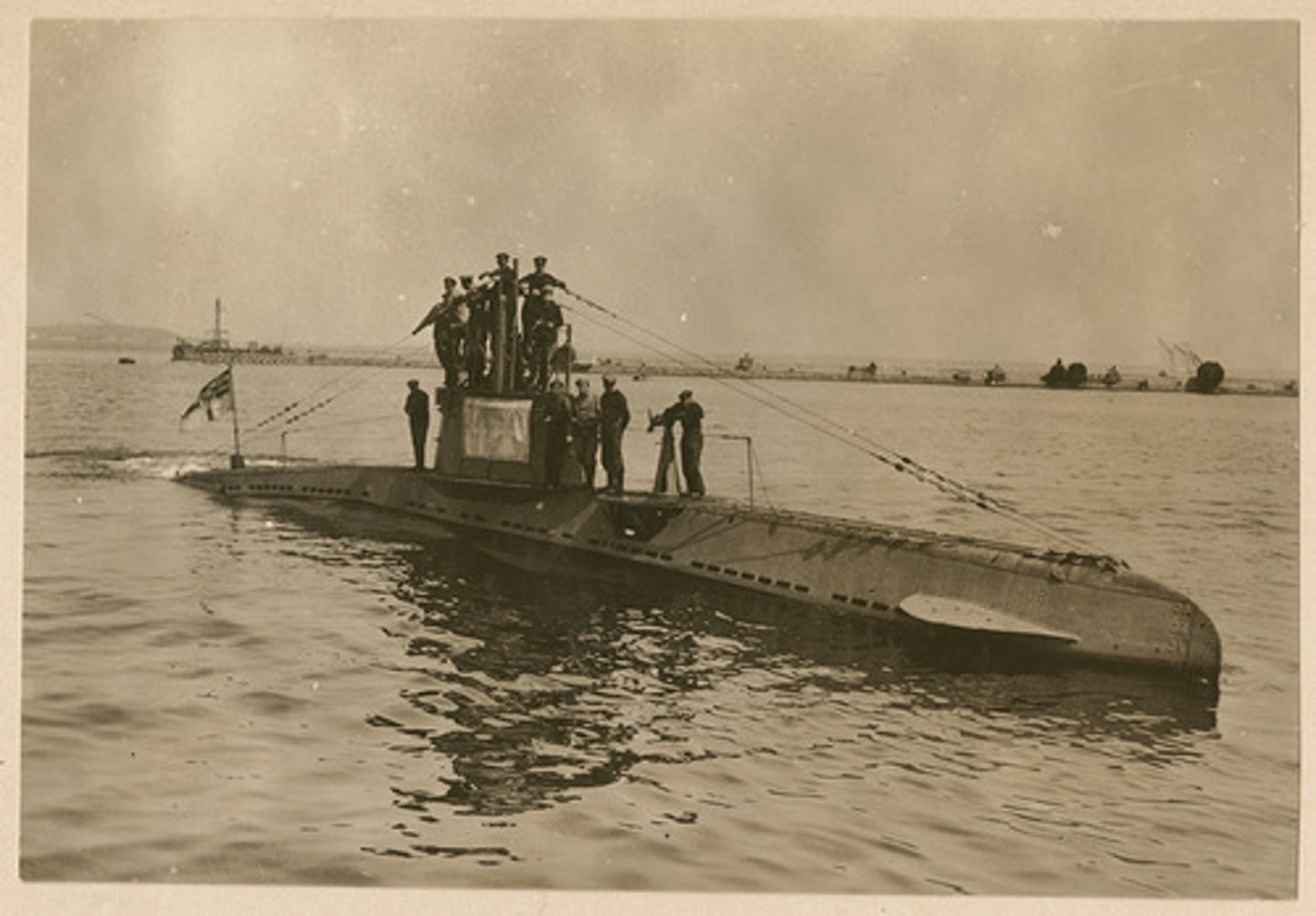
U-Boats
German submarines used in World War I

Gas Masks
A solution to a deadly problem. Gas was first used during the Battle of Ypres, and resulted in horrible injuries.

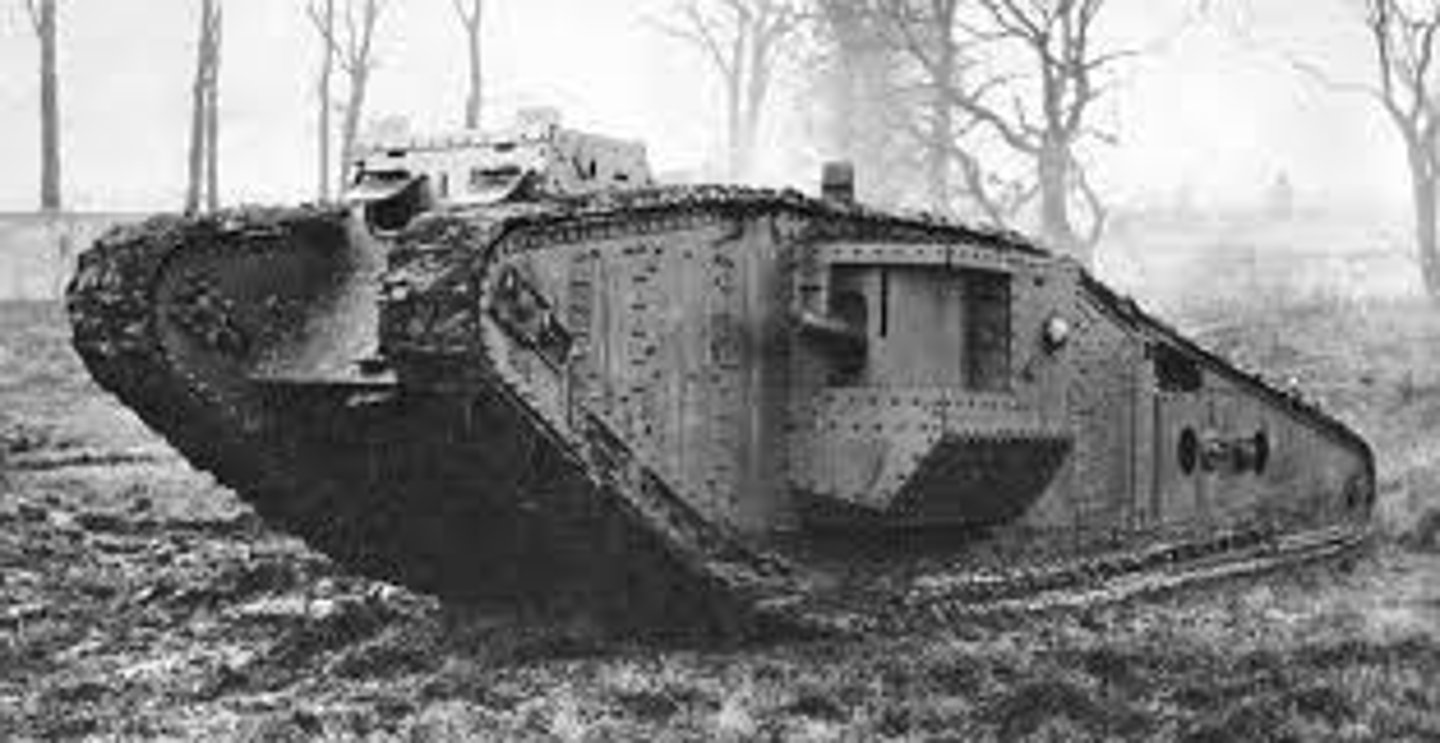
Tanks
Heavy armored vehicle which could travel over barbed wire and across enemy trenches

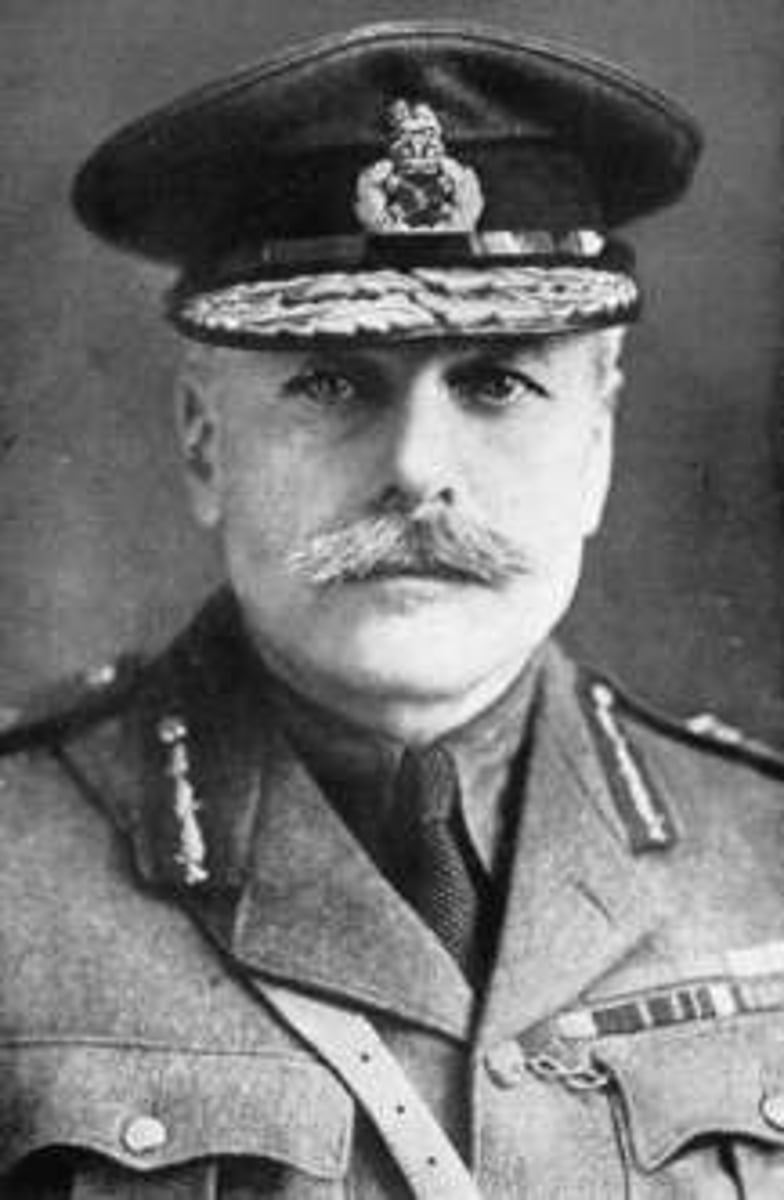
Douglas Haig
Controversial British commander on the Western Front and the driving force behind some disasters like Somme and Passchendaele

Arthur Currie
First Canadian promoted to general after victory at Vimy Ridge. Became commander of all Canadian corps. Believed in thorough and meticulous training

Enemy Aliens
Immigrants in Canada from the central power nations who were considered a threat to the Canadian war effort in World War 1

Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.

Rationing
A system of allocating scarce goods and services

Conscription
compulsory enlistment for state service, typically into the armed forces.

Women during WW1
Took over the roles and jobs of men overseas, organized large groups, and gained the right to vote

November 11, 1918
Armistice Day (Now known as Remembrance Day)

Paris Peace Conference
The peace conference that decided the terms of WWI peace and Treaty of Versailles.

Treaty of Versailles
(1919) Treaty ending World War I; required Germany to pay huge war reparations and established the League of Nations

War Guilt Clause
In treaty of Versailles; declared germany and austria responsible for WWI; ordered Germany to pay reparation to Allied powers

Victory Bonds
Bonds advertised by the Government to encourage Canadians to give money during the war, with a guaranteed return on investment.

Military Service Act
a 1917 Act that made conscription compulsory for all Canadian men between the ages of 20 and 45, calling up the younger men first
Wartime Elections Act
an Act that gave the vote to Canadian women related to servicemen, but cancelled the vote for conscientious objectors and immigrants from enemy countries

100 Days Offensive
A series of battles between August 1918 and November 1918 in which the Allies, led by the Canadian corps, pushed father and faster through France and Germany than they had previously been able to, which led to Germany's surrender
The Great Depression
a time period during the 1930s when there was a worldwide economic depression and mass unemployment

Fascism
Political system based on a strong, centralized government headed by a dictator, and believes in racial superiority

Appeasement
Satisfying the demands of countries in an effort to maintain peace and stability.

Prisoner of War
a person captured in war, especially a member of the military
Operation Fortitude
Codename of fake operation to decieve the Germans into believe an invasion would occur at Calaise

Battle of the Atlantic
Germany's naval attempt to cut off British supply ships by using u-boats. Caused Britain and the US to officially join the war after their ships were sunk. After this battle, the Allies won control of the seas, allowing them to control supply transfer, which ultimately determined the war. 1939-1945

Adolf Hitler
Austrian-born founder of the German Nazi Party and chancellor of the Third Reich (1933-1945). Hitler's invasion of Poland (1939) and the subsequent outbreak of World War II. His regime was infamous for the extermination of millions of people, especially European Jews. He committed suicide when the collapse of the Third Reich was imminent (1945).

Invasion of Poland
Germany invaded, breaking their agreement, so Britain and France declared war, starting World War II

Pearl Harbor
Base in Hawaii that was bombed by japan on December 7, 1941, which eagered America to enter the war.

Censorship
Control of what people read or write or see or hear; efforts to prohibit free expression of ideas.

Internment
Temporary imprisonment of members of a specific group

Statute of Westminster
The 1931 British law that declared Canada and the other Dominions to be fully independent.

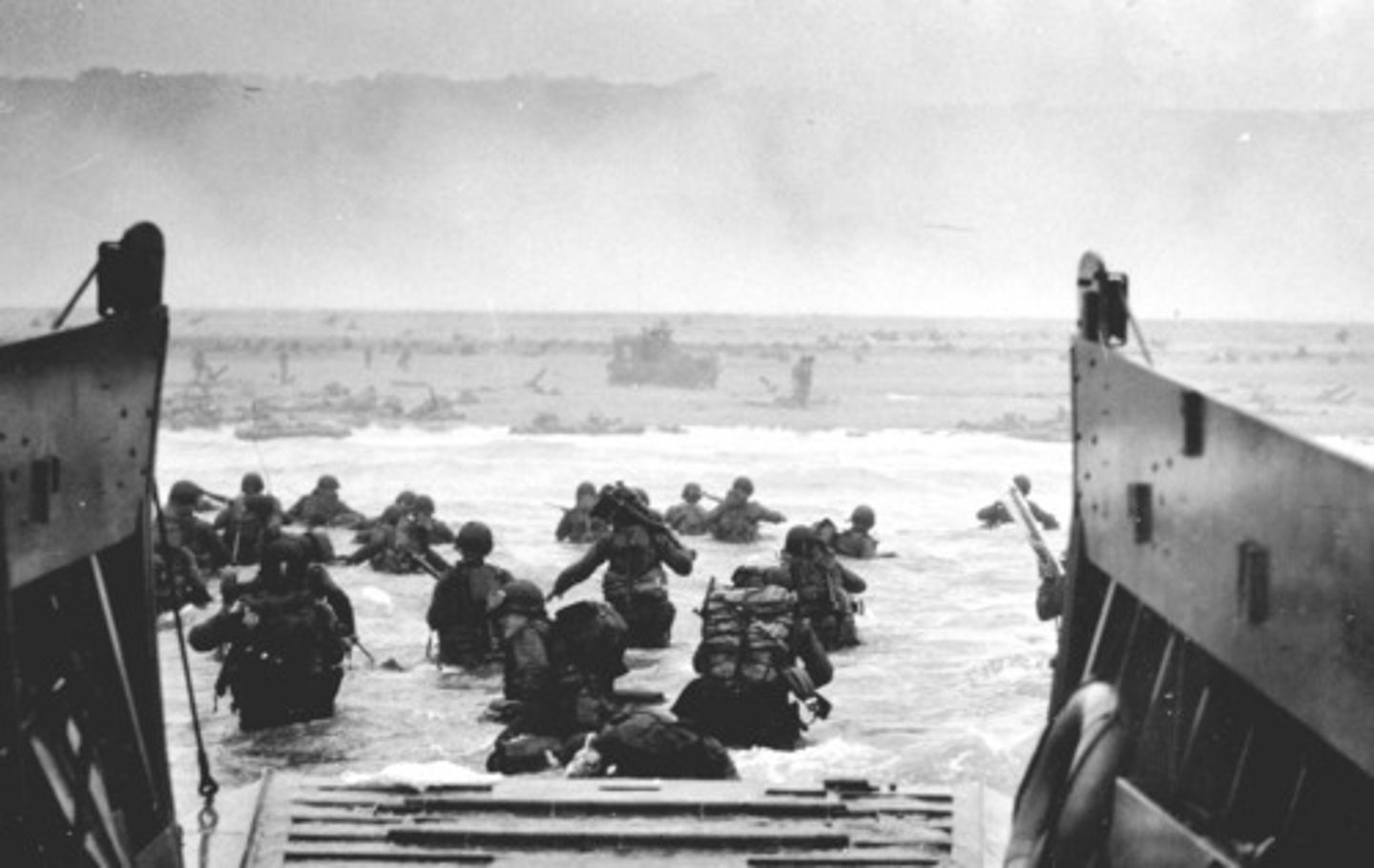
D-Day
Allied invasion of France on June 6, 1944

Battle of Dieppe
attack by Canadians in 1942 on coastal town of Dieppe, France

Non-Aggression Pact
an agreement between Germany and the Soviet Union stating Germany would not invade the Soviet Union.

Battle of Britain
A series of battles between German and British air forces, fought over Britain in 1940-1941

Blitzkrieg
"Lighting war", typed of fast-moving warfare used by German forces against Poland in 1939

League of Nations
an international organization formed in 1920 to promote cooperation and peace among nations

War Measures Act
Gave the government sweeping powers to ensure "the security, defence, peace, order, and welfare of Canada"

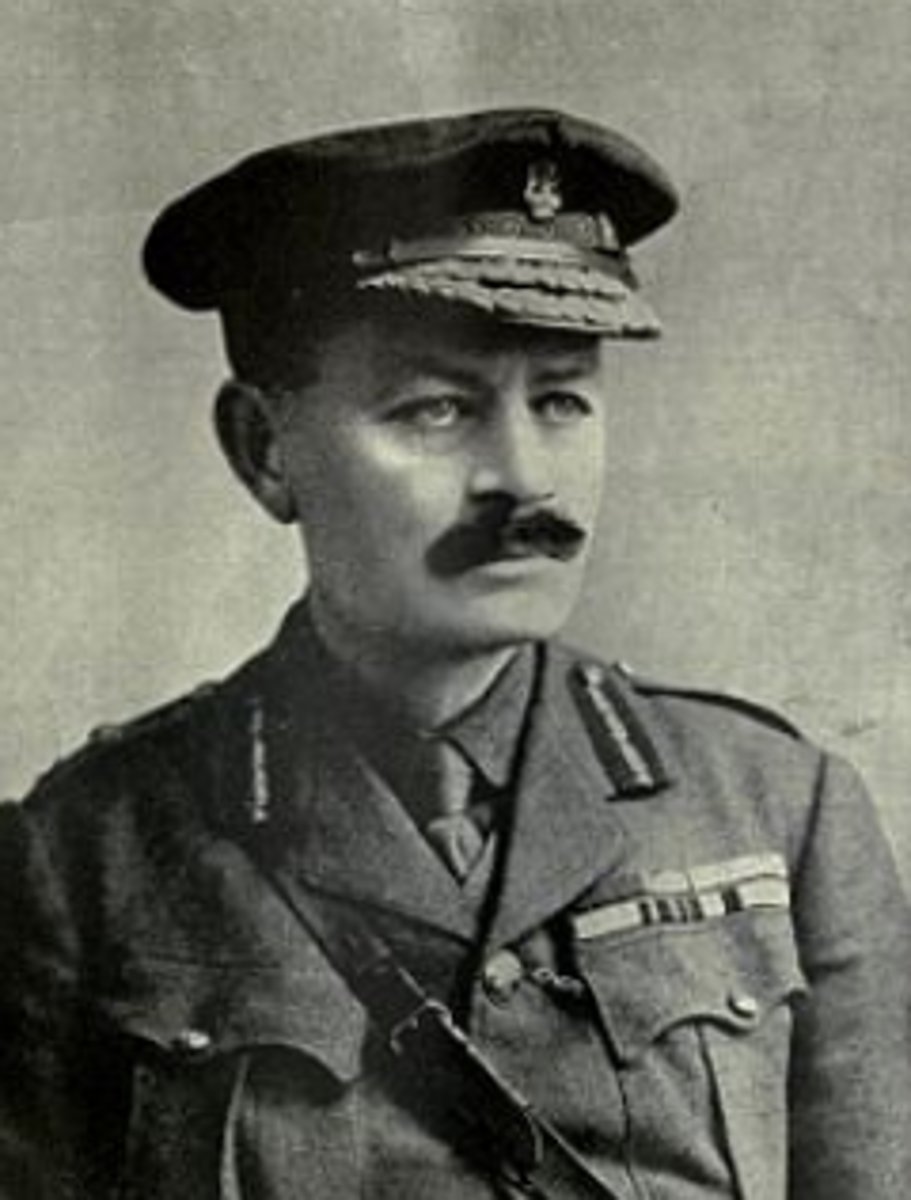
Julian Byng
A British Army officer who served with distinction during World War I with the British Expeditionary Force in France, in the Battle of Gallipoli of the Dardanelles campaign, as commander of the Canadian Corps, and as commander of the British Third Army.

Sam Hughes
The man in charge of Canada's armament industry (Minister of Militia) He took advantage of his position by awarding large government contracts to his friends who were profiteers. Bad quality items were made and sent over for the soldiers to use.

Battle of Somme
A WW1 battle ending in a stalemate, the bitter three-month conflict is notable for the high number of casualties- 1.25 million men killed or wounded - and the first use of tanks in warfare, and Douglas Haig, the "Butcher of the ______"

Winnipeg General Strike
Massive protest by workers in over labour issues in 1919

Black Tuesday
A name given to October 29, 1929, when stock prices fell sharply.

Bennett Buggy
Car with its engine taken out and pulled by horses

Pogey
relief payments by a government, sometimes in the form of vouchers for food and other essentials
Transient
A person with no fixed address, travelling from city to city during the depression looking for work
Xenophobia
a fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers
Persons Case
a court case in which the Famous Five successfully fought to have women declared "persons" under Canadian law in 1929
Balfour Report
the conclusions of the 1926 Imperial Conference that acknowledged that Canada was an autonomous community within the British Empire
Chanak Affair
British went to war against Turkey 1921, but Canada chose not to go help them
King-Byng Crisis
a situation that occurred in 1926 when Governor General Byng refused Prime Minister King's request to dissolve Parliament and call an election
Bennett's New Deal
An economic reform program designed to solve the problems of the Great Depression. Government intervention, including fairer tax systems, UI, workplace reforms, old age pensions and support for farmers
On-to-Ottawa Trek
In 1935, hundreds of single unemployed men hopped freight trains for Ottawa demanding work, wages and an end to government relief camps. The trek was stopped in Regina.
Operation Overlord
the code name for the Allied invasion of Europe at Normandy on June 6, 1944; also known as D-Day
