HSM 210 First Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Part One
What factors would we look for in a country to see if their “healthcare system” is a real “system?”

Social and cultural beliefs and value
Physical environment
Political and Legal Climate
Who pays the costs, and for what do they pay
Government taxes. Private insurers, Employers, and individuals pay for
Private Insurers Public Insurance
Cost care iniatives

How costs are controlled
Control costs by limiting medical services they will pay for by making patients wait longer.
By rationing medical services/supply

How do doctors get paid

Salaries
Capitations
Performance-based initiatives
Fee Services

Who owns the hospitals?

Non-profit Organizations
Private Organizations.
3. Public Organizations

The differing emphasis between primary and specialist care
Specialists are specific conditions that require a specialized physician to provide care, Primary care is for those who need preventative care
The differing emphasis between public health and healthcare delivery
Private Healthcare focuses on treating an individual illness and Public focuses on prevention.
Medical Education
Varies in cost, funding, and specialization requirements across countries
Out-of-pocket contributions from patients
Out-of-pocket contributions from patients

systems may require co-pays, deductibles, or direct payments, while others fully cover costs.

The role of healthcare managers

Oversee hospital operations, policy implementation, and cost management

Accessibility

Not often accessible since the U.S system makes Insurance and Primary care cost unaffordable also being that the system forces those to delay treatment until the condition becomes severe.
Measures how easily people. can get healthcare

Quality of care

Assessed by:
i. Providers Performance
ii. Patient Outcomes
iii. Safety Measure

Equity
Adequate distribution of healthcare resources
Differences in social determinants

Individual behaviors
diet, mental state, and smoking all impact health
Mental health:
Recognition, funding, and accessibility
Obesity:
Growing public health issue tied to diet, activity, and policy
Environment:
Pollution, sanitation, and climate affect public heal
Systemic prejudice:

Disparities in healthcare accessibility based on race, gender, and socioeconomic studies
Class structure:
Income inequality influences healthcare quality and access
The role of demographics

Aging population:
Older populations increase demand for healthcare and long-term care
Develop. Chronic disease
E. The “price/volume” dilemma

Moral hazard:
When insured individuals overuse healthcare because they don’t bear the full cost.
The role of “out of pocket” contributions:
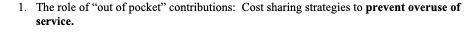
Cost sharing strategies to prevent overuse of service.
Sustainability:
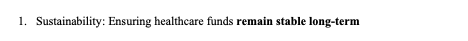
Ensuring healthcare funds remain stable long-term
The different roles that the government plays in delivering and financing of healthcare

Regulation, financing, direct service provision, and public health initiatives
The role that employers play in the financing of healthcare

Employers often provide private insurance, particularly in the U.S
The role of societal values in structuring the healthcare system
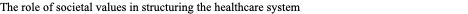
Cultural beliefs shape policies, such as universal coverage vs. market-based systems
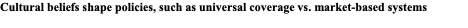
Three models for wealthy countries outside the US
Bismarck
Employer-based insurance with government regulations
Uses private health insurance plans which are financed through payroll deduction
Used in Germany, Japan, Switzerland, and some parts of Latin America
National Health Service (Beveridge)

Government-funded and operated healthcare, financed by government tax payments.
Low cost per capita, the government controls how much doctors can charge for there. Services
Used in the United Kingdom, and Spain
National health insurance
Publicly funded but privately delivered healthcare, has elements of both the Bismark and Beveridge models
i. Healthcare is private but the payer is a government-run insurance program that every citizen pays into.
Controls costs by limiting medical services they will pay for by making patients wait longer