Ap PreCal Test Prep
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
A function is increasing on an interval if...
as the input values increase, the output value increase.
A function is decreasing on an interval if...
as the input values increase, the output value decrease.
A function is concave up if......
The rates of change are increasing.
A function is concave down if......
The rates of change are decreasing.
Average rate of change of f on the interval [a,b]
f(b)-f(a)/b-a
The slope of a function at any given point gives...
the rate of change of the function at that input.
A positive rate of change indicates that the function output is....
increasing
A negative rate of change indicates that the function output is....
decreasing
Point of inflection
point on the graph where the concavity changes, indicating a maximum or minimum rate of change.
one-to-one function
A function where each input has a unique output
A relative minimum occurs when a function f...
changes from decreasing to increasing
A relative maximum occurs when a function f...
changes from increasing to decreasing
Absolute minimum
the least output of a function
Absolute maximum
the greatest output of a function
Multiplicity
the number of times a factor occurs in a polynomial function
A polynomial of degree n has...
exactly n complex zeroes (real or imaginary) and at most n-1 extrema
If x=a is a real zero of a polynomial with an odd multiplicity , then...
The graph of the polynomial passes through the x-axis at x=a (slide for greater than 3)
If x=a is a real zero of a polynomial with an even multiplicity , then...
The graph of the polynomial bounces and is tangent at the x-axis at x=a
Odd Funtion
f(-x) = -f(x) rotational symmetry around the origin.
even function
f(-x)=f(x) symmetry across the y-axis.
End behavior of a polynomial f with an even degree and a negative leading coefficient
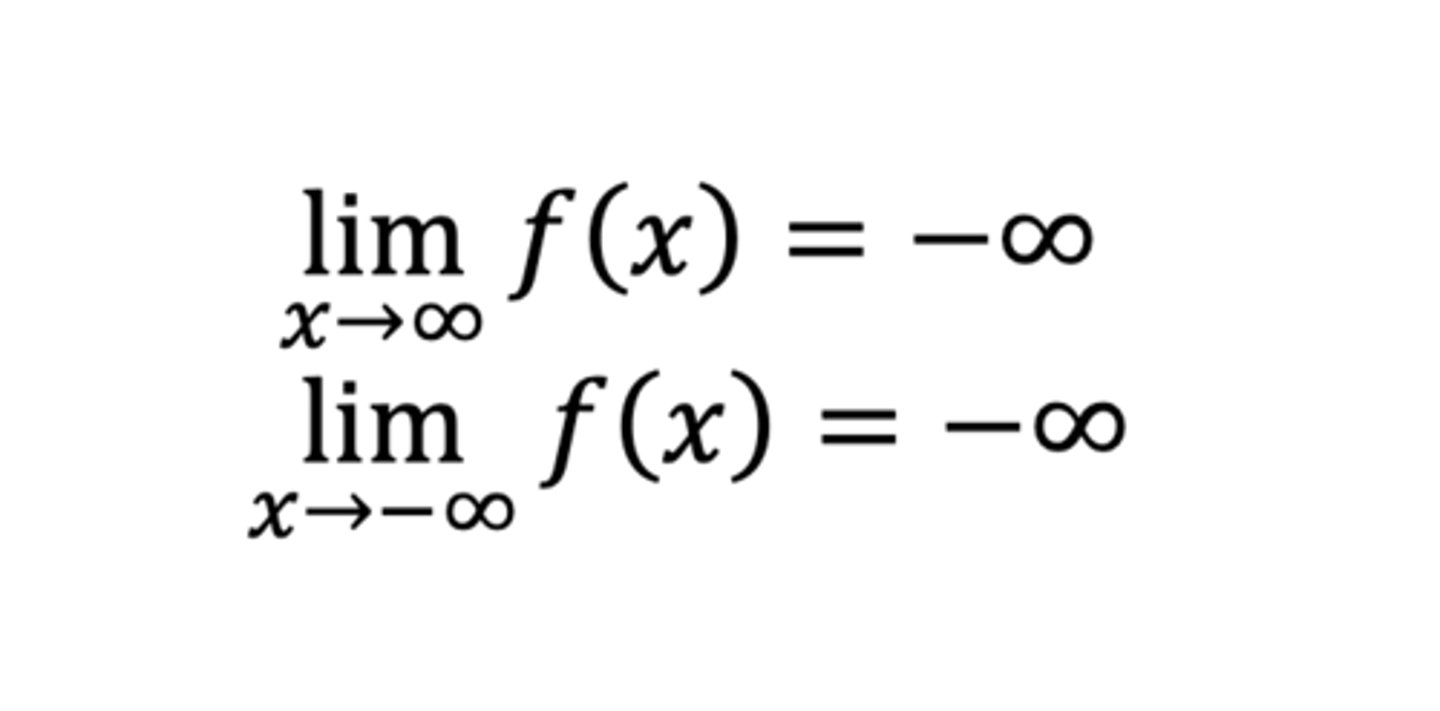
End behavior of a polynomial f with an odd degree and a positive leading coefficient
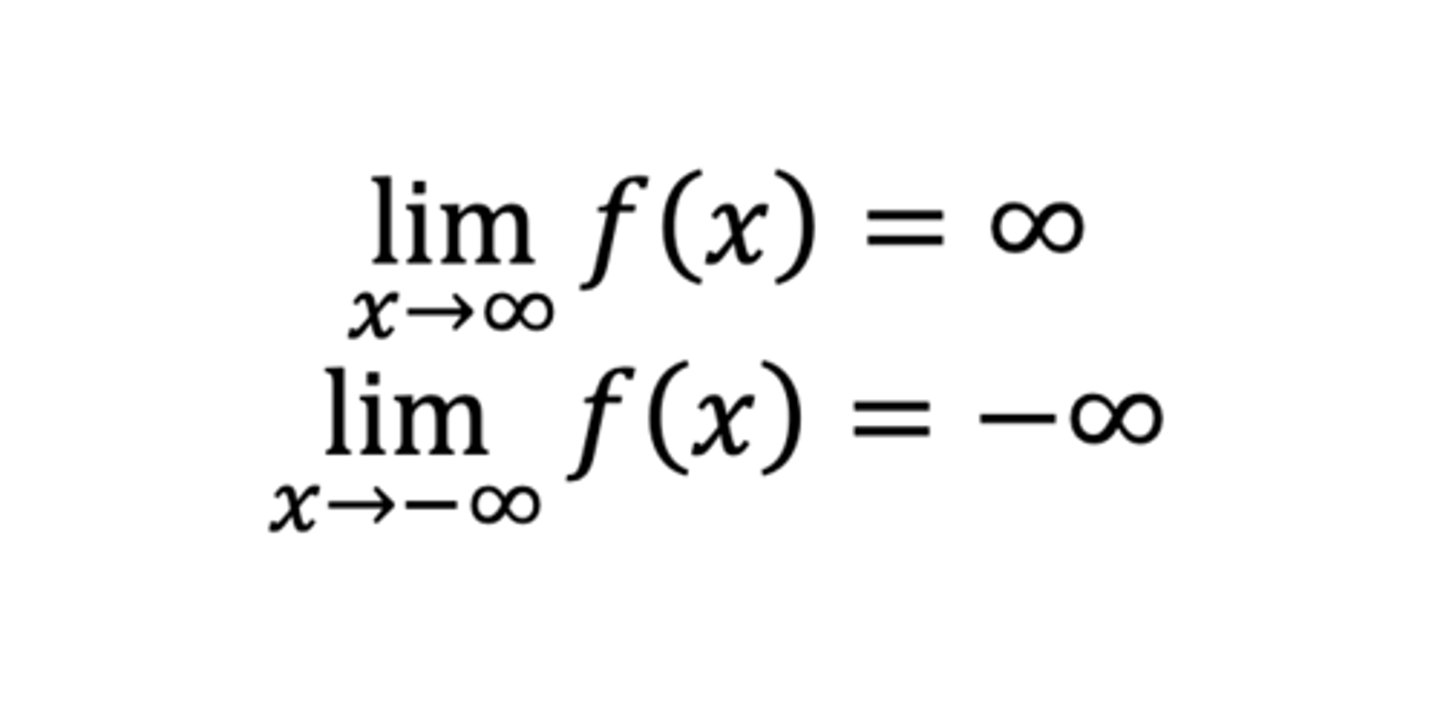
End behavior of a polynomial f with an odd degree and a negative leading coefficient
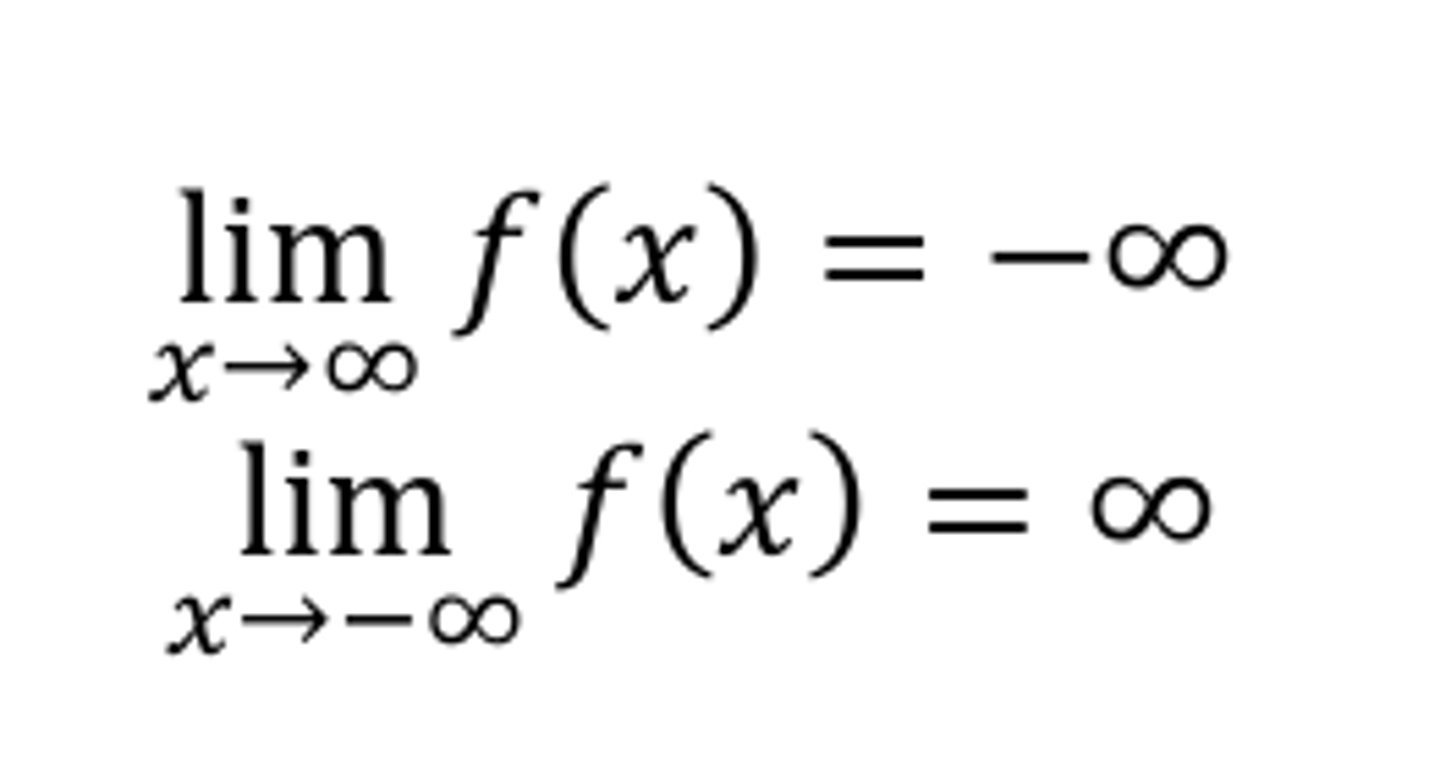
End behavior of a polynomial f with an even degree and a positive leading coefficient
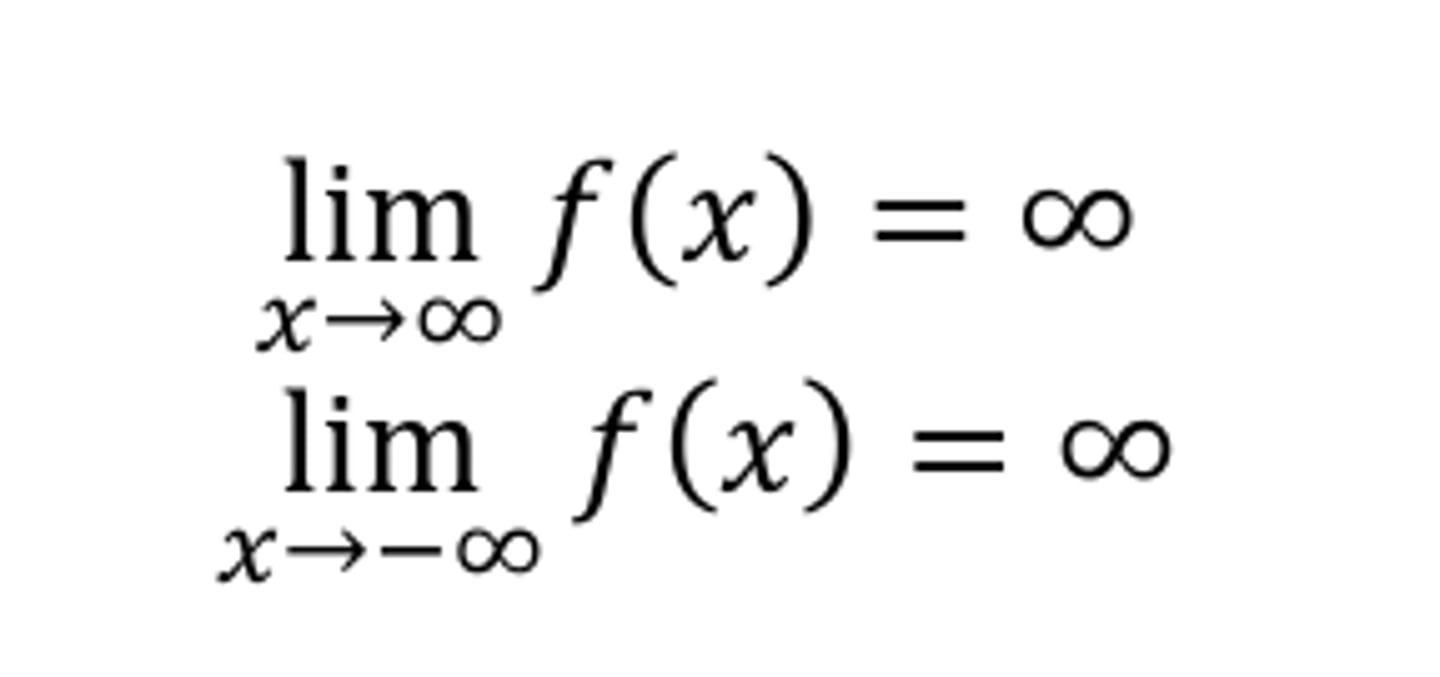
If a rational function, f, has a horizontal asymptote at y=b, then...
Then both end behaviors approach b without bounds.
A rational function has a zero at x=a if ...
x=a is a zero of the numerator but NOT the denominator
For rational functions, a slant asymptote occurs when...
the degree of the numerator is exactly one more than the degree of the denominator
A function f(x) = ab^x demonstrates exponential growth if...
b>1
A function f(x) = ab^x demonstrates exponential decay if...
0<b<1
Key features of log where the base is greater than 1
Domain: x>0, range: All Real Numbers, VA @ x=0, increasing and concave down
Key features of exponential where the base is greater than 1
Domain: All real numbers, range: y>0, HA @ y=0, increasing and concave up
e^a(ln)b
b^a
logb(1)

logb(b)

logb(mn)
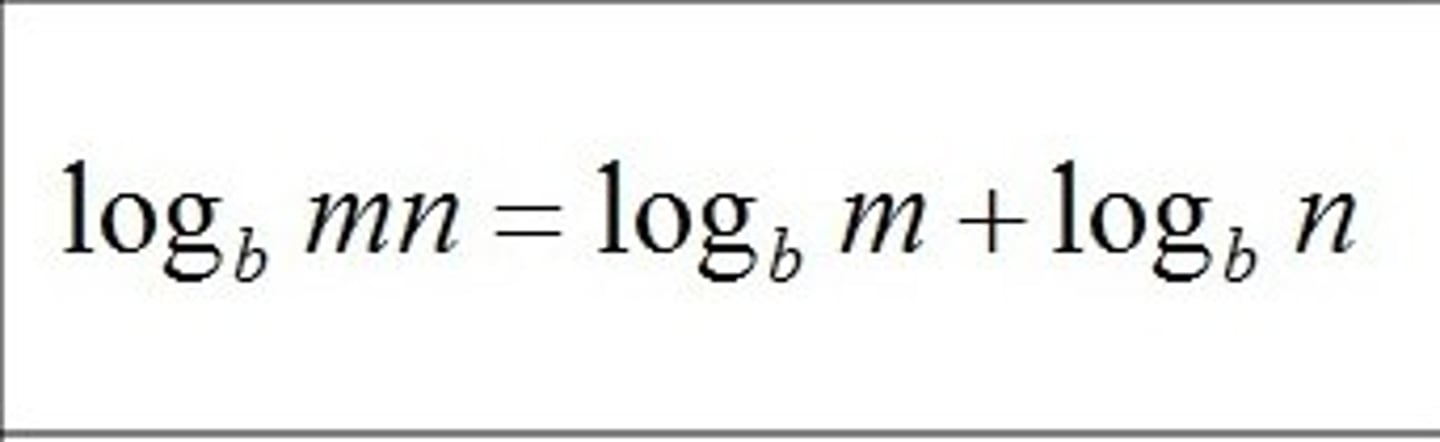
logb(m/n)
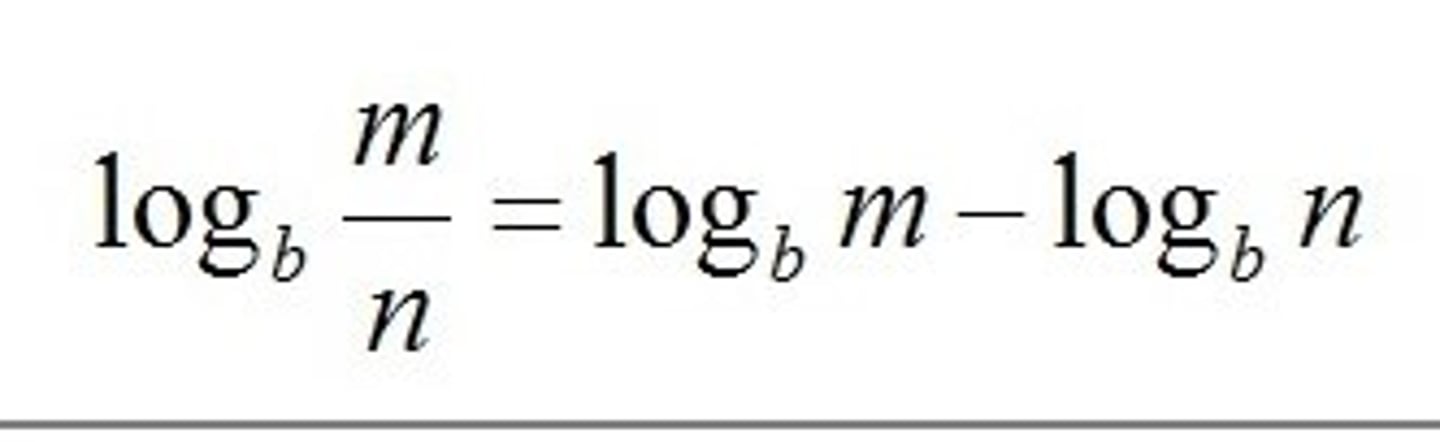
Pythagorean Identities
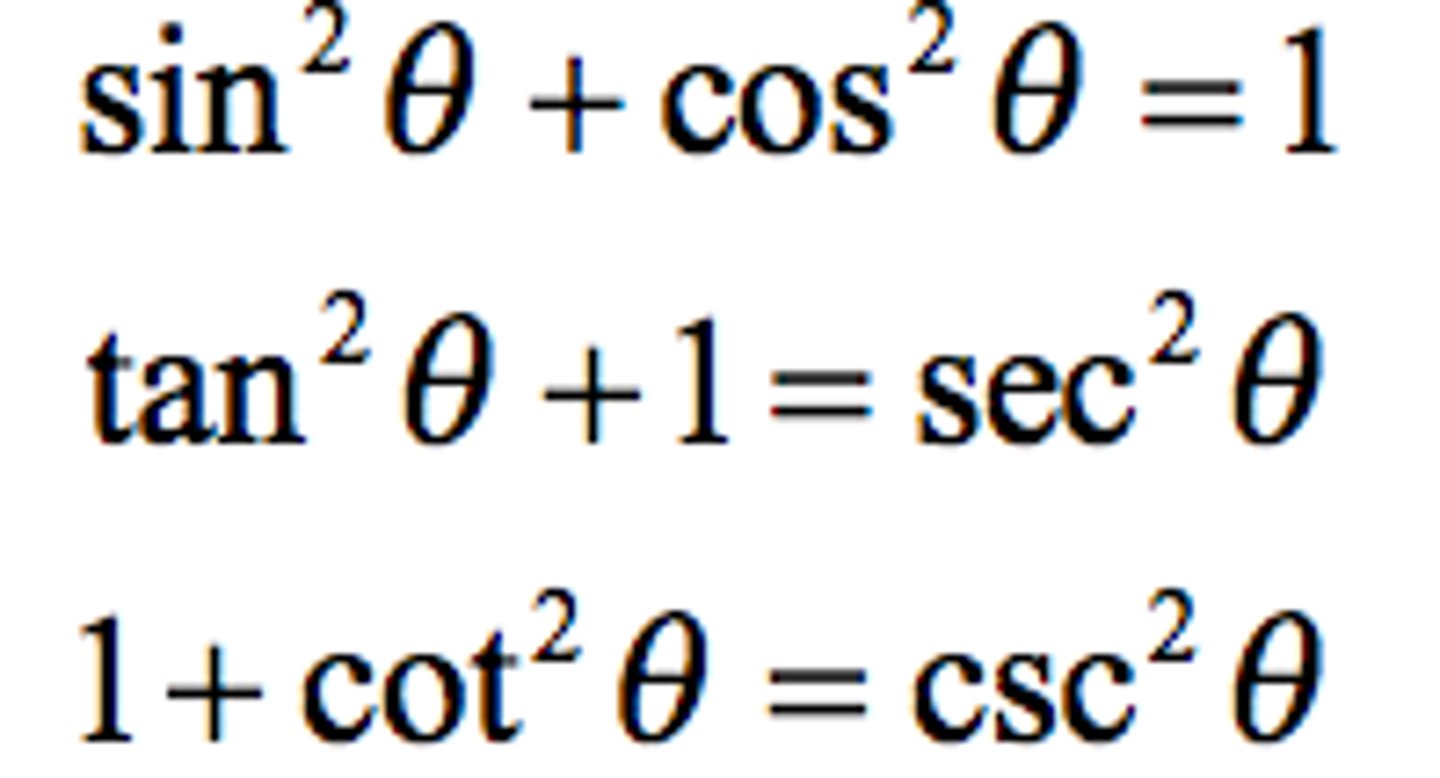
Reciprocal Identities
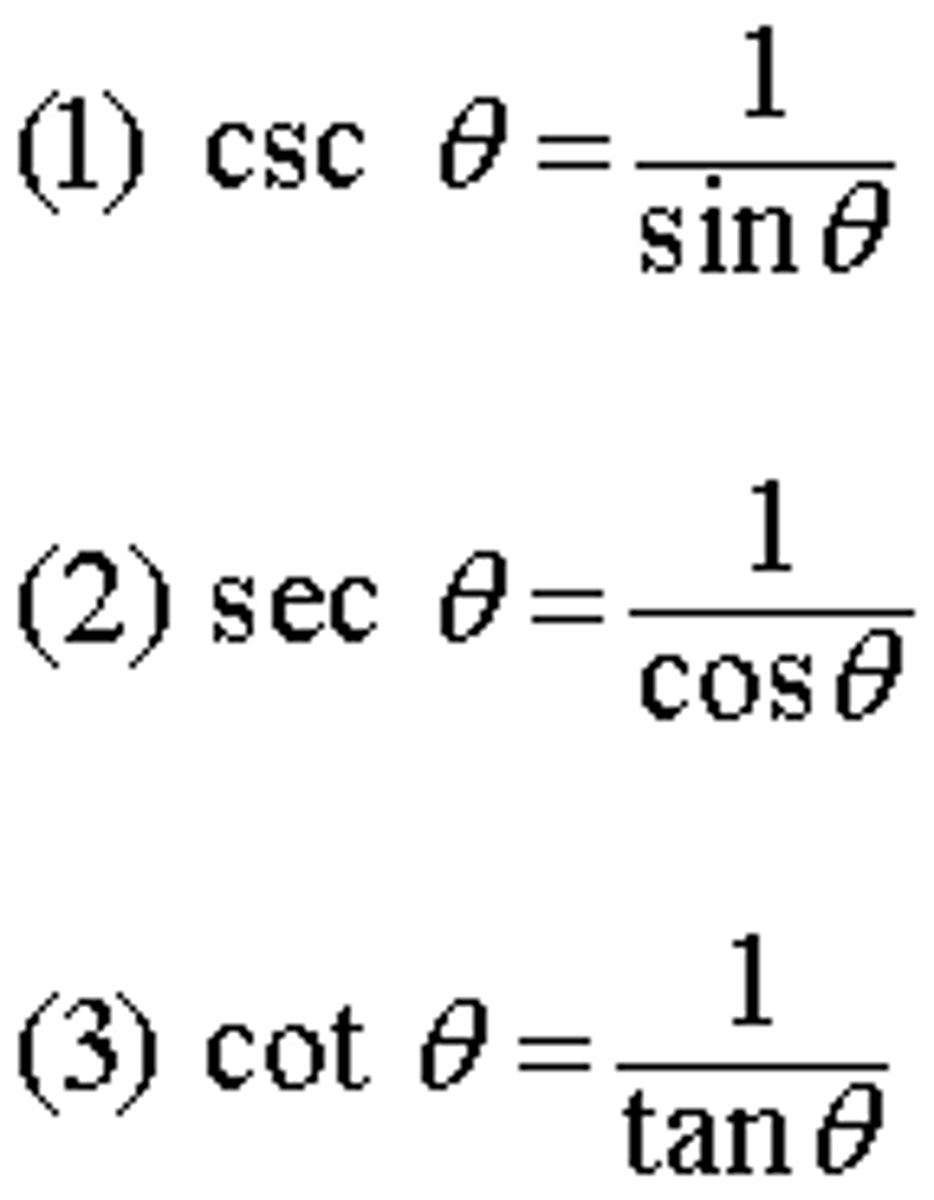
cos(A+B)
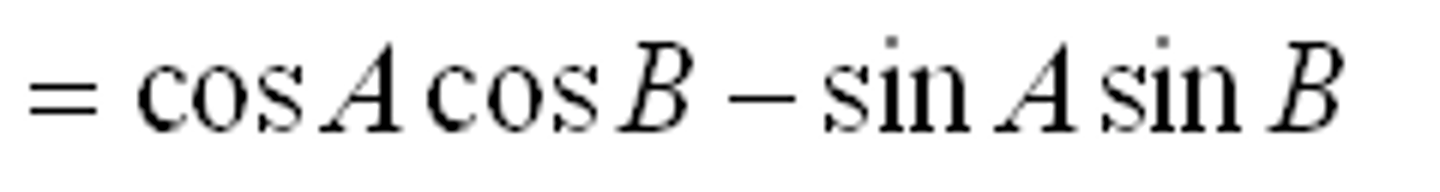
cos(A-B)
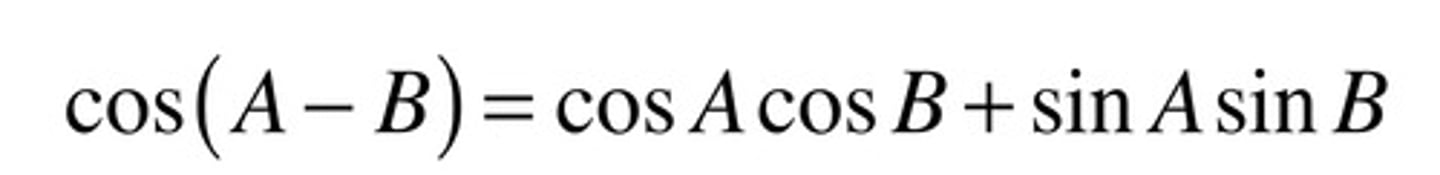
sin(A+B)
sinAcosB+cosAsinB
sin(A-B)
sinAcosB-cosAsinB
cos(2x)
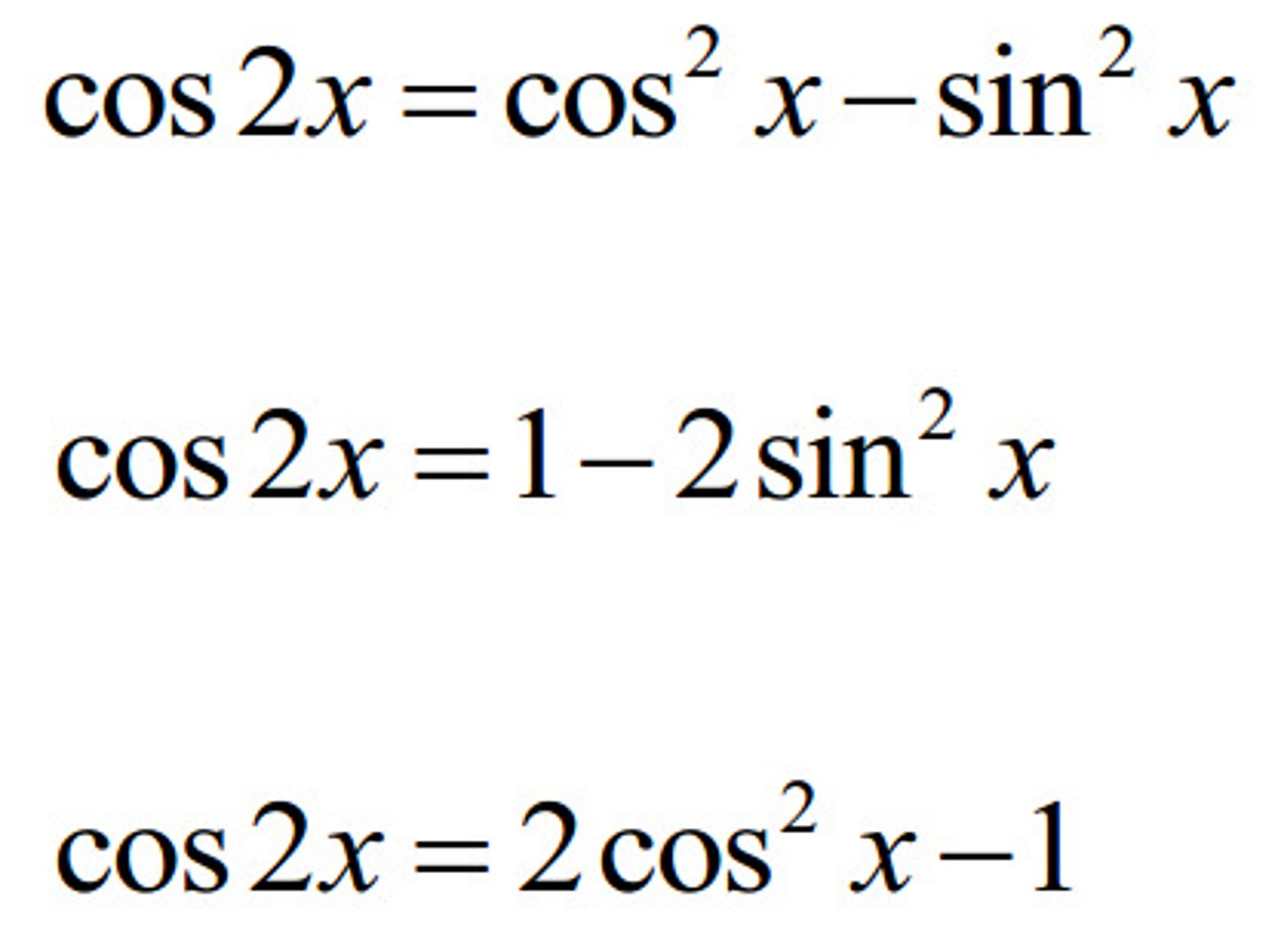
sin(2x)
2sinxcosx
Given (x, y) in Cartesian coordinates, determine polar coordinates, (r, theta)
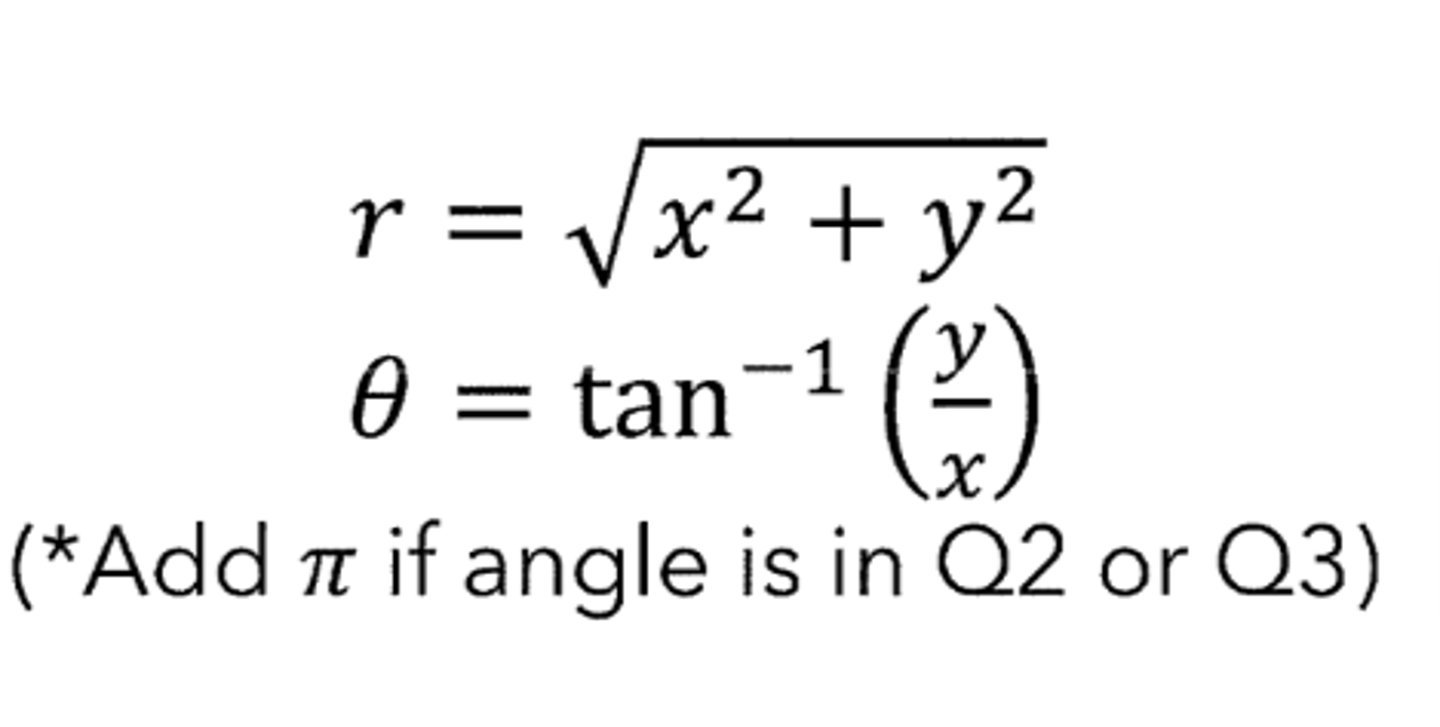
Given (r, theta) in polar coordinates, determine Cartesian coordinates, (x, y)
x = rsin(theta), y = rsin(theta)
A polar function r = f(theta) is increasing if...
as theta increase, r increases
A polar function r = f(theta) is decreasing if...
as theta increase, r decreases
The distance between a point on a polar function r=f(theta) and the origin is increasing if...
r is positive and increasing or r is negative and decreasing
The distance between a point on a polar function r=f(theta) and the origin is decreasing if..
r is positive and decreasing or r is negative and increasing
A function is linear if over equal-length input intervals, output values...
change by a constant amount
A function is quadratic if over equal-length input intervals, output values...
change by a constant second difference
A function is exponential if as input values change ________________, output values change _________________.
additively; multiplicatively
A function is logarithmic if as input values change ________________, output values change _________________.
multiplicatively; additively
The average rates of change on a linear function are...
constant
The average rates of change of a quadratic function...
are CHANGING at a constant rate or follow a linear pattern.
tan(theta) gives the __________ of the terminal ray of theta.
slope
Domain and range of y = arcsinx

Domain and range of y = arccosx

Domain and range of y = arctanx

f(x)= tan x has vertical asymptotes at ....

f(x)= cot x has vertical asymptotes at ....
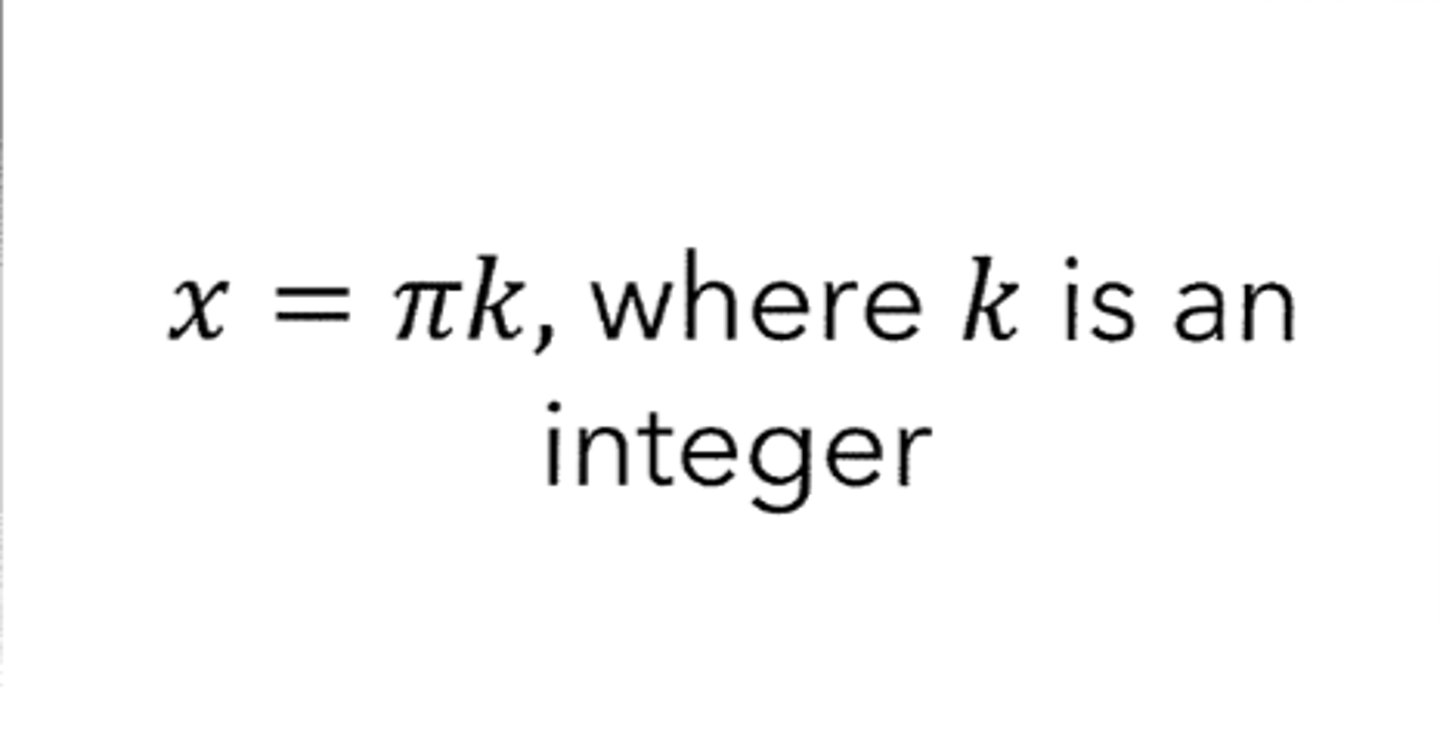
Determine the amplitude, period, midline, and phase shift of f(x)=asin(b(x-c))+d
Amplitude: |a|
Period: 2pib (flip answer)
midline: y=d
phase shift: c units to the right
y = tan(bx) has a period of
pi*b
f(x) + c
vertical translation of c units
f(x-c)
horizontal translation of c units
cf(x)
vertical dilation of c
f(cx)
Horizontal dilation by a factor of 1/c
-f(x)
reflection over the x axis
f(-x)
reflection over y-axis
Pascal's Triangle
What does the constant e represent?
the base rate of growth for all continually growing processes, e~2.718
A positive residual indicates that the predicted value is an _________________________.
underestimate
A negative residual indicates that the predicted value is an _________________________.
overestimate