Gymnosperms
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Seed plants are____? And what do they produce?
heterosporous, that produce megaspores and micro spores that give rise to megagameteophyte and a mircogametophytes
What is the definition of a seed?
A matured ovule,( which is a structure that develops into the seed) that contains the embryo
In seed plants the __ is called the nucellus
Megasporangium
What does the immature ovule consist of?
Megasporanguim, which is the structure in which megaspores are produced by one to two additional layers of tissue(integumments)
What are the events that led up to the evolution of an ovule?
Retention of megaspores within a megasporangium, which is fleshy and called the nucellus in seed plants (Megasporanguim no longer releases the spores)
Reduction in the number of megaspores mother cells in each Megasporanguim to one
Survival of only one of the 4 gametophyte megaspores produced by the mother cells in each, leaving a megaspore in the megasporangium
Formation of a female gamtophyte inside a single functional megaspore- female no longer free living and is retained in the Megasporanguim
Development of the embryo(young sporophyte) within the female gamtophyte retained in the megasporangium
Formation of a integumentary that completely envelops the megasporangium, expect for the opening called the micropyle
Modification of the apex of the megasporangium to receive mircospores or pollen grains
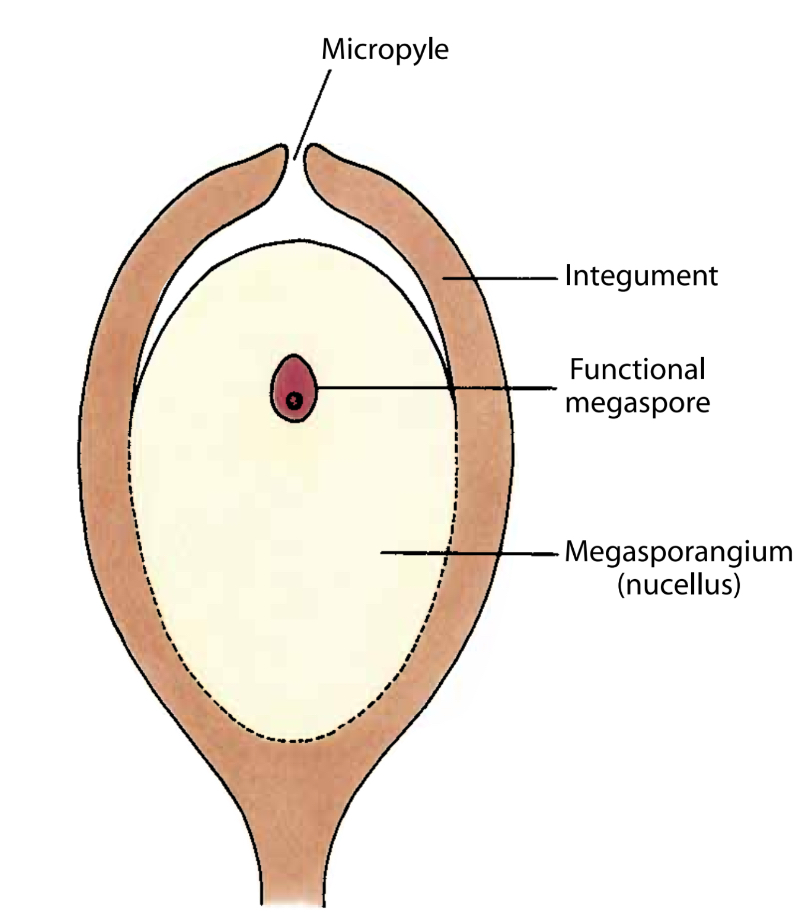
Just before fertilization, a gymnosperm ovule contains..?
The nucellus contains a megagametophyte comprised of nutritive tissue and archegonia
With the evolution of the ovule, the unit of dispersal is shifted from the megaspore to the…?
The seed, the embryo containing megasporangium with integuments.
A seed consists of a ___, ___, and a ___.? And how does this occur?
Embryo, stored food and a seed coat.
When the ovules are ready for fertilization the nucellus that contains a megagametophyte that has nutritive tissue and archegonia
After fertilization the integumentary develop a seed coat, the embryo develops within the seed before dispersal
What are the 4 phyla of gymnosperm (seed bearing plants)
Coniferphyta
Cycadophyta,
Gnetophyte
Ginkophyta

What are the characteristics of a Progymnosperms?
Between intermediate between those of seedless vascular trimerophytes and those of seed plants.Produced secondary xylem (wood)
Presence of a Bifacial Vascular cambium ( produced both secondary xylem and phloem and is believed to have evolved first.
A eustele evolved in this group

What is a micropyle
Opening in a Integument, its a formation of a integument that completely envelops themegasporangium
What is the characteristics of Bennetitales- which are an extinct gymnosperms
Mesozoic gymnosperms that disappeared during the Cretaceous
Palm-like leaves that resemble living cycads. Presence of flowerlike reproductive structures that were bisexual in some species
Some believe that are members of the same evolutionary line as angiosperms
In gymnosperms, the microgametophytes develop as what…?
Pollen grains, water is not required from transport the sperm to the eggs, the pollen grain is transferred (by wind) to the vicinity of a megagametophyte within and ovule
What phylum of gymnosperms produce nonmotile sperm?
Coniferphyta and gntophytes
Which group has a pollen tube haustorial?
Cycads and Ginko
After pollination, the endosporic microgametophyte produces a tubular outgrowth called what…?
Pollen tube
Characteristics of Coniferophyta
Numerous and widespread comprise of 70 genera with include 630 species
Tallest Vascular plant redwood
Drought resistant features
Woody plants that have needlelike leaves or scale-like leaves that are often covered in a waxy cuticle
Includes pine, firs, spruces, larches, hemlocks of Pinaeae Crypress and Junipers of Cupressaceae (associated with evergreen)
What are the characteristics of pine leaves?
Arrangement of leaves that is unique among living conifers, needlelike leaves spirally arranged and borne singly on the stems
Shrunken Stomata
After a year or two of growth it Produces its leaves in bundles called facicles, which each contain a specific number of leaves. Surrounded by transfusion tissue
What is the longest lived tree?
The Bristlecone Pine (pines longaeva)
In the pine life cycle, meiosis occurs in the….?
Microsporocytes—> undergo meiosis and produces four haploid micro spores
In pines, the immature gametophyte consists of?
Two prothallus cells, a generative cell and a tube cell
Fascicles in Pine do what?
They are wrapped at the base by a series of small scale like lives, they are short shoots in which the activity of the apical meristem is restricted
Determinate branch(restricted growth)
What is the seed-scale complex of an ovule consist of?
The ovuliferous scale with bears two ovules and a subtending sterile bract
The seeds of pines are often shed when?
The autumn of the second year following the initial appearance of the cones and pollination
In the yews family taxaceae they produce what?
A solidarity ovule is borne in a high reduced cone and a surrounded by a fleshy, cup like structure (Aril)
Which phylum of gymnosperms have palmlike plants that are found in tropical and subtropical regions?
Cycadophyta
Which gymnosperms in a Cycadophyta native to the United States?
Zamia Intergrifolia, native to Florida
In a gneotyphye characterized by two strap shaped leaves growing from a massive woody stem, what species is this?
Welwitschia