Topic 17 - Acyl chlorides:
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
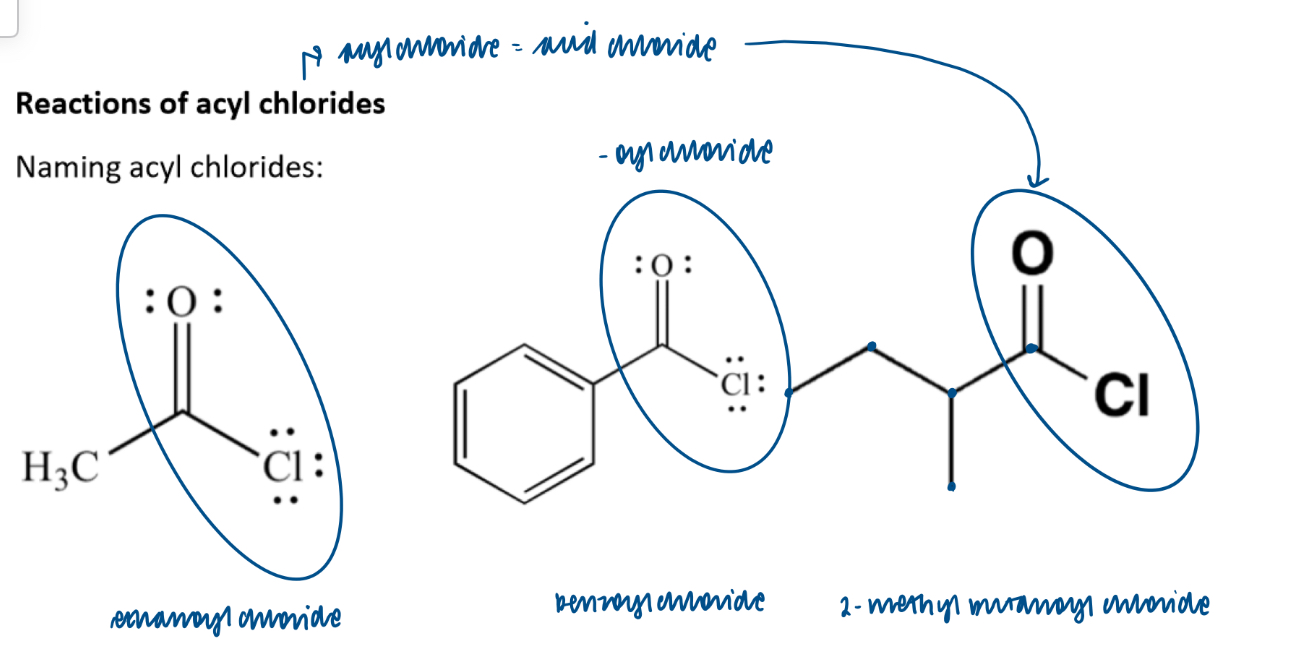
Acyl chlorides - naming:
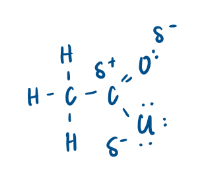
Explain why acyl chlorides are so reactive:
2 polar bonds (C=O and C-Cl)
C-Cl bond is quite weak as it is a large atom so a longer bond
Therefore extremely reactive compound
Formation of acyl chlorides:
add PCl5 to carboxylic acids
As PCl5 is added - steamy fumes of HCl is produced (which turn damp blue litmus paper red)
HCl is a toxic gas therefore reaction should be carried out in a fume cupboard
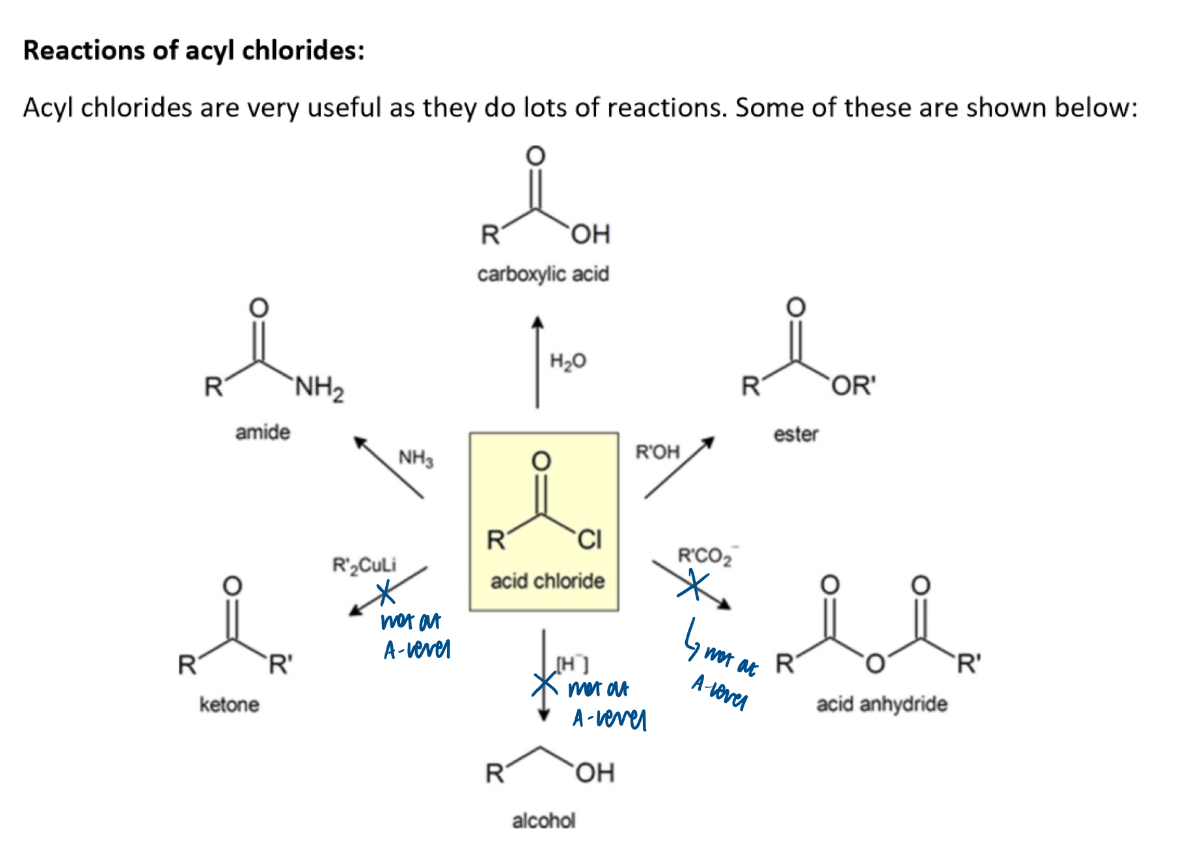
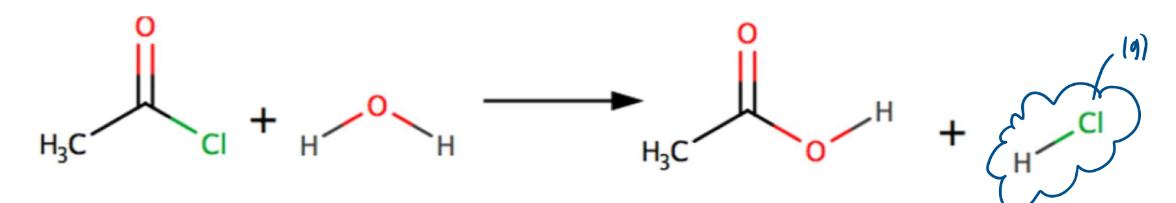
Reaction of acyl chlorides with water:
makes a carboxylic acid (and HCl)
Steamy fumes which turn damp blue litmus paper red
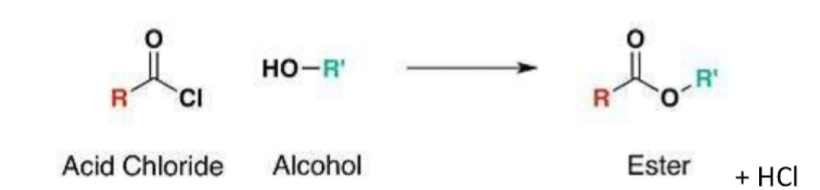
Reaction of acyl chlorides with alcohols:
forms an ester (and HCl)
Same reaction as with a carboxylic acid (acyl chloride used in place of acid)
However - acyl chlorides are more reactive than carboxylic acids, therefore acid catalyst is not needed in order to progress the reaction
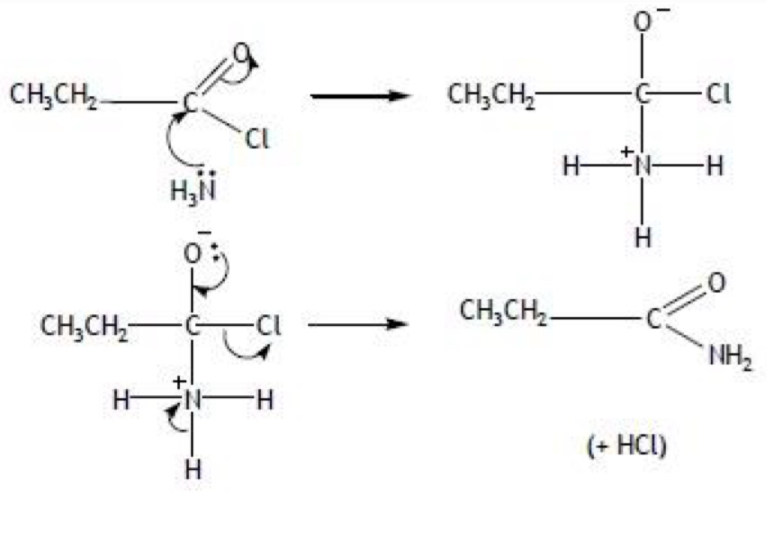
Reaction of acyl chlorides with ammonia:
forms an amide (and HCl / NH4Cl)
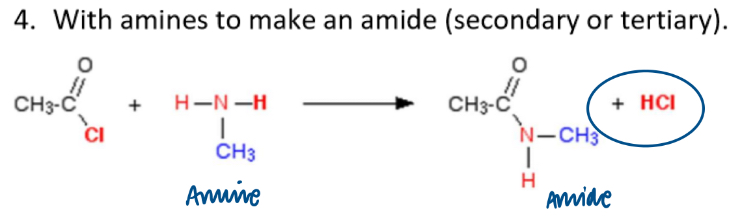
Reaction of acyl chlorides with amines:
forms an amide (secondary or tertiary) (and HCl)
Summary of reactions of acyl chlorides: