Fungi, Invertebrates, Vertebrates & Plant Nutrition
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering fungi, animal diversity, chordate features, and plant nutrition topics from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Extracellular Digestion (Fungi)
Process in which fungi secrete enzymes outside their bodies to break down food, then absorb the dissolved nutrients.
Mycelium
Interwoven mass of fungal hyphae that forms the main vegetative body and maximizes surface area for absorption.
Hypha (plural: Hyphae)
Microscopic, thread-like fungal filament; many hyphae collectively make up a mycelium.
Plasmogamy
Fusion of the cytoplasm of two fungal cells during sexual reproduction, producing a dikaryotic stage.
Karyogamy
Fusion of two haploid nuclei in fungi, resulting in a diploid nucleus that undergoes meiosis to form spores.
Dikaryotic Cell
Fungal cell containing two genetically distinct nuclei (n + n) that have not yet fused.
How fungi contribute to Nutrient Cycling
Fungi play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by decomposing organic matter, breaking down complex organic substances into simpler compounds, which are then returned to the soil, enriching it and supporting plant growth.
Fungal Fermentation
Use of fungi (e.g., yeast) in food production such as bread, beer, cheese, and soy products.
Chytrid Fungus
Aquatic fungus causing global amphibian declines by infecting skin and disrupting osmoregulation.
White-Nose Syndrome and impact
White-Nose Syndrome is a devastating fungal disease affecting hibernating bats, caused by the fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans. It disrupts their hibernation and leads to significant population declines across North America.
“Zombie Ant” Fungus
Ophiocordyceps species that infect ants, alter behavior, and ultimately kill the host to release spores.

Porifera (Sponges)
Basal animal phylum with porous bodies, no true tissues, and filter feeding via choanocytes.
Spicule
Structural skeletal element (silica or calcium carbonate) embedded in sponge body for support and defense.
Sessile (Sponges)
Lifestyle in which adult sponges remain anchored to a substrate and do not move.
Self-Assemblage (Sponges)
Ability of dissociated sponge cells to re-aggregate and form a functional sponge body.
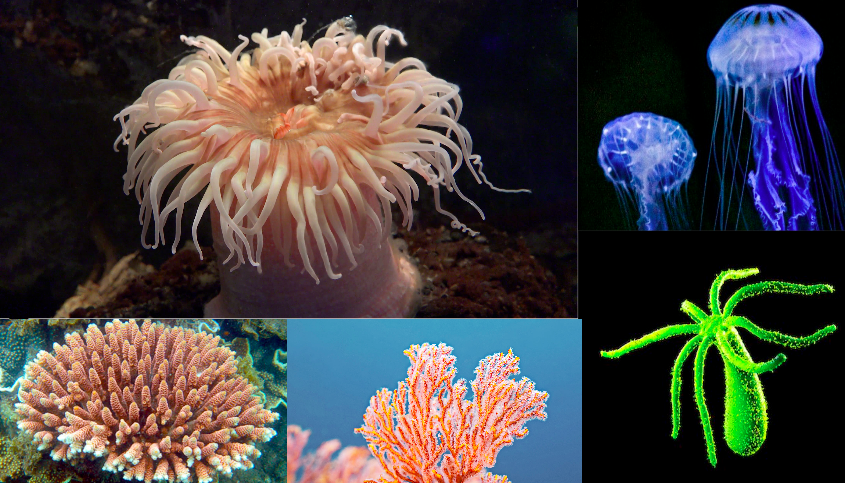

Cnidaria
Phylum including jellyfish, corals, and hydras, characterized by radial symmetry and a gastrovascular cavity. Major evolutionary steps with muscles and nerve net.
Radial Symmetry (Cnidaria)
Body plan arranged around a central axis, allowing interaction with environment from all directions.
Gastrovascular Cavity
Single opening digestive compartment in cnidarians and flatworms that functions in digestion and circulation.
Cnidocyte
Specialized stinging cell of cnidarians containing a nematocyst for defense and prey capture.
Nematocyst
Coiled, venomous harpoon within a cnidocyte that rapidly everts to sting prey or predators.
Polyp
Sessile, tubular cnidarian body form with mouth and tentacles facing upward (e.g., coral, sea anemone).
Medusa
Free-swimming, bell-shaped cnidarian form with mouth and tentacles on the underside (e.g., jellyfish).
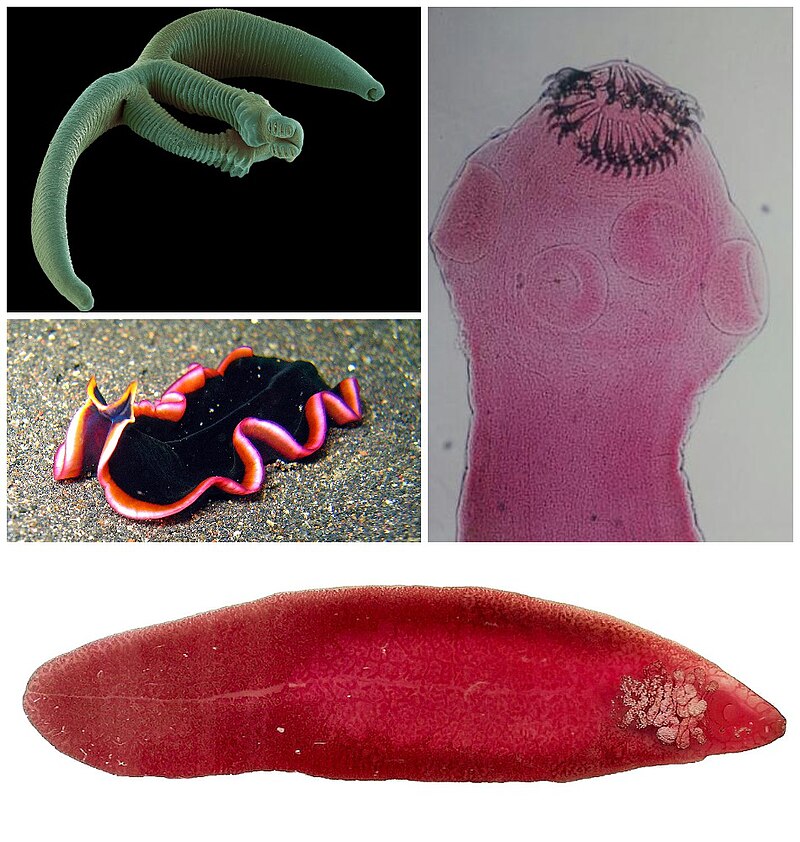
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
Acoelomate phylum with flattened bodies, bilateral symmetry, and a gastrovascular cavity.
Tapeworm (Cestode)
Parasitic flatworm lacking a digestive tract; transmitted via ingestion of cysts in under-cooked meat.
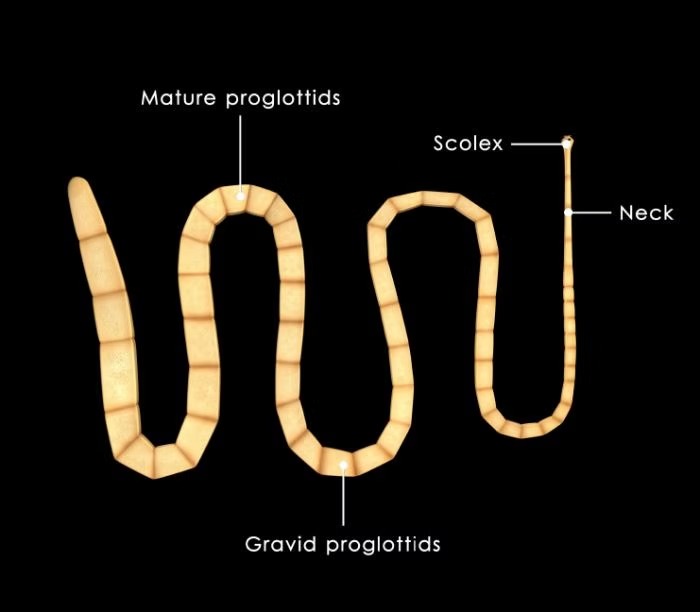
Proglottid
Repetitive reproductive segment of a tapeworm that produces eggs; not true segmentation like annelids.

Nematoda (Roundworms)
Phylum of unsegmented, pseudocoelomate worms with complete digestive tracts and cuticle molts.
Hydrostatic Skeleton
Support system where fluid-filled pseudocoelom provides rigidity for muscle action (seen in nematodes).
Pinworm
Enterobius vermicularis; intestinal nematode transmitted by fecal–oral route, common in children.
Heartworm
Dirofilaria immitis; mosquito-borne nematode infecting the hearts of dogs and cats.

Annelida
Segmented worms (earthworms, leeches) with true coelom and closed circulatory system.
Segmentation Advantage
Repeated body units allow localized muscle control, redundancy, and specialization of segments.
Earthworm
Soil-dwelling annelid that aerates soil, increases nutrient availability, and improves drainage.
Leech Therapy
Medical use of leeches (Hirudinea) for anticoagulation, reducing blood pooling, and tissue graft success.
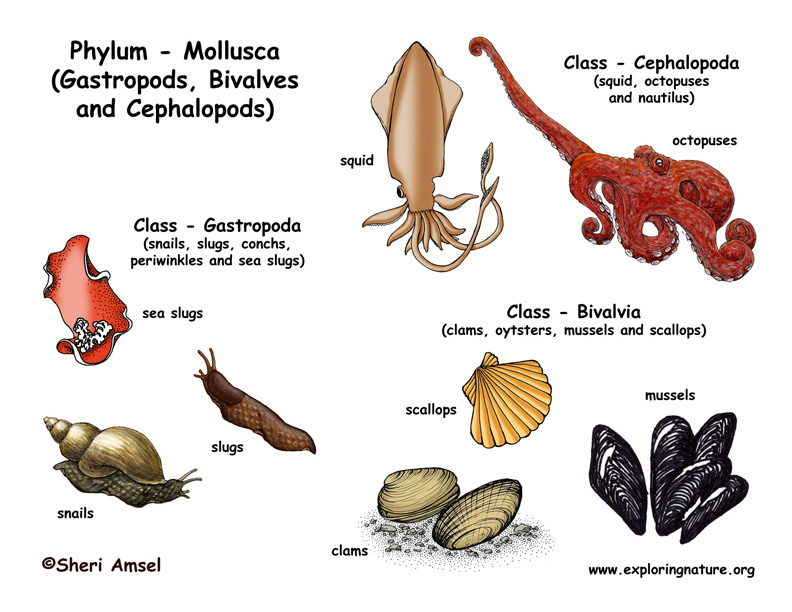
Mollusca
Phylum with soft bodies, muscular foot, visceral mass, and mantle; includes snails, clams, octopuses.
Gastropoda
Molluscan class of snails and slugs; undergo torsion and often have a single spiral shell.
Cephalopoda
Molluscan class of octopuses, squids, cuttlefish; characterized by tentacles, beak, and complex brains.
Bivalvia
Molluscan class with two-part hinged shells (clams, oysters) and filter-feeding gills.
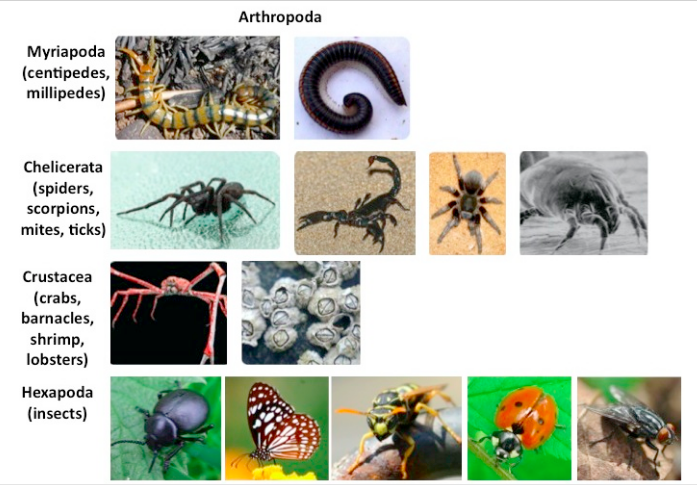

Arthropoda
Largest animal phylum with segmented bodies, jointed appendages, and chitinous exoskeleton.
Insect Success Adaptations
Flight, metamorphosis, waterproof cuticle, specialized mouthparts, and high reproductive rate.

Echinodermata
Marine phylum with pentaradial symmetry as adults, calcareous endoskeleton, and water vascular system.
Water Vascular System
Network of fluid-filled canals in echinoderms that powers tube feet for movement, feeding, and respiration.
Tube Foot
Hydraulic appendage of echinoderms used for locomotion, adhesion, and gas exchange.
Chordata Key Traits
Dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, pharyngeal slits, and post-anal tail at some life stage.
Tunicate
Sessile marine filter feeder that retains chordate features (esp. notochord, nerve cord) in larval stage.
Cartilaginous Fish
Sharks, rays; differ from bony fish by having a cartilaginous skeleton and lack of swim bladder.
Bony Fish Groups
Ray-finned and lobe-finned; lobe-fins are pivotal for tetrapod evolution.
Amphibian Land Adaptations
Limbs with digits, lungs, cutaneous respiration, and reproduction tied to water (eggs without shell).
Reptile Land Adaptations
Amniotic egg, keratinized scales, lungs with expandable rib cage, internal fertilization.
Bird (Aves) Adaptations
Feathers, hollow bones, endothermy, four-chambered heart, and high metabolic rate for flight.
Plant Macronutrient
Essential element (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S) required in large amounts for plant growth and function.
Nutrient Deficiency Symptoms
Visible plant disorders such as chlorosis (N), purple leaves (P), or scorched margins (K).
Root System
Underground plant organ responsible for anchorage, water and mineral uptake, and storage.
Shoot System
Above-ground plant parts (stems, leaves, flowers) responsible for photosynthesis and reproduction.
Dermal Tissue
Protective outer covering of plants, including epidermis and cuticle.
Vascular Tissue
Conductive plant tissue consisting of xylem and phloem for transport of water, minerals, and sugars.
Ground Tissue
Plant tissue for photosynthesis, storage, and support.
Xylem
Vascular tissue transporting water and minerals upward from roots via tracheids and vessel elements.
Phloem
Vascular tissue that moves sugars and other organic products from sources to sinks (bidirectional).
Cohesion-Tension Mechanism
Process where water is pulled up xylem by transpiration, cohesion between water molecules, and adhesion to walls.
Root Pressure
Positive pressure in roots generated by active mineral uptake, pushing xylem sap upward (minor contributor).
Stomata
Pores in leaf epidermis flanked by guard cells that regulate gas exchange and water loss.
Guard Cell
Specialized epidermal cell that changes turgor to open or close a stoma.
Cuticle (Plant)
Waxy layer on epidermis reducing water loss and providing protection.
Adhesion (Water Transport)
Attraction of water molecules to xylem cell walls aiding upward movement.
Cohesion (Water Transport)
Attraction between water molecules that maintains a continuous column in xylem.