HIGHWAY Q2
1/270
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Modules 4-6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
271 Terms
Highway Design
Geometric + Structural
AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials)
Is a non-profit association representing highway and transportation departments in the 50 states of America, the District of Columbia and Puerto Rico
Its primary goal is to foster the development, operation and maintenance of an integrated national transportation system.
Clear information and guidance through a variety of road signs & Avoiding abrupt changes in the traffic as well as the road standards
Drivers expect highway agency to provide them with:
BASIC CONSIDERATIONS ON GEOMETRIC DESIGN OF HIGHWAYS
Must be suitable for the traffic volume
Must be consistent and mist avoid surprise changes in alignment, grade and distance
Must be pleasing to the user and those who live along with it
Must be complete
Should be as simple as possible from the standpoint of the builder
Should be maintained at the least cost
Must be safe
Road Network
Composed of various types of roads, each of which performs a particular service in facilitating vehicular travel between points of trip origin and destination.
Consideration for Classification
Legal control
surface type
function
geometric elements
location
traffic volume
Urban Roads
Principal arterial/ freeways/ expressway
Minor Arterial
Collector Street
Local Street
Rural Roads
Principal arterial/ freeways/ expressway
Major and Minor Arterial
Collector Street
Local Street
Freeways
Through movement exclusively
Surface Arterials
Through movement primary and some live accessCol
Collectors
Traffic movement to higher rank roads, access to abutting properties
Local Roads
Access to abutting land and local traffic movement
Philippine Road System
National Road
Provincial Road
City Road
Municipal Road
Barangay Road
Tourism Road
Farm to Market Road
Highway Capacity
Maximum number of vehicles that are reasonably expected to pass a given point over a given number of time
Measured in terms of number of vehicles per hour (veh/hr)
As. the volume of traffic approaches capacity, the average speed is markedly reduced
Depends on the average length of vehicles and the average spacing of moving vehicles which depends on the reaction time of the driver
Reaction Time
period of time that elapsed before muscular reaction occurs
Perception Time
interval of time required before reaction begins
Perception time + reaction time=
2.5 seconds
Highway Capacity
v/s (where s=v(t), t=2.5s then + overall length of design vehicle)
Design Hourly Volume (one way)
ADT (planned traffic) x K/100
Design Hourly Volume (two way)
ADT (planned traffic) x K/100 x D/100
DHV as a percentage of ADT for different types of roads as recommended by AASHTO:
Rural roads – 15%
Recreational roads – 35%
Urban roads – 8%
Design Speed
The speed determined for design and correlation of the physical feature of a highway that influences vehicles operation
It is the maximum speed that can be maintained over a specified section of the highway when weather and traffic conditions are so favorable that the design features (tightness and super elevation of curves, sight distance, and grade) of the highway govern
Selected to achieve a desired level of operation and safety on the highway
Level
Relatively flat
Horizontal and vertical sight distance are generally long and can be achieved without much construction difficulty or major expenses
Rolling
•Natural slopes that often rise above and fall below the highway grade with occasional steep slopes that restrict the normal vertical and horizontal alignments
Mountainous
•Sudden changes in ground elevation in both the longitude and transverse directions
•Requires hillside excavations to achieve acceptable horizontal and vertical alignment
Design Vehicles
Used to determine critical design features such as radii at intersections and turning roadways as well as highway grades
Passenger cars, trucks, trailers, buses, motorcycles, etc.
Principal Elements
•Pavement
•Travel lanes
•Shoulders
• Median
Marginal Elements
•Curbs
•Sidewalks
•Drainage channels and side slopes
•Traffic barriers
•Frontage roads
•Noise control
•Roadside control
•Pedestrian crossings
•Curb-cut ramps
•Bicycle facilities
•Bius turn outs
•Park and ride facilities
Traffic Lane
portion of the pavement allotted for the use of single line of vehicles
Cross Slope
slope of the surface of a pavement measured at right angles to the horizontal alignment
Steeper slope are strongly recommended to flow rainwater away more rapidly reducing the water thickness on the road pavement
TRAFFIC LANE / TRAVEL LANE
Widths usually vary from 2.7m to 3.6m
3 or 3.3m – on 2-lane, 2-way rural roads / low speed facilities
2.7m on low traffic urban areas with extreme right-of-way concerns
DESIRABLE WIDTH IS 3.65 meters.
All roads should be designed to accommodate trucks, buses and passenger cars with safety and convenience
Minimum width of traffic lane depends upon the width of the design vehicle and upon the lateral clearance between passing vehicles and clearances from abutments or overpasses or from curbs and gutter
Total Width of the highway
= 𝑠𝑢𝑚 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑤𝑖𝑑𝑡ℎ 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐 𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑒𝑠 𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑑 + 𝑖𝑠𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑠 + 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑏𝑠 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑔𝑢𝑡𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑠 + 𝑠ℎ𝑜𝑢𝑙𝑑𝑒𝑟𝑠 𝑜𝑟 𝑤𝑎𝑙𝑘𝑤𝑎𝑦𝑠 + 𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠 𝑜𝑟 𝑑𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛𝑠 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑜𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟 𝑓𝑒𝑎𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒
Shoulder
Minimum Width – 1.0 m (DPWH Manual)
Minimum width of 1.5 m for AADT greater than 1250
No difference in elevation between surface of the shoulder and the surface of the pavement
Median
section of a divided highway that separates the lanes in opposing directions
Functions of Median
To separate opposing traffic streams
To prevent U-turn and enhance the safety to traffic flow
Makes turning of vehicles smooth and safe operation
To provide space to install traffic signs or other traffic managing facilities
To provide storage lane for left turn vehicles at the intersections
To provide a haven in case of emergency
To minimize headlight glare in night time
Reduces conflicts and accidents between opposing streams of traffic
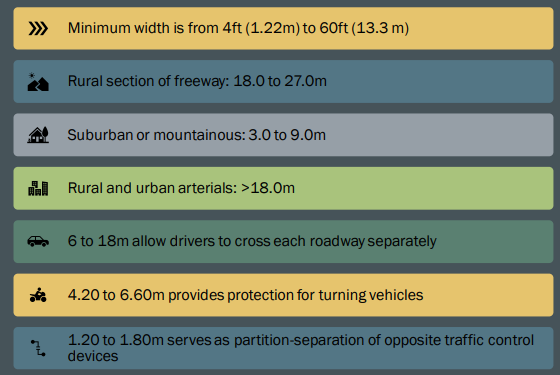
Width of mediam shoulder
Flexible
undergo a dynamic deflection upon impact and generally impose lower impact forces
semi rigid

Rigid

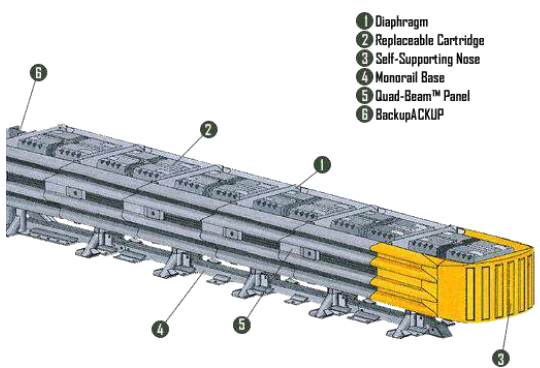
Crash Cushion
Grade Line
the longitudinal profile of the highway as a measure how the centerline of the highway rises and fall
it affects the performance or speed of a vehicle
it appears on a profile taken along the road centerline
it is a series of straight lines connected by parabolic vertical curves to which straight grades are tangent
Curb
Raised structures that are used mainly to delineate pavement edges and pedestrian walks
Used to control drainage, improve aesthetics and reduce right of way
Purpose of Curb
drainage control
Roadway edge delineation
Road of way reduction
Aesthetic
Delineation of pedestrian walkways
Sidewalk
Wherever roadside and land development conditions affect regular pedestrian movement along a highway, a sidewalk or path suitable to the conditions should be provided.
Sidewalk
Widths in lower speed residential areas may vary from 1.2 to 2.4 meters.
A good minimum width for a sidewalk that allows two people to pass is 1.8 meters.
less than 1.5 m wide require the addition of a passing section every 60m for accessibility
for pedestrian access to schools, parks, shopping areas, and transit stops and sidewalks in commercial areas should be provided along side of the street.
Drainage Channel
perform the important function of collecting water and conveying surface water
Open channel ditches
most economical drainage channe
Side Slopes
should be designed to enhance roadway stability and provide a reasonable opportunity for recovery for an out of control vehicle
Drainage Channel
perform the important function of collecting and conveying surface water from the highway right-of-way
Should have adequate capacity for the design runoff, provide for unusual stormwater with minimum damage to the highway and be located and shaped to provide a smooth transition from the roadway to the back slope
The most economical method of constructing a roadside channel usually entails the formation of open-channel ditches by cutting into the natural roadside terrain
Desirable grade of channels depend on the velocity of flow
Frontage Roads
-Roads used to control access to nearby arterial highways, while also functioning as a street facility serving adjoining properties and maintaining traffic circulation on each side of the arterial
-Segregates local traffic from higher speed through traffic and intercept driveways of residences and commercial properties along the highway
outer separation” - the area between the through traffic on the arterial and the local traffic on the frontage road
Noise Barrier
Used to an increasing extent in recognition of the adverse effect that noise can have on people living on, working on, or otherwise using land adjacent to highwayR
Roadside Control
Used by highway authorities to keep the full width of right-of-way unaffected for public highway purposes
Used to minimize interference to through traffic movement
Tunnel
Long, narrow terrain ridges where a cut section may be either costly or have environmental consequences
Narrow rights of way where all of the surface area is needed for street purposes
Large intersection areas or a series of intersections on an irregular or diagonal pattern
Railroad yards, airport runways, or similar facilities
Existing or planned parks or similar land uses
Locations where right-of-way acquisition costs exceed the cost of tunnel construction and operation
Pedestrian Crossing
safe access to all destinations that are accessible to motorists, plus they will want to access to other destinations that are not accessible to motorists such as trails and parks
must be able to cross streets and highways at regular intervals. Unlike motor vehicles, pedestrians cannot be expected to go far out of their wat to take advantage of a controlled intersection.
Marked crossings
are not only used to advice pedestrians where to cross the street but also send a message to motorists that they are in, or approaching, a pedestrian area
The width is 4 meters
Raised Crosswalks
are typically used at midblock locations to serve not only as a visual element for motorists, but also to slow traffic speeds
Pedestrian refuge
allows pedestrians to cross one direction of traffic at a time
Curb-Cut ramps
These are needed to accommodate persons of disabilities
These are necessary to provide access between the sidewalk and the street at pedestrian crossing
The minimum curb ramp width should be 0.9m, the maximum curb ramp grade should be 6% and the maximum cross slope on a sidewalk should be no more than 2%.
bikeway min width
1.22m
how many bikes per hour in one way?
1275 bikes
how many bikes per hour in two way?
1900 bikes
Bike speedway
11 to 24 kph
CLASS I BICYCLE FACILITY : BIKE PATH OR TRAIL
completely separated roadway designed for the exclusive use of bicycles; typically separated by open space or barrier
CLASS II BICYCLE FACILITY : BIKE LANE
a portion of the roadway, which has been designated for exclusive use by bicycle normally distinguished by a paint stripe, curb or barrier
CLASS III BICYCLE FACILITY : SHARED ROADWAY OR BIKE ROUTE
a roadway that has been officially designated and marked as bicycle route but which is used both by motor vehicle and bicycle traffic
Bus turnout length
min of 60m and max of 185m
bus min width
3.6m
bus turnout thickness for asphalt
at least 100mmbus t
bus turnout thickness for concrete
230mm
Intersection
It is the general area where two or more highways join or cross, within which are included the roadway and roadside facilities for traffic movements in that area
At-grade intersection
Intersection area is part of every connecting road or street
in which traffic is directed into definite paths is called channelized intersection
Can be 3-leg, 4-leg or multi-leg
Roundabout
intersection with a center island around which traffic must travel counterclockwise and in which entering traffic must yield to circulating traffic
may be mini, single-lane or multi lane roundabout
Interchange
A system of interconnecting roadway in conjunction with one or more highway separations providing for the interchange of traffic between two or more intersecting highways, usually without at-grade crossings of through and major turning movements
Main line
track constantly used for train operation
Sliding
track other than a main line
Track gauge
shortest distance between inner side surface of two rail heads of a track measured
Station
place used by passengers to get in and out of trains or for the loading and unloading of cargo
Signalling yard
place mainly used for mutual passing or waiting for a train
Shunting yard
palce mainly used for the shunting of rolling stock or the composition of a trainD
Depot
place mainly used to accommodate and maintain rolling stock
Train
a group of rolling stock composed for operation on track outside a station
Rolling stock
locomotive, passenger cars , freight cars and special-purpose cars
operation safety device
signalling safety devices, level crossing safety devices and safety communication devices
Signalling safety devices
devices to display railway signals and devices to automatically reduce the train speed or stop a train, etc. in accordance with the signal indication in order to ensure the safe operation of a train, etc
Signals
objects indicating the operating conditions of a train, etc. to railway staf
Signs
physical movement and so forth to mutually indicate intentions between railway staf
Markers
objects indicating the position, direction and conditions, etc. of specific items to railway staff
Gauge and Slack
The gauge shall be decided to ensure the smooth running of rolling stock, taking the structure of vehicles and others into consideration.
At curves, appropriate slack shall be provided in accordance with the curve passing performance of rolling stock
Curve Radius
shall be adopted based on the standard minimum curve radius to ensure the smooth running of rolling stock, taking the curve passing performance and running speed of vehicles and the cant, etc. into consideration.
Cant
A circular curve shall be provided with cant in accordance with the gauge, radius of curve and speed of rolling stock, etc. It must be ensured that the largest value of the cant will not adversely affect the stability, etc. of rolling stock which is either travelling at a low speed or which is stationary.
Transition Curve
shall be provided between a straight line and a circular curve or between two circular curves depending on the structure, degree of cant and travelling speed of rolling stock, etc.
Grade
shall be determined in consideration of the power performance, braking performance and speed of operation, etc. of rolling stock and the standard steepest grade for main lines is given below.
Vertical Curve
In places where the grade changes, a vertical curve shall be introduced to prevent the derailing of rolling stock and to prevent any unpleasant feeling on the part of passengers, taking the speed of train operation and rolling stock performance, etc. into consideration
Construction Gauge
shall be determined to ensure the safety of rolling stock and passengers, etc. vis-a-vis the pitching or rolling, etc. of travelling rolling stock and no structure shall be introduced within the construction gauge.
Width of formation level
shall be determined to ensure the safety of passengers and workers, etc. in consideration of the pitching motion of travelling rolling stock and the track structure, etc
center-to-center distance of adjacent tracks
shall be determined by adding a margin to the width of rolling stock in consideration of pitching motion to ensure its safety and of the passengers. This distance shall be widened at curves, etc. in response to the expected swaying, etc. of rolling stock.
track and civil engineering structure
shall be determined to ensure the safety and security of the rolling stock and railway facilities in consideration of the structure of rolling stock, train weight and sub-grade conditions, etc.
building construction
shall be constructed so as not to compromise the safety of the rolling stock and passengers
disaster prevention devices, safety devices and evacuation devices
shall be installed to avoid entry of unwanted persons and of falling objects onto the tracks. Similarly, measures shall be applied to prevent damage to the facilities which may be brought about by accidents or any untoward incidents happening in the perimeter area.
Station Facilities
effective track length, platform length/width, etc. shall be determined so as to ensure smooth train operation with consideration for passenger safety
Smooth transfers between railway line
Smooth transfers between railway and road-based and other modes of transport