8. Globular and Fibrous Proteins
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
protein structure review
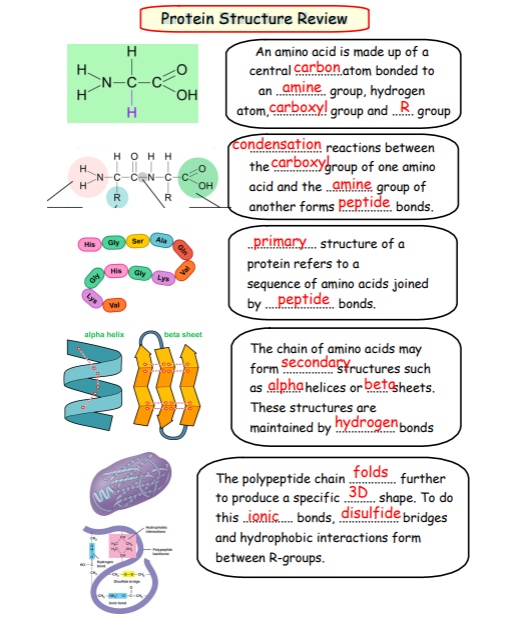
Explain what determines the structure of a tertiary protein.
- the specific sequence of the amino acids
- determines the type and position of the R groups
- which determines the bonds formed between R groups
- These bonds include, vanderwall forces Ionic bonding Disulphide bridges hydrophobic interactions
Compare the structure of tertiary and quartenary protein structures.
-Tertiary structures consist of one folded polypeptide chain
-Quartenary structures consist of more than one polypeptide chain joined together
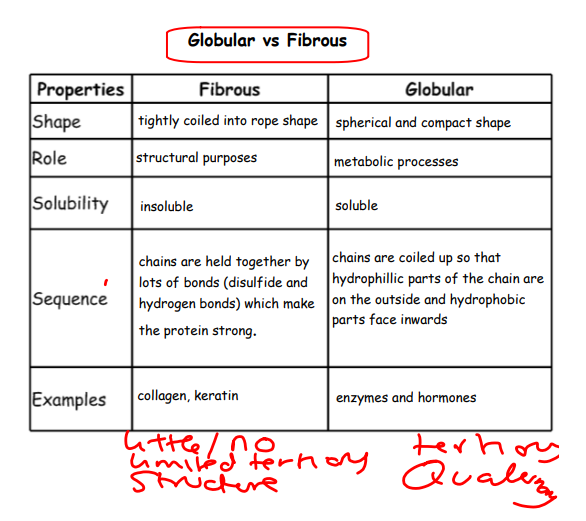
What are fibrous proteins?
Long chains of repeated amino acids with limited folding
What are globular proteins?
Folding of the amino acid chains occurs to form compact, spherical shapes
Use of Fibrous protein
Fibrous proteins are required for structural purposes e.g. collagen and keratin (components of skin and hair). Fibrous proteins are insoluble
Use of globular proteins
Globular proteins are required for metabolic reactions to occur e.g. enzymes, hormones, receptors. They are soluble
State the definition of soluble:
dissolved in water
State the definition of insoluble:
does not dissolve in water
State the definition of hydrophobic:
insoluble/will not associate with/ repels water
State the definition of hydrophilic:
soluble/will associate with/attracted to wate
Describe the structure of a globular protein:
spherical shape
some globular proteins are quaternary proteins because they consist of more than one polypeptide chain
Bonds form between R groups dependent on their type and position which causes further folding
What are Polar R groups?
attract other polar molecules e.g. water and are said to be hydrophillic.
What are non- polar R groups?
hydrophobic and repel water
How are polar R-groups located in the tertiary protein?
These r-groups arrange themselves on the outside of the protein facing the aqueous environment.
How are non-polar R-groups located in the tertiary protein?
These r-groups arrange themselves on the inside of the protein facing away from the aqueous environment.
Describe the structure and properties of globular proteins:
Begin as long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Protein folds into tertiary/quaternary structures due to the formation of ionic bond, disulfide bridges and hydrohobic interactions between R-groups.
As they fold globular proteins become very compact and are spherical
They have hydrophilic R-groups on the outside which interact with water making them soluble protein
What are 3 different types of globular functions::
Myoglobin
Protease enzyme
Haemoglobin
What is the function of haemoglobin?
Protein binding site for oxygen so it can be carried around the body in RBCs.
What is the function of protease enzymes?
Protein that is found in the stomach that catalyses the breakdown of proteins into amino acids.
What is the function of myglobin?
Protein binding site for oxygen so it can be carried around the body in muscle tissue.
Suggest why the structure of globular proteins enables them to carry out such functions
Hydrophillic r group will be on the outside which makes the protein soluble Hydrophobic R groups will be on the inside
Deduce the overall shape of fibrous proteins:
tightly coiled to form rope shape
Explain how fibrous proteins primary structure fold into the secondary alpha helix
- secondary due to H bonds forming between amino acids
- not folded into a spherical 3D structure
-They have a limited tertiary structure/due to limited bonding between R groups
Deduce what property fibrous proteins may have.
hydrophobic R group on the outside repel water this makes fibrous proteins insoluble
Describe the fibrous protein structure and properties:
1. Fibrous proteins are made from very long polypeptide chains of repeated amino acid sequences 2. They have hydrophobic R-groups on the outside which prevents them from interacting with water making them insoluble proteins
Describe the amino acid sequence in the primary structure of collagen:
repeated sequences of amino acids and every second one is glycine
How many alpha chains make up one collagen molecule?
3
→ The amino acid chains fold to form alpha helices
Explain how collagen fibres form:
Hydrogen bonds form between chains creating cross-links.
Chains of collagen associate to form fibrils.
suggest a property of collagen and a use of collagen based on that property:
It is flexible and has a high tensile strength making it suitable for structural support
Suggest why the collagen chains are staggered when forming fibrils
To avoid creating weak points anywhere along the chain