Chapter 11: Water Treatment
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
_____ is commonly used in the improvement of water quality.
aeration
Municipalities aerate drinking water that is drawn from underground aquifers to remove the ____________, volatile organic compounds.
foul-smelling H2S and organosulfur compounds,
Aeration of drinking water also results in reactions that produce _____ from the most easily oxidized organic material.
CO2
If necessary for reasons of odor, taste, or health, most of the remaining organics can be removed by subsequently ___________, although this process is relatively expensive
passing the water over activated carbon
What is aeration?
the process of circulating, mixing, or dissolving air into a liquid or substance.
What are 4 advantages of Aeration of water?
1) removes foul-smelling H2S and organosulfur compounds
2) produces CO2
3) remaining organics can be removed
4) increases oxygen content which oxidizes water-soluble Fe2+ to Fe3+
After aeration, ______ in the water are removed.
colloidal particles
in water purification, if the water is excessively hard, ____ and ____ are removed.
calcium, magnesium
what are the 4 key steps in water purification?
1) Aeration
2) Settling and precipitation (use Al or Fe salt to precipitate colloids)
3) Hardness removal
4) Disinfection
If the water comes from wells in areas having limestone bedrock, it will contain significant levels of ____ and _____ ions.
Ca2+, Mg2+
Calcium can be removed from water by?
the addition of phosphate ions
How are calcium ions removed from hard water?
Ca2+ is removed by precipitation and filtering of CaCO3.
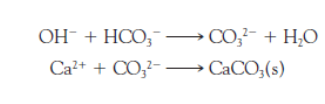
How are magnesium ions removed from hard water?
After removal by filtration of CaCO3 and Mg(OH)2, the pH of the water is readjusted to near-neutrality by bubbling carbon dioxide into it.
Magnesium ions precipitate as insoluble _____, when the water is made sufficiently alkaline when the OH ion content is increased.
Magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2
In terms of causing sickness and death, ____ contaminants of water are almost always much more important than ____ ones.
biological, chemical
What is disinfection?
the elimination of microorganisms that can cause illness.
Many microorganisms in raw water are present as a result of contamination by human and animal ____.
feces
What are the three key microorganisms eliminated from water?
1) bacteria like salmonella and E. coli
2) viruses
3) protozoans
When filtering raw water that is obtained from rivers, lakes, or streams contains a multitude of ____, some of which consist of or contain microorganisms.
tiny particles
When filtering water, any of the small suspended particles are composed of ___, and resulted from the erosion of ___ and ___, whether by _____ or due to plowing of land for ____, ___, or _____.
clay, soil, rock, natural forces, agriculture mining, commercial housing development
The suspended particles increase the water’s ____, and thereby reduce the ability of light to penetrate deeply enough to support photosynthesis.
turbidity
the suspended particles increase the water’s turbidity and thereby reduces the ability of light to ____.
penetrate deeply enough to support photosynthesis
The larger of the particles suspended in water are often removed from the water by simply filtering it by?
passing it through a bed of sand
The sand retains suspended solids of all types, including microorganisms, down to about ___ micrometers in size.
10
In the removal of colloidal particles by precipitation, most municipalities allow raw water to settle, since this permits large particles to ____ or to be ____.
settle out, readily separated
during the removal of colloidal particles by precipitation, much of the insoluble matter, which originates from rocks and soil, and from the ____ and ____ of water-based plants and animals, will not precipitate spontaneously since it is suspended in the water in the form of ____.
disintegration, decomposition, colloidal particles.
colloidal particles must be removed from drinking water for both ____ and ___ reasons.
aesthetic, health-safety
What are colloidal particles?
particles that have diameters ranging from 0.001 to 1 micrometer and consist of groups of molecules or ions that are weakly bound together.
How are colloidal particles removed?
- a small amount of either Fe2(SO4)2, or Al2(SO4)2 is dissolved in the water.
- The water is made neutral or alkaline in pH 7 and up.
Both the Fe3+ and Al3+ ions produced from the salts form gelatinous hydroxides that physically incorporate the colloidal particles and form a removable precipitate.
water can be purified of most contaminant ions, molecules, and small particles including viruses and bacteria by ?
passing or forcing it through a membrane where the pores are microscopic in size
Explain the reverse osmosis process.
- Water is forced under high pressure to pass through a semipermeable membrane composed of organic material.
the unwanted particles in the water are filtered through the pores of the membrane and the water that reaches the other side will be purified.
Water aeration removes what type of dissolved gases?
a) H2S
b) CO2
c) VOC
d) CH4
a,c
How do you remove odor and improve the taste of water?
a) producing CO2
b) passing over activated carbon
c) removing iron
d) removing VOC
b
How are calcium ions be removed from wastewater?
a) adding phosphate
b) adding carbonate
c) adding OH-
d) aeration
a,b,c
How are magnesium ions removed from wastewater?
a) adding phosphate
b) adding carbonate
c) adding OH-
d) aeration
c
what are the main microorganisms in wastewater
a) viruses
b) protozoans
c) bacteria
d) fungus
a,b,c
what substances are removed by filtering wastewater?
a) suspended particles
b) Ca2+ ions
c) bacteria
d) colloidal particles
a
What is the range of size of colloidal particles?
a) 2-10 micrometers
b) 5-15 micrometers
c) 0.001-1 micrometer(s)
d) 10-20 micrometers
c
Colloidal particles are removed by..
a) adding phosphate
b) adding iron (III) sulfate
c) adding alum
d) aeration
b,c
reverse osmosis is used to removed?
a) salts
b) Ca and Mg
c) bacteria
d) viruses
a
The most common water purification agent used in North America is
_____.
hypochlorous acid, HOCl
HOCl is a neutral, covalent compound that kills _____ as it passes through their ____.
microorganisms, cell membranes
at the molecular level, HOCl is used to deactivate essential enzymes by oxidizing some of their side chains that involve ___.
sulfur
is disinfection by chlorinate relatively expensive or inexpensive?
inexpensive
chlorination is more common that ozonation in North America because the raw water is generally _____.
less polluted.
HOCl is not stable in _____ form so it cannot be stored.
concentrated
For large-scale installations, HOCl is generated by dissolving ______ gas in water. Then, a very dilute aqueous solution of chlorine in water contains very little aqueous Cl2 itself. What does this reaction look like?
molecular chlorine gas in water
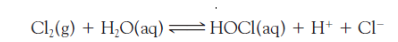
in small-scale applications of chlorination, as in swimming pools, handling cylinders of Cl2 is _____ and ____.
inconvenient, dangerous
HOCl is generated from _____, or is supplied as an aqueous solution of _____.
calcium hypochlorite, Ca(OCl)2, sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl.
in water, an ____ reaction occurs to convert most of the OCl- in the substances above to HOCl.
acid-base
_____ and _____ contributes Urea in swimming pools.
swimmers sweat, urine
Urea can react directly with _____ to produce ____-
HOCl, NCl3
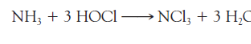
Maintenance of an alkaline pH also prevents the conversion of dissolved ammonia to the mono- and dichloramines, ____, ____, and especially to, ____, which is a powerful eye irritant
NH2Cl, NHCl2, NCl3
NCI3 is a powerful ____.
eye irritant
Significant _____and _____ problems from exposure to chloramines in
the air around indoor swimming pools have been reported when appropriate ventilation is not available
eye irritation, respiratory
Chlorine must be constantly replenished in outdoor pools since ___ and the short wavelength components of ___ in sunshine are absorbed.
UV-A, UV-B
An important drawback to the use of chlorination in disinfecting water is the production of ______, some of which are toxic
chlorinated organic substances
Examples of these important chlorinated organic substances by-products are the group of halogenated acetic acids (haloacetic acids), such as ______.
CH2Cl-COOH
The U.S. EPA restricts their collective annual average chlorine concentration to ____ppb maximum
60
Dichloroacetic acid, CHCl2-COOH, is a more potent carcinogen than _____.
chloroform
_____, is a more potent carcinogen than chloroform.
Dichloroacetic acid, CHCl2-COOH
A more general problem of the unintended consequences of the chlorination of water lies in the production of trihalomethanes, THMs. Their general formula is _____, where the three X atoms can be chlorine or bromine.
CHX3
The THM of principal concern is chloroform, CHCl3, which is produced when ?
hypochlorous acid reacts with organic matter dissolved in the water
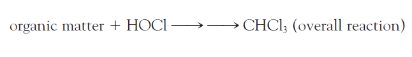
The U.S. EPA has set a maximum contaminant level goal, MCLG, of ____ppb for THMs in drinking water.
70
SODIS is the acronym for ?
solar disinfection
SODIS (solar disinfection) has two steps, explain them.
the first step exposes transparent plastic bottles of raw water to sunlight, allowing for the destruction of pathogens by their absorption of UV-A
The second step absorbs the heat reflected back into the water from aluminum plates
other techniques of purification: Ceramic filters are made from clay and are effective if the pore size is controlled to filter out microbes by ____ ?
Water is also ____ as a result of the filtration.
size exclusion.
clarified
Another method of water purification is biosand filtration.
in a biosand filter, what lies in the biological zone?
a dense population of microorganisms
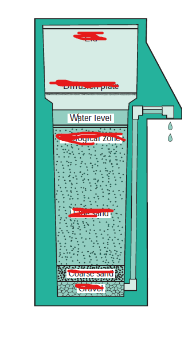
label the parts of this biosand filter from top to bottom.
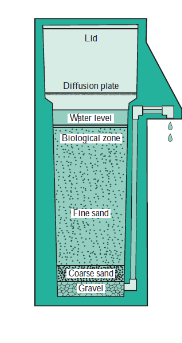
biosand filters flow raw water ______ through a bed of fine sand.
vertically
the microorganisms in the biological zone of a biosand filter consume the _____ that become absorbed onto and trapped by the sand particles.
water-borne pathogens
The sand and gravel of a biosand filter remove the _____, clarifying the water and improving its taste.
larger particles
The sand and gravel of a biosand filter remove the larger particles, ____the water and improving its ____.
clarifying, tatse
The inorganic contaminant of greatest concern in groundwater is the ____ ion, which occurs in both rural and suburban aquifers.
nitrate, NO3
Although uncontaminated groundwater generally has nitrogen levels of
__-__ ppm , about __% of shallow aquifers in the united states now have nitrate levels that exceed __ppm.
4-9ppm, 9%, 10ppm
The elevated levels of about ___ppm can result from agricultural activity, with values as high as____ppm found at some sites in India.
100ppm, 400ppm
Excess nitrate ion in drinking water is a potential health hazard since it can result in methemoglobinemia in ____ as well as adults with specific ____ deficiency
newborn infants, enzyme
Bacteria, e.g., in unsterilized milk-feeding bottles or in the baby’s stomach, reduce some of the nitrate to_____.
to nitrite ion, NO2.
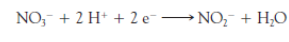
The nitrite combines with and oxidizes the iron ions of the ____in blood from Fe2+ to Fe3+ and thereby prevents the proper absorption and transfer of oxygen to cells.
hemoglobin
The nitrite combines with and oxidizes the iron ions of the hemoglobin in blood from ___ to ___ and thereby prevents the proper ___ and transfer of ___ to cells.
Fe2, Fe3+ ,absorption, oxygen
The baby turns____and suffers ____ failure. This occurrence is the of
methemoglobinemia, or blue-baby syndrome
blue, respiratory
nitrites in food and water could subsequently react with amines to produce ____
N-nitrosamines
N-nitrosamines are amines in which two ___ groups and an ____ unit are bonded to the central nitrogen.
organic groups, -N=O
N-nitrosamines are produced in the ___.
stomach
N-nitrosamines are also an environmental pollutant in ____.
drinking water
Nitrosamines can form in processed meats when ____ react with _____ in the meat
nitrites, amines
the perchlorate ion is an _____ agent.
oxidizing
perchlorate does not accumulate in soil because it is highly ____.
water-soluble
large quantities of ammonium perchlorate are manufactured for use as oxidizing agents in solid rocket propellants, _____, _____, and _____.
fireworks, batteries, air bags
concentrations of perchlorate in drinking water in the US southwest range from _ to __ ppb
5 to 20
The most common water purification agent used in North America is
a) biosand
b) ozone
c) HOCl
d) ceramic filter
HOCl
which are true for disinfection by chlorination?
a) effective
b) inexpensive
c) kills microorganisms
d) stable
a, b, c
In large-scale installing, HOCl is generated by
a) Ca(OCl)2
b) NaOCl
c) Cl2 gas in water
d) from O3
c
in swimming pools, HOCl is generated by
a) Ca(OCl)2
b) NaOCl
c) Cl2 gas in water
d) from O3
a, b
significant respiratory and eye irritation problems happen in swimming pools due to
A. Ca(OCl)2
B. NCl3
C. NaOCl
D. NH3
b
which are toxic byproducts of chlorination
a) CHCl3
b) NH3
c) NaOCl
d) CHCl2 -COOH
a,d
what are other techniques for water purification
a) SODIS
b) ceramic filters
c) biosand filters
d) boiling water
all
which are important contaminants in groundwater?
a) HOCl
b) NO3-
c) NDMA
d) CLO4-
b, c, d