Alkenes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What are alkenes?
unsaturated hydrocarbons
What are the general formula for alkenes?
CnH2n
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
Because of the C=C bond - high electron density
What is the simplest alkene?
Ethene
Why can't the double bond in an alkane rotate?
p orbitals overlap to form pi orbital
What are the only intermolecular forces in alkenes?
Van der Waals forces
Are alkenes soluble in water?
No, non-polar bonds
Are alkenes or alkanes more reactive? Why?
Alkenes more reactive due to electron density in double carbon bond
What are electrophiles?
Electron pair acceptors. An electrophile is either a positively charged ion or has a positively charged area (δ+).
What are the bond angles in alkenes?
120
What is the general formula of a cycloalkene?
CnH2n-2
What is meant by addition?
Joining together of molecules
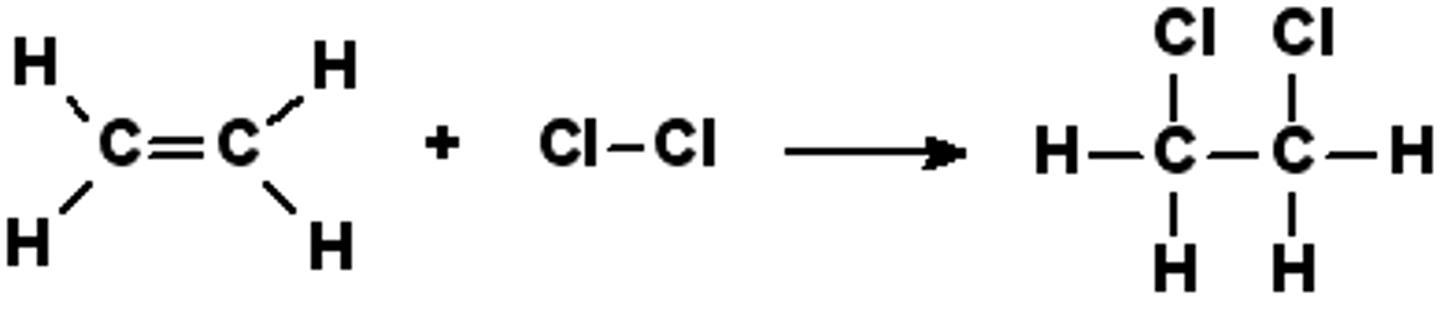
Which area of an alkene determines how it reacts?
The double bond - region of high electron density
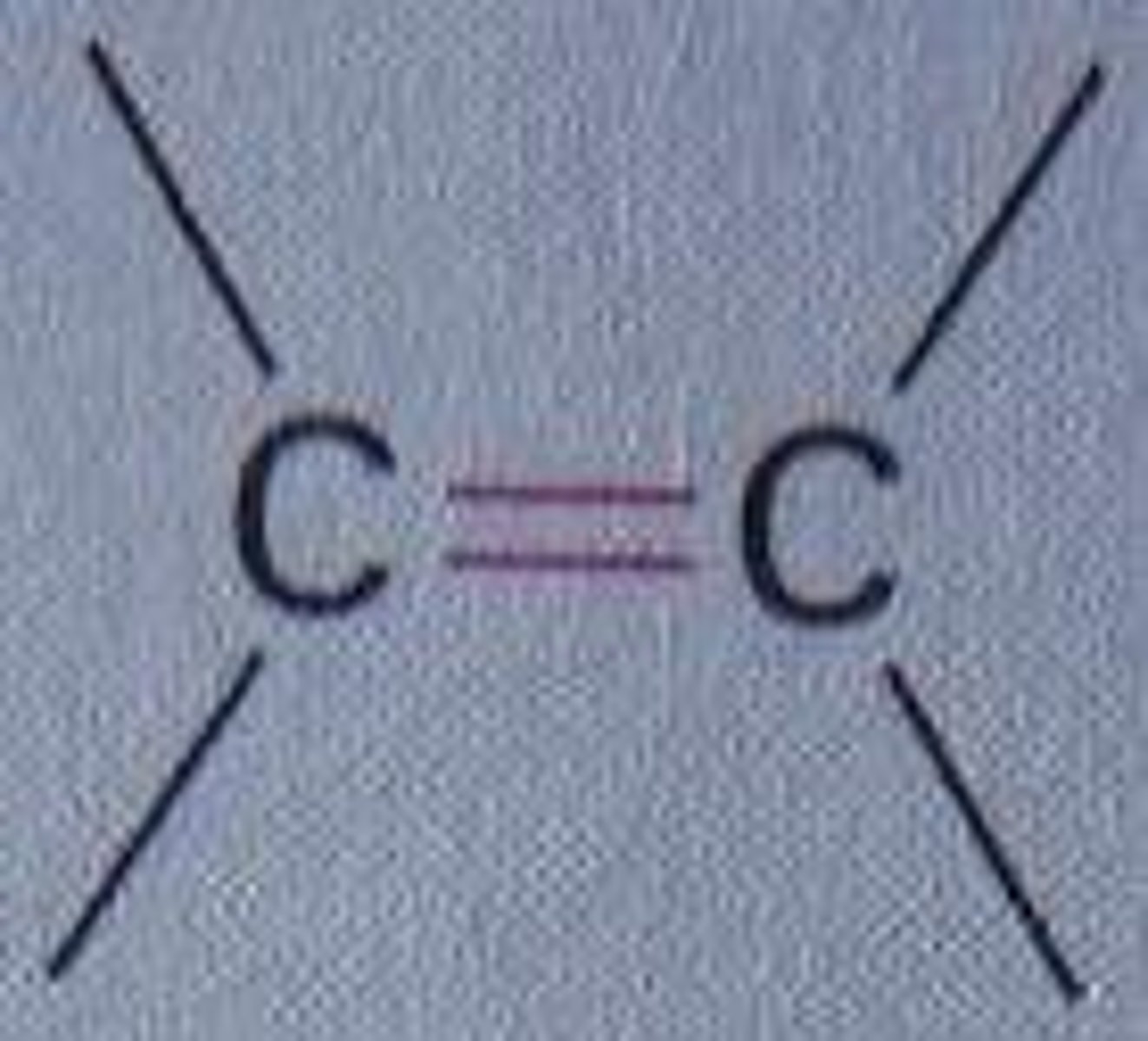
What process do alkenes react by?
electrophilic addition
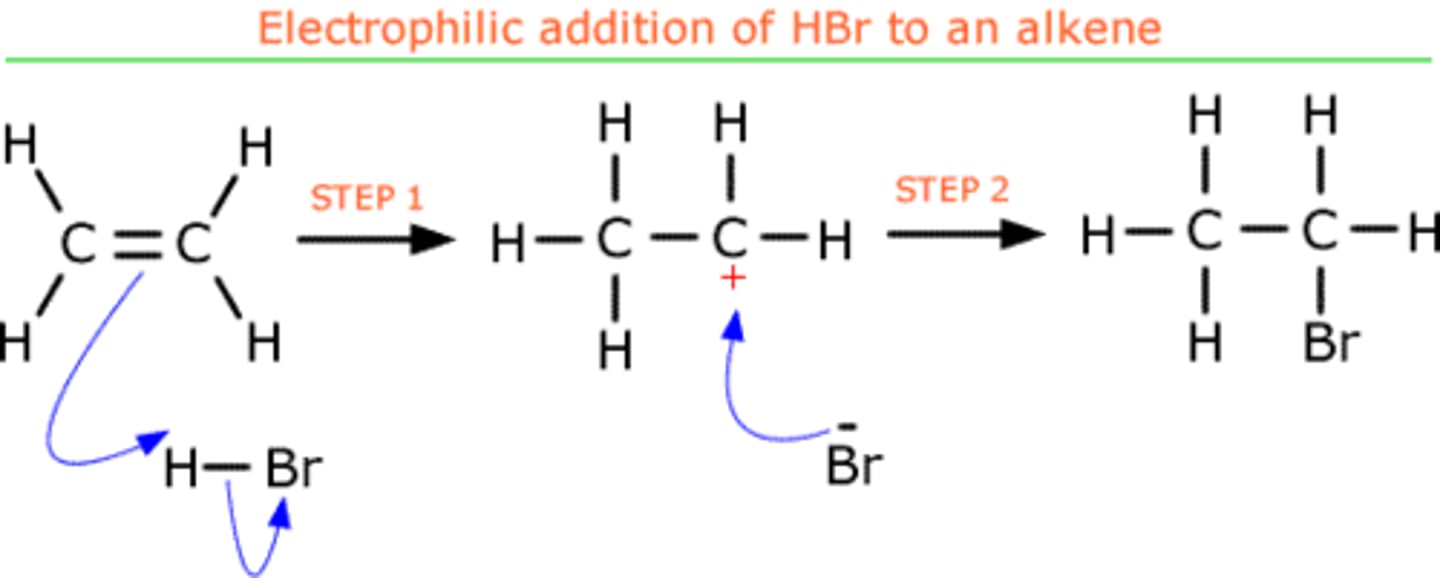
What is electrophilic addition?
A type of addition reaction in which an electrophile is attracted to an electron-rich centre or atom, where it accepts a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
In a hydrogen halide, which side is slightly positively charged?
the hydrogen atom
In a hydrogen halide, which side is slightly negatively charged?
the halide atom
What is heterolytic fission?
Where one atom in the bonding pair receives both electrons from the shared pair
What is a carbocation intermediate?
An intermediate molecule in a reaction which has a positive charge on a carbon atom
How many products can be created in electrophilic addition with a symmetric alkene?
Just one
How many products can be created in electrophilic addition with an asymmetric alkene?
Two possible products - isomers
What affects the stability of a carbocation?
More alkyl groups attached to it, the more stable the compound
What is an alkyl group?
An alkane with a hydrogen atom removed
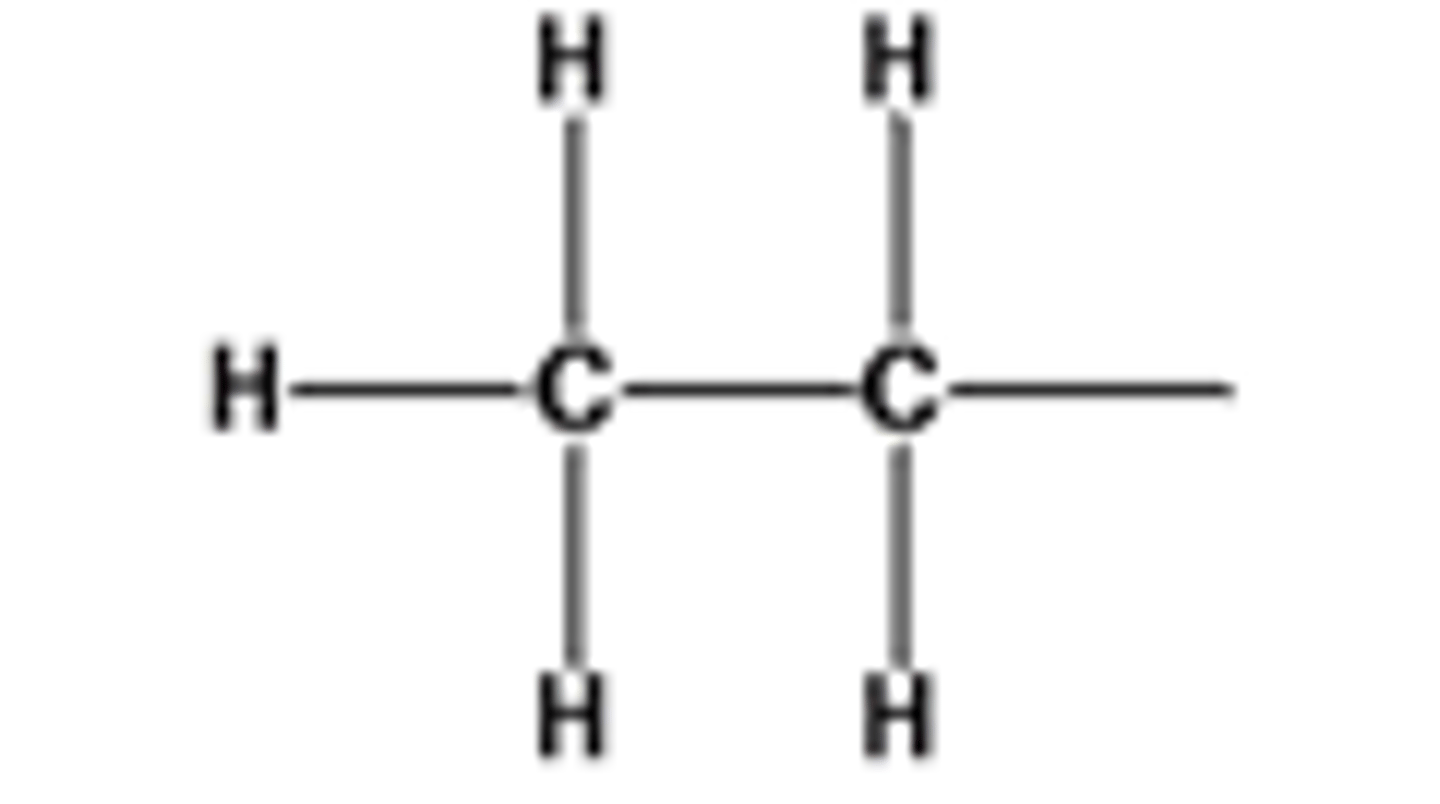
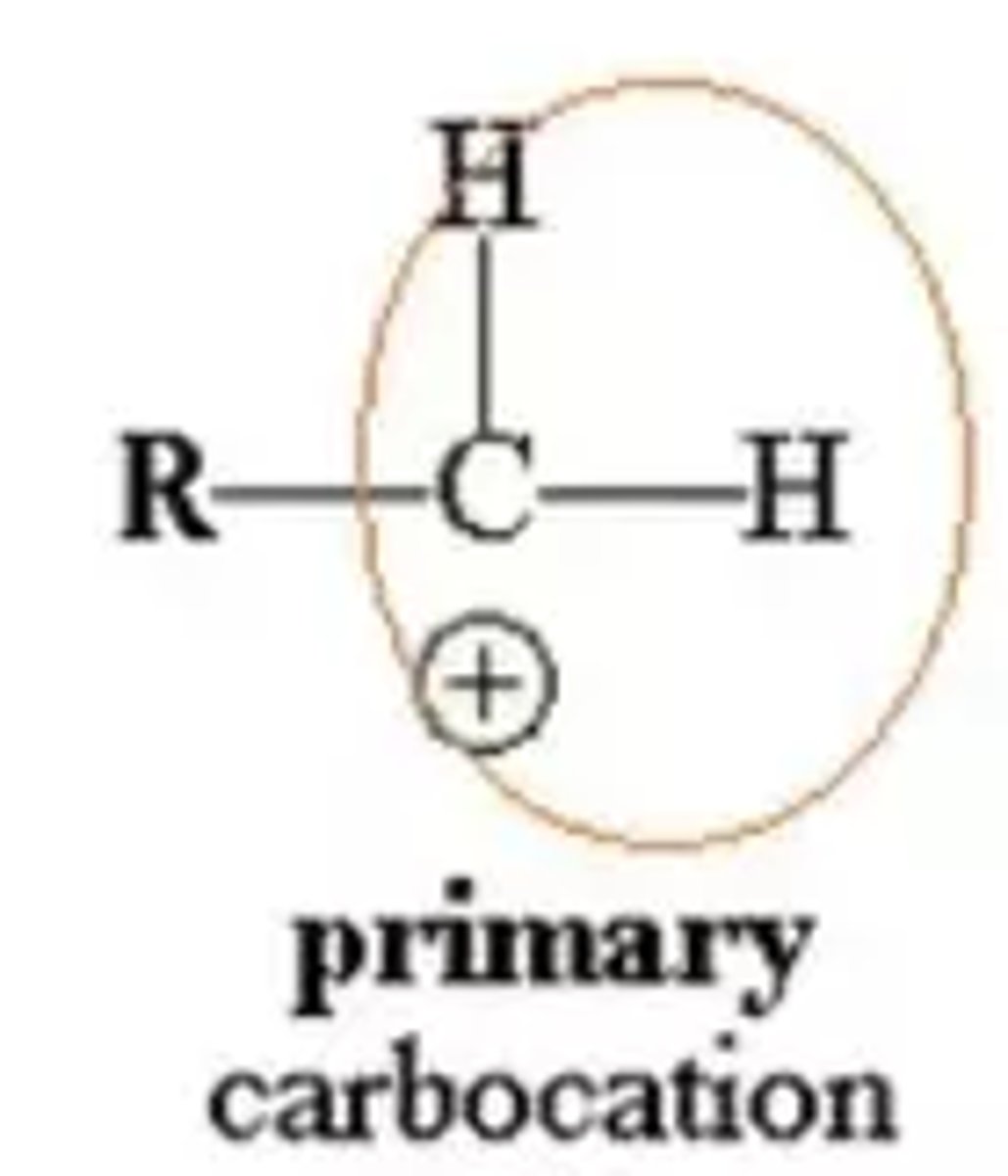
What is a primary carbocation?
The positive carbon atom is attached to one alkyl group
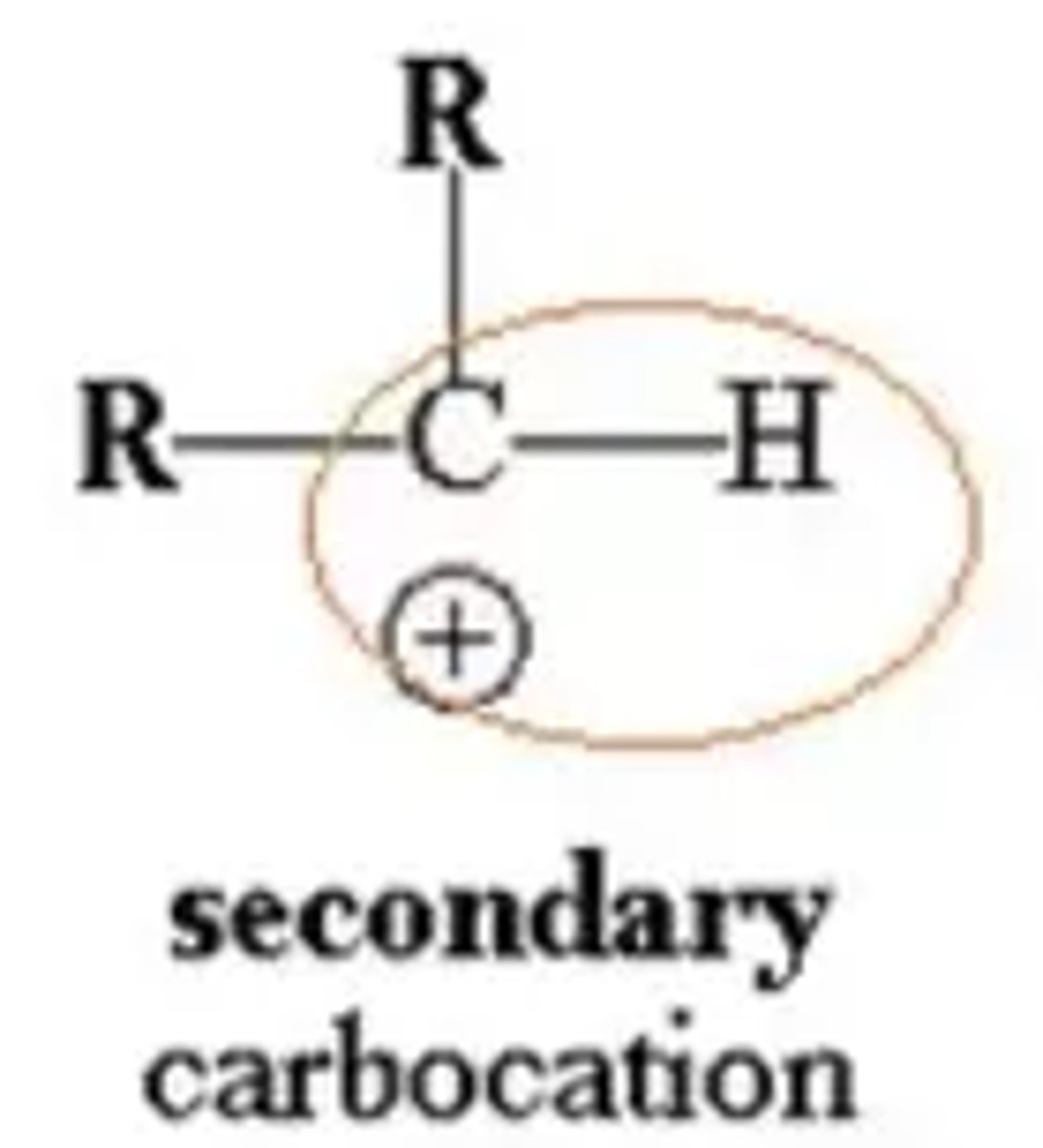
What is a secondary carbocation?
The positive carbon atom is attached to two alkyl groups
A secondary carbocation is more ______ than a primary carbocation
stable
What makes the secondary carbocation more stable than the primary carbocation?
In primary carbocations the positive charge is stabilised by only one alkyl group whereas in secondary carbocations, the positive charge is stabilised by two alkyl groups.
Why is a secondary carbocation more likely to create the major product?
It's more stable, so exists for a longer period of time and is more likely to form the product.
What is the positive inductive effect?
This is when alkyl groups in a carbocation feed electrons toward the positive charge, stabilising it.
What is the difference between electrophilic addition with a halogen and electrophilic addition with a hydrogen halide?
- Halogen has an induced dipole, while hydrogen halide has permanent dipole
- Halogen makes only one product with asymmetric alkene, whereas hydrogen halide makes major and minor product
How can we use electrophilic addition with a halogen to test for the presence of an unsaturated molecule?
- Add drops of bromine water and gently shake test tube
- If substance is unsaturated, then the bromine will add across the double bond and the product of the reaction will be colourless.
What are the two categories of polymers?
Addition polymers and condensation polymers
What are monomers?
Smaller units from which larger molecules are made
What are polymers?
Molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together
What are the monomers of addition polymers?
alkenes
Are addition polymers reactive?
no they are unreactive
Why are addition polymers unreactive?
main carbon chain is mainly non polar
saturated chains
What does the repeating unit of a polymer show?
The arrangement of atoms that are repeated in the polymer chain
What is poly(phenylethene) also known as?
Polystyrene
What is PVC?
Poly(chloroethene) or polyvinyl chloride
What is PVC used for?
pipes, aprons, insulation
What are plasticisers?
Small molecules that get between polymer chains, forcing them apart and allowing them to slide across each other
When added to PVC, what do plasticisers create?
flexible PVC