digestive system 1+2+3
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
gastrointestinal tract
mouth
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small & large intestines
accessory digestive organs
salivary glands
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
lips
orbicularis oris muscle
connective tissue
skin
numerous sensory receptors and blood vessels (hence red color)
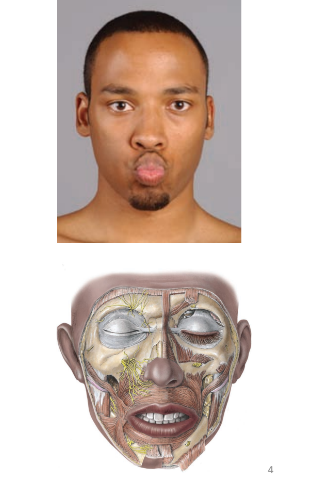
cheeks
lateral walls of mouth
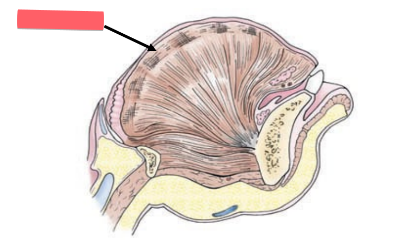
hard palate
roof — ____ ______ (bone)
maxilla and palatine bones
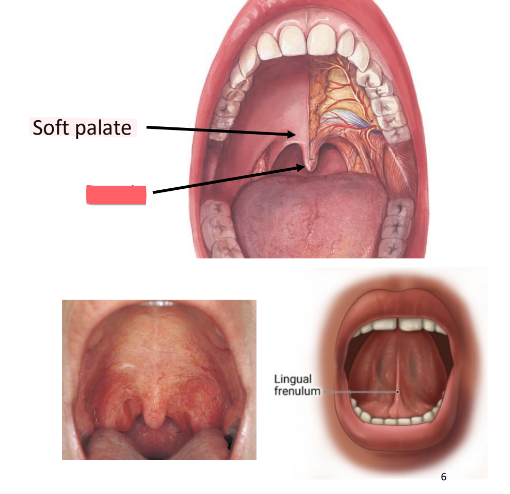
soft palate
muscular arch: skeletal muscle
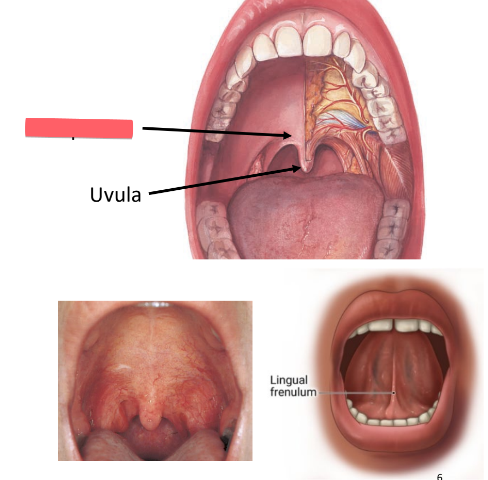
uvula
cone-shaped projection of soft palate
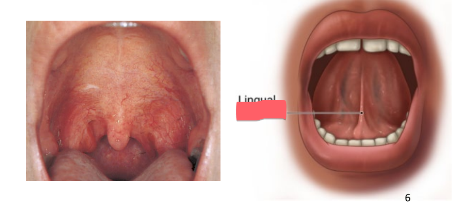
frenulum
fold of tissue under tongue: restricts movement
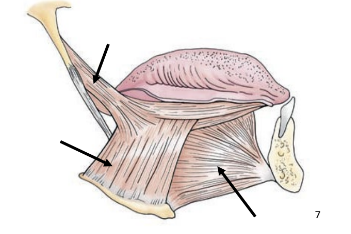
intrinsic muscle
interwoven skeletal muscle of tongue
extrinsic muscle
outside tongue, attached to base of tongue
originate on hyoid and other structures
ex: hyoglossus, styloglossus, genioglossus
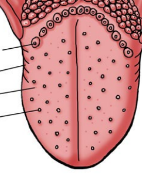
papillae
(dorsal surface)
small raised areas
contain taste buds
create sensitive surface with some friction
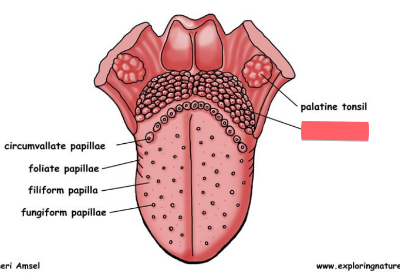
lingual tonsil
lymphoid tissue on posterior portion of tongue
taste map
the _____ ___ is wrong and outdated
5th flavor discovered: umami
savory (like steak, mashed potatoes)
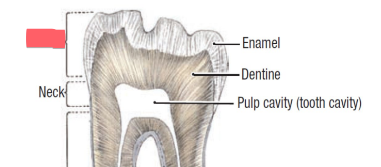
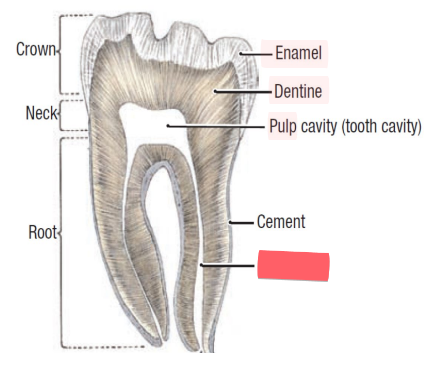
crown
exposed portion of teeth
root
anchors tooth firmly in jaw
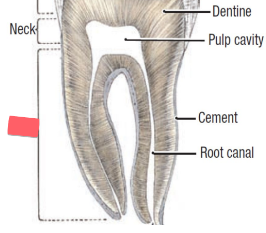
periodontal ligament
CT anchoring teeth to jaws
gingiva (gums)
mucous membrane of jaw
alveolus
socket (cavity) in bone that holds teeth
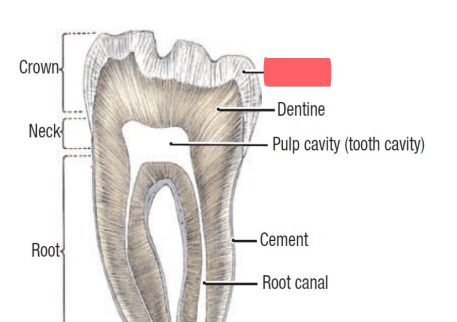
enamel
of teeth
mostly CaPO4 (hydroxyapatite)
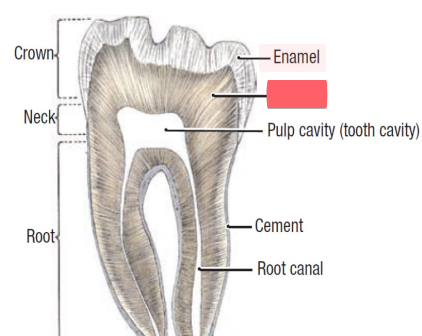
dentin
bone like material inside teeth
pulp
of teeth,
nerves
blood vessels
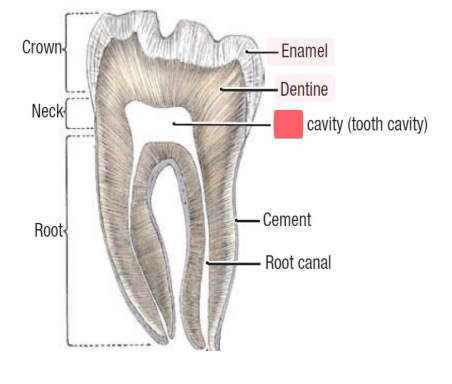
root canal
canal of teeth in which pulp is found
saliva
99% water
enzymes:
lysozymes: destroy bacteria
digestive enzymes
mucous: lubrication
salts
maintain proper pH for digestive enzymes

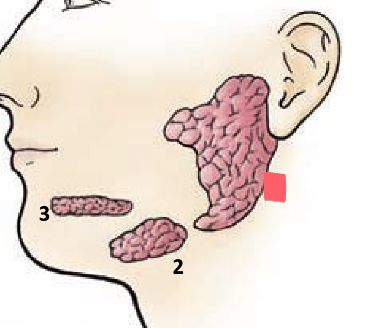
parotid glands
located inferior and anterior to ear
drains into oral cavity near 2nd upper molar
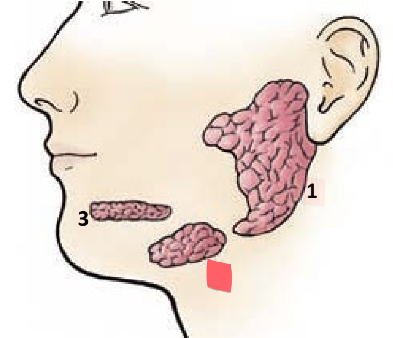
submandibular glands
located just inside the mandible
empties into the floor of the mouth
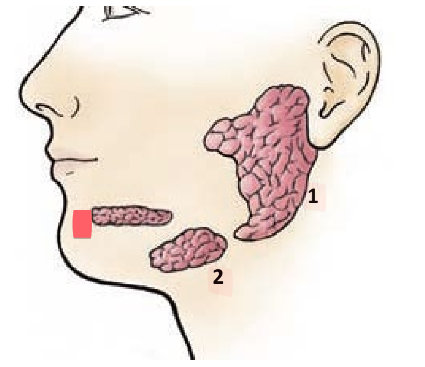
sublingual glands
located under mucosa in floor of mouth
empties into floor of mouth
mumps
viral infection that swells the salivary glands
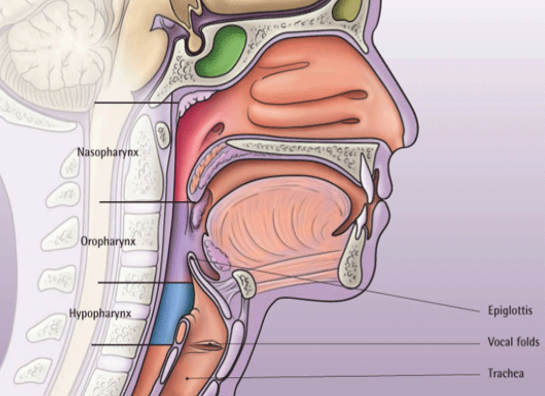
pharynx
structure:
lined with stratified squamous epithelium
mucous membrane (lubrication)
skeletal muscle
swallowing
__________ begins as a voluntary action
sets off reflexive opening/closing of openings (ex. nasal cavity)
past mid-esophagus: completely involuntary (under autonomic control)
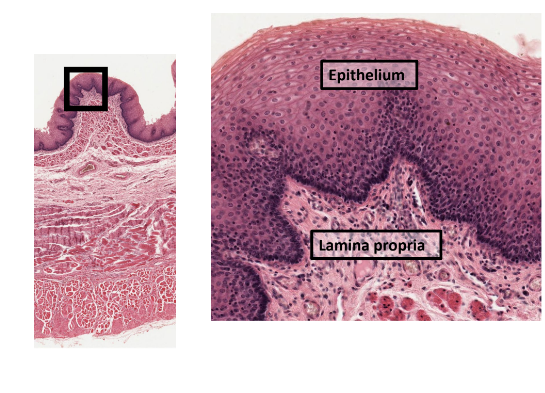
mucosa (GI)
epithelium (inner lining)
stratified squamous at beginning and end of tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, anal canal
simple columnar in middle
stomach & small and large intestine
lots of glands
submucosa (GI)
(CT)
rich blood/nerve supply
elastic and collagenous fibers allow GI tract to expand
lacteals: lymphatic vessels—absorb fats
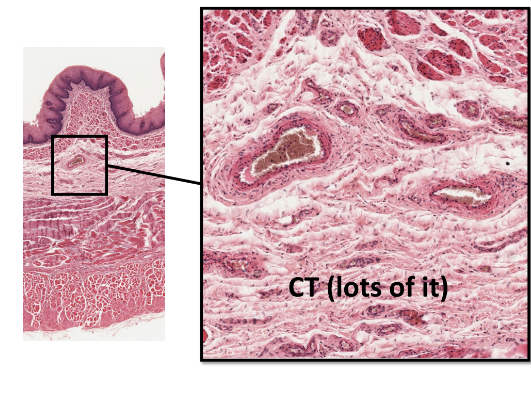
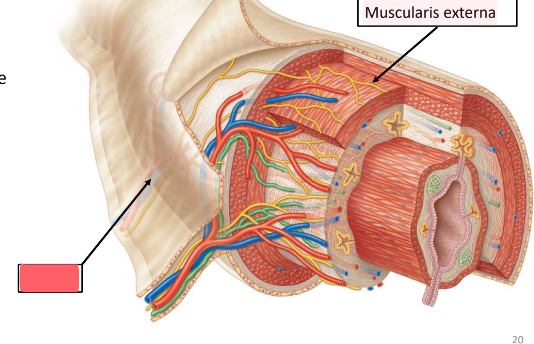
muscularis externa
of the GI tract
moves materials along tract
mechanical digestion
multiple layers of smooth muscle
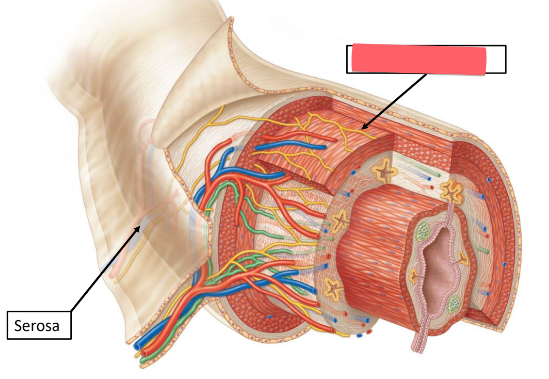
serosa
outer CT of GI tract
enteric
special intrinsic nervous system of gut (intestines)
parasympathetic
rest and digest nervous system of gut
(sympathetic does opposite: inhibit digestion, movement, secretion)
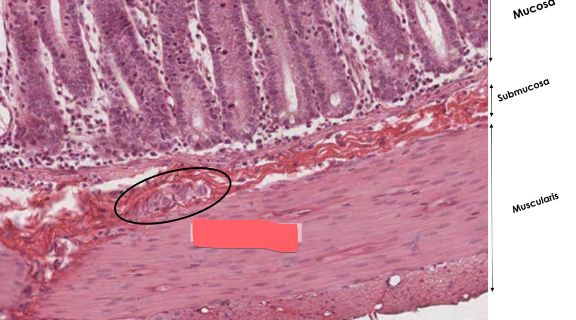
submucosal plexus (meissner’s plexus)
in the submucosa
activates glands
innervates layer of smooth muscle that squeezes mucosa and coaxes out secretions
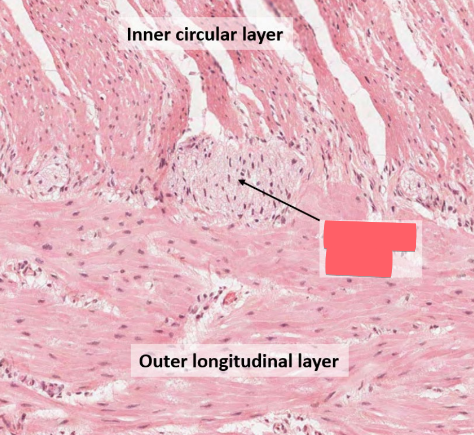
myenteric plexus
major nervous supply to muscularis
peristalsis (involuntary constriction)
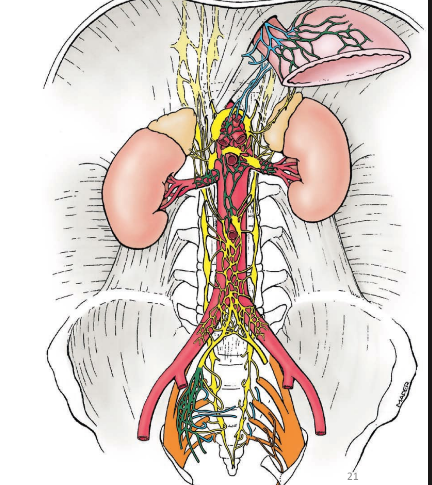
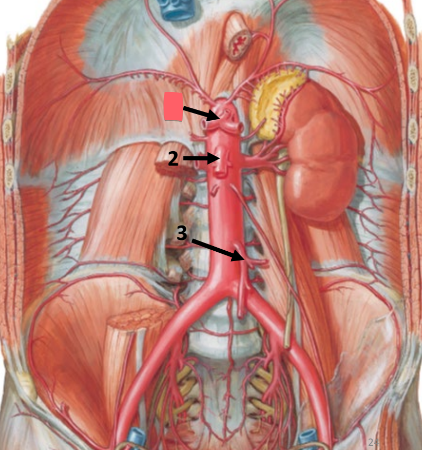
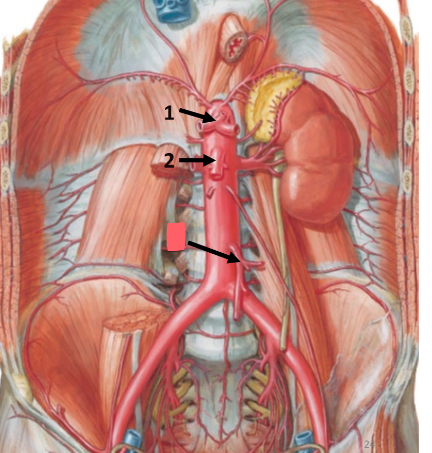
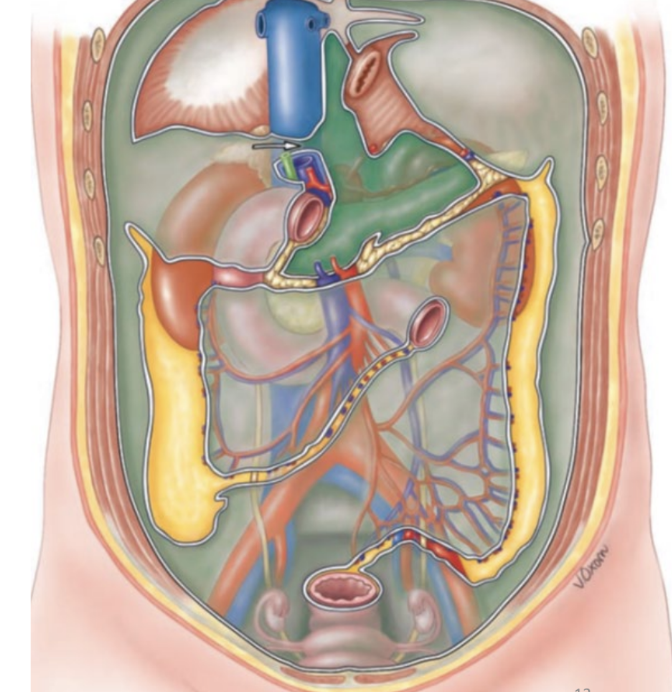
celiac trunk
left gastric artery
common hepatic artery
splenic artery
supplies esophagus, stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder
summary: most upper quadrant organs
superior mesenteric artery
supplies duodenum, pancreas, jejunum, ileum, cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon
summary: all small intestine, some of large intestine
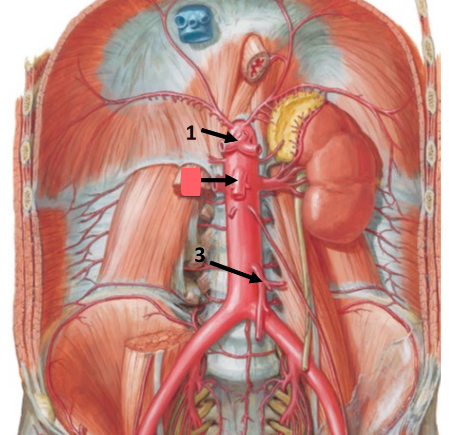
inferior mesenteric artery
supplies transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum
summary: large intestine + remainder of digestive tract
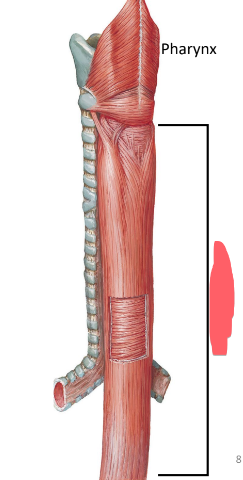
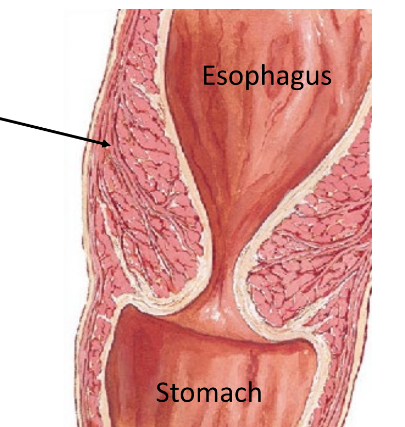
esophagus location
posterior to trachea
begins at larynx
passes through hiatus in the diaphragm to join the stomach
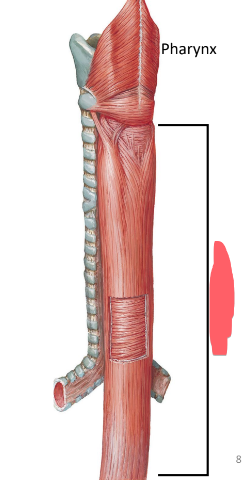
esophagus structure
stratified squamous epithelium
submucosa—blood vessels and nerves
muscularis externa
upper 1/3: skeletal muscle
middle 1/3: skeletal and smooth muscle
lower 1/3: smooth muscle
serosa—outer CT layer
gastro-esophageal sphincter
prevent stomach contents from entering esophagus
smooth muscle
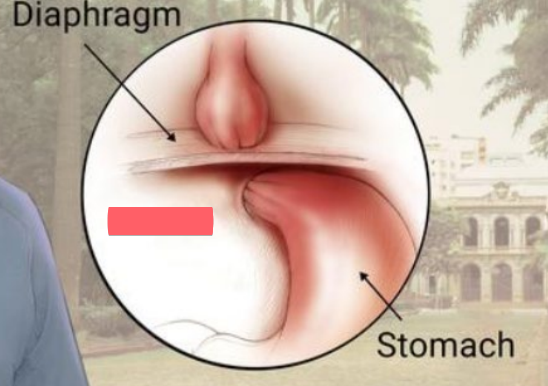
hiatal hernia
stomach bulges through the diaphragm
parietal peritoneum
lines body cavity—inner surface of the abdominal and pelvic walls
visceral peritoneum
covers outer surfaces of organs
peritoneal cavity
space between the two which contains a small amount of peritoneal fluid—same configuration as pleura/pleural cavity
peritoneum
same general principle as pleura: produces lubricative fluid
folds (double layers)
special peritoneal membranes
isolate organs
protect organs
support organs and blood vessels
attach organs to the body wall
store fat
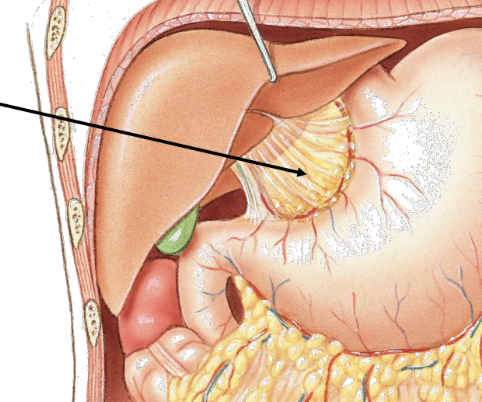
lesser omentum
special peritoneal membrane
attaches lesser curvature of stomach to liver
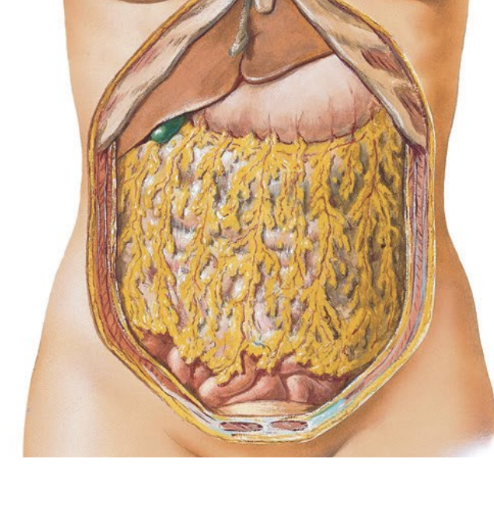
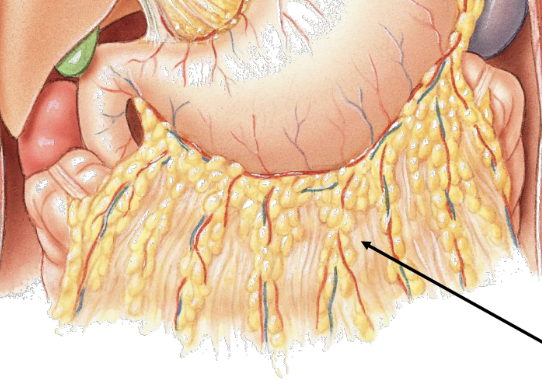
greater omentum
special peritoneal membrane
suspended from inferior curvature of stomach like an apron
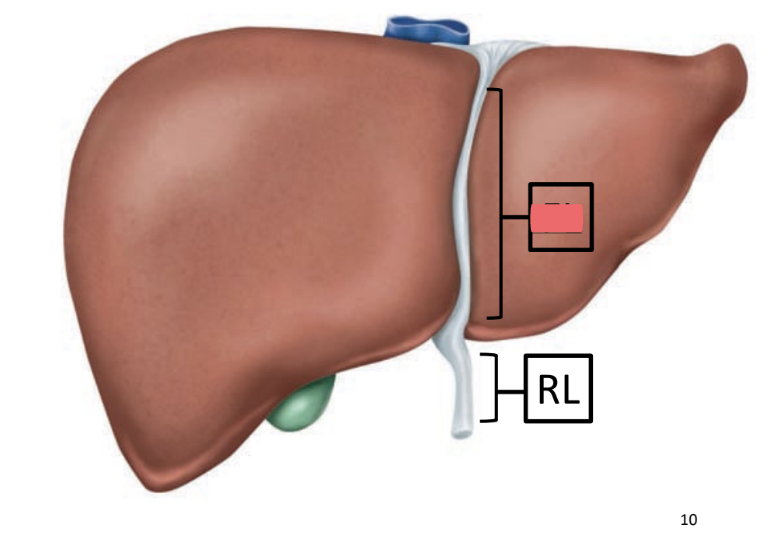
falciform ligament
attaches liver to inferior diaphragm, anterior body wall
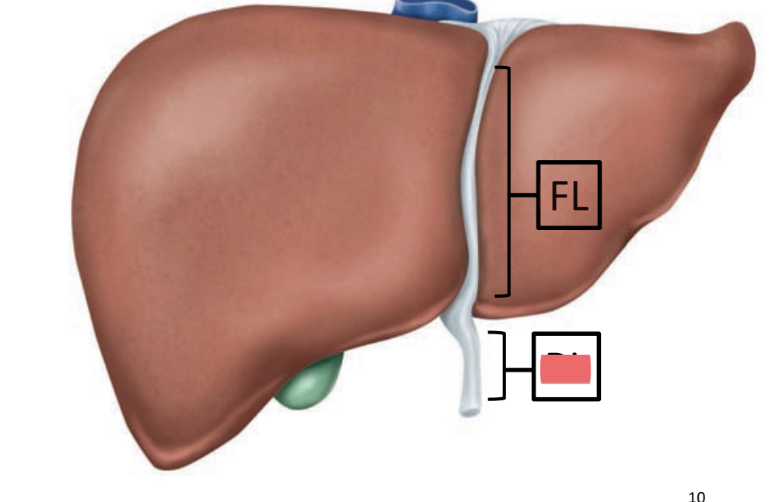
round ligament
remnant of umbilical vein (carried O2 rich blood from placenta)
mesentery
attaches and suspends small intestine from posterior abdominal wall & spine
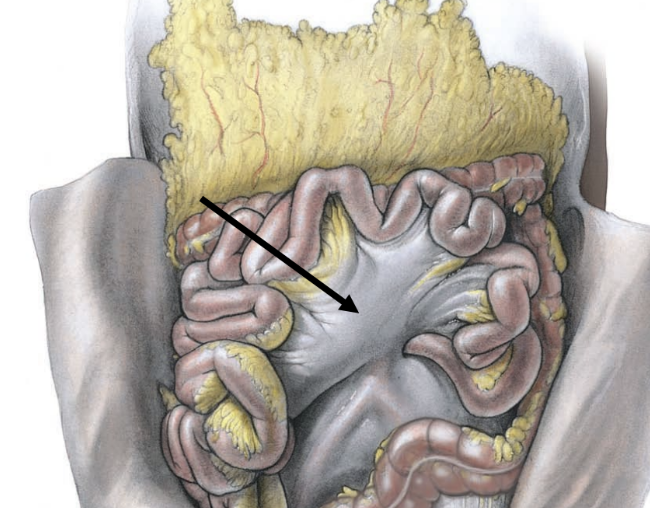
mesocolon
attaches and suspends large intestine to posterior abdominal wall
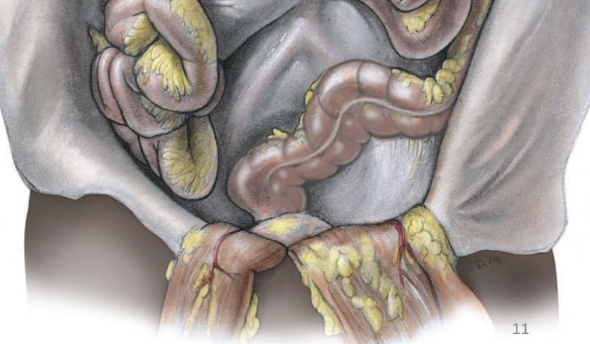
retroperitoneal organs
(behind the peritoneum)
organs that only have visceral peritoneal on their anterior surface OR do not come in contact with the peritoneum at all
parts of pancreas
kidneys
duodenum
ascending & descending colon
chyme
acidic paste of stomach
mechanical mixing of food and production of ______
initiates major protein digestion
storage of _____ until it passes into the duodenum
minimal absorption (e.g. some drugs, alcohol)
stomach location
upper left quadrant between esophagus and small intestine
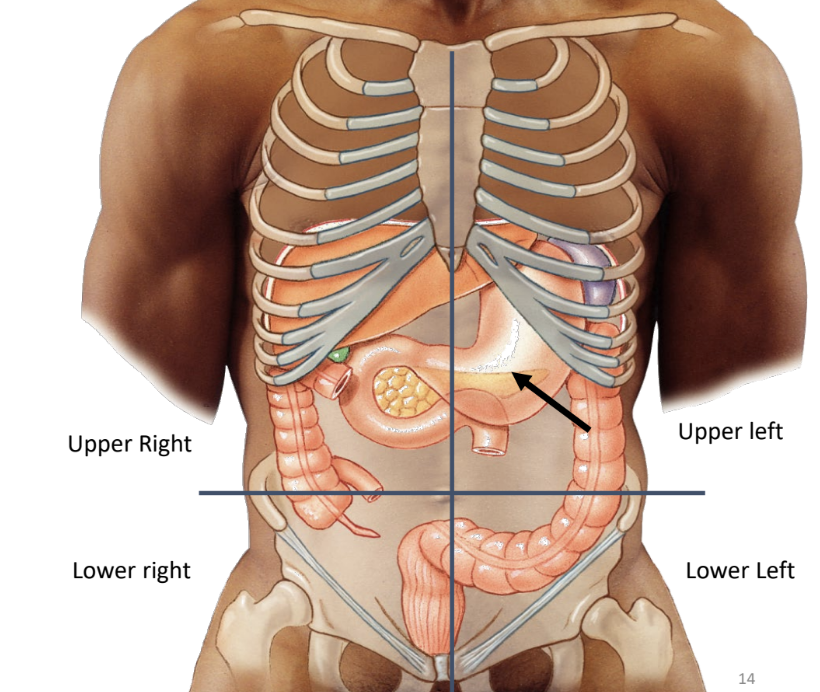
stomach borders
lesser curvature: superior
greater curvature: inferior
stomach regions
cardia: immediately follows esophagus
fundus: superior dome
body: main central region
pylorus: entry to small intestine
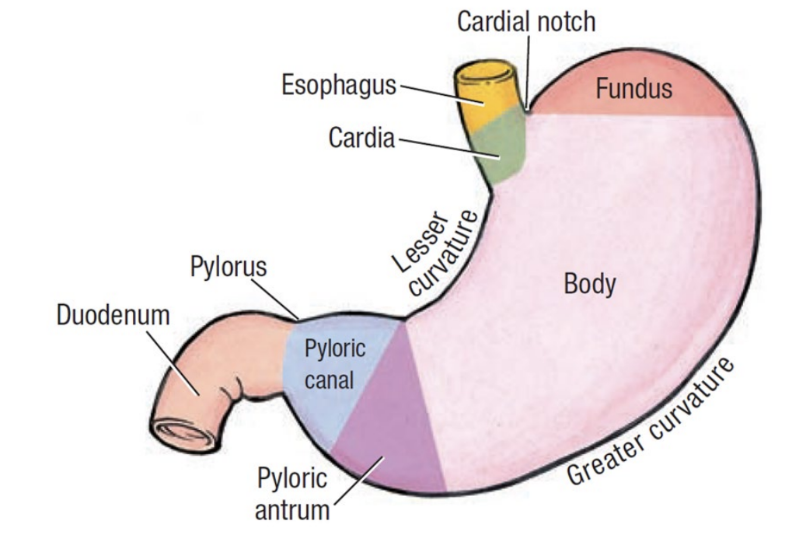
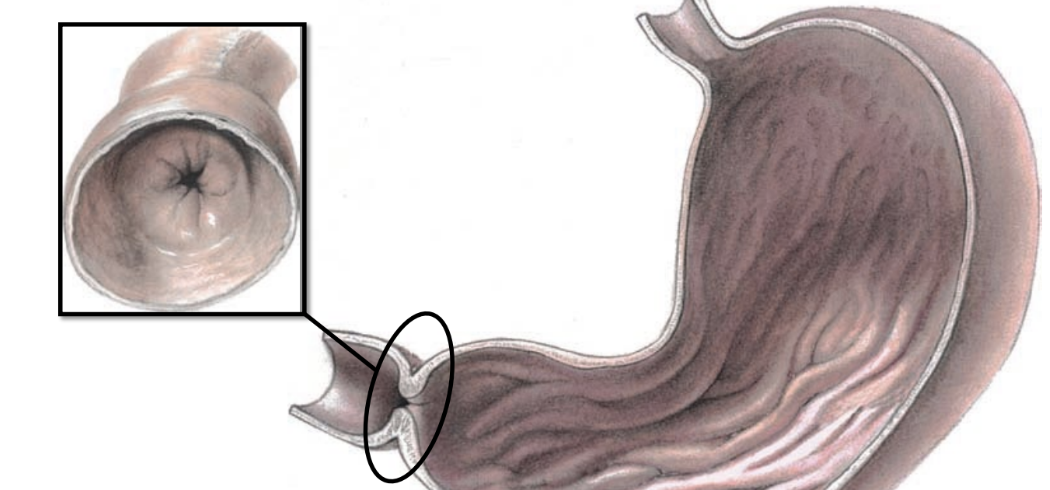
pyloric sphincter
relaxes to let chyme exit stomach & enter small intestine
mucosa (stomach)
(layers of stomach wall)
simple columnar epithelium
submucosa (stomach)
(layers of stomach wall)
nerves and blood vessels
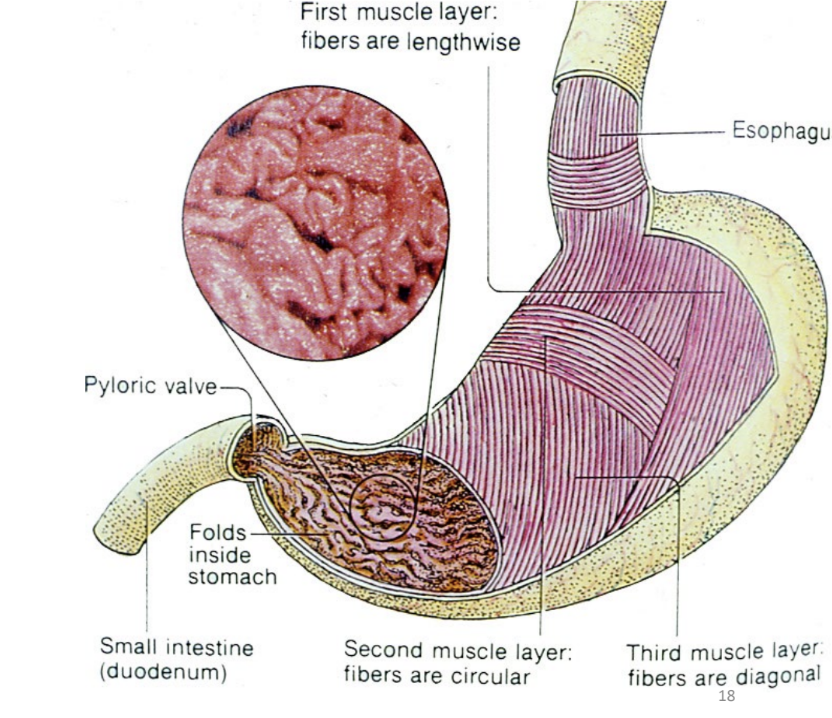
inner oblique, middle circular, outer longitudinal
(layers of stomach wall inner to outer) — muscularis
3 layers of smooth muscle
_____ _______
______ _______
_____ ____________
3 layers: better 3D compression/churning
serosa (stomach)
(layers of stomach wall)
connective tissue
rugae
folds of mucosal layer
permit stomach to distend
increase surface area for secretion and digestion
disappear as stomach expands
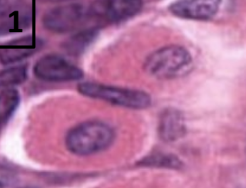
parietal cells
produce HCl which decreases the pH of stomach contents
produce intrinsic factor required for B12 absorption
chief cells
zymogenic cells
produce inactive pepsinogen
converted to active enzyme pepsin for protein digestion by HCl
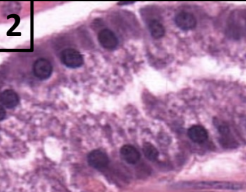
gastric mucous cells
produce bicarbonate-rich mucous
protects stomach lining from HCl
(mucus produced by goblet cells in intestines)
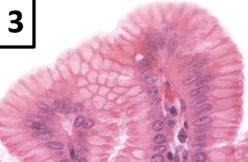
digestive hormones
communication between system and CNS
communication among organs
enteroendocrine cells
stomach & intestines
hormone producing cells
example:
gastrin (from G cells): increase GI activity + acid secretion
small intestine
major site of chemical digestion
mechanical mixing
major site for absorption of nutrients
propels undigested nutrients or materials to large intestine
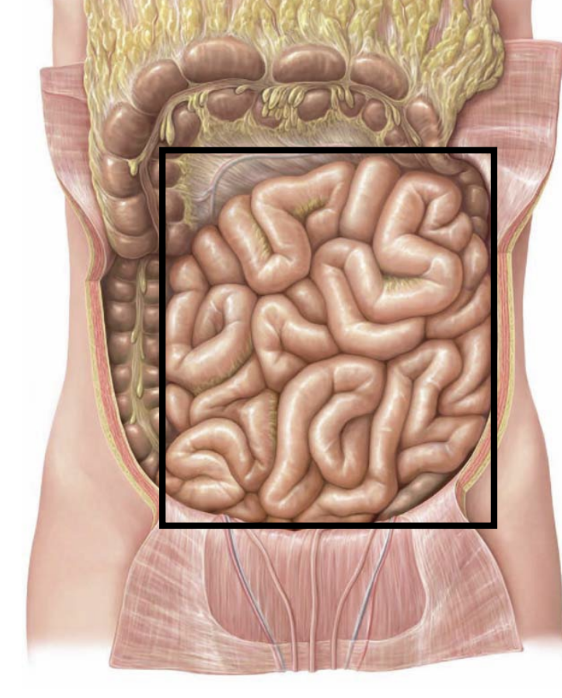
small intestine location
extends from pyloric sphincter (A) to large intestine (B)
occupies central and lower portion of abdominal cavity
primary functions
digestion and absorption
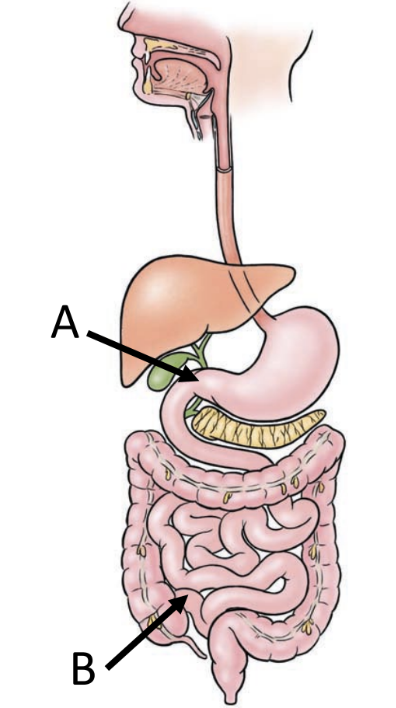
duodenum
region of small intestine
C-shaped region
first 10 inches of small intestine
retroperitoneal
duodenal papilla
opening in ________
bile from common bile duct
enzymes from pancreatic duct
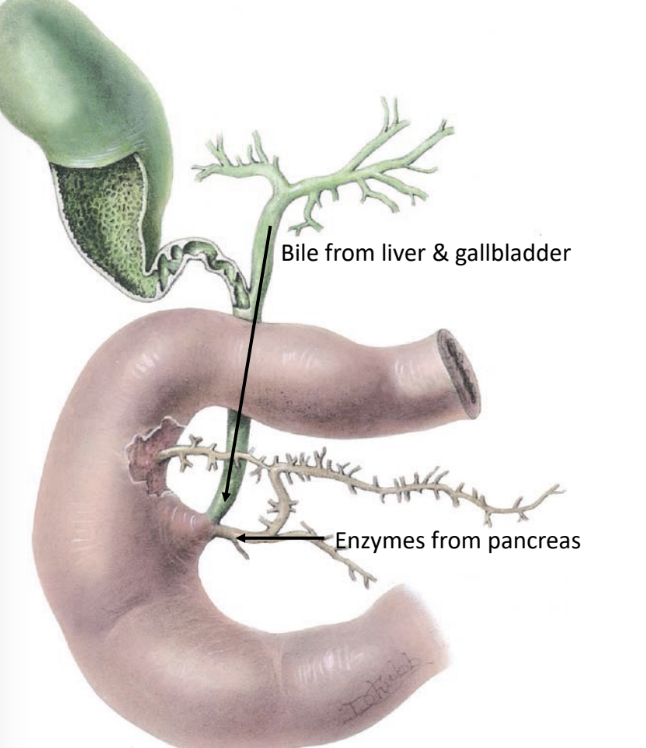
brunner’s glands
secrete alkaline solution
protects intestinal (duodenal) lining from acidic chyme
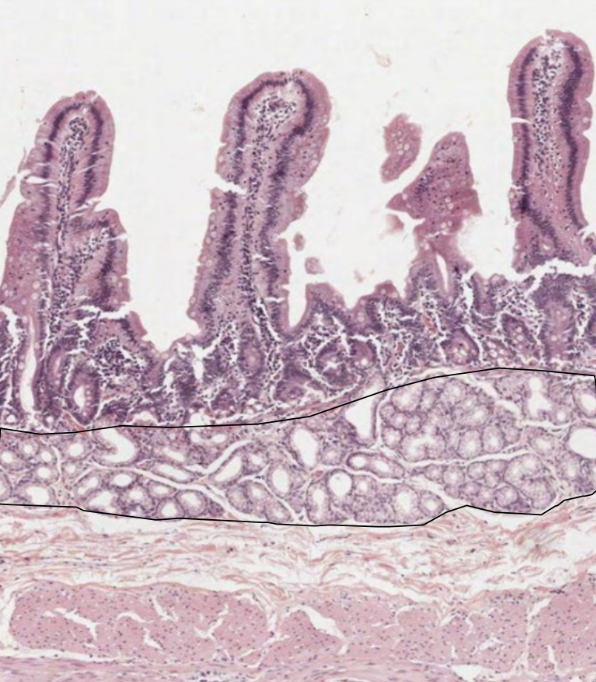
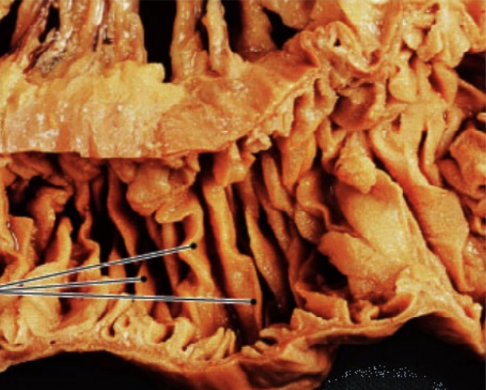
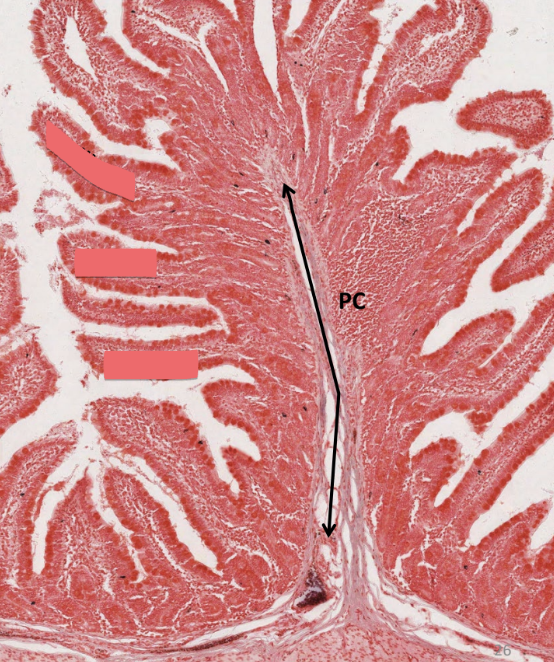
plicae circulares
deep folds of submucosa
increase surface area for digestion and absorption
do NOT disappear as intestine expands (unlike gastric rugae)
villi
small finger-like projections
emerge off of plicae
further increase surface area
capillary network
lacteal: transports digested fats
PC: plica circularis
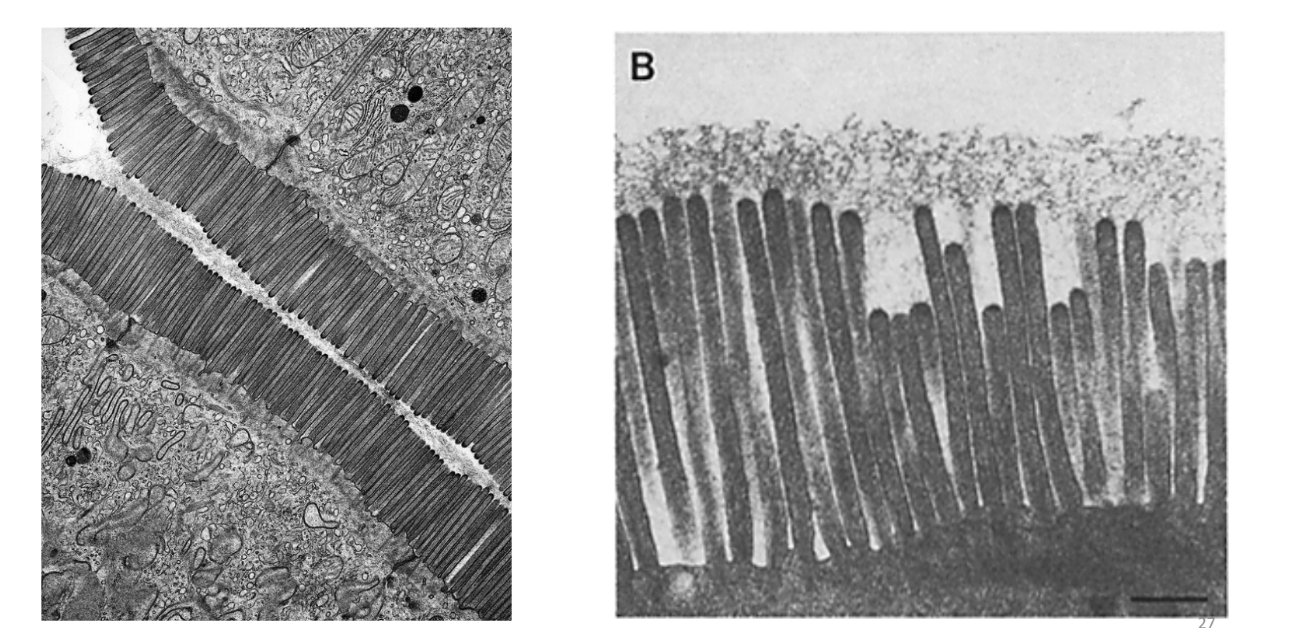
microvilli
even more absorptive surface area on each cell in the intestinal wall
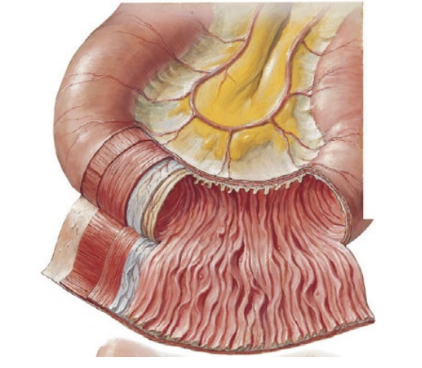
jejunum
region of small intestine
middle section
slightly larger lumen
many plicae circulares
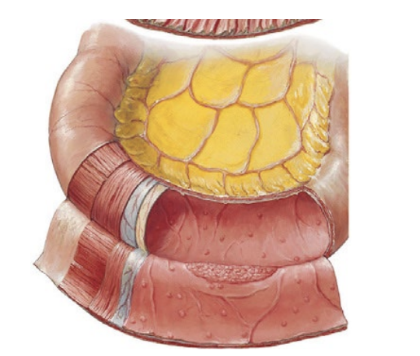
ileum
region of small intestine
third region of small intestine
very few plicae circulares
contains peyer’s patches
clusters of lymphatic tissue
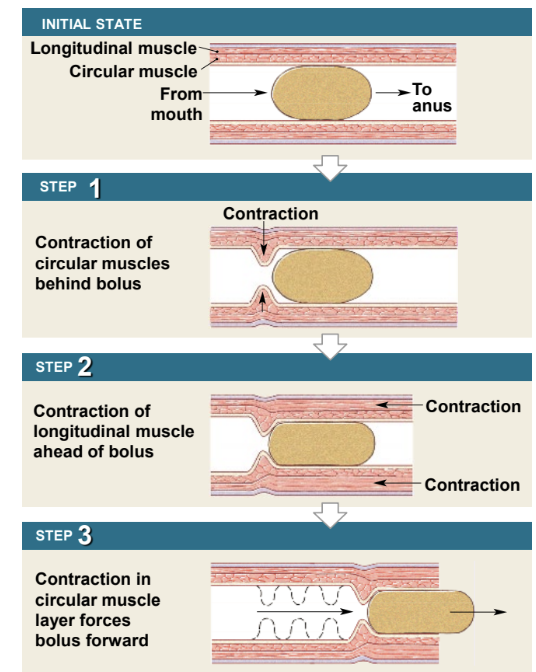
peristalsis
involuntary wave-like movement
entire tract from esophagus to large intestine
functions to mix and propel food through GI tract
involves muscularis layer
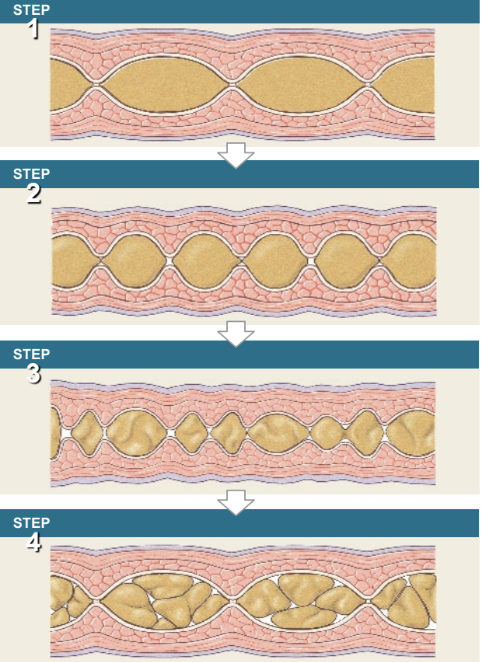
segmentation
occurs primarily in intestine
localized contraction in areas where food is present
mixes food with enzymes
aid in digestion & absorption
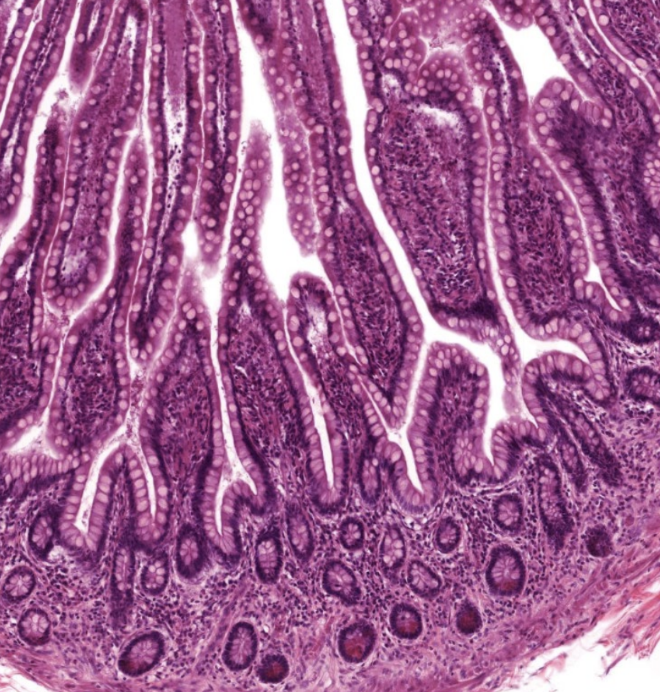
intestinal glands
found on surface of villi and in crypts at base of villi
enzymes
digestive
antibacterial
hormones
affects GI function
large intestine location
begins at end of ileum in lower right quadrant
extends superiorly to liver
runs left to spleen
descends on left pelvis
terminates at anus
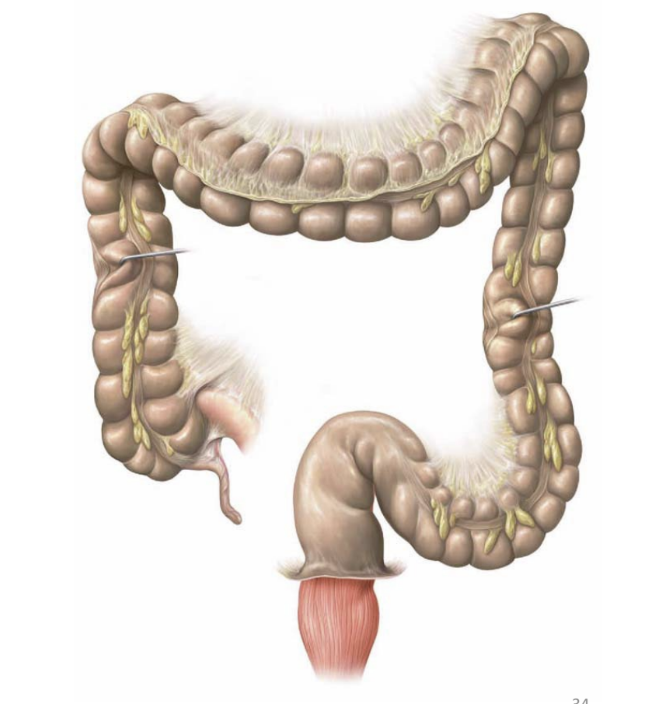
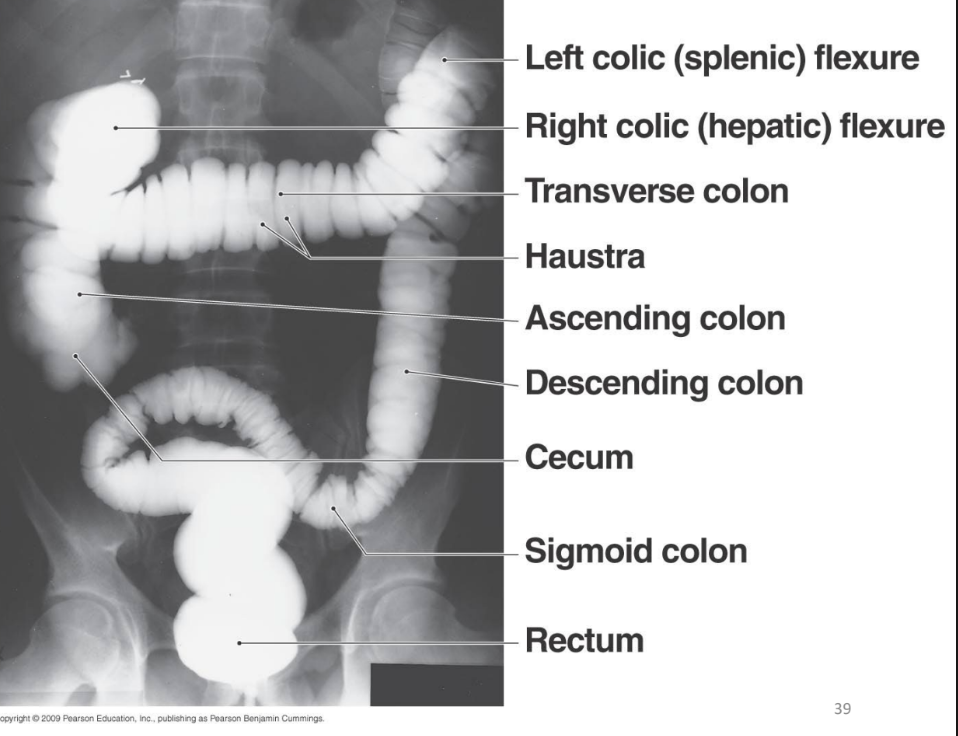
ascending colon
right side
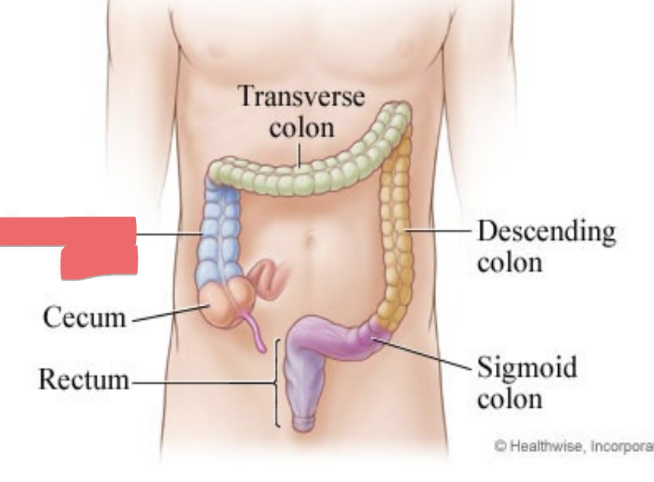
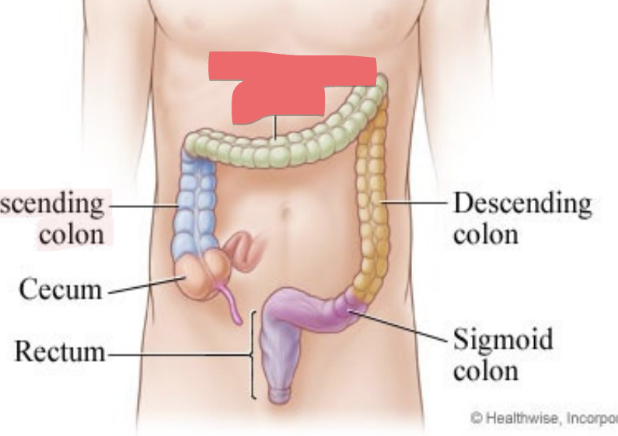
transverse colon
passes from right to left
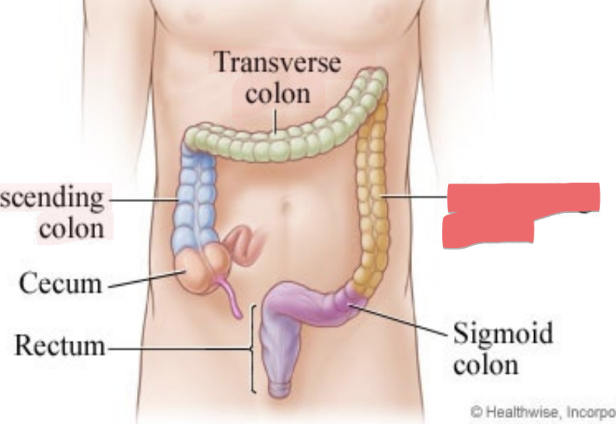
descending colon
left side
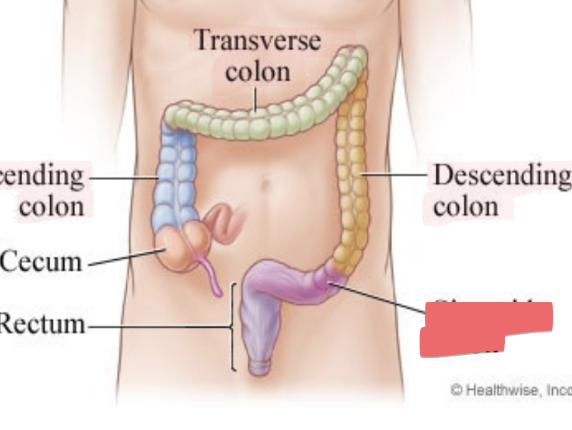
sigmoid colon
S-shaped
from left side to center of body
rectum
in midline, leads to anal canal
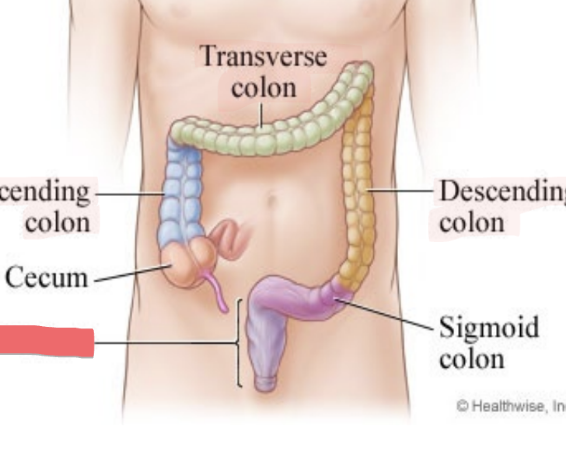
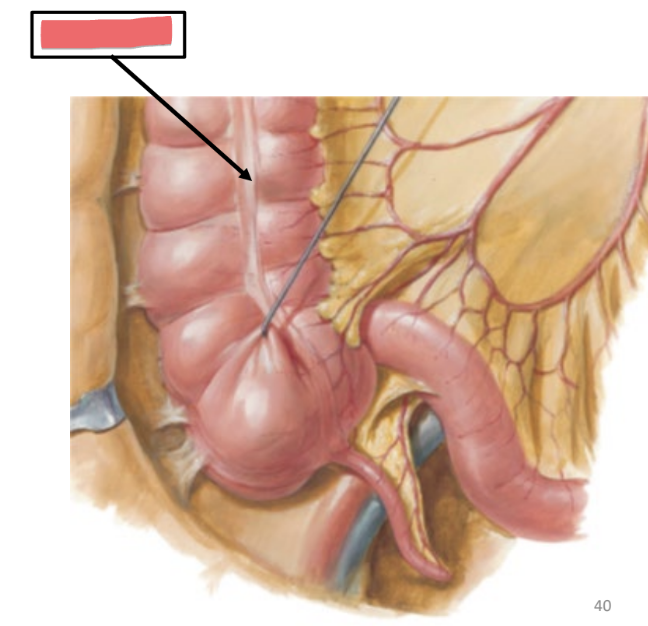
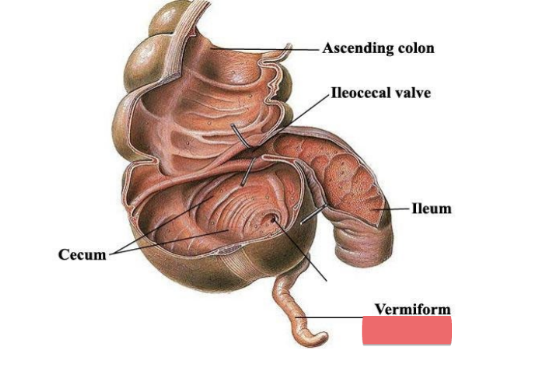
cecum
dilated pouch at junction of small & large intestines (projects off appendix)
lower right quadrant
ileocecal valve guards opening
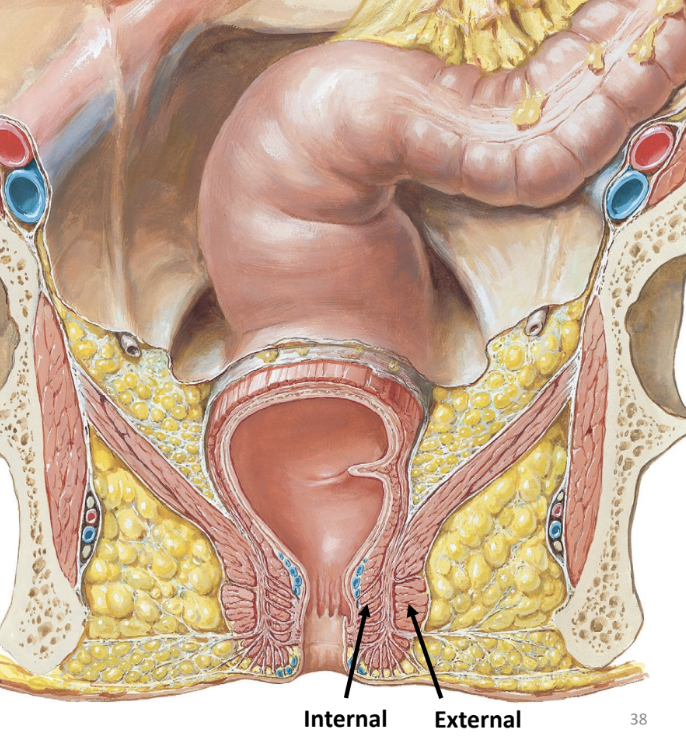
anal canal
of large intestine
passageway leading to the anus (external opening)
sphincters guard opening
internal anal sphincter — smooth muscle
external anal sphincter — skeletal muscle
neat and tidy
the colon is not as ____ ___ ____ in an actual body
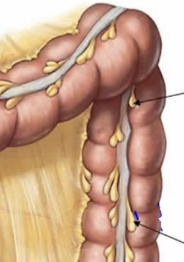
taenia coli
structural specialization of large intestine
long strip of smooth muscle
forms stripe along large intestine
haustra
sac-like regions in large intestine
epiploic appendages
fat-filled pouches of large intestine
large intestine function
completes absorption of water
formation, storage, and explusion of feces
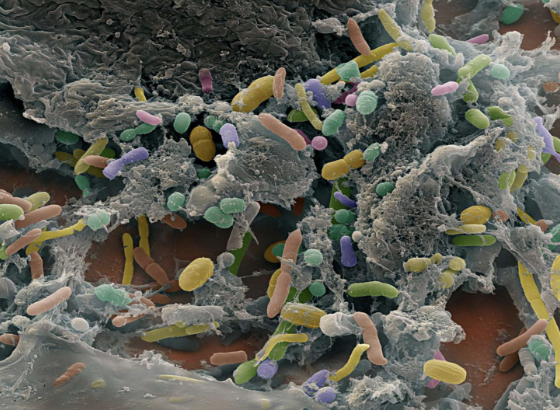
contains “normal flora” (bacteria)
manufacture vitamins
fat soluble A, D, E, K
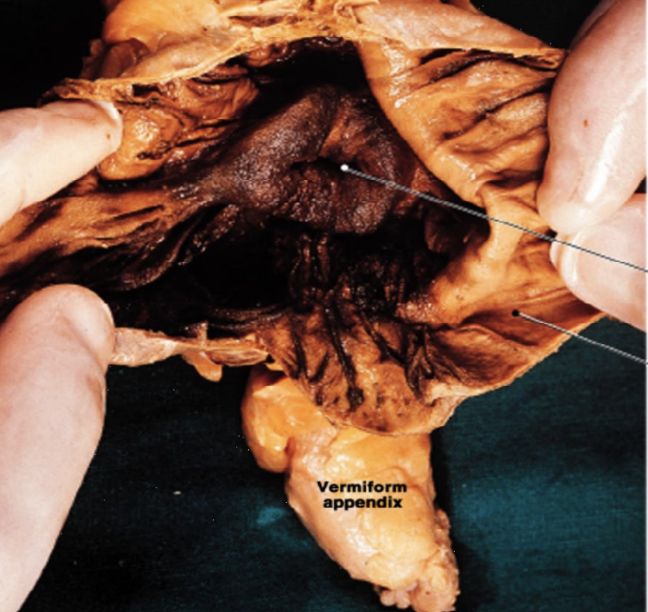
appendix
location
lower right quadrant
usually retro-cecal (behind cecum)
structure
finger-like projections (2-3 inches long)
blind pouch
contains lymphatic tissue
appendicitis
bacterial infection
liver
metabolism of nutrients
detoxification: toxins, drugs
synthesis of major blood proteins: albumin, fibrinogen, etc.
storage
fat
glycogen
iron
vitamins
production of bile by hepatocytes

bile
yellowish-green fluid composed of water, cholesterol, bile pigments (bilirubin) & bile salts
function
emulsification of fat
bile is NOT produced in the gallbladder