Coordinationand response
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
CNS (Central Nervous system)
Composed of brain and spinal cord which contains relay neurons.
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
Composed of cranial nerves, spinal nerves, peripheral nerves which contains sensory neurons and motor neurons.
Sensory organs
Skin, eyes, nose, ears, and tongue
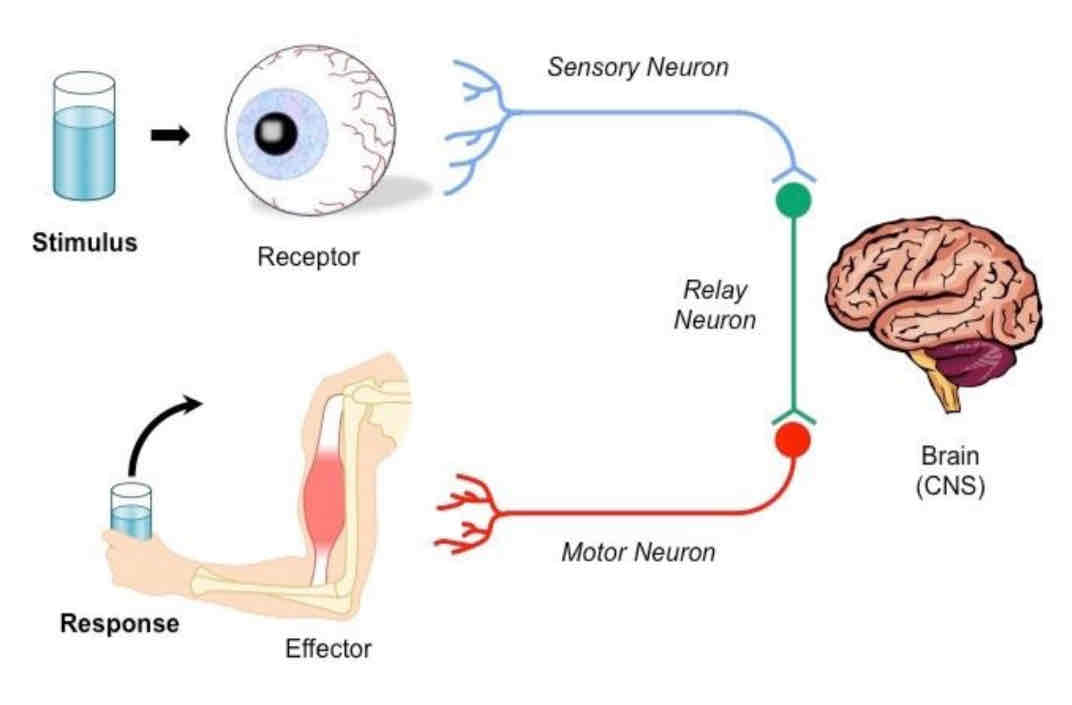
Coordinate response
Stimulus
Receptor
Sensory neurons
Relay Neuron
Brain and spine
Motor neurone
Effector
Response
neurons
Neurons are elongated cells, consisting of body and long, thin axon.
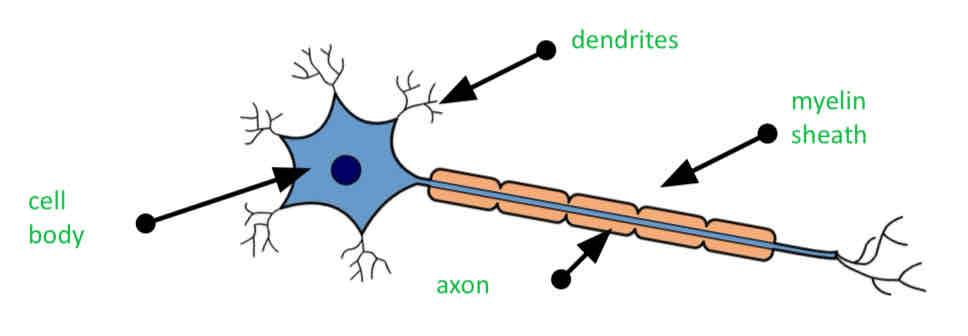
Dendrites
Extended from the cell body and connect with other neurons, allowing electrical impulses to pass from one to the other (make connection with other neurons)
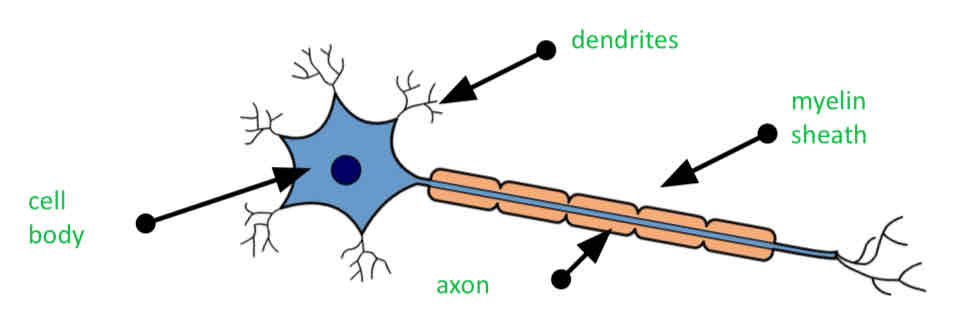
myelin sheath
Insulating liquid that wrapped the axons which speeds up nerve impulse
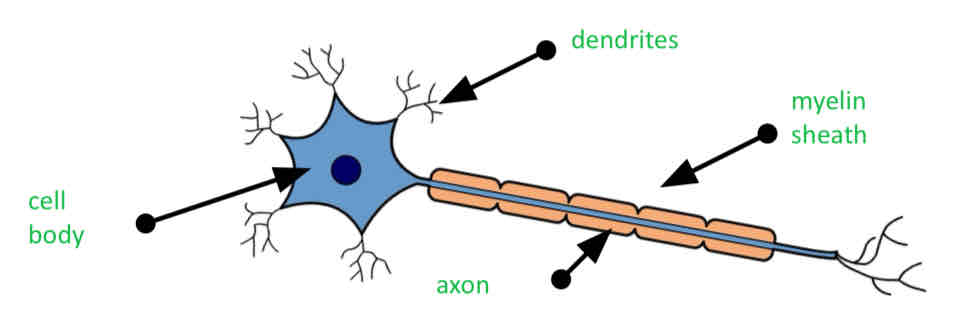
Axons
Send the Nerve impulses across the cell
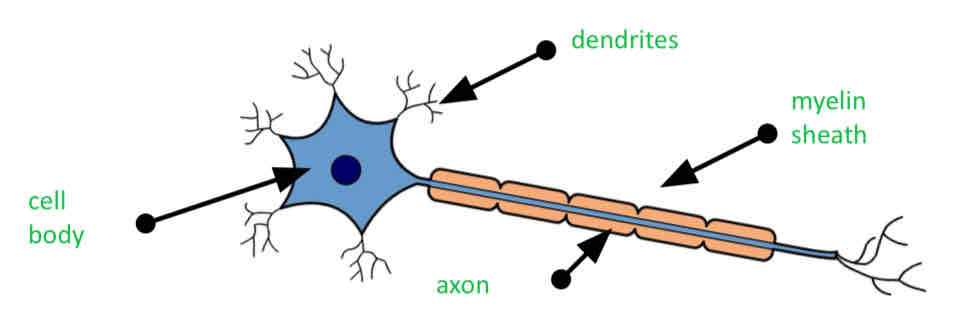
Cell body
Main system of the neurons
What are motor neurons?
Motor neurons transmit messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
What are sensory neurons?
Sensory neurons transmit messages from senses, receptors such as the eye or nose to the brain or spinal cord
What are reflexes?
Fast , automatic protective biological control systems that linked a stimulus to a response (protect from danger)
How does a reflex arc response happen?
Reflex reactions happen without you having to think about them - they are involuntary. This is because the central nervous system sends electrical signals to the muscle before the brain can pick up the message.
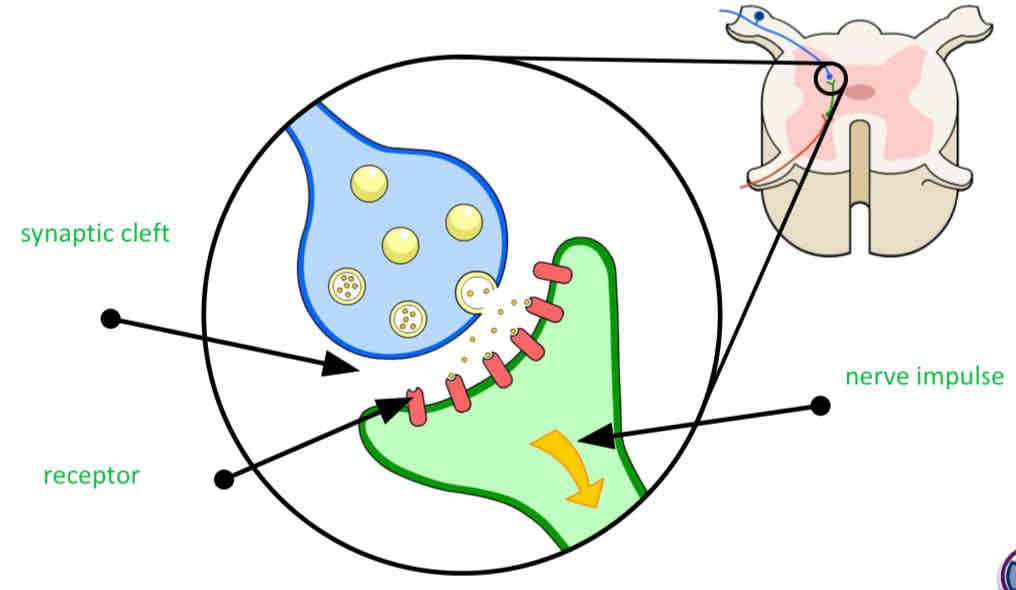
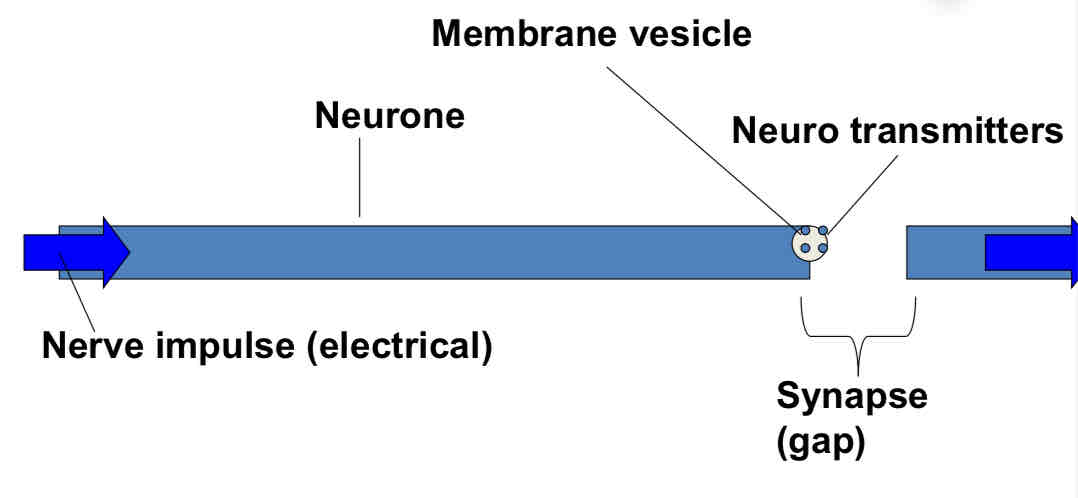
What is a synapse?
Function between to neurones across which electrical signal pass
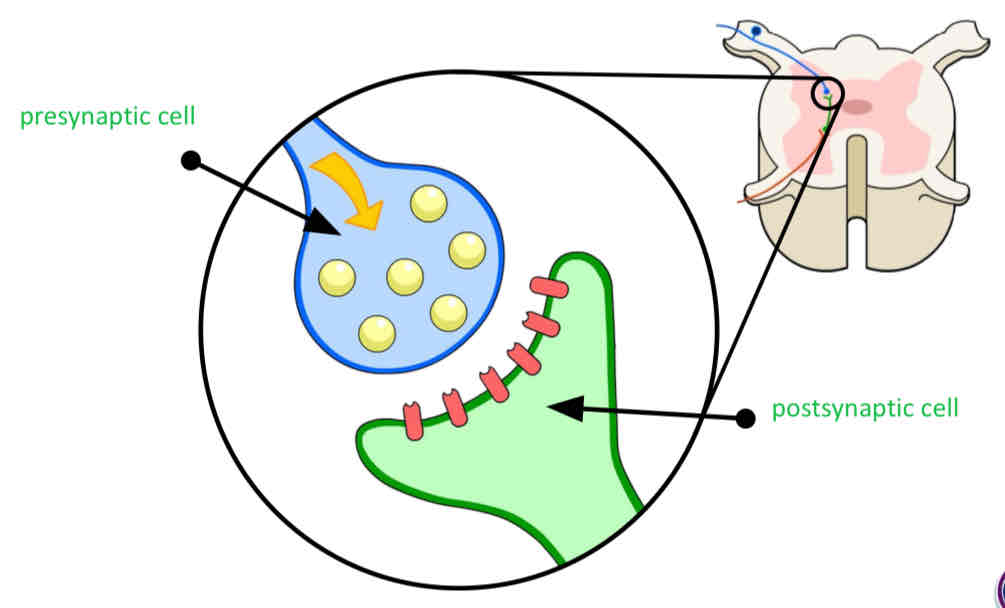
The release of neurotransmitters
When a nerve impulse arrives at the end of one neurone it triggers the release of neurotransmitter molecules from synaptic vesicles.
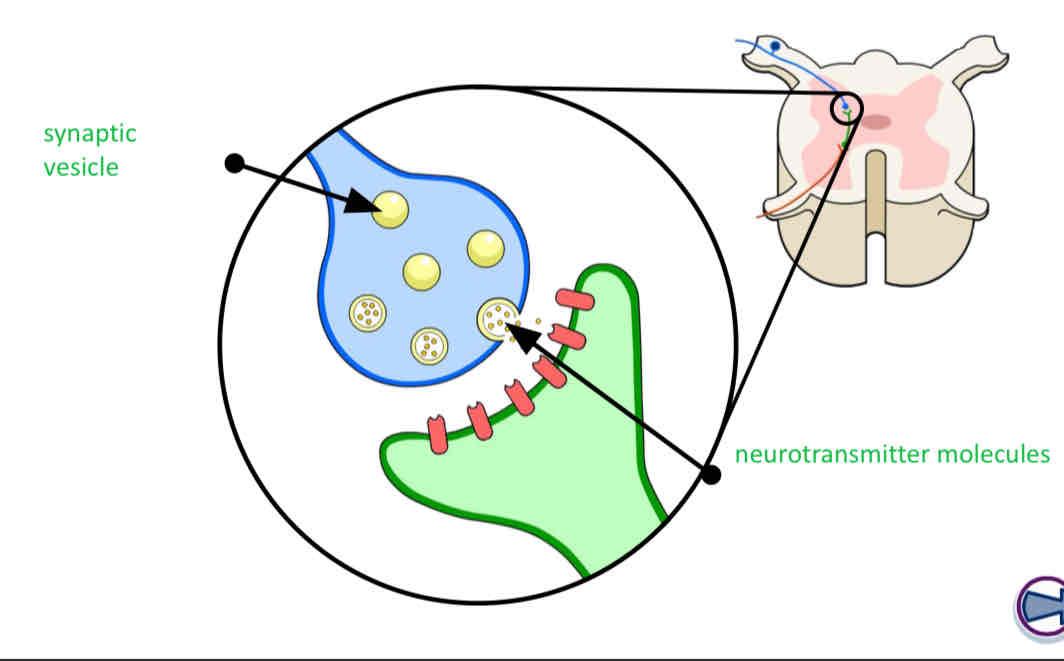
Continuing the impulse
The neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind with receptors on the next neurone, triggering another impulse
Nerve Transmission – The synapse
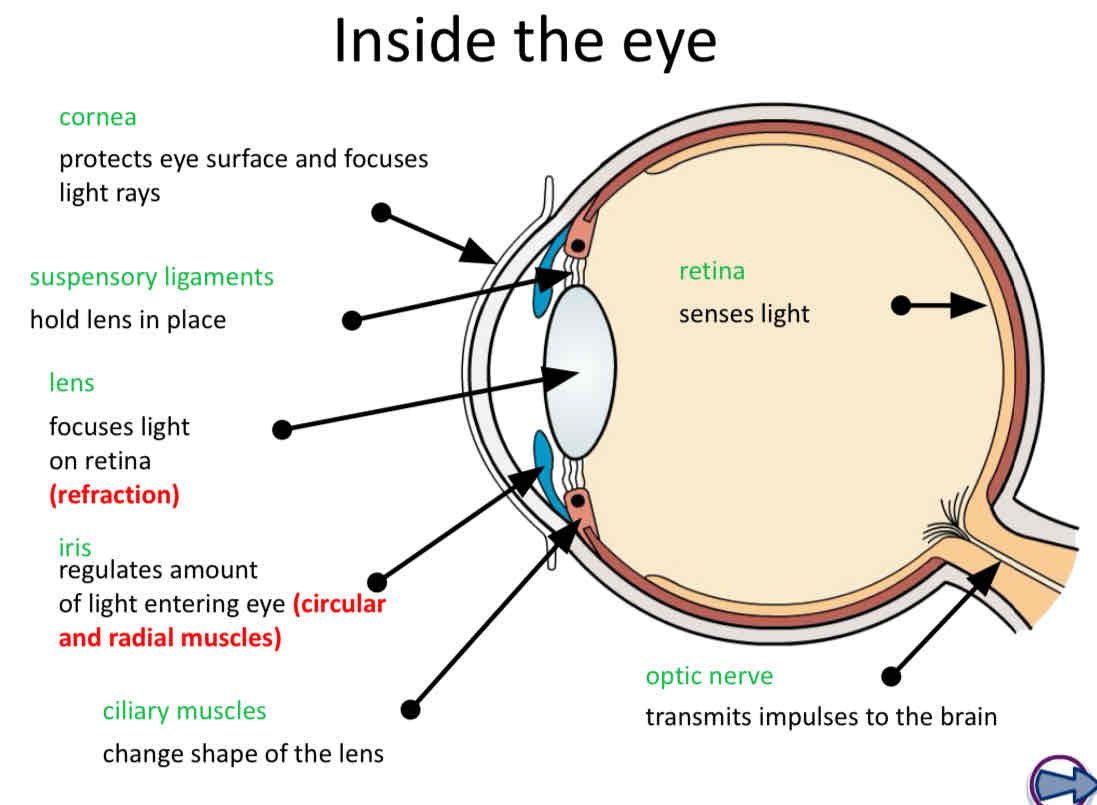
What are the main structures of the eyes and their functions?
Iris reflex
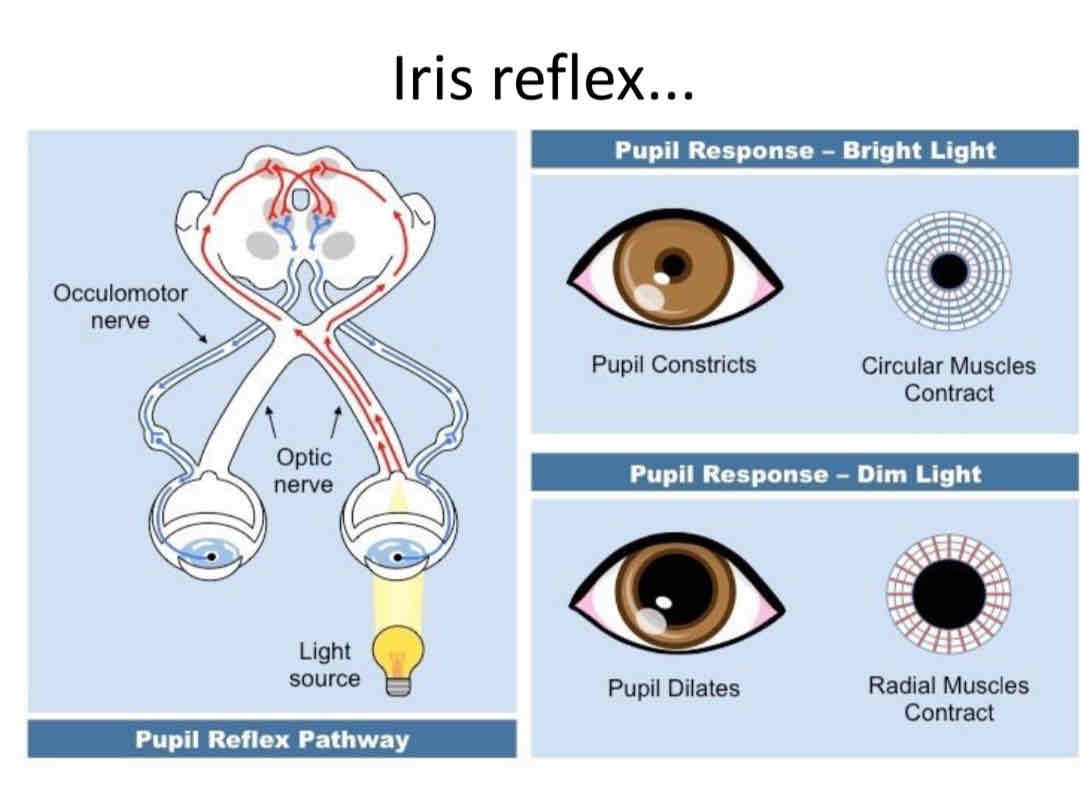
Pupil response - Bright light
Pupil constricted ( smaller)
Circular muscles contract
Radial muscles relaxed
Pupil response - dim light
Pupil dilates (bigger)
Circular muscles relaxed
Radial muscles contracted
Accommodation of light - near/close
Ciliary muscles contract
Suspensory ligaments ‘slacken’ (become slack)
Lens becomes FAT
Light is refracted more (bent)
Accommodation of light - Far/distant
Ciliary muscles relax
Suspensory ligaments ‘tighten’ (become taught)
Lens becomes FLAT
Light is refracted less (bent)
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers release in the blood stream which target certain organ
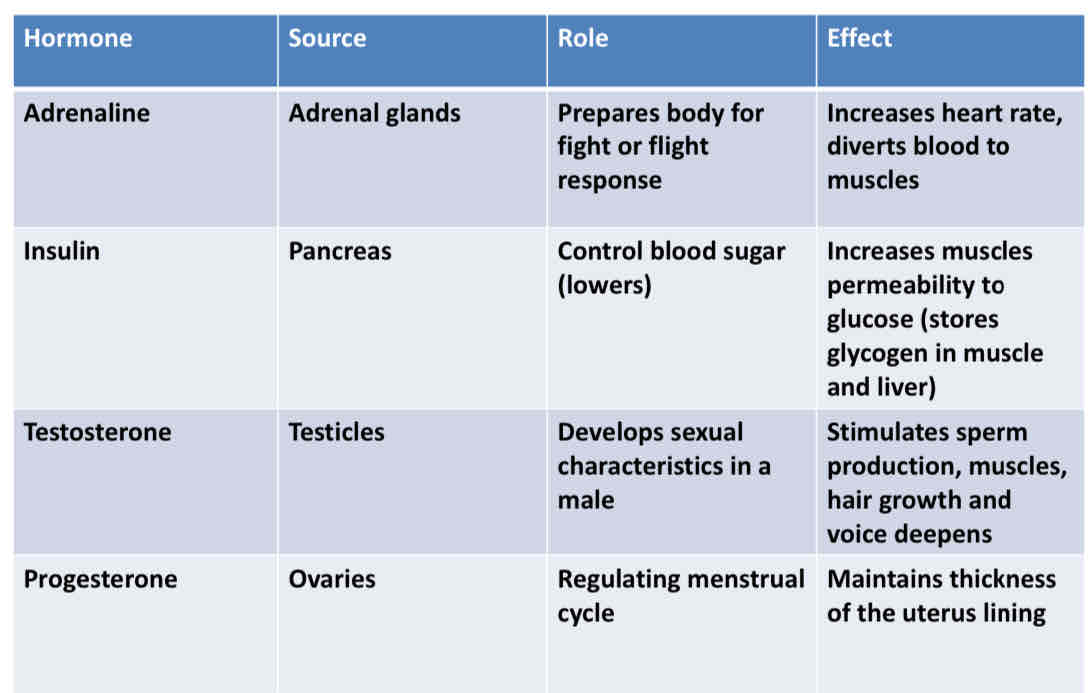
What are the sources and roles of the following hormones? (Adrenaline, Insulin,Testosterone,Progesterone,Oestrogen)
The main differences between the hormonal and nervous system
Nervous system
Speed of action : faster
How is the signal transmitted :Electrical impulse signals along axon
How long does the signal last :Shorter lived
Hormonal System
Speed of action : Slower
How is the signal transmitted : Chemical messenger in blood stream.
How long does the signal last :Can last months or even years
What are the main types of stimuli that plants respond to?
Three types:
Light
Water
Gravity
What is a tropism?
a growth movement in response to a stimulus.
Are there different types of tropisms?
Light: phototropism
Water: hydrotropism
Gravity: geotropism
How do roots and shoots respond to stimuli?
Shoots:
Shoots grow towards sunlight. They are
positively phototropic.
Shoots grow away from gravity. They are
negatively geotropic.
Roots:
Roots grow away from sunlight. They are
negatively phototropic.
Roots grow towards gravity. They are
positively geotropic.
Positive phototropism
Auxins produced in the shoot tip move to the shaded side of the plant
The auxins cause the cells on the shaded side to elongate and get bigger
Growth ( bends ) towards the light
Positive geotropism
Gravity pulls the Auxin down towards the roots where they rest on the bottom side of the root structures.
Auxins retard root cell growth
Root cells elongation and growth is inhibited by Auxin therefore the other side of the root grows faster and the roots grow towards gravity.
Gravity pulls the Auxin down towards the roots where they rest on the bottom side of the root structures.
Homeostasis
the maintenance of a constant internal environment.
Body water content
Body temperature
Maintenance of internal body temperature
Body temperature is maintained at 36 degrees. The body loses heat when the environment is too hot, and retains heat when the environment is too cold.
Role of skin in temperature regulation
Mechanisms to retain heat
Basic insulation
The fat layer in the skin acts as an insulator
Skin hair follicles stand up to trap a layer of air around the skin which is also an insulator
Shivering
Increased metabolism in muscles increase heat circulation
Vasoconstriction
Heat is carried in the blood
If blood goes near the skin surface, then heat radiates out of the body
Constriction of the skin arterioles reduce the amount of blood flowing near the skin surface to retain heat in the blood
Mechanisms to lose heat
Sweating
Sweat is a mixture of water, salt and urea
Water evaporates from sweat which causes the skin (and body) to cool down
Vasodilation
Dilation of skin arterioles increase the amount of blood flowing near the skin surface to allow more heat to radiate out of the body