acceleration
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Newton's second law states that the acceleration experienced by an object is directly proportional to the net applied force. This practical investigates the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration by measuring the applied force and acceleration of a trolley.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
aim
investigate the effect of varying the force on the acceleration of an object of constant mass, and the effect of varying the mass of an object on the acceleration produced by a constant force
independent variable
applied force
dependent variable
acceleration of the trolley
control variable
trolley
equipment
trolley
adjustable ramp
string
pulley
masses
tape
card
balance
2 light gates
data logger
clamp
stand
ruler
setup
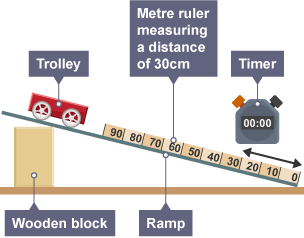
prop up using the clamp and stand and adjust the slope of the ramp until the trolley just starts to move on its own (to reduce effects of friction)
place the light gates along the ramp so the card passes through both of them
connect light gates to data logger
record the length of the card
fasten the card to the top of the trolley
record the combined mass of the trolley and card on the balance
add the mass to the string
connect the string to the trolley
steps
hang the string and mass from the edge of the ramp
release the trolley
record the velocity of the trolley and time taken from the data logger
repeat experiment by adding more mass from on top of the trolley
acceleration = change in velocity/time taken