UNT Principles of Biochemistry Exam 3 Review: Chapter 16
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What do carbohydrates provide?
Energy
Who was Emil Fischer?
German-born scientist who won the Nobel prize in chemistry in1902, for his studies on sugars, purine derivatives, and peptides
Monosaccharides are:
-The building blocks of all carbohydrates
-It is a carbohydrate that cannot be simplified to a simpler carbohydrate
-General formula: CnH2nOn; n varies from 3 to 8
What is a monosaccharide containing an aldehyde group?
Aldose
What is a monosaccharide that contains a ketone group?
Ketose
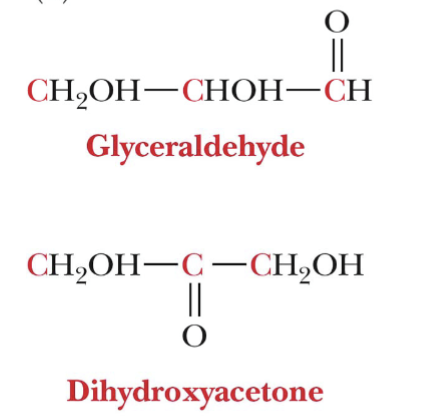
What are the only two trioses?
Glyceraldehyde (aldotriose) and Dihydroxyacetone (ketotriose)
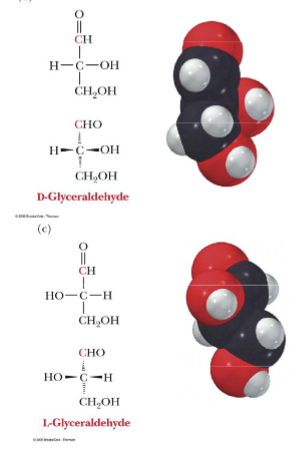
Stereoisomers are:
Three-dimensional molecules with structure and space-filling.
2n-2
Ex. L-glyceraldehyde and D-glyceraldhyde
Fischer Projections are:
A two-dimensional drawing projections with horizontal lines representing bonds projecting forward and vertical lines projecting the rear.
*the carbon atom in the intersection will not be shown
Monosaccharide with -OH on penultimate carbon on right
D-monosaccharide
Monosaccharide with -OH on penultimate carbon on left
L-monosaccharide
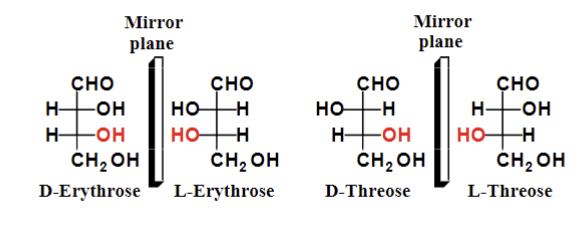
Stereoisomers that are mirror images
Enantiomers
Ex. D-erythrose and L-erythrose
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images
Diastereomers
Ex. D-erythrose and D-threose
Diasteroisomers/Epimers are not:
Mirror images and Superimposable
Enantiomers are:
nonsuperimposable mirror images
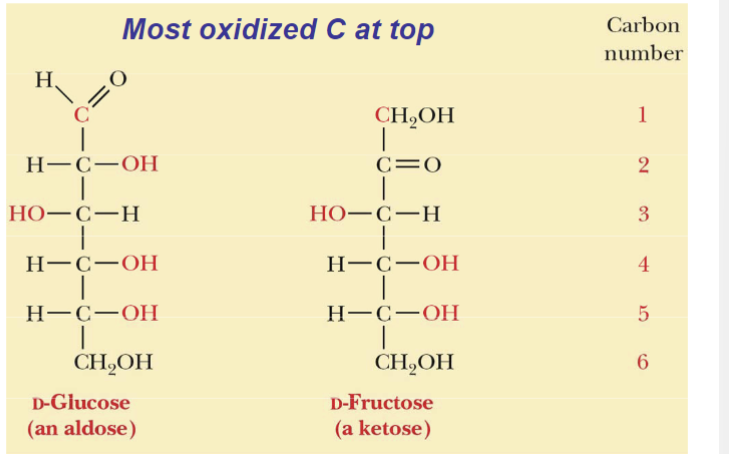
What are examples of aldose and ketose?
D-glucose (aldose)
D-fructose (ketose)
Trioses are the simplest:
Carbohydrate monosaccharides
What contains a stereocenter and exists as a pair of enantiomers?
Glyceraldehyde
What happens if a sugar forms a cyclic molecule?
Interaction between functional groups on distant carbons C1 to C5 make a cyclic hemiacetal
What makes a hemiketal formation?
Cyclization using C2 to C5
What happens to the carbonyl carbon in both cyclic molecule formations?
It is a new chiral center and becomes a anomeric carbon
Anomeric carbons
Have a new stereocenters resulting from cyclic hemiacetal formation
Anomers
Carbohydrates that differ in configuration only at their anomeric carbons
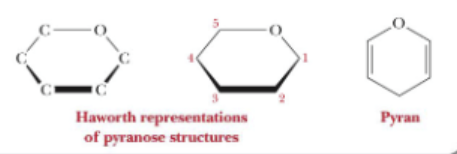
What kind of projections present five- and six-membered hemiacetals as planar pentagons or hexagons?
Haworth projections
What is the most commonly written projection with the anomeric carbon on the right and hemiacetal oxygen to the back right?
Haworth projections
Extra: the (B-) means (-OH) on the anomeric carbon is cis to the terminal, while (a-) is trans
What infix stands for a six-membered hemiacetal ring?
Pyran (pyranose)
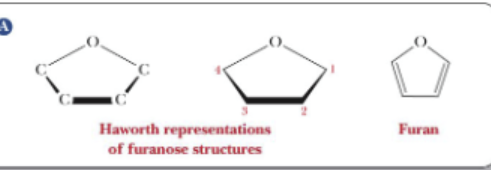
What is the infix for a five-membered hemiacetal ring?
Furan (furanose)
What does reducing sugar do?
It reduces an oxidizing agent
What results in a negative Tollens reagent test?
Presence of anomeric carbons involved in glycosidic linkage
What results in a positive Tollens test?
an unbonded anomeric carbon that is free
What produces a lactone?
Oxidation of a cyclic hemiacetal form
What does the Tollens reagent use as a oxidizing agent?
Silver Ammonia Complex Ag(NH3)3+
What is a recent method for detection of glucose?
The use of glucose oxidase
What is ascorbic acid?
Vitamin C, which is synthesized both biochemically and industrially from D-glucose
What two molecules are physiologically active and found in most body fluids?
L-ascorbic acid is oxidized to L-dehydroascorbic acid and both are found in most body fluids
The reduction of C=O group of a monosaccharide gives a
Polyhydroxy compound called alditol
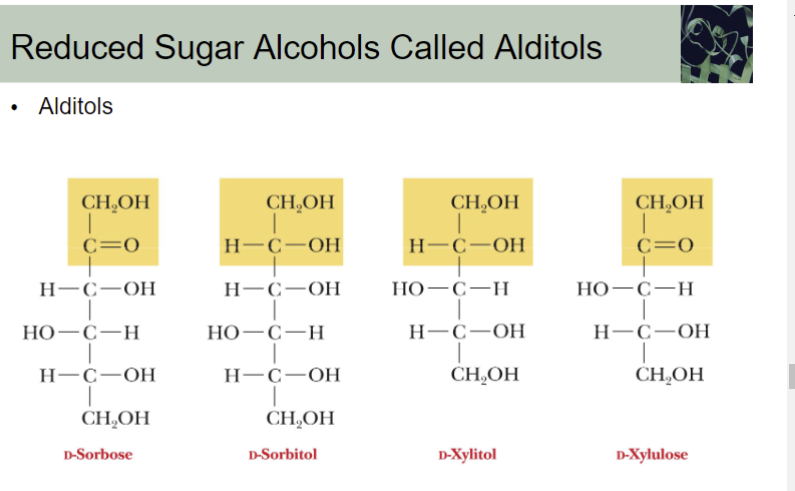
Deoxy sugar is:
a sugar in which one of the hydroxyl groups has been reduced to a hydrogen
Ex. Deoxyribose (reduced sugar), Ribose (parent sugar), Galactose (parent sugar), and Beta-L-Fucose (reduced sugar)
How are phosphoric esters formed?
Phosphoric esters are frequently formed by the transfer of phosphate group from ATP; important in metabolism of sugars to provide energy
Glycosidic Bond Formation
A glycoside is a carbohydrate that an -OH of an anomeric carbon is replaced by -OR
A glycosidic bond is a bond from the anomeric carbon to the -OR group
*Basis for the formation of polysaccharides/oligosaccharides
What are the two different disaccharides of alpha-D-Glucose
Alpha (1,4) Glycosidic bond
Alpha (1,6) Glycosidic bond
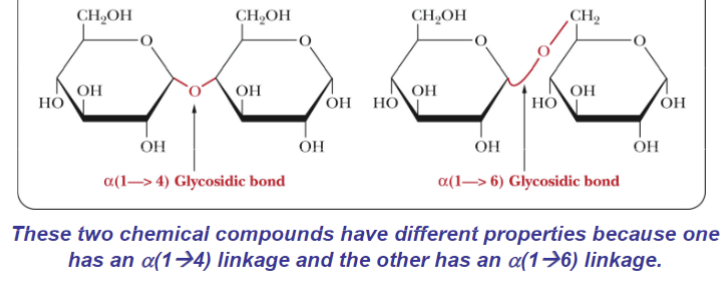
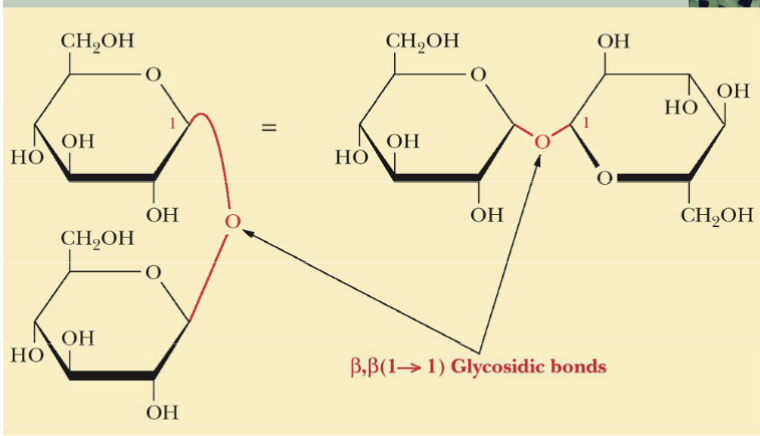
Disaccharide of Beta-D-glucose
B,B (1→1) Glycosidic bonds
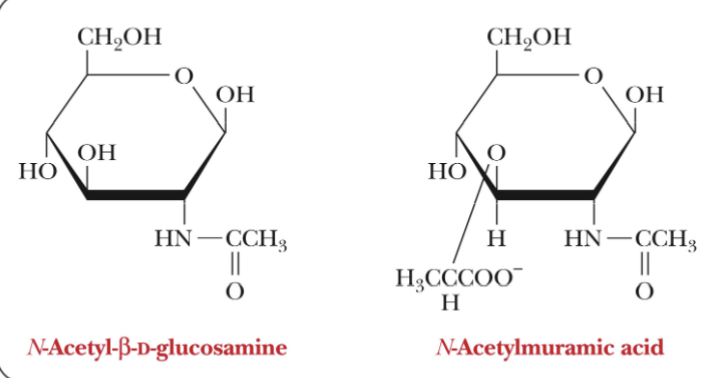
Important components of bacterial cell wall:
Amino sugars
Glycosidic linkages are responsible for:
Bonding of monosaccharides to form oligosaccharides and polysaccharides
Sugars undergo and form:
Undergo oxidation reactions and form esters
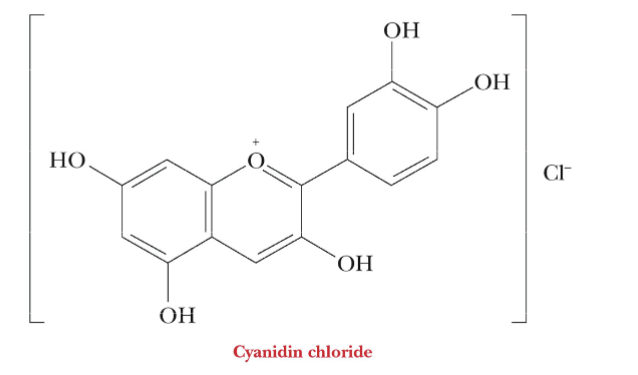
What influences the red and blue colors of flowers?
The red and blue colors are sugar derivatives called anthocyanins
The pigments involve various sugars bonded to the compound cyanidin and its derivatives
What are flavors considered?
Sugar Glycosides
Ex. cinnamon and vanilla
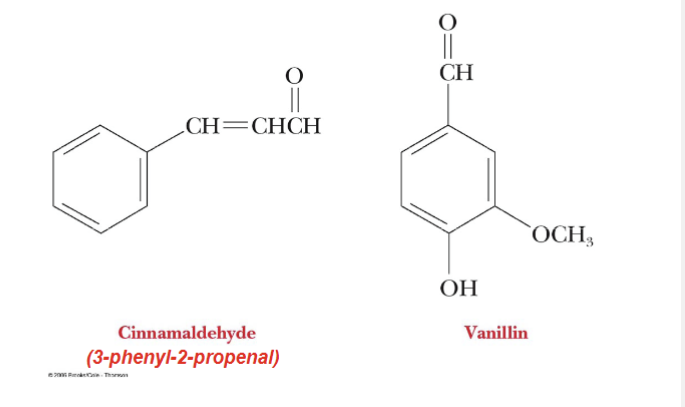
Some uses of Laetrile involve:
A controversial use of the glycosteroid is it’s use as a cancer treatment
*side note: has a bitter almond flavor, the flavor in the kernel of the peach or apricot is due to laetrile
Sucrose (hydrolyzed by sucrase or invertase)
Made up of D-glucose and D-fructose followed by alpha-1,2-glycosidic bond
Table sugar, from juice of sugar cane and sugar beet (splenda)
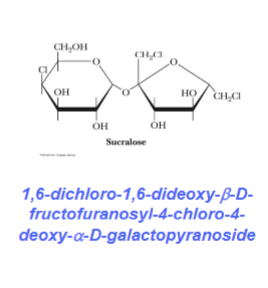
Lactose (hydrolyzed by lactase)
Made up of D-galactose and D-glucose followed by Beta-1,4-glycosidic bond
Galactose is a C4 epimer of glucose
Found in human milk and cow milk
Maltose (hydrolyzed by maltase)
Made up of D-glucose joined by an alpha-1,4-glycosidic bond
Formed from hydrolysis of starch and found in germinating seeds such as barley and starch
Differs from cellulose by the conformation of glycosidic linkage
Polysaccharide
When many monosaccharides are linked together (poly-many)
What is the major structural component of plants?
Cellulose
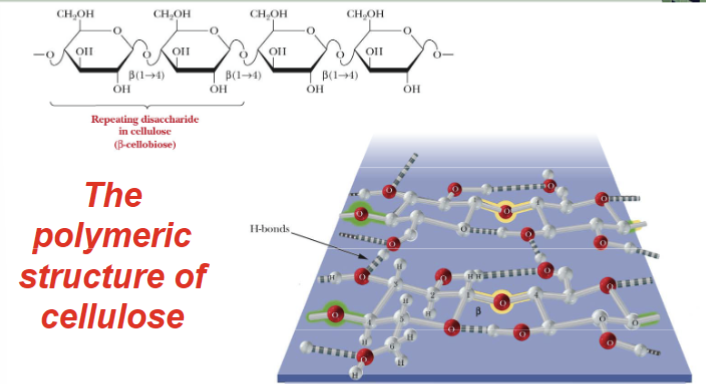
Cellulose is
A repeating disaccharide
structural polymer
The monomer of cellulose is beta-anomer of glucose, and it gives the rise to long-chains that hydrogen bond to one another
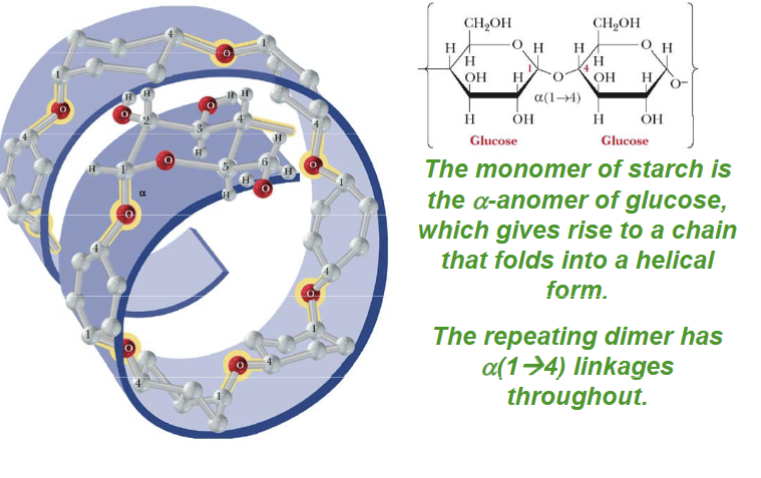
The structure of amylose consists of:
continuous, unbranched chains up to 4000 alpha-D-glucose joined by alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds
The structure of amylopectin consists of:
a highly branched polymer consisting of 24-30 units of D-glucose joined by alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds and branches created by alpha-1,6-glycosidic bonds
Starch
is used for energy storage in plants and is a polysaccharide of alpha-D-glucose units; can debranch enzymes by cleaving at alpha-1,6 glycoside linkages and alpha-(1→6) glycosidase
alpha-amylase=endoglycosidase
Starch→glucose + maltose
beta-amylase=exoglycosidase
cleaves maltose units off nonreducing end of polymer chain
Glycogen (energy-storage polymer) is more highly branched than:
Amylopectin
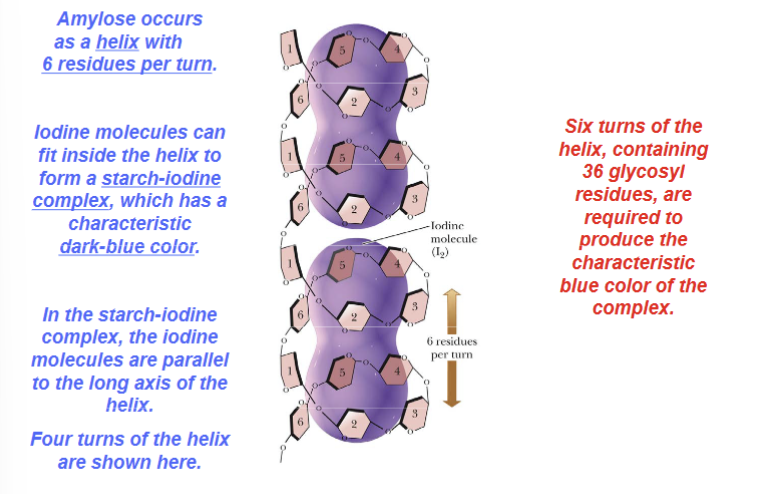
What can fit inside amylose to form the starch-iodine complex?
Iodine
Polysaccharide storage granules in:
Plant starch granules in stroma of chloroplasts and amyloplasts
Animal glycogen granules are in liver and muscle cells
(polysaccharides are important components of cellwalls)
Chitin (armor) structural polymer
Major structural components of exoskeletons of invertebrates (cell walls, exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans; crabs)
Composed of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosamine joined with beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds
Bacterial Cell Walls are:
Prokaryotic cell walls are constructed to serve as the framework of the repeating unit
Have gram-positive bacteria on peptidoglycan layers
Gram-negative bacteria on outer lipid bilayer membrane and inner lipid bilayer membrane
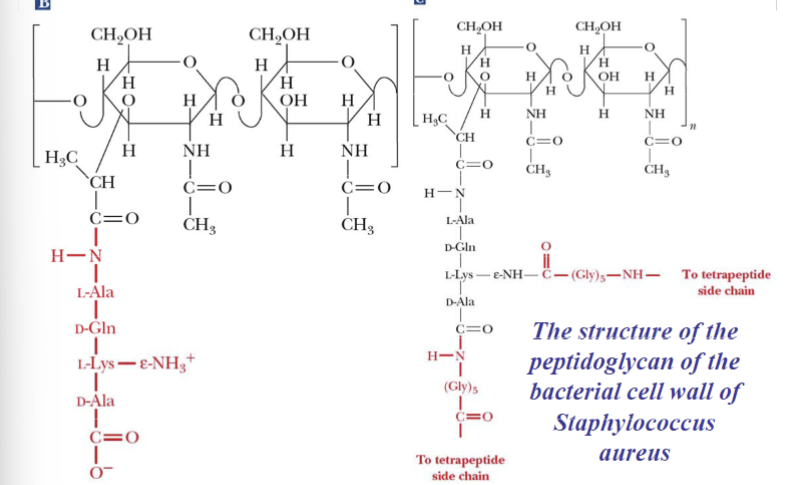
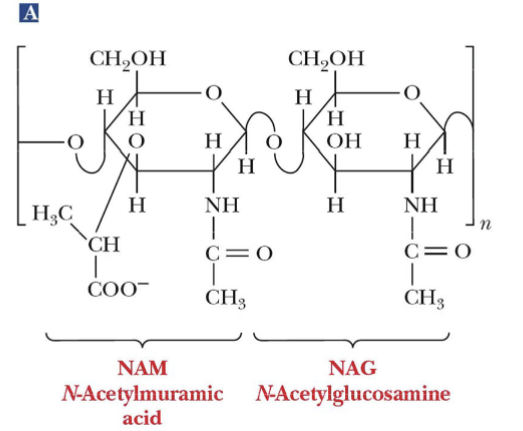
NAM
N-Acetylmuramic acid
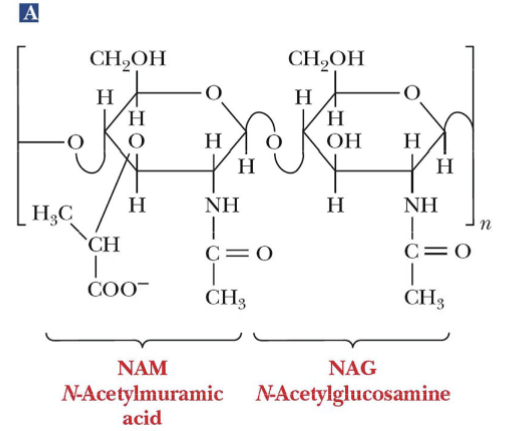
NAG
N-Acetylglucosamine
Gram staining:
a method to differentiate bacterial species with staining dyes based on the chemical and physical properties of cell walls
separate into two groups; gram-negative (pink-red color) and gram-positive (purple-blue color)
Primarily detects peptidoglycan which is in gram-positive bacteria
Plant walls consist of:
Cellulose
Pectin (intercellular cementing material)
Ligin (major polysaccharide of cell walls, especially in woody plants)
What are the components of Glycosaminoglycans?
Heparin: natural anticoagulant
Hyaluronic acid: component of vitreous humor of the eye and lubricating fluid of joints
Chondroitin & Keratan sulfate (connective tissue components)
Glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) are polysaccharides that:
Are based on a repeating disaccharide where one monomer is an amino sugar and the other has a negative charge due to sulfate or a carboxylate group
components of proteoglycans
Which carbohydrate units covalently bond to a polypeptide chain?
Glycoproteins
Antibodies are:
Glycoproteins (frequently play a role in immune response)
Oligosaccharides act as:
antigenic determinants
The first antigenic determinants were discovered in:
blood group substances
individuals are classified according to four blood types: A, B, AB, and O
at the cellular level, the biochemical basis for classification is the group of small-membrane bound carbohydrates
What is both soluble and integral transmembrane proteins?
Proteoglycans
Distinctions between blood type groups depend on
Oligosaccharide portions of glycoproteins on the surface of red blood cells (RBC’s)
Discovered by Karl Landsteiner
ABO Blood Classification:
Type A; nonreducing end is NAGal, GalNAc
Type B: Gal
Type AB: Both types are present (Gal and NAGal)
Type O: neither are present