Unit 5: Earth Science - Rocks, Minerals, and Erosion
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What is a rock made from?
made up of one or more pure, naturally occurring, non-living, crystal-like materials called minerals.
What is a mineral?
an element (a pure substance) or a compound (two or more elements combined).
What is the Mohs Hardness Scale?
A scale developed to identify minerals according to their hardness, ranging from 1 (very soft) to 10 (very hard).
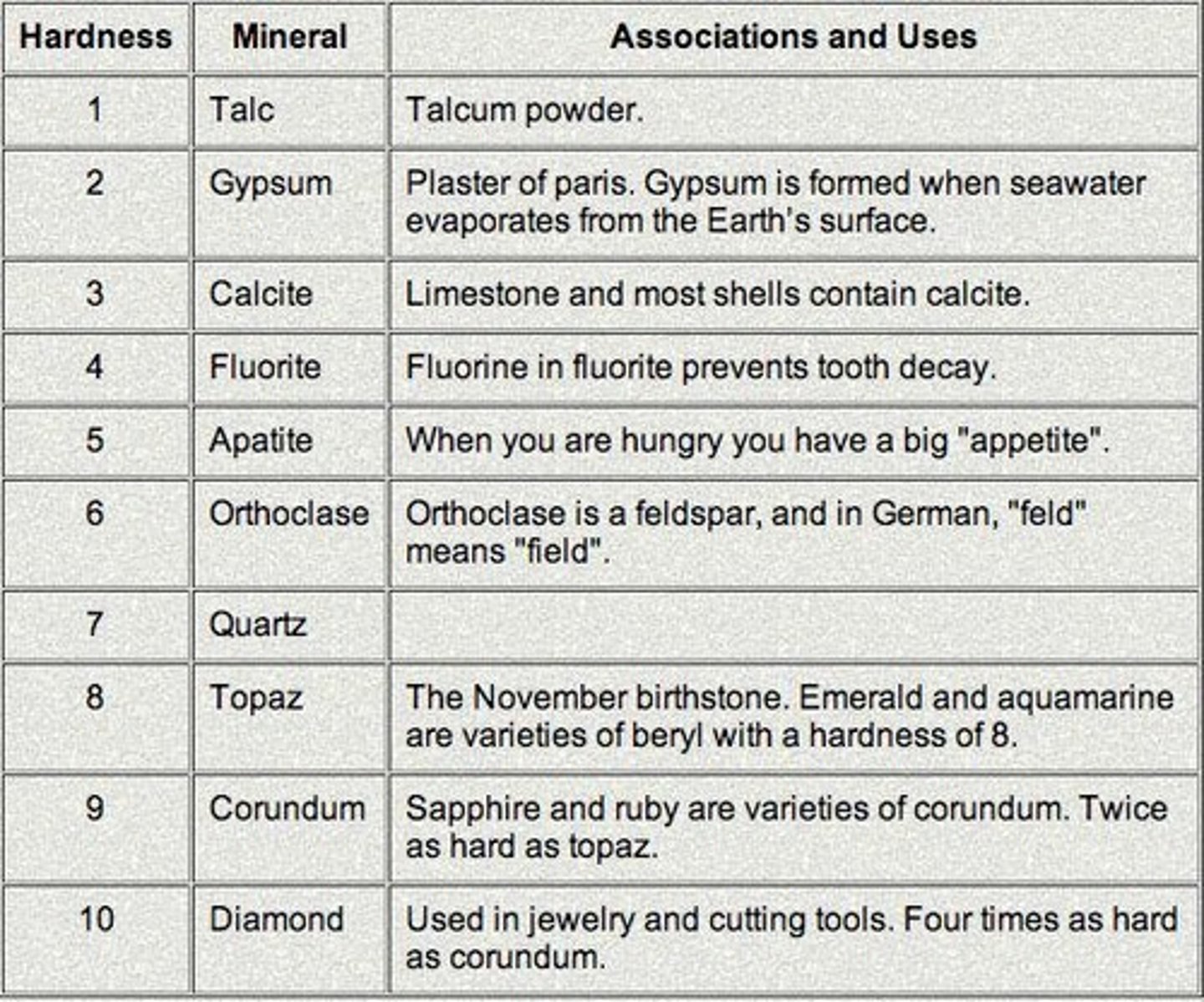
Who created the Mohs Hardness Scale and when?
was created in 1812 by German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs.
What are the hardest and softest minerals on the Mohs Hardness Scale?
Diamond is the hardest mineral (10), and talc is the softest mineral (1).
What are the six major crystal systems used to identify minerals?
Crystals are the building blocks of minerals and help in their identification.
List four clues to identify minerals besides hardness.
1) Lustre - the shininess of the mineral. 2) Color - can vary if the mineral is pure or not. 3) Streak - the color of the powdered form of the mineral. 4) Cleavage and Fracture - the way a mineral breaks apart.
What is igneous rock and how is it formed?
forms when hot magma or lava cools and solidifies.

What does the term 'igneous' mean?
originates from the Latin word for fire.
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Magma is melted rock found below the earth's crust, while lava is magma that has erupted onto the earth's surface.
What is intrusive rock?
formed when magma cools and hardens below the earth's surface (e.g., granite).
What is extrusive rock?
formed when lava cools and solidifies on the earth's surface.
What percentage of all rocks on Earth are sedimentary rocks?
make up about 75% of all rocks visible on Earth.
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
formed from sediments that are packed in layers and cemented together.

What is stratification?
the arrangement of visible layers in sedimentary rocks.
What is compaction in the context of sedimentary rocks?
is the process of squeezing layers of sedimentary rock together by the weight of sediment and water.
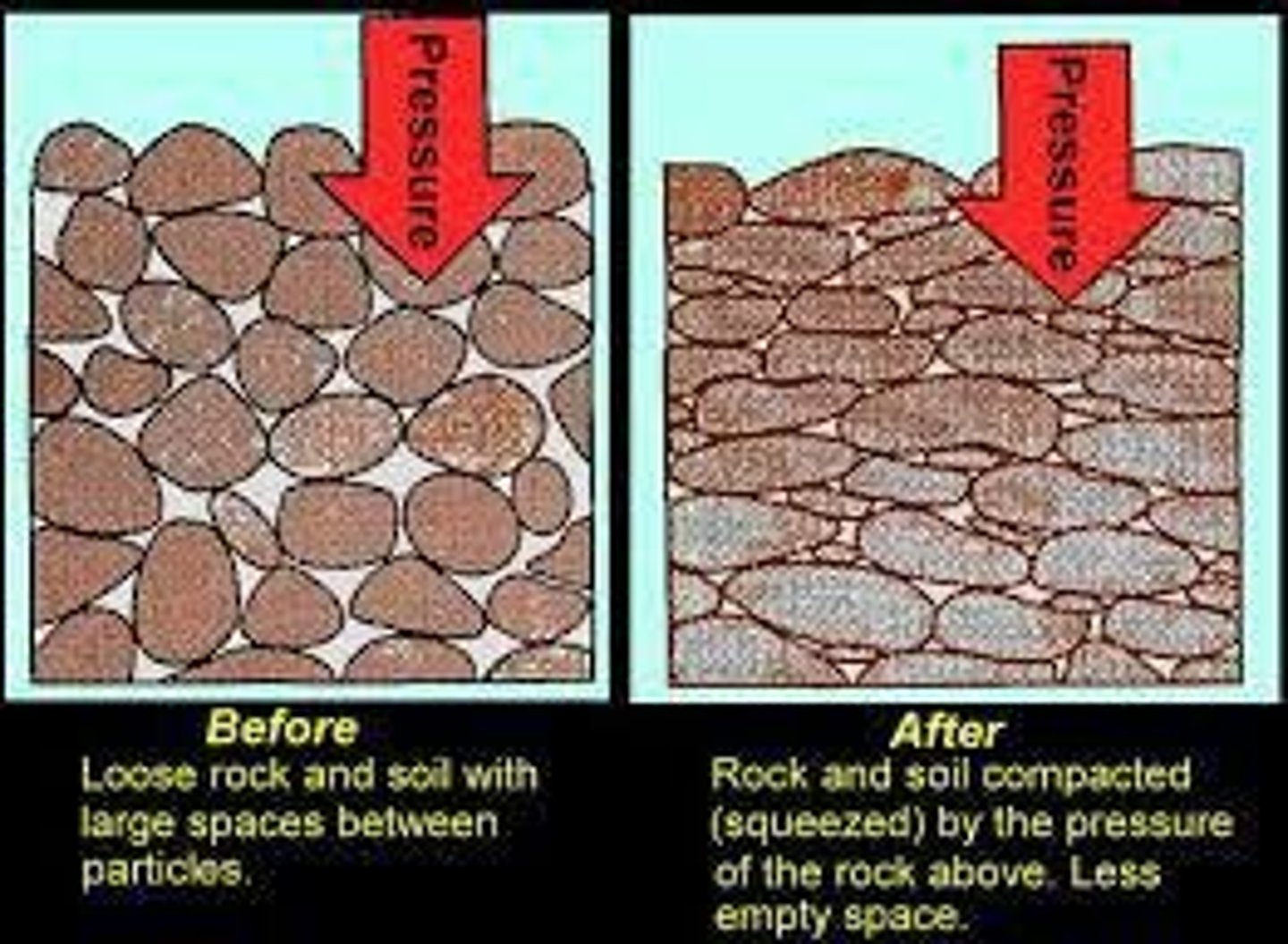
What is cementation?
is the process where minerals dissolve in water and form a natural cement that binds sediment together.
What does metamorphic rock mean?
means 'changed form' and is formed under high pressures and heat.

What does the type of rock formed depend on?
depends on the conditions of temperature, pressure, and the minerals present.
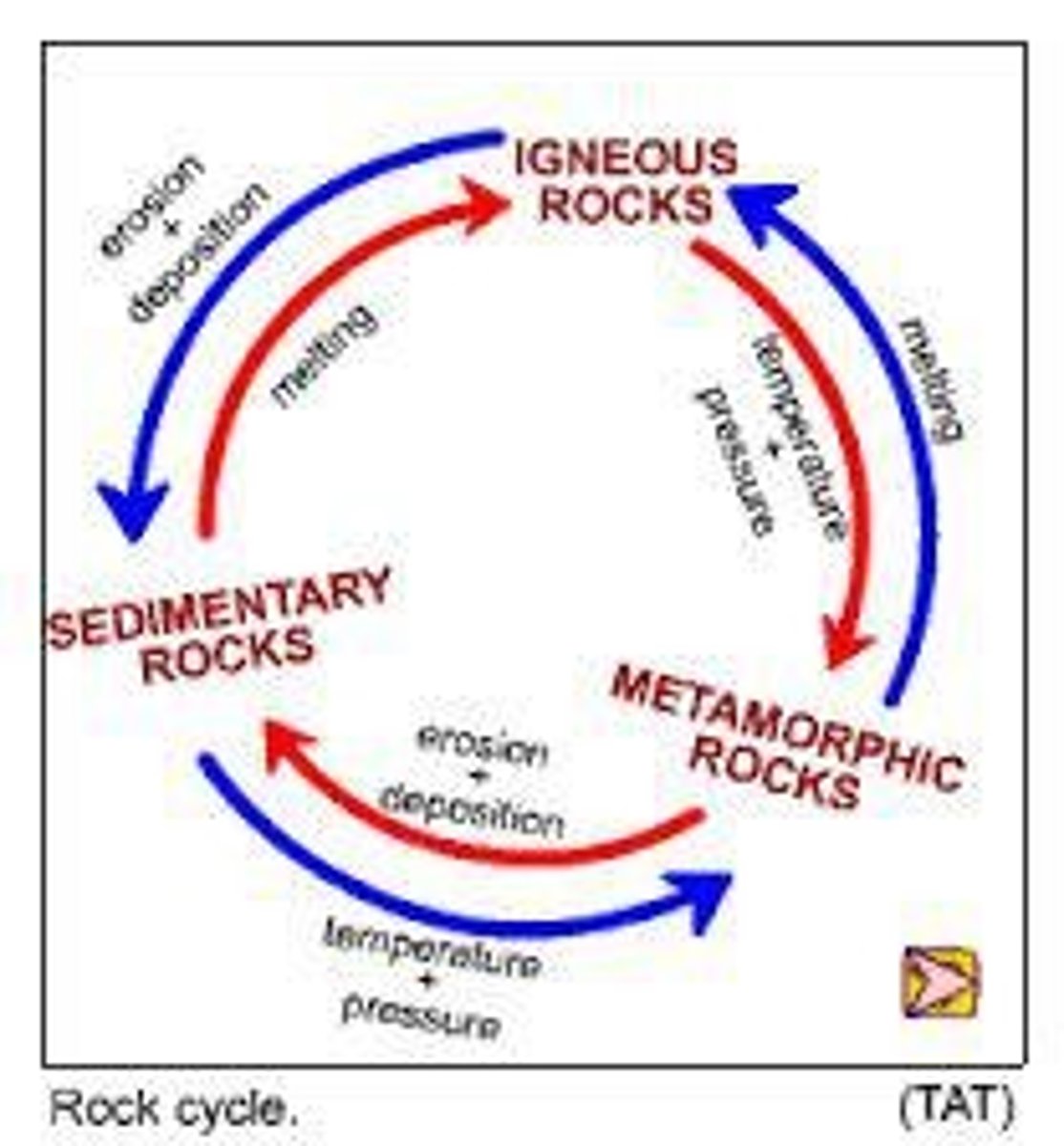
What is the rock cycle?
an ongoing process where rocks change due to weathering, erosion, and other geological processes.
How is soil formed?
formed from the weathering of rocks and the decomposition of organic matter.
What are compost and humus?
Compost is decomposed organic material used to enrich soil, while humus is the dark organic material in soil formed from the decay of plant and animal matter.
Define fertile soil, soil profile, and topsoil.
Fertile soil is rich in nutrients and supports plant growth; soil profile is the vertical section of soil layers; topsoil is the uppermost layer of soil, rich in organic matter.
What is leaching?
is the process by which nutrients are washed away from the soil by water.
What is soil composed of?
S is formed from compost (decaying plant matter), rock, sediments, living material like twigs and leaves, and dead worms or insects.
What is humus?
is the dark-colored portion of soil that is very fertile.
What are the layers of a soil profile?
The top layer is called topsoil (contains humus and small grains of rock), the second layer is lighter in color with less humus and minerals, and the third layer contains larger rocks beginning to break down into soil.

What is erosion?
is the movement of rock and mineral grains from one place to another.
What is sediment?
comes from larger rocks that have been broken down or worn away through weathering.
What is mechanical weathering?
is the physical break-up of rocks, such as gravity causing rocks to fall and break apart.
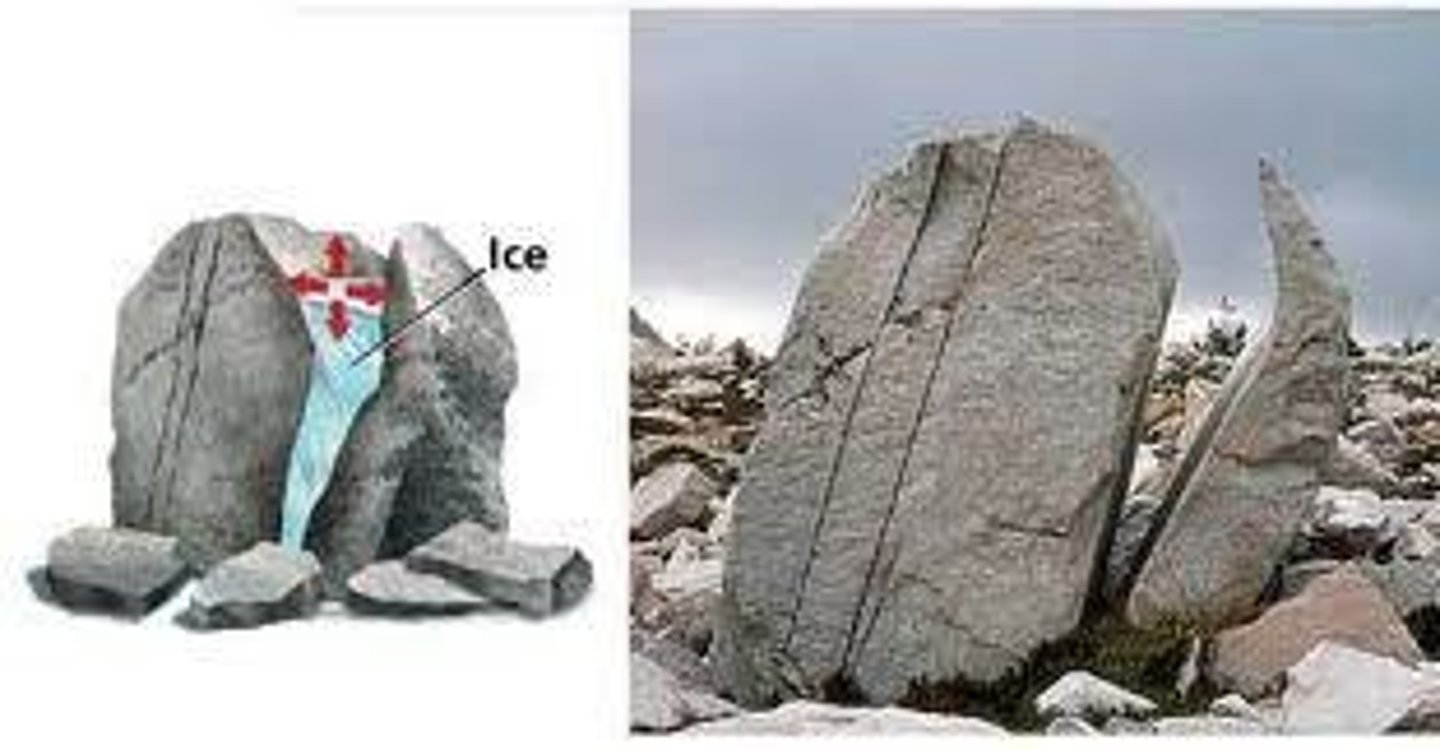
What is frost wedging?
occurs when water runs into cracks in rocks, freezes at night, and expands, eventually breaking the rock apart.

What is sedimentation?
is the process where eroded material is deposited and built up.
What is chemical weathering?
breaks down minerals through chemical reactions, such as acidic rain breaking down limestone.
What is biological weathering?
is the physical or chemical breakdown of rock caused by living organisms, like plants and bacteria.
How do glaciers cause striations?
scrape across bedrock, causing striations, which are scrape marks.
What is a moraine?
is eroded sediment that gets pushed out of the way and piled up along the sides of glaciers.
What are erratics?
large rocks left behind by glaciers.
What is abrasion in the context of erosion?
occurs when wind blows loose sediment that strikes against other rock, wearing it down.
What are some ways to protect against landslides?
Ways to protect against landslides include building retaining walls, improving drainage, and monitoring dangerous slopes.
What is the earth's crust?
layer we walk on, varying in thickness from 5km to 60km, and includes areas where minerals, oil, and gas are mined.
What is the mantle?
is found under the crust, made of rock material, with the upper mantle being solid and the lower mantle having a taffy-like consistency.
What is the lithosphere?
formed by the earth's crust and the upper mantle.
Who was Alfred Wegener?
a scientist who proposed the theory of continental drift.
What evidence did Wegener discover to support his theory?
Wegener discovered various geological and fossil evidence that suggested continents were once connected.
What did Wegener name his Supercontinent?
Pangaea.
What technology revealed that the ocean's floor is not flat?
Sonar (sound wave technology).
What is sea floor spreading?
The process by which new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and gradually moves away from mid-ocean ridges.
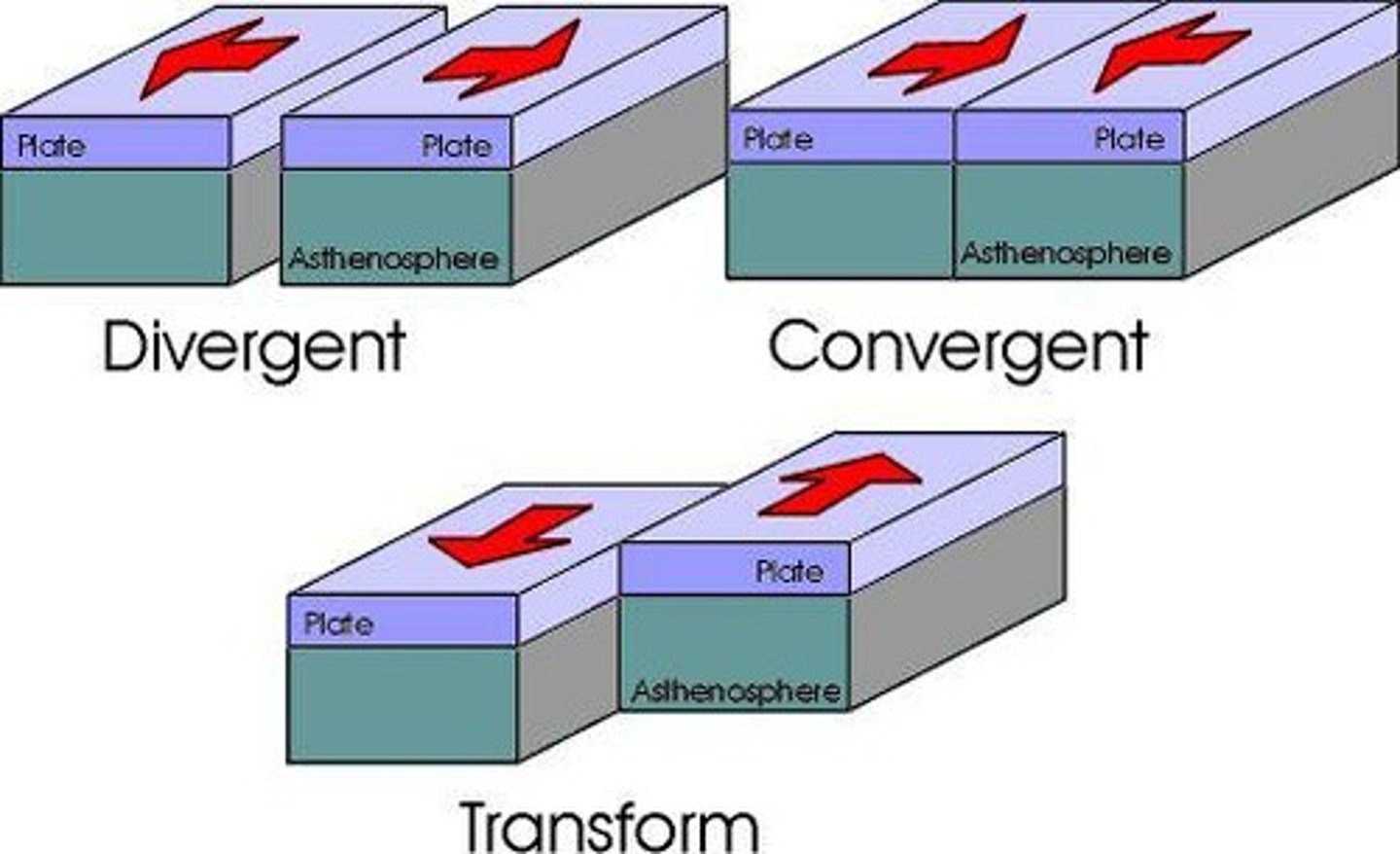
What is plate tectonics?
The theory that describes the large-scale movements of Earth's lithosphere, which is divided into tectonic plates.
What are two types of tectonic plate interactions?
Plates pushing together are called convergent boundaries, while plates pulling apart are called divergent boundaries.
What causes Earth's plates to move?
One explanation is convection currents in the mantle, where warmer materials rise and cooler materials sink.
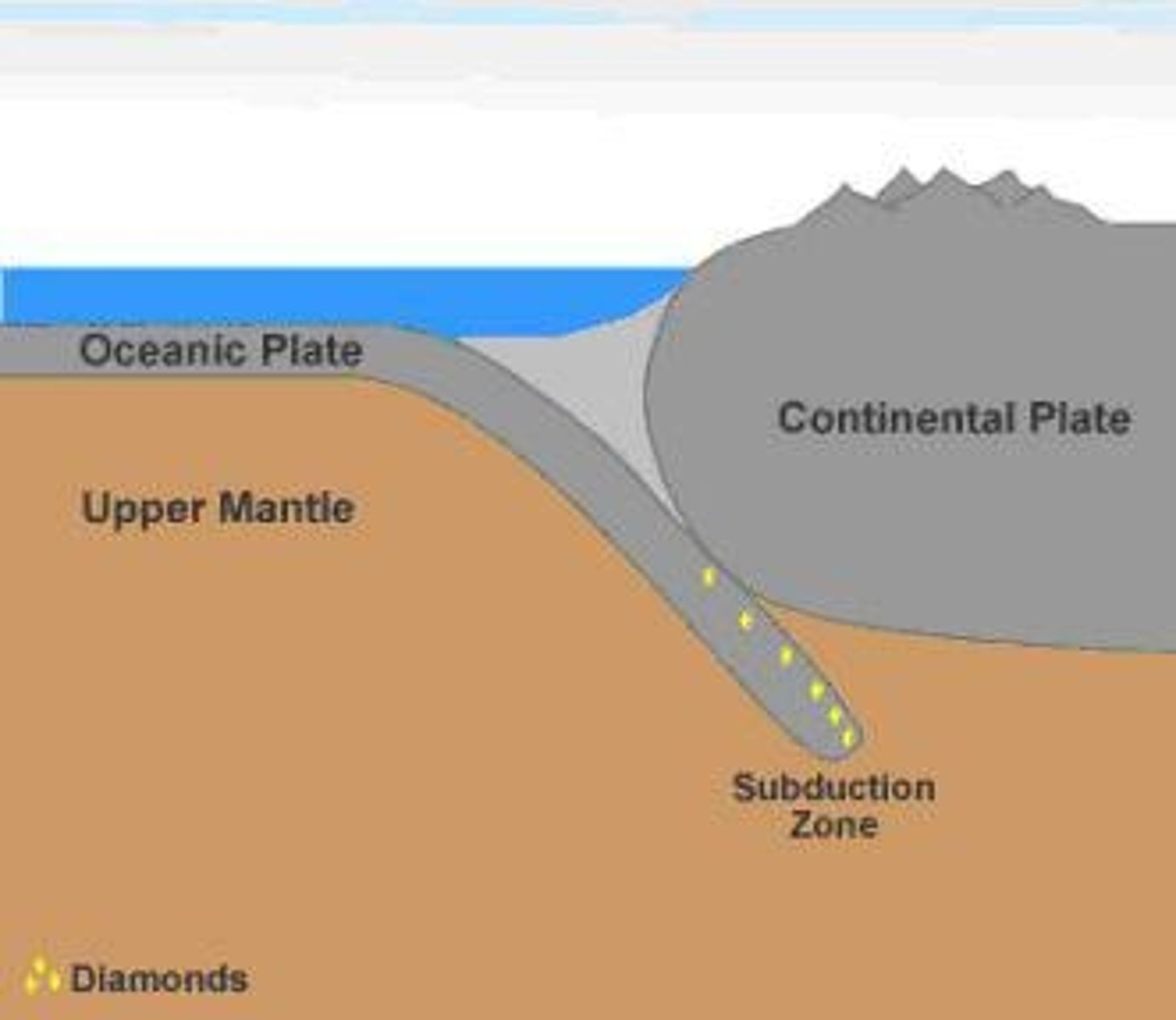
What are subduction zones?
Regions where one tectonic plate moves under another and sinks into the mantle.
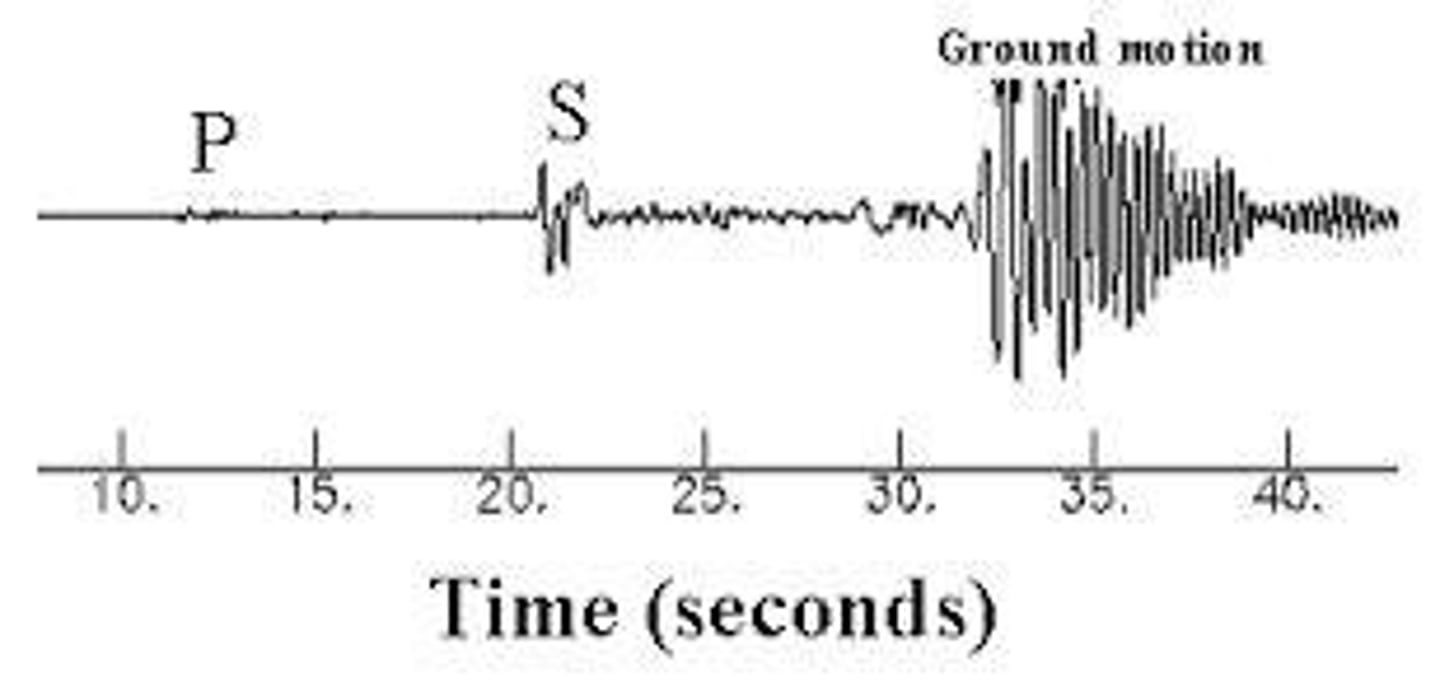
What device do scientists use to measure earthquakes?
A seismograph.
What is the Richter Scale?
A method of measurement used by seismologists to describe the strength of earthquakes.
What do seismic waves refer to?
Energy waves that travel outward from the source of an earthquake.
What are aftershocks?
Smaller quakes that occur after the initial earthquake.
What are Primary (P) waves?
The fastest type of seismic waves that can pass through solids, liquids, and gases, causing slight vibrations.
What are Secondary (S) waves?
Seismic waves that travel more slowly than P waves and can only pass through solids.
What are Surface waves?
The slowest seismic waves that cause the most damage, moving the ground in a rolling motion.
What is the focus of an earthquake?
The place deep in the Earth's crust where the earthquake begins.
What is the epicenter of an earthquake?
The point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of the earthquake.
What is a normal fault?
A fault that occurs due to tension forces, where rock generally moves down.
What is a reverse fault?
A fault that occurs due to compression forces, where rock generally is forced upward.
What is a strike-slip or transform fault?
A fault that occurs due to shear forces, characterized by horizontal movement.
What is a volcano?
An opening in Earth's crust that releases lava, steam, and ash when it erupts.
How are volcanoes formed?
When tectonic plates push against one another, one plate can be subducted, melting into magma that erupts through cracks.
What are dormant volcanoes?
Volcanoes that are not currently active.
What is the Ring of Fire?
A circle of volcanoes around the edge of the Pacific Ocean that pour out lava, fire, and steam.
What causes most mountains to form?
Most mountains are formed by large areas being uplifted due to the movement or heating of tectonic plates.
What are the two types of rock deformation that can occur under pressure?
Rocks can either fold or fault.
What is an anticline and a syncline?
An anticline is the top part of folded rock, while a syncline is the bottom part.
What happens when brittle rock breaks?
It forms a fault.
What is thrust faulting?
Thrust faulting occurs when slabs of rock move up and over each other due to compression.
What characterizes fault block mountains?
They are distinguished by sheer rock faces formed when underground pressure causes a rock mass to break away.
What are complex mountains?
Mountains formed by a combination of different processes, where parts of the crust are bent and broken under compressive forces.
What do fossils provide clues about?
Fossils provide clues about when life began and the history of rock and life on Earth.
What is the difference between a mold and a cast in fossil formation?
A mold is a cavity left in rock after the hard parts of an organism dissolve, while a cast is formed when sediment fills the mold and hardens.
What are the four types of fossils?
1. Petrified fossils, 2. Carbonaceous fossils, 3. Original remains, 4. Trace fossils.
What are petrified fossils?
Fossils formed when water dissolves calcium and silica, turning the bones into a rock-like substance.
What are carbonaceous fossils?
Fossils formed when an organism is buried under sediment, leaving a thin layer of carbon residue.
What are original remains?
Fossils that consist of the actual organism or parts of it, preserved in substances like tar, ice, or amber.
What are trace fossils?
Fossils that provide evidence of animal activity, such as footprints, burrows, or worm holes.
What is the principle of superposition?
In undisturbed rock layers, younger rocks are found on top of older rocks.
What is relative dating?
A technique used to order timelines of events by examining the position of rocks in strata.
What is an index fossil?
Fossils used to determine the relative age of a layer of rock.
What is radiometric dating?
A method that measures the amounts of certain elements in a rock to determine its age, based on the half-life of the parent element.
What is radiocarbon dating?
A method using Carbon-14 to find the age of fossils, bones, and wood up to 50,000 years old.
What are the largest divisions of geological time?
Eons, which are divided into Eras, and Eras into Periods.
What is petroleum?
A naturally occurring mixture of hydrocarbons, including bitumen, coal, oil, and gas, formed from decomposed organic material.
What are Vibroseis Trucks used for?
They send seismic energy waves into the Earth to analyze the consistency of geological formations.