DID (Pharmacology)- Antiprotozoals (FINAL)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What bacteria cause Malaria?
- plasmodium vivax
- plasmodium ovale
- plasmodium falciparum
What is the Malaria Life Cycle?
1) bite of infected female mosquito
2) entry into hepatocytes
3) exoerythrocytic stage- hypnozoite
4) hepatocyte ruptures
5) asex erythrocytic stage- symptoms
6) cyclic fever pattern
7) erythrocytic form
Malaria Pharmacotherapy is needed to...
erdicate erythrocytic AND hepatic parasite
T or F: P. vivax and P. ovale have a dormant hepatic stage (hypnozoite)
True
- can lead to relapse
What are the various categories of antimalarials?
1) Tissue schizonticides
- liver forms
2) Blood schizonticides
- erythrocyte forms
3) Gametocide
- sex stage and prevent transmission to mosquito
4) Prophylactic drugs
- when traveling to Africa, Asia, S. America
What are the diff classes of antimalarials?
- arteminisinins
- quinolines, quinine, quinidines
- folate synthesis inhibitors
- abx (tetra)
- lumefantrine
Erythocytic Schizonts include...
- artemisinins
- chlorowuine
- mefloquine
- quinine
- quinidine
- pyrimethamine
- suldafoxine
- tetracycline
Erythocytic and hepatocyte Schizonts include...
- atovaquone
- proguanil
What is an example of a primary and latent liver stage gametocyte?
primaquine
What areas of the globe tend to be chloroquine resistant?
africa, s. america, and asia
What chemoprophylaxis tx should be used in chloroquine-resistant areas?
- malarone
- artemisinin
- mefloquine
- quinine
- haflofantrine
*chloroquine can be used in non-resistant areas
MOA of Artemisinin
reactivity with heme produces oxidative stress in parasites (heme toxicity and ROS) -sesquiterpene lactone endoperoxide - endoperoxide bridge -
PK of Artemisinin
- synthetic have better solubility and efficacy
- t1/2= 1-3 hrs (not good for prevention)
- active metabolite it dihydroartemisinin
- induce CYP2B6 and CYP3A4
Therapeutic aspects of Artemisinin
- very potent and fast-acting
- best parasite clearance and fever resolution
- standard therapy for falciparum
T or F: Artemisinin Combo therapy (ACTs) are recommended for UNCOMPLICATED falciparum malaria
True
AE of Artemisinin
- NVD
- dizziness
- neutropenia
- anemia
- hemolysis
Artemisin in contraindicated in...
1) pregnant pts
- cause abortion, congenital defects, stillbirth
- not recommended in 1st trimester
2) children
- especially those <5kg
MOA of Chloroquine
Induce MDR1 pump and Pfcrt expression
- Lysosmotropic prevents heme detox
PK of Chloroquine
- 100% absorbed PO
- GIVE DOSE AFTER MEAL
- deposited in tissues
- needs loading dose
- slow infusion for IV
- metabolized by CYPs (desethylchloroquine)
- eliminated in URINE
- t1/2= 3-5 days
Therapeutic aspect of Chloroquine
- not active against liver stage
- drug of choice for uncomplicated nonfalciparum and sensitive falciparum
- reduced fever in 1-2 days
- clears parasitemia in 2-3 days
**SAFE IN PREGNANCY!
AE of Chloroquine
- pruritus
- NVH
- urticaria
- anorexia
- retinopathy
- hemolysis in G6PDH deficient
- cardiac arrrhythmias and arrest
T or F: Chloroquine can also be used to RA
True
- can cause irreversible ototoxicity
Chloroquine in contraindicated in/with...
- pts w/ psoriasis, porphyria, myopathy, retinopathy
- antacids (block absorption)
- anticonvulsants
- increase risk of arrythmia
Amodiaquine Quick Facts
For short-term seasonal malaria chemoprevention
- very similar to chloroquine
- combo tx for falciparum in chloroquine-resistant malaria
- toxicities: agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, hepatotoxicity
Piperaquine Quick Facts
Bisquinoline
- primary choice in uncomplicated falciparum in Asia
- long t1/2= 28 days
- good for post-tx prophylaxis
Quinine and Quinidine Quick Facts
blood schizonticide against all 4
- gametocidal against vivax AND ovale
- not gametocidal against falciparum and hepatic stage
T or F: Quinidine is a detrorotary stereoisomer of quinine
True
MOA of Quinine and Quinidine
Induce MDR1 pump and Pfcrt expression
- same as Chloroquine
Mechanism of Resistance of Quinine and Quinidine
attributed to PfMDR1
PK of Quinine and Quinidine
- malaria pts accumulate drugs more
- more drug is plasma bound
- prolongs half life (18 hrs)
- quinidine has shorter t1/2
- LIVER metabolism
- RENAL excretion
- metabolized by CYP3A4
Therapeutic aspects of Quinine and Quinidine
More toxic and less effective than chloroquine
- PO falciparum good for chloroquine resistant regions of uncomplicated
- PO used w/ abx
- no prophylaxic use
What is Babesiosis?
Quinine + Clindamycin
AE of Quinine and Quinidine
- cinchonism- NVDH, tinnitus
- hypoglycemia
- hypotension
- hypersensitivity rxn
- hematologic abnormalities
- cardiotoxicity
- Blackwater fever
- QT prolongation
Quinine and Quinidine contraindications
- D/C if hypersensitivity/hemolysis
- don't give w/ mefloquine OR aluminum antacids
- monitor glucose
- increases plasma levels of digoxin and warfarin
T or F: Mefloquine is used as prophylaxis and combo tx
True
- synthetic 4-quinoline methanol
- UNCOMPLICATED falciparum in CQ-resistant regions
MOA of Mefloquine
Similar to Chloroquine
- associated w/ intra-erythrocytic hemozoin
- blood schizonticidal falci. and vivax
Anti-malarial Spectrum of Mefloquine
- not active against hepatic stages or gametocytes
- resistance in Asia
Mefloquine resisitance if associated with...
PfMDR1
PK of Mefloquine
- given only PO and is well-absorbed
- 18hr peak plasma
- elimination t1/2= 20days
-
What is the BBW on Mefloquine?
- neurologic
- psychiatric
- vivid dreams
AE of Mefloquine
- NVD
- abdominal pain
- hematologic effects
- cardiac abnormalities/issues
- neuropsychiatric toxicities
Mefloquin CIs
- do not admin w. quinine, quinidine (causes heart issues)
- pts w/ psych conditions
- pts w/ seizures
- pts with heart probs
Primaquine is used to...
eradicate DORMANT forms of vivax and ovale
- synthetic 8-aminoquinoline
Anti-malarial Spectrum of Primaquine
Gametocidal against latent hepatic forms
- weak activity against blood schizonts
- chemoprophylaxis
- prevents relapse
- radical cure of acute vivax and ovale
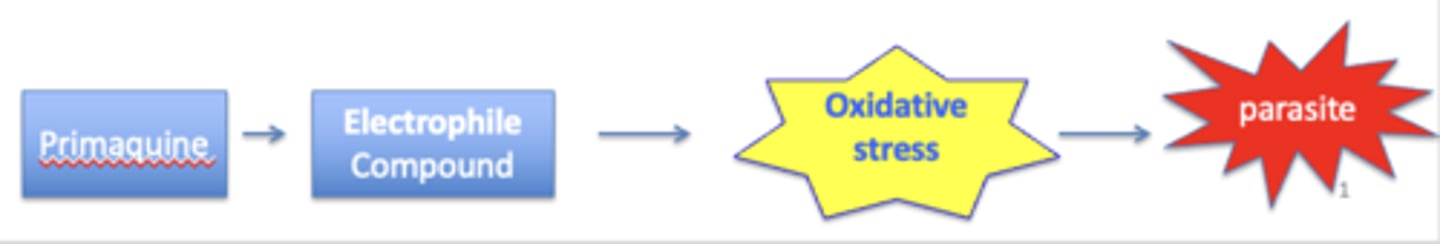
PK of Primaquine
- PO
- metabolized and excreted in URINE
- metabolites are less effective and more toxic
AE of Primaquine
- Leukpenia
- Agranulocytosis
- Leukocytosis
- Cardiac arrythmia
- hemolysis and methhemoglobinomia (G6PH deficiency)
Primaquin CIs
- avoid in pts w. blood cell disorders and myelosuppression (quinine)
- don't give IV (hypotension)
- monitor G6PDH levels
**AVOID IN PREGNANT PTs
MOA of Atovaquone
inhibits parasite mitochondrial ETC of parasite
- active against tissue and blood schizonts
Mechanism of Resistance of Atovaquone
SNP (Y268S/C/N) in mitochondrial sytochromeb gene
- + proguanil decreases resistance
PK of Atovaquone
- PO absorption increase w/ fatty food
- t1/2= 2-3 days
- excreted unchanged in FECES
- tx and prophylaxis of falciparum
AE of Atovaquone
- NVD
- rash
- fever
- tetra and rifampin decrease plasma conc. by 1/2
**DO NOT USE IF PREGNANT!
Lumefantrine MOA
similar to chloroquine
- does not cause cardiac complications like Meflo or Quinidine
Lumefantrine (coartem) quick facts
first line therapy for chloroquine-resistant flaciparum
- give PO w/ food
- t1/2= 3-4 days
- CYP3A4
AE of Coartem
- rash
- N/H
MOA of Pyrimethamine and Proguanil
Inhibits folate biosynthesis
- SELECTIVE inhibition of plasmodial DHFR
- used w/ sulfa drugs which block DHPS
- slow acting
- NOT gametocidal
- always used in combo
MOA of Abx for anti-malarial tx (tetra, doxy, clindamycin)
Block protein sysnthesis in apicoplast
- act slowly and always combined
- Blood schizonts
- can be used for amebiasis and toxoplasmosis
What are the determinants of drug resistant malaria?
- t1/2
- PK
- host immunity
- vector and environment
- transmission
- mutation in parasite
- cross-resistance
- multi-resistance
What is Amebiasis?
Caused by Entameoba histolytica
- colitis and dysentery
- ab pain
- bloody diarrhea
- tissue death
Drugs that treat Extraluminal vs luminal
Extraluminal
- metronidazole
- tinidazole
Luminal
- diloxanide
- iodoquinol
- paromomycin
What drug class are Metronidazole and Tinidazole in?
Nitromidazoles
MOA of Metronidazole and Tinidazole
Inhibits nucleic acid synthesis by disrupting DNA and causing strand breakage
- action dependent on reduction of nitro group in protozoa
- kills trophozoites (NOT CYSTS)
PK of Metronidazole and Tinidazole
- PO t1/2= 8hrs (M); 12-14hrs (T)
- eliminated in teh URINE
- tinidazole is better
AE of Metronidazole and Tinidazole
- NVDH
- dry mouth
- metallic taste
- pancreatitis
- severe CNS toxicity
- BBW= possible carcinogenic effect
CIs of Metronidazole and Tinidazole
- avoid alc (NV)
- potentiates coumarin anticoags
- phenyto and phenobabr increase elimination
**AVOID IN PREGNANT PTs
T or F: Iodoquinol is a hydroxyquinoline
True
- effective luminal amebicide
MOA of Iodoquinol
Inteferes w/ heme metabolism of protozoa
- not active against trophozoites and extraintestinal
- retained in intestine
- excreted through FECES
AE and CIs of Iodoquinol
- NVD
- pain
- take w/ meals
- neropathy, renal, thyroid
- D/C w/ signs of iodine toxicity
T or F: Paromomycin Sulfate is an Aminoglycoside abx
True
- luminal amebicide
- USA main choice
- used in amebiasis and leishmaniasis
AE of Paromomycin
- NVD
- GI distress
- renal tox in pts w/ renal probs