MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Accounting ?
It’s providing both financial and non-financial information that will help decision-makers to make good decisions
→ data that can be quantified, Ex : Tesla can quantify the number of cars they have, customer too,
Differences between Financial and Management Accounting ?
Financial accounting reports financial information for external stakeholders, while management accounting, provides detailed data for internal decision-making.
Financial statements ?
→ annually
Management accounting frequence ?
→ no requirements, can be done daily, weekly, monthly,…
Financial statements focuses on ?
→ historic information
Management accounting focuses on ?
→ past information to prepare projections of future trends
Management accounting ?
combines accounting, finance and management with the leading-edge techniques need to drive successful businesses.
direct materials ?
→ costs that are visible, directly traceable (ex. raw materials to make a product)
indirect materials ?
→ not visible, not directly traceable (ex. electricity)
direct labour ?
→ directly involved in the overall production process
indirect labour ?
→ not directly involved in the overall production of goods, (accounting, administrative, marketing staff)
Direct Expenses ?
expenses for a particular product (ex the hire of a specialist piece of equipment to manufacture a specific product.)
Indirect expenses ?
It’s all expenses that can’t be identified within a product, service or department (ex. light and heat of the factory, insurance of premises etc.)
Overheads ?
→ all indirect costs.
Indirect materials, Indirect labour and indirect expenses
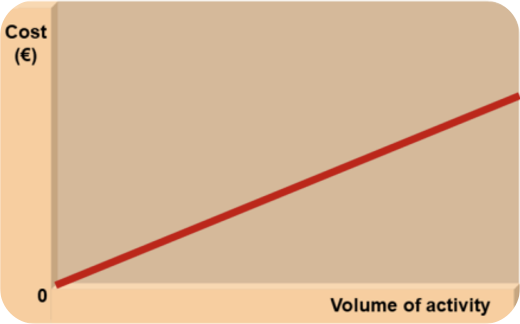
Variable costs ?
vary in direct proportion to the volume of activity. (→ direct materials and direct labour.) the more units there is, the more there will be costs.
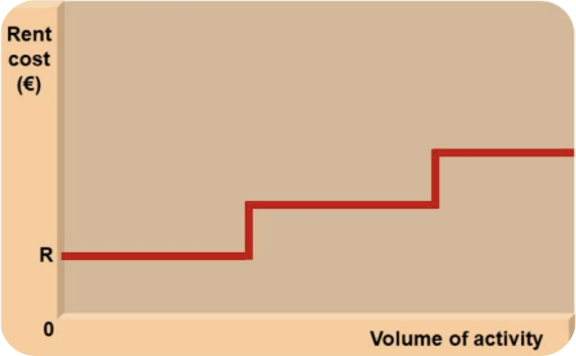
Step-fixed (semi-variable) costs ?
Costs are only fixed within the normal or relevant range of output. (→ the rent of a factory is a fixed cost for a period. If the factory receives more units than his capacity, it would need to rent extra factory space)
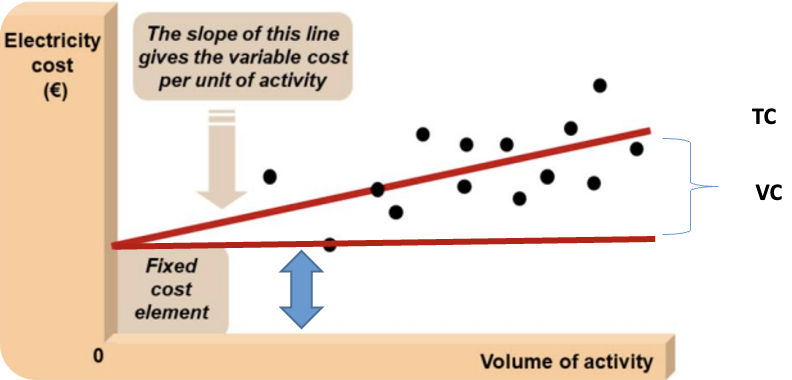
Semi-variable (Mixed) costs ?
costs that are part-fixed and part-variable. It’s a fixed cost and a variable cost (ex : electricity costs which include the supply charge and the usage charge, fixed + variable)
TOTAL COST ?
= FIXED COST + VARIABLE COST
The High-Low method ?
→ it’s selecting the periods with the highest and lowest activity levels and comparing the change in costs from both levels.
Variable cost (VC) per unit ?
Change in Costs = Variable Cost (VC)
Change in Output (units)
Marginal Cost per unit is the variable cost of ?
→ producing one extra unit (direct materials, direct labour, variable overhead)
Contribution ?
Sales - Variable cost = Contribution → It’s the difference between sales value (selling price) & marginal or variable cost of sales
Profit = ? (1)
Sales - Variable Cost - Fixed cost
Profit = ? (2)
Contribution - fixed cost
BEP in units formula ?
Fixed Cost / Contribution per Unit
Sales price per unit ?
total sales
total sales per unit
Var. cost per unit ?
total variable cost
Sales in units
BEP in sales revenue ?
Selling price * BEP in Units
Margin of safety (MOS) in Units ?
= Budgeted sales Units - BEP in units
Margin of safety (MOS) in sales revenue ?
Budgeted sales in € - BEP in €
How to have the MOS in % ?
MOS in Units
Budgeted sales Units * 100
Marginal Costing statement ?
Sales
Less variable costs
= Contribution
Less Fixed costs
= Profit (Loss)
Target Profit formula in units ?
Fixed Cost + Target Profit
Contribution per Unit
Proposed figures ?
→ Planned figures → Budgeted sales
Contribution per Unit ?
selling price - Variable cost per unit.
Break even analysis ?
→ marginal costing statement
Contribution Margin Ratio (CMR) ?
Contribution (total or per unit)
Sales (total or per unit)
Target Profit in sales revenue formula ?
Target profit in units * selling price per unit
NPV’s advantages ?
Takes into account the time value of money
Considers all future cash flows
Provides an absolute result rather than a percentage
NPV’s disadvantages ?
Can be difficult to calculate as it requires an understanding of discounting
It requires the business to have decided upon an appropriate discount rate
Layout of the cash flow ?
Years / Cash flows / Discount Factor (DF) / Present Value (PV)
Net present Value (NPV)
IRR ?
discount rate that produces a zero NPV.
To calculate IRR you should… ?
have 1 NPV answer and one negative NPV answer
If the IRR is less than the required rate of return … ?
→ the project should be rejected
Appraisal techniques used in the capital budgeting ?
Payback period, NPV, IRR
Advantages of Payback period ?
easy to use & to understand
when the payback period is shorter than the project's lifetime, it’d be accepted. If longer, reject it.
good method to use if there’s uncertainty about the future
Disadvantages of Payback period ?
Ignores cash flows after the initial cost has been recouped
Ignores the time value of money & does not discount future cash flows into their present value
Ignores the size of the investment project & its overall cost & benefit
If the NPV is at 0 … ?
→ means that the project is earning exactly the discount rate.
Positive NPV ?
→ it’s earning more than the discount rate
Negative NPV ?
→ It’s earning less than the discount rate.
For a project to be acceptable, it must earn a … ?
→ positive NPV
If 2 projects have positive NPV’s … ?
→ the project with the highest NPV will be chosen
Advantages of IRR ?
Uses the time value of money in calculations
If IRR > the required rate of return, accept the project, if not → reject.
Disadvantages of IRR ?
Can be difficult to calculate IRR & to explain it to non-finance people
Doesn’t provide results in euros but in a %
Profits retained … ?
earnings
Profites pay … ?
dividends to shareholders
retained earnings ?
Profites that the company makes
Short term ?
finance for up to one year
Medium term ?
Matching approach ?
It’s to finance non-current (fixed) assets & permanent current assets using long & medium-term sources of finance.
Aggressive approach ?
is to maximise the amount of short-term finance used and to minimise the amount of long-term finance
Conservative approach ?
is to maximise the use of long-term finance and minimise the use of short-term finance
Advantages of retained earnings ?
Doesn’t result in a dilution of ownership or change in co
There may be reduction in financial risk due to lower gearing level
No repayment date
Disadvantages of retained earnings ?
Less funds available to pay dividends
Debt capital may be more suitable if interest rates are low
It’s the case that there’s not enough retained earnings available in the form of cash balances as amounts tied up in inventory
Tighter credit control ?
is a management strategy that involves closely monitoring and restricting credit extended to customers to reduce the risk of bad debts.