Astronomy
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Terrestrial planet
A type of planet that is primarily composed of rock and metal, having a solid surface and lacking rings. Examples include Earth, Mars, Venus, and Mercury.
Giant Planet
A large planet that is predominantly composed of gases, lacking a definitive solid surface. Examples include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
-large diameter high mass, low density
Mercury
No atmosphere leading to temperature swings
shrinking planet, due to its contracting Iron core
no moon
Venus
runaway greenhouse effect, and hottest planet. appears to rotate backwards, and has volcanic plains
no moon
Earth
has liquid water, and a protective magnetic field.
active plate tectonics
only known planet, capable of supporting life
one moon
Mars
core of iron oxide dust,
has the largest volcano in the solar system
jupiter
largest planet, with composition most similar to the sun. 91 moons
saturn
complex ring system
with a density less than water; has the moon titan, <145 others
Uranus
discovered in 1781, rotating on a side tilt, blue in color, coldest atmosphere
Neptune
found by calculations not observations, fastest wind speeds in the solar systems, emits more heat than receives from the sun
Asteroids
lie within the asteroid belt, orbiting Mars and Jupiter
Kuiper belt object
compostion of water ice and rock, included pluto and other dwarf plantes
comets were most likely to originate here
Solar nebula
hot inner disk —> cold outer disk. near the sun = higher temp : only metal and rock survives
lower temp: ice and gas remain frozen
Planetesimals
small grains sticking toigether like comets and asteroids
protoplanets
expand by pulling in material, the impacts of the material make them hot and molten
Moon formation theory
1) fission theory
2) capture theory
3) co-creation theory
4) collisional ejection theory : formed as a result of earth being hit
Asteroid composition
iron and silicon
materials most abundant in the outer disk of the solar nebula
water ice, methane, amonia, helium, hydrogen
Center of mass
distance of each start proportional to the inverse mass of the star. Center of mass will be closer to the more massive star
NON Binary observation system
a star does not rotate with respect to us. (Blueshift — moving towards shorter wavelengths
binary system
the star moves around the C.O.M — creating a redshift — larger wavelengths
Radial Velocity
the component of an object's velocity along the line of sight between the object and an observer: measures doppler shift
Geological Processes
1) Impact cratering by meteorites
2) plate tectonics
3) volcanoes
4) erosion
Plate tectonics
subduction zones: movement of the plate
creates new crust, anf then the internal heat rises, driving the creation of plate tectonics
volcanoes
produce: ash, gas, lava
Moon/mercury: formed by cosmic impact
venus/earth/mars: created by magma from mantle
erosion
wind and water smooths the surface
venus = thick atmosphere —> strong winds
mars = active winds and dust devils
Titan = atmosphere of nitrogen and methane creating erosion
Planets with Magnetic fields
Earth
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
heat needed for magnetic fields
formation heat, radioactive decay, tidal heating
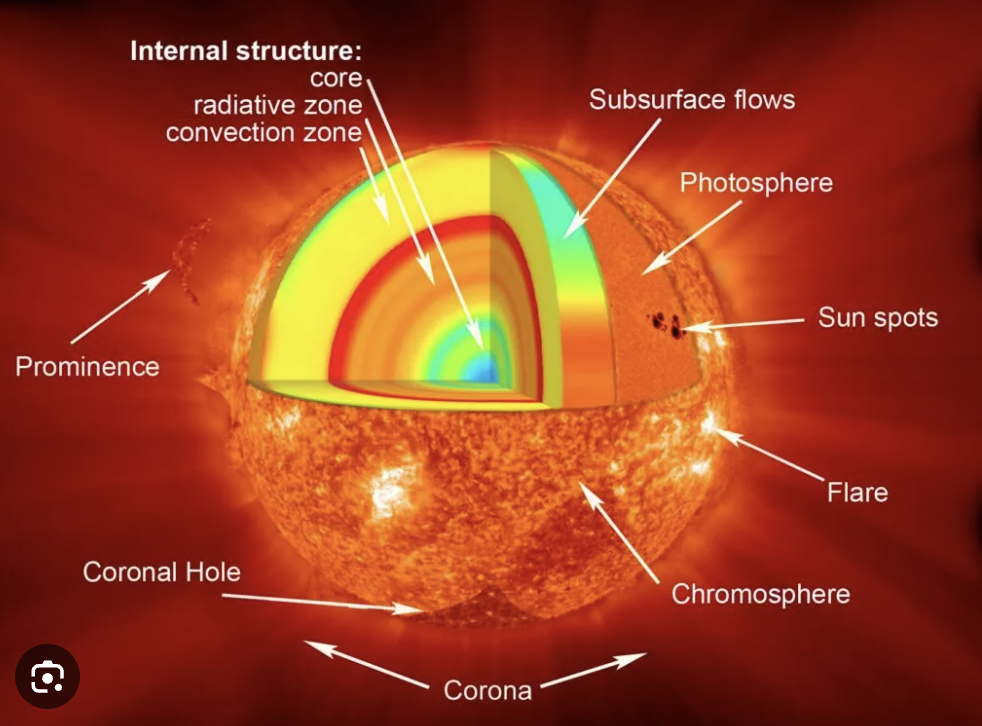
Suns layers
core,radiative zone, prominence, convection zone, corona, photosphere, sunspot, chromosphere, coronal hole
Core
Energy is produced in the core
energy is lost and passes through the radiative zone, the through the convection zone to the atmosphere
sunspots
dark features on the surface of the sun
chromosphere
thin transport layer, appearing red because of the hydrogen line
corona
hottest part of the solar atmosphere
prominence
loops of plasma, extending along magnetic fields
solar flares
releases a bright flash of energy photons, associated with coronal mass ejections
suns dynamo
generates its magnetic fields converting motion into electricity
differential rotation
states that the speed of the suns rotation varies according to our latitude
Einstein Revolution
determined mass and energy are equivalent E= MC²
fission
splitting a larger atom into two or more smaller ones
fusion
combing two or more small atoms into a larger one
Nuclear Particles
each partical of normal matter has a antimatter twin
electron - positron
proton-antiproton
neutron - antineutron
Leptons
neutrinos — no charge and no mass
muons
tau
consequence of the suns high temperature
results in a ionized gas “plasma”
solar pulsations
sun waves vibrate, these ossilations have a period of 5 min
Helioseismology
astronomers probe conditions inside the sun
Solar Neutrinos
were undetectable because they oscillate between different types in earths atmosphere
note: discovered by Raymond Davis Jr.
solution to neutrino detection problem
1) discovery of the three types (electron, moun, tau)
2) Sudbury: detecting all three types, finding neutrinos to have a small non-zero mass.