COSI 325 Chapter 11: Neuroanatomy
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
What are the two divisions of the nervous system?
CNS
PNS
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord
What is the peripheral nervous system?
Everything else besides the brain and the spinal cord:
Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Tracts
What are the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Sensory PNS
Motor PNS
What are two divisions of the sensory PNS?
Special Sensory
General Sensory
What is the special sensory division of the sensory PNS?
saved for senses that can only be produced in one place
ex: smell, taste, equilibrium, vision
What are the two divisions of the general sensory division of the PNS?
somatic sensory
visceral sensory
What is the somatic sensory division of the general sensory?
more superficial
skin
pain from temperature
feeling vibration
proprioception
touch
What is the visceral sensory division of the general sensory?
sensory to deeper structures (deep organs)
dull pain: stomach ache
discomfort from abdominal distension
chest pain
What are the two divisions of the motor sensory division of the PNS?
Somatic Motor
voluntary movement
skeletal muscle
Autonomic Motor
involuntary movement
smooth muscle
cardiac function
What are the two divisions of the autonomic motor system?
Sympathetic
fight or flight response
sweat, elevated HR —> fear responses
Parasympathetic
rest and digest
lowers hear rate
BOTH ARE NEEDED FOR SURVIVAL
How does the sympathetic nervous system interact with the somatic motor nervous system?
Sympathetic system brings in information from the environment and then send it out to illicit motor responses —> sympathetic sends message to somatic to voluntarily run when faces with fear
What is another word for hindbrain?
rhombencephalon
What is another word for midbrain?
mesencephalon
what is the deep part of the brain called?
Diencephalon
core/space inside
what is the superficial part of the brain called?
telencephalon
space outside
What do the diencephalon and the telencephalon make up?
prosencephalon
What do the diencephalon, telencephalon, and the prosencephalon make up?
cerebrum/forebrain
What are the three parts of the hindbrain?
pons, cerebellum, medulla oblangata
What are neurons?
neurons are the most functional unit of communication in the nervous system.
contain a cell body and a long body called an axon
communicate via action potential in cell
can be:
excitatory: makes something happen
inhibitory: prevents something from happening
What are the parts of a neuron?
nucleus
cell body
axon
dendrites
myelin sheath
nodes of ranvier
Axon terminal buttons
Do neurons touch in order to communicate?
No! when neurons communicate they actually do not touch the axon terminals fire a signal to the dendrites
Why is myelin important?
the axon has myelination that allows for communication to move quickly via insulation provided by lipid fat
What do dendrites do?
bring info into the neuron
How to the nodes of ranvier effect the way the message moves down the axon?
when information moves along the axon it hops from node to node to node
it is not a continuous line
allows for the axon to send info to other cells dendrites quickly and efficiently
What is a difference between the myelin sheath and the soma (cell body)?
the myelin sheath is white matter —> therefore the axons are white matter
The some is gray matter —→ therefore the bodies are grey matter
What are the two places grey matter is found?
cortex
Cerebral Cortex: in our brain/cerebrum (big brain) we have a lot of cell bodies superficially
Cerebellum: cerebellar cortex
Nucleus
gray matter surrounded by white matter
within the brain stem there are collections of gray matter called nuclei —> nuclei found in the brain stem are cranial nerve nuclei —> this is where cranial nerves originate to be sent out
nuclei are also found in the diencephalon
What is the pre-synaptic cell?
the Axon terminal
What is the post synaptic cell?
the dendrites
what is the process that occurs between pre and post synaptic cells?
synapse!
what are the 3 places where white matter is found?
Tracts
commissural fibers
Association fivers
what is white matter?
a collection of axons
what is grey matter?
collections of cell bodies
What are the two ways in which tracts move?
tracts move up and down
How do commissural fibers move?
They move from left to right
what are the two types of tracts?
there are 2 main types of tracts
Ascending (Afferent): sensory tracts
Descending (efferent): Motor tracts
what do commissural fibers do?
they communicate between the left and right hemispheres
Ex: Corpus callosum!
How do association fibers communicate?
these fibers communicate anteriorly to posteriorly
What are glial cells?
glial cells are supporting cells to neurons
What are the 3 types of glial cells?
Astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
What do astrocytes do?
they are responsible for blood and brain barrier and how much of a neurotransmitter gets relayed to other neurons
What do oligodendrocytes do?
these create myelin for the central nervous system
what do Schwann cells do?
these cells create myelin but for the PNS
Are nerves part of the PNS or CNS?
Nerves are cells in the peripheral nervous system!
they are a collection of white matter
they take information from the periphery (ex:touch) and move it to the cranial nerves in the central nervous system
what is the composition of the spinal cord in terms of matter?
Spinal Cord
gray matter is on the inside
white matter is on the outside
What forms the Cranial Nerve Nuclei?
clumps of grey matter that occur because of the criss crossing of a bunch of pathways
What is the point of decussation and why is it important?
The point of decussation is the point where all these pathways are criss-crossing
It is important that this criss crossing occurs so that the left side controls the right side and vice versa
where is the point of decussation found?
Reticular formation
What happens in the reticular formation that leads to the forming of the cranial nuclei?
because so much is criss-crossing there is white and grey matter that is lost and left just hanging around and this is what forms those cranial nerve nuclei
What are the 3 meninges?
Pia Mater → soft and sheared against the brain
Arachnoid Mater
Dura Mater → hard and thicker than the other layers
what are meninges?
the three membranes (the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater) that line the skull and vertebral canal and enclose the brain and spinal cord.
List the organization of meninges and spaces of the brain (inner to outer)
Pia mater
subarachnoid space
Arachnoid mater
subdural space
Dura mater
epidural space
Skull
Where are pain receptors located in the brain?
pain receptors come from the dura → brain doesn’t feel any pain
headaches are pressure on the dura
What is special subarachnoid space?
The subarachnoid space is very vascular (has lots of vessels running through this space. Additionally, cerebral spinal fluid runs through this space providing cushion to the brain.
What are meningiomas?
these are tumors that occur within these spaces (subdural, subarachnoid, epidural)
Because they are layers outside the brain they are more easily removed
They are also not typically cancerous
What are some issues than occur within the subdural and epidural spaces?
You can have subdural and epidural hematomas
these typically are caused by trauma
it is a collection of blood within that space which places pressure on the brain, which is bad
why is it dangerous for there to be pressure on the brain?
An increase in intracranial pressure is a serious and life-threatening medical problem. The pressure can damage the brain or spinal cord by pressing on important structures and by restricting blood flow into the brain
What happens if cerebral spinal fluid does drain in the way it should?
This leads to hydrocephalus (water on the brain) —> a build up of fluid will start to put pressure on the brain which is dangerous
burrholes may be done to drill the fluid/blood
What happens if a tear occurs in the arachnoid mater?
These tears usually occur due to trauma
csf leaks into the subdural space and if this happens it can they start to leak out of our nose
this is dangerous bc if csf can get out into the environment bacteria can get into the brain → leads to encephalitis
lose of csf also leads to decreased cushioning of the brain
what is encephalitis?
infection of the brain
Why are the spaces between the meninges important?
allow for expansion of brain if there is a lot of pressure and it can expand without hurting itself
What is encephalopathy?
brain disease
acute brain problem (happens suddenly not like a degenerative disease like dementia)
Encephalopathy is a change in how your brain functions. You may feel confused, agitated or not like yourself. It can be a temporary disturbance or it could permanently damage your brain. There are many possible causes of encephalopathy, like an infection or an underlying condition. Treatment depends on the cause.
what is metabolic encephalopathy?
Metabolic encephalopathy is a problem in the brain. It is caused by a chemical imbalance in the blood. The imbalance is caused by an illness or organs that are not working as well as they should. It is not caused by a head injury. When the imbalance affects the brain, it can lead to personality changes.
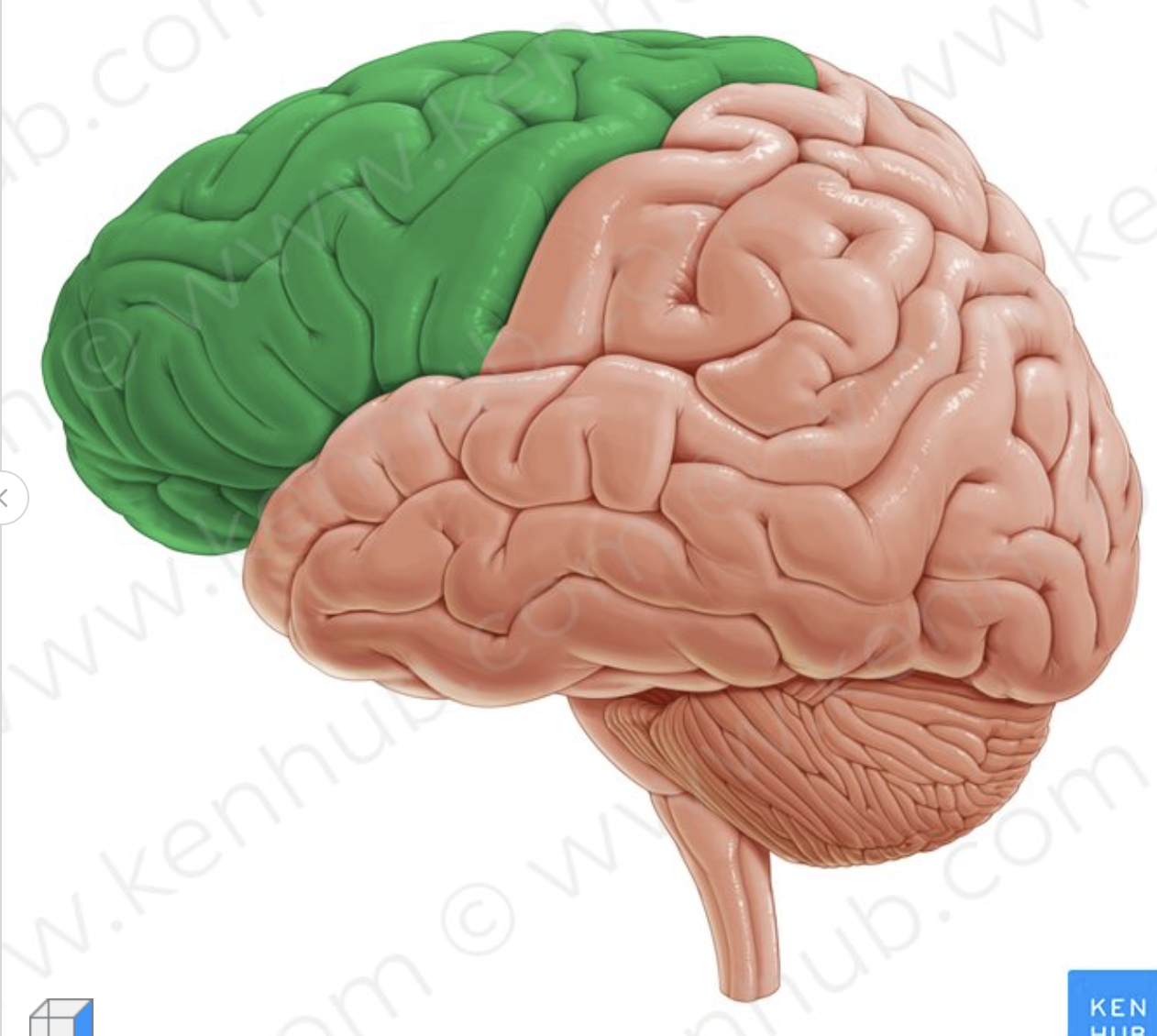
What lobe is in green?
frontal lobe
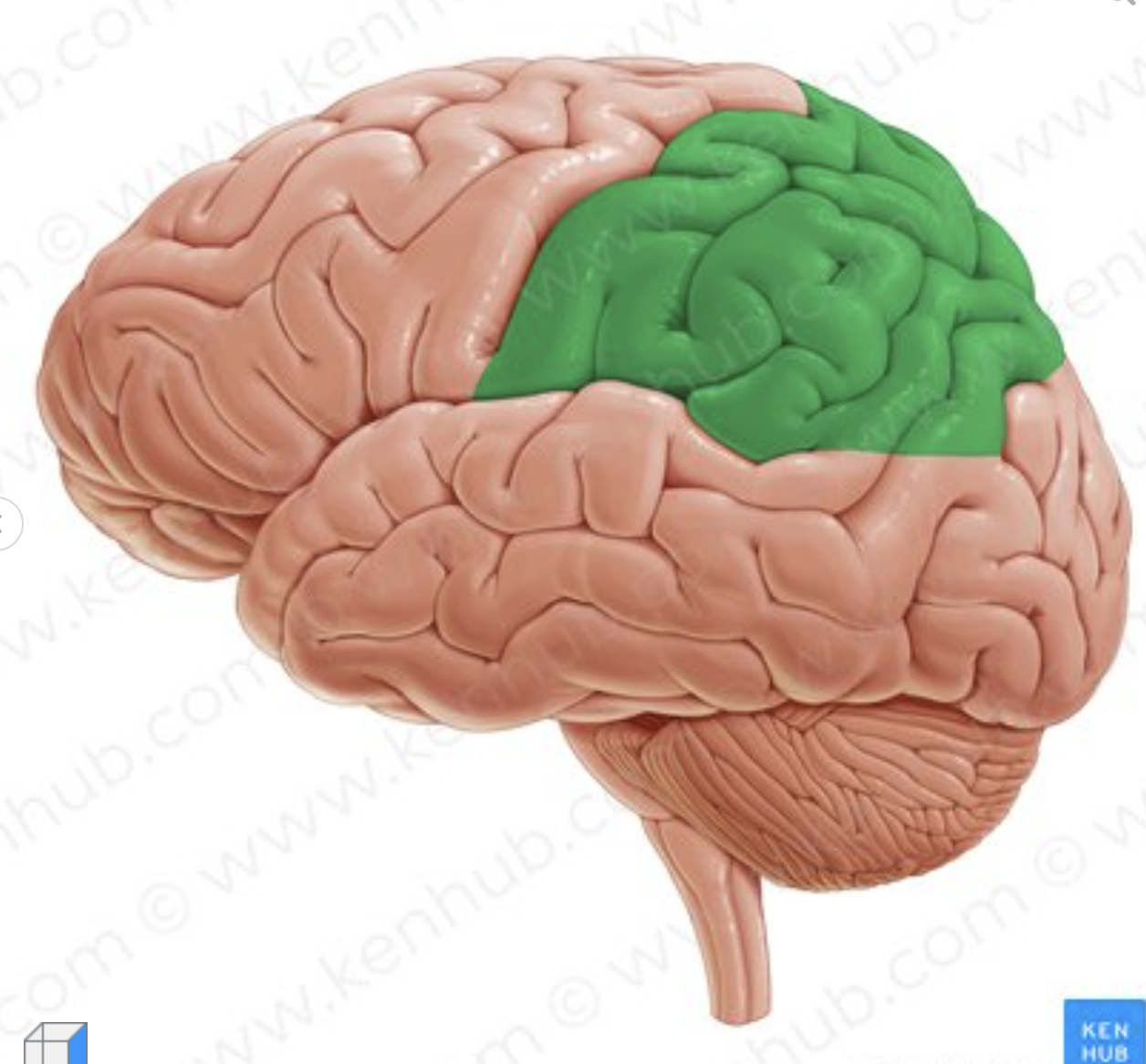
What lobe is in green?
parietal lobe
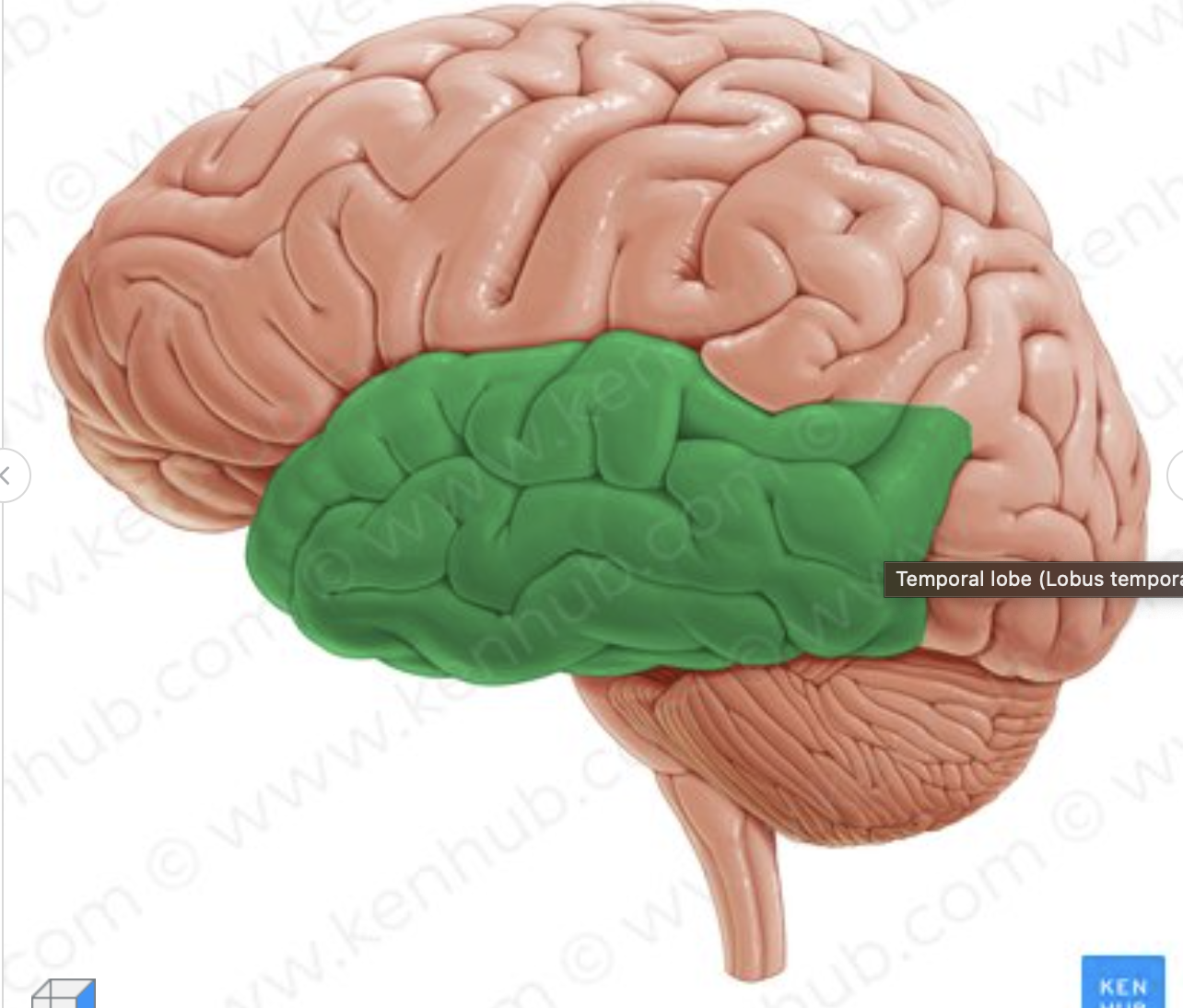
What lobe is in green?
temporal lobe
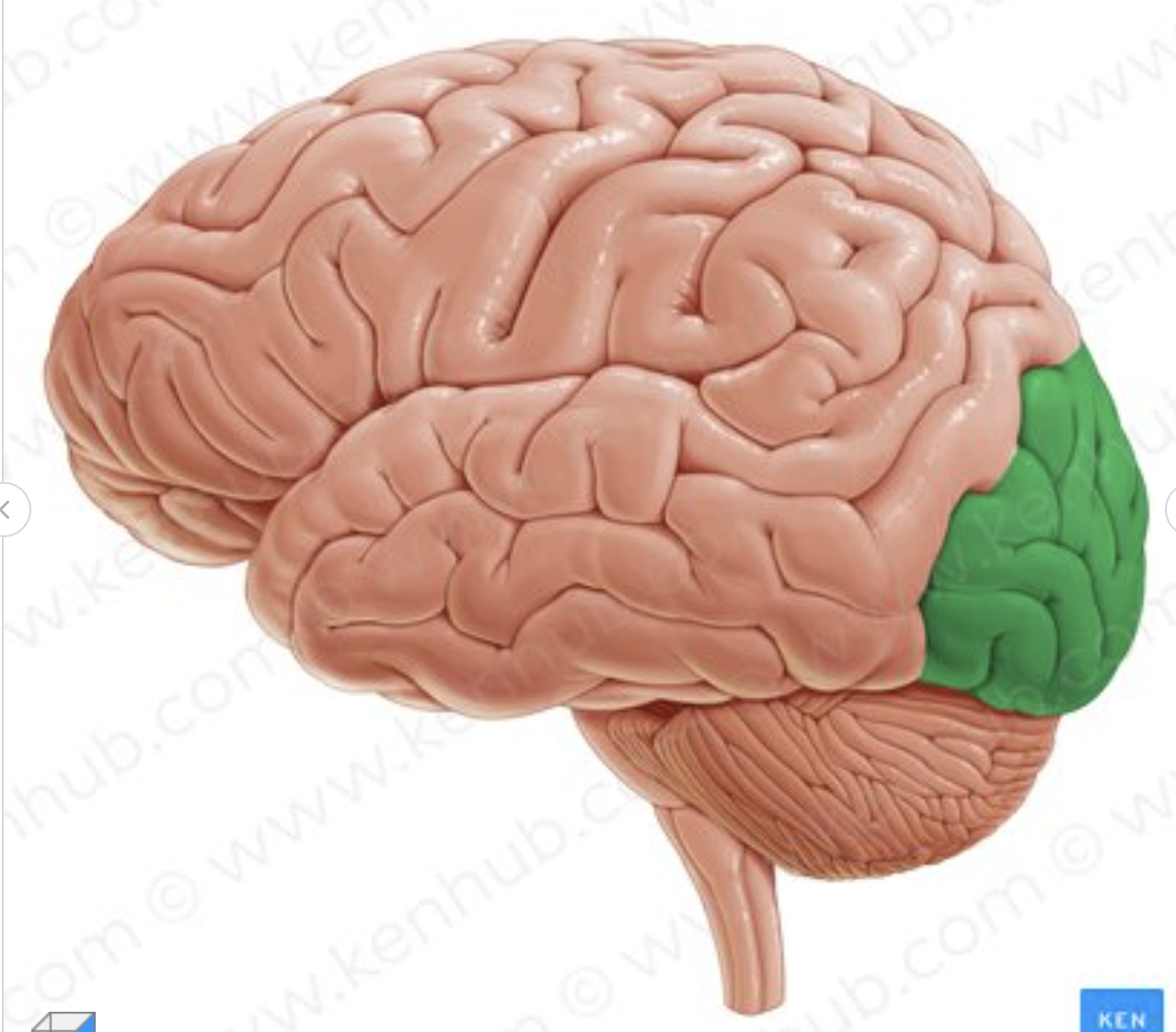
What lobe is in green?
occipital lobe
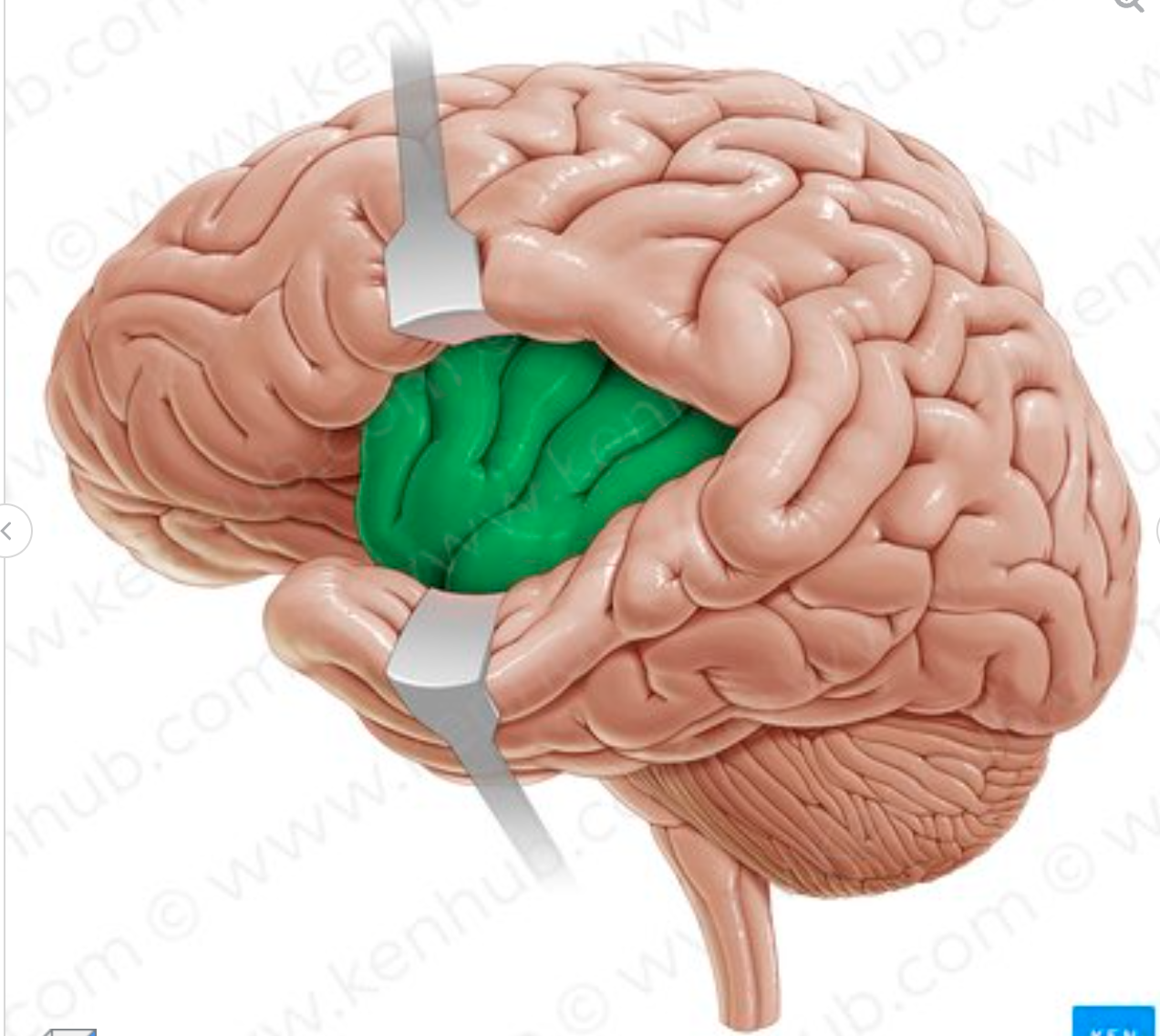
What lobe is in green?
Insular lobe
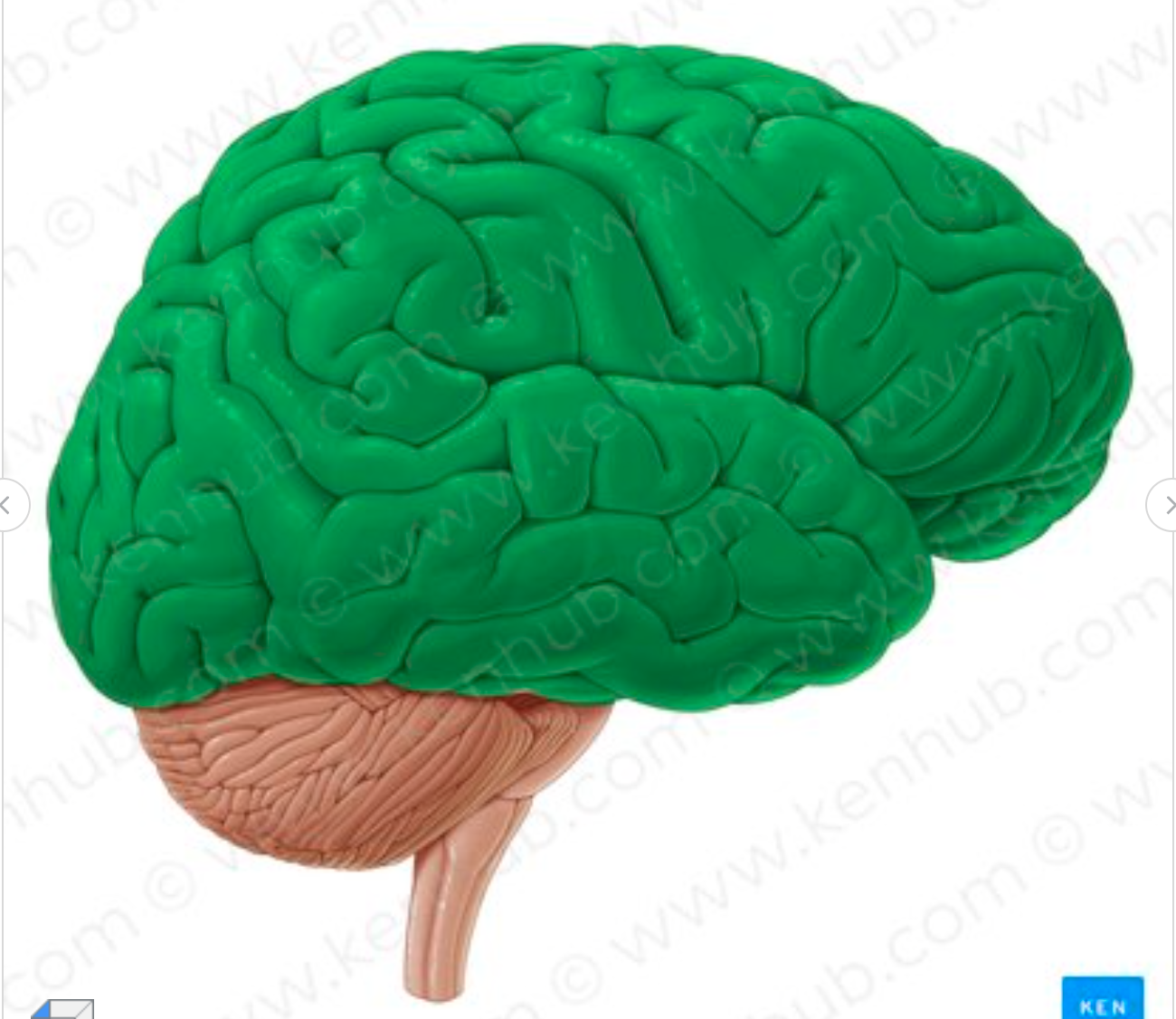
What structure is seen in green?
cerebrum (big brain)
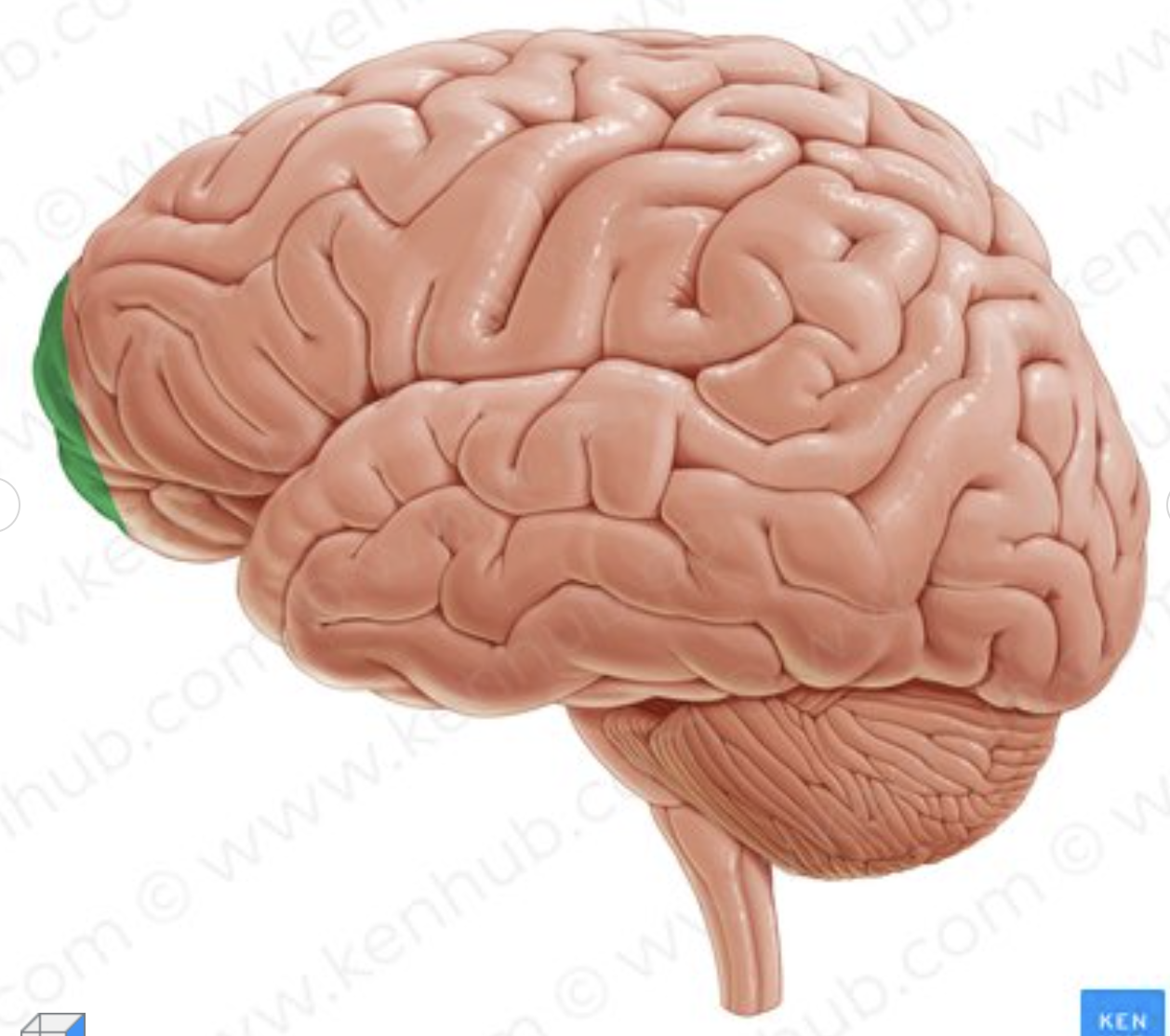
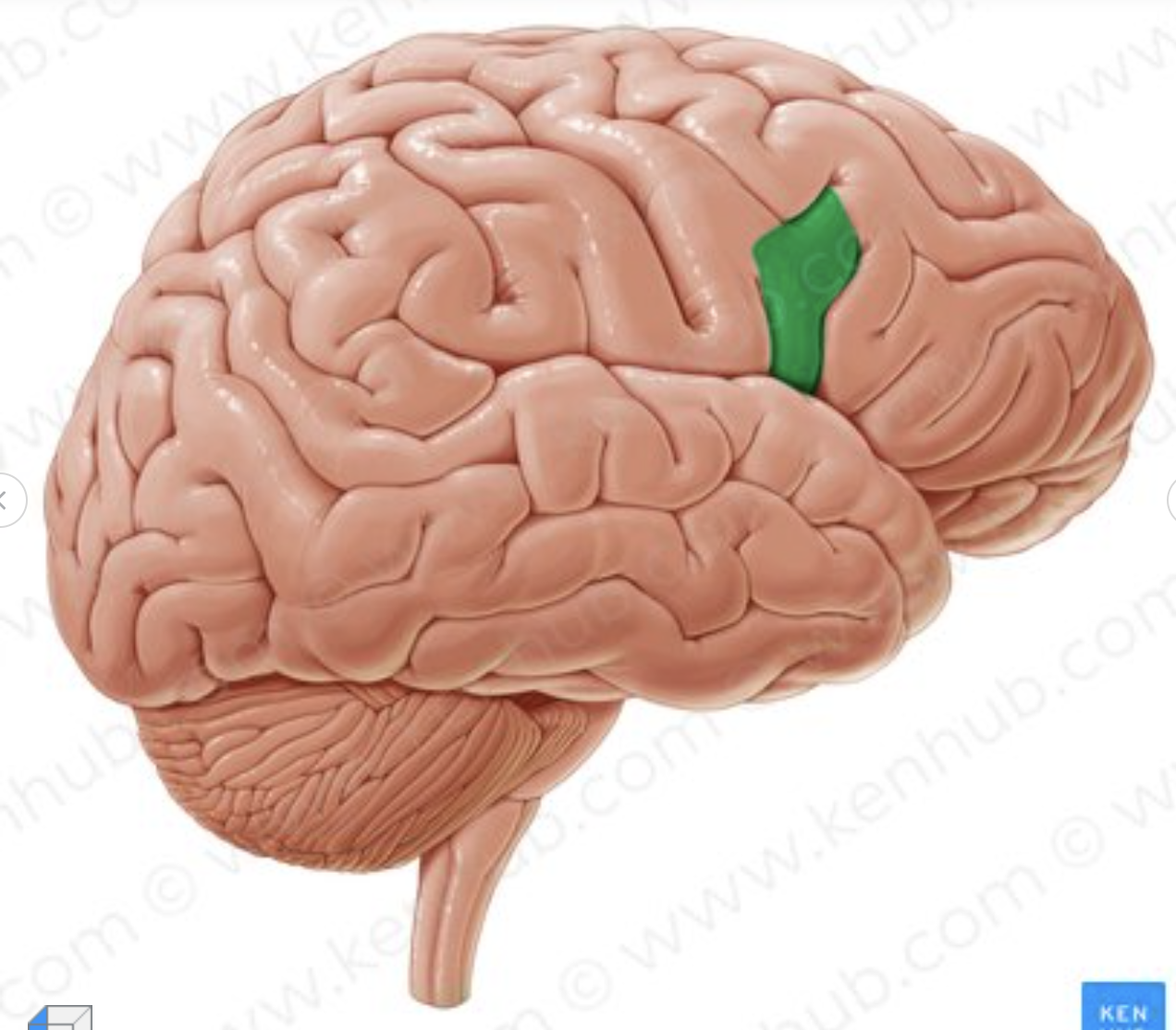
What is the section in green called?
frontal pole
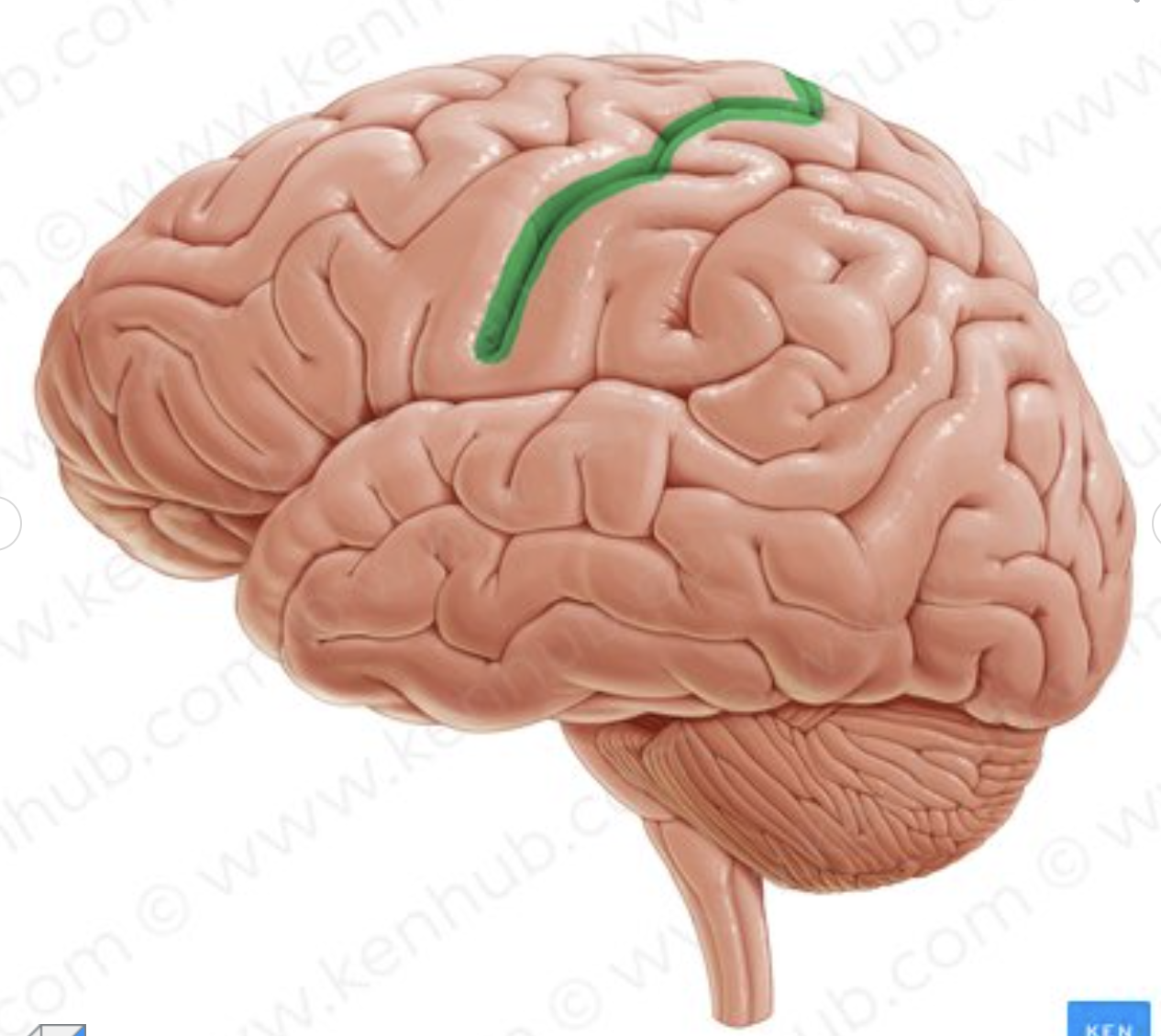
What sulcus is in green?
central sulcus
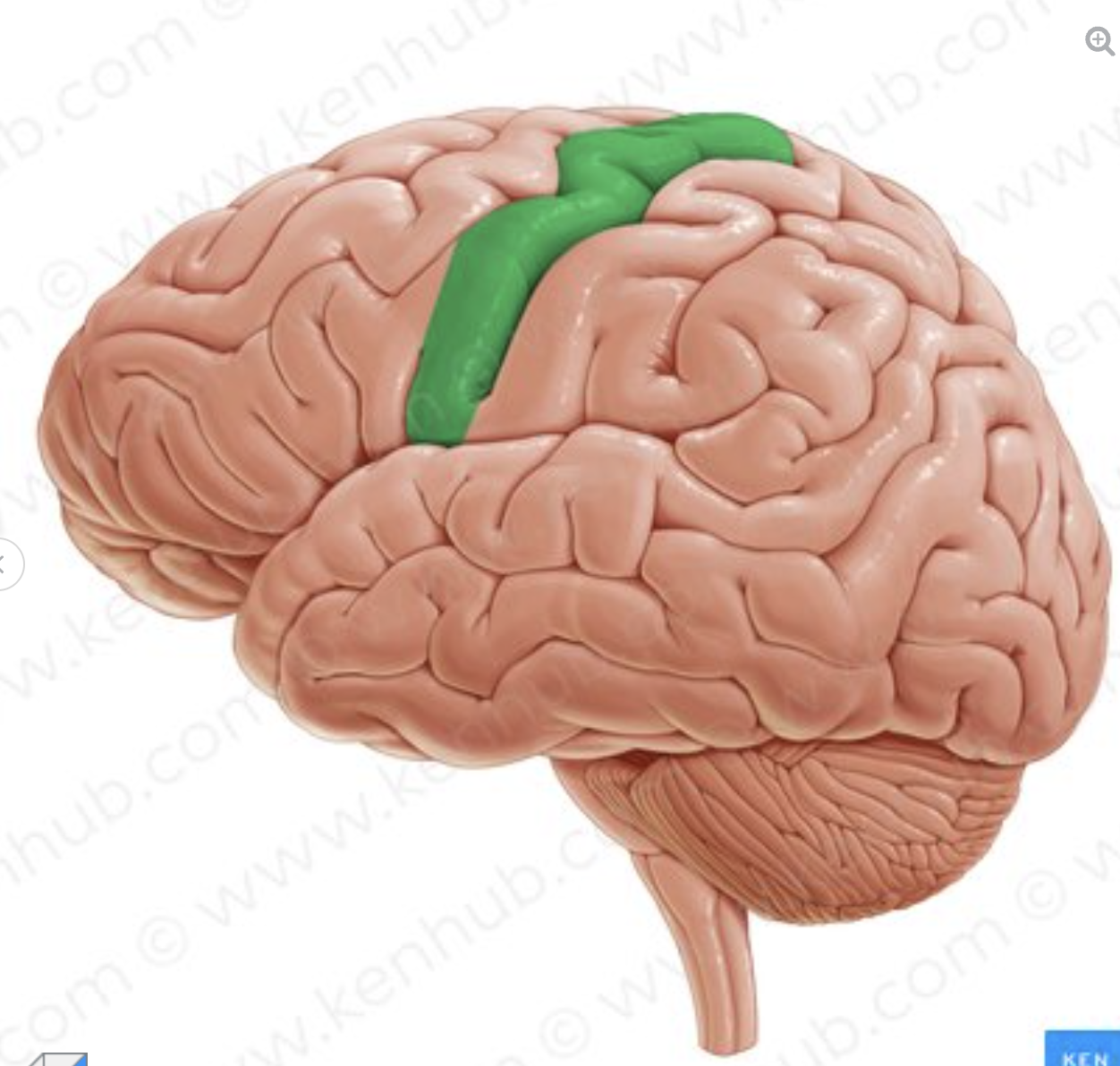
What is the gyrus in green
Precentral gyrus
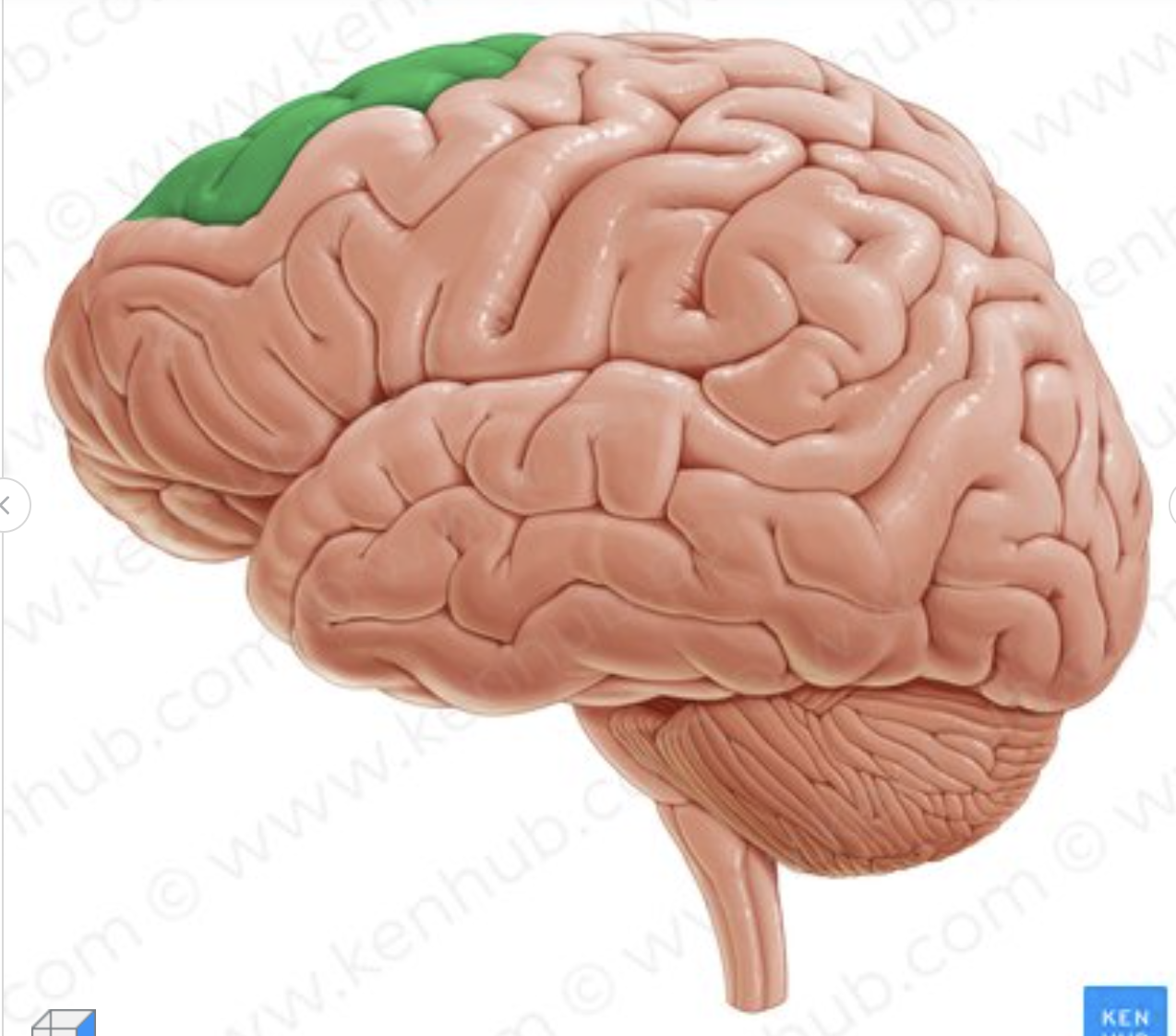
Which gyrus is in green?
Superior frontal gyrus
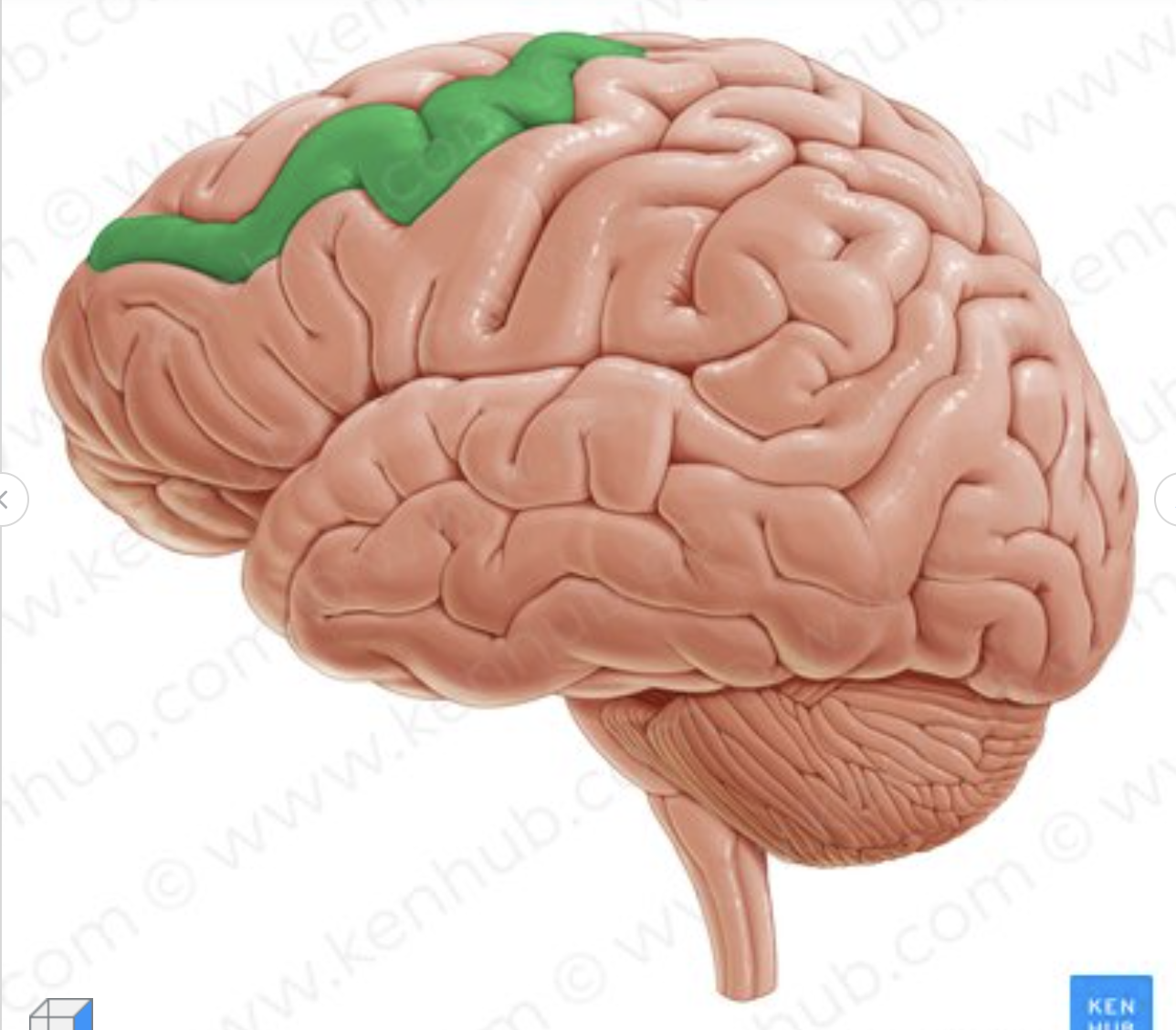
Which gyrus is in green?
Middle frontal gyrus
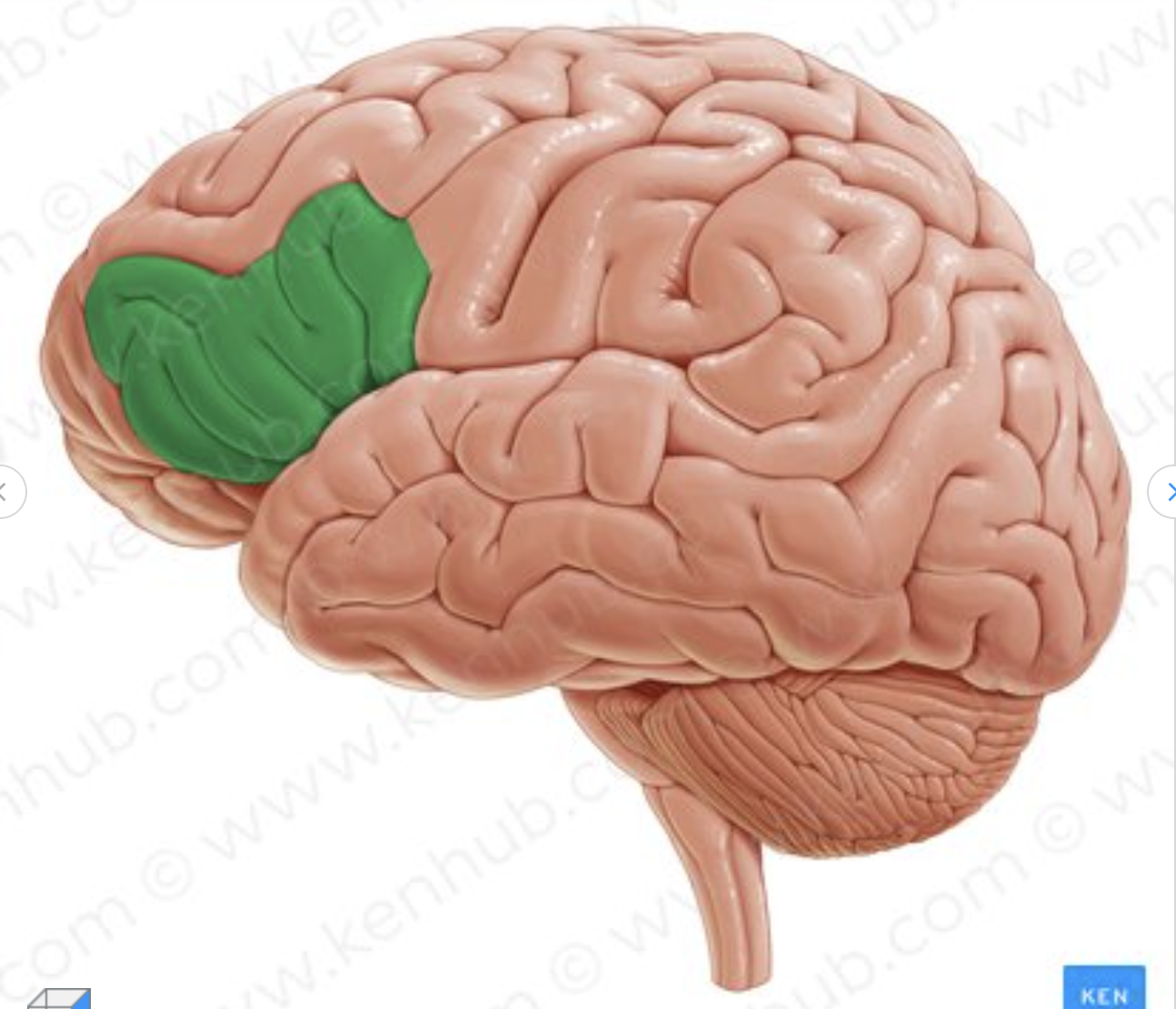
Which gyrus is in green?
Inferior frontal gyrus
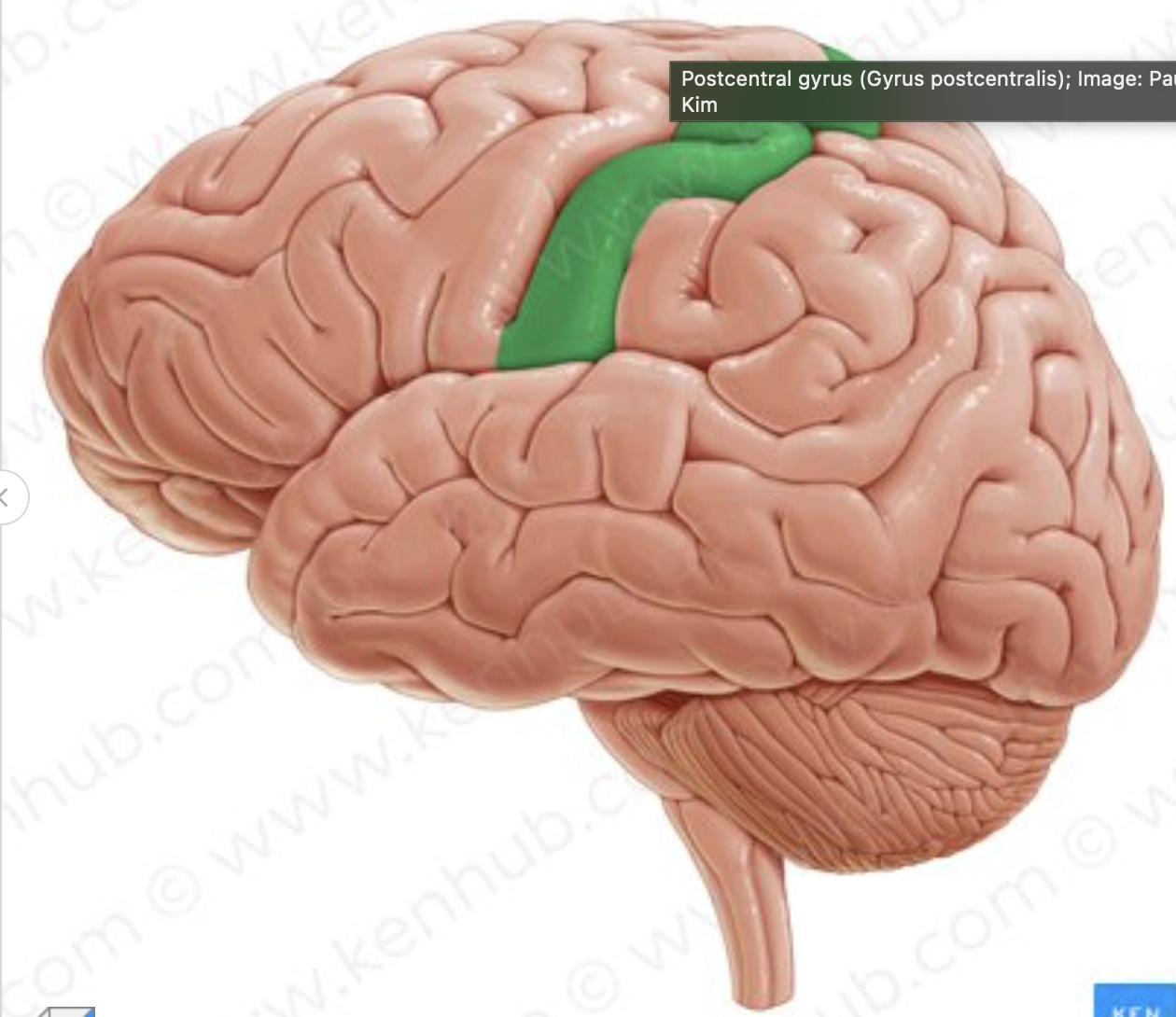
Which gyrus is in green?
postcentral gyrus
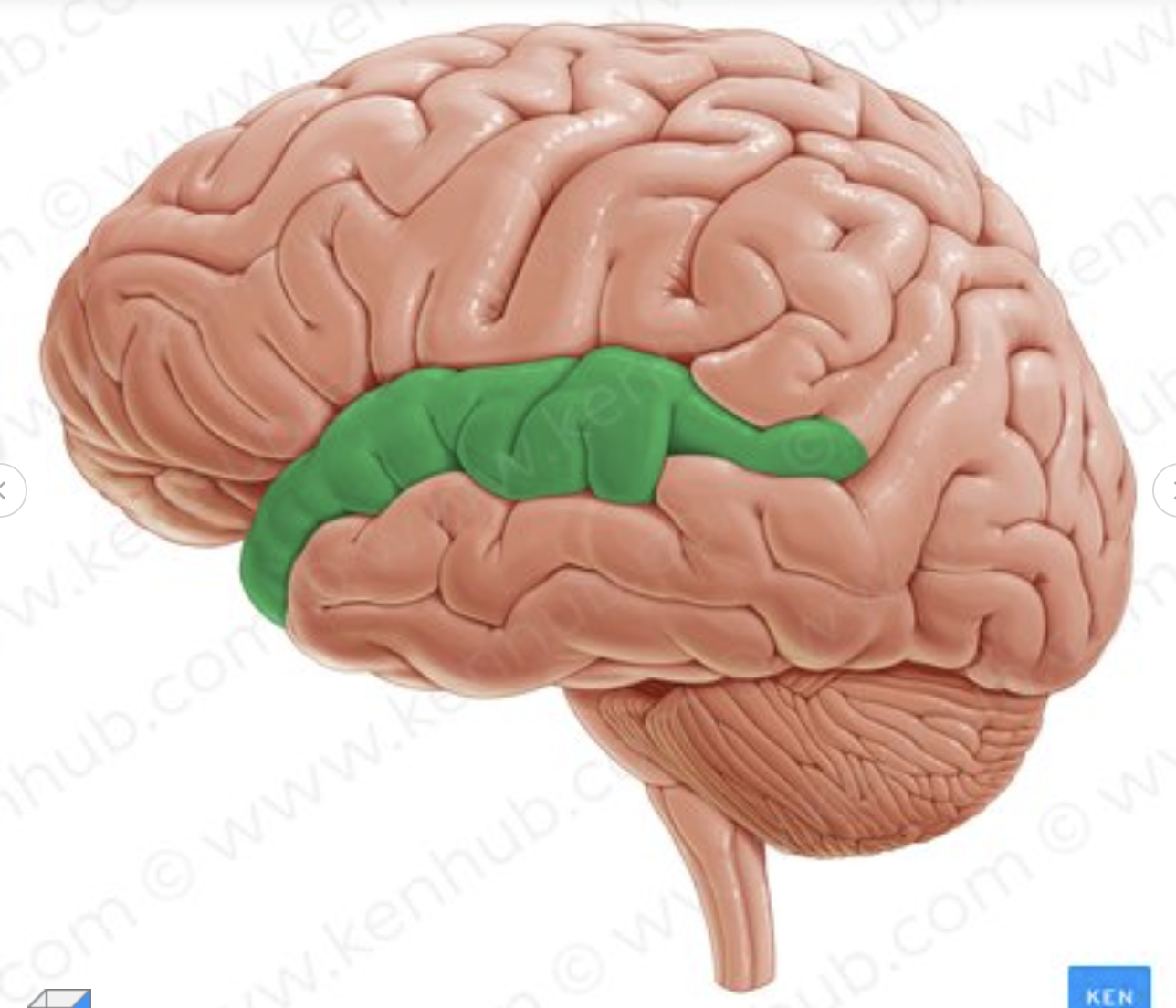
Which gyrus is in green?
Superior temporal gyrus
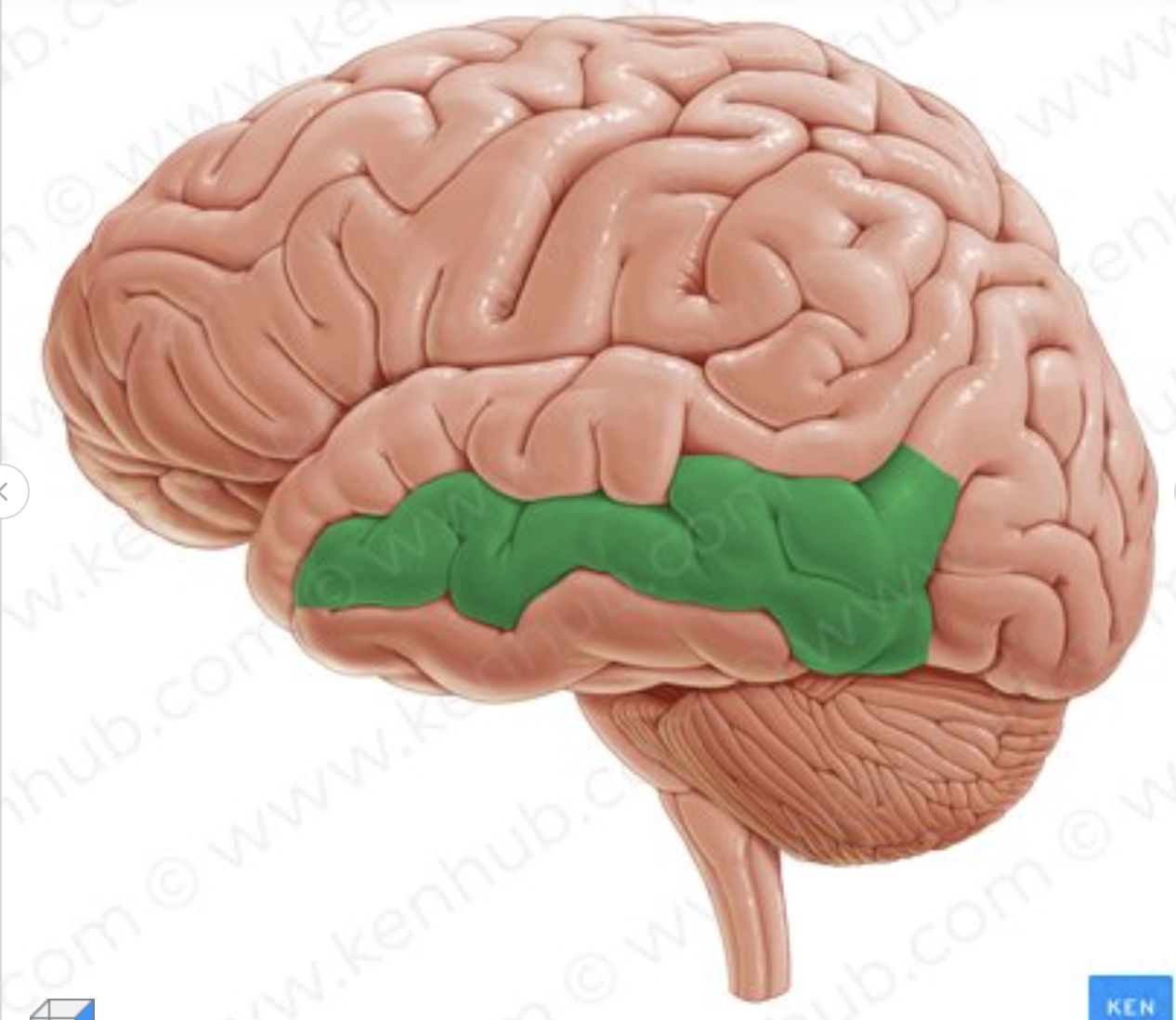
Which gyrus is in green?
Middle temporal gyrus
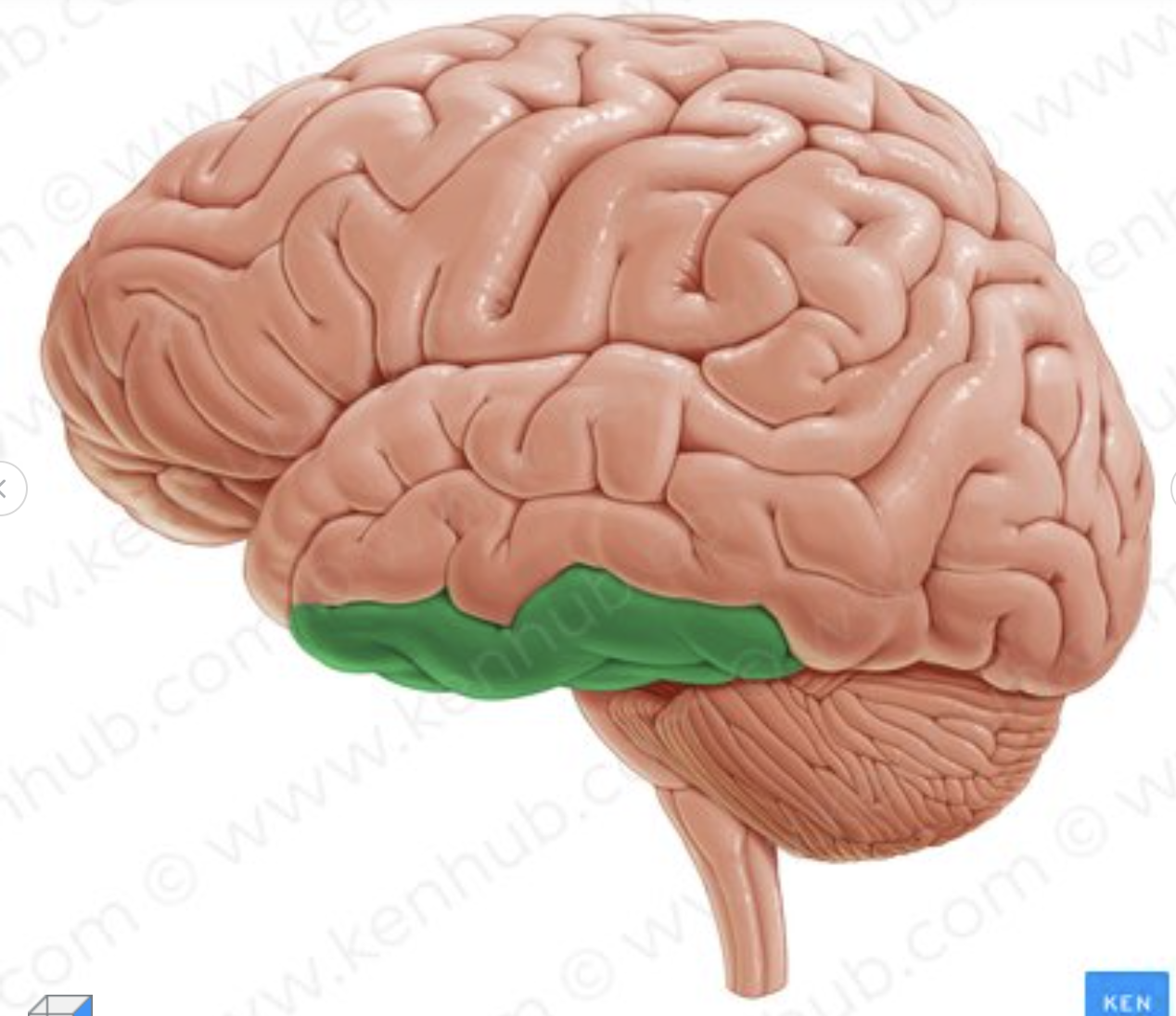
Which gyrus is in green?
Inferior temporal gyrus
which sulcus is in green?
calcarine sulcus
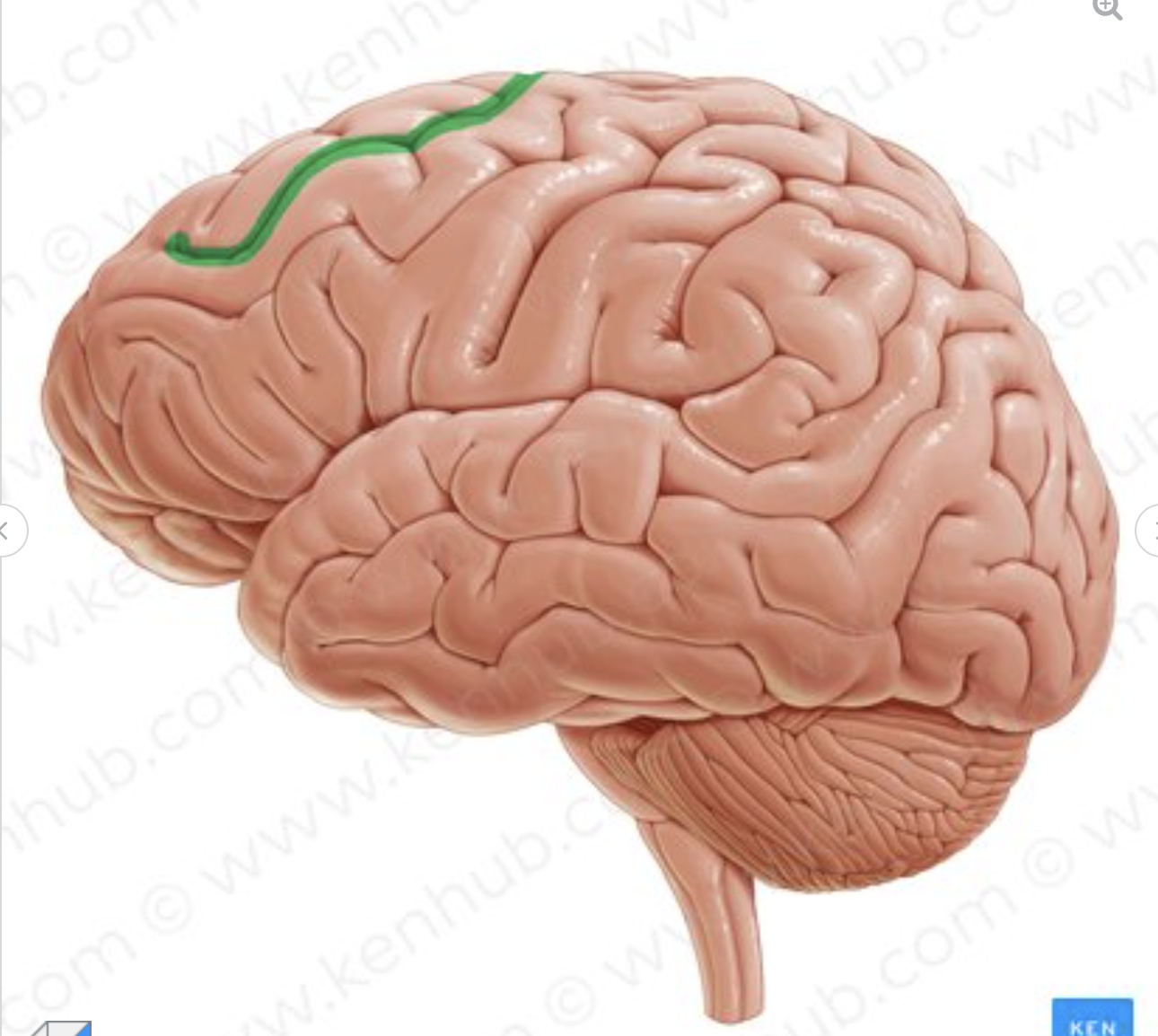
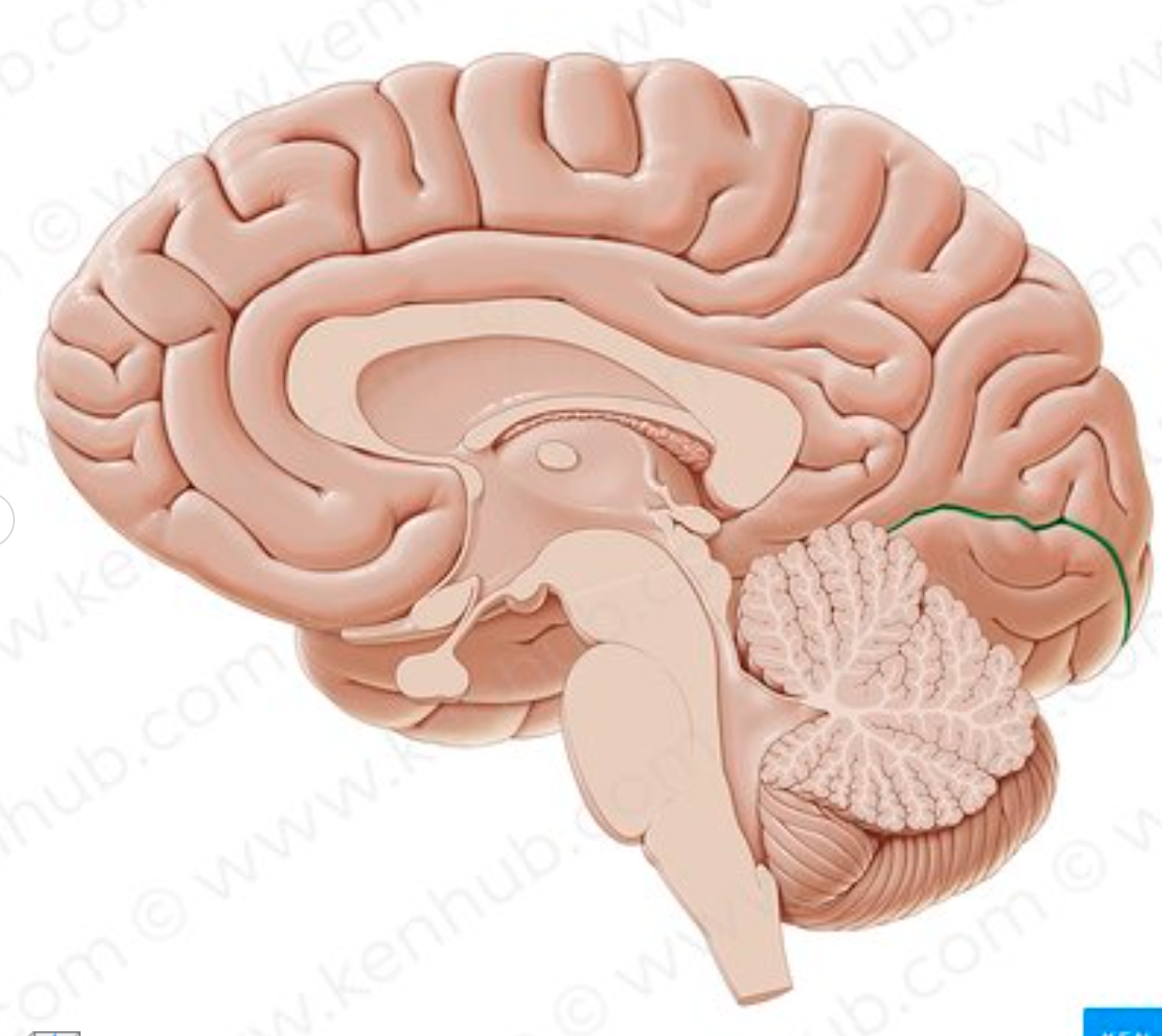
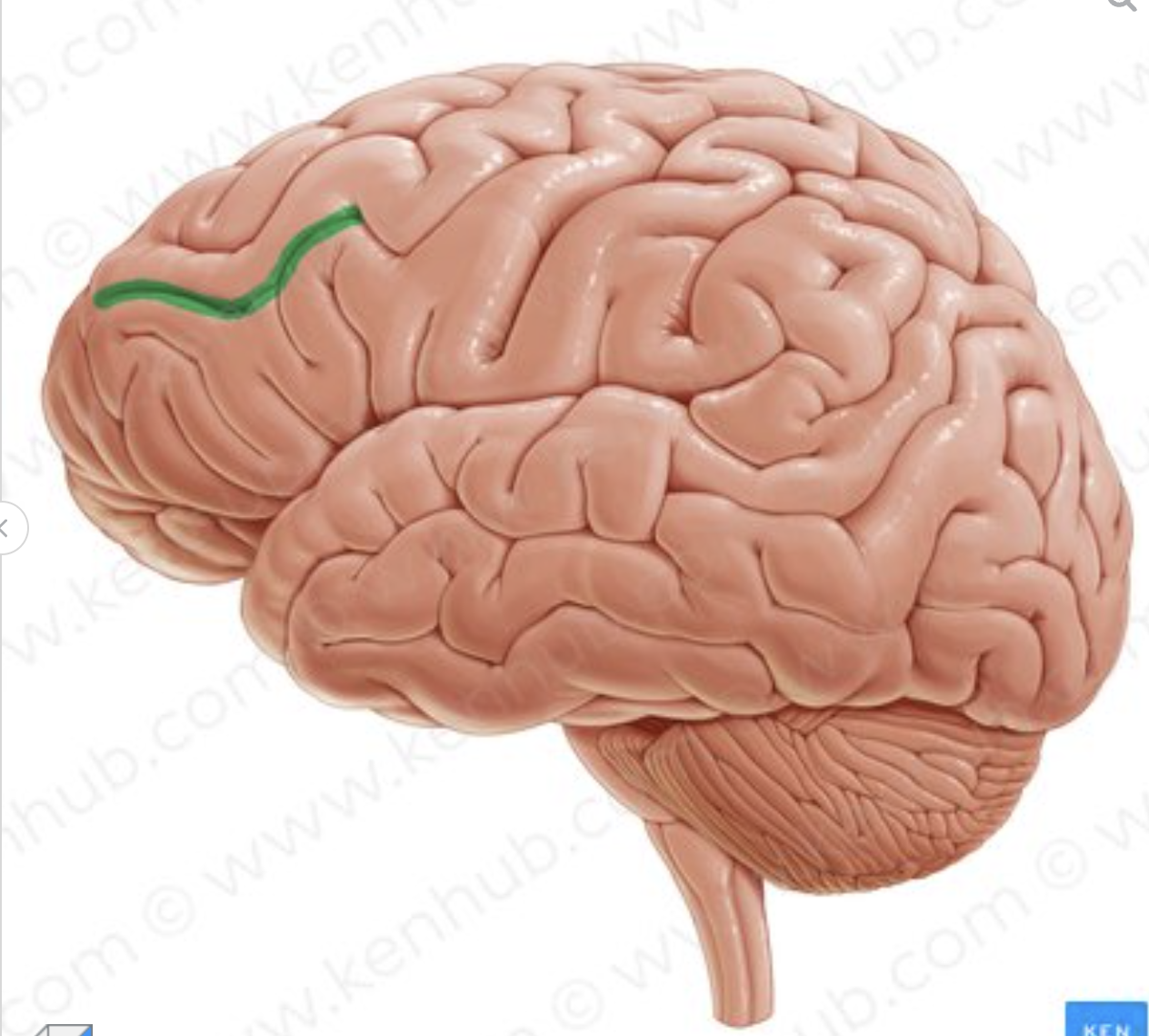
which sulcus is in green?
superior frontal sulcus
which sulcus is in green?
inferior frontal sulcus
What part of the inferior frontal sulcus is in green?
pars opercularis
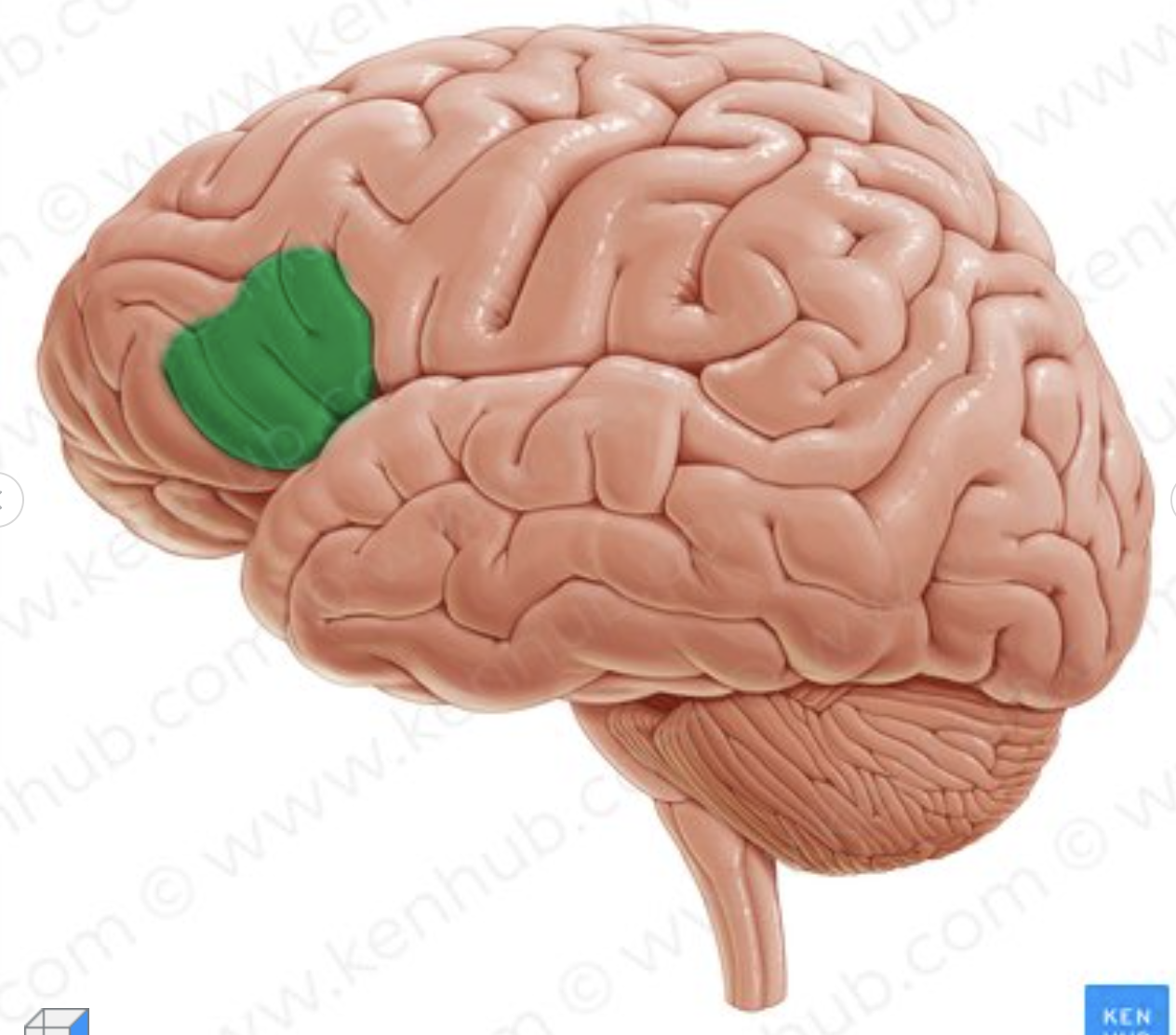
What part of the inferior frontal sulcus is in green?
pars triangularis
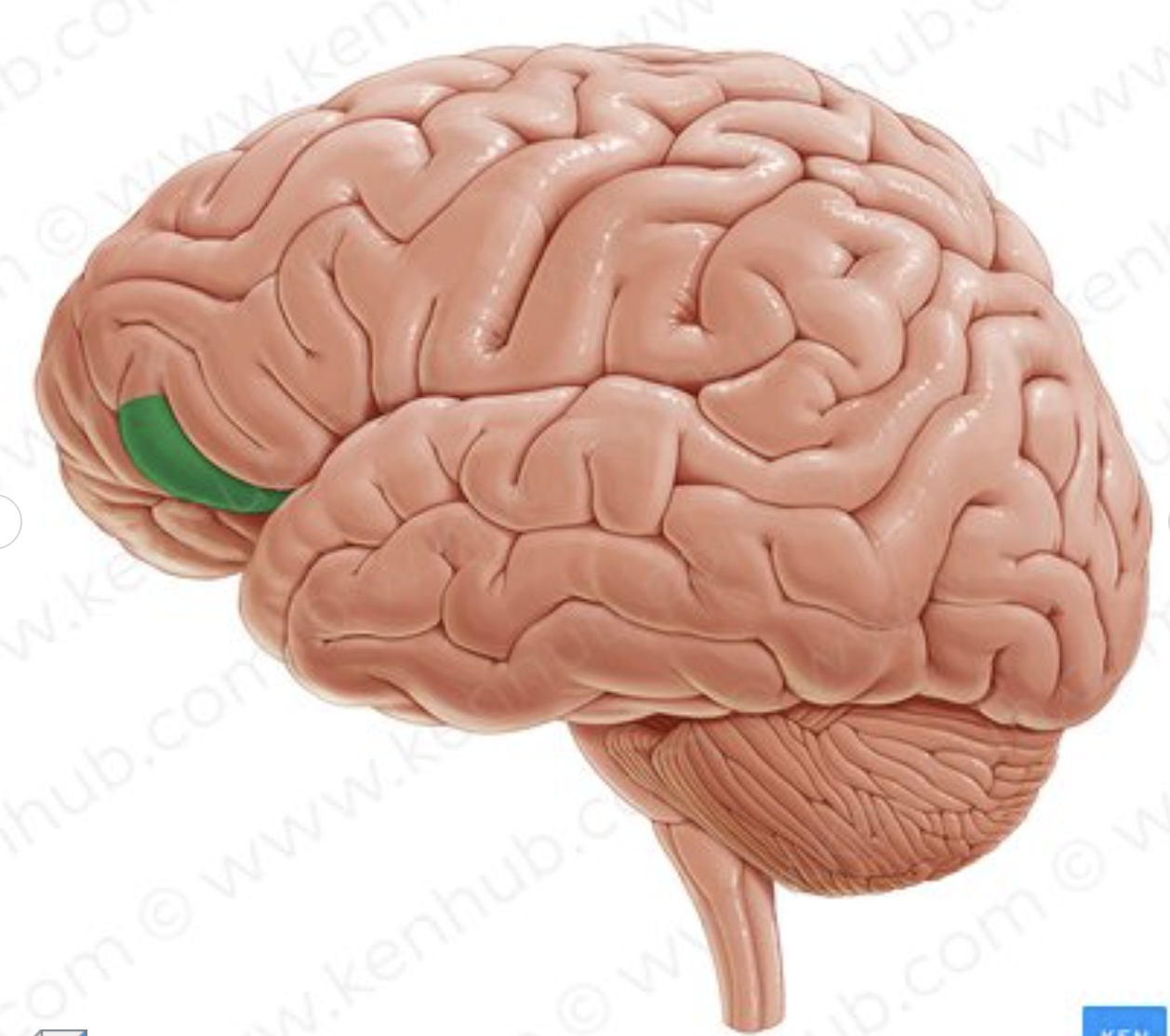
What part of the inferior frontal sulcus is in green?
pars orbitalis
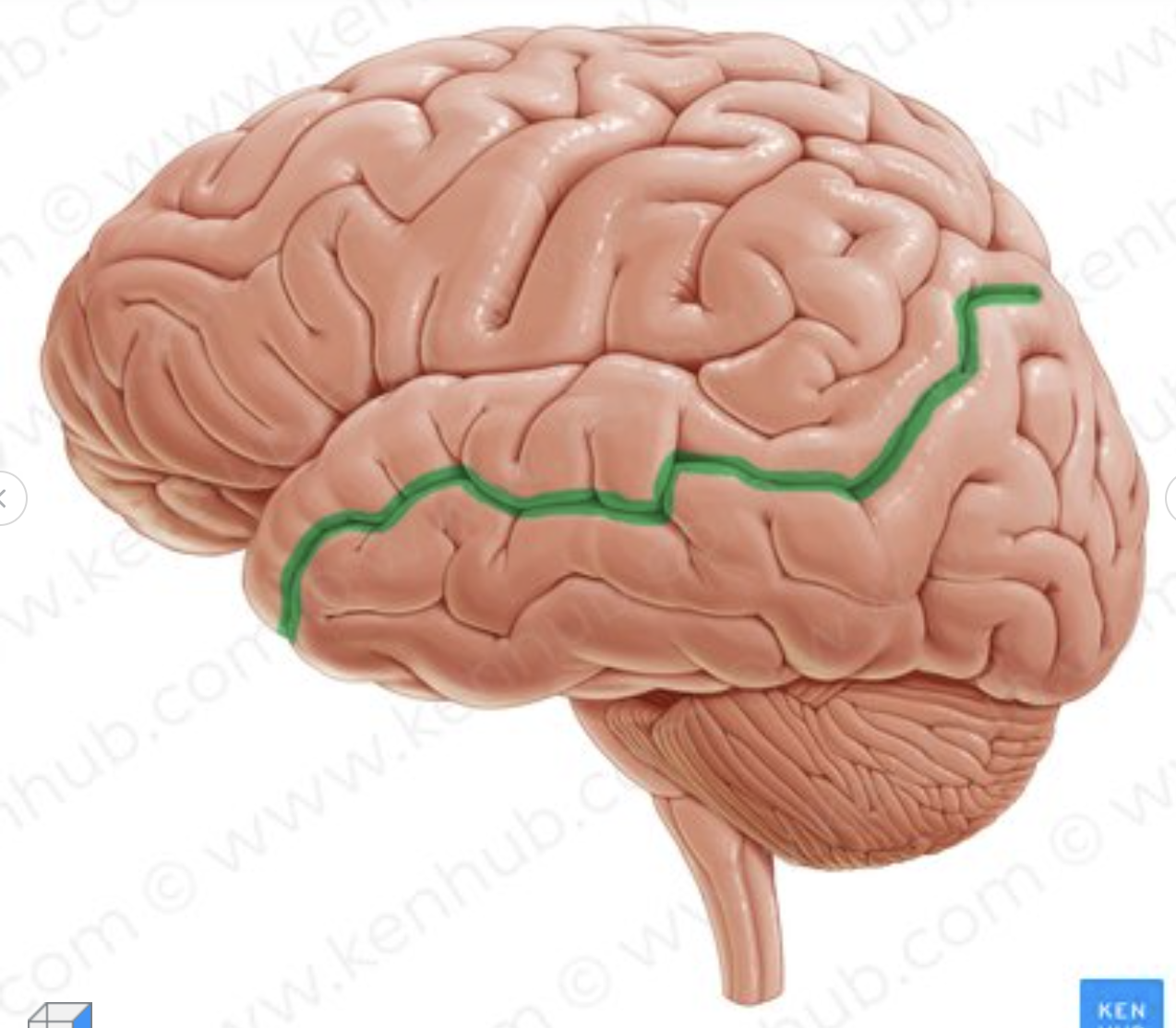
which is the sulcus in green?
superior temporal sulcus
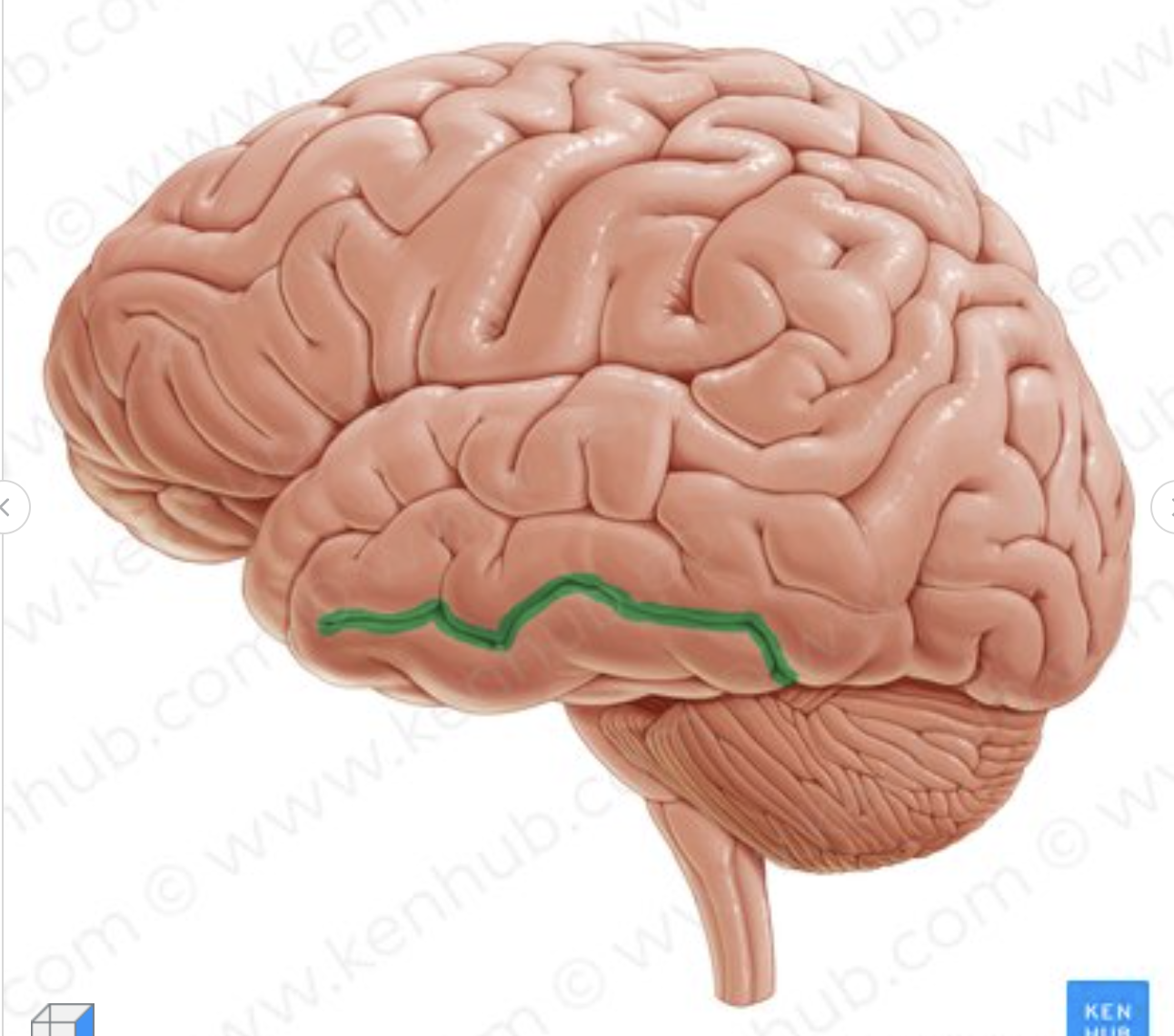
Which is the sulcus in green?
medial temporal sulcus
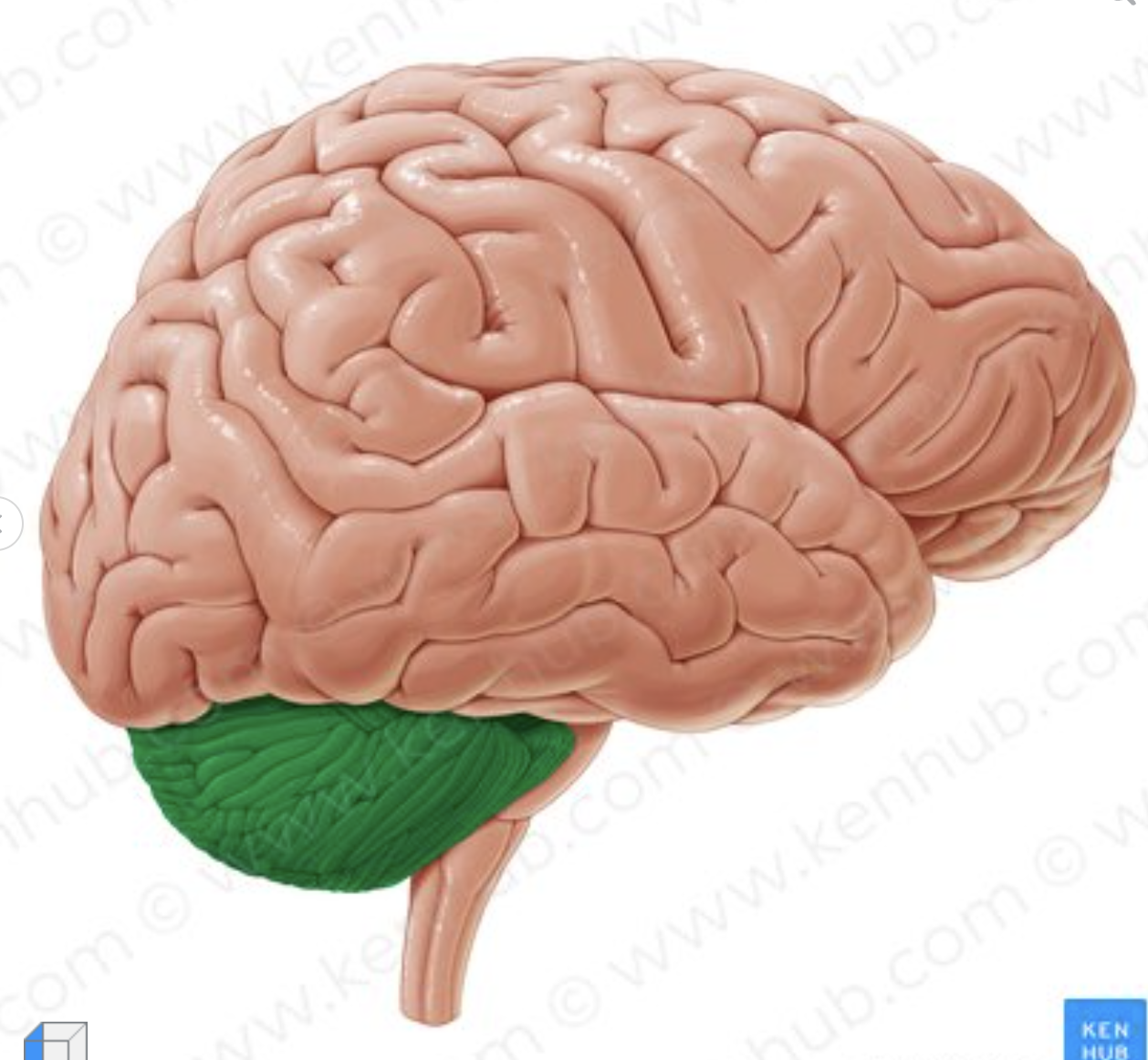
What structure of the brain is depicted in green?
cerebellum (little brain)
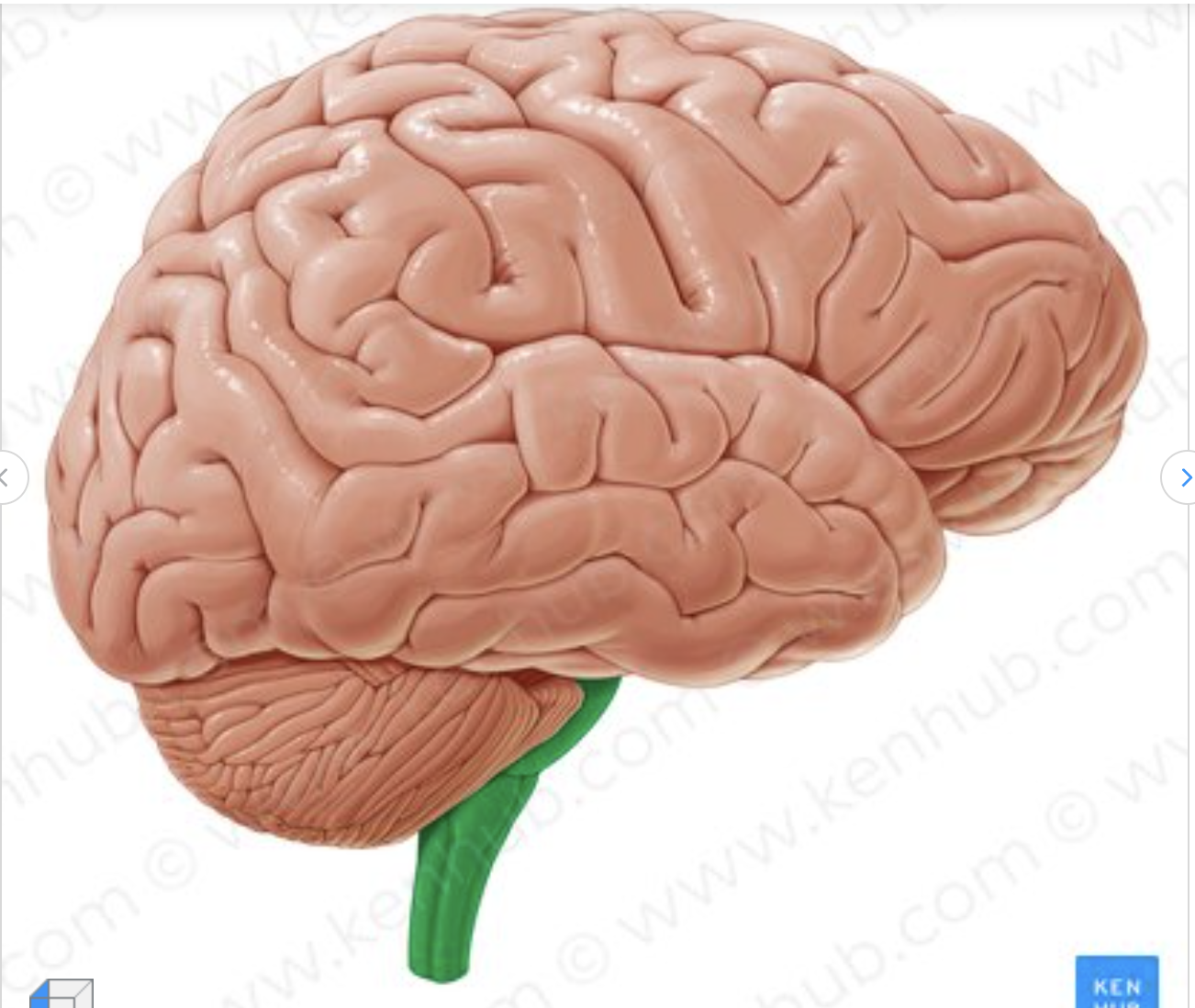
what structure of the brain is depicted in green?
brain stem
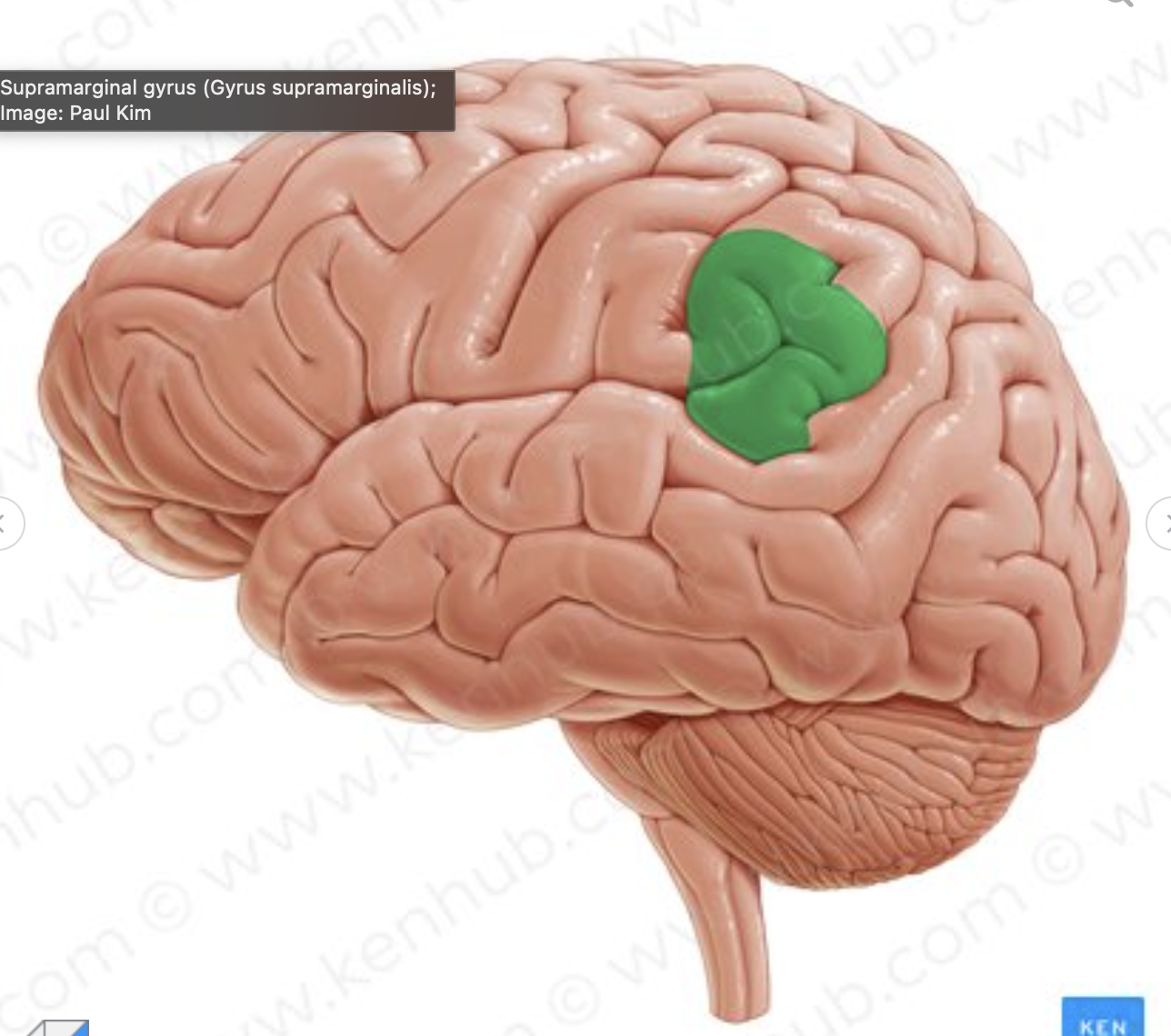
which gyrus is in green?
supra-marginal gyrus
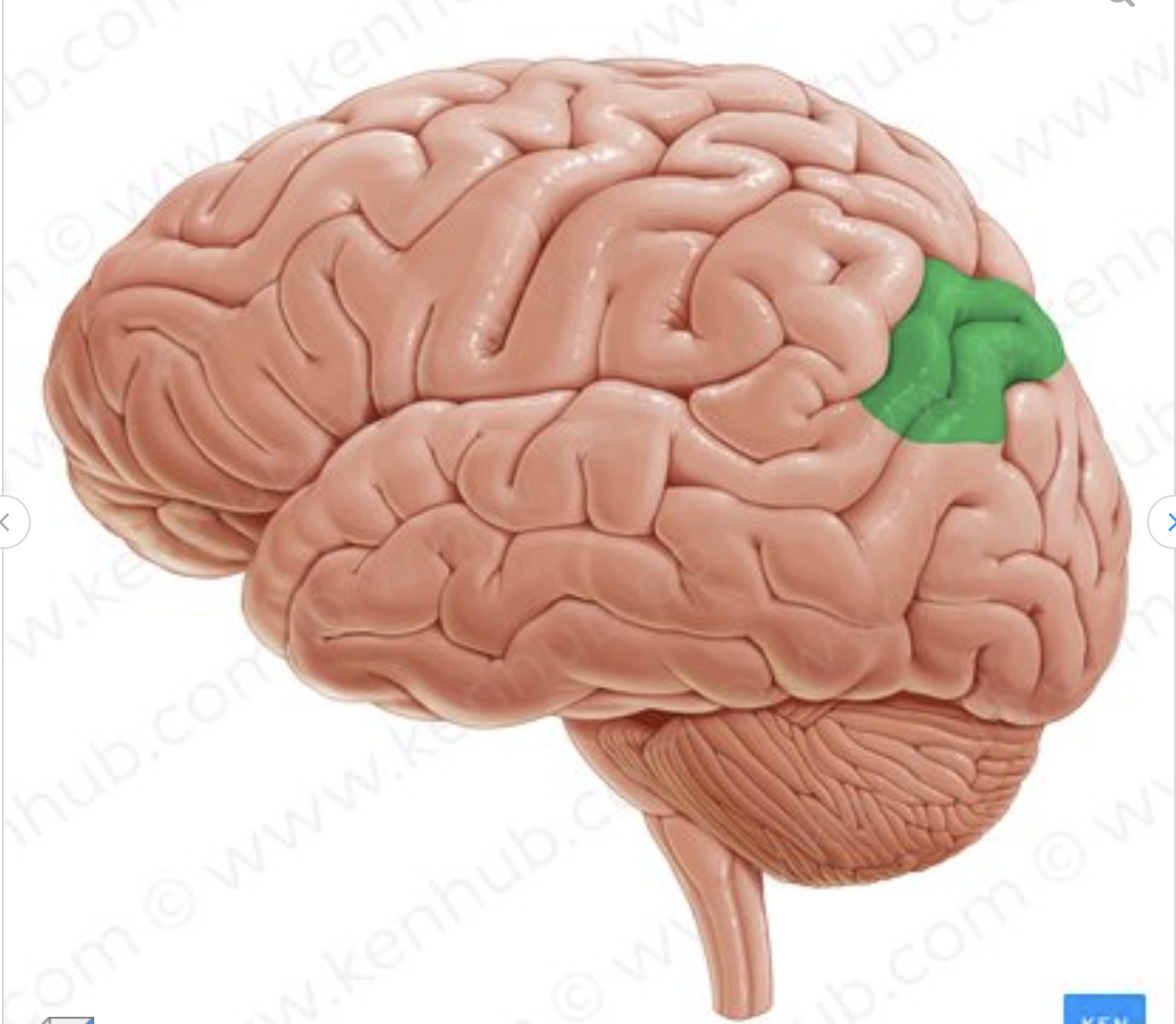
which gyrus is in green?
angular gyrus
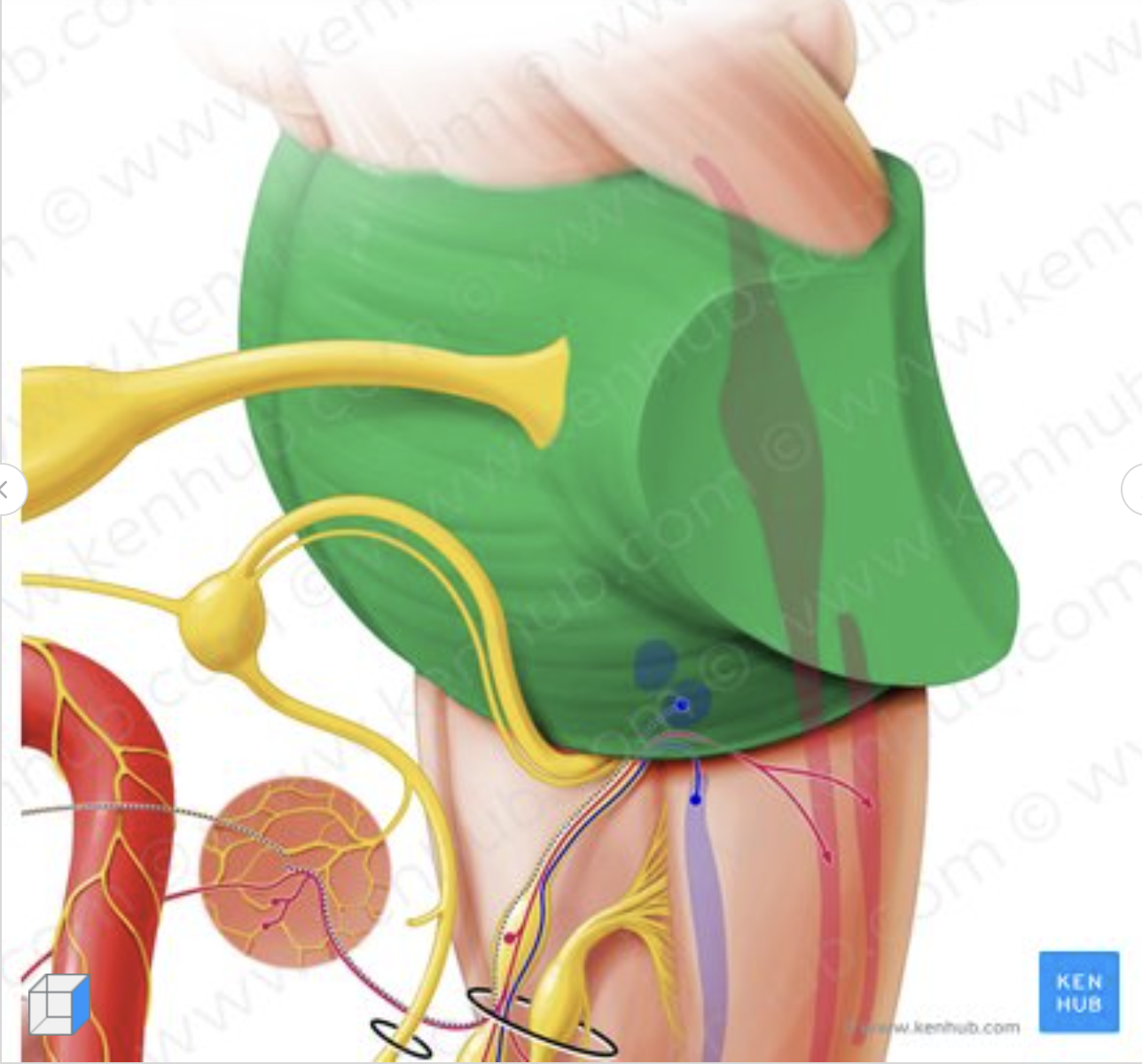
what structure of the brain stem is this?
pons
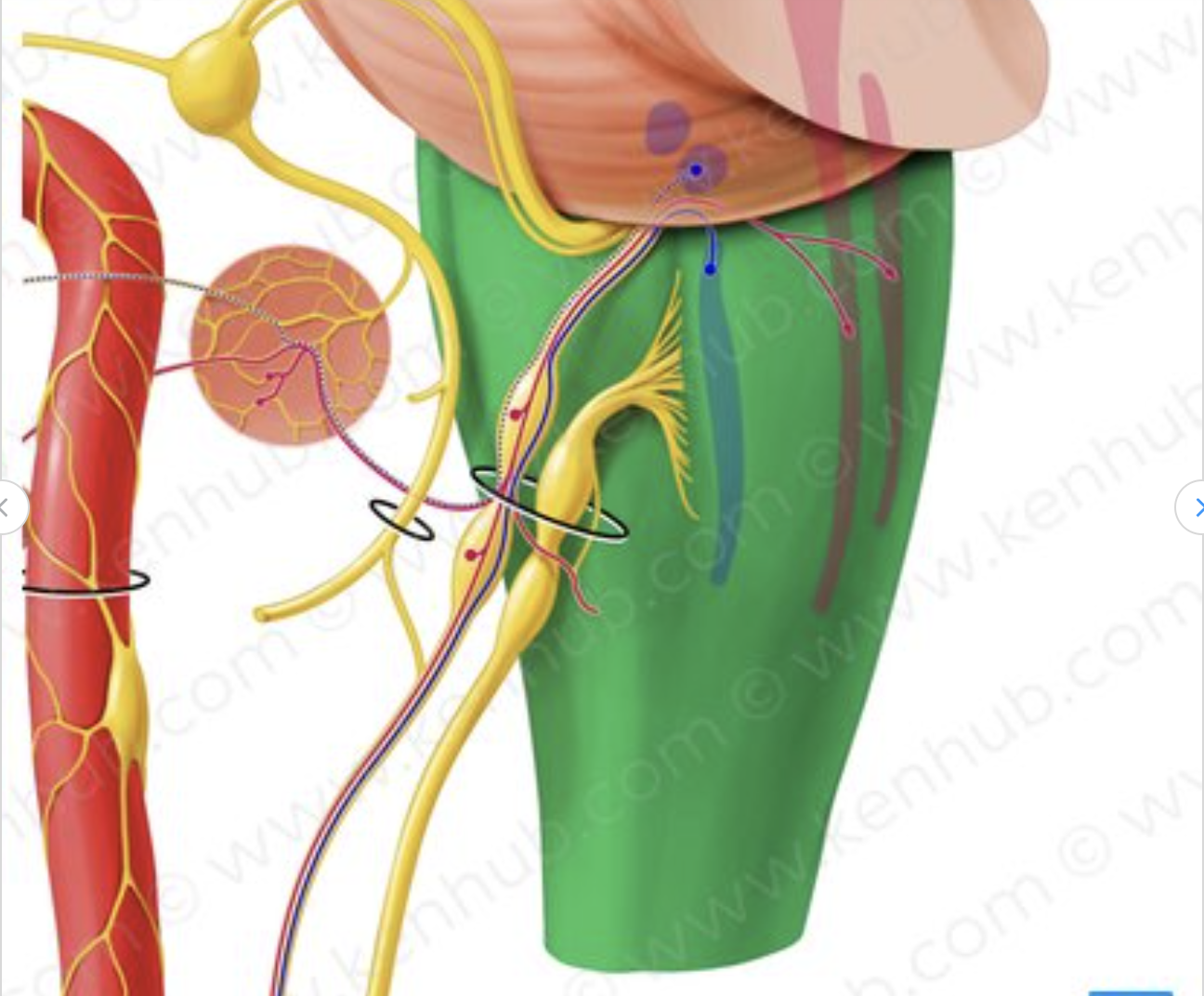
what structure of the brain stem is that?
medulla oblangata
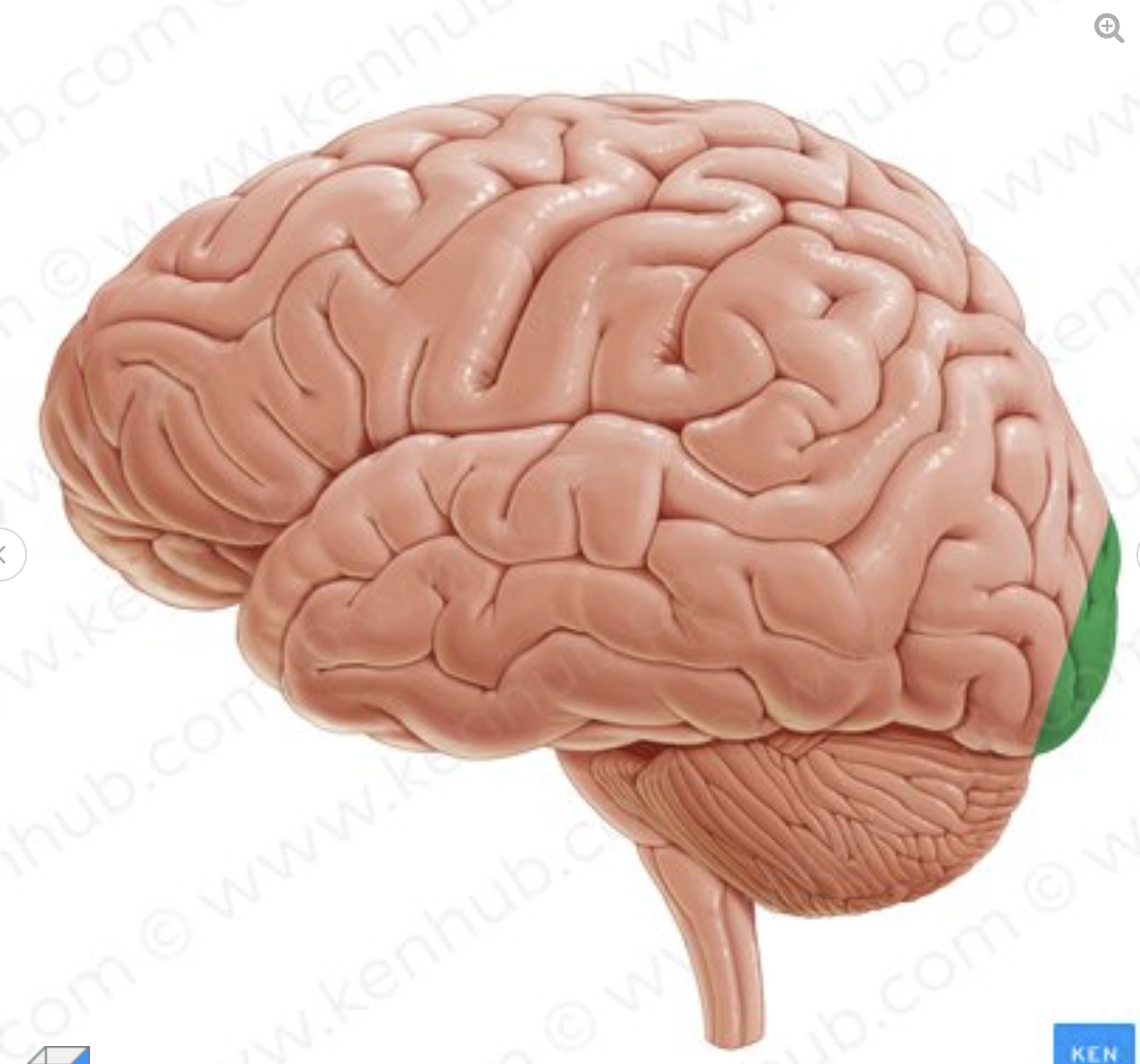
What structure is in green?
occipital pole
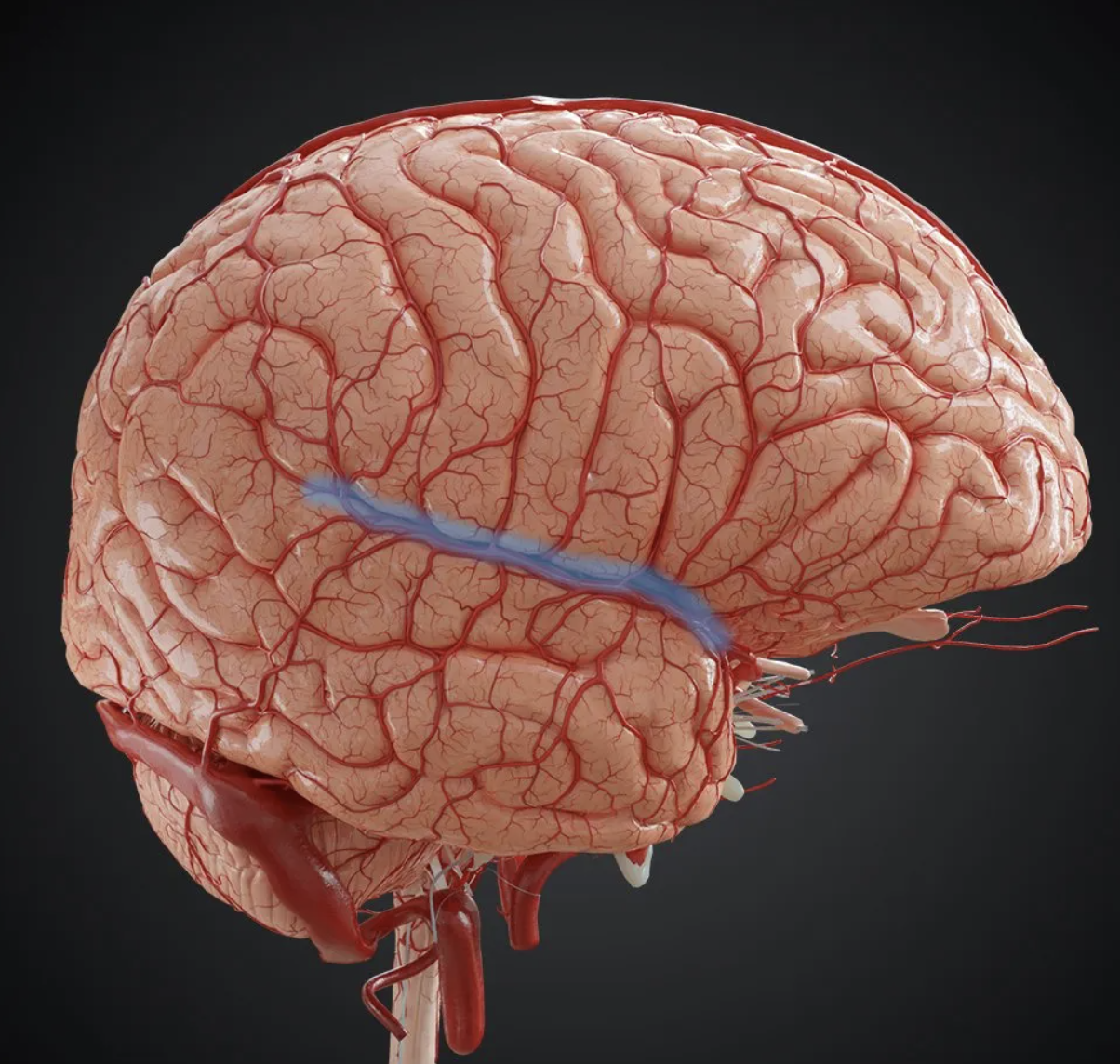
What is the blue structure called?
silvian fissure
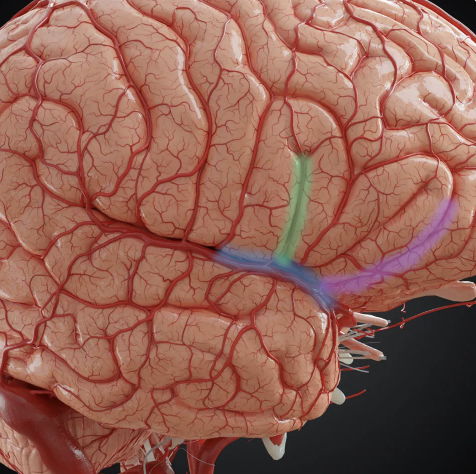
What is the green structure called?
ascending ramus
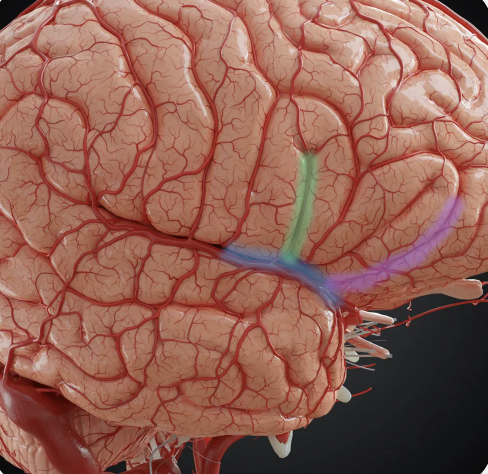
What is the purple structure called?
horizontal ramus
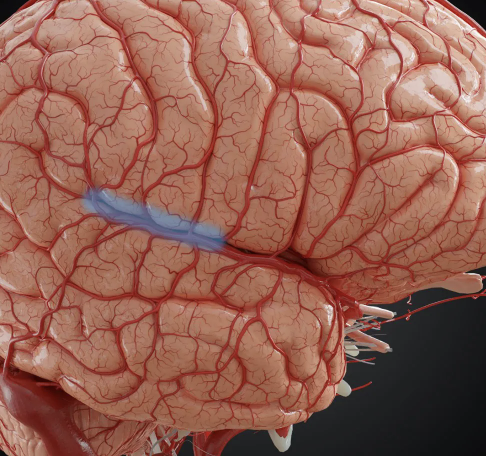
what is the blue structure called?
posterior ramus
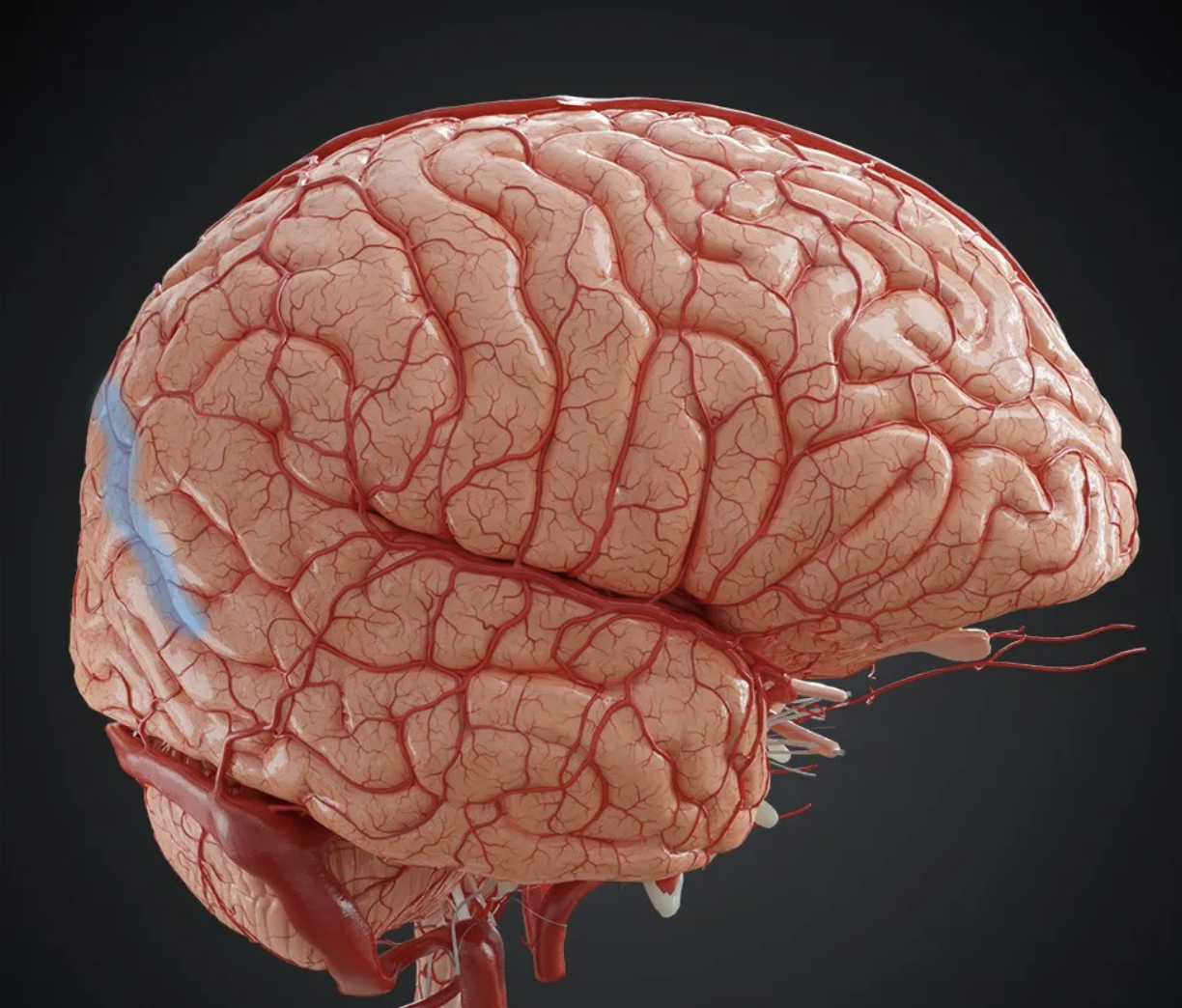
what is the name of the sulcus in blue?
Parietooccipital sulcus
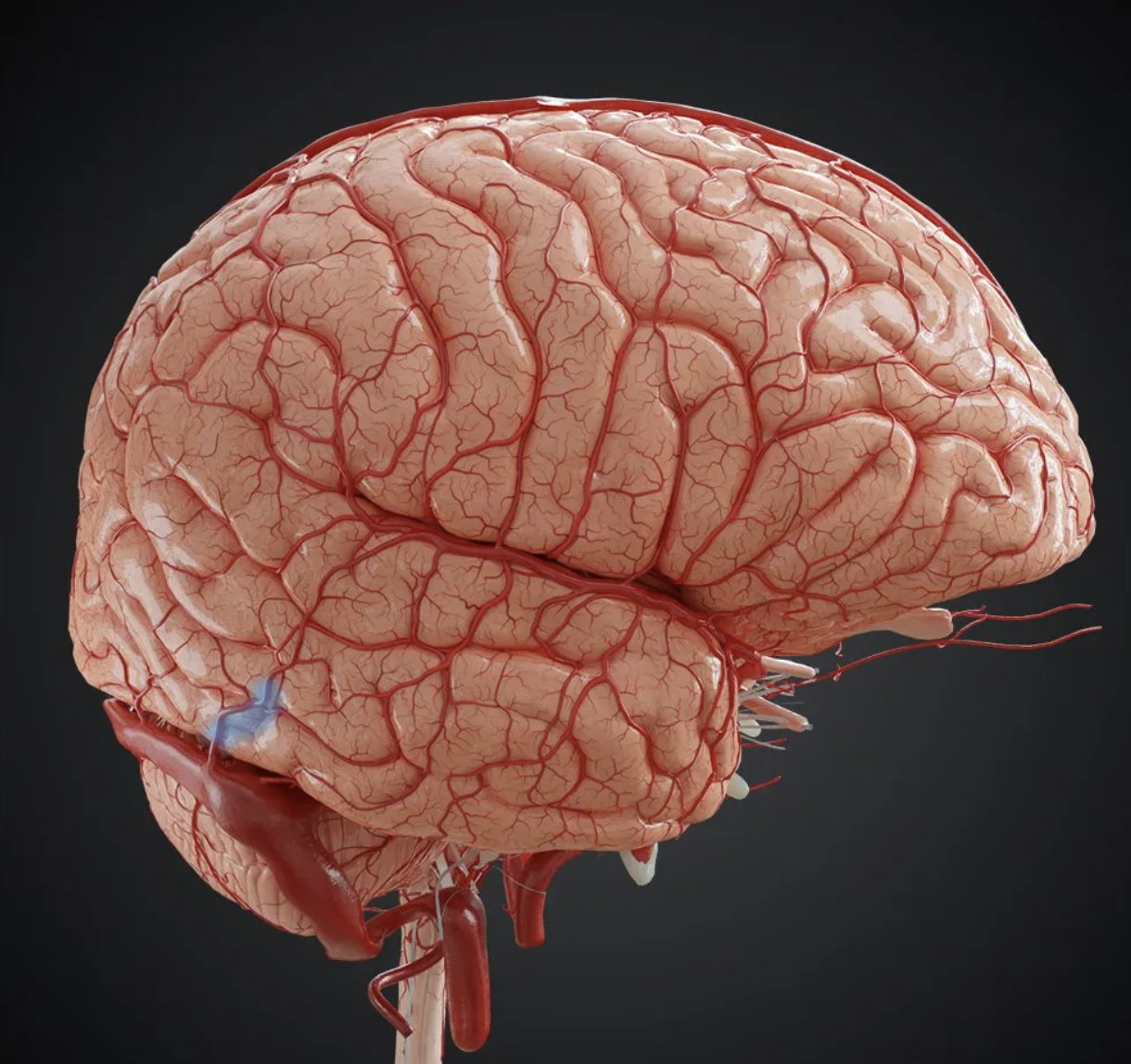
what structure is in blue?
preocciptal notch