2.6 macroeconomic objectives and policies
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
macroeconomic objectives
environmental protection
economic growth
low inflation (2.0%)
low unemployment(Keynes - 3% labour force)
current account
balanced fiscal budget(G=T)
greater income equality
policy areas for Govt to achieve these objectives
demand side policies - designed to impact AD
supply side policies - designed to impact AS
demand side policies
monetary policy
fiscal policy
monetary policy instruments
interest rates
quantative reasoning
how are interest rates used in monetary policy
monetary policy commitee (bank of england) meet 8x a year to set a loose rate - UK 4.75% - target CPI of 2%
e.g. if inflation forecast is above target then:
increase IR - increases saving - deflationary
if inflation forecast is below target then:
decrease IR - increases consumption -inflationary
why is quantative easing used
sometime the MPC beleive that a decrease in IRs alone wont be able to stimulate AD
so mpc decide to inject liquidity(cash) into financial markets
increase cash - increase loans - increase borrowing by business + consumer - increase I + C - increase AD
how is quantative easing used in monetary policy
the bank of england create money electronically which is used to buy bonds from the financial sector - i.e giving loans to banks
increase in price of bonds - decrease in interest rate on bond(yield)
e.g. £1000 bond - £80 a year 8%
£2000 bond - £80 a year 4%
commercial banks now have more money to lend because they have sold bonds in return for cash
fiscal policy instruments
government expenditure
taxation
expansionary fiscal policy
Govt intends to increase AD in the economy and spur econ growth
budget deficit - G>T
i.e spends more than it raises - injection>leakage
contractionary fiscal policy
Govt intends to decrease AD to slow down an economy, often to combat inflation
budget surplus - G<T
i.e saves more then it spends -
injection<leakage
balanced budget fiscal policy
Govt intends to have its revenue mathc its expendiutre to acheive fiscal stability and reduce risk of debt
G=T
types of taxation
direct taxes - tax on income
indirect taxes - tax on expenditure
examples of direct taxes
income tax
corporation tax
capital gains tax
inheritence tax
examples of indirect tax
VAT
excise duties
customs duties
supply side policies
market based policies
interventionist policies
market based policies
indirect way - remove barriers to productive capacity but doesnt directly increase it
reducing government intervention and letting market forces like supply and demand guide economic activity
decrease corporation tax
removing regulations
increase privatisation + deregulation
interventionist policies
policies were the government will directly intervene to raise producitivty capacity
improve education - knowledge and skills - alsp reduces occupational mobility
improved + new infrastructure - capital goods - attracts businesses which increase I
supply side policy affect on LRAS
shift right
strengths of supply side policies
avoids conflict with other objectives
increase productive capacity of economy
lower unemployment
reduce economically inactive population
some are not expensive
weaknesses of supply side policies
tax cuts often facour high earners - increase waelth inequaility
welfare cuts - impact low earners
time-lag - takes time to have effect
can be expensive e.g. infrastructure
supply side policies that increase LRAS will only beenfit the economy if there is sufficient AD
conflicts and trade - offs between objectives
econ growth vs price stability:
rapid econ growth lead to d.pull inflation
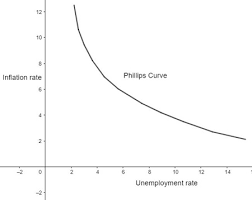
phillips curve - shows trade off between unemployment and inflation
low unemplotment vs price stability:
policies to reduce unemployment - increase inflation
econ growth vs environmental stability:
pursuing high growth - environmental degradation
econ growth vs balanced balance of payments:
high growth can lead to increase imports
unemployed vs balanced budget:
decrease unemployment - increase in G, budget deficit
short run philips curve
inverse relationship between rate of inflation and rate of unemployment
as umployment falls - TU’s and workers more bargaining power - increase wages - increase C - increase D.pull inflation
and vice versa
potential policy conflicts and trade offs
low interest rates vs contractionary fiscal policy
high interest rate vs expansionsary fiscal policy
contractionary fiscal policy vs interventionist supply side policies that require increase in G