Biology Topic 3: Organisms exchange substances with their environment
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
how is the size of an organism related to its SA:volume
large organisms have a low sa:vol
small organisms have a high sa:vol
how are large organisms adapted to facilitate gas exchange?
specialised exchange surfaces (alveoli, gills)
transport systems
thin, folded membranes within exchange surfaces
how is metabolic rate related to the sa:vol
higher sa:vol > higher metabolic rate
smaller organisms lose heat more rapidly, so heat is generated via metabolic processes
[and vice versa]
how are exchange surfaces adapted in unicellular organisms?
exchange occurs through the cell membrane
high sa:vol ratio to maximise rate of diffusion
concentration gradients in/out of the cell to transport substances via diffusion or active transport
do insects have a transport system?
no - oxygen is transported directly into respiring muscle cells
how is O2 exchanged in insects?
O2 enters the trachea via the spiracles
O2 dissolves into tracheal fluid, allowing O2 to be transported faster
when all O2 in the fluid is used up, muscle cells go into anaerobic respiration. this produces lactic acid, reducing the water potential of muscle cells
water from tracheal fluid enters the muscle cells via osmosis, so no more fluid is left in the trachea
this allows O2 to diffuse directly into the muscle cells without dissolving. this shortens the diffusion path, increasing diffusion rate
how is the tracheal system adapted for gas exchange?
spiracles can open or close to avoid water loss/regulate air flow
tracheal fluid allows gases to dissolve, facilitating diffusion
abdominal pumping increases pressure within the tracheal system, forcing air into the trachea from the spiracles, providing a rapid supply of O2 and fast removal of CO2
how does ventillation occur in fish?
ventillation achieves a unidirectional flow of blood
fish pushes its tongue down, opening the buccal cavity floor. this allows water to enter the fish
fish closes the mouth, raising buccal cavity floor and increasing internal pressure causing the operculum to open
pressure gradient between mouth and operculum cavities causes water to move over the gill filaments
O2 from the water is absorbed into the blood via lamellae in the gill filaments
what is the counter-current principle?
the lamellae capillary system ensures deoxygenated blood flows in the opposite direction to the flow of water
this maintains a steep O2 concentration gradient across the entire length of the capillary, so maximal O2 is diffusing into the blood
how are dicotyledonous leaves adapted for gas exchange?
stomata open and close, letting gases in/out of the leaf. stomata are close to the cells, reducing diffusion path
spongy mesophyll has air spaces and a large surface area. mesophyll cells absorb CO2 for photosynthesis, and release O2 as a product.
how are xerophytes adapted to minimise water loss?
sunken stomata - minimise water loss
curled leaves + stomata hairs - trap moist air around the plant, minimising water loss via transpiration or osmosis
thick waxy cuticle - prevents water from evaporating out of the cell by increasing diffusion distance
thin leaves/spindles - reduce surface area, preventing photosynthesis and thus transpiration
how are insects adapted to prevent water loss?
waterproof exoskeleton
spiracle hairs - trap moist air around the spiracles, preventing water loss via osmosis
which structures form the human gas exchange system?
alveoli
bronchioles
bronchi
trachea
lungs
alveoli
site of gas exchange in the lungs
bronchioles
connect the alveoli to the bronchi
enable to flow of air into/out of the lungs
large bronicholes contain cartillage
wall is composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
bronchi
pair of large tubes which connect the lungs to the trachea
enables air flow in/out of the lungs
layers of smooth muscle surrounded by C-ring cartillage
inner surface of cartillage is composed of loose tissue
epithelial layer with goblet/ciliated epithelial cells
trachea
windpipe - connects the bronchi and nose/mouth
wider than the bronchi
enables air flow in/out of the lungs
layers of smooth muscle surrounded by C-ring cartillage
inner surface of cartillage is composed of loose tissue
epithelial layer with goblet/ciliated epithelial cells
lungs
organs of gas exchange
what is the role of the alveolar epithelium?
surface for gas exchange
adaptations of the alveolar epithelium
one cell thick: short diffusion distance for faster gas exchange
large surface area: increases the rate of gas exchange
moist layer: gases can dissolve and diffuse across the membrane
concentration gradients: low O2 conc, so O2 comes in. high CO2 conc so CO2 moves out
oxygenated blood supply: O2 moves into the alveoli via diffusion
describe the role of cartilage in the mammalian gas exchange system
supports the trachea and bronchi
prevents the lungs from collapsing if there’s a pressure drop during exhalation
describe the role of the ciliated epithelium in the mammalian gas exchange system
found in trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
moves mucus away from the lungs to the throat (to be swallowed), preventing lung infections (as mucus can trap pathogens)
describe the role of goblet cells in the mammalian gas exchange system
found in the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles
secrete mucus which traps bacteria and dust, preventing lung infection (lysozymes then digest the bacteria)
describe the role of smooth muscle in the mammalian gas exchange system
contracts to constrict the airways, controlling the flow of air to the alveoli
describe the role of elastic fibres in the mammalian gas exchange system
stretch during exhalation, recoil during inhalation, helping to control the flow of air
describe the process of inspiration (ventilation)
diaphram and external intercostal muscles contract
rib cage raises upwards
this causes the volume inside the thoracic cavity to increase
thoracic cavity pressure decreases to below atmospheric pressure
pressure gradient between the lungs and atmosphere causes air to move into the lungs (air moves down the pressure gradient)
describe the process of expiration (ventilation)
diaphram relaxes
internal intercostal muscles contract
rib cage is lowered
volume in throacic cavity decreases, and pressure increases to above atmospheric pressure
pressure gradient between the lungs and atmosphere causes air to move out of the lungs (air moves down the pressure gradient)
describe the interaction between the external and internal intercostal muscles
antagonistic
when the internal contracts, the external relaxes and vice versa
what is a spirometer?
device used to measure lung volume
when lung volume is increased > inspiration
when lung volume is decreased > expiration
can measure tidal volume, vital capacity and breathing rate
for the graph - volume is on the y axis, time is on the x axis
what is tidal volume?
the volume of air in a normal breath at rest
usually 0.4 - 0.5dm3
what is the ventilation rate?
number of breaths taken per minute at rest
usually around 15
what is vital capacity?
maximum volume of air that can be breathed in and out of the lungs
what is forced expiratory volume?
maximum volume an individual can expire in one second
cannot be more than the total volume of gas in the lungs, as there’s always residual air in the alveoli ensuring they do not close
what is the residual volume?
the volume of air always present in the lungs
what is the expiratory reserve volume?
additional volume of air that can be exhaled on top of the tidal volume (e.g. during exercis)
pulmonary ventilation rate equation
PVR = tidal volume x breathing rate
how does lung disease affect gas exchange?
damages the alveoli, reducing their population in the lungs thus decreasing the surface area available for gas exchange.
can thicken the alveolar epithelium by increasing the amount of mucus in the lungs, increasing the diffusion distance for gas exchange
decreases oxygen levels in the blood > fatigue
increases CO2 levels in the blood (hypercapnia)
how do pollution and smoking increase chances of lung disease?
chemicals in cigarettes/pollutants damage the cilia. this means mucus cannot be swept from the lungs to the throat
this causes a build up of mucus in the lungs, blocking or irritating the airways
mucus build up can also damage the alveoli or thicken the alveolar wall, decreasing gas exchange
what occurs during digestion?
large biomolecules are hydrolysed to smaller molecules that can be absorbed across the cell membrane
how are carbohydrates digested?
carbohydrates are broken down by amylase and membrane-bound dissacharidases
amylase hydrolyses starch into dissacharides like maltose
dissacharidases hydrolyse dissacharides into monosaccharides like glucos
where does the digestion of carbohydrates occur in the body?
amylase is produced in the saliva and pancreas, and acts in the mouth, stomach and ileum
dissacharidases are attached to cell-membranes of ileum epithelial cells, and act in the ileum
how are lipids digested?
lipids are digested by lipases and bile salt action
bile salts bind to large lipid droplets and break them up into smaller droplets (emulsification). this increases the SA of lipid droplets, increasing the rate of digestion by lipase
lipase breaks down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids in the ileum
where does lipid digestion occur in the body?
bile salts are produced in the liver and act in the duodenum
lipase acts in the duodenum
describe the process of emulsification
bile salts are ampipathic
the hydrophobic end is inserted into the lipid droplets. since the lipid is also hydrophobic, the lipid and bile salt repel each other
this repeated repulsion breaks the lipid up into smaller droplets. this increases the surface area for lipase action
describe the role of micelles in lipid production
micelles transport digested lipids through the small intestine to the surface membrane of intestinal cells
at the cell membrane, lipids (fatty acids + monoglycerides) diffuse out of the micelles and into the intestinal cells
inside the cells, fatty acids and monoglycerides are assembled into triglycerides, then packaged into chlyomicrons
chylomicrons are released into the lymphatic system and deliver absorbed lipids around the body
describe the process of amino acid/glucose cotransport
sodium is actively transported out of ileum epithelial cells through action of the sodium-potassium pump. this creates a low concentration of sodium within the cell
sodium and glucose bind to the sodium-glucose cotransporter protein
concentration gradient between ileum lumen and the cell means sodium can move into the cell via diffusion, thus glucose also moves into the cell via co-transport (active)
once inside the cell, sodium and glucose dissociate from the protein. the protein undergoes a conformational change to its original shape
sodium moves out of the cell via active transport, glucose moves out of the cell via facilitated diffusion
how are proteins digested?
proteins are digested by endopeptidases, exopeptidases and dipeptidases (protease enzymes)
endopeptidases hydrolyse interior bonds in the polypeptide chain, creating separate chains
exopeptidases hydrolyse exterior peptide bonds in polypeptide chains, creating individual amino acids. dipeptidases are a type of exopeptidase
membrane-bound dipeptidases are attatched to the cell membrane of ileum epithelial cells
what are haemoglobins?
proteins with a quaternary structure (2 beta polypeptide chains and 2 alpha helixes)
group of chemically similar molecules (complex containing a haem group)
how do haemoglobin and red blood cells transport oxygen?
when blood passes through the lungs, O2 diffuses through the rbc and binds to the haem group of haemoglobin.
each haemoglobin can bind to 4 O2 molcules. this forms oxyhaemoglobin (in a reversible reaction)
when the rbc reaches the tissue, the oxygen and haemoglobin separate, and oxygen is released into the cells
how is haemoglobin adapted to its function?
polypeptide folding in the quaternary structure allows haemoglobin to have a hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic core
hydrophilic exterior means haemoglobin is soluble, and thus can easily be transported in the blood
hydrophobic core prevents the oxidisation of Fe2+ in the haem group into Fe3+ (as Fe3+ cannot bind to the oxygen)
what does it mean when haemoglobin is saturated?
when all of the oxygen binding sites have an oxygen (when it binds to 4 oxygen molecules)
what is the partial pressure of oxygen?
measure of oxygen concentration
more oxygen dissolved in cells = higher partial pressure
what is oxygen loading?
the uptake of O2 (by haemoglobin) in the lungs
what is oxygen unloading?
depositing of O2 (by haemoglobin) at the tissue
what is affinity of oxygen?
the tendency (of haemoglobin) to bind to oxygen molecules
how does the affinity of oxygen change?
during loading, the partial pressure of oxygen increases (so more oxygen)
this increases the affinity of oxygen for haemoglobin, as more oxygen can bind to haemoglobin
during unloading, the partial pressure of oxygen decreases (oxygen is used during cellular respiration)
this decreases the affinity of oxygen for haemoglobin, as there’s less O2 for the haemoglobin to bind to.
thus, oxygen is released in the respiring tissue
where does oxygen association occur?
haemoglobin + oxygen > oxyhaemoglobin
happens in the lungs (where O2 conc. is high)
when does oxygen dissociation occur?
oxyhaemoglobin > oxygen + haemoglobin
happens at the respiring cells (where O2 conc. is low)
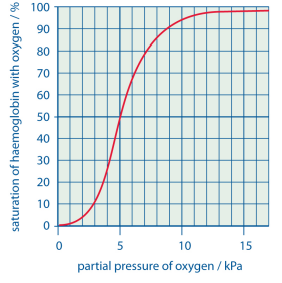
what does the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve show?
variance in haemoglobin saturation with partial pressure
saturation (%) - y axis
partial pressure (kPa) - x axis
why is oxygen binding cooperative?
binding of the first O2 molcule triggers a conformational change in haemoglobin, making further binding for the other 3 molecules easier
describe the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
bottom of the graph:
at low partial pressure, there is a low saturation as its difficult for the first oxygen molecules to bind
low partial pressure - at respiring cells
central region:
after the first molecule binds and protein undergoes conformational change, the saturation increases as its easier for the 2nd and 3rd molecules to bind (positive cooperativity)
top of the graph:
the likelihood of the 4th oxygen finding a binding site is low, so graph begins to plateau
high partial pressure - in the lungs
describe the Bohr effect
when CO2 is increased, the affinity for oxygen is decreased
dissolve CO2 is acidic, lowering of pH triggers a conformational change in haemoglobin
this reduces the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen as the oxygen can no longer bind
thus oxygen dissociation increases
how does haemoglobin vary across organisms?
species in areas with a low O2 concentration have haemoglobin with a higher affinity for oxygen, so oxygen association is easier and dissociation is harder.
fetal haemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen, as blood reaching the placenta has a lower oxygen saturation
how is blood circulated in a mammal?
mammals have a double circulatory system - blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit
describe the pattern of blood flow through the heart
deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium via the vena cava
passes from the right atrium through the triscuspid valve intro the right ventricle
from the right ventricle, blood is pumped out through the pulmonary artery to the lungs
[blood oxygenated via gas exchange in the lungs]
oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein
left atrium contracts, and blood moves through bicuspid valve to the left ventricle
left ventricle contracts, pumping blood through the aorta to the rest of the body
describe the gross structure of the heart
two muscular pumps: the right pumps deoxygenated blood, left pumps oxygenated blood
4 chambers (ventricles and atria) separated by valves
atria have thin walls > only have to pump blood to the lungs
ventricles have thicker walls > have to pump blood to the entire body/ withstand higher pressures
tricuspid valve: right atrium > right ventricle
biscupid valve: left atrium > left ventricle
describe the roles of the major blood vessels surrounding the heart
coronary arteries: supply oxygenated blood to the heart
pulmonary vein: transports oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
pulmonary artery: transports deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
vena cava: transports deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium
what is the role of the atrioventricular valves?
bicuspid and tricuspid valves
prevent the backflow of blood from the ventricles into the atria (maintain unidirectional flow) during ventricular systole
what is the role of the semilunar valves?
valves between arteries and ventricles
prevent backflow from arteries to ventricles during ventricular diastole
name the pressure changes that occur during the cardiac cycle
cardiac diasole
atrial systole
ventricular systole
explain the process of an atrial systole
atrial walls contract, increasing atrial pressure
behind AV valve increases, pushing them open
blood moves into the ventricles, increasing ventricular volume and decreasing atrial volume
during this, ventricular diastole occurs, so ventricular pressure is decreased
this occurs for 0.1 seconds
explain the process of ventricular systole
atria relax and ventricles contract, increasing ventricular pressure
ventricular volume is increased, and the increase in pressure makes the semilunar valves open (AV valves shut)
blood flows into the arteries
as ventricular pressure decreases, semilunar valves start closing
atrial diastole is occuring, so atrial volume is increasing
this is 0.3 seconds
explain the process of ventricular diastole
ventricles relax, so ventricular pressure decreases.
semilunar valves close
once ventricular pressure is less than atrial pressure, the AV valves open again and the cycle repeats
this is 0.4 seconds
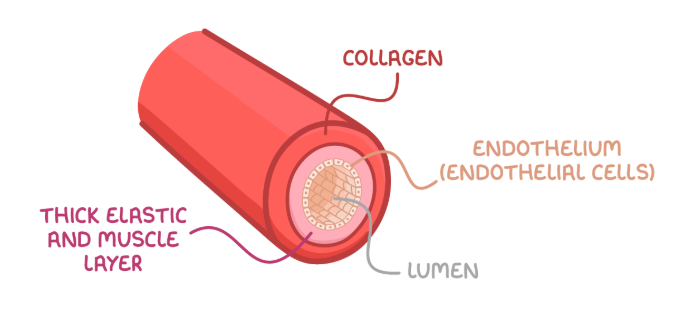
how is the structure of arteries related to their function?
arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart (bar the pulmonary artery)
thick, muscular and elastic walls > withstand high blood pressure
elastic layers > arteries can stretch and recoil with changes in pressure
smooth muscle > lined with endothelium to reduce friction for blood flow
no valves needed > blood is transported at such high pressure that backflow isn’t possible
small lumen > maintains high pressure
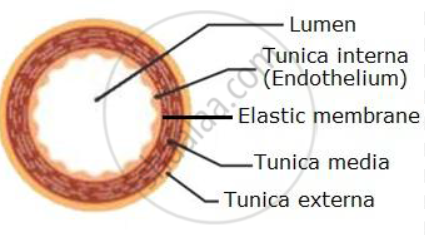
how is the structure of veins related to their function?
transport deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart (bar the pulmonary vein)
thin muscle layer > blood is transported at low pressure, vasoconstriction isn’t needed to control blood flow
thinner elastic layer > blood is transported at low pressure, so no stretch/recoil is required to prevent bursting
wide lumen > maximises the blood volume able to be transported to the heart
valves > prevent backflow as blood is transported at low pressure
how is the structure of arterioles related to their function?
transport blood from arteries to capillaries
thick muscle layer > can constrict/relax to control blood pressure
thinner elastic layer > blood is transported at a lower pressure
smooth muscle > allows vasoconstriction and vasodilation to control blood flow
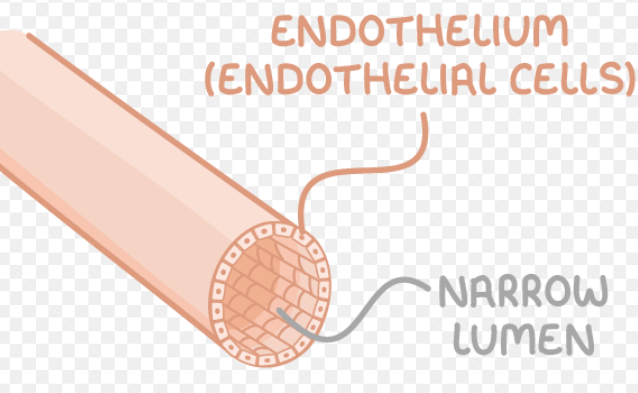
how is the structure of capillaries related to their function?
exchange substances between the blood and body tissues (site of metabolic exchange)
smallest blood vessel
one cell thick walls > minimises diffusion distance to optimise rate of gas exchange
highly branched/large surface area > optimises rate of gas exchange
narrow diameter > flattens red blood cells against the side of the capillary, decreasing diffusion distance to optimise rate of gas exchange
narrow lumen > blood flow slows down, allowing more time for diffusion
how is tissue fluid formed?
Capillaries have small pores in their walls
at the arterial end of the capillary, the hydrostatic pressure exceeds the osmotic pull
this causes small molecules and fluid to be pushed through the gaps out of the capillary, down the hydrostatic pressure gradient
large molecules (e.g. proteins) remain in the blood as they’re too big to pass out of the capillaries
how does tissue fluid return to the circulatory system?
at the venous end of the capillary, the osmotic pull is larger than the hydrostatic pressure
dissolved proteins lower the water potential of the blood, creating a water potential conc. gradient between the tissue fluid and capillary (low in the blood, high in the tissue fluid)
tissue fluid moves via osmosis into the capillary
what is the xylem?
tissue that transports water in the stem and leaves of plants
describe the cohesion-tension theory
water evaporates from the surface of the leaf due to transpiration. this lowers the water potential of the mesophyll cells
water molecules cohere to each other via hydrogen bonds between molecules, forming a continuous column of water (transpiration stream)
water is pulled up through the xylem via the transpiration stream. this creates tension in the xylem
for each water molecules lost through transpiration, another is pulled up through the roots/stomata
the water molecules also adhere to the walls of the xylem
what is the phloem?
tissue that transports organic substances (sucrose) in plants
describe the mass-flow hypothesis
at the source, sugars like sucrose are actively loaded into the sieve tube elements from the companion cells.
this decreases the water potential in the sieve tube elements
lowered water potential enables water to move into the sieve tube elements from the xylem and companion cells via osmosis
influx of water into the sieve tube elements increases the hydrostatic pressure at the source. this creates a pressure gradient between the source and sink
sucrose + other solutes move down the pressure gradient to the sink
at the sink, sucrose is actively transported out of the sieve tube elements. this increases the water potential at the sink
water thus moves out of the sink via osmosis, decreasing hydrostatic pressure
the process is maintained by loading at the source and unloading at the sink
explain how ringing experiments can be used to investigate transport in plants
demonstrates whether the phloem is responsible for transporting sugars
ring of bark (including phloem) is removed from the stem. the xylem remains in the stem
the stem swells above the area where the bark has been removed with fluid
fluid is tested for sugars
results:
if the fluid has a high concentration of fluids, it shows that translocation occurs in the phloem
also shows that sugars are transported from source to sink (leaves to roots)
explain how radiotracers can be used to investigate transport in plants
tracks the movement of specific substances within the plant
radioactive isotopes (like isotopes of carbon in CO2) are supplied to a leaf
isotope is used in photosynthesis/metabolic processes to produce radioactive organic substances, like sucrose
movement of radioactive substance is traced through the plant via autoradiography
results:
demonstrates the translocation occurs in the phloem
demonstrates that sucrose moves from source to sink