Epithelium (Laboratory)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Kidney
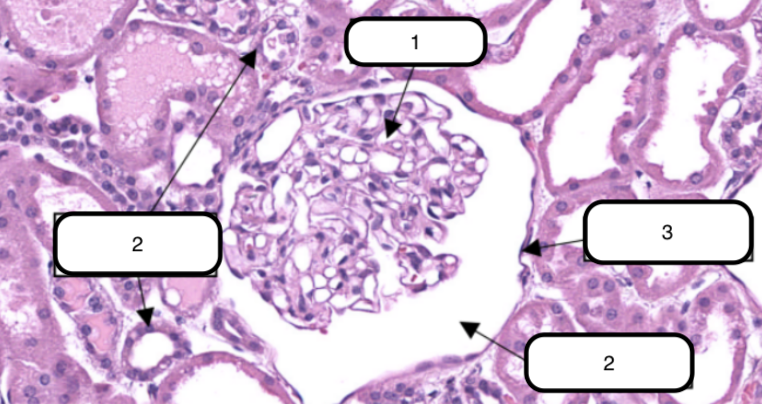
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
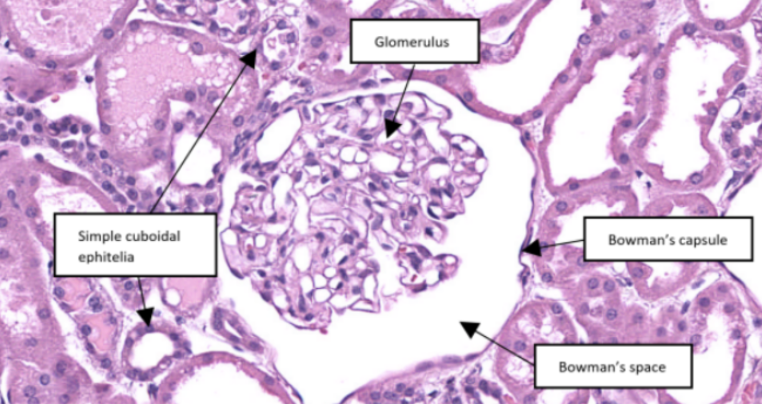
Glomerulus
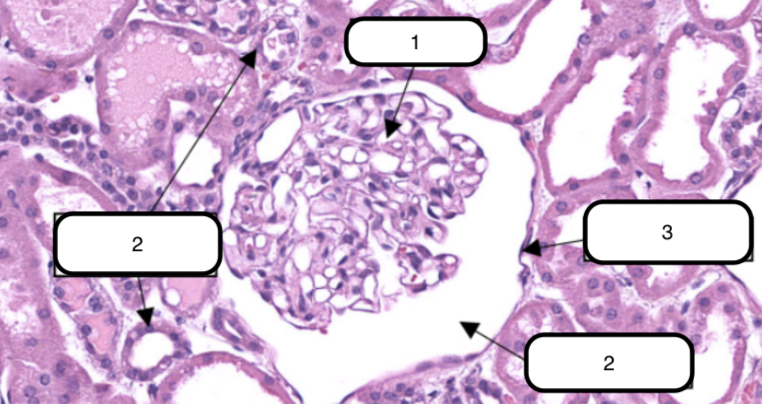
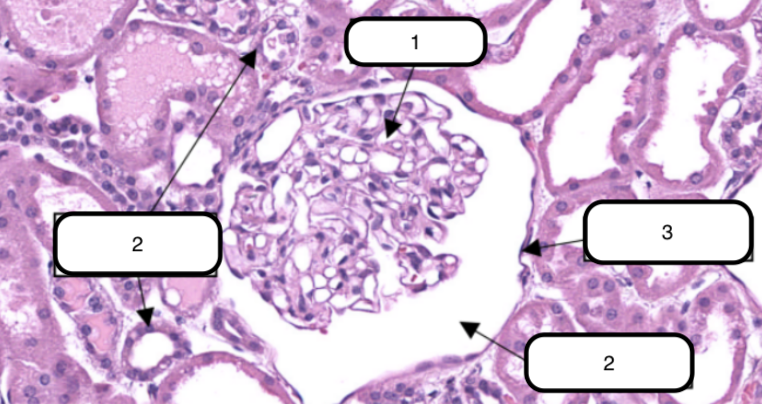
In this slide, identify the structure labeled #1
Glomerulus
In this slide, this is the ball-like structure made up of capillaries (glomerular capillaries), mesangial matrix (mesangium), and glomerular mesangial cells.
Simple cuboidal epithelium
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #2
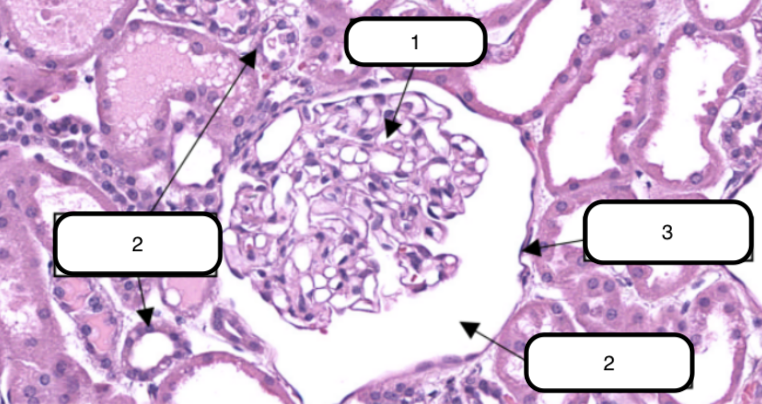
Bowman’s capsule
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #3
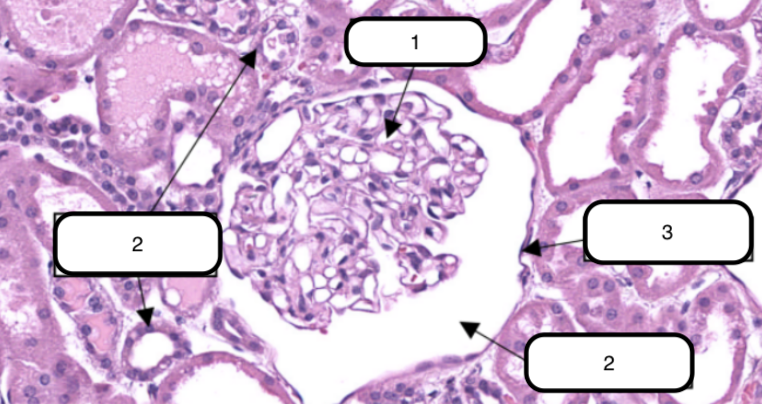
Bowman’s capsule
In this slide, this is a double-walled sac that envelops the glomerulus with parietal and visceral layer.
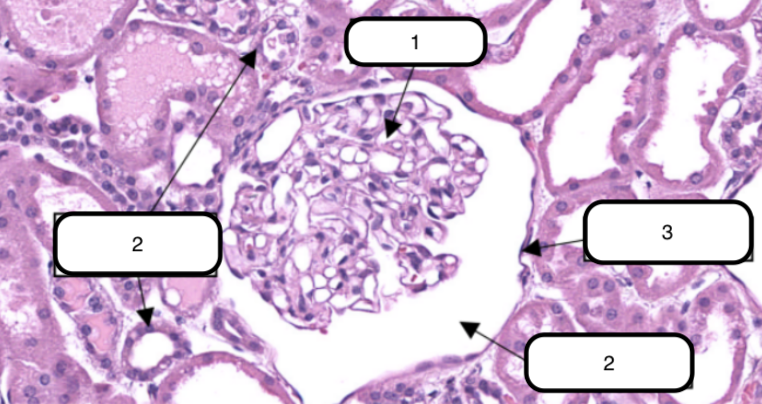
Bowman’s space
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #4
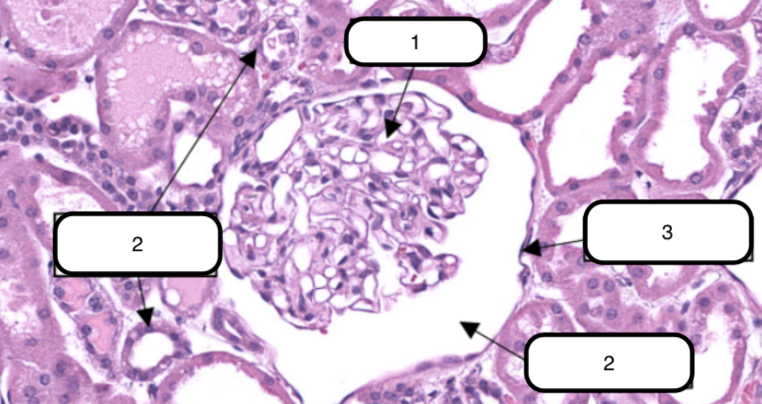
Bowman’s space
In this slide, this is the narrow cavity between the visceral and parietal layers.
Heart
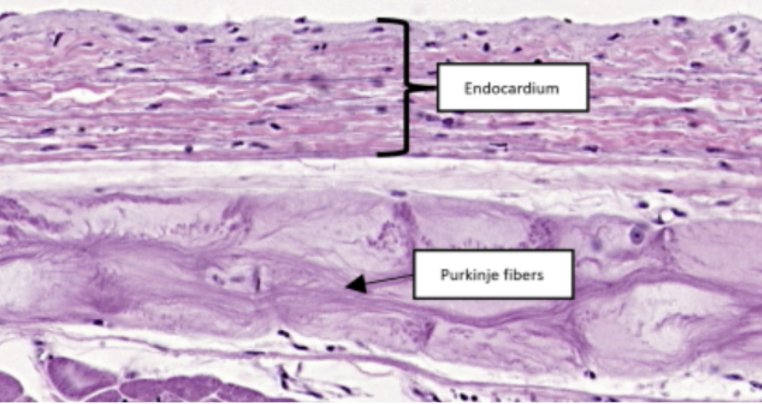
Endothelium
In this slide specimen, this is a simple squamous epithelium that lines the luminal surface of the heart and blood vessels.
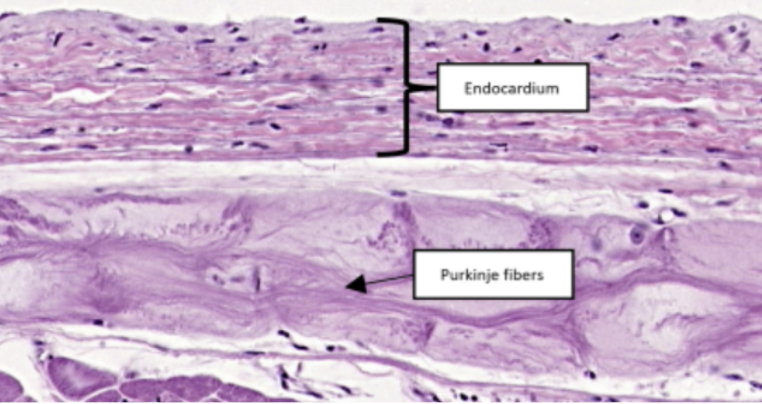
Endocardium
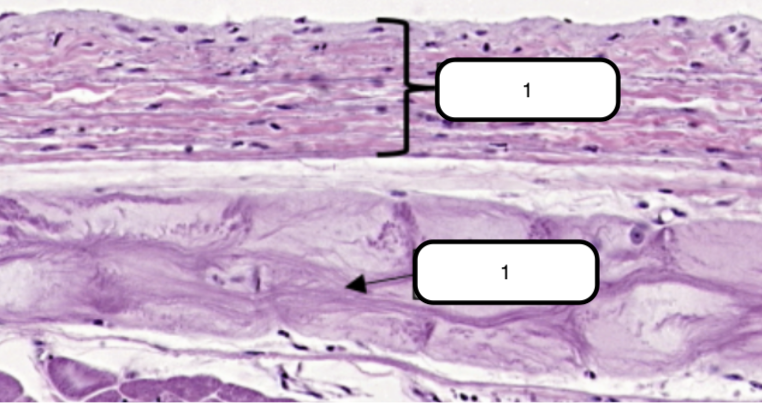
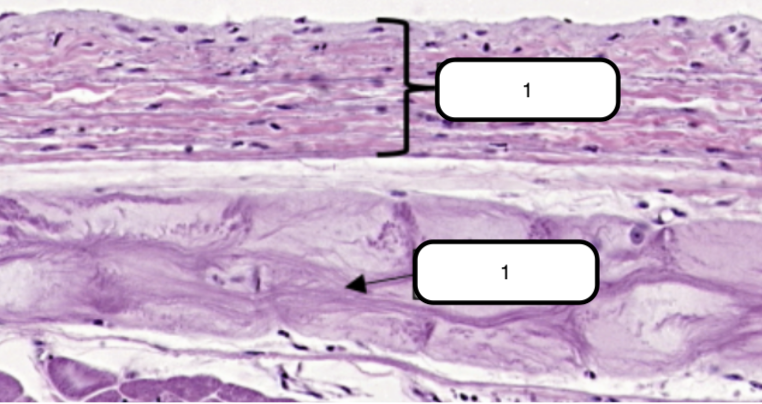
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #1
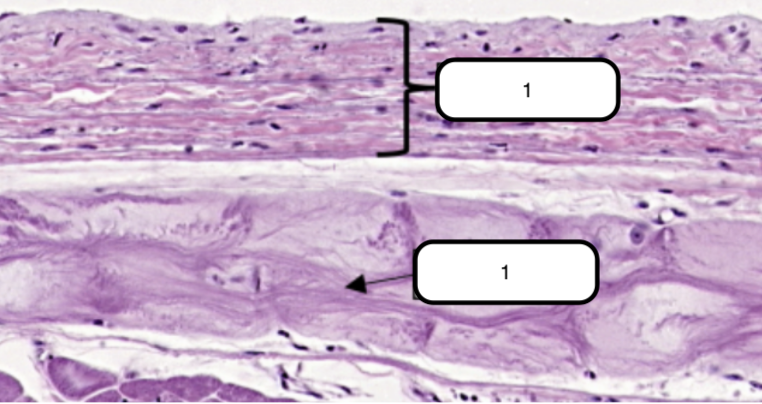
Endocardium
Simple squamous epithelium formed by a single layer of flattened cells on the free surface of the endocardium.
Purkinje Fibers
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #2
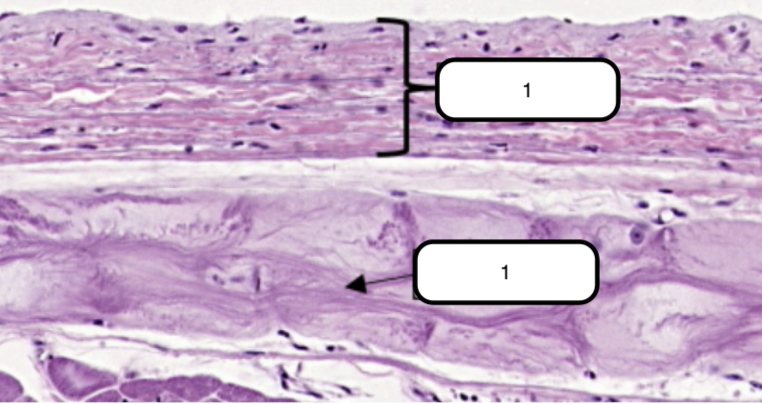
Purkinje Fibers
Modified cardiac muscles
Stomach
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
Fundus
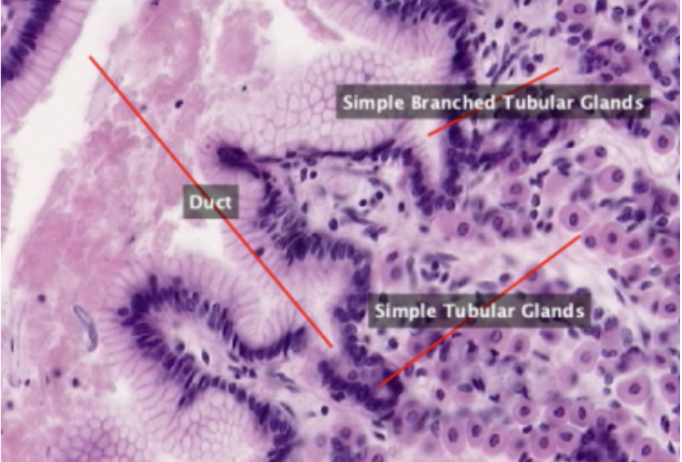
Section of stomach lined by simple epithelium and contains simple tubular and simple branched tubular glands.
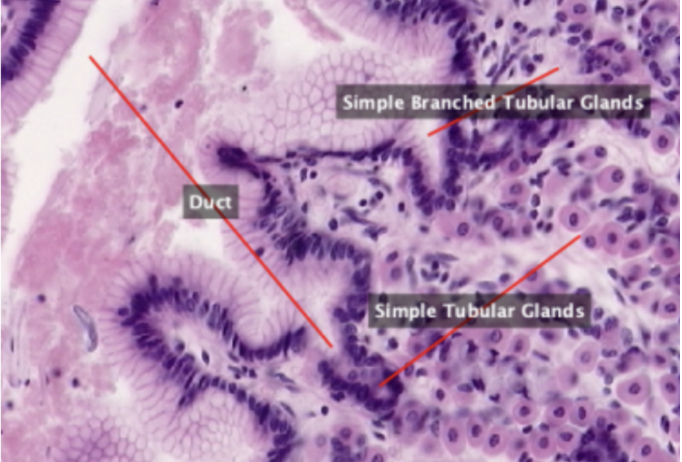
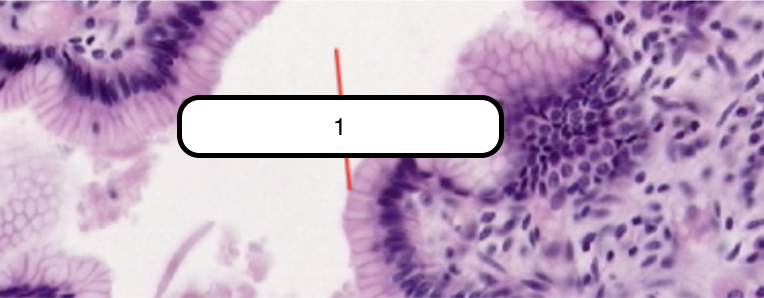
Simple Columnar Epithelium
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #1
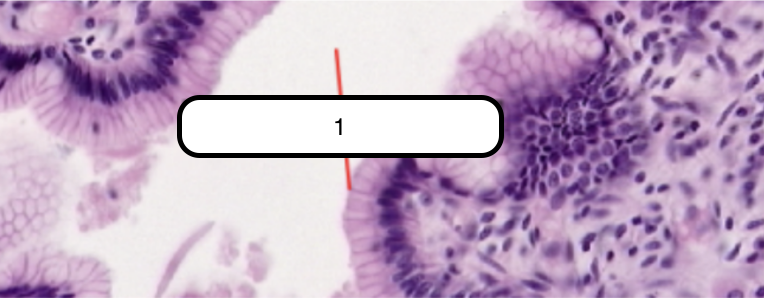
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Lines the luminal surface of the stomach and is composed of a single row of eosinophilic cells that are taller than they are wide. Generally oval, more basal than apical in location, and their long axes lie parallel to those of cells.
Simple Branched Tubular Gland
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #1
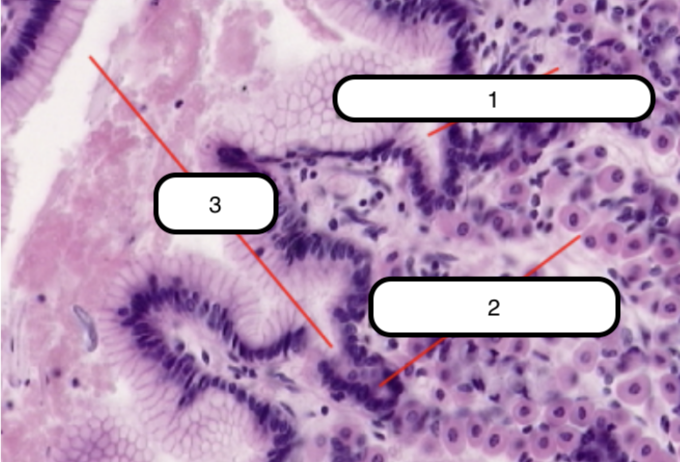
Simple Tubular Glands
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #2
Duct
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #3
Main Gastric (Fundic Glands)
Ducts that open into the surface epithelium.
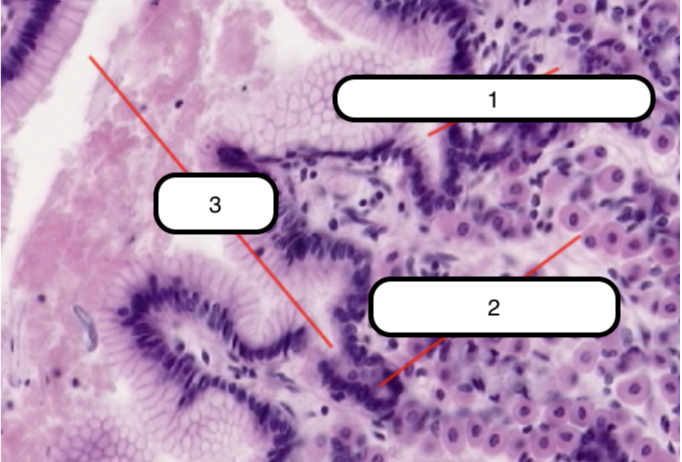
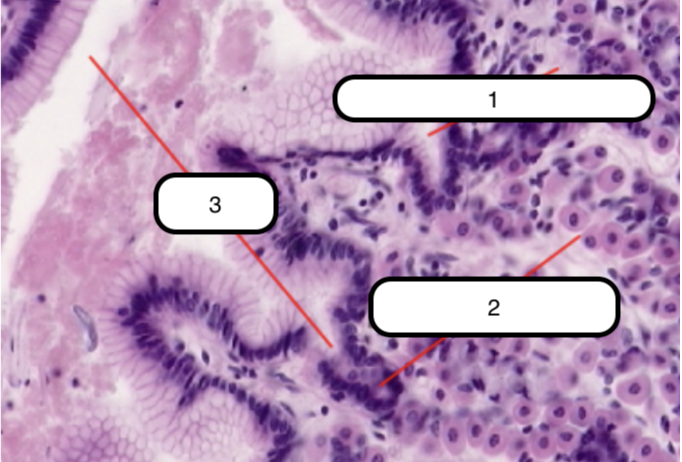
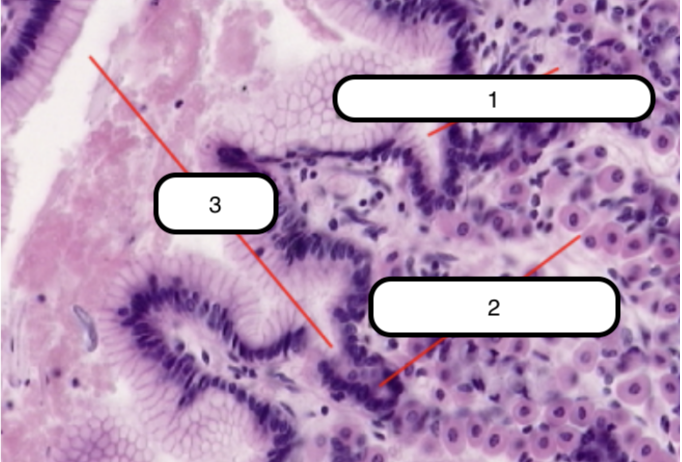
Trachea
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
Trachea
Permanently open hollow tube that is lined on its luminal surface by epithelium
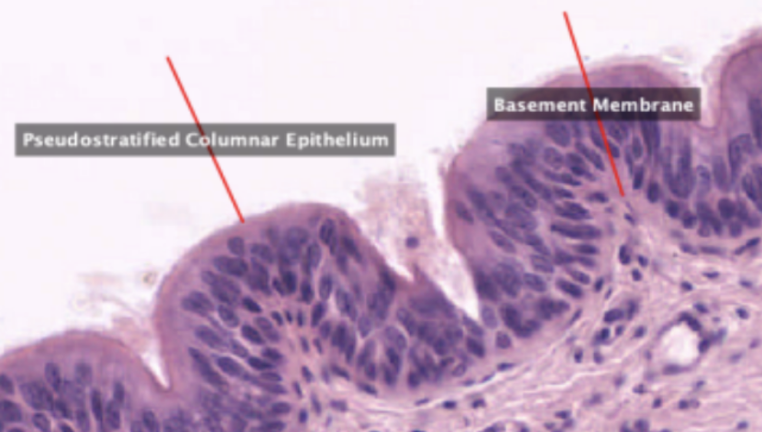
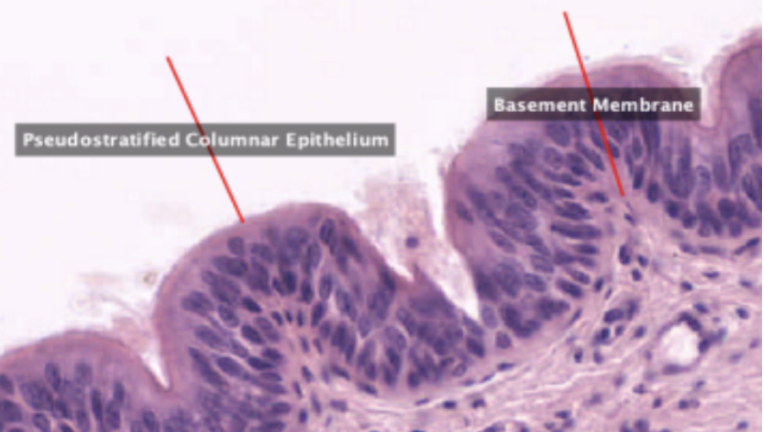
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #1
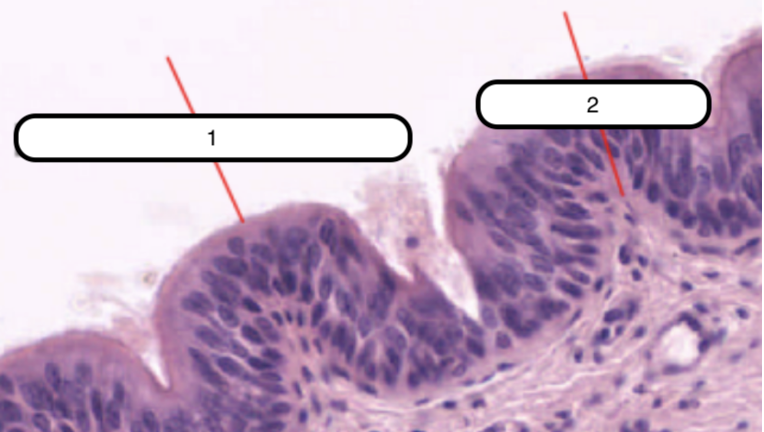
Basement Membrane
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #2
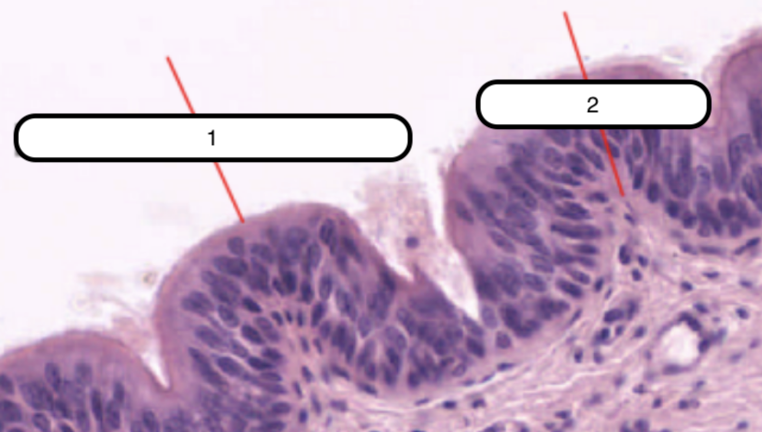
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
False stratified epithelium. Epithelium that consists of a single layer of columnar cells but may be mistaken as stratified epithelium because the nuclei of the cells are not on the same level.
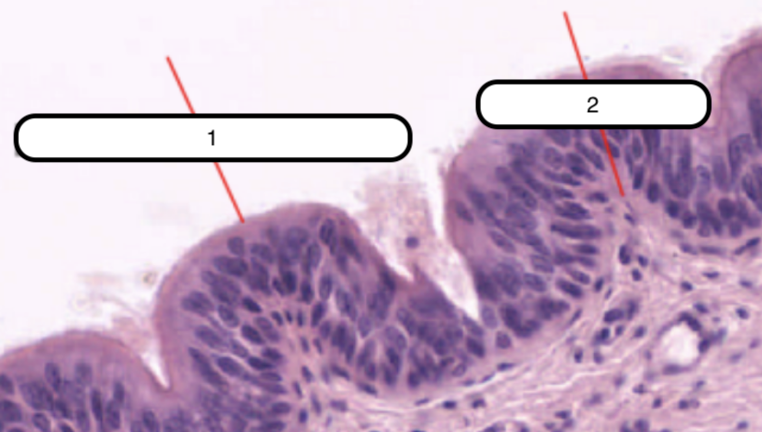
Basement Membrane
Eosinophilic and is very prominent in light microscopy. This is where the basal surface of epithelial cells rest.
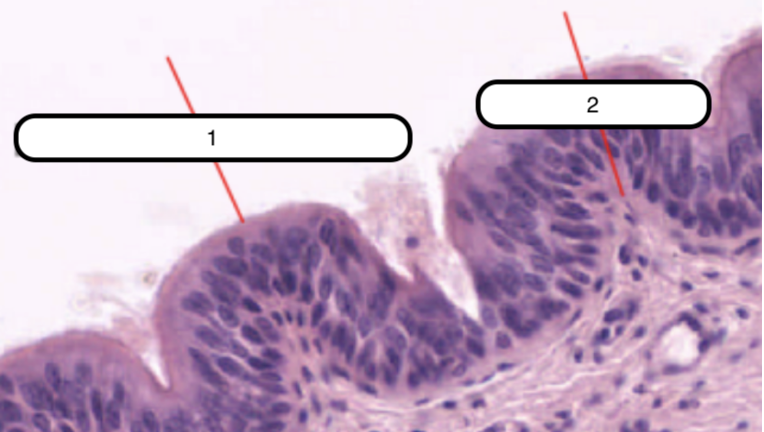
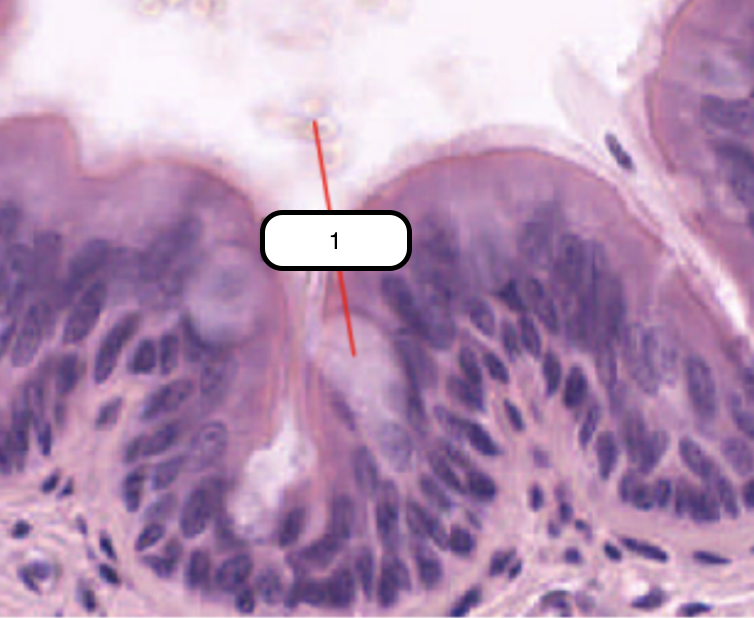
Goblet Cell
In this slide, identify the structure labeled as #1
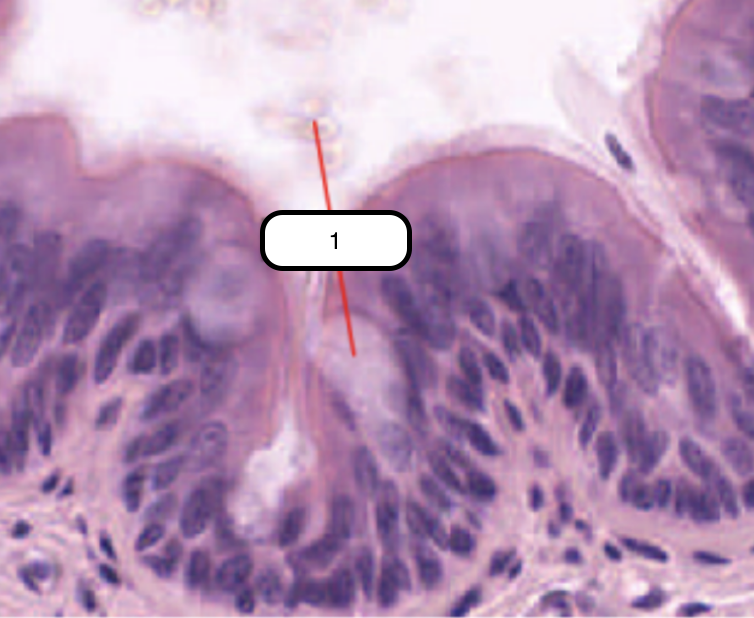
Goblet Cell
One of the cells that comprise the epithelium. Columnar and cup-shaped cell with a tapered base that rests on the basement membrane and an expanded apical region called theca. Theca has numerous secretory granules that contain mucin in vivo.
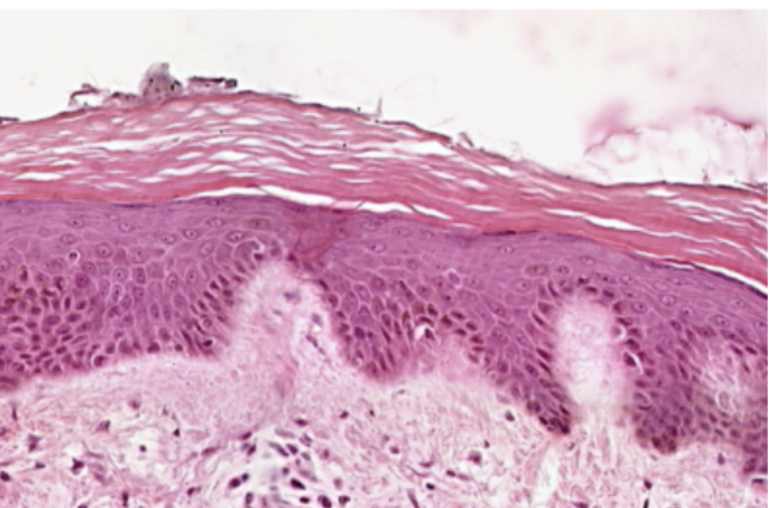
Thick Skin
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
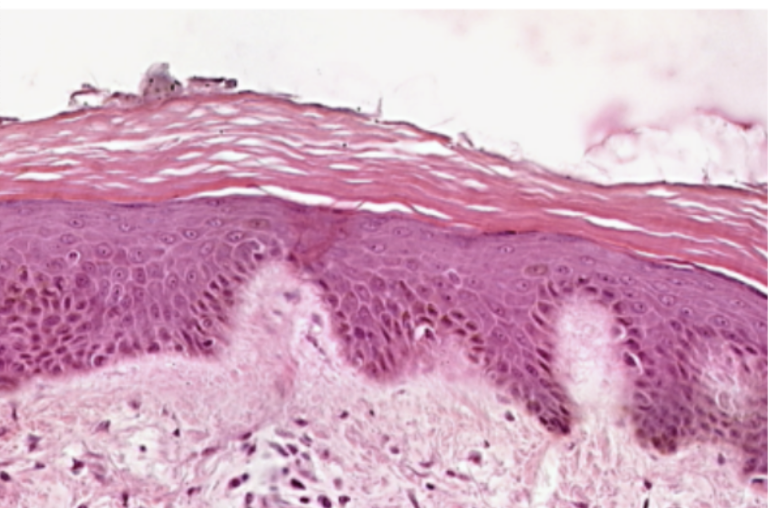
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
What epithelium can be seen in this slide?
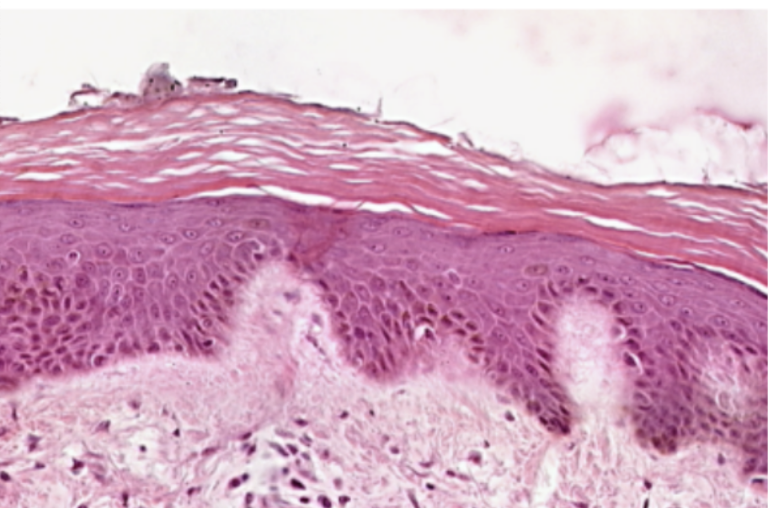
Keratinized Stratified Epithelium
Topmost layer of the specimen. Made up of several layers of cells where the most superficial layer, which is being shed in some areas, consists of dead cells without nuclei. Otherwise known as epidermis.
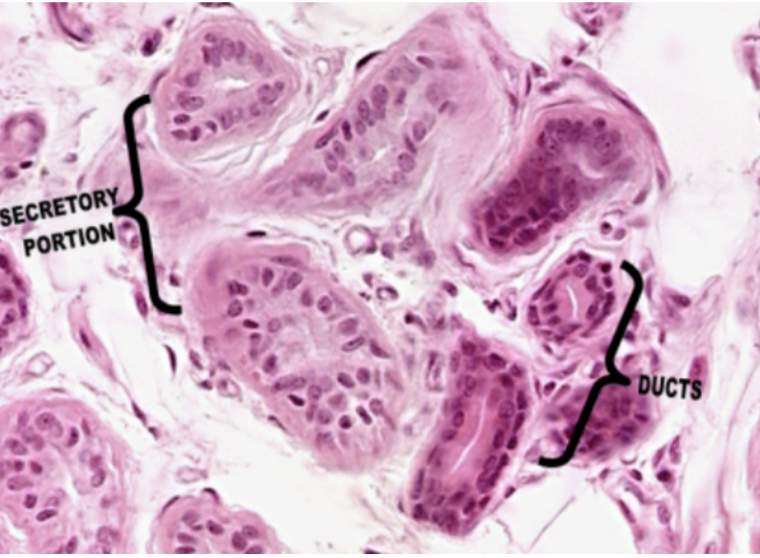
Sweat Glands
What glands is visible in this slide?
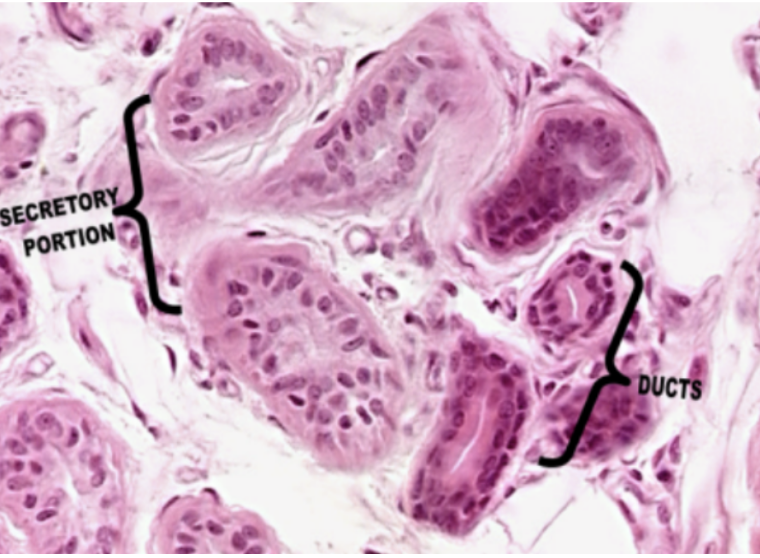
Sweat Gland
Morphologically a simple coiled tubular gland. It is also a serous gland (by nature of secretion) and a merocrine gland (by mode of secretion).
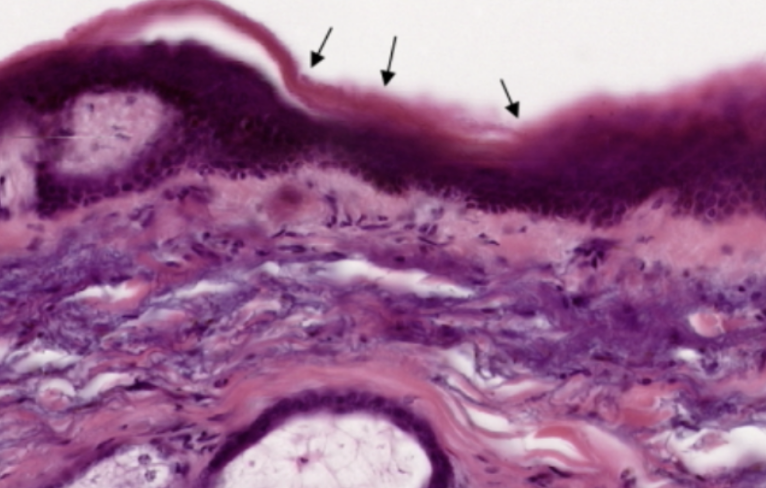
Skin of Scalp
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
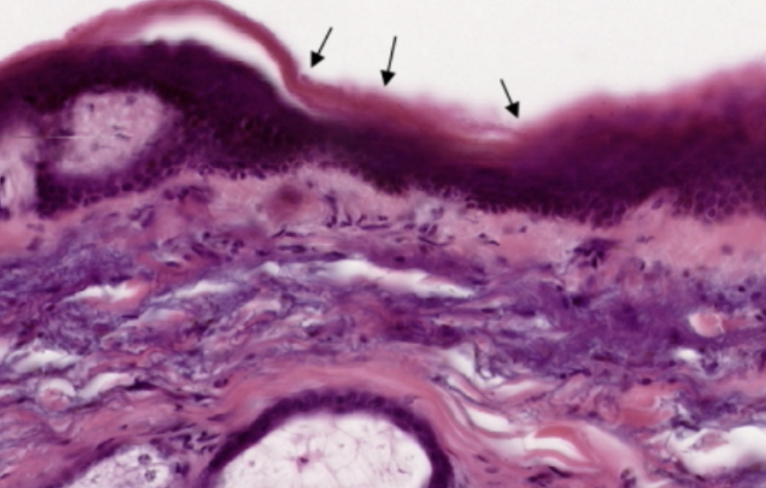
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
What is the topmost layer of this specimen?
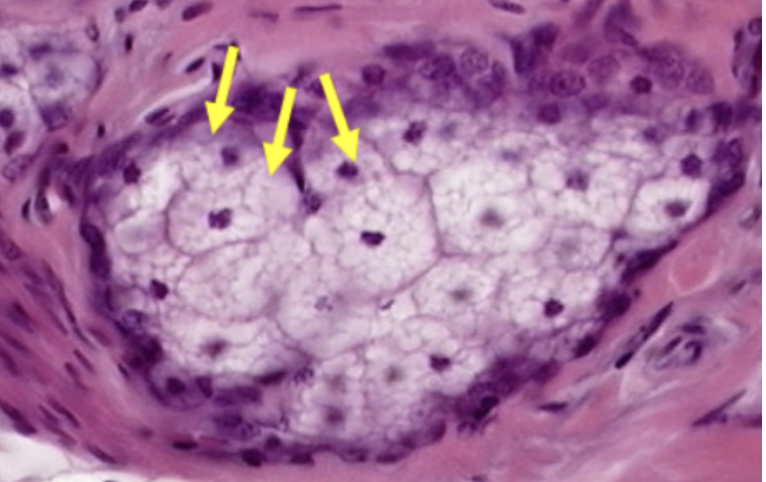
Sebaceous Gland
What gland is visible in this specimen?
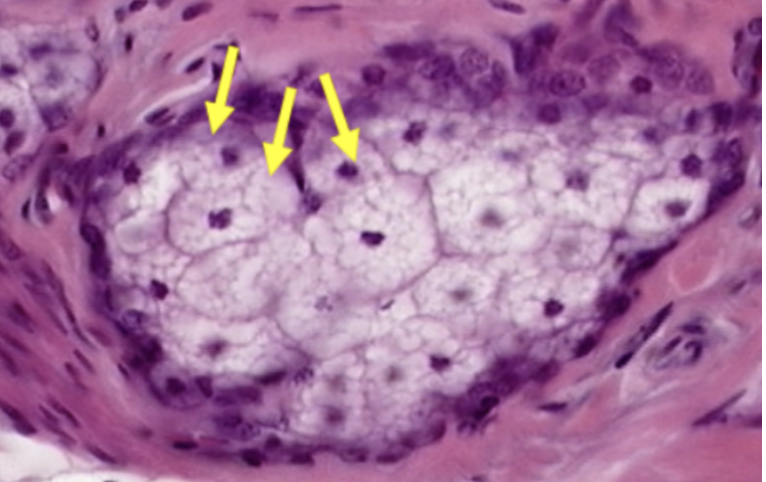
Sebaceous Gland
Mostly located superficially (closer to the surface epithelium) than the sweat glands. Morphologically simple branched alveolar gland. A holocrine gland as per the mode of secretion.
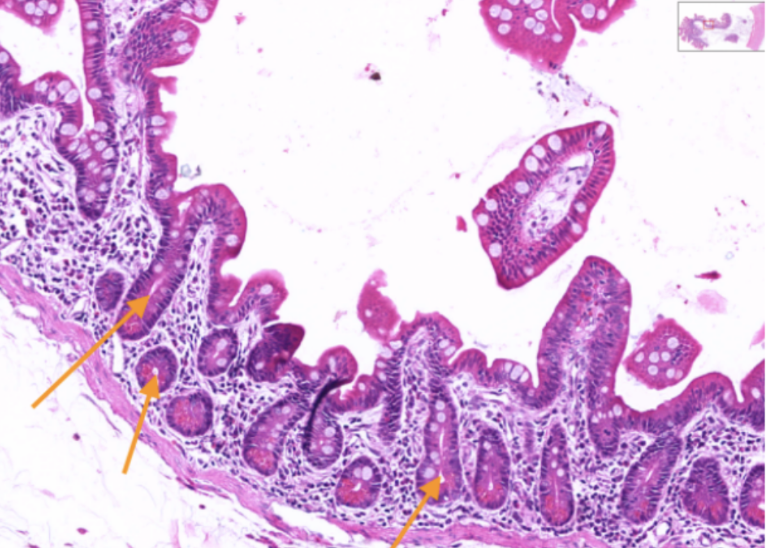
Jejunum
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
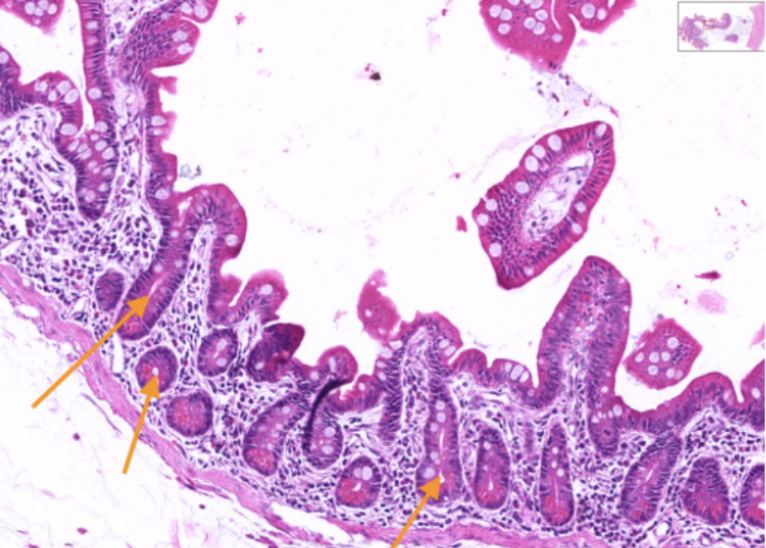
Crypts of Lieberkuhm
Identify the structures pointed by the orange arrow.
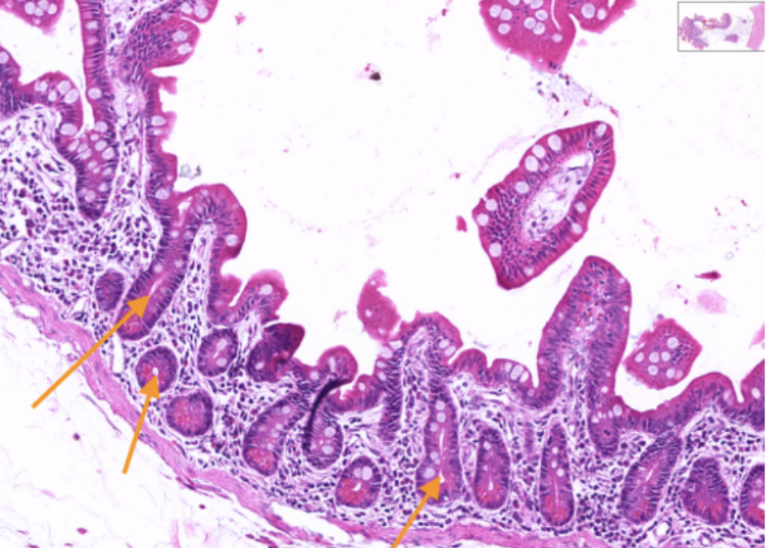
Crypts of Lieberkuhn
Ducts whose openings can be traced onto the surface epithelium.
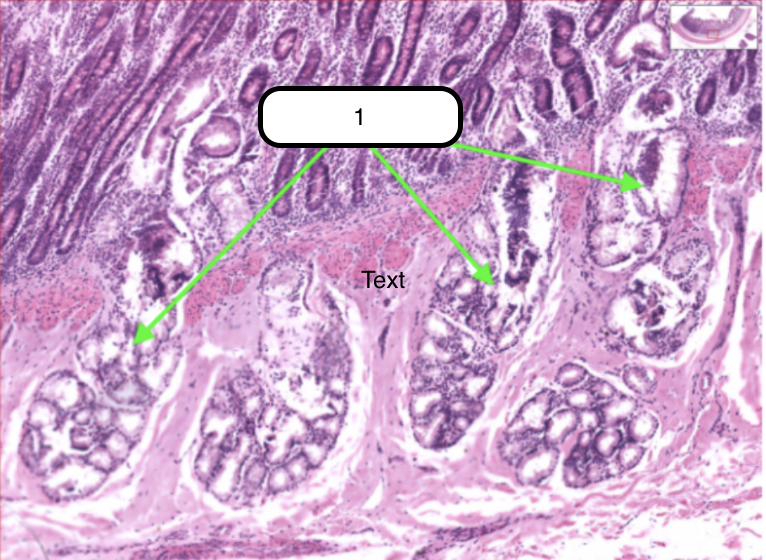
Duodenum
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
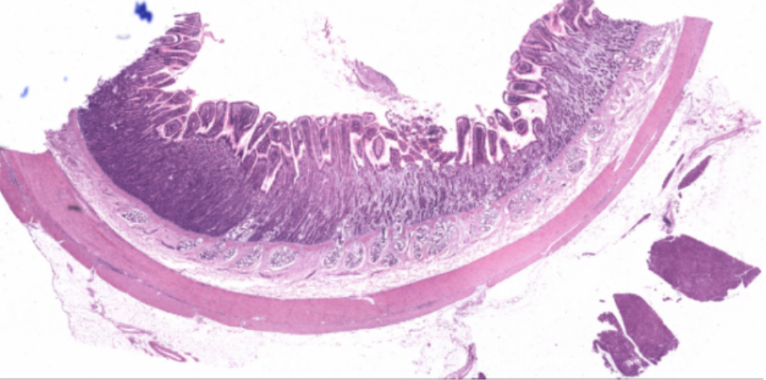
Brunner’s Glands
Identify the structure pointed by the green arrow.
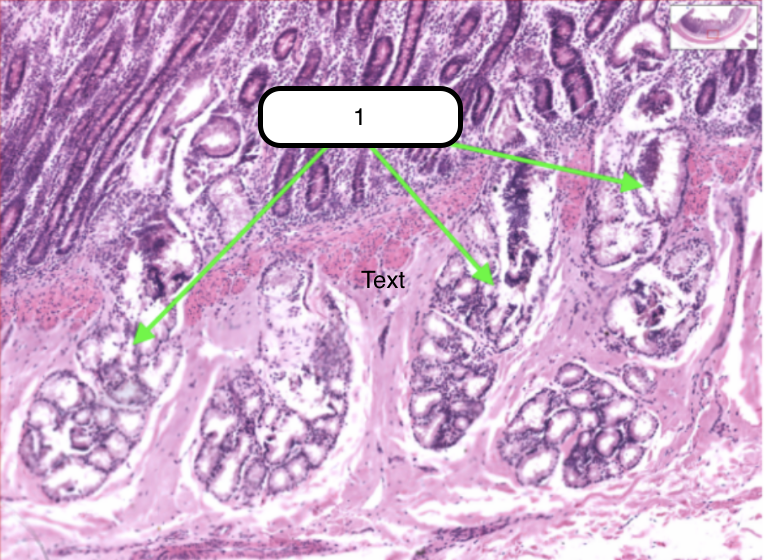
Brunner’s Glands
Compound coiled tubular mucous glands. Located deep of the crypts of Lieberkuhn
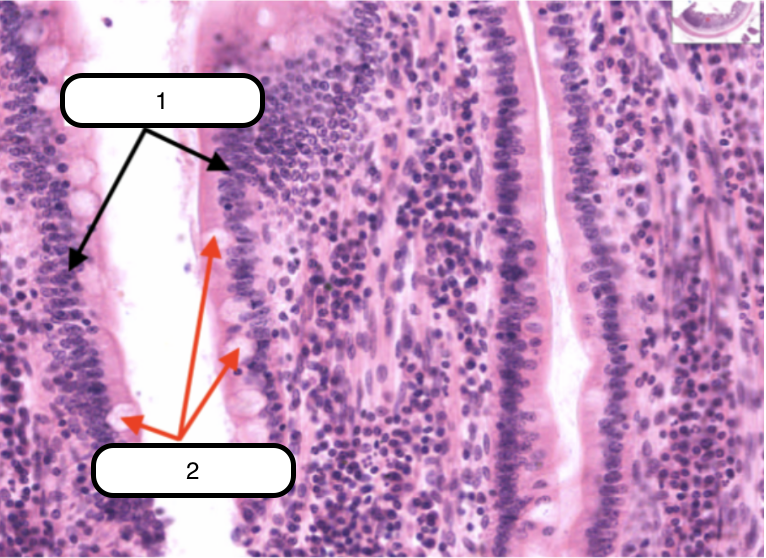
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Identify the structure labeled as #1
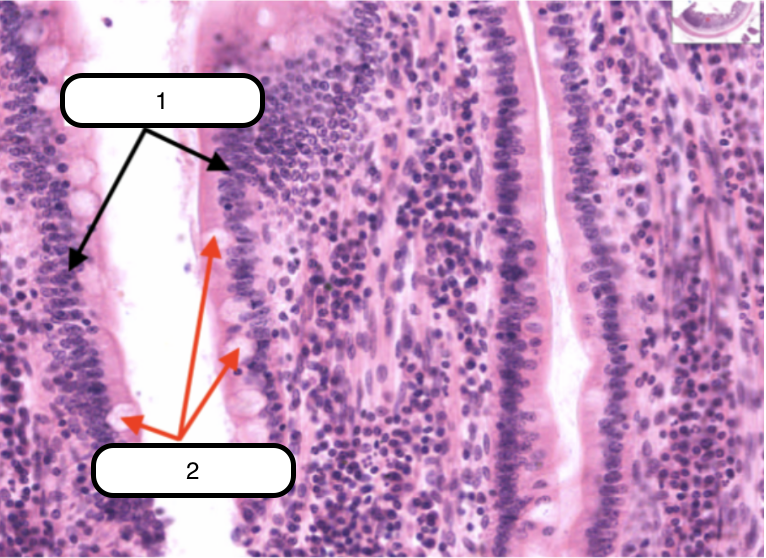
Goblet cells
Identify the structure labeled as #2
Ductus Epididymis
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?

Stereocilia
What surface modifications on epithelial cells can be seen in this specimen?
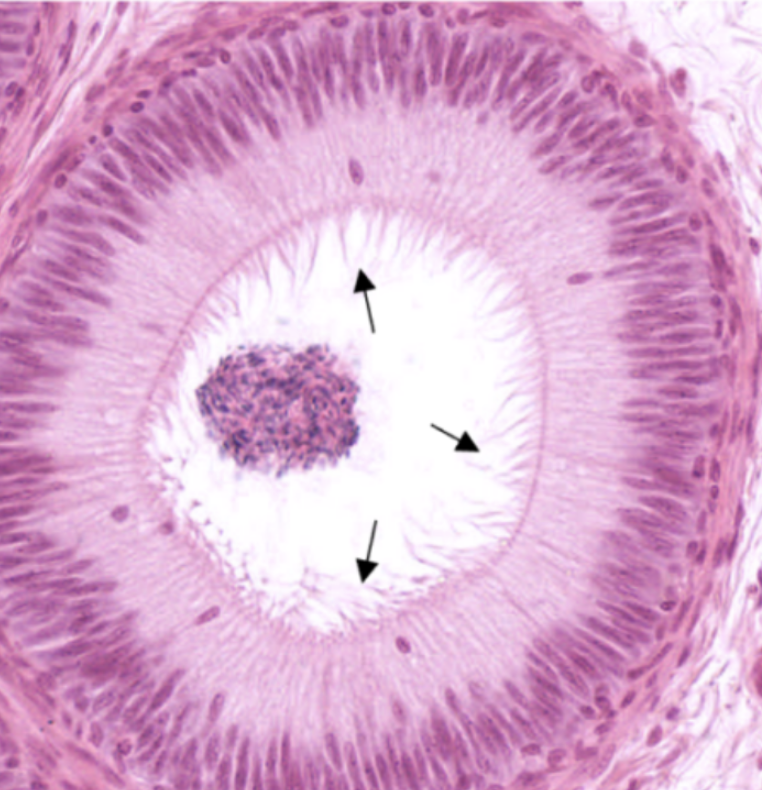
Urinary Bladder
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
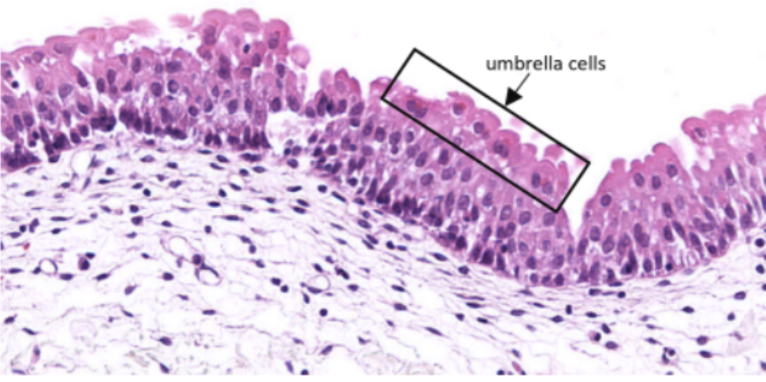
Umbrella Cells
Identify the structure pointed by the arrow.
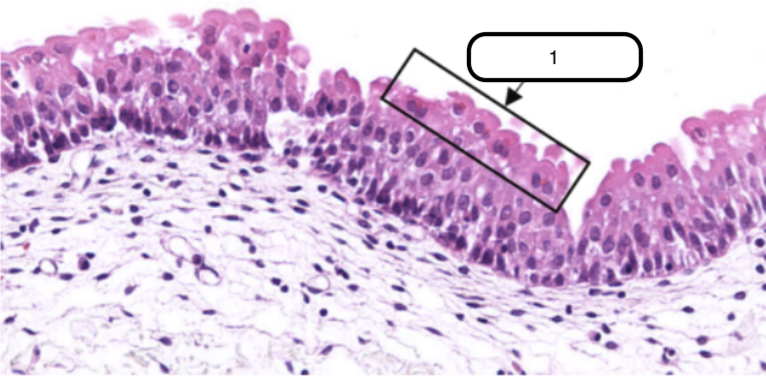
Relaxed Urothelium
What kind of specimen is this?
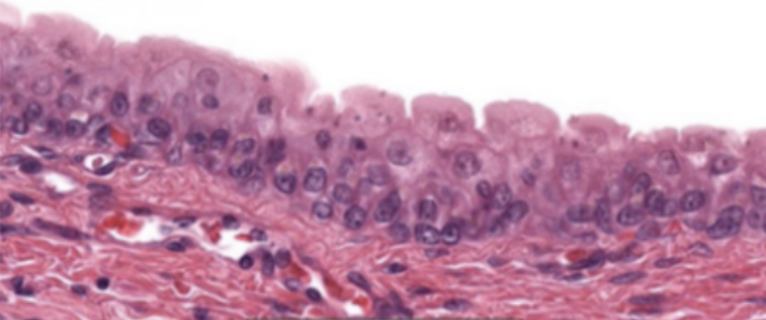
Stretched Urothelium
What kind of specimen is this?
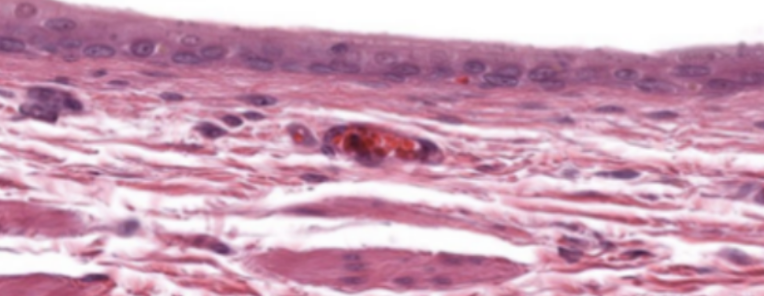
Choroid Plexus
What specimen is shown in this slide?
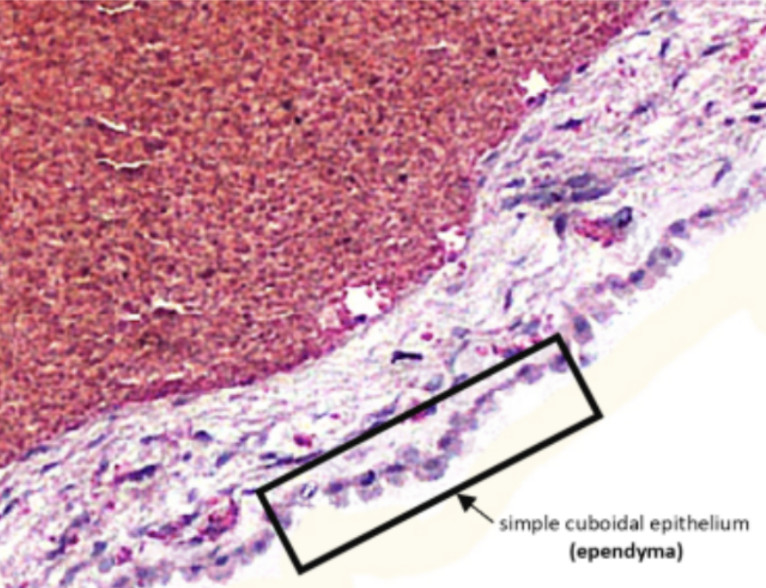
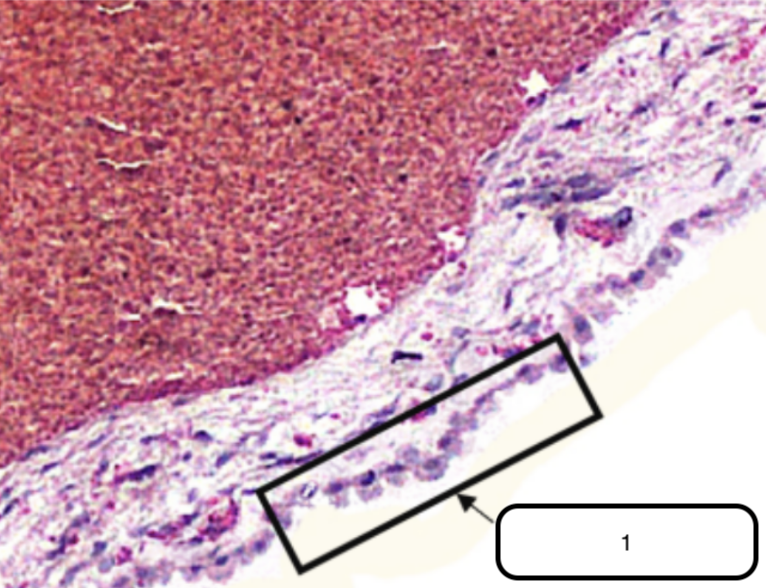
Ependyma (Simple Cuboidal Epithelium)
Identify the structure pointed by the arrow.
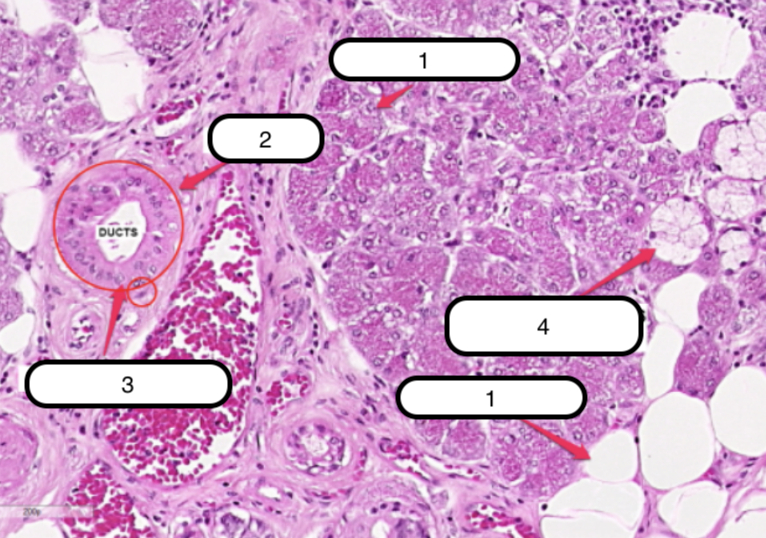
Submandibular Gland
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
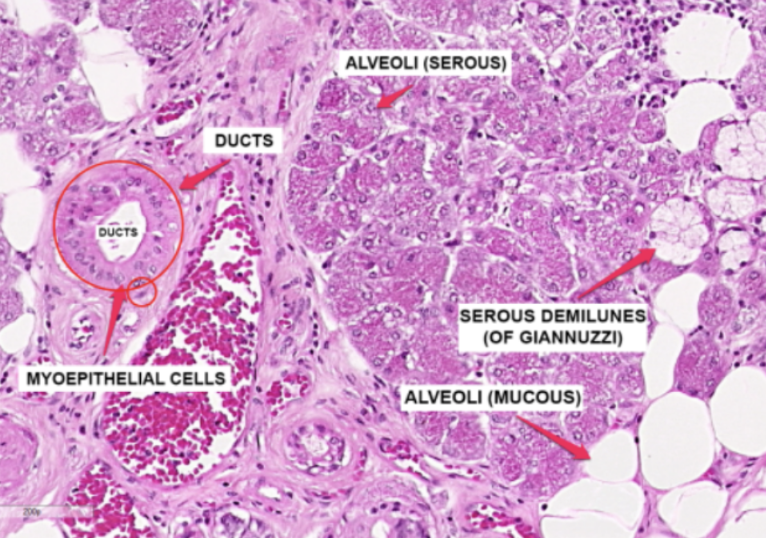
Alveoli (Serous)
Identify the structure labeled as #1
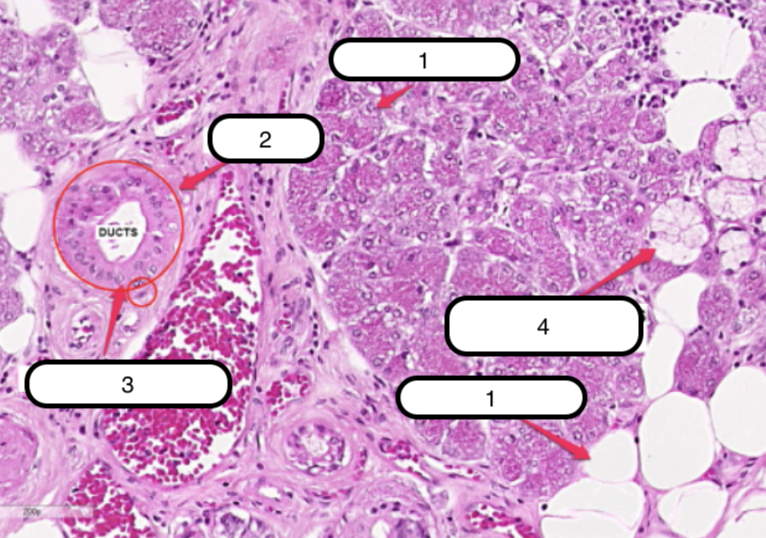
Ducts
Identify the structure labeled as #2
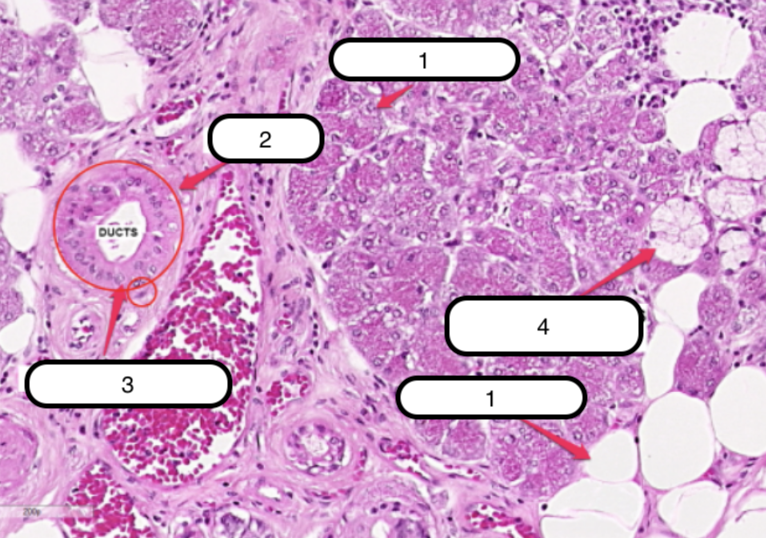
Myoepithelial Cells
Identify the structure labeled as #3
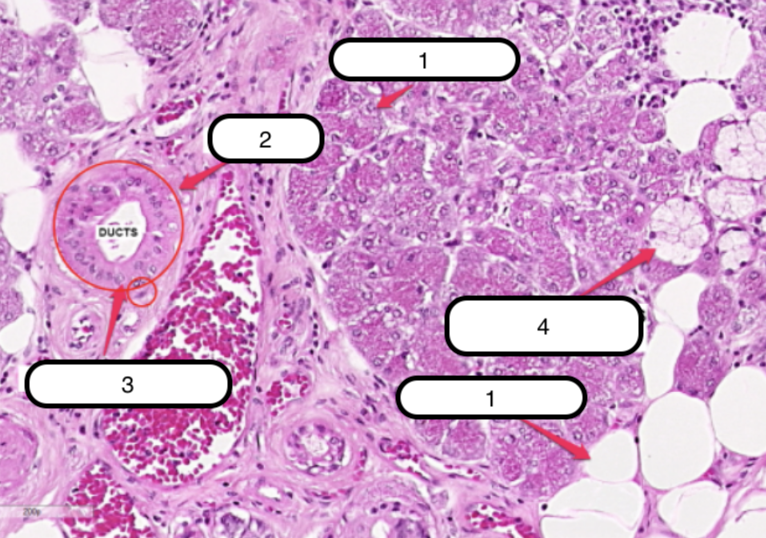
Serous Demilunes (of Giannuzzi)
Identify the structure labeled as #4
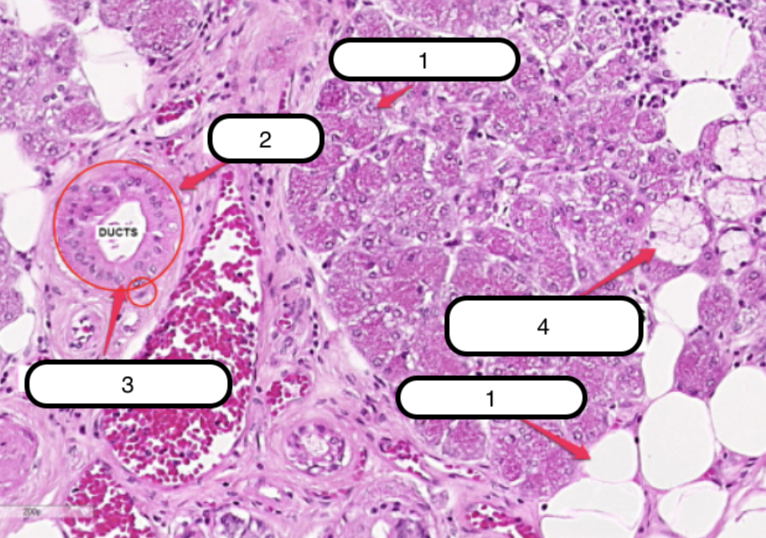
Alveoli (Mucous)
Identify the structure labeled as #5
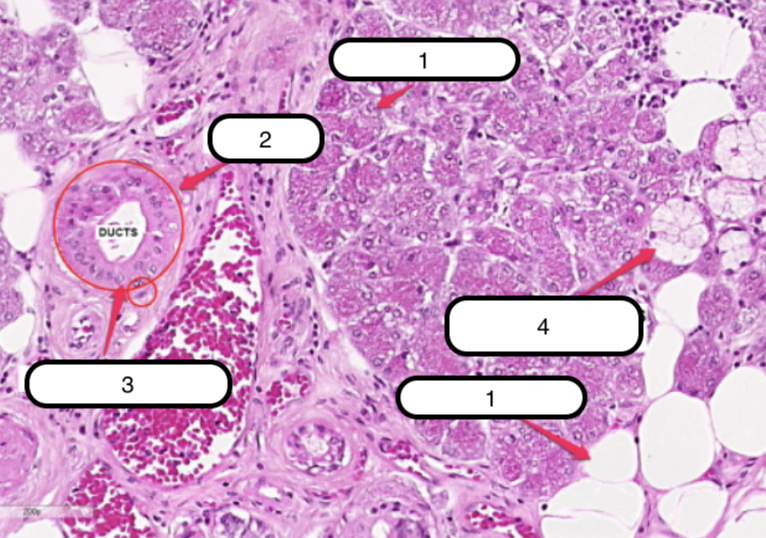
Serous Demilunes (of Giannuzzi)
Serous cells are arranged to form crescentic caps called?
Pituitary Gland
What organ specimen is shown in this slide?
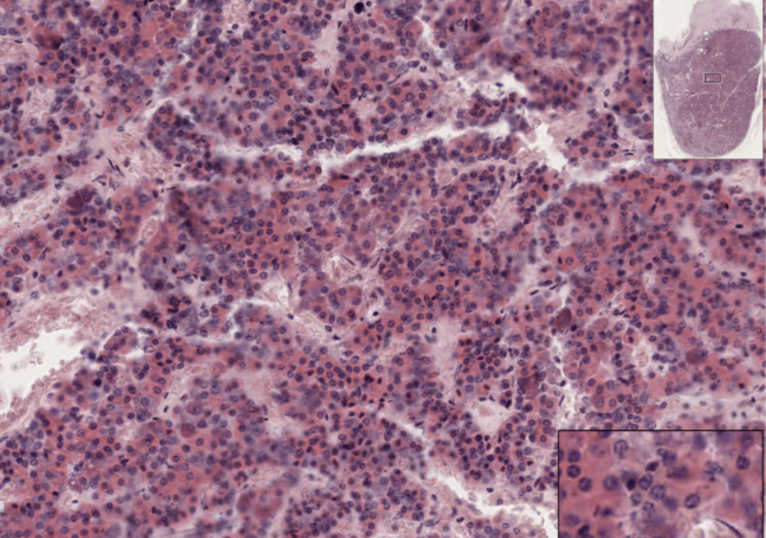
Sinusoidal Capillaries
The spaces are minute blood vessels called __________ that are lined by endothelium which refers to the simple squamous epithelium that lines the luminal surface of the heart and all blood vessels.