AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.2 Alkanes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the general formula for alkanes? (1)
CnH2n+2
How reactive are alkanes? (2)
- Alkanes are very unreactive
- But can burn in oxygen and react with halogens to produce halogenoalkanes
How does the boiling point of alkanes change with carbon chain length? (1)
The longer the carbon chain, the higher the boiling point due to stronger van der Waals' forces
How does branching in alkane isomers affect their boiling point? (3)
- More branching lowers the boiling point
- Due to weaker van der Waals' forces
- And less surface area contact between molecules
What is crude oil? (3)
- Crude oil is a complex mixture consisting mainly of alkanes
- Crude oil has no use in its raw form
- So it must be separated by fractional distillation to provide useful products
What is distillation? (1)
A method used to separate mixtures of miscible liquids based on differences in boiling points
What determines the height at which a molecule condenses during fractional distillation? (2)
- The boiling point of the molecule determines the height
- Molecules with higher boiling points condense lower down in the column
What is a fraction in fractional distillation? (1)
A fraction is a mixture of hydrocarbons with similar boiling points
Draw the apparatus used for fractional distillation. (3)
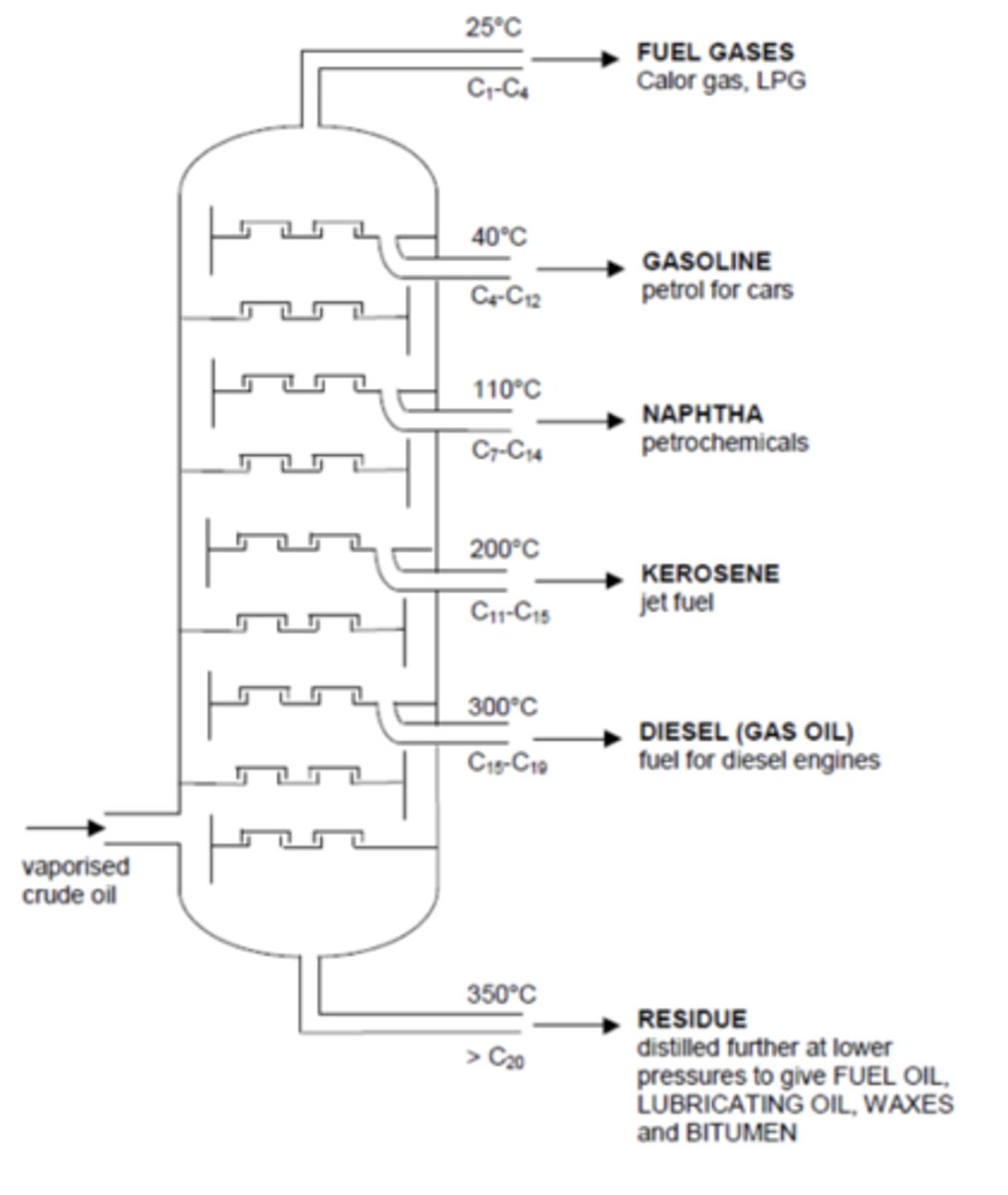
What happens to hydrocarbons as the carbon chain gets longer? (4)
- They become more viscous
- Harder to ignite
- Less volatile
- Have higher boiling points
What is cracking? (1)
Cracking is the breaking of long-chain molecules into smaller ones
Why is industrial cracking used? (2)
- To develop saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon chains
- To meet the demand for shorter hydrocarbons like naphtha
What does "saturated" mean in the context of hydrocarbons? (1)
Saturated hydrocarbons contain only single bonds
What does "unsaturated" mean in the context of hydrocarbons? (1)
Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain double bonds (at least one C=C)
What does "hydrocarbon" mean? (1)
A hydrocarbon contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms
What are the conditions for thermal cracking? (1)
High temperature (~1000K) and high pressure (~7000kPa)
What products are formed during thermal cracking? (1)
A high percentage of alkenes and straight-chain alkanes
What are the conditions for catalytic cracking? (1)
Lower temperature (~720K) and the use of a catalyst, such as zeolite crystals
What products are formed during catalytic cracking? (1)
Motor fuels, aromatic hydrocarbons, and cycloalkanes
Write the equation for the cracking of one molecule of octane (C8H18) to form hexane (C6H14) and one other product. (1)
C8H18 → C6H14 + C2H4
What is complete combustion of alkanes? (1)
Complete combustion occurs when alkanes react with excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water
How should combustion equations be balanced? (2)
- Combustion equations should be balanced alphabetically
- Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), then Oxygen (O)
What are the products of complete combustion of methane? (1)
The products are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O)
Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of methane. (1)
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
What happens during incomplete combustion of alkanes? (1)
Incomplete combustion produces carbon monoxide (CO) or carbon (C) due to a limited supply of oxygen
Write the balanced equation for incomplete combustion of methane producing carbon monoxide. (1)
CH₄ + 1.5O₂ → CO + 2H₂O
Write the balanced equation for incomplete combustion of methane producing carbon. (1)
CH₄ + O₂ → C + 2H₂O
How is carbon monoxide formed, and what problem does it cause? (2)
- The incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
- It is toxic
How are carbon particulates formed, and what problems do they cause? (2)
- Formed by the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
- They blacken buildings, cause respiratory problems, and contribute to global dimming
How can the problem of carbon monoxide and carbon particulates be reduced? (1)
Ensure a good supply of oxygen when burning fuels
What problem does carbon dioxide cause? (1)
Global warming
How can the problem of carbon dioxide be reduced? (1)
Burn fewer fossil fuels
How is sulfur dioxide formed, and what problem does it cause? (2)
- Sulfur dioxide is formed by the combustion of sulfur-containing compounds in fuels
- It reacts with water to form acid rain
How can the problem of sulfur dioxide be reduced? (1)
Remove sulfur from fuel before burning or use flue gas desulfurization
How are nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) formed, and what problem do they cause? (3)
- Nitrogen oxides are formed by the reaction of N₂ in the air with O₂
- At very high temperatures (e.g., in engines and furnaces)
- They react with water to form acid rai
How can the problem of nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) be reduced? (1)
Use catalytic converters in cars
How is water vapour formed, and what problem does it cause? (2)
- Formed by the combustion of fuels containing hydrogen
- It is a greenhouse gas
What does flue gas desulfurisation remove from fossil-fuel power plant emissions? (1)
Flue gas desulfurisation removes SO₂ from the gases emitted by fossil-fuel power plants
What substances are used in flue gas desulfurisation to neutralise sulfur dioxide? (1)
- CaO (calcium oxide) or CaCO₃ (calcium carbonate)
Write the balanced chemical equation for flue gas desulfurisation using CaO. (1)
CaO(s) + SO₂(g) → CaSO₃(s)
What harmful effect does sulfur dioxide cause if not removed from emissions? (1)
Sulfur dioxide causes acid rain
What is the primary function of catalytic converters in cars? (2)
- Catalytic converters reduce the amount of CO, NO, and particulates
- That are released into the atmosphere by the engine
What metals are typically used in the coating of catalytic converters? (3)
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Rhodium
How does the honeycomb structure of catalytic converters improve their effectiveness? (1)
- The honeycomb structure increases the surface area
- Making the converter more cost-effective and efficient
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs in a catalytic converter to reduce nitrogen oxides. (1)
2CO + 2NO → 2CO₂ + N₂
Why is the ceramic material in catalytic converters essential? (1)
The ceramic material can withstand high temperatures inside the combustion engine.
Write the overall reaction for the conversion of CO, NO, and hydrocarbons (C₈H₁₈) in a catalytic converter. (1)
C₈H₁₈ + 25NO → 8CO₂ + 12.5N₂ + 9H₂O