AP Human Geography - Unit 4 Political Geography (2019 CED)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
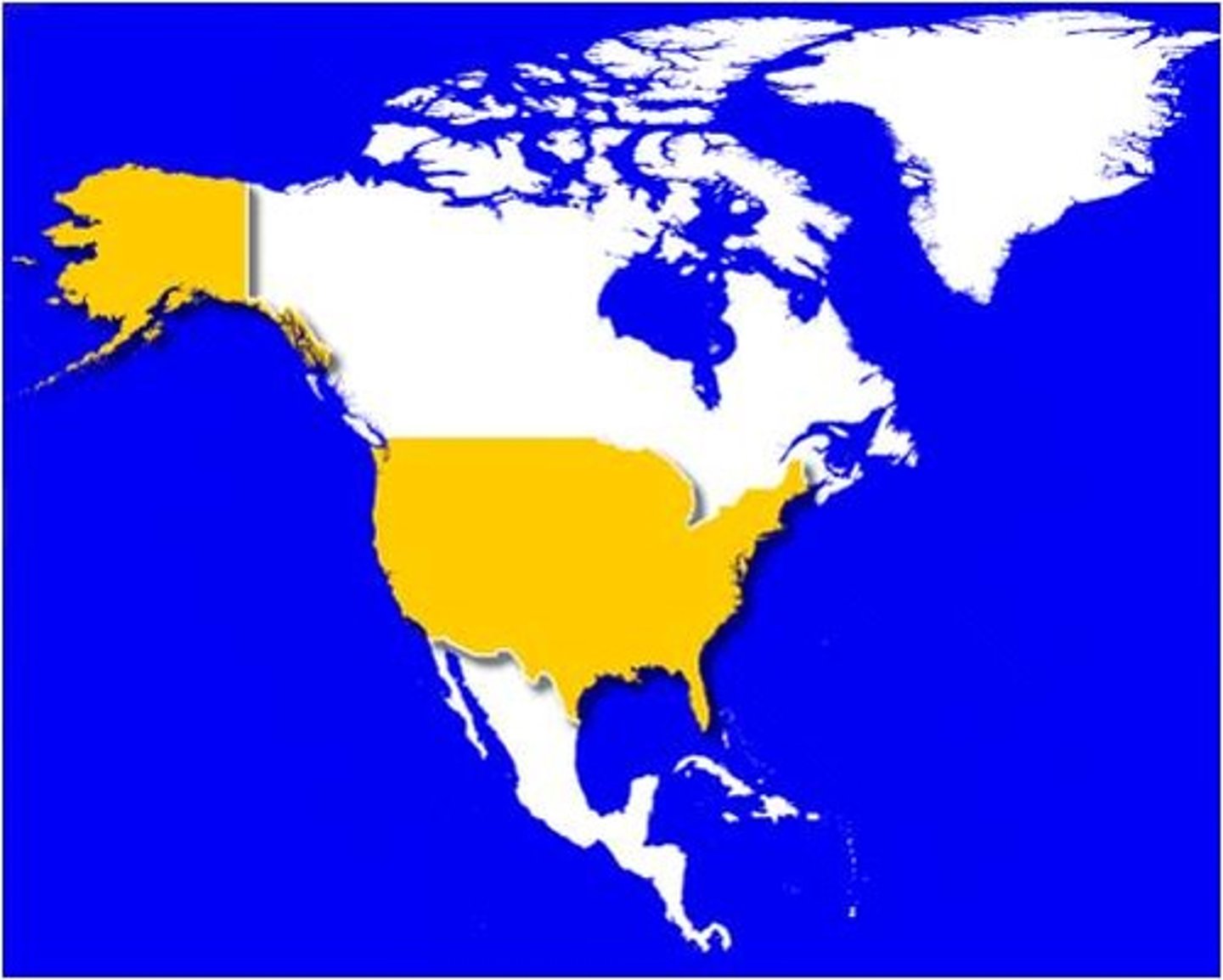
state
the largest political unit, the formal term for a country
nation
group of people who have a common cultural heritage, claim a particular space based on tradition as their homeland, beliefs and values that help unify them, and a desire to establish their own state or express self-determination in another way
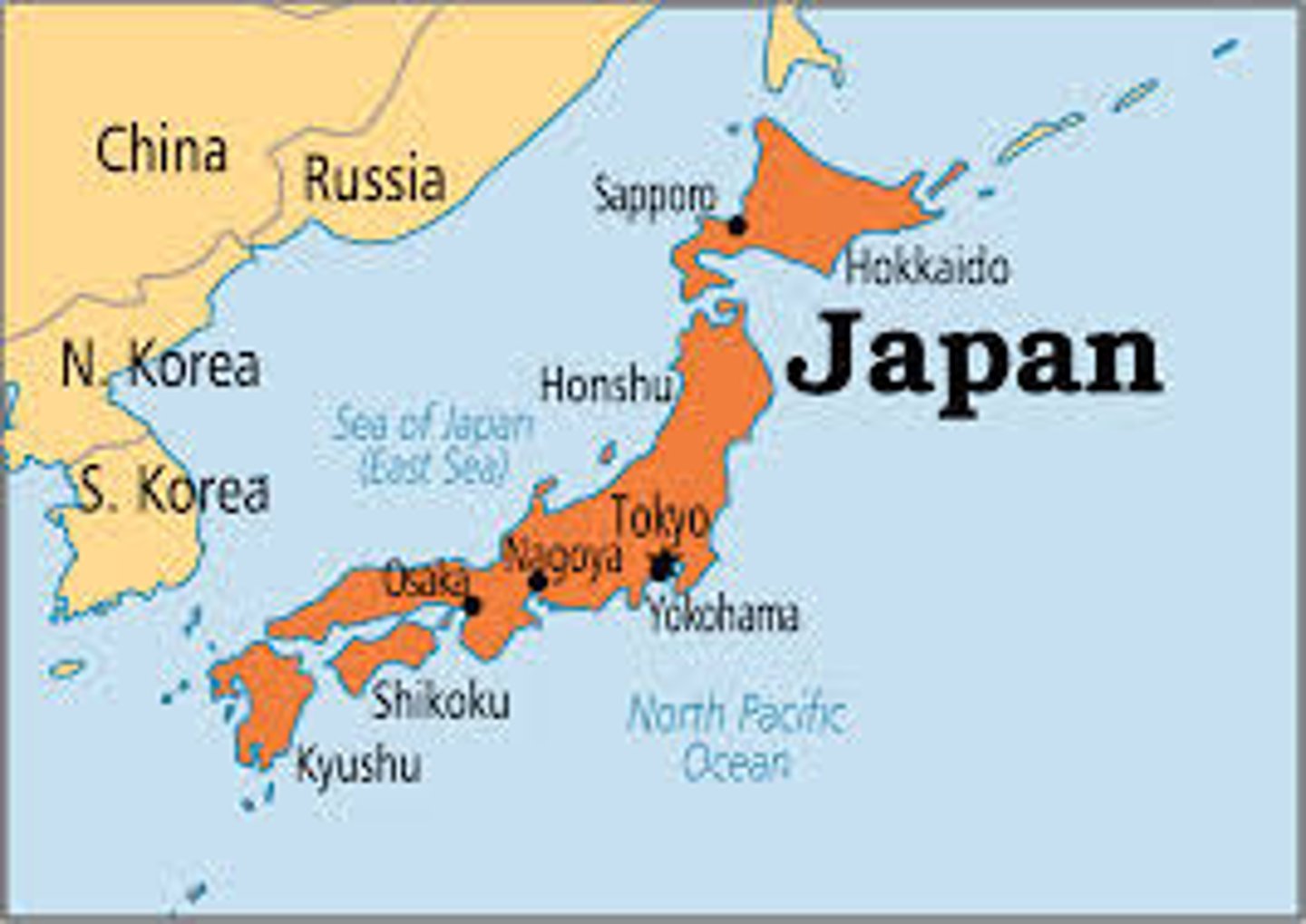
nation-state
singular nation of people who fulfill the qualifications for a state
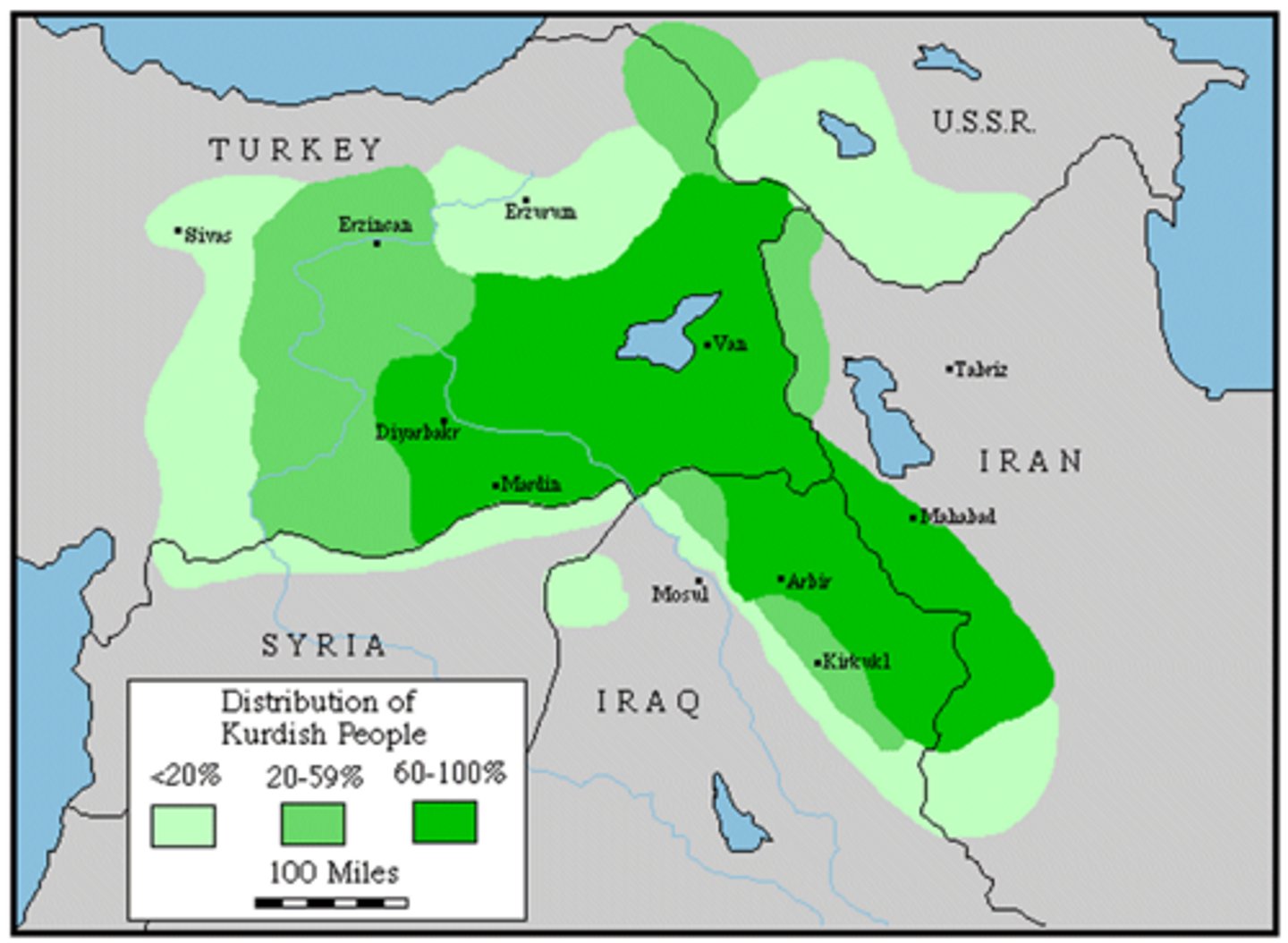
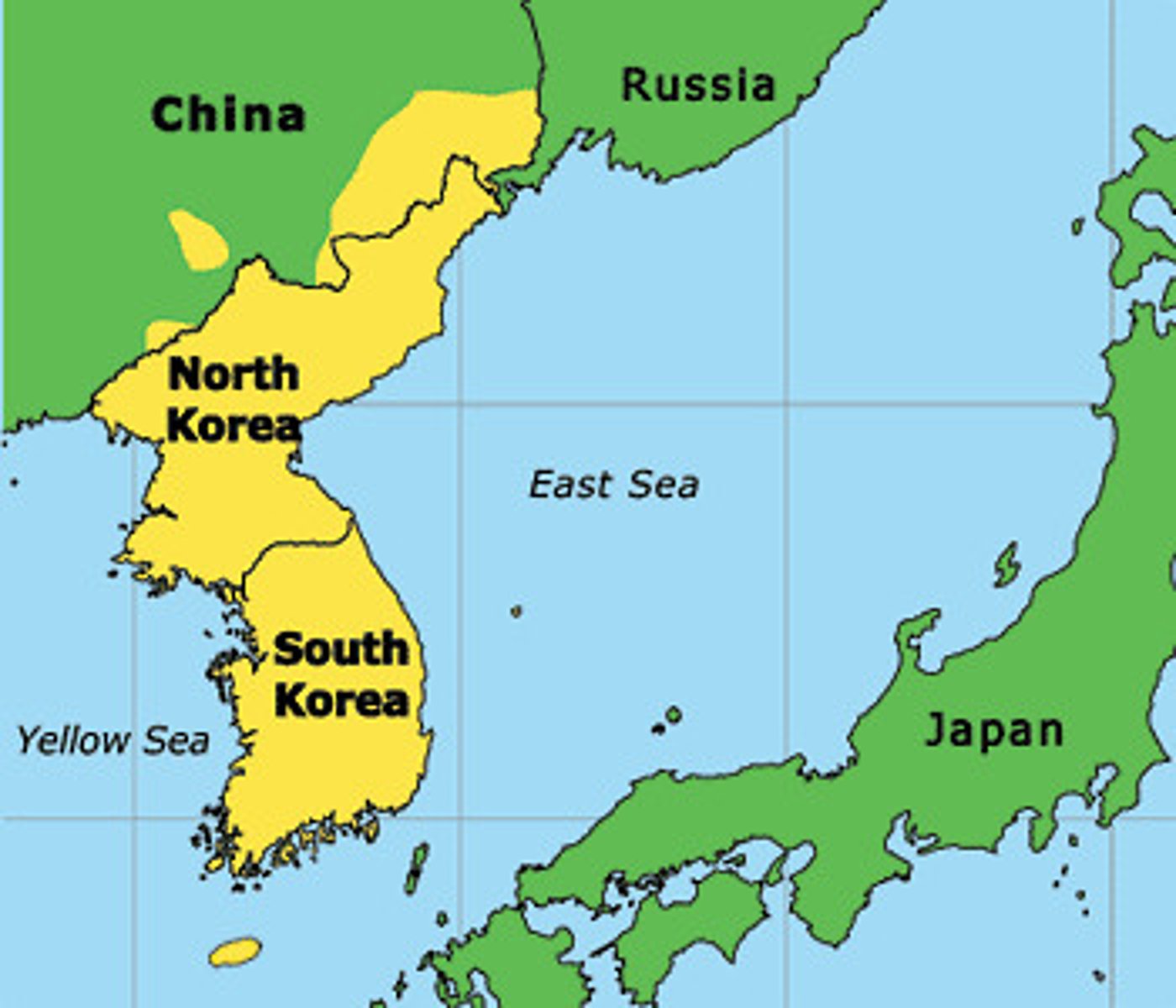
stateless nation
nations that have no independent political entity
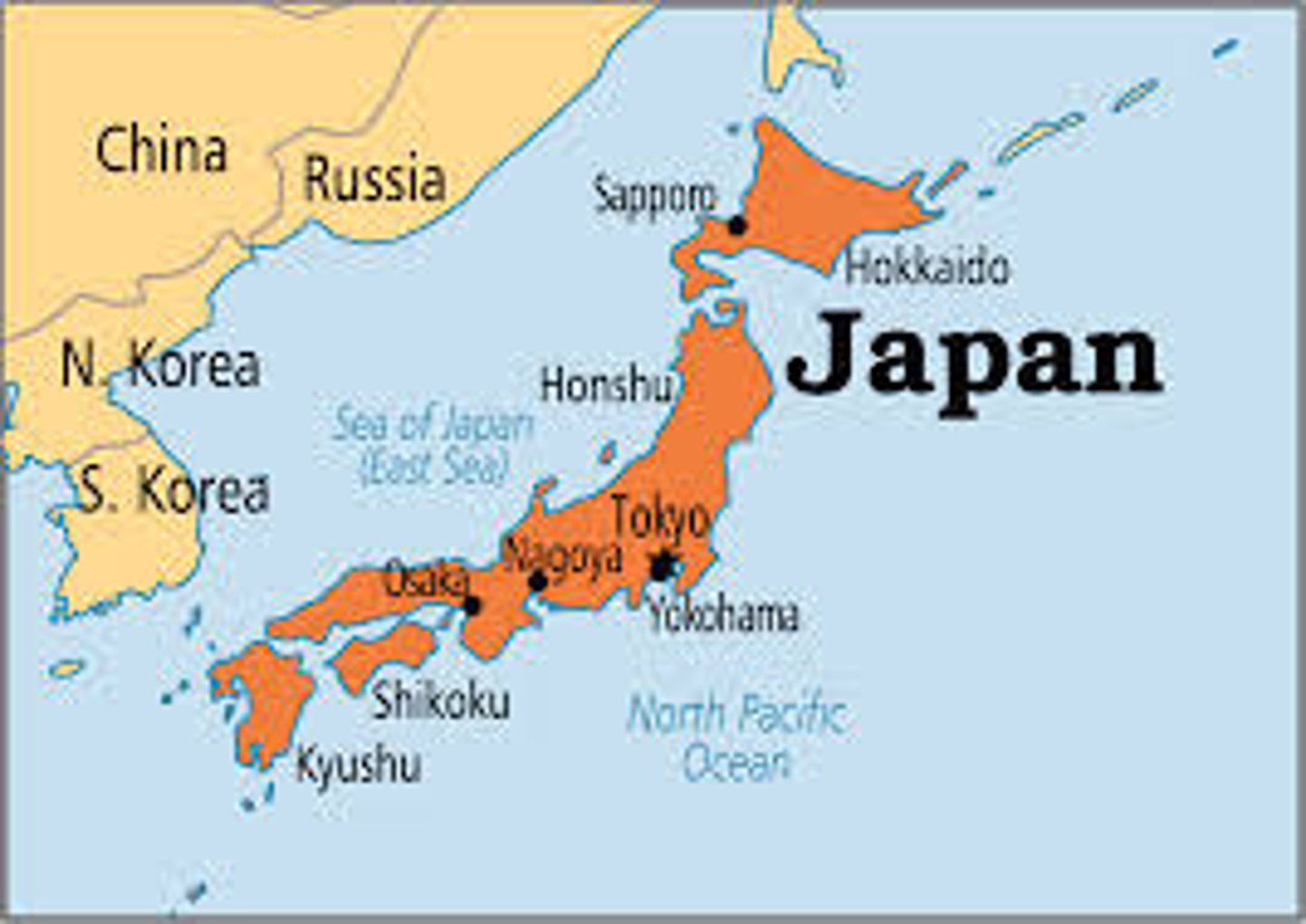
multinational state
country that contains more than one nation
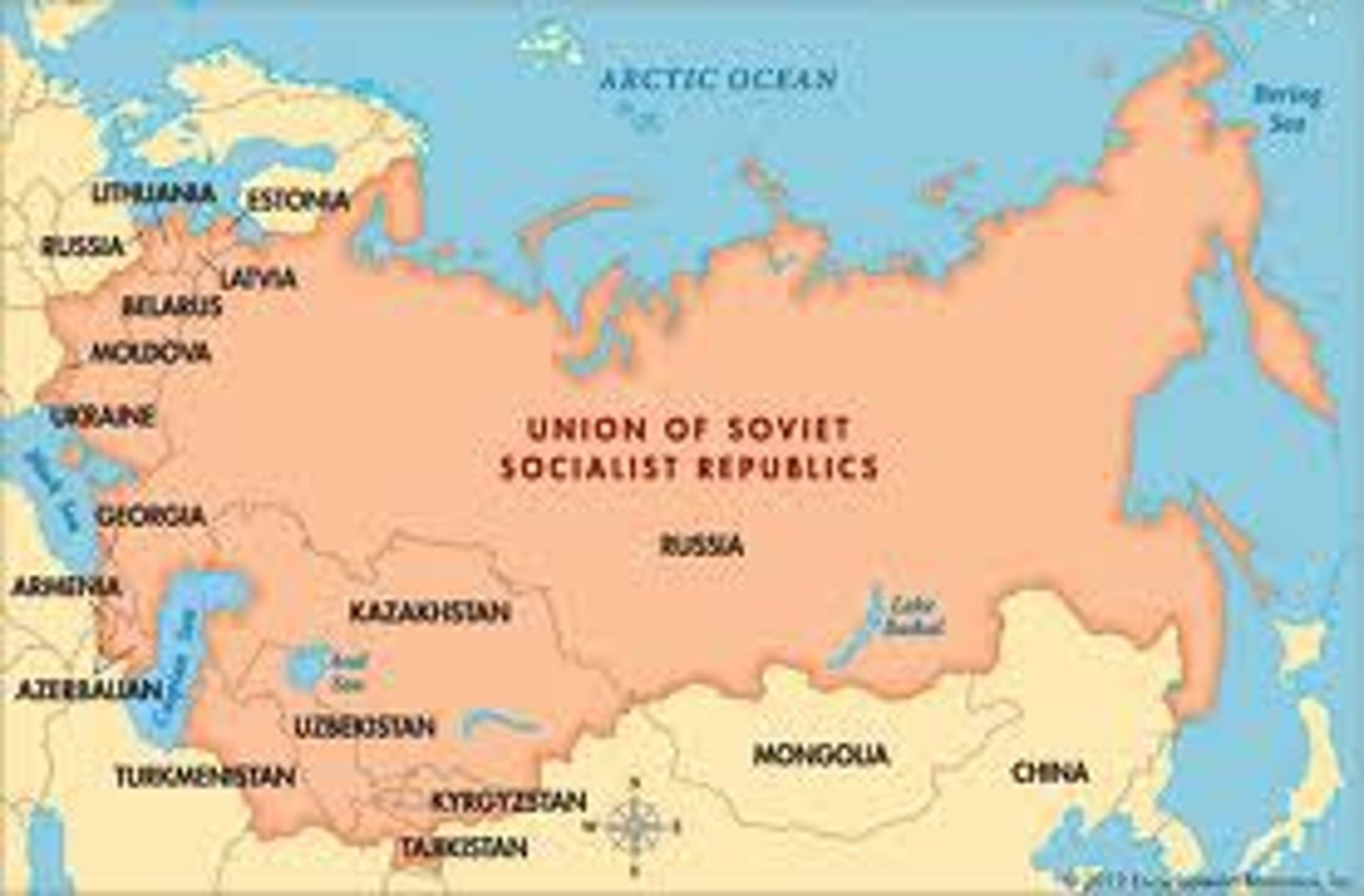
multistate nation
occurs when a nation has a state of its own but stretches across borders of other states
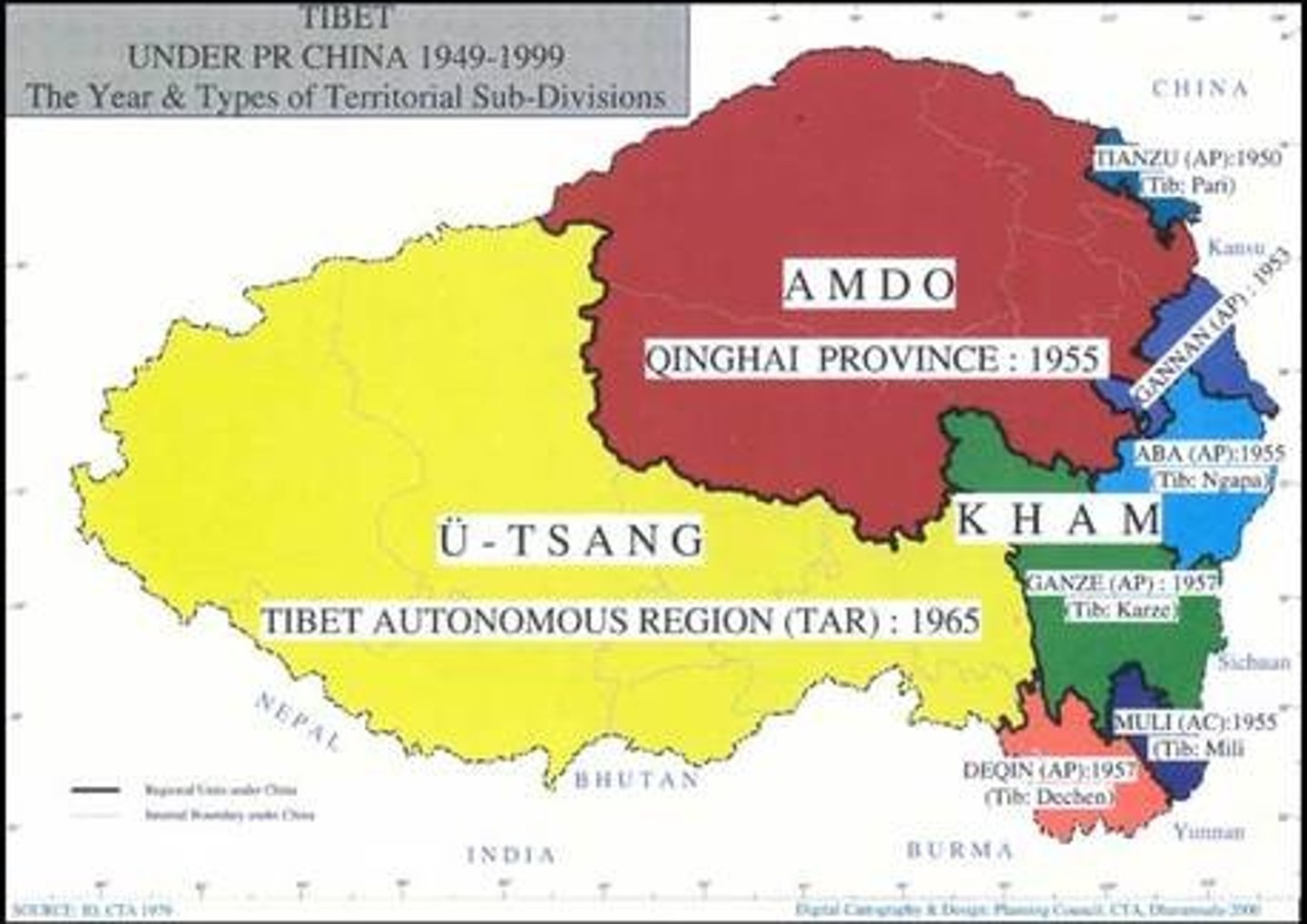
autonomous regions
defined area within a state that has a high degree of self-government and freedom from its parent state
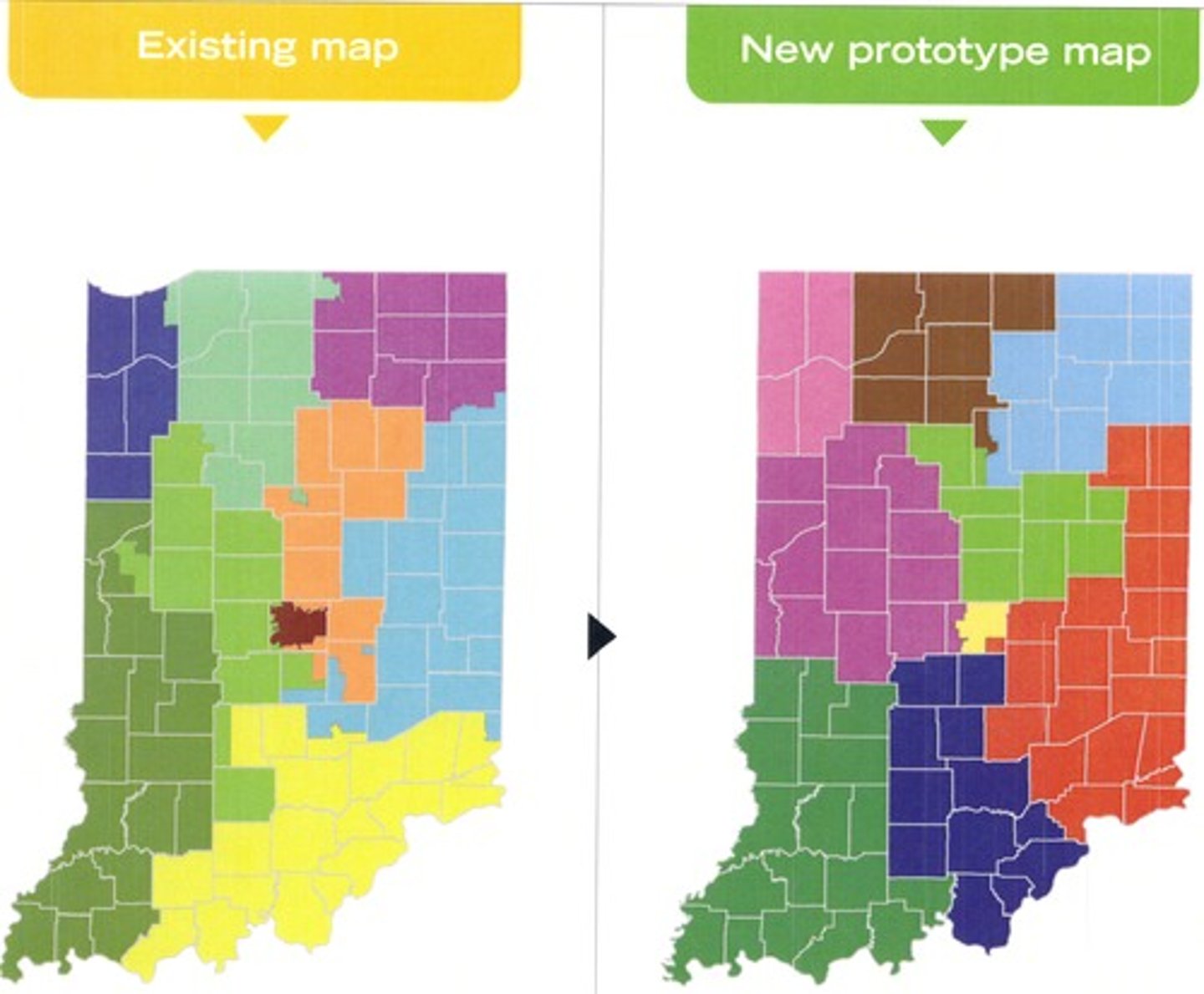
gerrymandering
the drawing of boundaries for political districts by the party or group in power to extend or cement their advantage
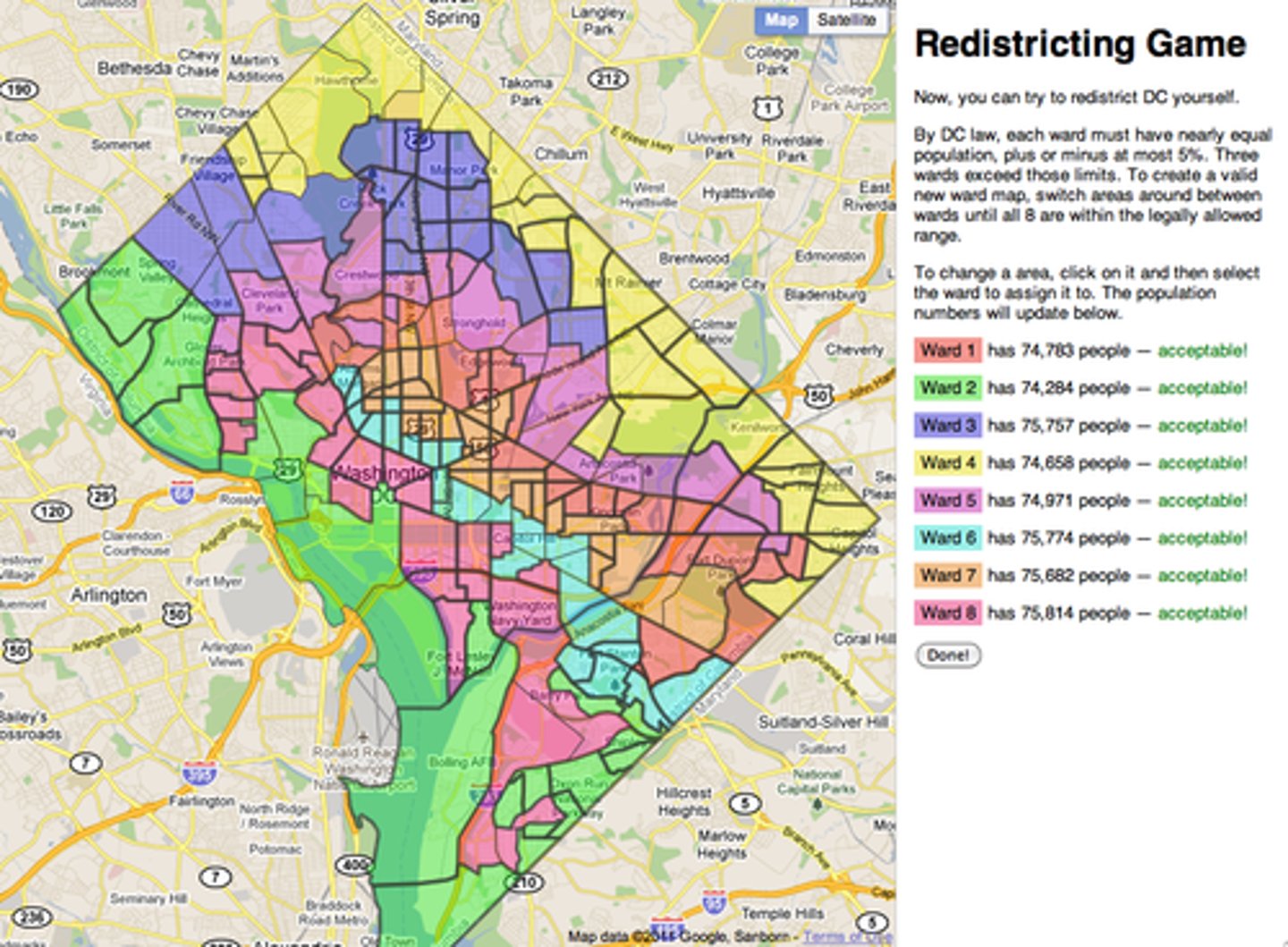
redistricting
redrawing district boundaries so that each district contains roughly the same number of people
territoriality
a willingness by one person or group of people to defend space they claim
defined boundaries
established by a legal document such as a treaty that divides one entity from another (invisible line)
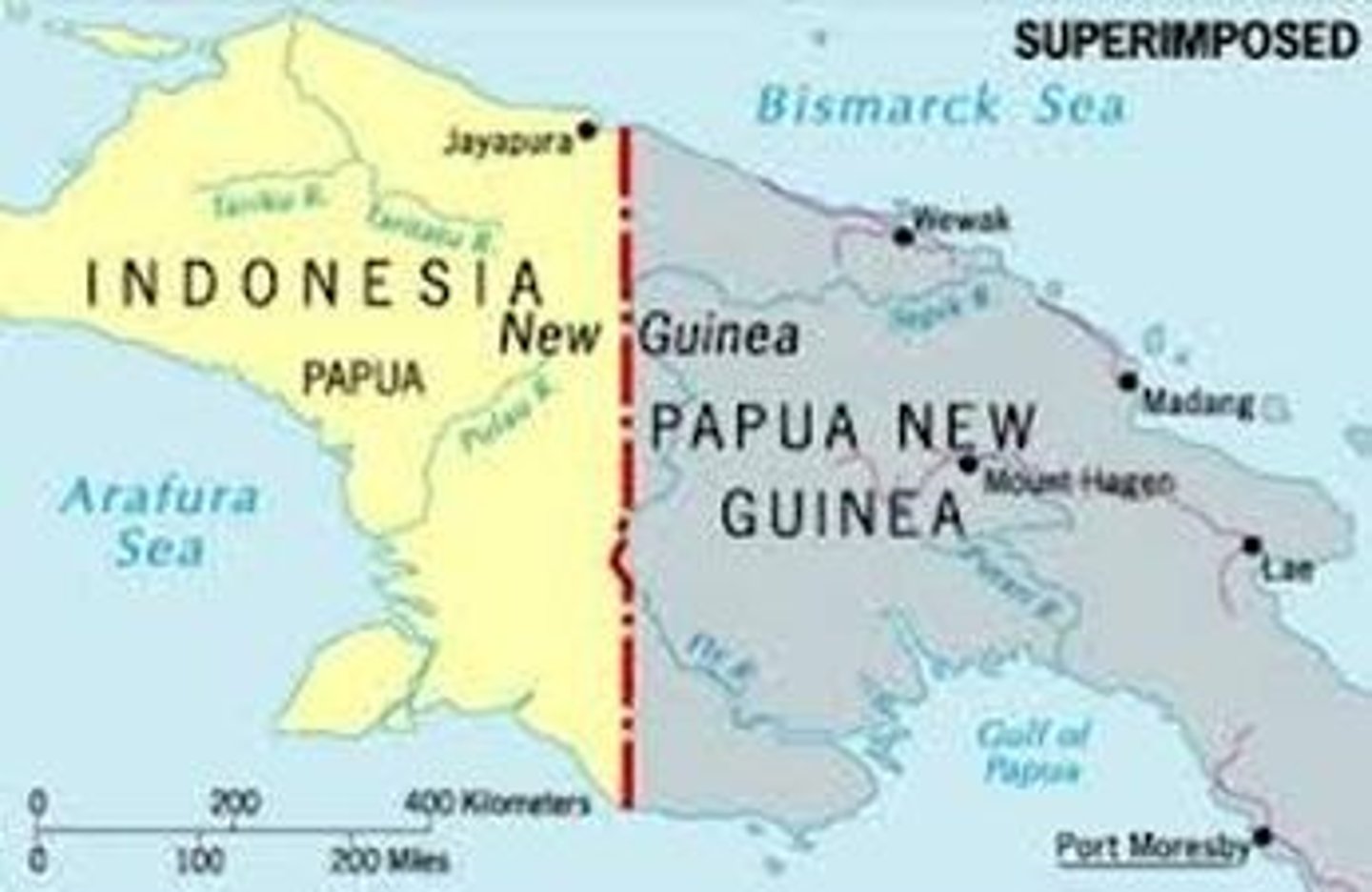
delimited boundaries
line drawn on a map to show the limits of a space
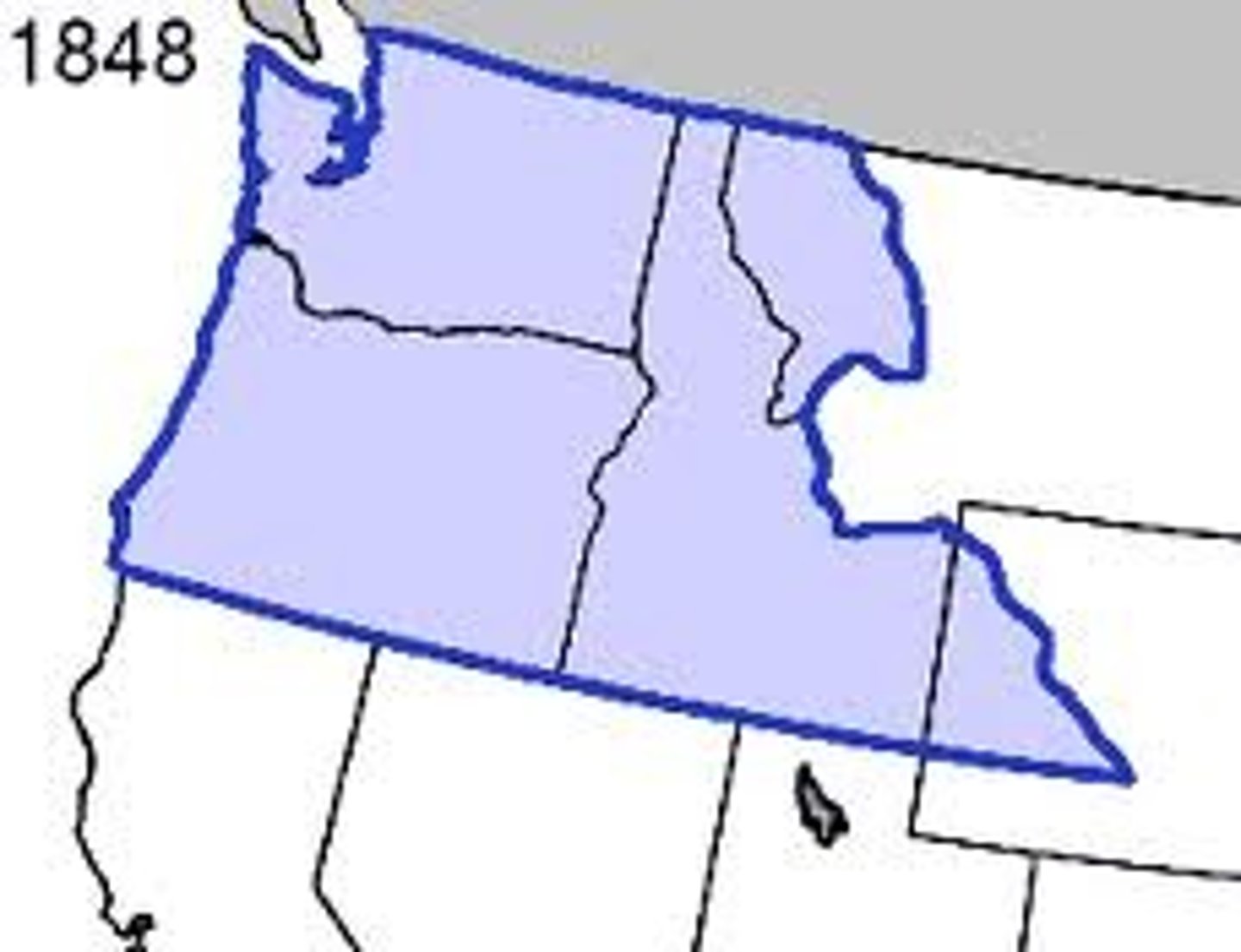
demarcated boundaries
identified by physical objects placed on the landscape

administered boundaries
determination of how boundaries will be maintained and crossed
sovereignty
the power of a political unit to rule over its own affairs

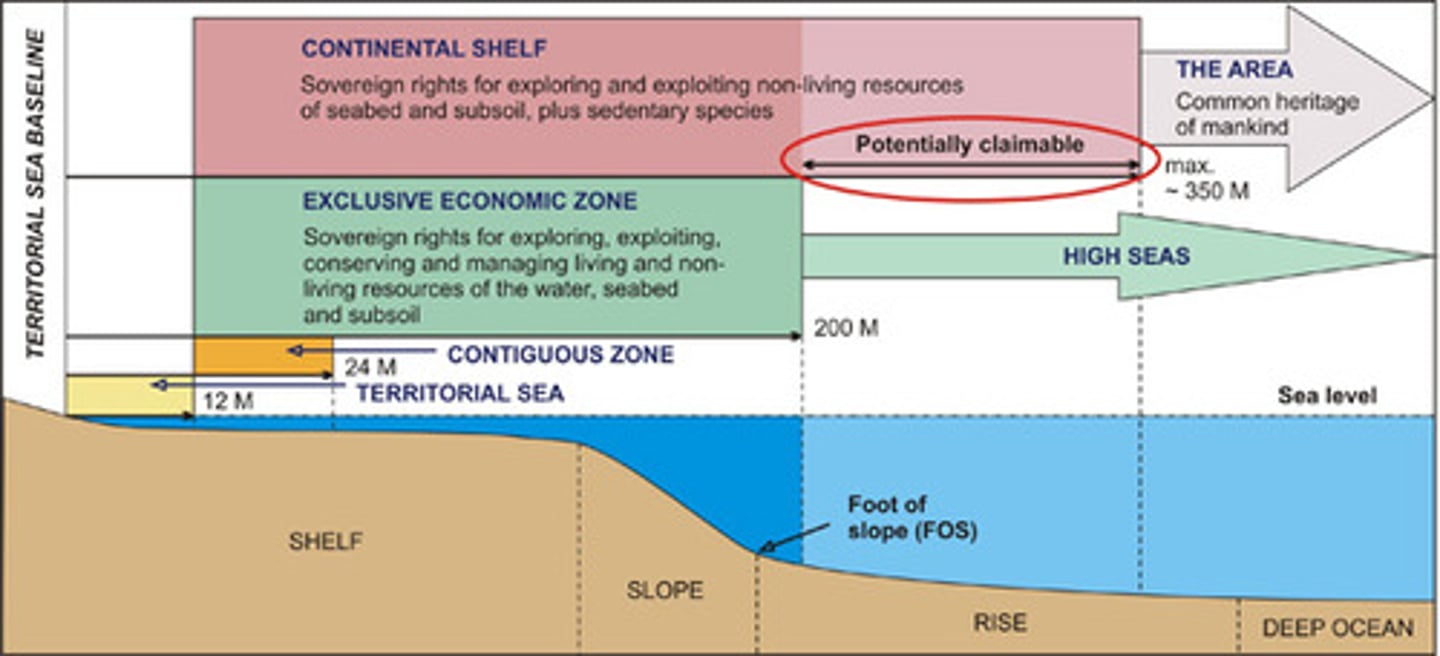
U.N. Law of the Sea
brought about by the United Nations, this convention was signed by over 150 countries and consists of four zones: territorial seas, contiguous zone, exclusive economic zone and high seas.
unitary states
governmental power is held primarily by the central government with very little power given to local governments

federal states
governmental power is shared between the central and local governments; displays a hierarchy of power
supranationalism
an alliance involving multiple countries for their mutual benefit such as economic, cultural or political/ military

devolution
transfer of political power from the central government to subnational levels of government
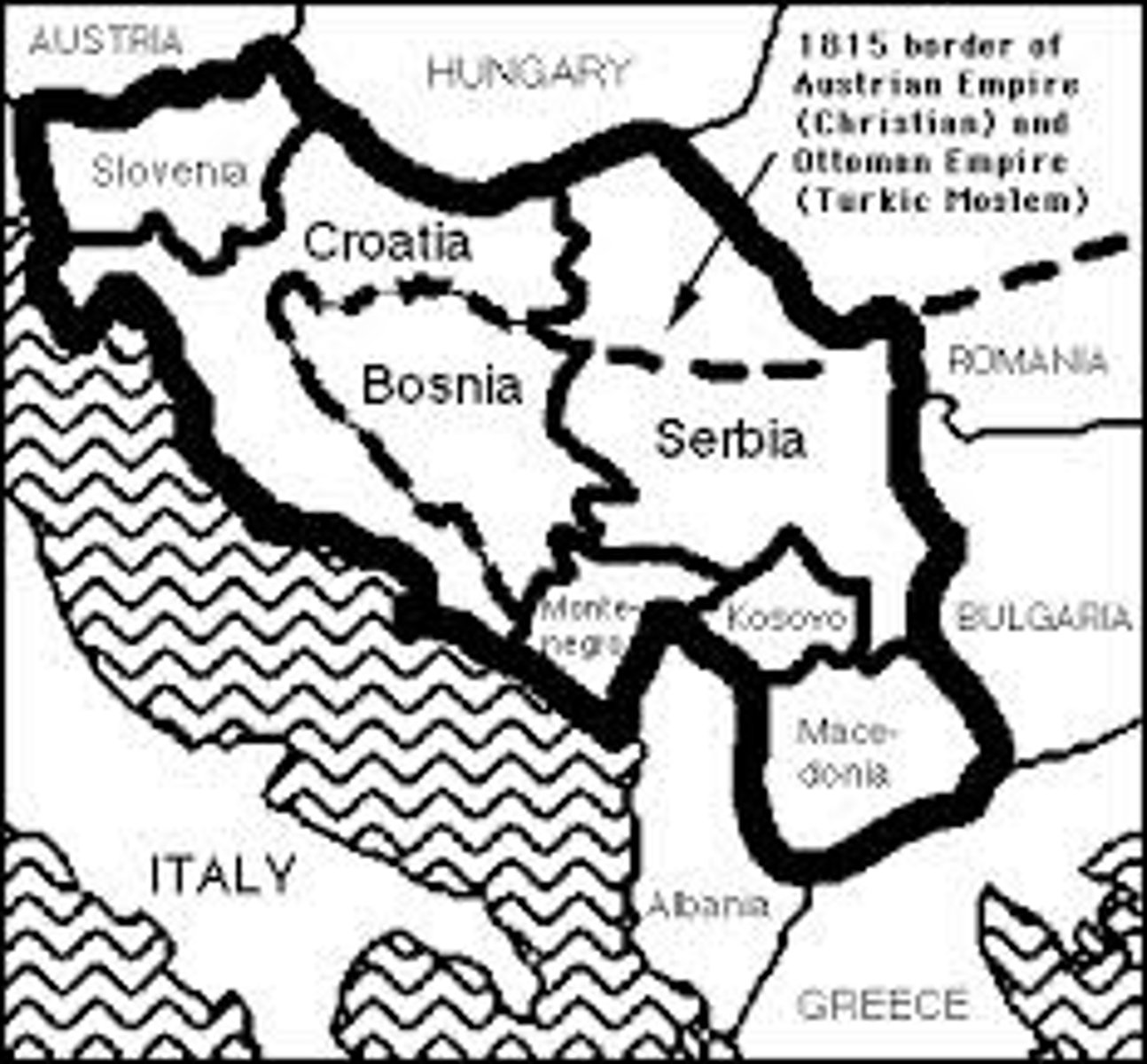
Balkanization
the fragmentation of a state or region into smaller, often hostile, units along ethno-linguistic lines
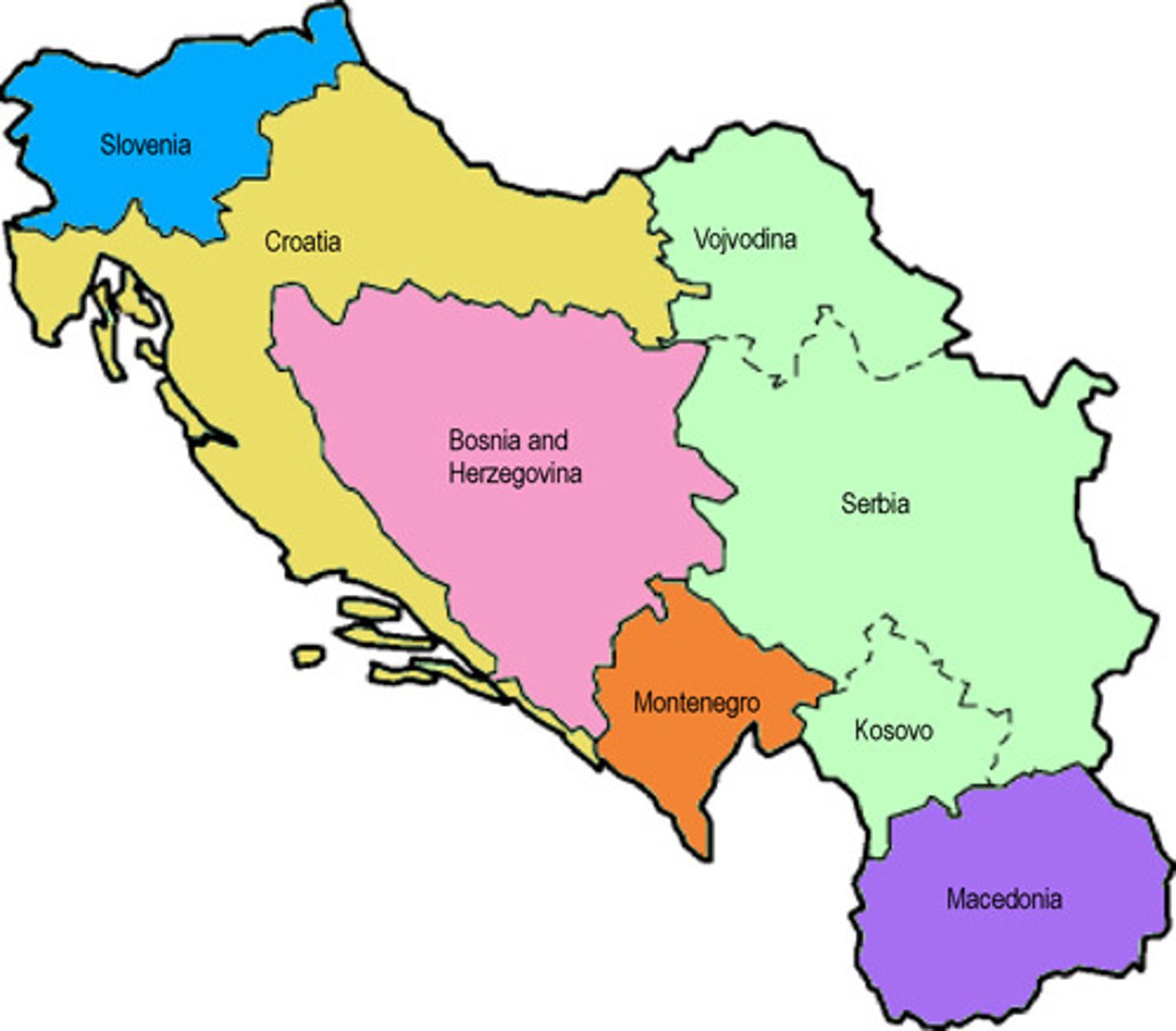
centrifugal forces
forces that "pull away from the center," or ones that tend to break apart states or keep one from forming
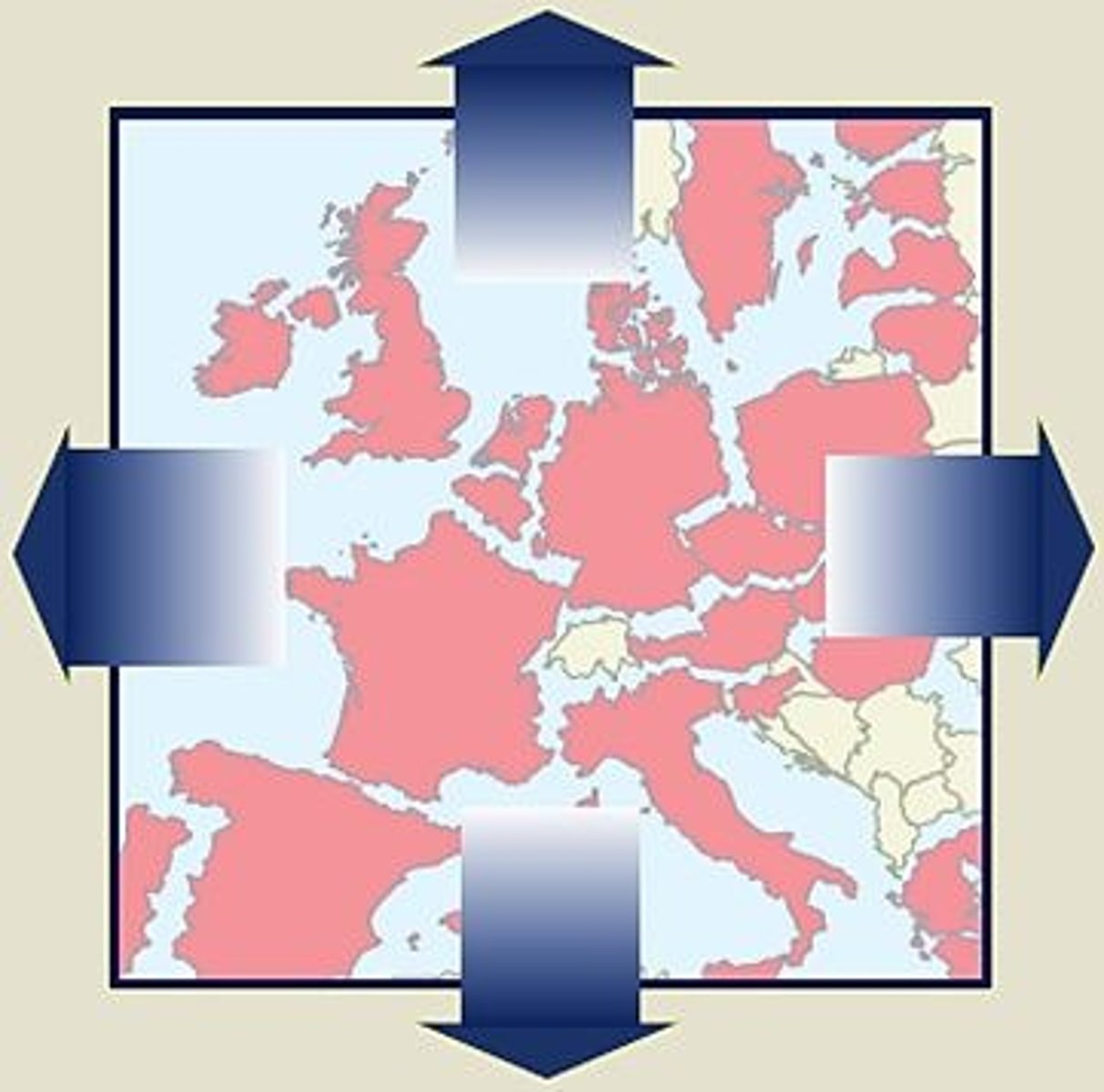
centripetal forces
forces that pull people together, such as religion, language, threats, nationalism, etc.

self-determination
concept that ethnicities have the right to govern themselves

colonialism
The attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

cultural cohesion
The capacity of different national and ethnic groups to make a mutual commitment to live together as citizens of the same state.
neocolonialism
A new form of global power relationships that involves not direct political control but economic exploitation by multinational corporations

shatterbelt
a region caught between stronger colliding external cultural-political forces, under persistent stress, and often fragmented by aggressive rivals (e.g., Israel or Kashmir today; Eastern Europe during the Cold War,...).
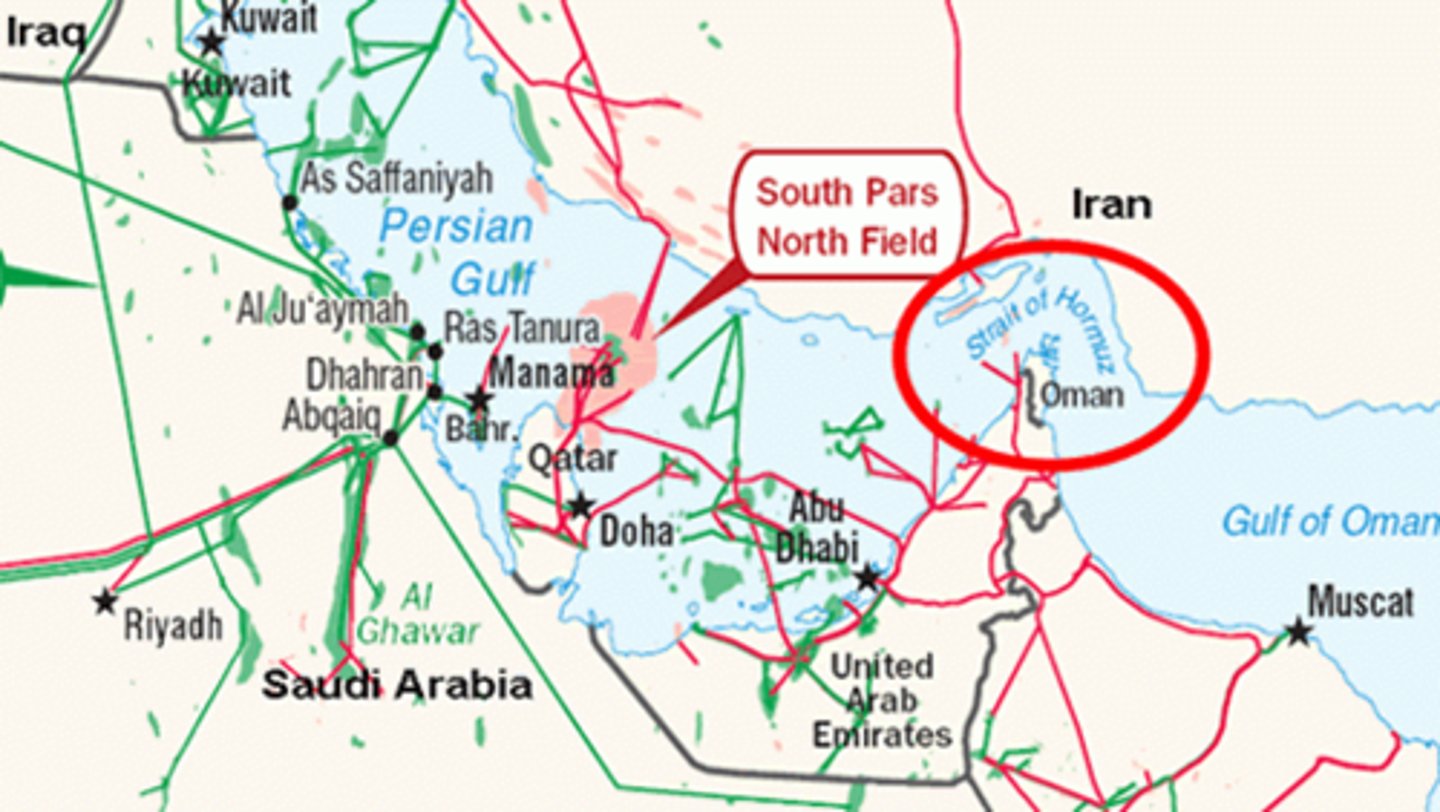
choke point
a strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water
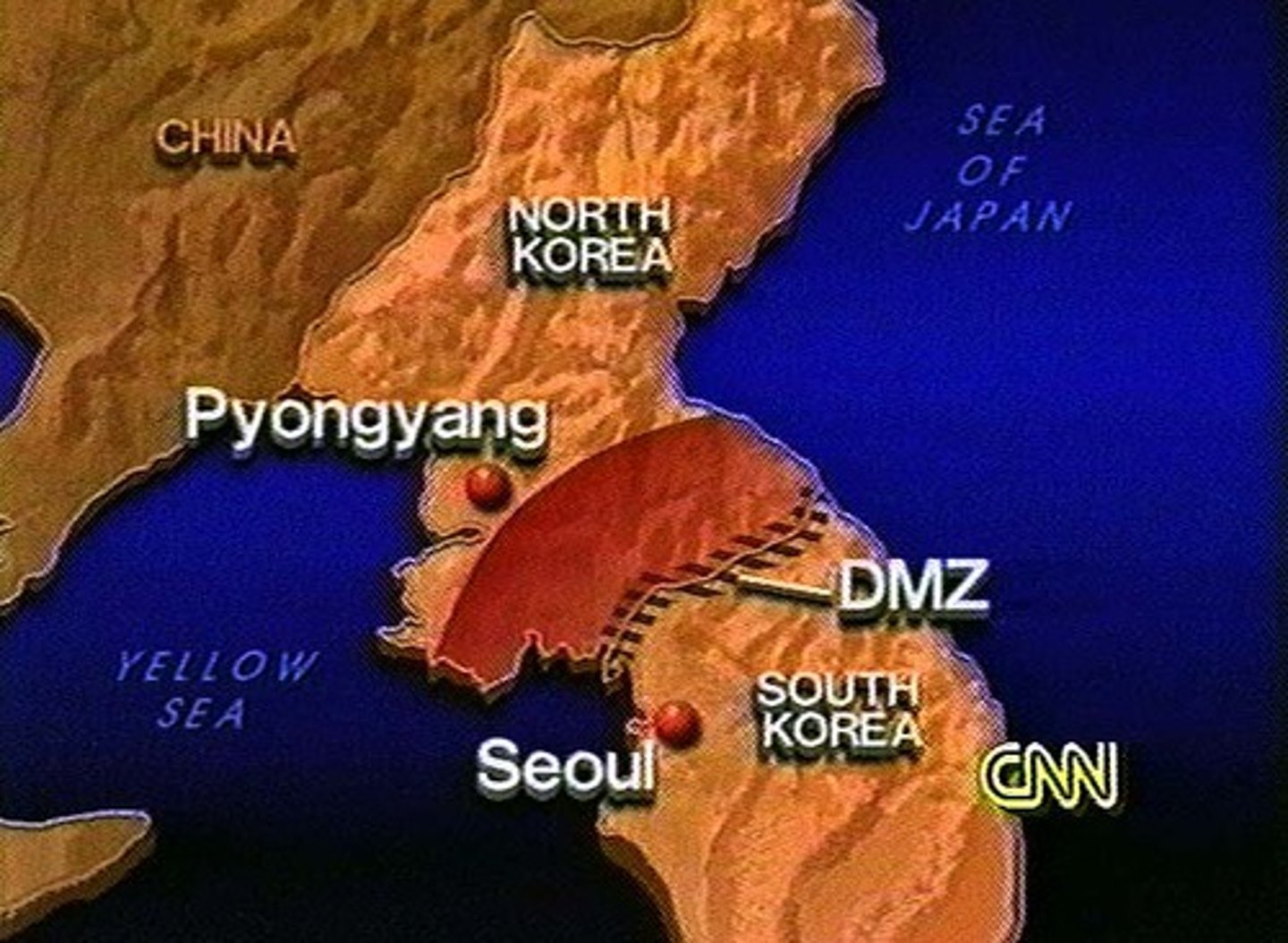
demilitarized zone
A zone from which military forces or operations or installations are prohibited
failed state
A state so weak that its political structures collapse, leading to anarchy and violence
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
the seazone extending 200 nautical miles from the coast over which a state has special rights as to the exploration and use of marine resources
ethnic separatism
desired regional autonomy expressed by a culturally distinctive group within a larger, politically dominant culture
ethnic cleansing
the mass expulsion or killing of members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in a society.

terrorism
Acts of violence designed to promote a specific ideology or agenda by creating panic among an enemy population

irredentism
a policy of cultural extension and potential political expansion by a country aimed at a group of its nationals living in a neighboring country
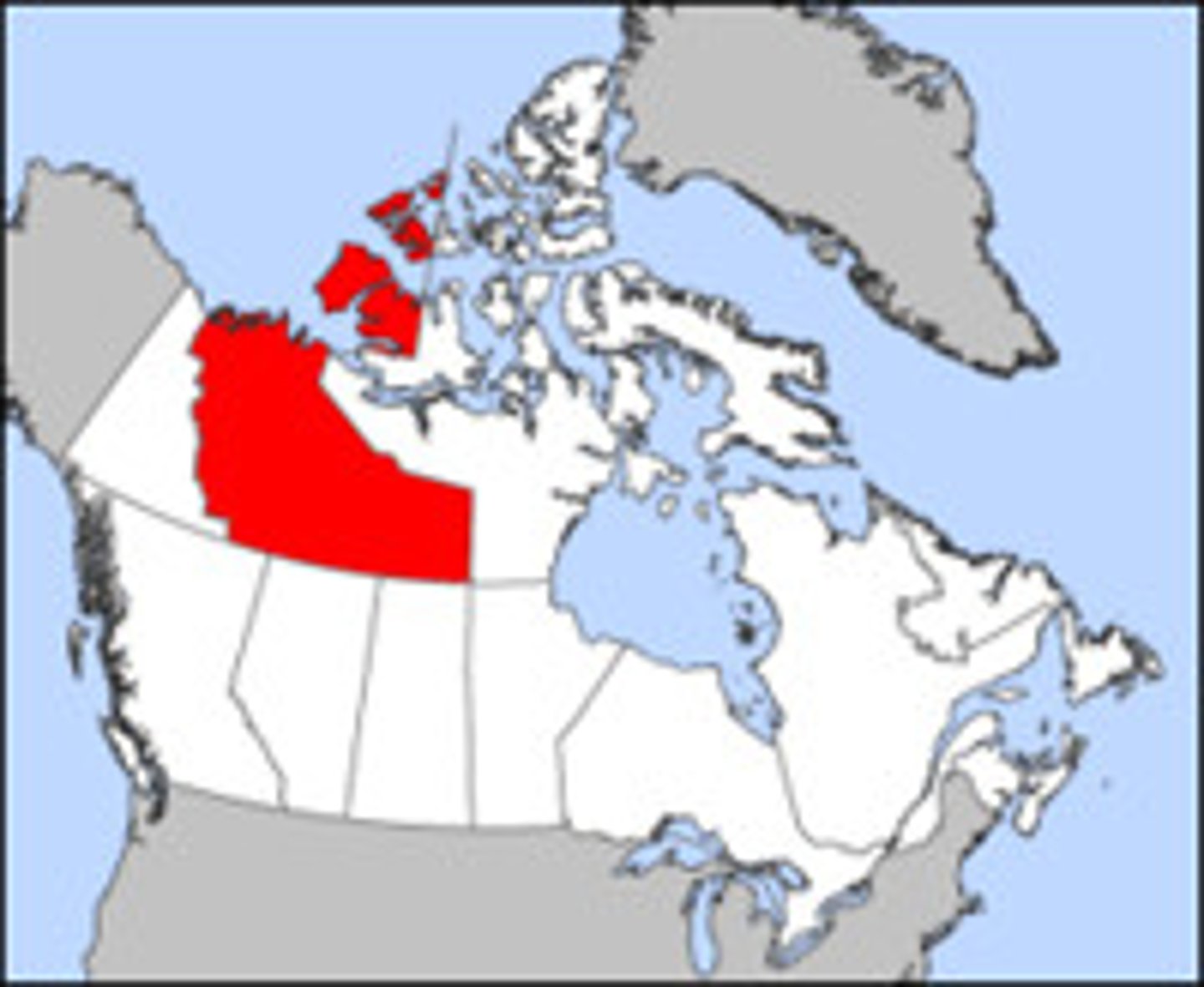
semi-autonomous region
an area which can govern itself in certain areas , but does not have complete power to govern (e.g. Nunavut in Canada, Puerto Rico and Native American reservation in the U.S.)
independence movements
a movement that is trying to gain political independence for some area that it thinks should be its own country
international sanctions
Actions taken by countries against others for political reasons, either unilaterally or multilaterally.

census
the official count of a population

reapportionment
the process of reassigning representation based on population, after every census
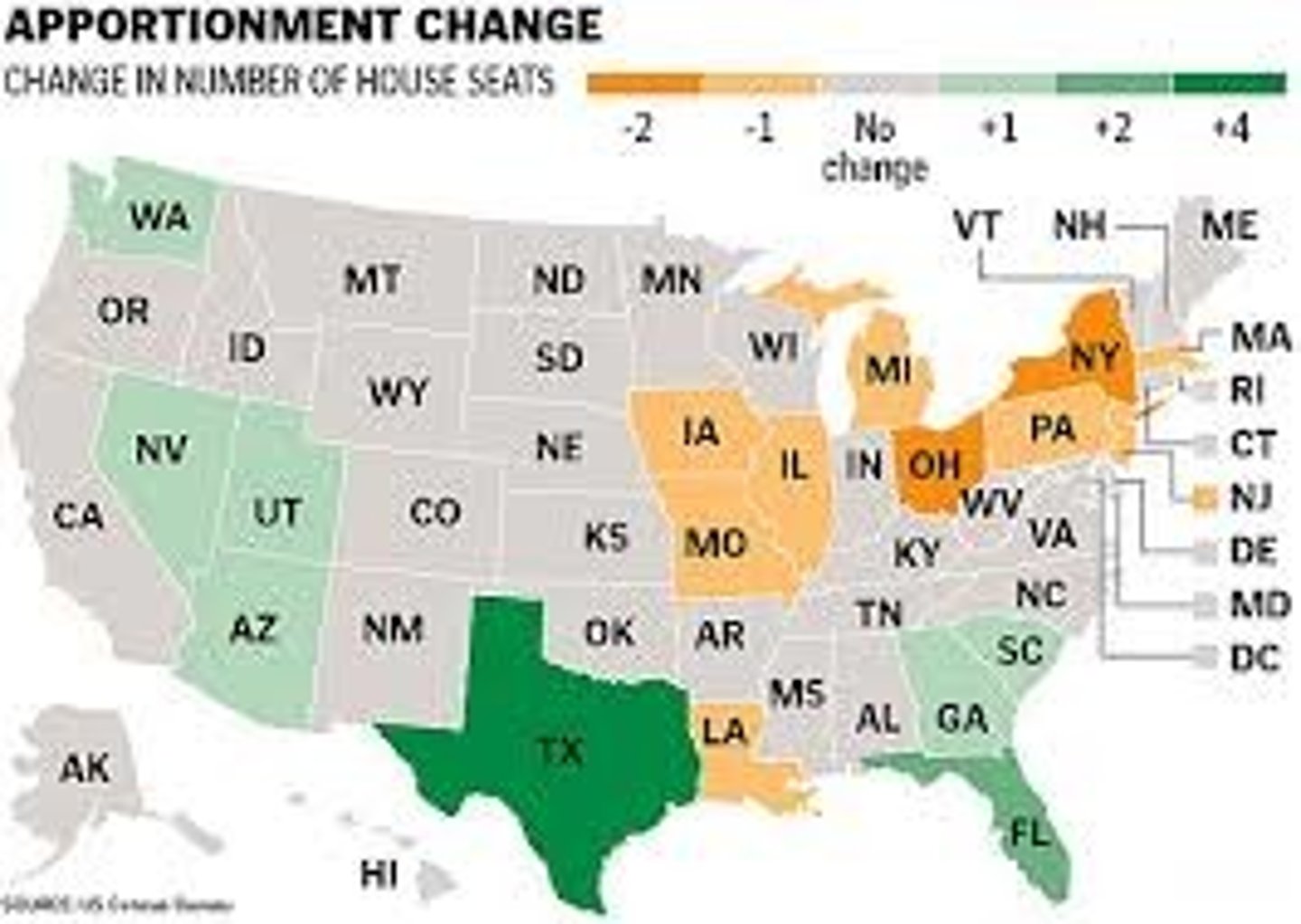
annexation
The adding of a region to the territory of an existing political unit.
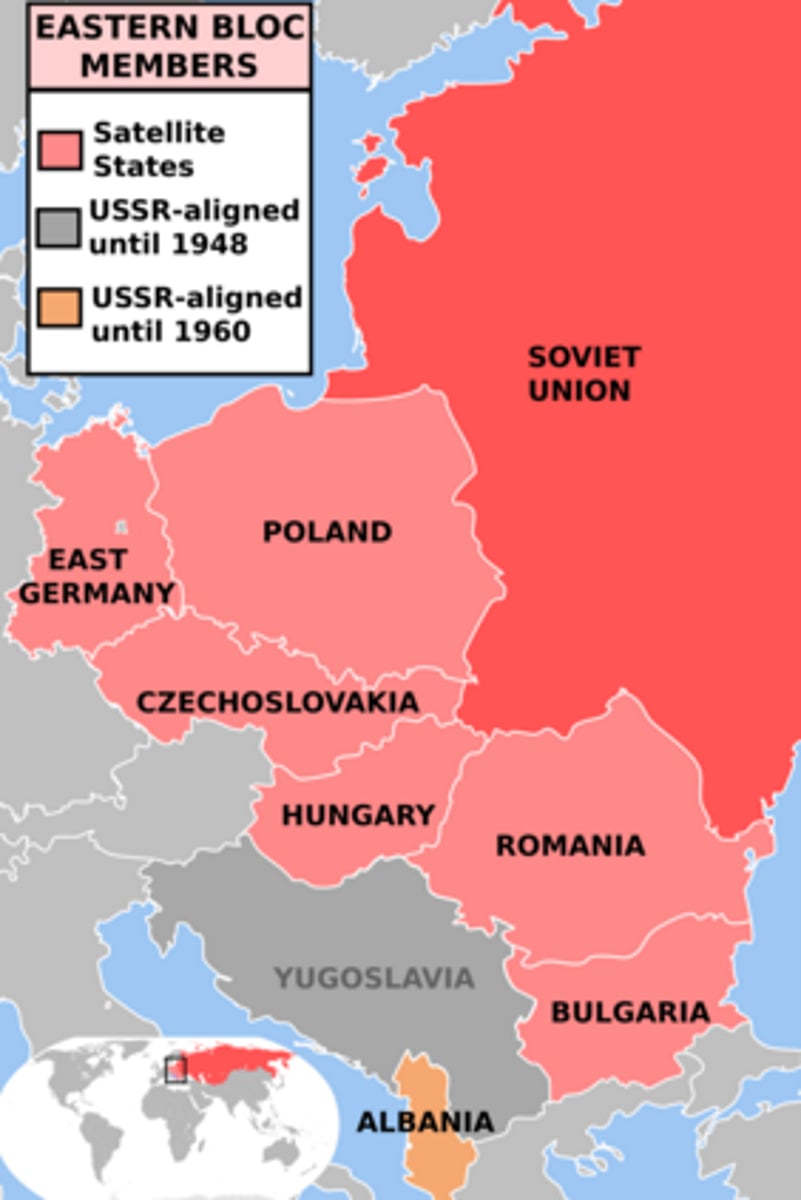
satellite state
A political term that refers to a country which is formally independent, but under heavy influence or control by another country.
genocide
the deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group or nation.
