Hygiene principles (diabetes and adrenal system disorders)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Type 1 (insulin deficient), type 2 (insulin resistant), gestational diabetes (occurs during pregnancy), other
What are the 4 major clinical types of diabetes.
7%
Diabetes mellitus affects approximately —% of the population. Almost 30% of these people are undiagnosed.
Hyperglycemia
abnormally increased concentration of glucose in the blood. This occurs from defective insulin secretion and/action. Chronic —————————— damages the eyes, kidneys, nerves (neuropathy), heart, and blood vessels (microangiopathy)
Ketoacidosis
Fruity acetone breath, excessive thirst (polydipsia), unusual hunger (polyphagia), frequency urination (polyuria), unexplained weight loss, weakness, nausea, dry skin and mucous membranes, flushed facial appearance, abdominal tenderness, rapid deep breathing, depressed sensory perception are cardinal signs and symptoms of what? Other symptoms include recurrence of bed wetting, repeated skin infections, malaise, drowsiness, headache, and marked irritability.
Type 1
Type — diabetes mellitus is characterized by sudden appearance of the following: constant urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, dramatic weight loss, irritability, weakness and fatigue, nausea, and vomiting.
Type 2
Type — diabetes mellitus is characterized by slow onset; includes any of the type 1 symptoms and/or the following: recurring or hard to heal skin, gum, bladder, infections, fatigue, blurred vision, tingling or numbness in hands or feet, and itching.
<70mg/dL
Dental hygiene care should not begin until the diabetic condition is controlled. If blood glucose levels are less than ——mg/dL, you should refer to a physician.
>240mg/dL
Dental hygiene care should not begin until the diabetic condition is controlled. If blood glucose levels are above ———mg/dL, you should refer to a physician.
80-100
Well controlled diabetes is characterized by blood glucose levels being within a normal range. (Concentration of ——mg/dL to ———mg/dL). Control is achieved through medications, diet, and exercise. Can be treated safely provided that their daily routine is not affected.
Ketoacidosis
The buildup of toxic acids in the blood
fasting plasma glucose
what does FPG stand for? This test should be taken after 8 hours of fasting?
Postprandial
What does PP stand for? This means that a test should be taken after eating a meal.
HbA1c
This is a glycated hemoglobin laboratory test indicating glucose levels over a 6-12 week period.
Stress
This causes the release of adrenaline. Adrenaline metabolizes glucose for, glycogen stored in the liver. Thus, this emotion can contribute to hyper glycemic condition becoming ketoacidotic.
Proinflammatory cytokines
Hyperglycemia progressively leads to an increase in these that destroy the connective tissue and bone. The chronic increased —————————— —————— levels augment inflammatory tissue destruction. Active periodontal infection can lead to a diabetic client becoming uncontrolled.
Gingival crevicular fluid
Increased glucose in the this may result in the proliferation of oral microflora, increasing risk of periodontal disease and caries.
B cells
In type 1 diabetes, these cells are destroyed so no insulin is secreted into the blood stream. There is no glucose in the body cell.
Type 2
In this type of diabetes, there is a periodic decrease in insulin secretion.
Adrenal glands
The ——————— glands are endocrine glands located at the superior pole of each kidney. Each gland contains an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Medulla functions as a sympathetic ganglion and secretes primarily epinephrine. The ——————— cortex secretes several steroid hormones with multiple actions.
Aldosterone
This is a hormone secreted by the adrenal gland of the kidney. It regulates salt and water balance by affecting renal distal tubules.
Cortisol
This is a hormone secreted by the adrenal gland of the kidney. It is anti-inflammatory, decreases bone formation, decreases muscle mass, increases blood glucose, increases glomeular filtration and modulates emotion. Often called the "stress hormone".
Androgens
These hormones secreted from the adrenal glans are associated with sexual maturation.
Epinephrine
Neurotransmitter secreted by the adrenal medulla (inner portion of the adrenal gland) in response to stress. Also known as adrenaline. Increases cardiac output
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter also secreted by the adrenal medulla (inner portion of the adrenal gland). Increases arterial pressure, and peripheral resistance.
Mineralocorticoids, all are derived from cholesterol (ex. Aldosterone), glucocorticoids (ex. Cortisol, primary glucocordicoid), and androgens (ex. Primarily testosterone).
There are 3 classes of adrenal steroids.
Aldosterone
This is an adrenal steroid (Mineralocorticoid). Essential to sodium and potassium balance. Promotes sodium retention, potassium excretion, and fluid retention. Maintenance of extracellular fluid. Its actions occur primarily on the distal tubule and the collecting duct of the kidney.
Cortisol
This hormone acts as an insulin antagonist. A wide variety of functions and effects which include: regulation of carbohydrates, fat, and protein metabolism, maintenance of inflammation, and maintenance of homeostasis during periods of physical or emotional stress. Also, increasing blood levels and peripheral use of glucose, and increasing liver glucose output. Peak levels of plasma ——————— is about the time of awakening in the morning. Periods of stress cause increased secretion of this hormone.
Glucocorticoids
Synthetic —————————— can affect the adrenal function. Cortisol like drugs are used in treatment of many diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, SLE, asthma, hepatitis, IBD, dermatosis, and mucositis. —————————— are used on a long term basis for patients during immunosuppressive therapy for organ transplants and joint replacements. In dentistry, corticosteroids are used during perioperative periods for reeducation of pain, edema, and Trismus after oral surgical and endo therapy.
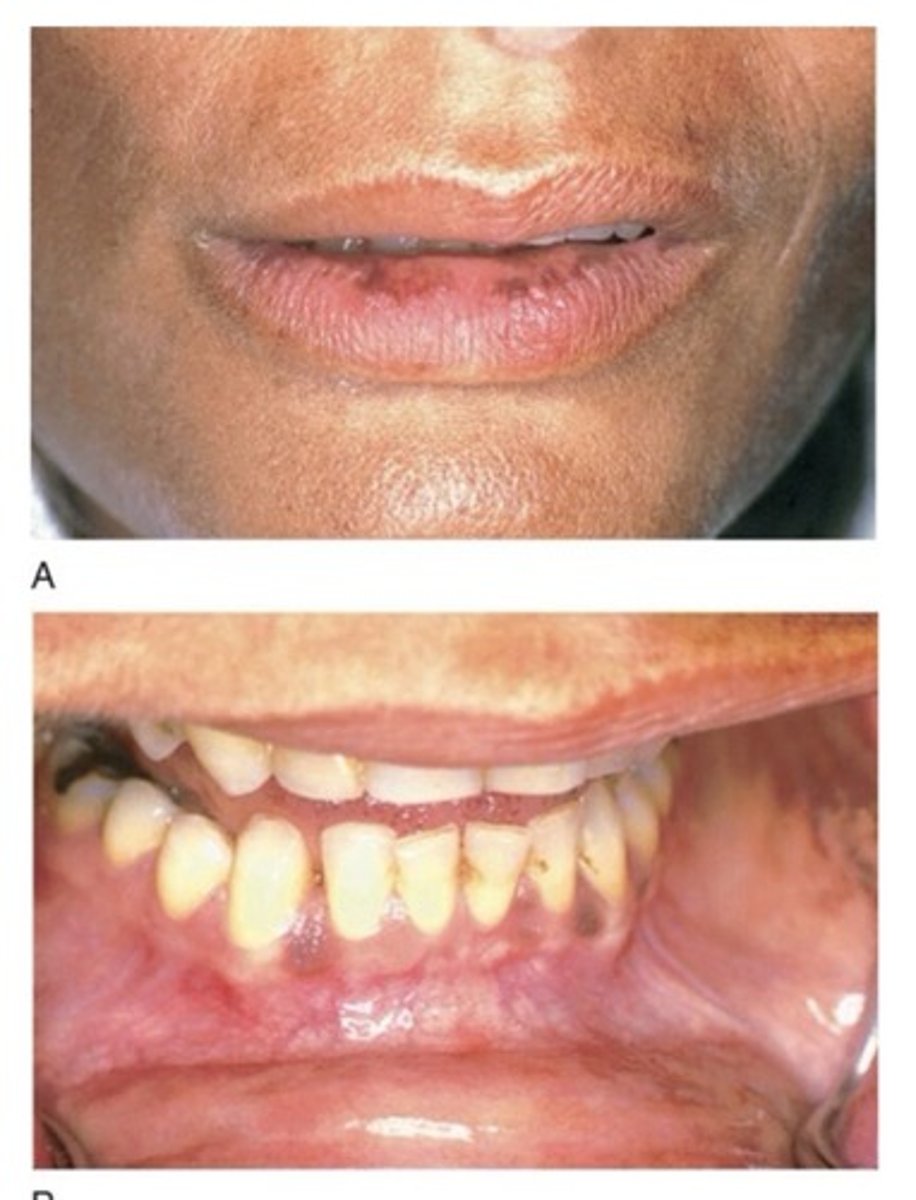
Addison's disease (Primary adrenocortical insufficiency)
This disease is caused by lack of cortisol and aldosterone. The lack of cortisol results in:
-impaired metabolism of glucose, fat, and protein
-hypotension
-increased ACTH secretion (hormone from the pituitary gland stimulates cortisol)
-impaired fluid excretion
-excessive pigmentation (bronzing of the skin)
-an inability to tolerate stress.
Aldosterone deficiency results in: inability to conserve sodium and eliminate potassium and hydrogen ions. This leads to hypovolemia (decrease in volume of blood plasma), hyperkalemia (too much potassium in blood), and acidosis (excessive acids in the body fluids).
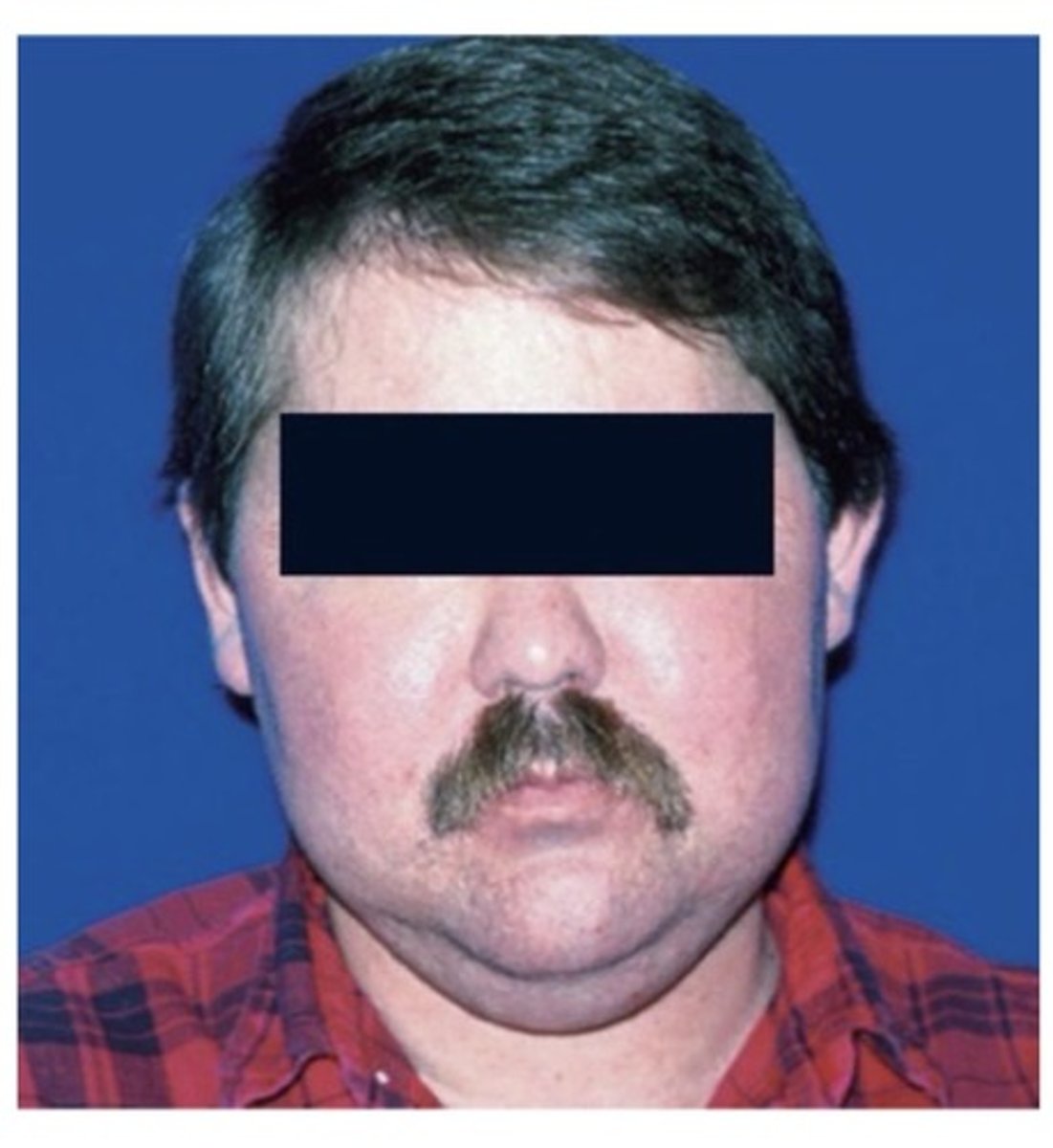
Cushing's syndrome (hyperadrenalism, glucocorticoid excess)
The most common form of hyperadrenalism is due to glucocorticoid excess (endogenous or exogenous). This is also known as ——————— ———————: produces weight gain, round or moon-shaped faces, a "buffalo hump" on the upper back, abdominal striae, hypertension, hirsutism, and acne. Other findings may include: glucose intolerance (diabetes mellitus), heart failure, osteoporosis and bone fractures, and impaired healing.
Blisebvowr [oiwr [goi
AO;WIERHGFIO[AWERHG[OIwhepih right