chapter 12
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
bacteria growth
increase in cell number, parent cell doubles in size and duplicates cell contents
budding
small new cell develops on the surface of an existing cell, yeast does this
binary fission
cell duplicates its contents and divides into two cells, most bacteria does this
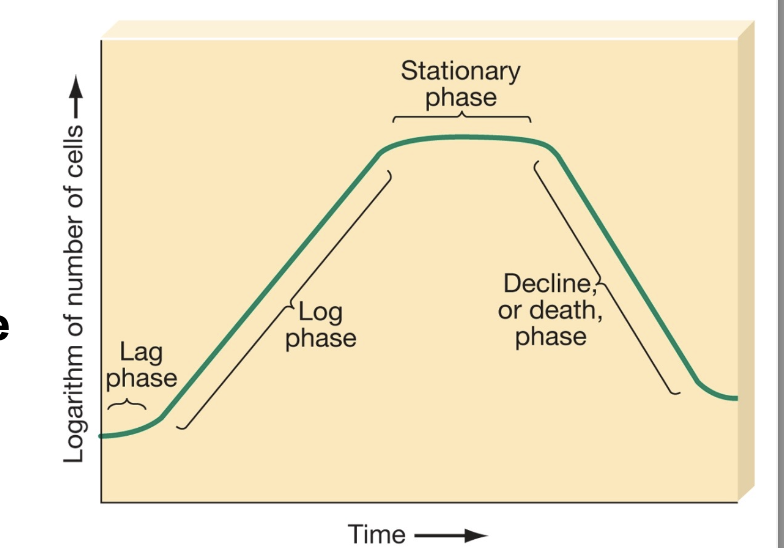
bacterial growth curve
Lag phase
organisms are active but not increasing that much in numbers
they are getting reading to divide by increasing in size
may be 1 hr to multiple days depending on species
Log phase
organism adapted to environment
growth occurs logarithmically or exponentially
dividing at their most rapid rate
can take 20 min to 20 hrs to double in size (generation time)
Stationary phase
limitation of nutrients
new cells produced at the same rate old cells die
Death phase
medium becomes less favorable
less nutrients, space, and more waste
dying at logarithmic rate
some produce spores
quorum sensing
molecular signaling system that lets other bacteria know what is out there and coordinate processes with each other like bio film
biofilm
large community of bacteria in one spot that is like a slimy layer and its a community where different bacteria have different jobs
sociomicrobiology
study of how bacteria behave and interact with each other
colony forming unit (CFU)
when a single bacterium is deposited on a plate it divides to form a colony
a colony is a distinct growth and clones from a single cell
count colonies to determine the number of cells on a plate
why are CFUs an underestimation
not every cell will survive on a plate
2 organisms might be too close so both colonies look like a single colony
nutritional requirements
2 ways to obtain CFUs
streaking for isolation
useful for getting single colonies
dilution plates
each amount of sample that you spread around the whole plate is diluted each time
useful for determining how many organism are in a specific sample
ways to count colonies
directly count CFUs on a plate
use a hemocytometer
put a sample of bacteria on a coverslip and slide with wells and a grid
count the number of bacterial cells in the squares of the grid
selective media
encourages the growth of some organisms but suppresses others
ex: MSA and MAC plates
MSA has high salt concentration so organisms that can’t survive in salty environments won’t grow
selective for gram + and differential for mannitol fermentation bc it has a pH indicator and has mannitol in it
differential media
has an ingredient that causes an observable change when a biochemical reaction occurs
ex: MAC, MSA
MAC differential for lactose fermentation bc it has a pH indicator and has lactose in it
turns yellow when there is not a lactose fermentor
also it is selective for gram - bacteria bc it has crystal violet and bile salts
enrichment media
has special nutrients in it for example blood agar and chocolate agar (lysed blood cells)
nutritional influences on bacteria growth
availability of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, trace elements, vitamins
physical influences
pH, temp, oxygen concentration, pressure, etc
temperature influence on growth
most enzymes have an optimal temp that is near the organisms optimal temp where the have the highest activity
when the temp gets too high the enzymes denature —> can’t carry out organisms function and organism dies
organisms that infect humans have similar optimal temp to humans
names of organism classifications at optimal temp
0-20º C —> psychrophile
15-45 —> mesophile
40-70 —> thermophile
70 - 100 —> extreme thermophile
pH influence on growth and classifications
enzymes work best at optimum pH and have a range
pH 0.1 to 5.4 —> Acidophile
Neutrophiles pH 5.4 to 8.0
Alkaphiles pH 8.0 to 11