Chemistry - Unit 3 Test Review
1/76
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What did Bohr propose in his model of the atom?
Bohr proposed that electrons travel in distinct orbits around the nucleus, with each orbit corresponding to a specific energy level.
What are energy levels?
Energy levels are the fixed energies an electron can have, with each level representing a specific distance from the nucleus.
To move from one energy level to another, an electron must _____ or ______ just the right amount of energy.
Gain or Lose
What is a quantum of energy?
The amount of energy required to move an electron from one energy level to another.
TRUE or FALSE: The energy levels of am atom are equally spaced.
False
What is the quantum mechanical model?
A model that describes the behavior of electrons in atoms as wave functions, incorporating principles of quantum mechanics and probability.
What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in an atom?
It determines the probable distribution of electrons in an atom (their positions in energy levels).
What is an atomic orbital?
A region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding an electron, characterized by specific shapes and energy levels.
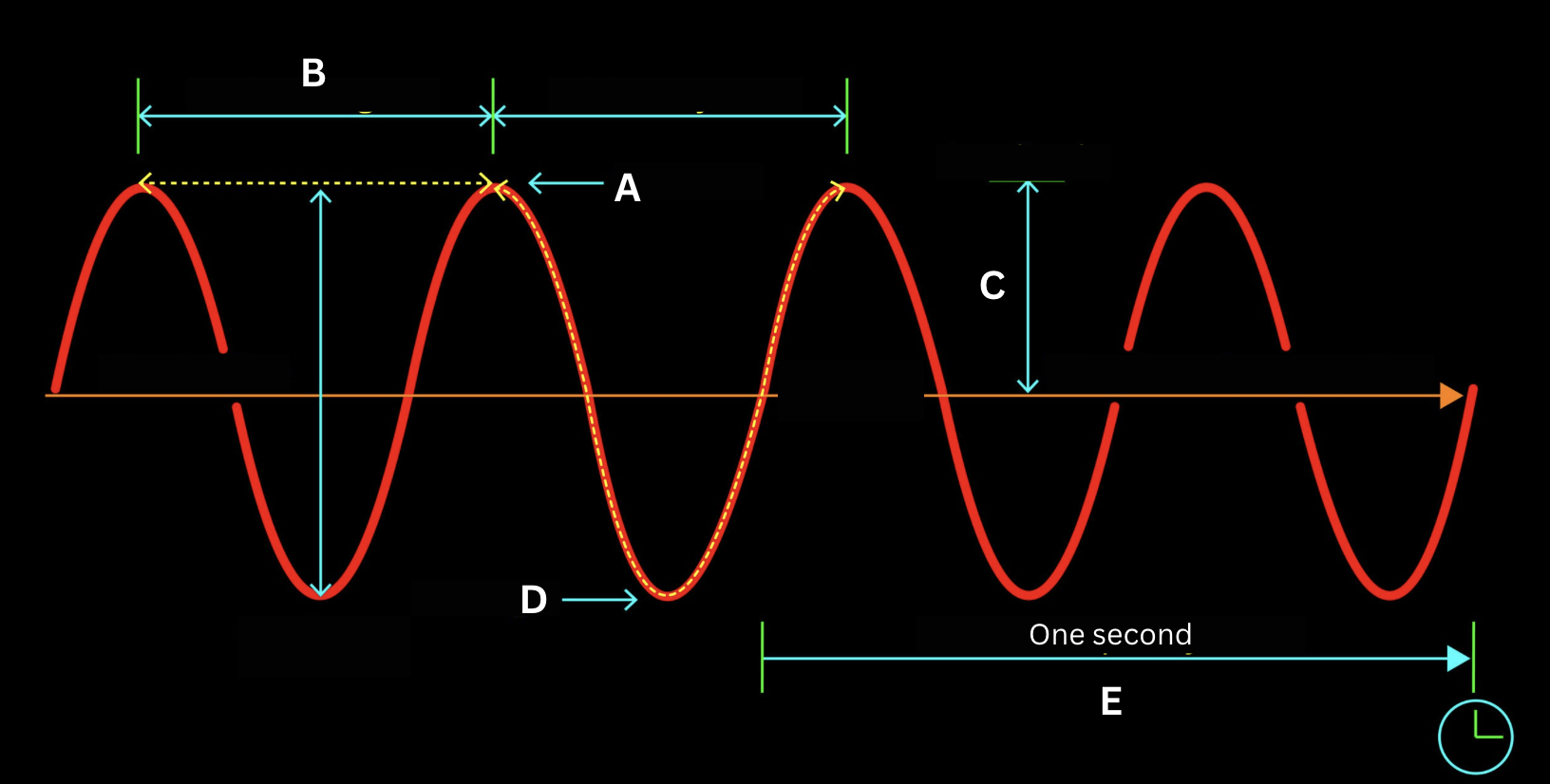
Identify the structure of the electromagnetic wave labeled by the letter A.
Crest
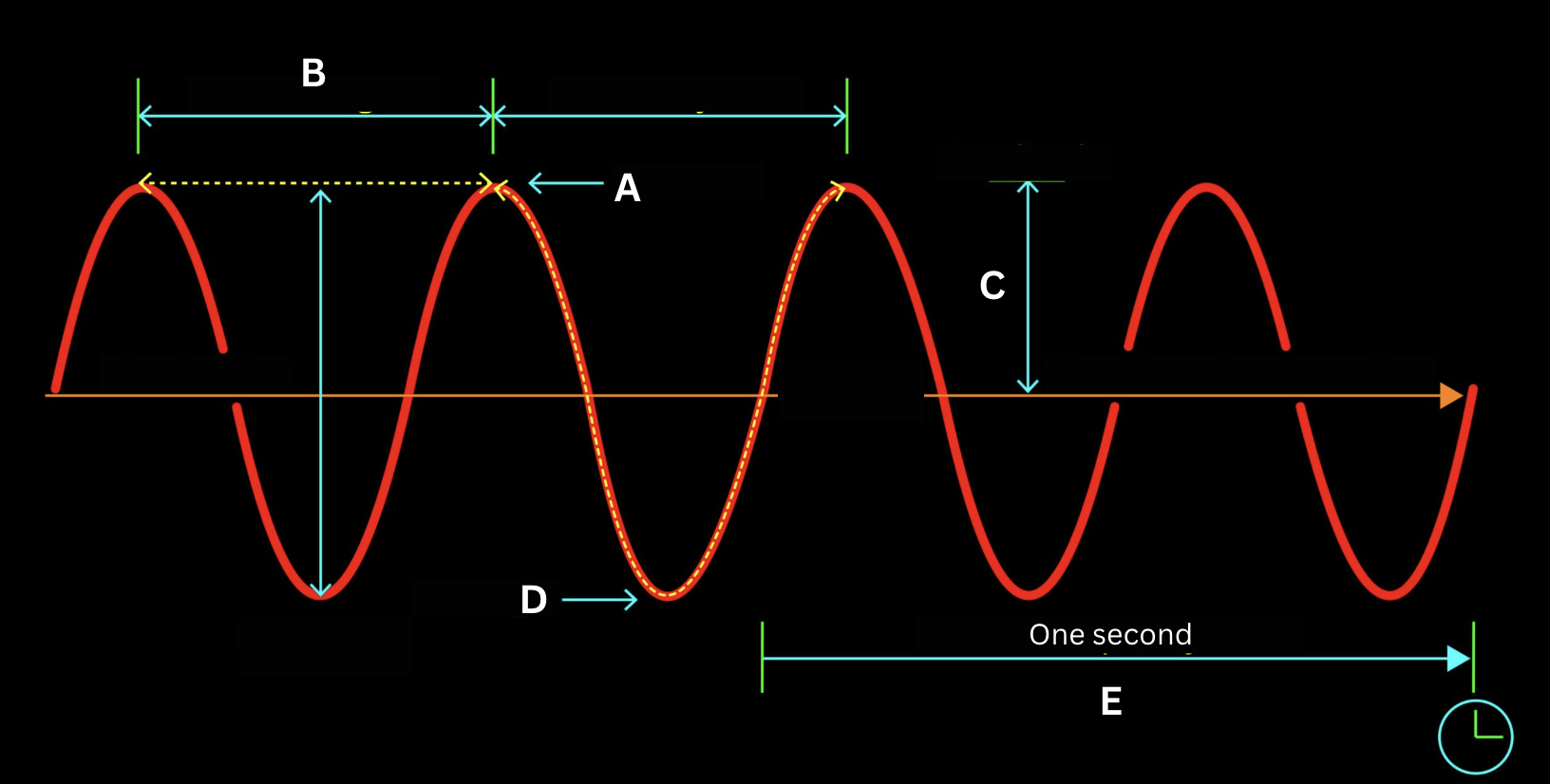
Identify the structure of the electromagnetic wave labeled by the letter B.
Wavelength
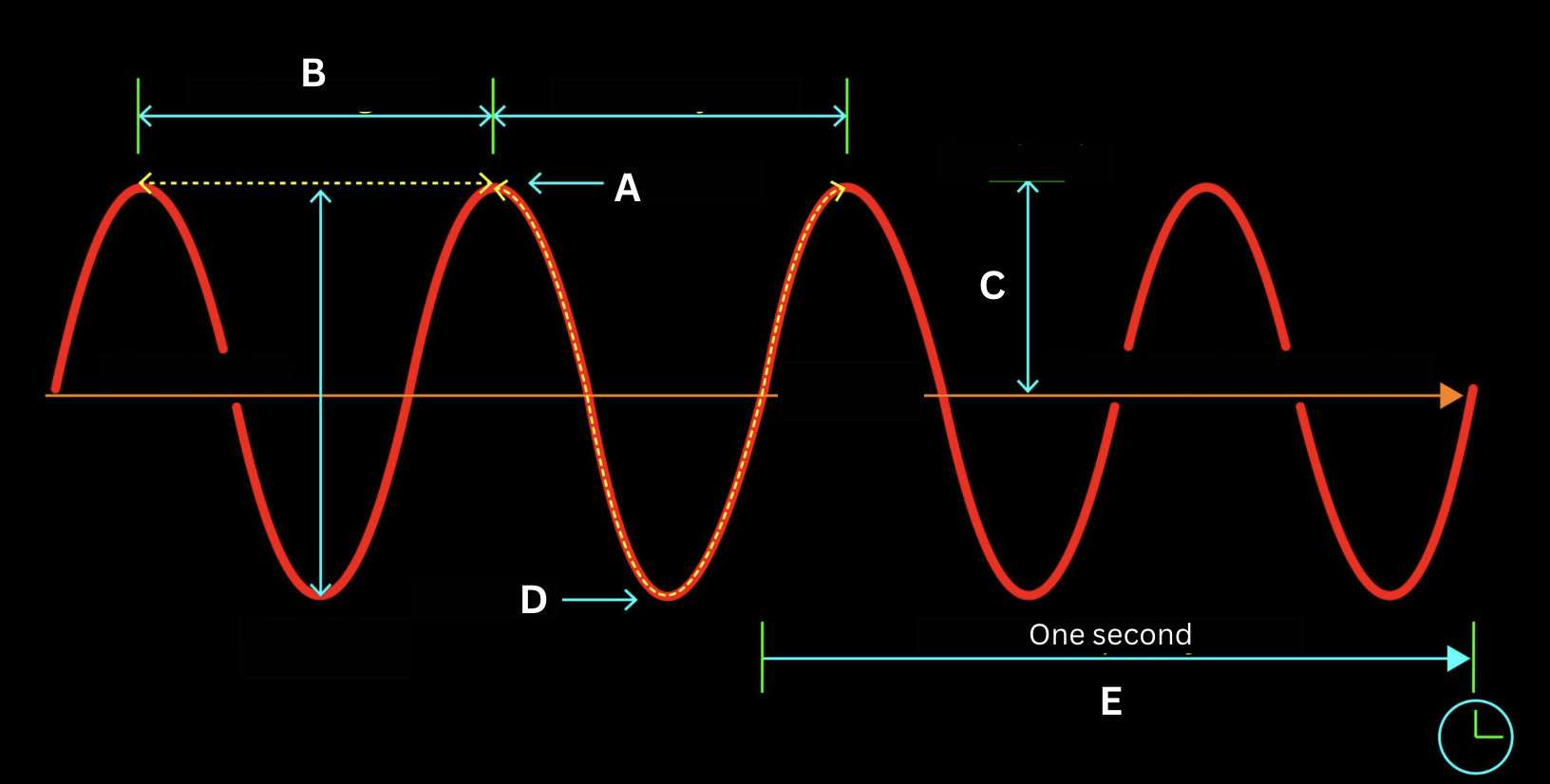
Identify the structure of the electromagnetic wave labeled by the letter C.
Amplitude
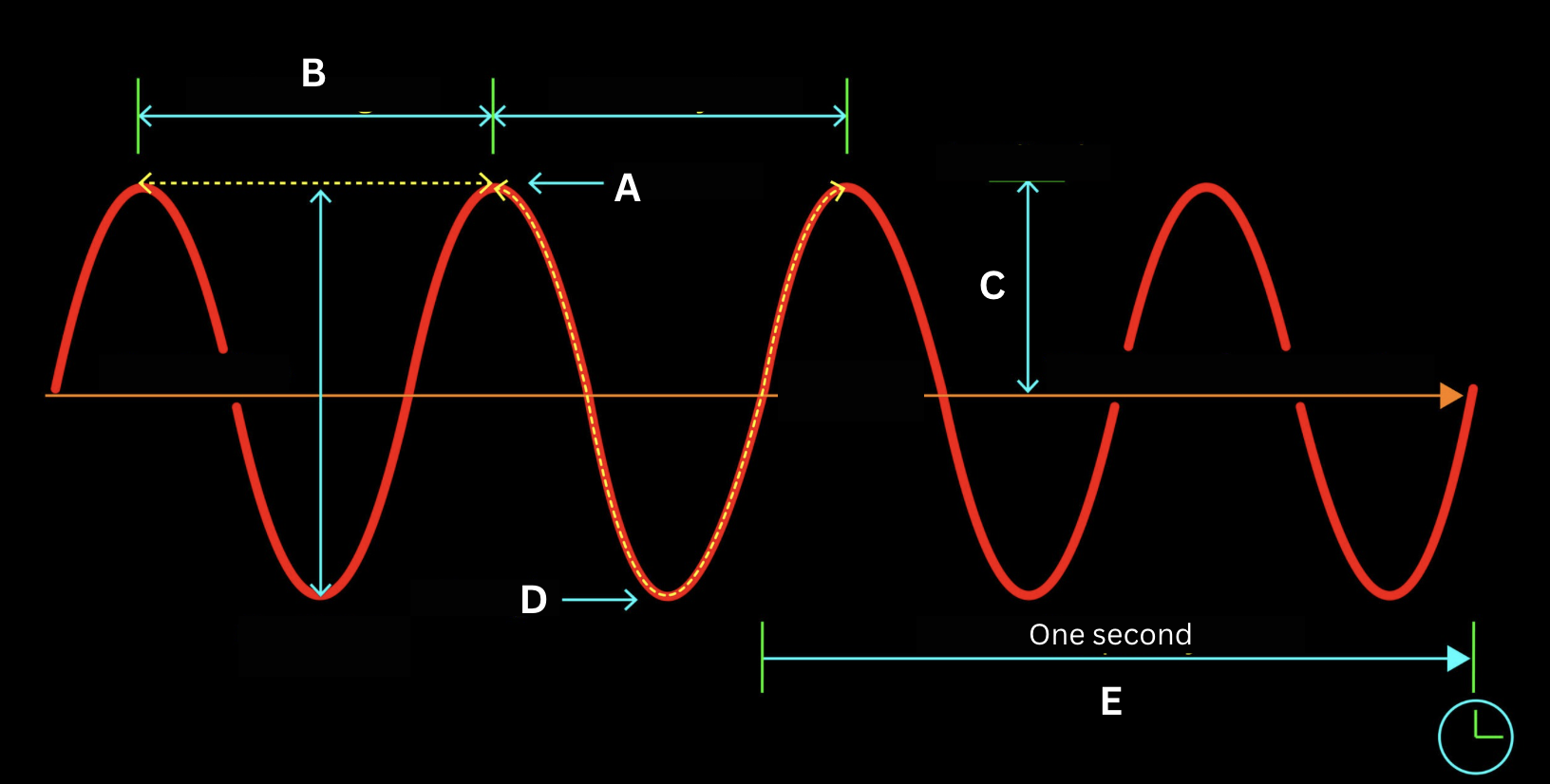
Identify the structure of the electromagnetic wave labeled by the letter D.
Trough
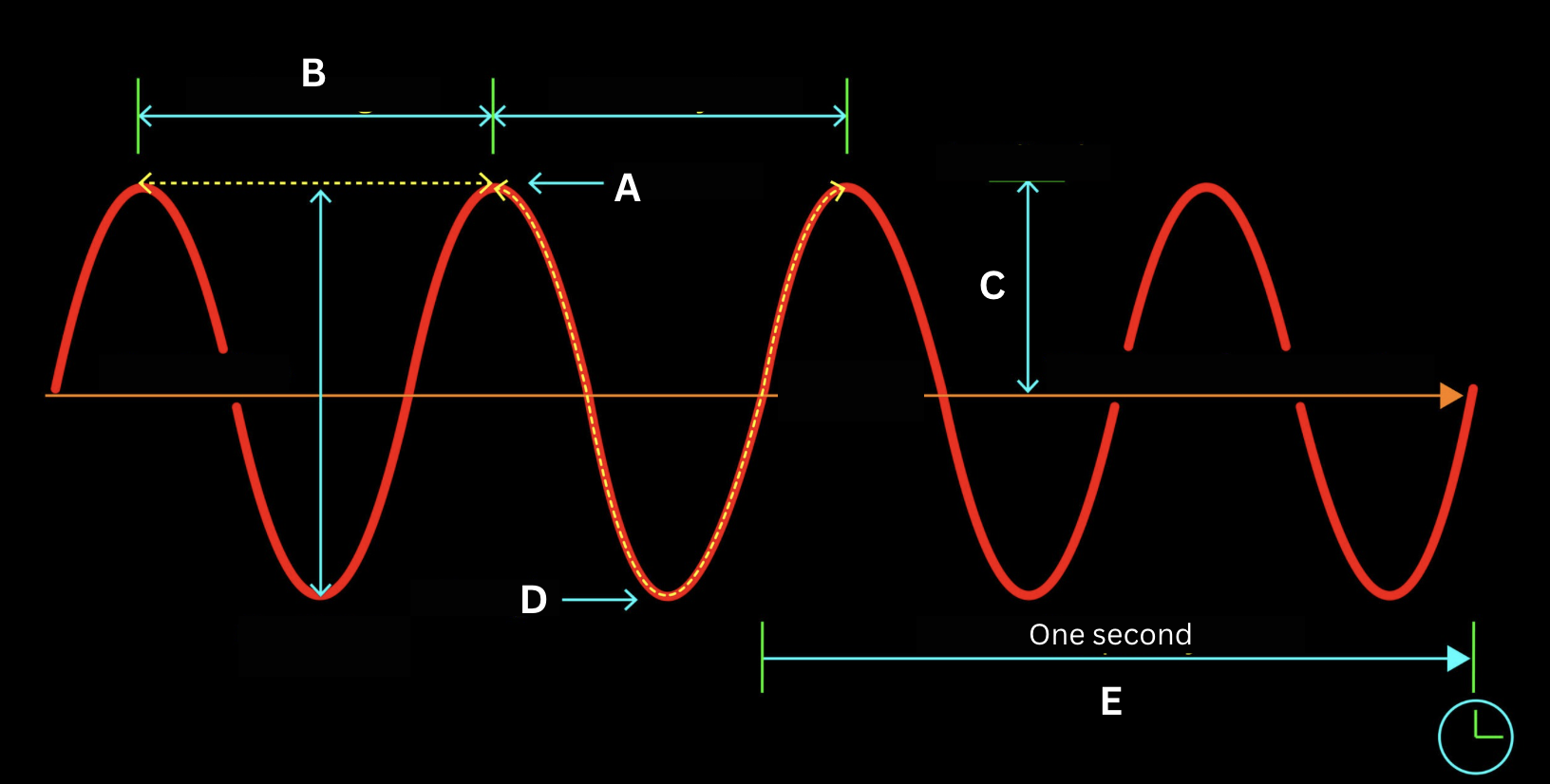
Identify the structure of the electromagnetic wave labeled by the letter E.
Frequency
______ light waves can be seen by humans.
Visible
TRUE or FALSE: Ultraviolet waves have the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency.
False
What does the electromagnetic spectrum represent?
The range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, radio waves, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What type of wave cannot be seen but felt by the skin?
Infrared waves
What type of wave is constantly used to communicate with satellites or listen to music in the car?
Radio waves
TRUE or FALSE: Can radar be used to measure the speed of moving objects?
True
Wavelength is represented by which Greek symbol?
λ - Lambda
What are the three units that can be used to describe frequency?
1/s, s^-1, Hz
Frequency is represented by which Greek symbol?
ν - Nu
What is the definition of the speed of light?
The speed of light is the distance a wave travels in a second, denoted by the symbol C. (3.0×10^8 m/s)
What is the equation that represents the speed of light?
The equation that represents the speed of light is C(m/s) = λ(m)ν(1/s).
What is the equation that represents energy?
The equation that represents energy is E(J) = h(J⋅s) ν(1/s). H represents Planck’s constant.
What is the significance of Planck’s constant in relation to energy?
Planck's constant (h) is a fundamental constant that relates the energy of a photon to its frequency, indicating that energy is quantized in discrete packets. (6.63×10^-34 J⋅s)
If an electromagnetic wave has a long wavelength, it will have a _____ frequency.
Low
What is a photon?
A photon is a quantum of electromagnetic radiation, representing a particle of light that carries energy proportional to its frequency.
What does the Aufbau Principle determine about electron configurations?
The Aufbau Principle states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before filling higher energy levels (ex. the 4s orbital is lower in energy than the 3d orbital).
What does the Pauli Exclusion Principle determine about electron configurations?
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers, meaning each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
What does Hund’s Rule determine about electron configurations?
Hund's Rule states that electrons will fill orbitals of the same energy singly before pairing up, maximizing the total spin.
What is the electron configuration for the element Krypton?
1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6 4s^2 3d^10 4p^6
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of the element Strontium?
[Kr] 5s^2
Write the electron configuration for a Sodium ion with a +3 charge.
1s^2 2s^2 2p^4
How many valence electrons are in a Neon atom?
Neon has 8 valence electrons. It is a noble gas with a full outer shell.
How many valence electrons are in a Potassium atom?
Potassium has 1 valence electron. It is an alkali metal and has a single electron in its outermost shell.
How many electrons can be held in an orbital? Why?
An orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons due to the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
How many orbitals are in the 2s sublevel?
The 2s sublevel contains 1 orbital.
How many orbitals are in the 4p sublevel?
The 4p sublevel contains 3 orbitals.
How many electrons are in the 1s sublevel?
The 1s sublevel contains 2 electrons.
How many electrons are in a d orbital?
A d orbital can hold a maximum of 10 electrons.
How many orbitals are in a d sublevel?
The d sublevel contains 5 orbitals.
How many orbitals are in an f sublevel?
The f sublevel contains 7 orbitals.
How many sublevels are in energy level 4?
Energy level 4 contains four sublevels: s, p, d, and f.
How many orbitals are in energy level 3?
Energy level 3 contains 9 orbitals: 1 s, 3 p, and 5 d orbitals.
Why does Copper’s electron configuration not follow the Aufbau principle?
Copper's electron configuration is an exception to the Aufbau principle because it achieves greater stability with a filled d subshell. Therefore, it has a configuration of [Ar] 4s¹ 3d¹⁰ instead of the expected [Ar] 4s² 3d⁹.
TRUE or FALSE: Metals are defined as malleable, lustrous, solid, and conductors of heat and energy.
True
What is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?
The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know both the exact position and momentum of a particle. This principle highlights the inherent limitations in measuring quantum systems.
What type of element ONLY forms positive ions?
Metals
What type of atoms has more than 4 valence electrons?
Nonmetals
What type of atom gives away electrons during chemical reactions?
Metals
What is a metalloid? What elements are considered metalloids?
Metalloids are elements that have properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. Common metalloids are boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and tellurium (Te).
Where are metalloids located on the periodic table?
Metalloids are located along the “staircase” that divides metals and nonmetals on the periodic table.
What is atomic radii?
Atomic radius is ½ of the distance between the nuclei of two joined atoms of the same element.
What are the trends among the elements for atomic size?
Atomic size generally increases down a group and decreases across a period from left to right due to the increasing positive charge in the nucleus and the addition of electron shells.
What is the modern period organized by?
The modern periodic table is organized by increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
Alkali metals occupy which group in the periodic table?
Group 1A
What are the elements in group 2A called?
Alkaline Earth Metals
What are the main characteristics of halogens?
Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals found in group 7A of the periodic table. They typically have seven valence electrons and readily form salts with alkali metals.
Elements within a group have the same number of ______.
Valence electrons
TRUE or FALSE: The majority of elements in the periodic table are metals.
True - metals make up about 75% of the periodic table.
What are the trends among the elements for atomic radii? Why?
Atomic radii tend to increase down a group due to the addition of electron shells, while they decrease across a period from left to right because of increasing nuclear charge, which pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
What is the correlation between atomic radii and electronegativity and ionization energy?
As atomic radii increase, electronegativity and ionization energy generally decrease. This is because larger atomic size means the outer electrons are farther from the nucleus, making them less tightly held.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond.
Why do electronegativity trends exclude the noble gases?
Electronegativity trends exclude noble gases because these elements already have a full valence shell.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.
How are ionization energy and electronegativity different?
Ionization energy refers to the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom, while electronegativity measures an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond.
What are the trends among the elements for ionization energy? Why?
Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group due to the increasing nuclear charge and distance from the nucleus.
How did Mendeleev organize his periodic table?
Mendeleev organized his periodic table by increasing atomic mass.
What is an ion? What are the terms used for positive and negative ions?
An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons, resulting in the atom being charged. Positive ions are called cations, while negative ions are called anions.
What are the trends among the elements for ionic size? Why?
Ionic size generally decreases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, while it increases down a group because of the addition of electron shells.
TRUE or FALSE: Anions are larger than the atoms from which they formed.
True
What is shielding?
Shielding refers to the effect where inner electrons partially block the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons, affecting their energy levels and reactivity.
What are the trends among the elements for shielding? Why?
Shielding increases down a group due to the addition of electron shells, which increases the distance between the nucleus and outer electrons, reducing effective nuclear charge. Shielding is constant across periods.
What are the trends among the elements for metal reactivity? Why?
Metal reactivity increases down a group as outer electrons are farther from the nucleus, making them easier to lose, while it decreases across a period from left to right.
What are the trends among the elements for nonmetal reactivity? Why?
Nonmetal reactivity increases up a group as the outer electrons are closer to the nucleus, making it easier to gain electrons. Across a period, reactivity increases from left to right due to higher electronegativity.
What is the octet rule?
The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons.