6.2.1 Cloning
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is cloning?
The process leading to the formation of a clone
What is meant by a clone?
A genetically identical copy of an organism
What are the advantages of cloning?
Only need one parent
Fast
More efficient
Same environment suitable for both parent and offspring
What are the disadvantages of cloning?
Reduces genetic diversity
No variation
Smaller gene pool
Organisms more vulnerable to environmental changes and disease
More likely to pass down recessive alleles
Selection is impossible
Could lead to overcrowding which increases competition
What process does natural cloning in plants involve?
Vegetative propagation
What is vegetative propagation?
Process of reproduction through the vegetative parts of the plant (rather than through reproductive structures)
Give 7 types of natural cloning in plants
Tubers
Leaves
Bulbs
Corms
Runners
Suckers
Rhizomes
Describe the process of natural cloning in tubers
Type of underground stem
e.g. potatoes
Tuber grows into one or more plants
These then go on to produce many new tubers
Describe the process of natural cloning in leaves
Clones grow on leaf margins
These drop off the leaf and take root
Describe the process of natural cloning in bulbs
Type of fleshy underground stem with fleshy leaf bases
e.g. onions
Over-wintering mechanism
Contains one or more apical buds
Each of these apical buds grow into a new plant in the spring
Describe the process of natural cloning in corms
Type of solid underground stem with scaly leaves and buds
Over-wintering mechanism
Remain in the ground over winter
The buds form new plants in the spring
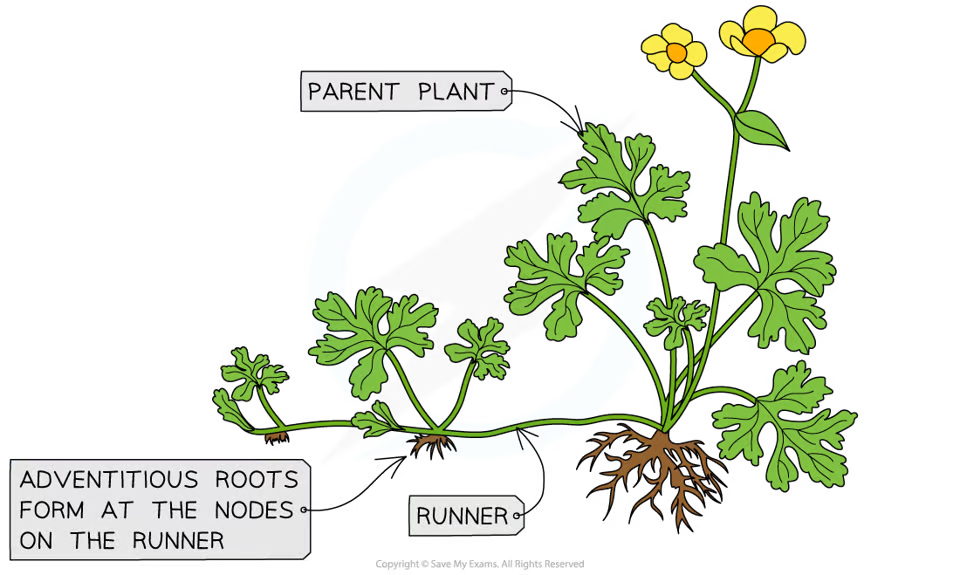
Describe the process of natural cloning in runners
Plant have horizontal stems (called runners) that form over the soil surface
Root forms under nodes of runners
Runner dies when the plant can survive by itself
E.g. strawberry plants
Describe the process of natural cloning in suckers
Plant has a horizontal stem (sucker) that grows from the root of many trees and shrubs
The sucker dies and the new stem grows as a separate organism
E.g. cherries
Describe the process of natural cloning in rhizomes
Plant has a horizontal stem (rhizome) that grows horizontally underground
The rhizome dies and the new stem grows as a separate organism
E.g. ginger
What are the advantages of vegetative propagation in agriculture?
Some plants cannot reproduce sexually
Quicker than growing from seed/ sexual reproduction
Produces uniform yield with predictable quality
Easier to harvest
Can be done at any time of year
What are methods of artificial cloning in plants?
Tissue culture AKA micropropagation
Cuttings
What are different types of cuttings?
Root cuttings
stem cuttings
leaf cuttings
scion cuttings (dormant woody twigs)
How are plant cuttings used as a cloning technique?
Use a healthy shoot cut from a healthy plant
Cut stem at a slant between nodes
Dip in rooting powder. Rooting powder contains auxin which promotes mitosis and cell differentiation
Roots grow
Cutting placed into soil
Cover with plastic bag to reduce transpiration
What is tissue culture or micropropagation?
Series of techniques used to grow new tissues, organs or plants from certain tissues cut from a sample plant
Why is tissue culture/ micropropagation only possible for plants and not for animals?
many plants cells are totipotent, unlike animal cells
So an entire plant can be reproduced from any of these cells
Describe the process of micropropagation/ tissue culture
A sterile environment should be used to prevent contamination of fungi or bacteria
Cut the plant into small pieces, called explants
Sterilise explants using dilute bleach or alcohol
Place explants in sterile growth medium. This contains suitable nutrients and plant growth substances needed e.g. auxin and cytokinin
This stimulates the cells of each explant to divide by mitosis to form a callus (mass of undifferentiated totipotent cells)
Grow different clumps in different growth media so they differentiate into different plant tissues
Transfer tiny plants to a greenhouse to allow it to grow further
What are the advantages of artificial cloning in plants?
Offspring has same desirable characteristic
Fast
Can be carried out where sexual reproduction is not possible
Grow plants that are hard to grow from seeds
What are the disadvantages of artificial cloning in plants?
Tissue culture is labour intensive
Expensive to set up facilities
Susceptible to same pests and diseases
Can lead to rapid spread of disease as no genetic variation
Compare the equipment and techniques of taking cuttings with those used for micropropagation
Micropropagation needs more equipment
Micropropagation needs more skills
Micropropagation produces more clone offspring
What are examples of natural cloning in animals?
Identical twins
Some small animals that reproduce asexually e.g. aphids
How are identical twins formed?
Egg is fertilised by sperm
Forms a zygote
Zygote undergoes a few mitotic divisions to form an embryo
Embryo splits in two to form two identical embryos
These grow to result in the birth of two identical offspring
What are three methods of artificial cloning in animals?
Artificial embryo twinning (reproductive cloning)
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) (reproductive cloning)
Therapeutic cloning (non-reproductive cloning)
How does embryo twinning produce artificial clones?
Embryo is divided into two half embryos
These are inserted into a surrogate mother
The surrogate mother gives birth to identical twins
How does somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) produce artificial clones?
Animal to be cloned donates a somatic (body) cell
The egg cell is extracted from the egg donor and enucleated (nucleus is removed and discarded)
The nucleus from the somatic cell is injected into the enucleated egg cell
The hybrid zygote cell is treated to encourage it to divide by mitosis
The embryo is implanted into the surrogate mother for gestation and birth
What is an example of SCNT being used?
Dolly the sheep
What is the use of therapeutic cloning?
Clone cells to replace dead or damaged cells that cause a loss of function in an individual
How does therapeutic cloning produce artificial clones?
Embryos are cloned as in reproductive cloning
Embryos are removed and subdivided
Each embryo cell is a totipotent stem cell that can be cultured and artificially differentiated into any type of specialised cell
What are some examples of conditions that therapeutic cloning can be used to treat?
Parkinson’s Disease
Diabetes
Grow organs for organ transplants (so no rejection)
What are some uses of reproductive cloning?
Livestock farming
Clone animals with desirable characteristics for maximising agricultural output
Help preserve endangered species
Remove less desirable characteristics from the gene pool over time
What are some arguments for artificial cloning in animals?
Produces many animals with desirable characteristics
Produces many animals with unusual combinations of characteristics
Clone individuals from endangered species to increase yield
Use to research effects of genes and hormones
Use to test medicinal drugs, so don’t need to test on animals or people
Used in repairing damage caused by disease or accidents
What are some arguments against artificial cloning in animals?
Lack of genetic variation
Increases risk of whole herd to diseases and pests
Doesn’t increase genetic diversity
Animals produced with little regard for their welfare
Poor success rate of adult cell cloning
Adult cell cloning is expensive
Cloned animals may be less healthy and have shorter life spans
Ethical issues surrounding embryo use in research: is it right to create life simply to destroy it?