NeoPeds Final
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
92 questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What are the 5 stages in embryonic lung growth?
Embryonic Period
Pseudoglandular Period
Cannalicular Period
Saccular Period
Alveolar Period
What is happening in the Embryonic Period? (Day 26-52) ?
Development of the trachea
Lungs are small buds arising from the esophagus
What is happening in the Pseudoglandular Period? (Day 52- W16)
Subdiving (bronchial branching) of the conducting airways begin
Cilia appear
What is a baby called when born in Pseudoglandular Period?
Fetal dimis (baby born dead)
What is happening in the Canalicular Period? (Week 17-29)
Lung lobes are now recognizable
Alveolar ducts are formed
Type 1 (form alveolar capillary membrane) and Type 2 (begins producing surfactant) primitive alveoli develop
What is happening in Saccular Period? (Week 26-36)
Alveoli are beginning to develop
Good development of Surfactant
What is happening in the Alveolar Period? (Week 36- term)
Alveoli are still groing and everything is just increasing in number
What is surfactant?
Phospholipids (PC)
Phosphatidylglycerol (PG)
Neutral lipids
Protiens
What is the purpose of surfactant and what does it do?
It helps reduce surface tension allowing lung expansion and make it easier to breathe
When does immature surfactant appear?
Anything before 35 weeks
When does mature surfactant appear?
At 35 weeks (PG)
What are ways to detect surfactant is present in a baby?
Look at amniotic fluid
Level of PC L/S (Lecithin/Sphingomyelin) 2:1
How do we know when lung maturity is determined?
When L/S ratio is at 2:1
What is the pressure difference between right and left heart pressure wise for baby circulation?
Baby in utero right side is stronger when born left is stronger ???
How does the blood flow from the placenta to the baby?
Deoxygenated blood goes through arteries (Fetus to mother)
Oxygenated blood goes through veins (Mother to fetus)
Shunt that is encountered??? Confused
How does the flow of blood look in a baby compared to an adult?
SVC/IVC- RA- Tricuspid valve- RV- Pulmonary valve- PA- Lungs- PV - LA- Mitrial Valve- LV- Aortic valve- Aortia
What does the baby have in the heart as a afetus compared to what adults have?
PDA
Ductus Arteriosis
Describe maternal history risk factors?
Previous C-section
Hx of Placenta previa or abruption
Hx of birth trauma
Congenital anomalies
Recurrent spontaneous abortions
Premature delivery
What is Preeclampsia and what problems can be associated with it?
Blood pressure higher than 160/110
Proteinuria
Pulmonary edema
Thrombocytopenia
Headache
Grand mal seizure
Describe the two amniotic fluid disorders?
Polyhydramnios
Oligohydramnios
What is Polyhydramnios?
Too much fluid, indicates problem with fetus swallowing (neuro disfunction)
What is Oligohydramnios?
Too little fluid indicates problem with urinary system (kidney function)
What are some signs of preterm labor?
Back pain
Menstrual like pains
Pelvic heaviness
Vaginal discharge
Vaginal bleeding
What are some complications to preterm labor?
Sepsis
RDS
Retinopathy
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Cerebral palsy
Hemorrhage
Necrotizing entercolitis (esophagus death )
What are some interventions to stop pre-term labor?
Intravenous hydration
Magnesium sulfate
Indomethacin
Positiong (put mom on side)
B-mimetic (rarely used)
When there is fetal asphyxia what can happen to the babies lungs?
Neonate unable to generate negative force to open alveoli and push out fluid
How can fetal asphyxia occur with a fetus?
Cord getting wrapped around neck ??? Nuchal Cord
What is primary apena with a baby?
infant will respond to stimulation by re-initiation of bx.
What is secondary apnea with a baby?
Asphyxia continues, the infant begins irregular gasping respiratory efforts which then slowly decrease in frequency
What is intrauterine asphyxia?
What happens to the cardiovascular system when there is periods of intrauterine asphyxia?
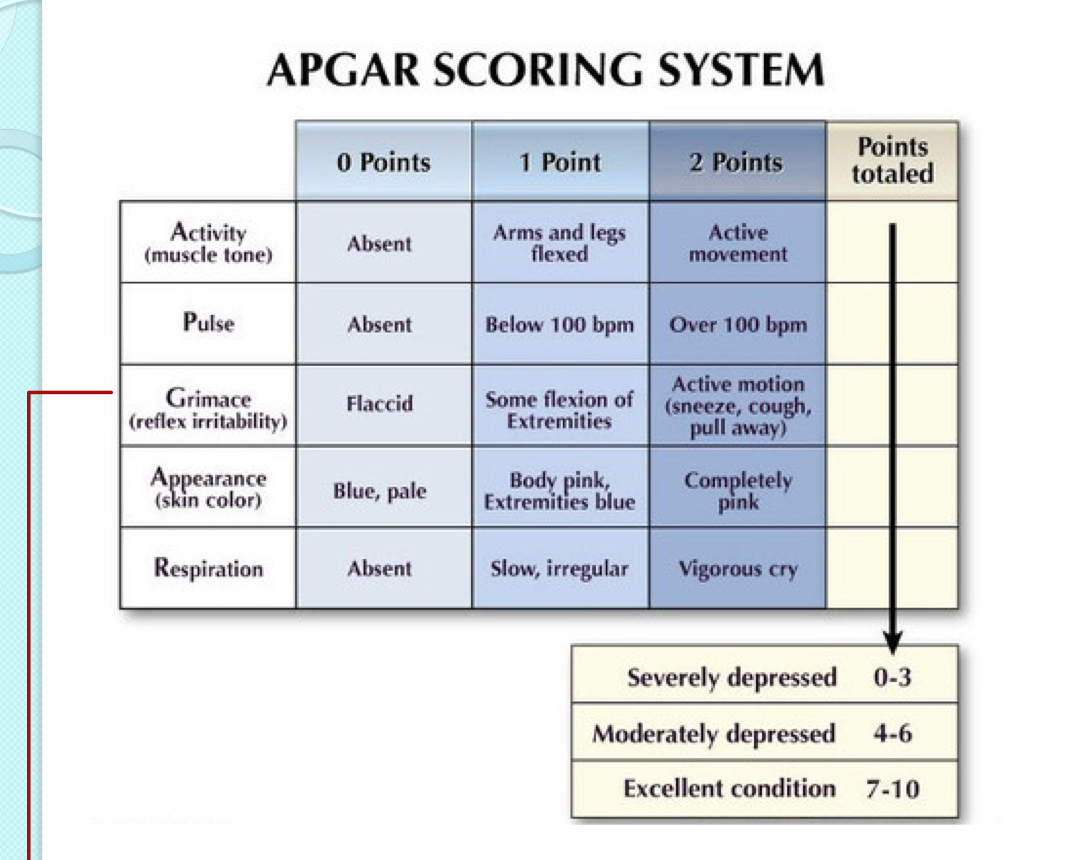
Know how to give an appropriate Apgar Score when provided with pt data?
Appearance (Color)
Pulse (HR)
Grimace (Response to Stimulation)
Activity (Muscle Tone)
Respirations
Know what is included in the gestational age assessment ? (Ballard Score)
Ear recoil
Sole creases
Skin appearance
Lanugo (hair)
What is vernix?
Helps protect baby skin and helps it stay not dry
At what age does Vernix appear in which gestational age?
20-24 wks by 36 weeks begins to disappear
Be able to tell the gestational age of a pt with the information from the slides
Put the gestational age chart and example of foing the chart
Know what gestational age gelatinous and transparanent skin forms?
25-26 wks- gelatinous by 35 weeks starts to flake
Pectin products for skin
Know what gestational age you find Lanugo?
Usually all over body at 26 weeks
Usually gone by 32 weeks
Know what gestational age you will find sole creases?
26 wks small creases appear
30 wks creases cover top portion of sole
34 wks creases cover 2/3 of sole
When does Ear recoil appear?
34 wks cartilage forms
When does Breast Tisue appear?
By 27 wks small bud of tissue develops
Know the purpose for the physical exam of the neonate?
Not everyone knows how far along they actually are
The nature of respirations includes what values?
Know what causes Jaundice?
Low bilirubin levels turns skin yellowish color
Know the importance of encironmental control?
Cluster care ???
Know some skin care recommendations for premature neonates?
Pectin bases tape
Why is the skin of the preemie sensitive?
there skin hasnt fully developed its protective layer
What do we do or give if an infants bilirubin levels are too low?
phototherapy
Know what is included withing the pulmonary examination?
Auscultation
Palpation
Percusion
Inspection
Know what lab tests are performed on respiratory disease pt?
Know why PFT’s in neonatal and pediatric pt are hard to measure and the special considerations involved?
Pt Cooperation
Environment
Know the CXR positoins and which one you would use for an intubated pt?
What will you see on a baby xray with asthma?
Hyperinflation
Hyperlucent (Airtrapping) DARK
What will you see on a baby xray with meconium?
Bilateral infiltrates (chunky)
Air trapping
what will you see on a baby xray with CF?
Over airfilled
Mucus plugging
Hyper-aeration
what will you see on a baby xray with ARDS?
Fluffy infiltrates
Light lung appearance
what will you see on a baby xray with TTN?
Stringy infiltrates
Hyper-aerated
Fluid filled streaks
What is a diaphragmetic hernia?
Opening in diaphragm that allows abdominal organs to migrate into chest cavity
No bagging but intubate asap
What will you see with a diaphragmatic Hernia?
Sunken abdominal canity
Barrel chest
Vital deterioration
Decrease BS
Bowel sounds in chest
How do we fix diaphragmatic hernia?
Surgery
What is PIE have on a CXRAY actually? (Pulmonary interstital emphysema)
Atelectasis
Small dark streaks and cysts
Black paint flicked onto with background
Know the normal structures important to an RT on an X-ray ?
Heart
Ribs (bones)
Diapghram
Airways
Lungs
Organs in upper abdomen
What are indications to do an ABG on a neonatal or pediatric baby?
Signs of RD
Change in clinical course without reason
Post ventilator change
Ensure proper ventilator settings
Assess oxygenation and ventilation
Know the difference sources of blood collection for neo/peds pts?
Umbilical Artery
Brachial
Radial
Temoral artery
Femoral
Capillary stick
Know about pulse oximetry?
Contains 2 LEDs
Light passes through blood and tissue
measures SpO2 level
transcutaneous monitoring ?
Measures oxygenation at the tissue
Can cause burn
Dont use as often
What are the indications/contraindications for CPAP?
Cardiac instability (contraindications)
Decrease WOB (indications)
Improve oxygenation (indications)
Understand the physiologic effects of CPAP?
Physically holds alveoli open during exhalation
Needs spontaneous breaths
When would CPAP be considered a failure in when use on pediatric and infant pts?
Identify commonly used to delivery systems and interfaces?
Identify advantages to using CPAP over mechanical ventialtion?
Describe how to manage pts recieving CPAP?
Identidy common complications and how they can be avoided?
Know how to wean a pt off of CPAP?
How can adjustments in inspiratory and expiratory Positie airway pressures affect respiratory function?
Describe the effects of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation on respiratory function?
Describe NPPV on respiraoty function for babies
Identify respiratory disorders in infants and children most amenable to trial of noninvasive ventialtion?
What disorders are most common to need NIV before Invasice
Identify common complications/Contraindications to NPPV?
Determine inital vent settings for various pt sizes?
Explain when mechanical ventilation is indicated in neonatal and pediatric pts?
I
Identify potential complications associated with mechanical ventialation and how to minimize these complications?
Foe example talk about how high VT can cause baratrauma and significantly hurt the baby
What does pressure control do?
Bx are delivered with a preset pressure during the set time and frequency
Volumes vary
What does volume control do?
Delivers a set volume during a preset time and frequency
Pressures will vary
What does dual control breath PRVC do?
Takes a set Vt while regulating pressure
Pressure varies
What control do we normally put babies on?
Pressure control
How would we wean a baby from MV?
When would be a good time to try to wean a baby?
What is HFOV?
Describe the relative role frequency and tidal volume play during high-frequency ventilation?
Settings, Indications and Complications associated with HFV?
Review etiology, assessment and major alterations of the lungs and management of IRDS?
Review etiology, assessment and major alterations of the lungs and management of PPHN?
Review etiology, assessment and major alterations of the lungs and management of TTN?
Review etiology, assessment and major alterations of the lungs and management of MAS?
When do we know when to give surfactant?
What kind of surfactant is there to give to babies?
Know the difference cardiac instabilities?
K
Know the Hemodynamics of a baby?
Know how to figure out a R to L and a L to R shunt?