Microevolution
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is microevolution?
1. evolutionary change within a species or small group of organisms, especially over a short period.
2. small, measurable evolutionary changes within a population from generation to generation.
How is antibiotic resistance related to microevolution?
Bacteria can evolve in a short period of time in response to environmental pressures (antibiotics).
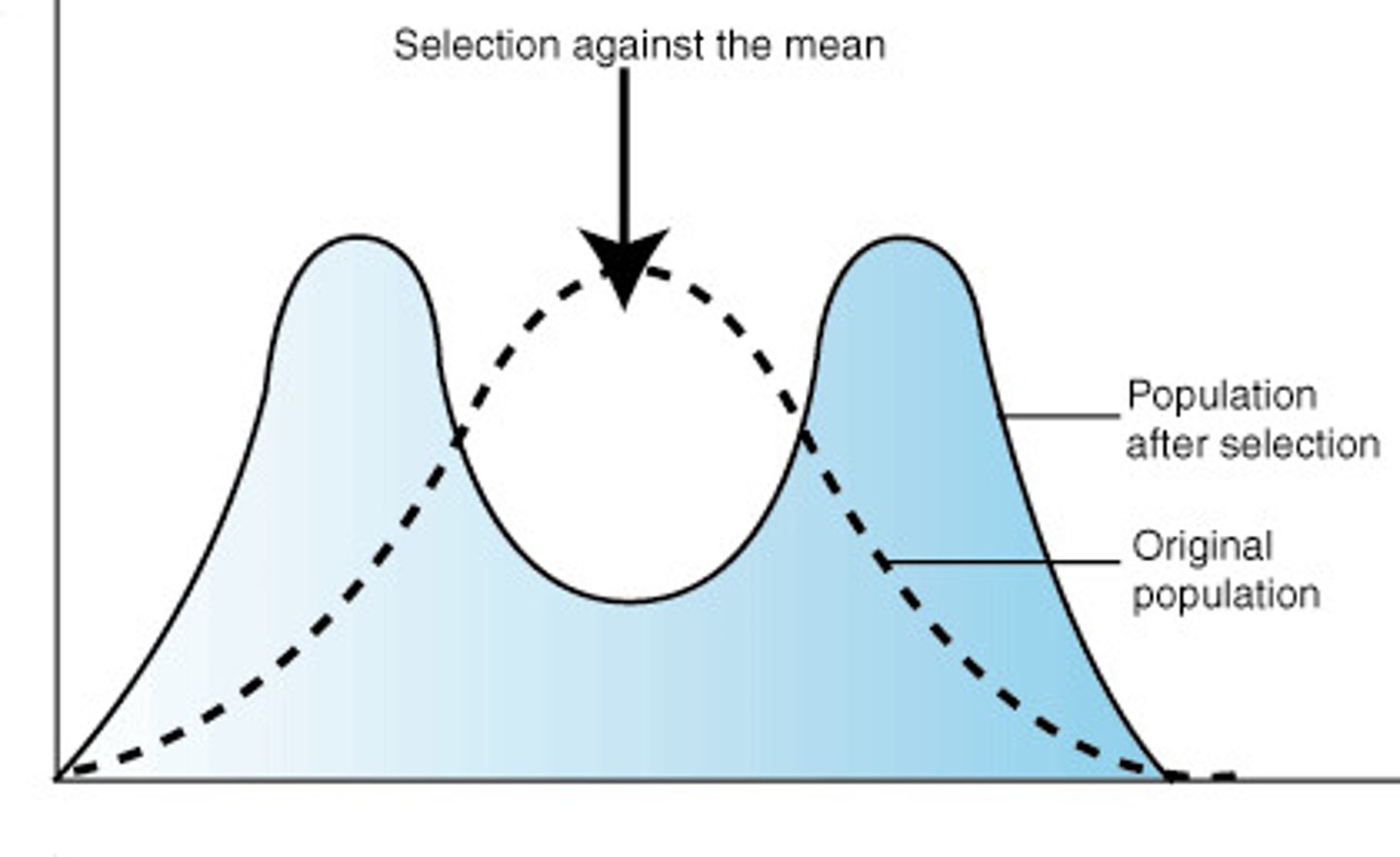
What is stabilizing selection?
favors intermediate variants and acts against extreme phenotypes
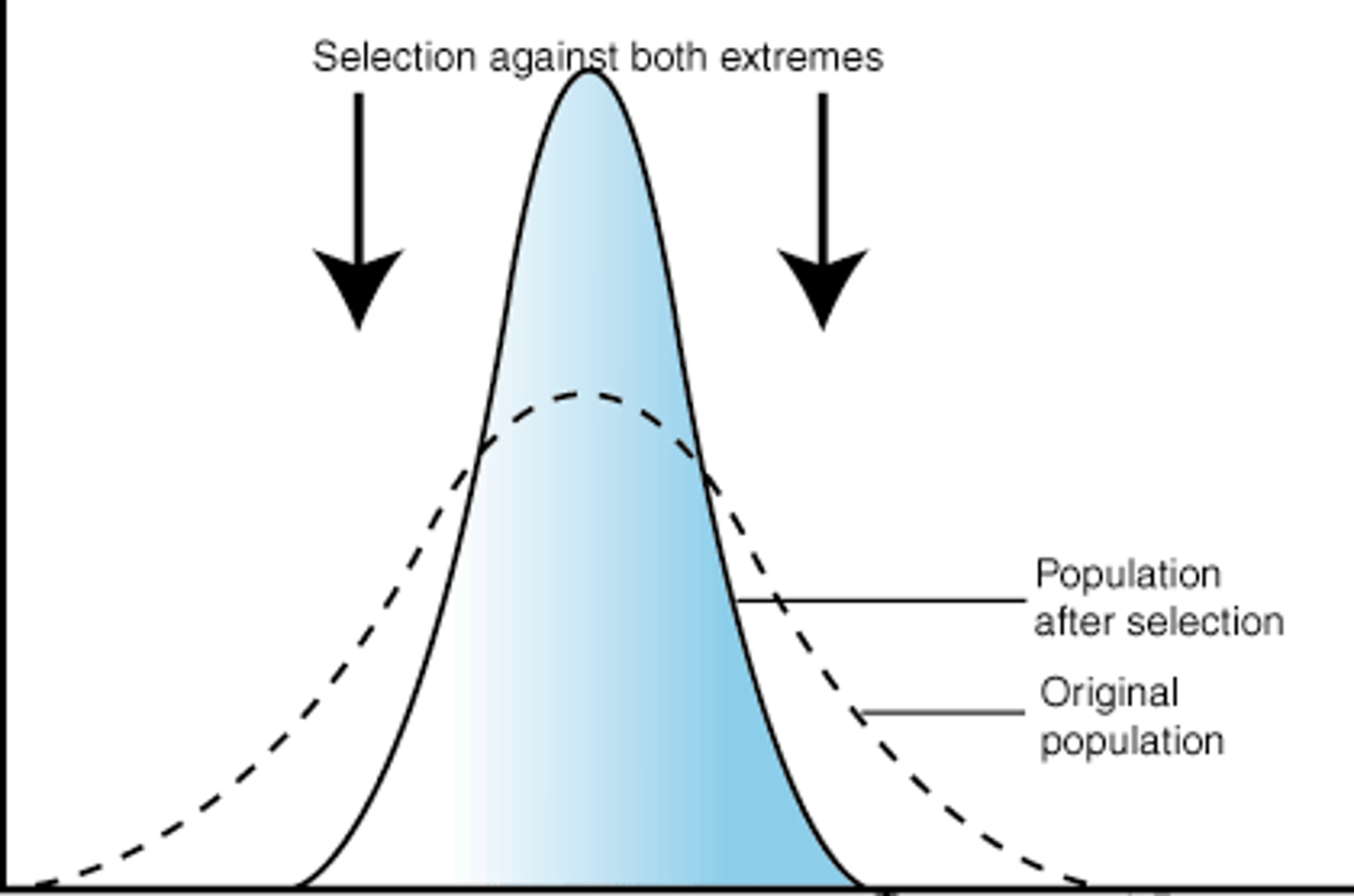
What is directional selection?
1. favors individuals at one end of the phenotypic range
2, Caused by shifting conditions
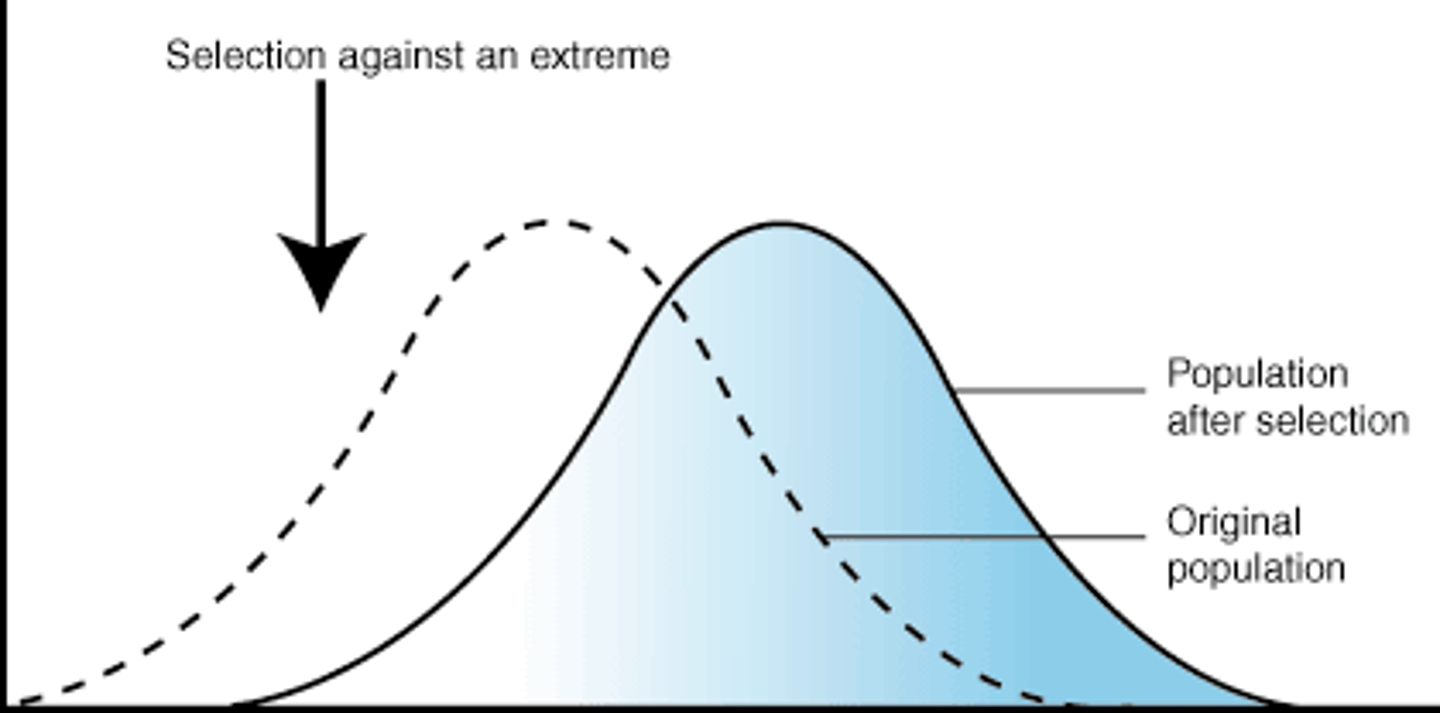
What is disruptive selection?
favors individuals at both extremes of the phenotypic range
How can phenotypes shift in a population?
1. Genetic mutation
2. Gene flow
3. Nonrandom mating
4. Genetic drift
5. Natural or artificial selection
Which selection pressure is most likely to lead to the creation of new species?
disruptive
What is genetic mutation?
1. changes in the genetic material (DNA)
2. ultimate source of allele differences (variation).
What is gene flow/migration?
movement of alleles from one population to another
What is nonrandom mating?
Selection of mate according to phenotype (not random)
What is sexual dimorphism?
high degree of male/female sexual traits
What is genetic drift?
A change in allele frequencies caused by random events
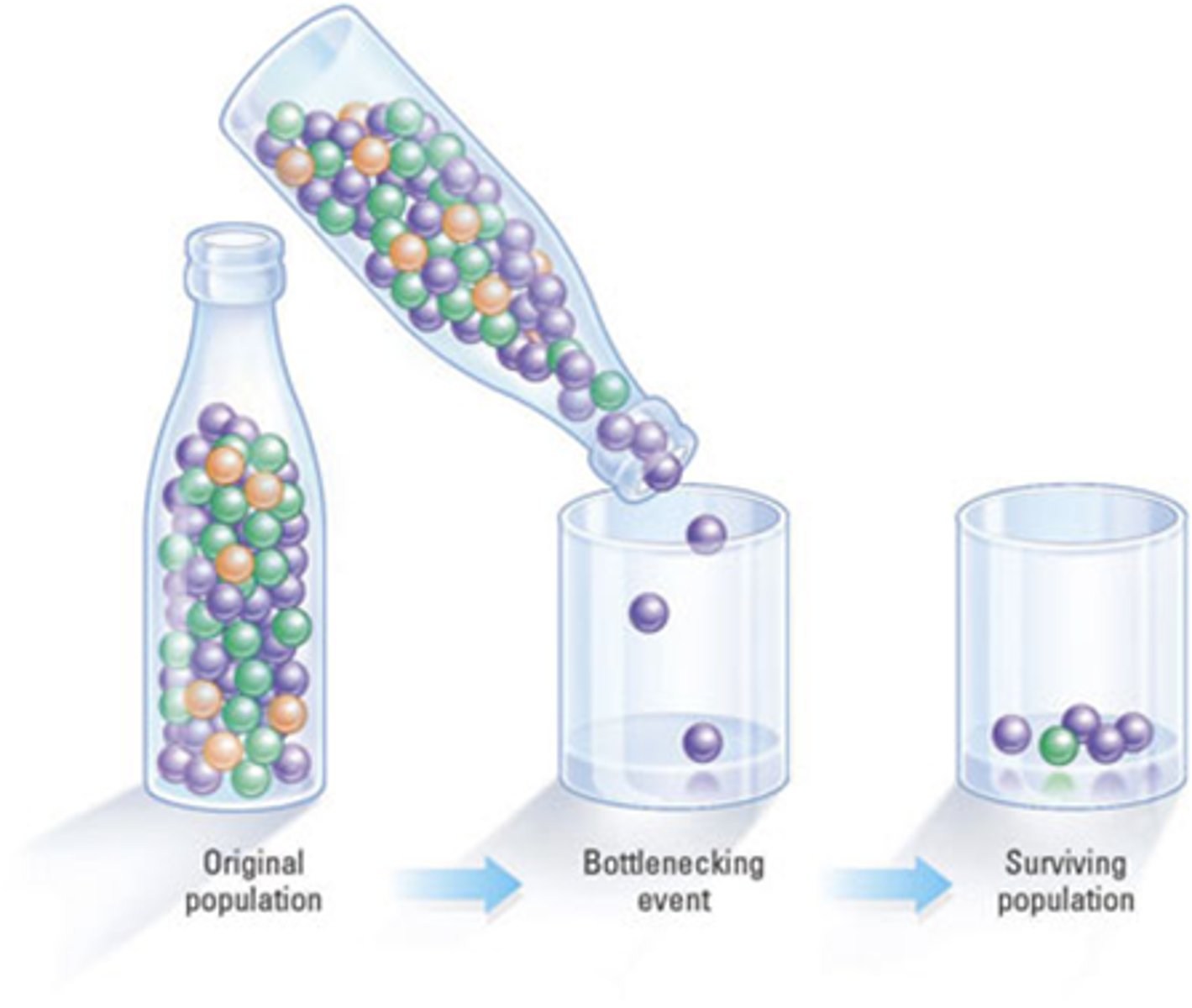
What is the bottleneck effect?
genetic drift that occurs after an event greatly reduces the size of a population
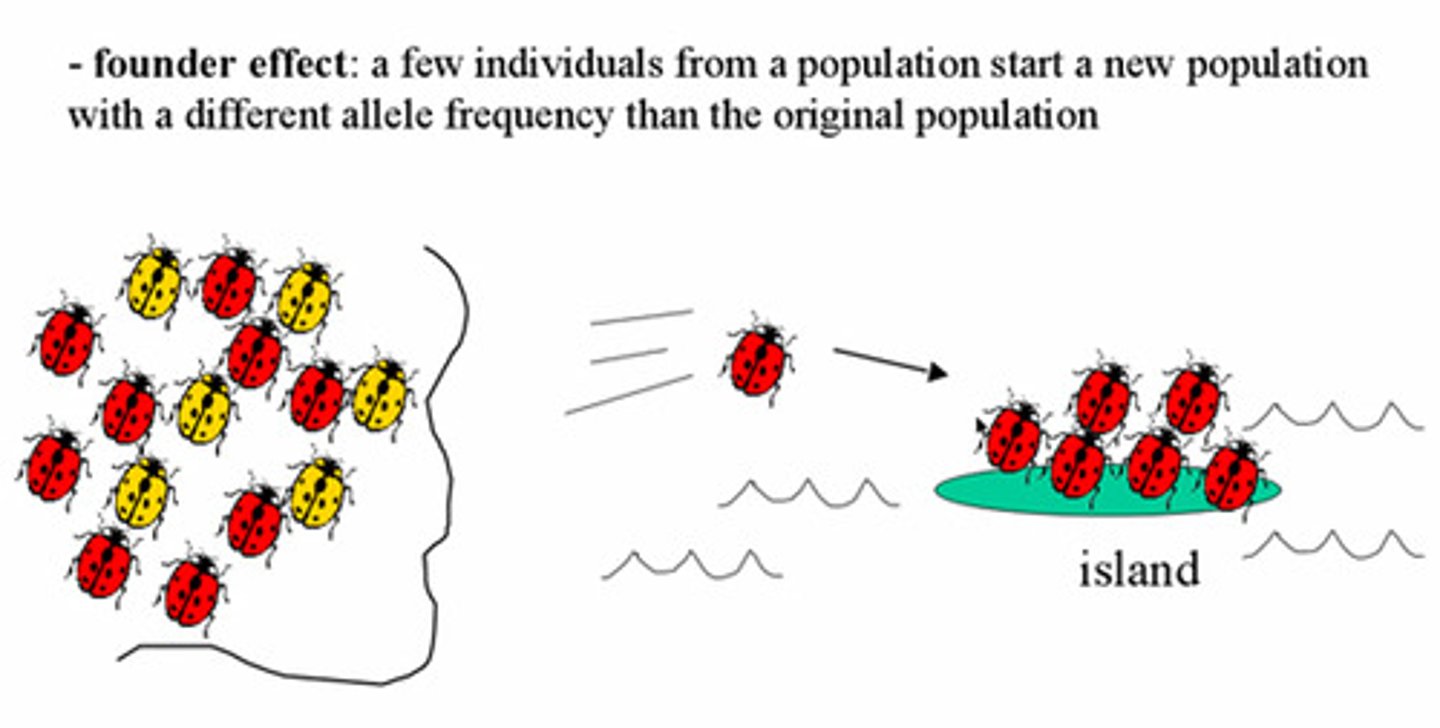
What is the founder effect?
change in allele frequencies as a result of the migration of a small subgroup of a population.
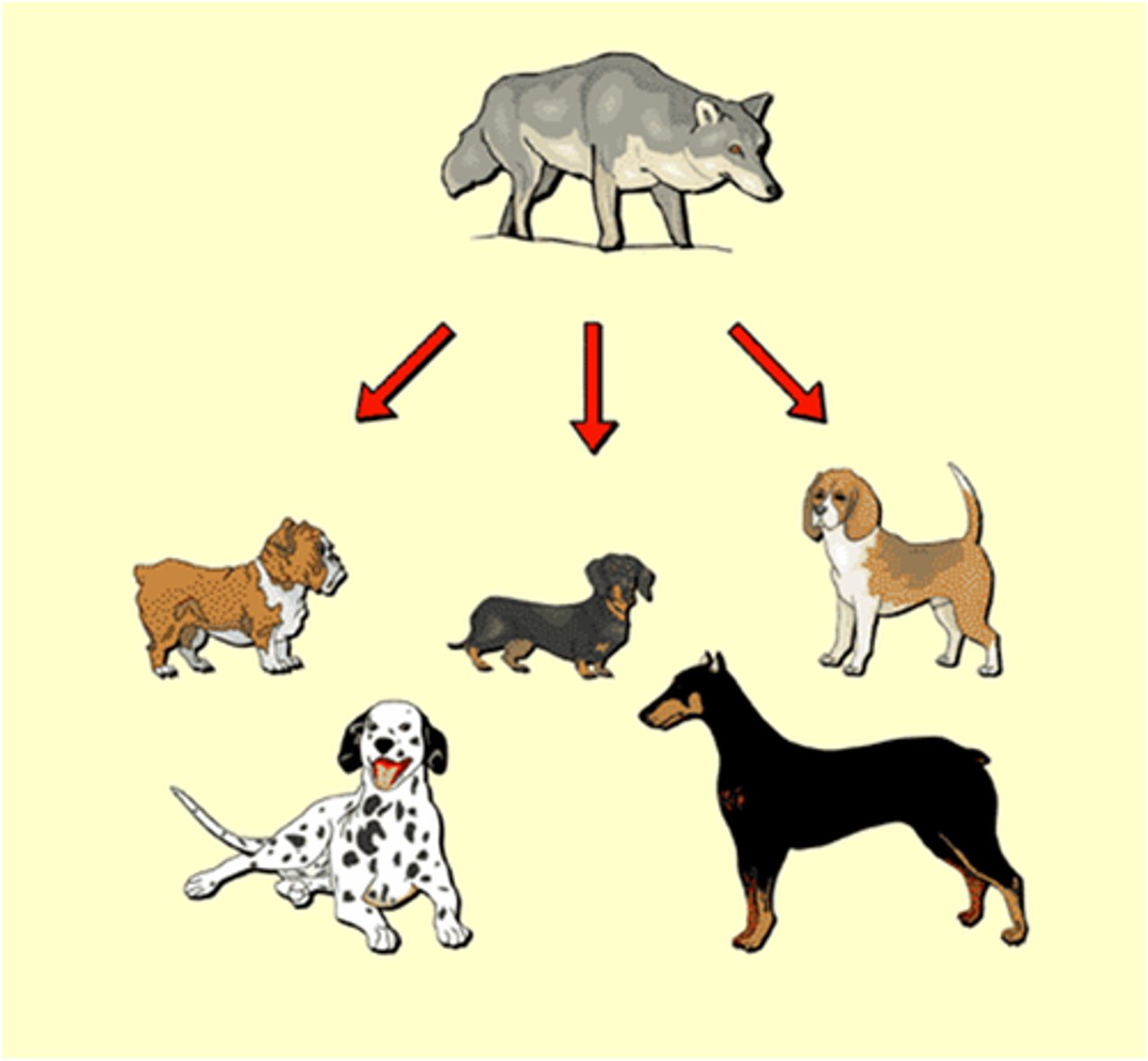
How is artificial selection different from natural selection?
1. Artificial selection is when humans decide the desirable traits (controlled process).
2. An example would be a dog and wolf. A domestic dog is the same species as the wolf, but their phenotypes are different.