Chapter 12.4: Characteristic and Types of Glial Cells, Myelination
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Glial cells (neuroglia)
nonexecitable, support cells in CNS and PNS
same number of glial as there are neurons
account for half volume of NS
Glial characteristics
mitosis
protect and nourish neurons
physical scaffolding for nervous tissue
guide migrating neurons during development
critical normal function at neural synapses
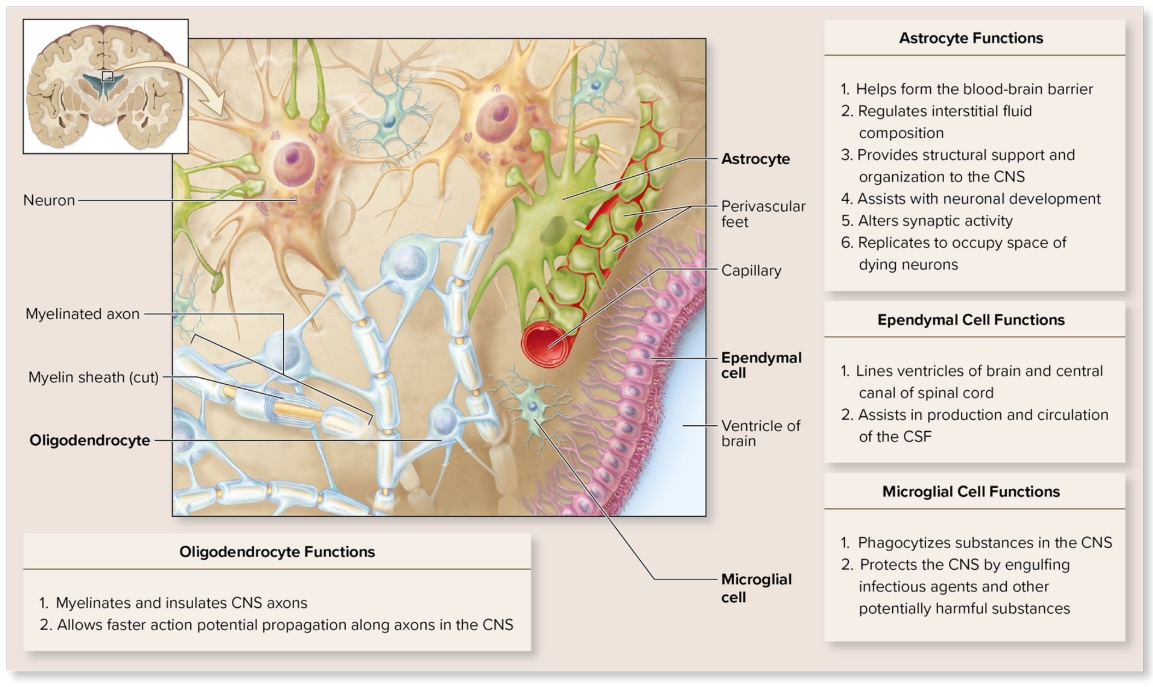
Glial cells within CNS: Astrocytes
star-shaped
processes end in perivascular feet
most abundant glial in CNS
form blood-brain barrier by wrapping feet around brain capillaries
regulates fluid composition
regulates potassium concetration
form structural support for nearby neurons
assist neuronal decelopment
alter synaptic activity (add, eliminate, influence)
occupy space of dying neurons
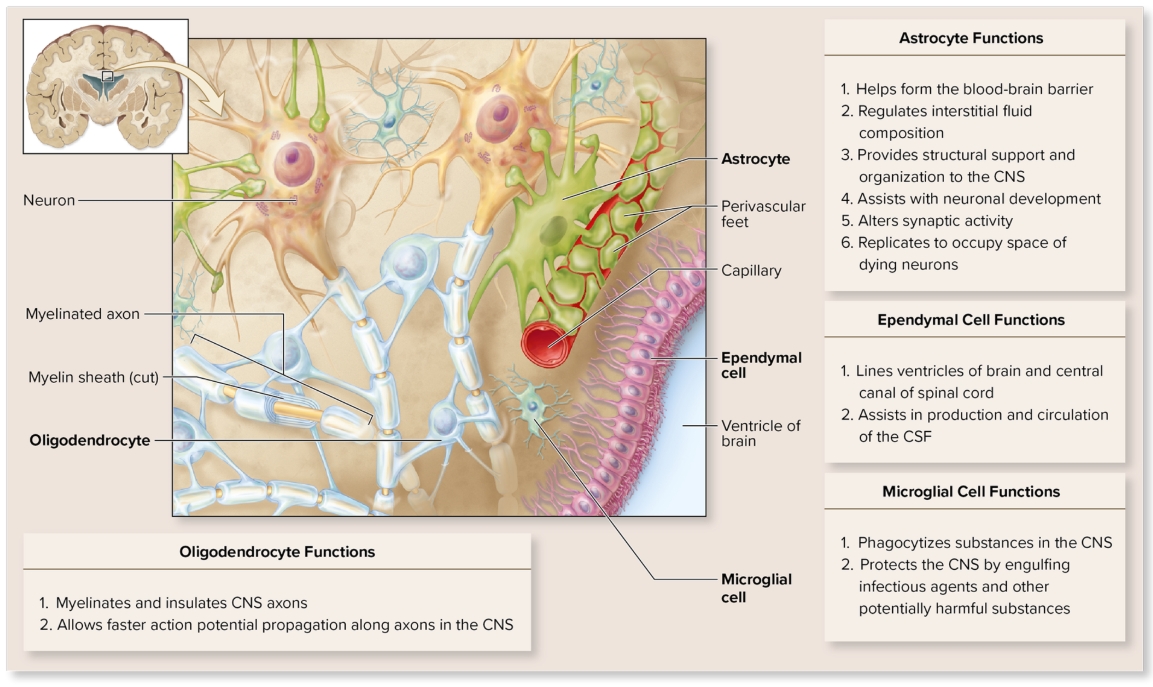
Glial cells within CNS: Ependymal
line cavities in brain and spinal cord
part of choroid plexus which produces cerebrospinal fluid
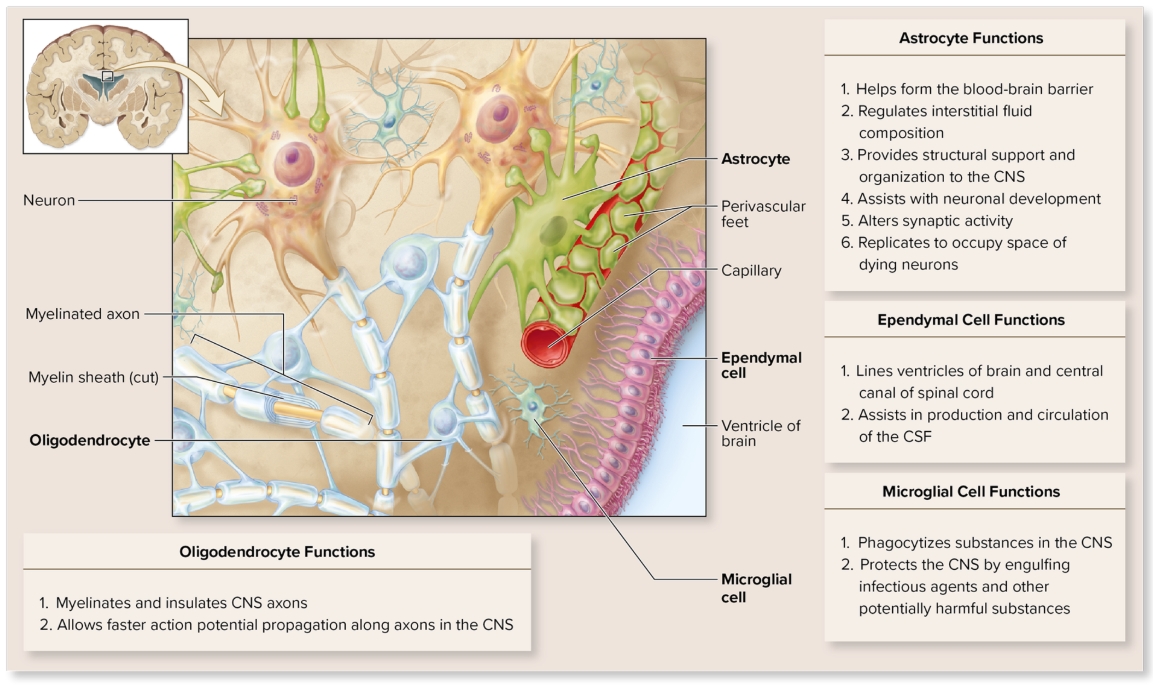
Glial cells within CNS: Microglia
small cells wander CNS and replicate infection
phagocytic cells of immune system
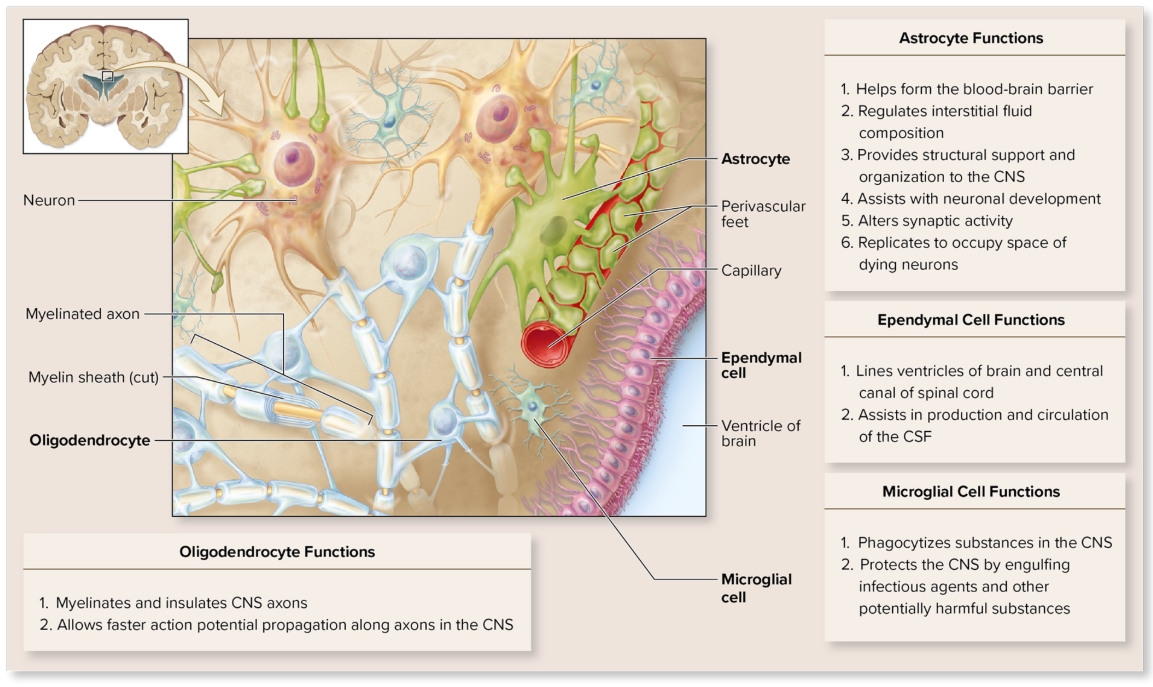
Glial cells within CNS: Oligodendrocytes
large cells with slender extensions
extensions wrap around axons of neurons forming myelin sheath
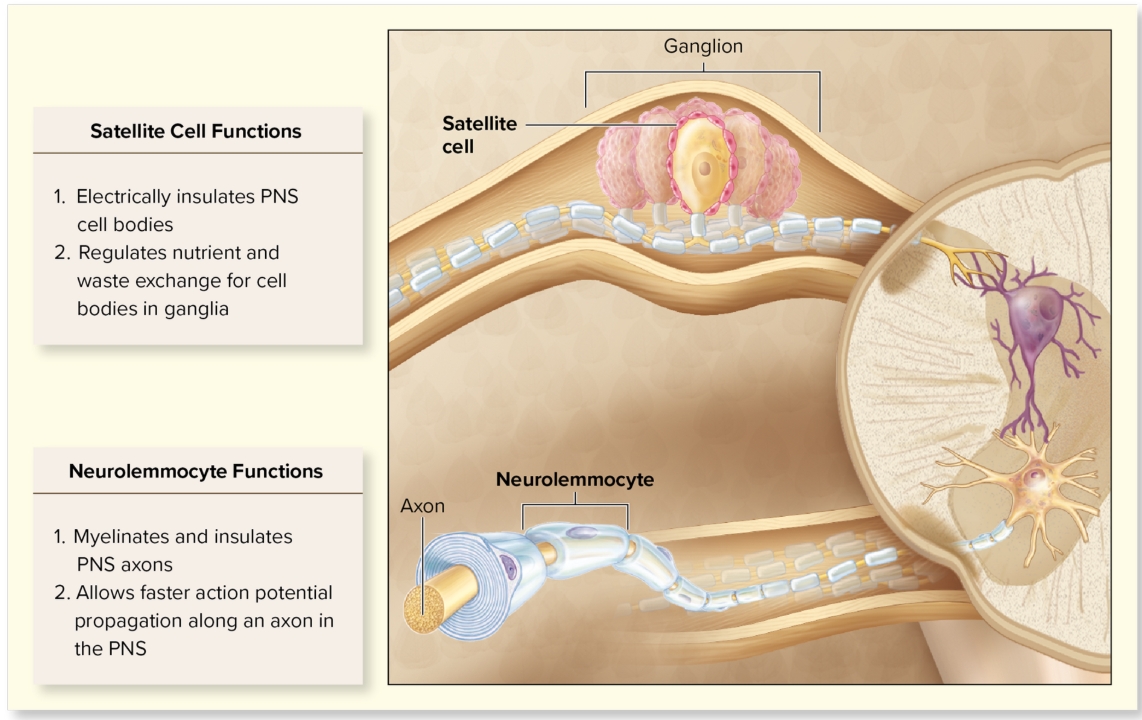
Glial cells within PNS: Satellite
around neuronal bodies in ganglion
electrically insulate and regulate exchange of nutrients and waste
Glial cells within CNS: Schwann (neurolemmocytes)
elongated, flat cells
surround PNS axons with myelin
allow faster potential propagation
Myelination
process wrapping axon with myelin
Myelin
several layers of membrane of glial cells
high lipid content gives glossy-white appearance and insulates axon
glia are Schwann cells in PNS; oligodendrocytes in CNS
schwann cells encircle neuron axon, wrap it forming myeling sheath
schwann cells cytoplasm and nucleus pushed to peripher forming neurilemma
schwann myelinate only 1 mm of axon, several are needed
gaps are nodes of ranvier
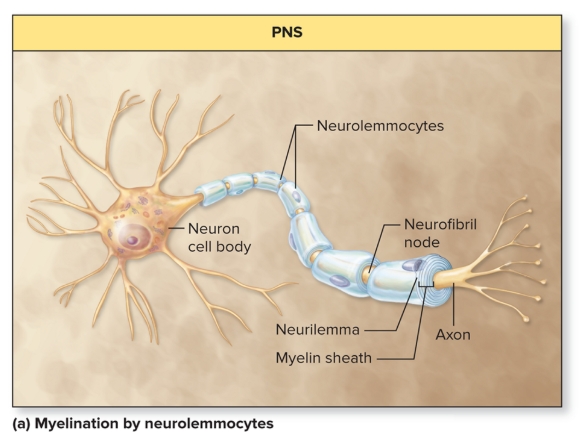
Myelin in PNS
schwann cells encircle neuron axon, wrap it forming myeling sheath
schwann cells cytoplasm and nucleus pushed to peripher forming neurilemma
schwann myelinate only 1 mm of axon, several are needed
gaps are nodes of ranvier
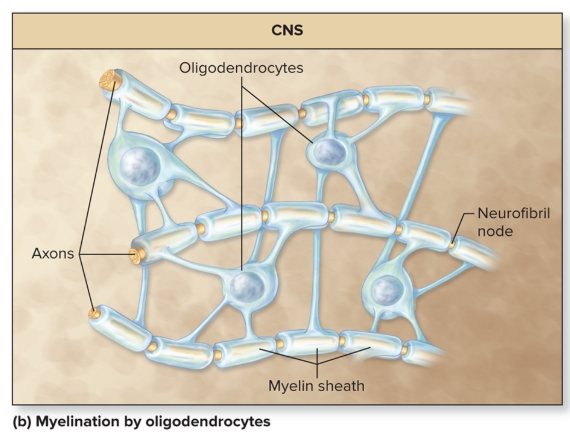
Myelin in CNS
oligodendrocytes myelinate 1 mm of multiple axons, each at multiple spots
no neurilemma formed
neurofibril nodes between adjacent wrapped segments