Marine Conservation Bio Exam 3 FSU
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is Aquaculture?
The act of growing aquatic organisms under controlled conditions
What are the types of aquaculture
products
scale
closed
open
1. products-sport fishery to commerce
2. scale-ponds, sea ranches
3. closed- fish spend their entire lives in pens
4. open-reared to size and then release
What is Fishmeal?
A protein-rich powder made from cooked, dried, and ground fish products that is used as feed in aquaculture or fertilizer
What are the negative effects of aquaculture?(8)
1. Wasted Biomass
2. Water Usage Impacts
3. Ecosystem Level Interactions
4. Loss of Mangroves and Salt Marshes and Nursery Habitats
5. Decimate Local Markwts
6. Genetic Limitation
7. Escaped can Lead to Invasive Species
8. Increased Predation
Can aquaculture compensate for declining wild stocks?
In theory it can. HOWEVER, the way aquaculture is being practiced today cannot compensate for declining wild stocks. If anything, todays' aquaculture is perpetrating the declination in wild stocks
What is pollution?
Impurity caused by contamnation
the presence of pollution in the environment is a product of human activity which have harmul effects or objective effects
What is point-source pollution?
any discrete and confined convyeyance
.includes pipes, containers, feed lots, and vessels which
pollutants may be discharged
What is non-point source pollution?
Multiple sources rather than a single discrete source
.May be harder to identify
What is Bioaccumulation?
When a substance does not break down and accumulates in an organism over time
What is Biomagnification?
When a substance that doesn't breal down accumulates in an organism and further accululates theough consumption uo trophic levels
What are biomarkers?
Some aspect of the body is used to measure the effects of the pollutants
ex) enzymes, hormone concentrations, phenotypic anomolies
What is eutrophication?
Eurtophication is the increase in primary productivity and organoc matter om aquatic systems caused by excess nutrients(nitrogen and phosphorus)
What are the sources of eutrophication(excess input of nitrogen and phosphorus)?(4)
1. Farm Runoff
a) fertilizer
b) fecal material from farm animals
2. Sewage
3. Nitrogen from Nitrogen Fixation by Leguminous Crops
4. Atmospheric Deposition of Nitrogen from Fossil Fuel
Combustion
What are the effects of eutrophication? (3)
1. Increased Algal Growth and Habitat Loss
excess phytoplankton can shade out corals and benthic
plants
2. Harmful Algal Blooms(HABs)
ex)red and brown tide
Toxic to fauna and people
Cause mass mortality of fauna
3. Hypoxia and Anoxia
dead phytoplankton sink and their decomposition utilizes
oxygen
worst in coastal zones
both lead to mortality
permanent reduction or loss of biodiversity
Hypoxia
Environment with less than 2-3 mg/L of O2
Anoxia
Environment with no O2
What are EDC's?
EDCs are Endocrine Disrupting Compounds. EDCs are compounds that when in sufficient concentrations elicit responses under the control of endocrine hormones
What are the sources of EDC to the marine environment? (5)
1. Aerosols
2. Runoff
3. Landfill Leakage
4. Industrial Waste
5. Sewage Discharge
Prescription drugs are peed out and end up in the ocean
What are the effects of EDC's? (6)
1. Thin Eggs
2. Abnormal Gonad Morphology
3. Reduced Rates of Gamete Production and Release
4. Reduced Gamete Quality
5. Gender Reversals
6. Changes in Reproductive Behavior
Be able to choose another pollutant, name its sources to the marine environment, and name and explain its effects.
Sound Pollution
diesel engines, jetskis, and boats, and sonar cause it
fish experience altered behavior along with temporary or permanent hearing loss. Croakers, drums, and toadfish use sound to reproduce. Larvae use the sound of reefs to find their way back for recruitment.
What are the two effects of CO2 pollution
1. Global Warming
CO2 causes ocean acidification not GW
2. Ocean Acidification
What are the effects of global warming on the marine environment? (5)
1. Temperature Rise
By 2100, Temp will incerase by 2-11.5 degrees farenheit
2. Changes in Deep Water Circulation
Deepwater formation is impacted by rising temp
Loss of water sinking
More freshwater from glacial melting
feedback loop: heat is not released to atmosphere, water
further warms
3. Lower Dissolved Oxygen
Is temp dependent
Animals use more O2 in warmer temps
4. Melting of Polar Ice
Warmer air and sea temps
Higher latitudes absorb most heat
5. Other Effects
Weather events, sound velocity, sea level rise
What are the biological effects caused by global warming in the marine environent? (4)
1. Physiological
2. Effects on Distributions
3. Effects on Phenology and Species Interactions
4. Adaptation
Explain the biological effects caused by global warming in the marine environent (4)
1. Physiological
Changes in respiration and metabolic rates(inc)
Chages in primary productivity(decr)
Changes in stratification bc upwelling decreases
Slowed growth rates
Slowed reproductive rates
Increase in Disease Spread
2. Effects on Distributions
3 deg C temp change shifts isotherms of 300-400km in lat
shift in deoth, move poleward, and deeper to maintain
ideal temps
Invasive species increase
Increase in pioneer, highly mobile, weedy, and opportunistic
species
3. Effects on Phenology and Species Interactions
Decoupling of phenological relationships
Means species will struggle to know when to migrate
and spawn
Mismatching of trophic levels and functional groups
4. Adaptation
Species with short generation times can experience
microevolution to adapt to warmer temps
What is phenology?
The timing of life history/cycle events that are triggered by environmental cues
ex) lighting, temp, and tides influence migration or spawning
What is ocean acidification?
Ocean absorbs CO2 , pH of ocean decreases and becomes more acidic. Surplus of H+
Explain the Process of ocean acidification
Ocean acidification occurs when CO2 is absorbed into the water at a high rate. It reacts with water molecules (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3). This compound then breaks down into a hydrogen ion (H+) and bicarbonate (HCO3-). The presence of all these hydrogen ions is what decreases the pH, or acidifies the ocean. Ocean acidification affects marine organisms that make calcified shells/skeletons. pH is expected to be 8 after 2025. pH is currently 8.1 and was 8.2 before industrialr revolution.
What are the three forms of calcium carbonate?
1. Calcite
2. Aragonite
3. Magnesium-Calcite
What organisms uses Calcite? (3)
1.Coccolithophores
2. Octocorals
3. Foraminifera
What organisms uses Aragonite? (2)
1. Scleractinian Corals
2. Pteropods
What organisms uses Magnesium-Calcite? (2)
1. Crustose Coraline Algae
2. Octocorals
Rank the dissolvability of calcium carbonate forms from hardest to easiest
Calcite> Aragonite> Magnesium-Calcite
What are the five effects of ocean acidification?
1. Physiological Effects
2. Metabolic Effects
3. Reproductive Effects
4. Trophic Effects
5. Habitat Effects
Explain the five effects of ocean acidification
1. Physiological Effects
Decrease in calcification rate
Coccolithophores have an increased growth rate
2. Metabolic Effects- internal regulation of pH
Shell dissolution to combat acidity of seawater
Photosynthesis and cellular transport inhibited
Greater metabolic Demand
3. Reproductive Effects
Impacts reproductive potential of orgs
Sea Urchin- impacts growth rates and reproduction
4. Trophic Effects
Causes trophic cascades by affecting lower levels of
trophic systems
Decline in predators and increase in phytoplankton
5. Habitat Effects
Decline in structure formers
More 3D structure= more habitats for other orgs
Tropical shallow corals harbors 20% of marine diversity
and increase productivity
Deep see corals harbor invert communities & provide
nurseries for fish
Deep sea coral could be more at risk due to shifting ASH
Are deep sea coral reefs or shallow coral reefs more at risk from ocean acidification?
Deep Sea Coral Reefs
How do organisms naturally disperse in the ocean? (3)
1. Water Circulation
Currents change direction
Gyres could deposit larvae
2. Flying or Swimming Organisms
Things get caught in seabird feathers
3. Rafting
Things hitch a ride on algal mats and driftwood
What is ASH?
Aragonite Saturation Horizon
What are the natural barriers to dispersal? (7)
1. Differences in Environmental Parameters
2. DIfferences in Biological Parameters
3. Geologic Events
Ex) Isthmus of Panama
4. Changes in Sea Level
5. Changes in Ice Levels
6. Limited Larval Dispersal
7. Larval Behaviors
All of these have led to a natural diversificaition of organisms
What is an introduced species?
species spread by human activaty that are not native to a region
synonymous terms: invasive, invader, nonindigenous, exotic, introduced and alien species
What is a range expansion?
when a species spreads to a new location through natural processes
What are the human vectors for species dispersal/introductions? (4-7)
1. Shipping, Drilling Paltforms, and Dry Docks
a) Internal- ballast water
b) External- fouling organisms
2. Movement of Live Organisms
a) aquaculture
escapes and release of species
b) packaging materials
can move algae which can become invasive
c)science and education
release orgs after study is completed
3. "Web as a Vector"
4. Canals
The creation of canals allows gived organisms a way to
migrate to places not previously possible
5. Conservation Efforts
Introduce a population to a new area in hopes of
preserving it
6. Scientific Research
7. Plant Restoration
Moving seagrass can trap orgs and introduce them to a
new area
What are Fouling organisms?
Organisms that can attatch/cement themselves to things
ex) ascidians, hydras, sponges, tunicates, barnicles
What are the impacts of invasive species (6)
1. Alteration of Structure
a) add structure
Makes more habitat for further invasions
ex) worms that create worm reefs, marshgrasses
b destroy structures
Causes a loss of habitat
ex) Isopod- Sphaeroma terebrans
erodes mangrove roots
2. Competition for Food or Space
Leads to displacement
ex) periwinkles comete w/ native snails
3. Predation to Native Species
4. Reductions in Recruitment
5. Introductions to Pathogens
ex) white spot from Asia has spread through the fish trade
6. Hybridization
Leads to loss of genetic diversity in native species
All of these cause changes in diversity, abundance, and distribution of native species
What are synergistic impacts?
The interaction of discrete conditions such that the total effect is greater than the sum of the individual parts or effects
What is genetic diversity?
the range of genetic variation in a population
What is phenotype?
the observed state of a trait that is based on genetic makeup and environmental factors
What is heritability?
a statistic that can be used to determine the likelihood a particular character will undergo directional evolution due to exploitation
What is an example of synergistic impacts and how they work?
Overexploitation of predators which causes a top-down release in urching for pop ecplosion. Cumulative overexploitation of reef fishes and alrge herbivors. This causes the release of algal food source from grazing. More food bottom-ip and less predation(top-down) causes urchin pop explosion. Disease outbreak kills all urchin. Top-down release on algae bc nothing is left to eat it. Combined with increased nutrients from eutrophication, warmer waters, and extra CO2, the algae pop explodes and overgrow corals. The corals are also weakened by disease and warmer temps, ocean acidification. The result is a completely different ecosystem. Every anthropogenic impact builds on the ones before it and concurrent with it
What is directional selection?
a mode of natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype
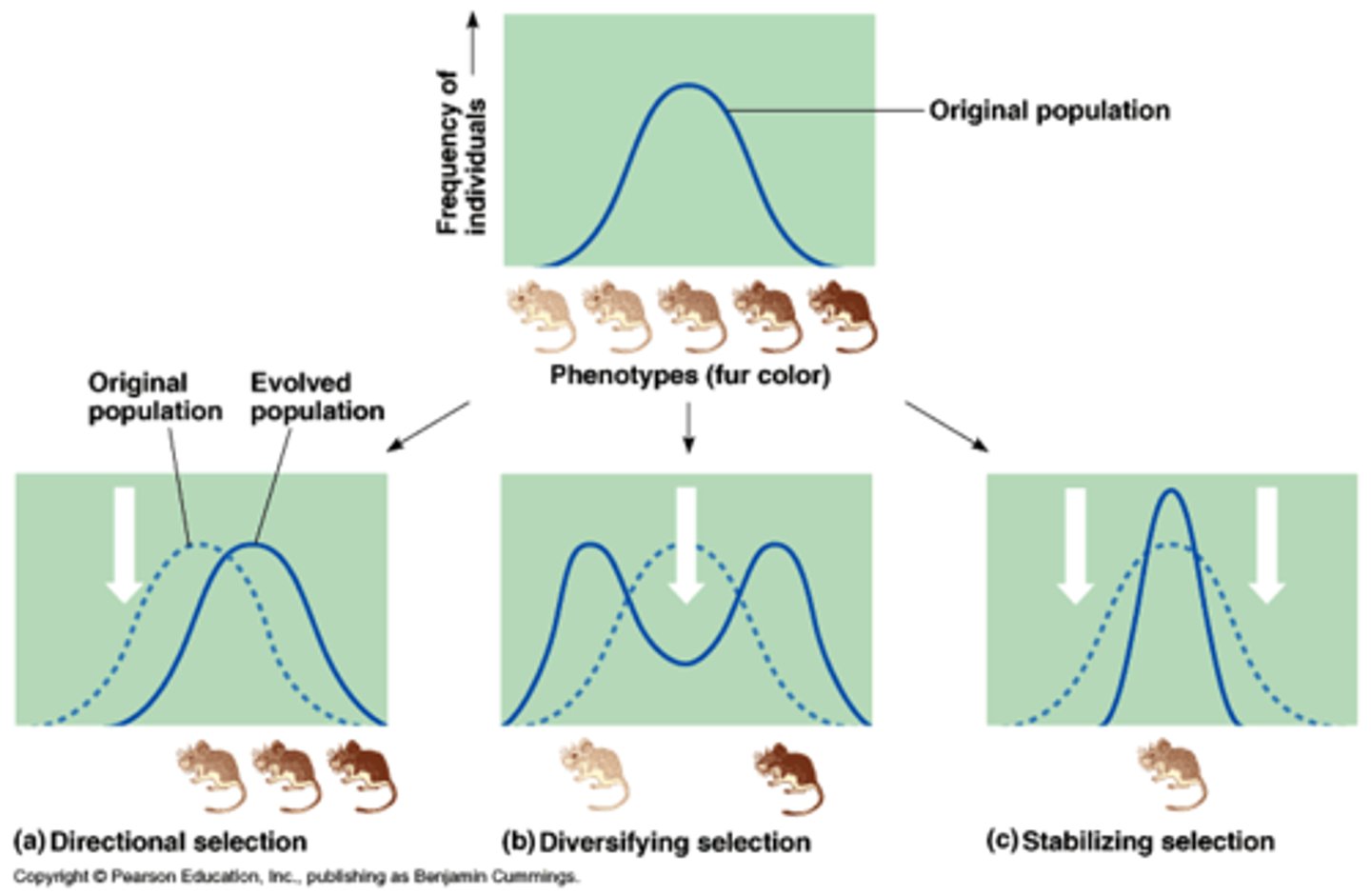
What are the characteristics that make organisms likely to experience directional selection?
1. Short Generation Times
2. Large Populations Times
3. Faster Rates of Evolution
What are the main lists of species at risk of extinction?
1. Endangered Species Act(ESA)
U.S. act to protect U.S. Species
Categorizes people as endangered or threatened
2. NOAA- Office of Protected Services
Lists 165 marine orgs as endangered/threatened
3. IUCN Red List
International list
Keeps track of orgs facing ectinction
4. CITES- convention on international trade in endangered species
Appendix 1- most critically endangered and can't be traded
Appendix 2- not currently threatened but could be if
exploitation isn't curtailed
can be traded w/ proper management
Appendix 3- organisms that are protected in at least 1 country
any country can list species
How does the ESA define endangered?
a specied in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant part of its range
How does the ESA define threatened?
a species likely to become endangered in the foreseeable future
Name the categories of IUCN Red List
1. Extinct
2. Extint in the wild
3. Critically endangered
4. Endangered
5. Vulnerable
6. Near threatened
7. Least concern
8. Data deficient
9. Not evaluated
What are the three types of extinction?
1. Ecological Extinction
2. Economical Extinction
3. Biological Extinction
What is Ecological Extinction?
population is reduced to such low numbers that the species can no longer carry out its role in its native ecosystem
What is Economical Extinciton?
population reduced to such a low level that the species is not profitable to capture
What is Biological Extinciton?
no specimens are left alive
What are the habitats found in the deep-sea ecosystem?
Soft Sediment Habitats
1. Continental Margin
2. Abyssal Plains
Hard Substrate Habitats
3. Seamounts
4. Canyons
Chemosynthetic Habitats
5.Hydrothermal Vents
6. Cold Seeps
7. Whale Falls
8.Sunken Wood and Organic Remains
What are the Deep Sea Soft Sediment Habitats? (2)
Soft Sediment Habitats
1. Continental Margin
.Includes shelf, slope, and rise
2. Abyssal Plains
. 75% of the seafloor
. very low sedimentation rates
What are the Deep Sea Hard Substrate Habitats? (2)
Hard Substrate Habitats
1. Seamounts
. Mostly hard-substrate but has soft portions
. Volcanic in origin
2. Canyons
. diversity hotspots
. conduits- transport organic matter to deep ocean
. structurally diverse
. larval sources adjacent to continental margins
. refuges from ocean acidification
What are the Deep Sea Chemosynthetic Habitats? (4)
Chemosynthetic Habitats
1..Hydrothermal Vents
. Ephemeral- events last 10s to 100 years
. Fastest growing orgs
. Found at spreading centers at mid-ocean ridges
. Large Biomass but low diversity
2. Cold Seeps
. Found in subduction zones
. Stable Environments
. Can last 1,000s of years
. Slowest groying at mm/year
3. Whale Falls
. Dead whales sink to seafloor
. Whale bones have lipids and their decomp produces
H2S and Methane
. Creates microbial mats
. Can last 100s of years
. Act as disperal and evolutionary stepping stone
for vent and seep fauna
4.Sunken Wood and Organic Remains
. Most ephemeral of deep-sea habitats
. Least well developed
What are the reasons we should care about the deep sea? (7)
1. It is the Largest Ecosystem
2. Substantial Reservoir of Biodiversity
.90% of benthic environment is in the deep sea
3. Provides Important Ecosystem Goods and Services
. Geochemical cycling
. Natural carbon burial
4. Global Ocean Conveyor Belt
. Upwelling zones- what happens in the deep sea comes
back to the surface and impacts fauna and humans
5. Intense Scientific Interests
. Good at tracking gradual long-term changes in
euphotic zone properties
. Scientists can track ocean productivity
6. Fauna are Very Vulnerable
7. Rapidly Increasing Anthropogenic Impacts
. Increasing bc we are depleting land and shallow water
resources and need to resort to deep sea
What are the characteristics that make the deep sea more vulnerable? (11)
1. Relatively Low Productivity Environment
2. Highly Dependent on Surface Productivity
. Food comes from surface
3. Relatively Low Energy and Disturbance Environment
. species aren't adapted to change and are more vulnerable
to disturbance
4. Bottom of the Bucket Effect
. the deep sea collects everything from land and overlying
layers
5. High Biodiversity Per Unit Area
. makes the deep sea take longer to recover
6. Large Habitat Areas
7. Broad Species Distributions
8. Unknown and Unexplored
. Can't brgin to estimate species richness
9. Complete Lack of Interest
10. Largely in International Waters
. no protection until recently
11. Life History Characteristics
. long-lived
. slow- growing
. late maturity
. slow biological rates
. adapted to low disturbance
What are the categories of anthropogenic impacts to the deep sea? (3)
1. Disposal
a) bottom of the bucket
b) indirect disposal
c) direct disposal
2. Exploitation
a) fisheries
b) mining
c) oil and gas
d) methane hydrates
3. Ocean Acidification and Global Warming
4. Synergistic Effects
5. Timing of Impacts
Explain the categories of anthropogenic impacts to the deep sea
1. Disposal
a) bottom of the bucket
. ultimate repository for disposal
ex)PCBs, DDTs, Methylmercury
b) indirect disposal
. litter, waste, ships lost at sea
c) direct disposal
. i) radionuclides and radioactive waste
. ii) chemicals and pharmaceuticals
. iii) sewage sludge, drilling and mining tailings
.iiii) CO2 Disposal
. poposition to sequester excess CO2 by turing it into
liquid form and dump it in the sea
. kills fish, impacts respiration
2. Exploitation
a) fisheries
. impacts benthos and seamounts by trawling
b) mining
.4 types in Deep Sea
i) Polymetalic Sulfides
. grow on seamounts and hydrothremal vents
. these and deep-sea coral habitats are impacted
. vent ecosystems are most resilient bc ephemerality
ii) Cobalt-Rich Manganese Crusts
. on seamounts
iii) Manganese Nodules
. on abyssal plains
iiii) Metaliferous Muds
c) oil and gas
. habitats imapcted include continental margins, cold
seeps, deep sea corals
. drilling muds and drilling cutting harms habitats by
burrowing fauna and smothering them, organic
enrichment, chemical pollutants, and inhibiting
larval settlement
d) methane hydrates
. methane is a GHG
. inputs more methane in atmosphere
. unstable bc methane can sublime
. highly flammable
. extraction can cause landslide
3. Ocean Acidification and Climate Change
4. Synergistic Effects
5. Timing of Impacts
What are the impacts of Ocean Acidification and Climate Change?
. both caused by excess CO2 in the atmosphere
OA
. affects orgs w/ calcium carbonate skeletons
. makes ASH get shallower
. primary productivity changes
CC
. ocean is warming where deep water circ occurs
. increased stratification
affects O2 supply and temp
changes in pH
What are the problems with mining?
1. Remove Hard Substrate
. kills fauna and subtrate is eradicated
2. Affect Surrounding Communities
. large volumes of sediment are resuspended
. plumes go downstream and smother fauna
What is the average depth of the ocean?
3800 meters
What are the life characteristics that make orgs more likely to go extinct?
1. Slow population turnover
. long life span
. slow growth rate
. low natural mortality
2. Low reproductive potential
. low fecundity
. single lifetime reproductive event
. long time between reproductive events
. older age at reproductive maturity
. male-female sex change
. aggregated spawning in predictable locations
. density dependent reproduction
3. Low capacity for recovery
. limited disperal abilities
. density-dependent effects on settlement or mortality rate
4. Restricted range geographically or with depth
. nearshore occurrence
. dependence on estuaries
5. Small population sizes
6. High trophic position
7. Reduced larval dispersal
8. Large body size
9. Long-life span
10. Target of fishery and also caught as bycatch