reading and writing
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
dual route model
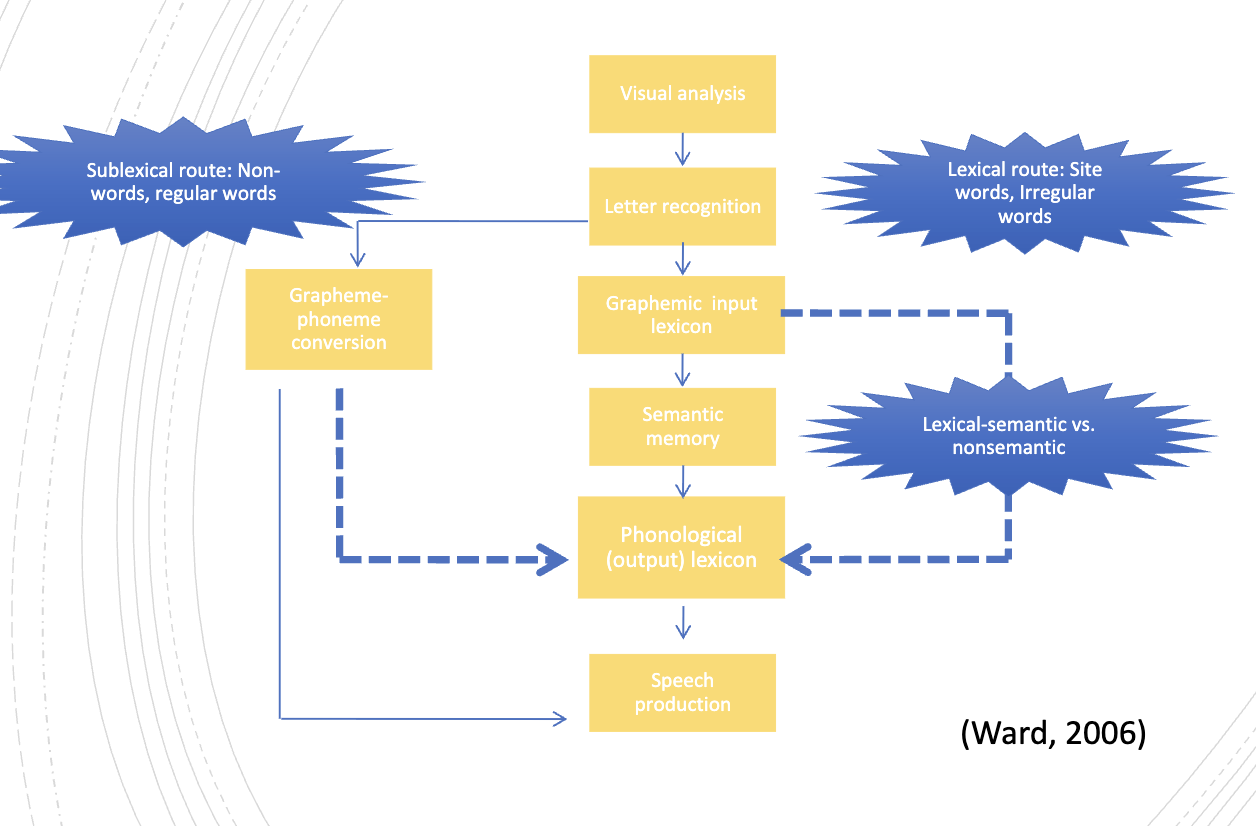
neural pathway of reading
sensor (converts image to be relayed for visual processing)
visual processing
letter analysis, orthographic input lexicon
orthography → phonology, integration of semantic, orthography, and phonology
phonological encoding
meaning
attention
neural structure of sensor (converts image to be relayed for visual processing)
retina
neural structure of visual processing (visual feature analysis)
primary then secondary visual cortices
neural structure of letter analysis, orthographic input lexicon
left fusiform gyrus: visual word form are (VWFA) in L occipito-temporal region
neural structure of orthography → phonology, integration of semantic, orthography, and phonology
left angular and supramarginal gyri
neural structure of phonological encoding
LIFG, insula, SMA
neural structure of meaning
left temporal gyrus (optional)
neural structure of attention
right superior parietal lobe
for the reading network, consider damage to …
white matter network structures
Posterior corpus callosum
Arcuate fasciculus
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
neural pathway of reading: peripheral processes
retina
sensor needed to relay image
primary then secondary visual cortices
visual feature analysis
left fusiform gyrus
letter analysis
orthographic input lexicon
right superior or left parietal lobe
attention
acquired peripheral alexias
Impairments up to the level of visual word form processing
pure alexia
visual alexia
Impairments to right (or sometimes left) superior parietal lobe
neglect/hemionopic alexia
attentional neglect alexia
Impairments up to the level of visual word form processing are which types of alexia?
pure alexia
visual alexia
Impairments to right (or sometimes left) superior parietal lobe
neglect/hemionopic alexia
attentional neglect alexia
have to do letter-by-letter reading → A-P-P-L-E, oh apple!
pure alexia
Serial processing due to impairments occurring between visual feature analysis and letter analysis
pure alexia
which alexia has impaired letter analysis or orthographic input lexicon?
visual alexia
better → butter, prince → price (note: errors are orthographically related)
visual alexia
Left versus Right neglect
neglect/hemionopic alexia
clock → block; clock → clot
neglect/hemionopic alexia
Impaired attention causing difficulties like migration errors
attentional neglect alexia
WIN FED → FIN FED
attentional neglect alexia
neural pathway of reading: central processes
Left angular and supramarginal gyri
Orthography to phonology conversion
Integration of semantics, orthography and phonology
Left IFG, insula, SMA
Phonological encoding (reading aloud)
Left middle and inferior temporal gyrus
Meaning
patients with ________ generally also have aphasia
central alexias
NOT peripheral alexias
acquired central alexias
surface alexia
phonological alexia
deep alexia
semantic alexia
Damage: Typically left temporal and temporoparietal lesions (impaired ____ pathway) which alexia?
surface alexia; what
Damage: Left perisylvian or superior temporal lesions (impaired ____ pathway) which alexia?
phonological alexia; where
which alexia has impaired orthographic input lexicon. Impaired recognition of site words
surface alexia
which alexia has reliance on grapheme-phoneme conversion (sounding out)
surface alexia
which alexia has impaired grapheme-phoneme conversion?
phonological alexia
which alexia has reliance on lexical-semantic route (site words)?
phonological alexia
which alexia is better with regular and non-words > irregular (yacht, pint) substitutions with visually- and semantically- related words (car for cab)
surface alexia
which alexia is better with real words > non-words (pseudowords are read as real words)
phonological alexia
which alexia is absent of semantic paralexias?
phonological alexia
which alexia has extensive left hemisphere lesions?
deep alexia
which alexia has impaired lexical and sublexical routes?
deep alexia
which alexia surface + phonological alexia?
deep alexia
which alexia has semantic paralexias (cat → dog)?
deep alexia
which alexia has severe pseudo-word reading impairment (inability to sound out words)?
deep alexia
which alexia has morphological errors, visual errors, imageability effects, content > function words
deep alexia
which alexia has impaired comprehension of texts, overall meaning?
semantic alexia
which alexia has temporal and frontal lobe lesions?
semantic alexia
what is a graphemic buffer?
buffer- im going to hold it in my head
short-term memory of holding letter sequence in head
which dysgraphia has damage: parietal lobe (where graphic motor plans are stored) or premotorarea
acquired dysgraphias: peripheral
acquired dysgraphias: peripheral have problems with…
Problems with visual shapes, case, or size
Problems with copying
Graphemic buffer problems: substitutions, additions
acquired dysgraphias: central
surface dysgraphia
phonological dysgraphia
deep dysgraphia
which dysgraphia has damage to inferior parietal lobe?
surface dysgraphia
which dysgraphia has impaired orthographic output lexicon (site words); reliance on sublexical route?
surface dysgraphia
which dysgraphia can spell regularly spelled words > Irregular (oshen for ocean) or unfamiliar words
surface dysgraphia
which dysgraphia has left perisylvian lesions?
phonological dysgraphia
which dysgraphia has damage to sound-grapheme conversion route; reliance on lexical route?
phonological dysgraphia
which dysgraphia has known words > unfamiliar words or nonwords
phonological dysgraphia
which dysgraphia is Phonological + surface dysgraphia (all routes are impaired)?
deep dysgraphia
assessments
WAB-R part 2 and BDAE subtests
Reading Comprehension Battery for Aphasia (RCBA)
PPT for semantic knowledge for single words, orthographic stimuli
“Unstandardized assessments” per LPAA
What types of reading activities do you want to engage in?
books, text messages, email (reading or writing), letter writing, menus and shopping lists, signs, labels, instructions, newspapers (articles or just headlines)
How do you think or feel about reading?
enjoyable, easy, confident, happy to try/work on it, motivated, importance, speed, frequency
reading treatments for peripheral alexias
Neglect treatments; OT referral
reading treatments for pure alexia
Multiple Oral Rereading (MOR)
reading treatments for surface alexia
Multiple Oral Rereading (MOR)
reading treatments for phonological alexia
Grapheme-phoneme conversion
reading treatments for deep alexia
Oral Reading for Language in aphasia (ORLA)
reading treatments for semantic alexia
Attentive Reading and Constrained Summarization discourse treatment (ARCS)
writing treatments for peripheral dysgraphia
Train font, strategies for STM, OT referral
writing treatments for surface dysgraphia
ACT and CART
writing treatments for phonological dysgraphia
ACT and CART
writing treatments for deep dysgraphia
ACT and CART
writing treatment follow what principle?
Specificity principle: specific targets and tasks
specificity principle for confrontation naming and dictation
confrontation naming = target what the pt wants to write
dictation = train writing phone messages
reading direct approaches
Multiple Oral Re-Reading (MOR)
Oral Reading for Language in Aphasia (ORLA)
Phoneme-Grapheme conversion tasks
reading indirect approaches
slow down
reduce distraction
use support from family
writing interventions
Anagram Copy Treatment (ACT) and Copy and Recall Treatment (CART)
Usually these patients are "word blind" and start off with inaccurate letter naming. To treat this we developed a tactile-kinesthetic approach in which we trained the patients to trace single letters first on a card with arrows, then on a card without arrows, then on their palm with a pencil. Once their accuracy in naming the letters as they traced on their palm improved we moved on to training letter naming for speed, then letter strings, whole words, etc.
pure alexia or mild surface
Grapheme-Phoneme conversion purpose
To directly target the underlying reading impairment
grapheme-phoneme conversion training:
Grapheme-phoneme correspondence at the sound level: _______
Blending of bigraphs: ______ combinations
Word-level with ___________
letter sounds
consonant-vowel combinations
targeted graphemes
what should you consider in grapheme-phoneme conversion training?
Consider developmental v. CATE progression
Consider linguistic variables (frequency, imageability, etc.)
grapheme-phoneme conversion stimuli
Train ___ not ___(5-10 items)
_____ or ____ may be equally effective
Do not use ________
Train deep not broad (5-10 items)
Nonwords or real words may be equally effective
Do not use pediatric materials