ANAT LEC Ch.9 The Muscular System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Muscle can be divided into 3 types
Smooth muscle
NON-Striated, Spindle shaped
UNI nucleated
Usually in walls of internal organs
INvoluntary
Ex. Pushes fluid/solids along DIGESTIVE tract and other systems
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, Branched
UNI nucleated
Only in Heart walls
INvoluntary
Ex. Pushes BLOOD thru vessels of the cardiovascular system
Skeletal Muscle
Non-Striated, tubular
Multi Nucleated
Attached to skeleton
VOLUNTARY
Ex. Moves the BODY by pulling on the bones
4 Shared Muscle type properties
Excitability, Contractibility, Extensibility, Elasticity
Excitability Def
Ability to respond to STIMULATION (nerves & hormones)
Contractibility Def
Ability to SHORTEN/EXERT a TENSION harnessed by connective tissue (tendons)
Extensibility Def
Ability to CONTRACT over a range of RESTING
Elasticity Def
Ability to RETURN to its original LENGTH after contraction
directly or indirectly attached to bones
Skeletal muscle are contractile organs _____
Epimysium
Dense IRREGULAR connective tissue that SURROUNDS muscle
Perimysium
DIVIDES muscle into internal compartments containing the FASCICLES
Endomysium
SURROUNDS each muscle FIBER
Sarcolemma
Membrane of skeletal muscle is
Sarcoplasm
The cytoplasm of skeletal muscle is
Network of TRANSVERSE Tubules (T Tubules) extending into the sarcoplasm
Helps with EXCITIBILITY
Deep indentations in the sarcolemma form
100-1000
Sarcoplasm contain ______ myofibrils
Sarcomeres
The smallest functional unit of muscle fibers are ____
Thin Filaments are made up of
4 proteins
F-Actin
Nebulin
Tropomyosin
Troponin
Tropomyosin & Troponin Characteristics
Regulatory proteins
Tropomyosin: Covers active site PREVENTING actin-Myosin interaction
Troponin: Holds tropomyosin in place, MUST MOVE in order to initiate contraction
Thick Filaments Characteristics
Composed of bundles of MYOSIN
Form cross-Bridges when interacting w/Thin filaments during CONTRACTION
Muscle exerts a PULL/TENSION
ONLY PULL, NO PUSH
A CONTRACTION occurs when
Interactions b/w THIN & THICK filaments in ea. sarcomere
Sliding Filament Theory
Microscopic level, contraction = size change in A/I/H/Z bands, zone, lines
Contractions RESULT from
Motor Unit (MU) Characteristics
Is a SINGLE motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it controls
Smaller MU = Finer control of movement
Larger MU = more force generated
Muscle contraction occurs when MU are stimmed
AMOUNT of MUs involved
FREQUENCY of stim of the MUs
Force is determined by
Hypertrophy Characteristics
Results from REPEATED/EXHAUSTIVE stim
muscles DEVELOP more MYOFIBIRILS & MITOCHODRIA
Enlarges size of muscle belly
Ex. Bulking muscle
you do NOT grow NEW muscle cells
Atrophy Characteristics
Lack of regular stimulation to the muscle
Loss of muscle tone/mass
muscle is smaller and weaker
due to loss of intracellular contractile proteins
3 Fiber types
White Fibers (fast)
Red Fibers (slow)
Pink Fibers (intermediate)
Fast (WHITE) Fiber Characteristics
Large diameter
Densely packed myofibrils
Large Glycogen reserves
Few Mitochondria
MAJORITY of skeletal muscle is FAST type due to their rapid response when stimmed
Slow (RED) Fiber Characteristics
Slow to fatigue
Small diameter, more mitochondria
3x longer to contract
Ex. Help hold your arm up (for long periods of time)
Intermediate (PINK) Fiber Characteristics
Mix of slow and fast
Fast Contraction speed
Mitochondria amt= intermediate
Fatigue resis. = intermed
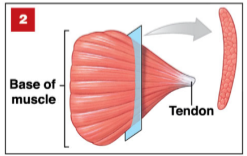
Convergent Muscle
Force produced
Split along multiple axes
Produce more force than parallel muscles of same size
Origin
the fixed/most PROXIMAL pt. of attachment
Muscles begin at the
Insertion
the moving part
most DISTAL pt. of attactment
Muscles terminate at the
4 Skeletal groups (based on actions)
Agonist, Antagonist, Synergist, & Fixators
Agonist
Prime mover of a limb
Antagonist
Actions opposed the agonist
Synergist
Assits the Agonist in a particular move
Fixators
Stabilize joints