Ch5 - Photosynthesis
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
1) Which would a car use: potential, kinetic or chemical energy?
Your car uses fuel as potential AND kinetic energy. The gas in your tank is potential--stored energy, the gas being combusted is kinetic.
2
New cards
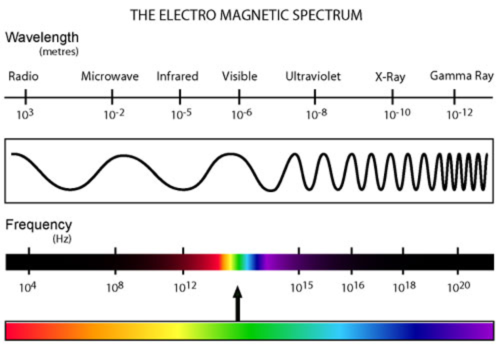
2) Which wavelengths of light have the most energy and which has the least energy?
Red has the least amount of energy while violet has the most amount of energy.
3
New cards
3) What molecules make glucose? (formula) where do these molecules come from?
The carbon creates the glucose, and it comes from the CO2 in the air.
4
New cards
4) Is algae eukaryotic? Are they autotrophs?
Yes, it is both eukaryotic and autotrophs.
5
New cards
5) Is the energy of the oils made by algae chemical energy? is it potential?
The oil from the algae makes potential chemical energy. Once it is burned, it becomes chemical kinetic energy.
6
New cards
6) When you use energy, it becomes kinetic energy. If you burn oil from a plant, does that also become kinetic energy?
Yes
7
New cards
7) What organelle carries out photosynthesis?
Chloroplast
8
New cards
8) What is an autotroph? Where do they get energy?
They get their energy from the sun and then they convert solar energy into chemical energy
9
New cards
9) Y/N: Do autotrophs remove CO2 from the air? Do they add O2 in the air? Do they feed the planet? Can they be a fuel source?
Yes, Yes, Yes, and yes (it can make biofuel)
10
New cards
10) What is the formula for photosynthesis? What is the formula formula for cellular respiration?
6CO2 + 6HO2 + Solar Energy -> C6H12O6 + 602 (Photosynthesis)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Energy (Cellular Repiration)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP Energy (Cellular Repiration)
11
New cards
11) What happens to the chemical energy produced by Photosynthesis?
Once plants make a glucose (energy) molecule, they must use it to live, grow, make fruit, carry out MORE photosynthesis. It takes 9 ATP chemical energy molecules to make 1 glucose molecule. Example with money. In order for you to make $38.00, it costs you $9.00. It takes a lot of energy to make a glucose molecule from CO2 in the air. It takes a lot of energy to split water molecules too.
12
New cards
12) Which organism has Chloroplasts? Which organism gives off O2 as a waste product? Whterm-6ich gives off CO2 as a waste product and ingest it's chemical energy?
1. Autotroph
2. Autotroph
3. Heterotroph
2. Autotroph
3. Heterotroph
13
New cards
13) Read page 110. If a land developer disturbs a 10,000m^2 and destroys cyanobacteria and plant life in the process, how much does this effect CO2 in the air? This land will not be sucking CO2 anymore. But how much less CO2 will be removed?
14
New cards
14) What are the imputes and outputs of photosynthesis?
Water, carbon dioxide, and energy in the form of sunlight are inputs, and the outputs are glucose and oxygen.
15
New cards
15) What process does the algae use to make biochemicals they use for energy storage.
Photosynthesis
16
New cards
16) Where is the carbon source for photosynthesis?
Comes from carbon Dioxide in the air.
17
New cards
17) In the first phase of photosynthesis, what does the plant convert light energy into?
Chemical Energy
18
New cards
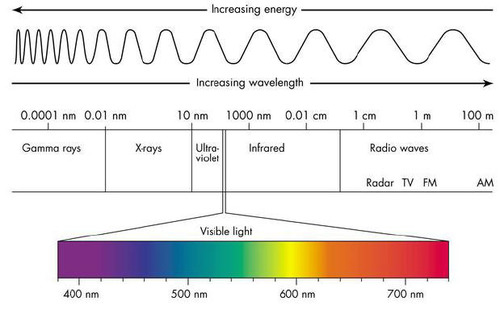
18) What colors are reflected in photosynthesis, what are absorbed?
blue- and red-light waves are absorbed, and green-light waves are reflected.
19
New cards
19) What is the conversion of inorganic carbon to organic carbon called?
Carbin Fixation
20
New cards
20) They make biofuels in Hawaii from algae because Hawaii has?
Hawaii has an algae farm because of its warmth and year-round sunlight.
21
New cards
21) Which are true, which are false:
1.When burned biofuel releases the same amount of CO2 that it took in photosynthesis.
2.When burned, biofuels release fewer pollutants than traditional fuels.
3.To produce enough algae-based biofuel to meet human needs,
algae need more CO2 than is available in the air.
4.Algal based biofuel requires more nutrients that corn based biofuel.
5.In additional to biofuel, algae make other products that can be used to generate electricity
1.When burned biofuel releases the same amount of CO2 that it took in photosynthesis.
2.When burned, biofuels release fewer pollutants than traditional fuels.
3.To produce enough algae-based biofuel to meet human needs,
algae need more CO2 than is available in the air.
4.Algal based biofuel requires more nutrients that corn based biofuel.
5.In additional to biofuel, algae make other products that can be used to generate electricity
1. True
2. True
3. True
4. False
5. False
2. True
3. True
4. False
5. False
22
New cards
22) Yes or No:
1.The US exports oil to the rest of the world.
2.Saudi Arabia has the largest petroleum oil reserves in the world.
3.35% of energy consumed in the US comes from petroleum.
4.11% of US renewable energy comes from renewable resources.
5.The US is investing money to developed more algae sources of biodiesel oil.
1.The US exports oil to the rest of the world.
2.Saudi Arabia has the largest petroleum oil reserves in the world.
3.35% of energy consumed in the US comes from petroleum.
4.11% of US renewable energy comes from renewable resources.
5.The US is investing money to developed more algae sources of biodiesel oil.
1. Yes
2. Yes
3. No
4. No
5. No
2. Yes
3. No
4. No
5. No
23
New cards
23) Which light color has the longest wavelength? What does this mean with energy?
Red has the longest wavelength, this means that it has less energy.
24
New cards
24) What does it mean when we see color?
The colors you see are reflected, not absorbed.
25
New cards
25) During the light reactions of photosynthesis, what happens to the water molecule?
O2 is being released as a waste product from the water. The water molecule is being split.
26
New cards
26) Using infographic 6.1, what pathway does the plant use to break down glucose? (Look on study guide to see infographic)
Pathway B
27
New cards
27) In the overall equation for photosynthesis, 6 molecules of CO2 result in how many molecules in what compound?
6 Molecules of Oxygen
28
New cards
28) Which molecule helps a plant absorb sunlight?
Chlorophyll
29
New cards
29) Where do light dependent reactions take place? Where do light independent take place?
The light dependent reactions happen on the thylakoid, but the light independent happens in the stroma(juice/cytoplasm) within the chloroplast.
30
New cards
30) Put in correct order.
a. CO2 is absorbed
b. Photons of light are absorbed by chlorophyll reflects green light
c. Water molecules are absorbed and then are split giving off O2 gas
d. Glucose is produced
e. Electrons from the split water help fuel the Calvin Cycle along with 9 ATP
a. CO2 is absorbed
b. Photons of light are absorbed by chlorophyll reflects green light
c. Water molecules are absorbed and then are split giving off O2 gas
d. Glucose is produced
e. Electrons from the split water help fuel the Calvin Cycle along with 9 ATP
It goes C, B, E, A, D
31
New cards
31) The Calvin cycle is another name for...
Light Independent
32
New cards
32) What is the end product of the Calvin cycle?
G3P (Glucose and other organic compounds)
33
New cards
33) If CO2 is removed from the plant's environment, what would happen to the production of glucose?
Without carbon dioxide, the plant's cells would not be able to perform photosynthesis and produce glucose. Photosynthesis would cease and the plant would not be able to produce high energy sugars- glucose.
34
New cards
34) If you continue to increase light intensity, what will happen to the rate of photosynthesis, as long as temperature remains the same?
As the light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis increases. However, the rate will not increase beyond a certain level of light intensity. At high light intensities the rate becomes constant, even with further increases in light intensity, there are no increases in the rate.
35
New cards
35) What would happen to the rate of photosynthesis when the temperature gets to 110 degrees F?
When it is hot out, less oxygen is produced.
36
New cards
36) Use infographic 5.3 which graph represents the effect of temperature on photosynthesis? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
Graph #1
37
New cards
37) Use infographic 5.3 to answer this question, which graph represents light intensity? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
Graph #2
38
New cards
38) Can plants release the energy from glucose during photosynthesis?
Plants never release energy during photosynthesis.
39
New cards
39) Is Oxygen an input of photosynthesis?
Yes
40
New cards
40) Is CO2 an output of photosynthesis?
No
41
New cards
41) Are photons an output of photosynthesis?
No
42
New cards
42) Is Glucose an input of photosynthesis?
No
43
New cards
43) Is water an output of photosynthesis?
No
44
New cards
44) What are the products of photosynthesis?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
45
New cards
45) Use infographic 5.4. A struggling student named Anita Bath, prepared two beakers with identical plants and spring water. She placed one beaker in the shade and the other under a full spectrum lamp. She changed the distance of the plant to the lamp to the beaker and recorded how many bubbles came up from the plant. What distance gives the greatest number of bubbles? What does this tell you about light intensity? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
20 cm gives greatest bubbles.
46
New cards
46) Use infographic 5.4 What are those bubbles? How do you know? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
O2, the formula for photosynthesis proves it.
47
New cards
47) Use infographic 5.4 If the student moved the plant right up against the light source, but heat is not a factor, what would happen to oxygen production? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
It would most likely remain at 110 because at some point rate of photosynthesis will level off, the plant cannot split water molecules any faster.
48
New cards
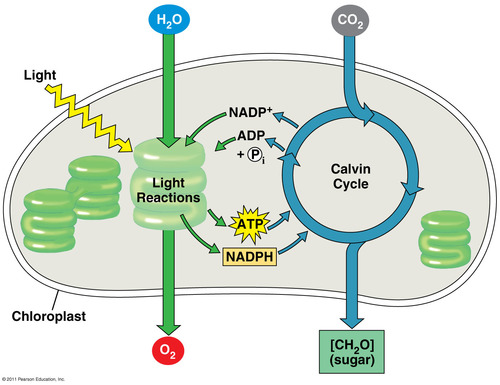
48) Infographic 5.5 What is being shown here? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
Photosynthesis
49
New cards
49) Label the numbers for infographic 5.5 (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
1. Calvin Cycle
2. Sucrose (export)
3. O2
4. Light
5. H2O
2. Sucrose (export)
3. O2
4. Light
5. H2O
50
New cards
50) Infographic 5.6 A biology student named Stew Piddy mixed a diluted solution of bromothymol blue indicator into test tubes A, B, C. Bromothymol blue changes to a yellow color when exposed to CO2. He placed a water plant sprig into test tube A and B. Test tube B was placed in 24 hours of darkness and A was placed under a full spectrum grow light. Which test tube is the control? At the end of the experiment, what colors are the test tubes? (Look at study guide to see the infographic)
C. Is the control
A. Blue became so much more O2 will be produced than CO2.
B. Yellow
C. Blue
A. Blue became so much more O2 will be produced than CO2.
B. Yellow
C. Blue
51
New cards
51. Which test tube would cellular respiration AND photosynthesis take place? Which would only be cellular respiration?
A. Plants do carry out cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
B. would only be cell respiration
B. would only be cell respiration
52
New cards
52) What happens to stomata when the temperature gets too hot? How does this affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Stomata (Leaf lips) are what gas exchanges takes place as well as transpiration. When the temperature gets too high, the stomata will close and not take in any CO2. O2 gas is not give off. The plant does this to prevent water loss due to transpiration. No photosynthesis is taking place when it gets too hot.
53
New cards
53) What is the role of water in photosynthesis?
To release oxygen
54
New cards
54) What happens when there is no sunlight? Circle all that apply.
*Chemical energy is produced using only H2O and CO2.
*Plants stop generating chemical energy from sunlight.
*Chloroplasts use their glucose reserves for ATP synthesis.
*The process of photosynthesis shuts down.
*Plants convert sugars into the fats and proteins that are also needed.
* Plants will carry out the Calvin cycle as long as there is an ATP reserve.
*Chemical energy is produced using only H2O and CO2.
*Plants stop generating chemical energy from sunlight.
*Chloroplasts use their glucose reserves for ATP synthesis.
*The process of photosynthesis shuts down.
*Plants convert sugars into the fats and proteins that are also needed.
* Plants will carry out the Calvin cycle as long as there is an ATP reserve.
*Plants stop generating chemical energy from sunlight.
*Plants convert sugars into the fats and proteins that are also needed.
*Plants will carry out the Calvin cycle as long as there is an ATP reserve.
*Plants convert sugars into the fats and proteins that are also needed.
*Plants will carry out the Calvin cycle as long as there is an ATP reserve.
55
New cards
55) Why do leaves appear yellow, red or orange in the fall?
When the chlorophylls dissolve, the other pigments show up in the leaves in the fall
56
New cards
56) Label the parts of infographic 5.1
1. Thylakoids
2. Stroma
2. Stroma
57
New cards
Extra) What does Potential, Kinetic, and Chemical Energy mean?
-Potential energy is stored energy in chemical bonds
-Kinetic energy is the energy of motion or movement
-Chemical Energy is potential energy stored in bonds of biological molecules. It breaks the bonds to release stored energy to do work.
-Kinetic energy is the energy of motion or movement
-Chemical Energy is potential energy stored in bonds of biological molecules. It breaks the bonds to release stored energy to do work.