water and carbon cycles - amazon rainforest case study
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
how much carbon is stored in the amazon?
thought that there are approximately 100 PgC in aboveground biomass (AGB) in Amazonia.
how big is the amazon?
The Amazon forest covers an estimated 5.3 million sq km and holds 17% of the global terrestrial vegetation carbon stock.
what is the carbon cycle in the amazon?
Untouched Amazon forests take in more carbon dioxide than they put back into the atmosphere - shows that the Amazon forests help reduce global warming by lowering the planet's greenhouse gas levels.
Dead Amazonian trees (which account for around 20% of above ground biomass) emit an estimated 1.9 billion tons (1.7 billion metric tons) of carbon to the atmosphere each year.
In a normal year, the Amazon rainforest absorbs about 2.2 billion tons (2 billion metric tons) of carbon dioxide. This means that untouched tropical forests act as a SINK for carbon.
what was the tipping point for the amazon to become a carbon source?
2022 → 20% of amazon has been deforested - a tipping point
amazon has become a source as opposed to a sink
what is rainfall like in the amazon?
very high
Average rainfall across the whole Amazon basin is approximately 2300 mm annually.
In some areas of the northwest portion of the Amazon basin, yearly rainfall can exceed 6000 mm.
what happens to the rainfall in the amazon?
around 1/3 of the rain in the Amazon basin is discharged into the Atlantic.
half of the rainfall in some areas may never reach the ground, being intercepted by the forest and re-evaporated → evaporation occurs from surface stores, or is released into the atmosphere by transpiration.
moisture contributes to the formation of rain clouds, which release the water back onto the rainforest. In the Amazon, 50-80% of moisture remains in the ecosystem’s water cycle.
what are the global effects of the amazon?
moisture created by rainforests travels around the world.
Moisture created in the Amazon ends up falling as rain as far away as Texas, and forests in Southeast Asia influence rain patterns in south-eastern Europe and China.
When forests are cut down, less moisture goes into the atmosphere and rainfall declines, sometimes leading to drought - have been made worse by deforestation
how has farming affected water and carbon cycles?
Pasturelands and croplands have a higher albedo and decreased water demand, evapotranspiration and canopy interception compared with the forests they replace.
Forests in the state of Mato Grosso:
Contributed about 50 km3 per year of evapotranspiration to the atmosphere in the year 2000.
Deforestation reduced that forest flux rate by approximately 1 km3 per year throughout the decade. By 2009, contribution dropped to 40 km3 per year.
In Rondônia, Brazil, one of the most heavily deforested areas of Brazil, daily rainfall data suggest that deforestation since the 1970s has caused an 18-day delay in the onset of the rainy season.
how have wildfires affected the amazon?
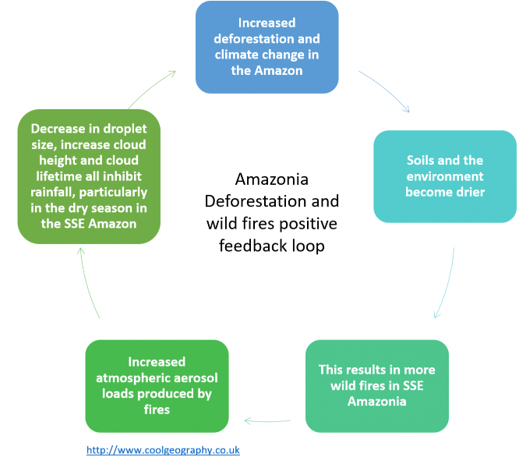
what are the effects of deforestation on the amazon?
Removing trees deprives the forest of portions of its canopy, which blocks the sun’s rays during the day, and holds in heat at night. This disruption leads to more extreme temperature swings that can be harmful to plants and animals → moist tropical soils quickly dry out.
top meter holds 66.9 PgC with around 52% of this carbon pool held in the top 0.3 m of the soil, the layer which is most prone to changes upon land use conversion and deforestation.
Deforestation releases much of this carbon through clearance and burning.
For the carbon that remains in the soil, when it rains soil erosion will wash much of the carbon away into rivers after initial deforestation + atmosphere via decomposition
what are the effects of deforestation on the water cycle?
1. There is increased soil erosion and weathering of rainforest soils as water acts immediately upon them rather than being intercepted.
2. Flash floods are more likely to happen as there is less interception and absorption by the forest cover.
3. Conversely, the interruption of normal water cycling has resulted in more droughts in the forest, increasing the risk of wild fires
4. More soil and silt is being washed into rivers, resulting in changes to waterways and transport
5. Disrupt water supplies to many people in Brazil
what were the stores in the carbon cycle?
roots, branches, leaves and trunks of trees and other vegetation
what released carbon in the amazon?
almost all the carbon that the rainforest absorbs - is also released when plants die and decompose or when rainfall washes away soil
how is water transported in the amazon?
trees release 20 billion tons of moisture into the atmosphere which helped clouds form
how has climate change impacted the water cycle?
led to higher temperatures and reduced rainfall, hwich ,akes the forest more vulnerable to fires and reduces the ability to absorb carbon dioxide
how does deforestation impact the water cycle?
when trees are cut down, there is less water to evaporate into the atmosphere, which can lead to less rain → can cause the land to become drier and less stable and can increase the risk of droughts and flooding
how does evaporation levels impact the water cycle?
trees absorb water from the soil and release it into the air through transportation when trees are cut down - can dry out the air
how does infiltration and runoff impact the water cycle?
roots soak up rainwater, which helps reduce runoff → deforestation - decreases infiltration and higher runoff
how much carbon do trees in the amazon hold?
around 1% of all the tree species in the Amazon account for half of the carbon locked in the vast South American rainforest.
how much carbon do dead amazon trees release?
emit an estimated 1.9 billion tons (1.7 billion metric tons) of carbon to the atmosphere each year.
what happens to rainfall in the amazon?
1. Up to half of the rainfall in some areas may never reach the ground, being intercepted by the forest and re-evaporated into the atmosphere.
2. Additional evaporation occurs from ground and river surfaces, or is released into the atmosphere by transpiration from plant leaves
3. This moisture contributes to the formation of rain clouds, which release the water back onto the rainforest → 50-80 percent of moisture remains in the ecosystem’s water cycle.
how does logging cause change in the carbon and water cycle?
involves cutting down trees for sale as timber or pulp.
timber is used to build homes, furniture, etc. and the pulp is used to make paper and paper products.
Logging can be either selective or clear cutting.
Selective logging is selective because loggers choose only wood that is highly valued, such as mahogany.
Clear-cutting is not selective. Loggers are interested in all types of wood and therefore cut all of the trees down, thus clearing the forest
how does road building impact carbon and water cycles?
trees are also clear for roads.
Roads are an essential way for the Brazilian government to allow development of the Amazon rainforest.
However, unless they are paved many of the roads are unusable during the wettest periods of the year.
Trans Amazonian Highway has already opened up large parts of the forest and now a new road is going to be paved
BR163 is a road that runs 1700km from Cuiaba to Santarem
The government planned to tarmac it making it a superhighway - damages the rainforest in 10 meters around it
how does energy development impact carbon and water cycles?
focussed mainly on using Hydro Electric Power, and there are 150 new dams planned for the Amazon alone.
dams create electricity as water is passed through huge pipes within them, where it turns a turbine which helps to generate the electricity.
Dams displace many people and the reservoirs they create flood large area of land, which would previously have been forest. - also alter the hydrological cycle and trap huge quantities of sediment behind them.
Belo Monte dam started operating in April 2016 and will generate over 11,000 Mw of power.
how does settlement and population growth impact water and carbon cycles?
Many people are migrating to the forest looking for work associated with the natural wealth of this environment.
Settlements like Parauapebas, an iron ore mining town, have grown rapidly, destroying forest and replacing it with a swath of shanty towns.
population has grown from 154,000 in 2010 to 220,000 in 2012. The Brazilian Amazon’s population grew by a massive 23% between 2000 and 2010, 11% above the national average.
what are the atmospheric impacts of deforestation?
Pasturelands and croplands (e.g. soya beans and corn) have a higher albedo and decreased water demand, evapotranspiration and canopy interception compared with the forests they replace.
forests in the state of Mato Grosso;
• Contributed about 50 km3 per year of evapotranspiration to the atmosphere in the year 2000.
• Deforestation reduced that forest flux rate by approximately 1 km3 per year throughout the decade.
• As a result, by 2009, forests were contributing about 40 km3 per year of evapotranspiration in Mato Grosso.
what impact does the amazon have on climate change?
Around 30% of anthropogenic carbon emissions come from burning the rainforests alone.
Forests that experienced disturbances such as logging and fires store 40% less carbon than undisturbed forests.
what were the impacts of climate change on the amazon?
• Some Amazon species capable of moving fast enough will attempt to find a more suitable environment.
• Higher temperatures will impact temperature-dependent species like fish, causing their distribution to change.
• Reduced rainfall and increased temperatures may also reduce suitable habitat during dry, warm months and potentially lead to an increase in invasive, exotic species, which then can out-compete native species.
• Less rainfall during the dry months could seriously affect many Amazon rivers and other freshwater systems.
• The impact of reduced rainfall is a change in nutrient input into streams and rivers, which can greatly affect aquatic organisms.
• A more variable climate and more extreme events will also likely mean that Amazon fish populations will more often experience hot temperatures and potentially lethal environmental conditions.
• Flooding associated with sea-level rise will have substantial impacts on lowland areas such as the Amazon River delta. The rate of sea-level rise over the last 100 years has been 1.0-2.5 mm per year, and this rate could rise to 5 mm per year.
what are the impacts of deforestation on rivers?
1. There is increased soil erosion and weathering of rainforest soils as water acts immediately upon them rather than being intercepted.
2. Flash floods are more likely to happen as there is less interception and absorption by the forest cover.
3. Conversely, the interruption of normal water cycling has resulted in more droughts in the forest, increasing the risk of wild fires
4. More soil and silt is being washed into rivers, resulting in changes to waterways and transport
5. Disrupt water supplies to many people in Brazil
how does temperature affect stores and flows?
average temp 25-30 which results in high rates of evapotranspiration
humid - high convectional rainfall from Jan-May 200-300 mm resulting in high atmospheric humidity
how does relief impact stores and flows?
made up of extensive lowlands → west andes have steep catchments which cause rapid runoff
water moves via overland flow and throughflow
how does geology impact stores and flows?
rocks are porous and have better capacity to store water
→ western part of the amazon catchment contains limestone and sandstone rocks
impermeable catchment
results in minimal storage capacity - increased rates of run off
how does vegetation impact the water cycle?
absorbs and stores water from the soul which is released through transportation
vegetation absorbs 90% of rainfall
each tree transpires 760 litres of water per year - whole forest = 76,000 litres
what are the biome characteristics?
climate = hot and wet - monthly temps range between 25-27% and rainfall averages 2677 per annum
constant, warm temps permit reproduction all year round which means natural selection takes place rapidly
forest stratification creates variations in temperatures, humidity, height and soil conditions
soils: are deep because warm, wet conditions encourage intense weathering of bedrock, heavy rainfall encourages intense leaching of soluble minerals which leads the soil acidic
what are the plant adaptations and ecological responses to climate?
Amazonia receives high levels of solar energy throughout the year which leads to high rates of photosynthesis and lots of biomass - due to the warm and wet climate this encourages nutrient growth
decomposers quickly decompose any dead organic matter → release mineral nutrients which are rapidly recycled by the roots
what are the ecological consequences of deforestation?
unless seeds germinate almost immediately after disposal, they are eaten or decompose rapidly
complex relationships between species
e.g. the Brazil nut tree is dependent in several species for its survival as the agouti is the only animal that can open the outer pod of the brazil nut and storing the nuts is responsible for dispersing nuts throughout the forest
what are the ways of protecting the Amazon rainforest in the future?
establishing clear property rights over land → the Brazilian government is keen to establish a land registry to reduce land grabbing and illegal logging
paying owners not to cut down trees - REDD is based on the idea that affluent countries should be paying poorer countries not to cut down trees → 4.5 billion was pledged to support this idea following the Copenhagen climate talks in 2009
encouraging people to buy forest products from legally registered sellers
ecotourism - protects rainforests from hunting, logging and mining and provides local employment e.g. the Posada Amazon lodge in the Peruvian Amazon, is jointly run by an eco-tour operation and the local Eseieja community
how does precipitation and evaporation impact the water cycle in the amazon?
amazon basin receives between 2000-3000mm of rainfall annually, making it one of the wettest areas - rainfall largely influences by the intertropical convergence zone which shifts seasonally
plants absorb water through their roots and release water vapor through stomata - around 25-50% of the Amazon’s rainfall is recycled within the basin through this process
how do river systems and water flow impact the amazon’s water cycle?
rainforest's dense canopy slows down water runoff and reduces the rate of soil erosion, maintaining the region's hydrological balance.
system helps regulate the flow of rivers, preventing extreme flooding events and maintaining water quality.
how does the amazon’s water cycle influence regional climate?
Amazon contributes to regional rainfall patterns in South America. For example, it drives moisture flow toward the Andes Mountains and the southeastern parts of the continent.
Disruption of the water cycle, particularly due to deforestation, can lead to severe consequences for agriculture and water resources far beyond the boundaries of the rainforest.
how does carbon sequestration occur in the amazon?
Photosynthesis: Trees and plants in the Amazon absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis, storing carbon in their biomass (trunks, leaves, roots, etc.) and soil. The Amazon sequesters approximately 1-2 billion metric tons of CO₂ per year, making it one of the largest carbon sinks globally.
Biomass Storage: The Amazon stores an estimated 150-200 billion tons of carbon in its vegetation and soils.
how does respiration and decomposition occur in the amazon?
Plant Respiration: Plants release CO₂ back into the atmosphere during respiration, but this is balanced by the carbon they absorb during photosynthesis.
Decomposition: Dead plants, leaves, and organic material decompose in the forest floor, a process carried out by bacteria and fungi that release CO₂.
what are some strategies being used to stop deforestation?
Protected Areas & Indigenous Reserves – Large portions of the Amazon are designated as protected national parks and indigenous lands. These areas are legally safeguarded against deforestation.
Stronger Law Enforcement – Governments in Brazil, Peru, and Colombia have increased monitoring and enforcement against illegal logging, mining, and land grabbing.
Satellite Monitoring & AI Technology – Organizations like the Amazon Conservation Association use satellites and AI to detect deforestation in real time, allowing for quicker interventions.
Zero-Deforestation Supply Chains – Companies like Nestlé and Unilever have pledged not to source products like soy or beef from deforested land, reducing demand for deforestation-driven agriculture.
Reforestation & Restoration Programs – Initiatives like Brazil’s “Amazon Fund” finance reforestation projects, and groups like the Trillion Trees Initiative work on large-scale restoration.
what are some examples of sustainable farming in brazil?
The Xingu Seed Network (Brazil) – This initiative, led by indigenous and local communities, promotes reforestation through agroforestry by collecting and planting native seeds. It has restored over 6,000 hectares of degraded land.
Paiter Suruí Carbon Project (Brazil) – The Suruí indigenous people use agroforestry to cultivate coffee while protecting their forest, generating income through sustainable agriculture and carbon credits.
what are some examples of community based resource management in the amazon?
Bolsa Floresta (Brazil) – A state program in Amazonas that pays families a monthly stipend for protecting forests and engaging in sustainable livelihoods like fishing, ecotourism, and agroforestry.
Chocó-Darién Conservation Corridor (Colombia) – A community-led conservation project where Afro-Colombian and indigenous communities manage the land while sustainably harvesting cocoa and medicinal plants.
what are some carbon credit strategies in the amazon?
Tambopata-Bahuaja REDD+ Project (Peru) – A conservation project that protects 600,000 hectares of rainforest, generating carbon credits that fund sustainable livelihoods like beekeeping and ecotourism.
Jari Pará REDD+ Project (Brazil) – A large-scale carbon credit initiative that helps prevent deforestation while investing in sustainable agriculture and reforestation.