Triangles of the Neck (4/10)
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
true or false: fascial planes divide the neck into 4 main fascial compartments—this has implications for migration of infection
true
name the 4 fascial planes of the neck
investing fascia
pretracheal fascia
carotid sheath
prevertebral fascia
what does the investing fascia surround?
encircles the neck as a whole
surrounds superficial muscles (trapezius and SCM)
(not a Q) investing fascia
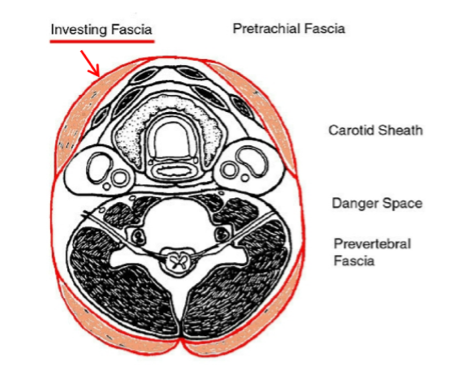
(not a Q) investing fascia
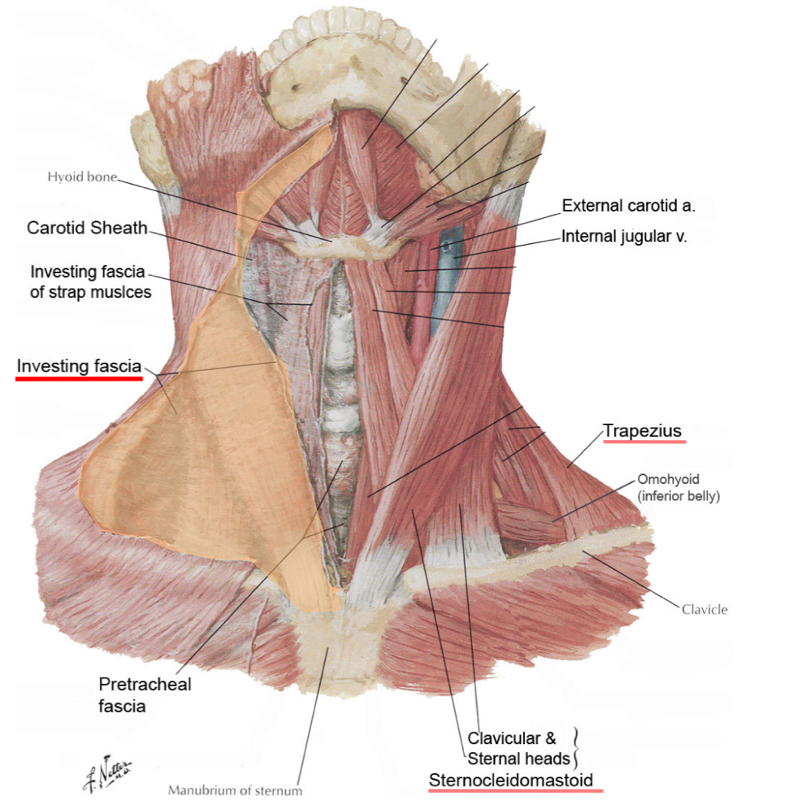
name the 2 heads of the SCM
clavicular head
sternal head
what does pretracheal fascia surround?
viscera
(thyroid, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, trachea)
what is the buccopharyngeal fascia?
the part of the pretracheal fascia that covers the posterior surface of the pharyngeal muscles
true or false: the trachea is an entirely cartilaginous structure
false
the trachea is a C-shaped cartilaginous structure closed off posteriorly by muscle
(not a Q) pretracheal fascia
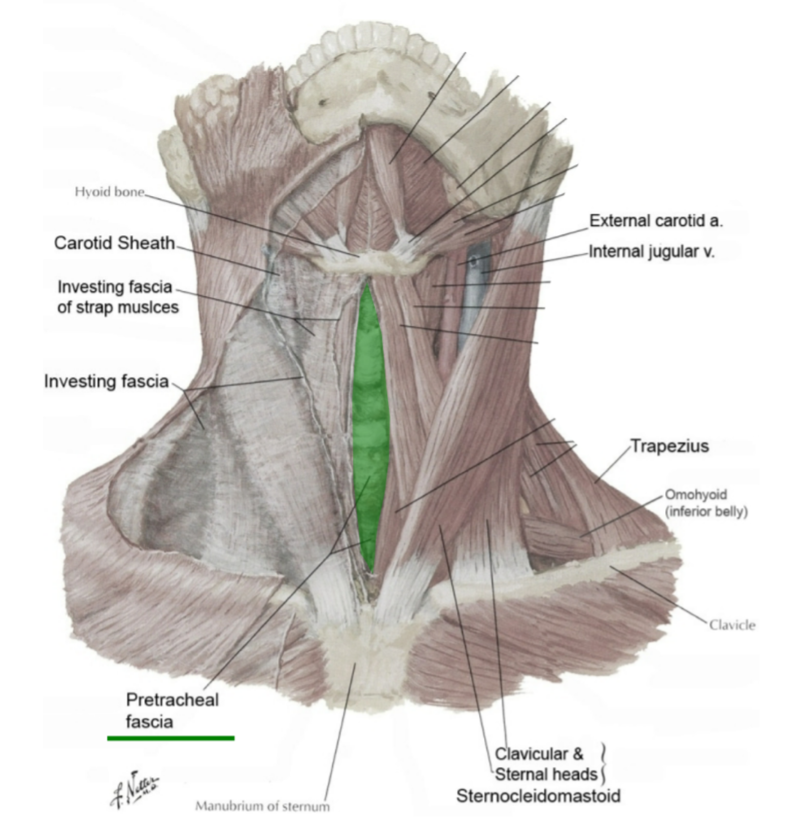
(not a Q) pretracheal fascia
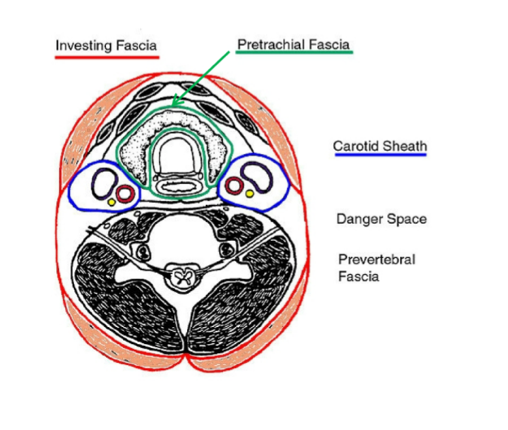
what does the carotid sheath surround?
neurovascular bundle
(contains carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, vagus nerve)
what do the common carotid arteries branch off of?
the R carotid artery branches off of the brachiocephalic trunk
the L carotid artery branches off of the aortic arch
(not a Q) carotid sheath
*there is a L and R carotid sheath, one on either side
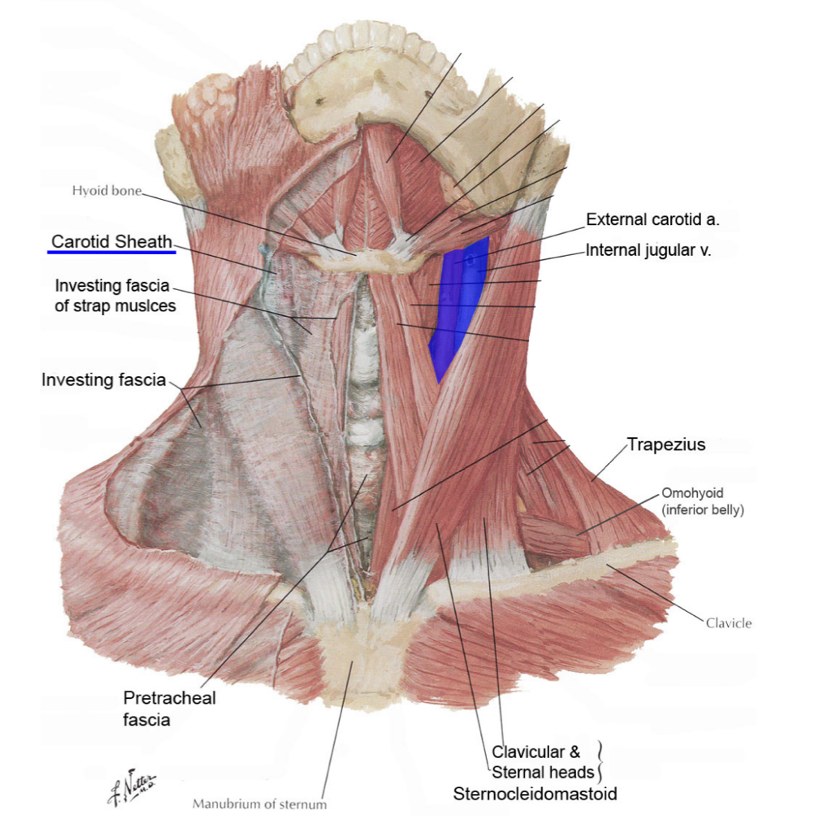
(not a Q) carotid sheath
what does prevertebral fascia surround?
epaxial muscles
prevertebral muscles
scalene muscles
vertebra
(prevertebral fascia surrounds all these structures in a continuous sheath)
what do prevertebral muscles include?
longus capitis
longus colli (reference structure on axial images)
(not a Q) prevertebral fascia
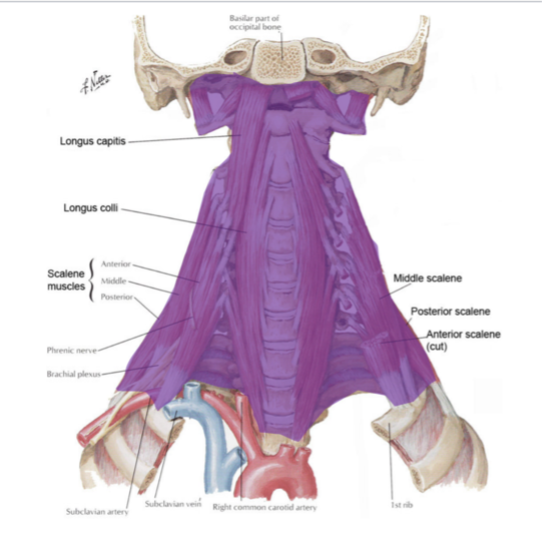
(not a Q) prevertebral fascia

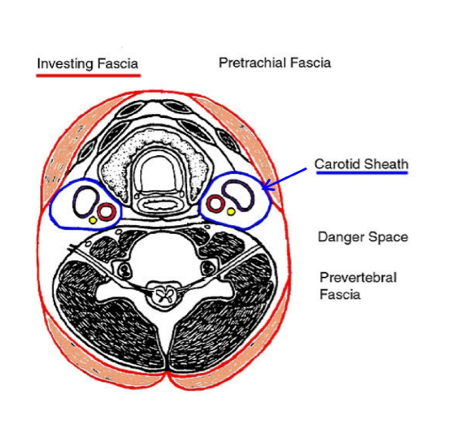
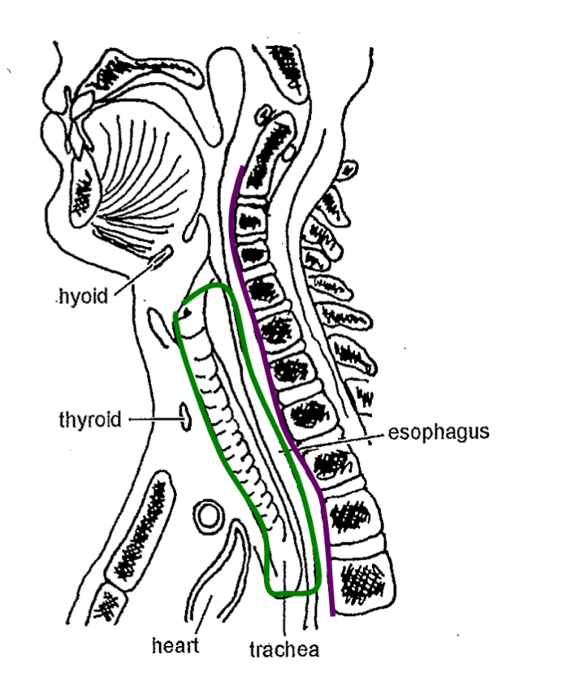
where is the retropharyngeal space (AKA danger space) located?
between prevertebral fascia and the buccopharyngeal fascia
(not to be confused with the “danger zone,” which is on the face)
what does the retropharyngeal space contain?
loose areolar tissue
what does the retropharyngeal space communicate with, and what is its clinical significance?
it communicates with the superior mediastinum
provides a route for infection to spread from the neck to the thorax
(not a Q) retropharyngeal/danger space
*green = buccopharyngeal fascia; purple = prevertebral fascia
what are the attachments of the SCM?
the SCM passes obliquely from the sternum and clavicle to attach to the mastoid process and occipital bone
what structure divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles?
SCM
(not a Q) triangles of the neck
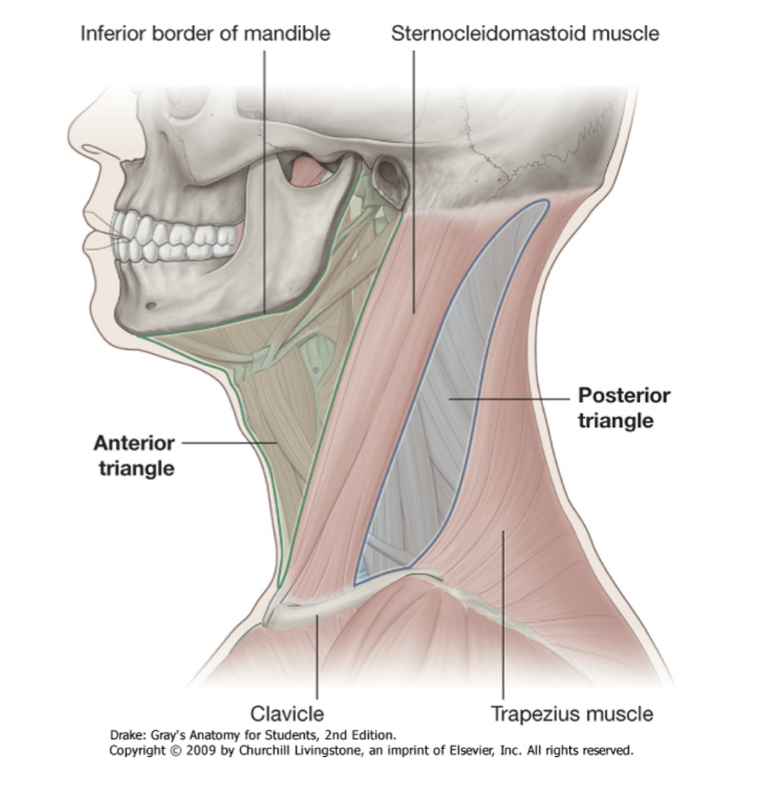
what is the anterior boundary of the posterior triangle of the neck?
posterior border of SCM
what is the posterior boundary of the posterior triangle of the neck?
anterior border of trapezius
what is the base of the posterior triangle of the neck?
superior border of clavicle
what is the roof of the posterior triangle of the neck?
investing layer of deep cervical fascia
what is the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck?
prevertebral fascia covering the splenius capitis, levator scapulae, and scalene muscles
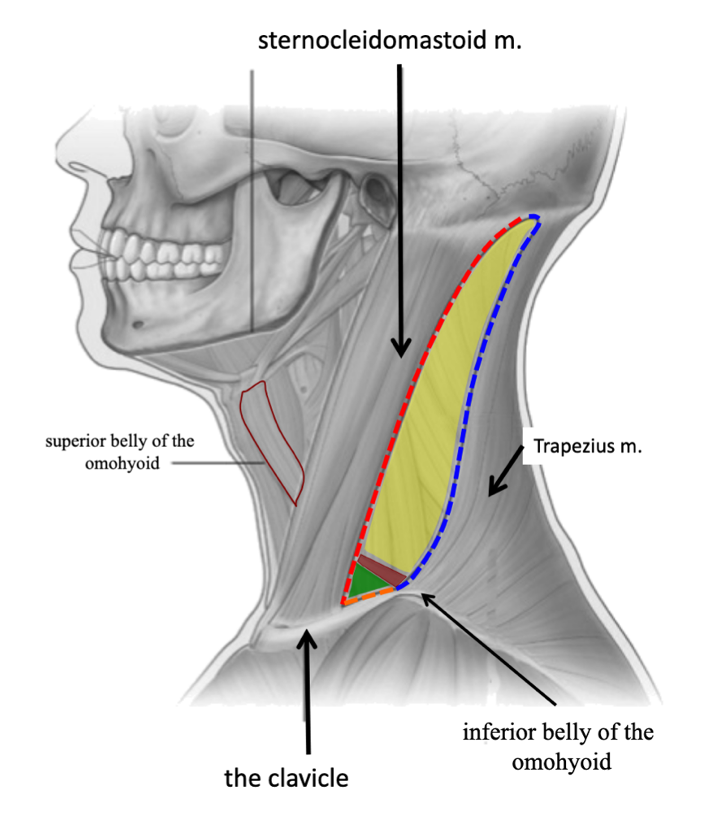
what structure divides the posterior triangle of the neck into 2 smaller triangles?
inferior belly of the omohyoid
the posterior triangle of the neck is subdivided into what named smaller triangles?
occipital triangle
supraclavicular triangle
name the contents of the posterior triangle of the neck
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
cutaneous branches of the cervical plexus
inferior belly of the omohyoid
thyrocervical trunk
subclavian artery and vein
name the most specific triangle of the neck in which the subclavian artery and vein are located
supraclavicular triangle
(not a Q) posterior triangle of the neck
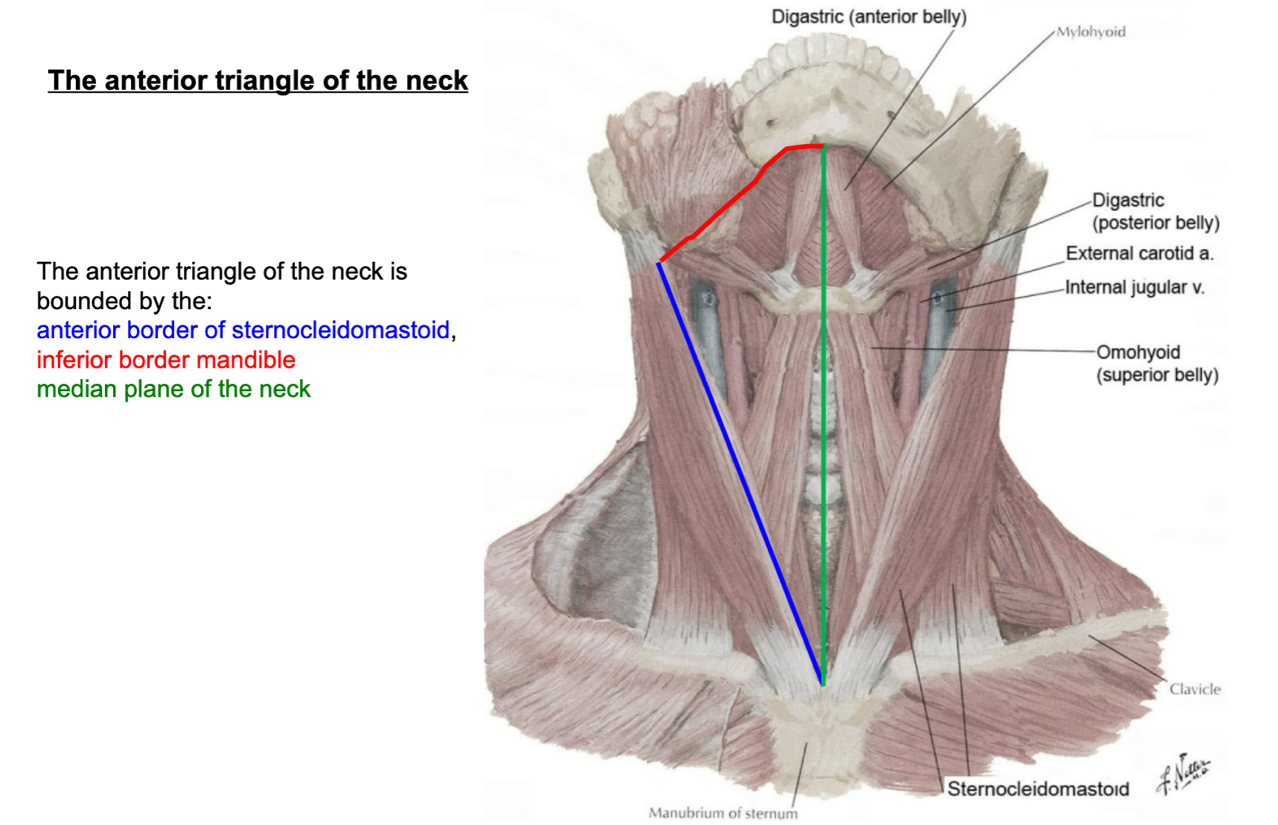
name the boundaries of the anterior triangle of the neck
anterior border of SCM
inferior border of the mandible
median plane of the neck
(not a Q) anterior triangle of the neck
*there is a L and R anterior triangle of the neck, separated by the median plane of the neck
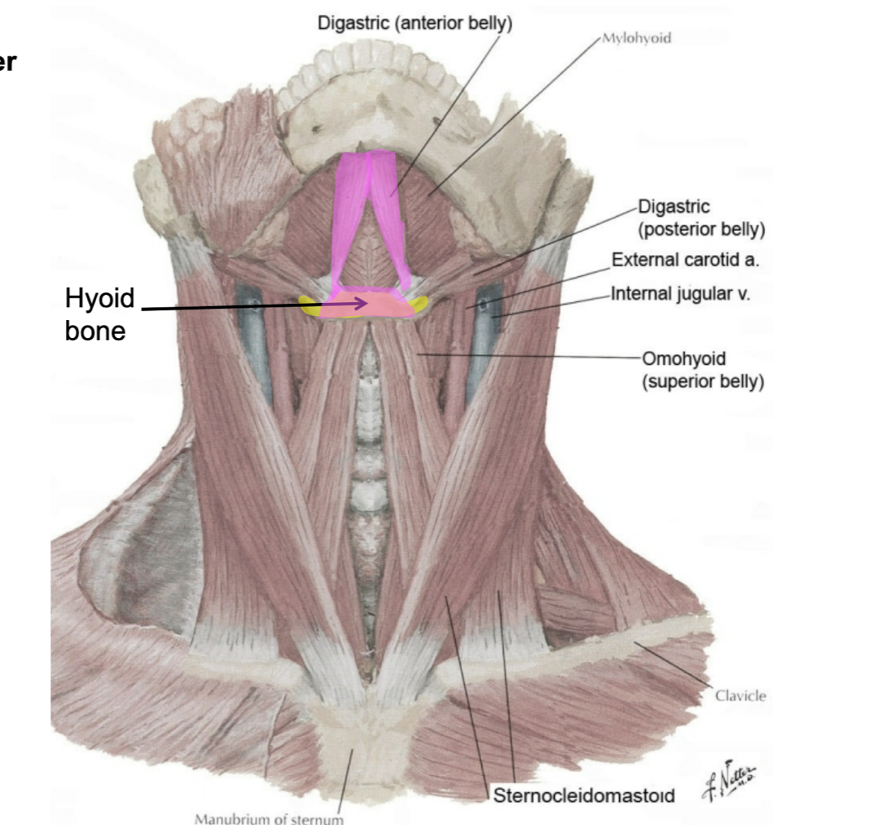
name the subdivisions of the anterior triangle of the neck
submental triangle
digastric triangle
muscular triangle
carotid triangle
is the submental triangle paired or unpaired?
unpaired
name the apex of the submental triangle
chin
name the base of the submental triangle
hyoid bone
name the L/R borders of the submental triangle
R and L anterior belly of digastric muscles
name the floor of the submental triangle
mylohyoid muscles
what are the contents of the submental triangle?
submental lymph nodes
what is unique about the hyoid bone?
it does not articulate with another bone
(not a Q) submental triangle
is the digastric triangle paired or unpaired?
paired
what is the superior boundary of the digastric triangle?
mandible
what is the inferior boundary of the digastric triangle?
posterior belly of digastric
what is the medial boundary of the digastric triangle?
anterior belly of digastric
what is the floor of the digastric triangle?
mylohyoid
name the contents of the digastric triangle?
stylohyoid muscle
facial artery and vein
submandibular gland
submandibular lymph nodes
the stylohyoid muscle is parallel to what muscle?
posterior belly of digastric
(not a Q) digastric triangle
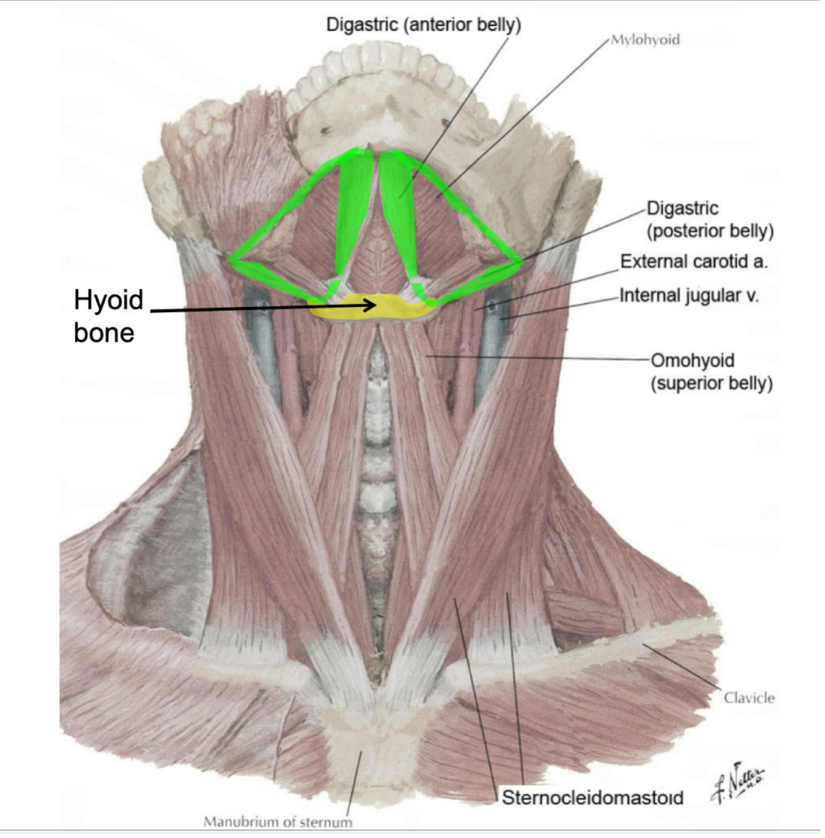
name the boundaries of the muscular triangle of the neck
median plane of neck
superior belly of omohyoid
SCM
name the contents of the muscular triangle
infrahyoid muscles
thyroid gland
parathyroid glands
larynx
trachea
esophagus
(not a Q) muscular triangle
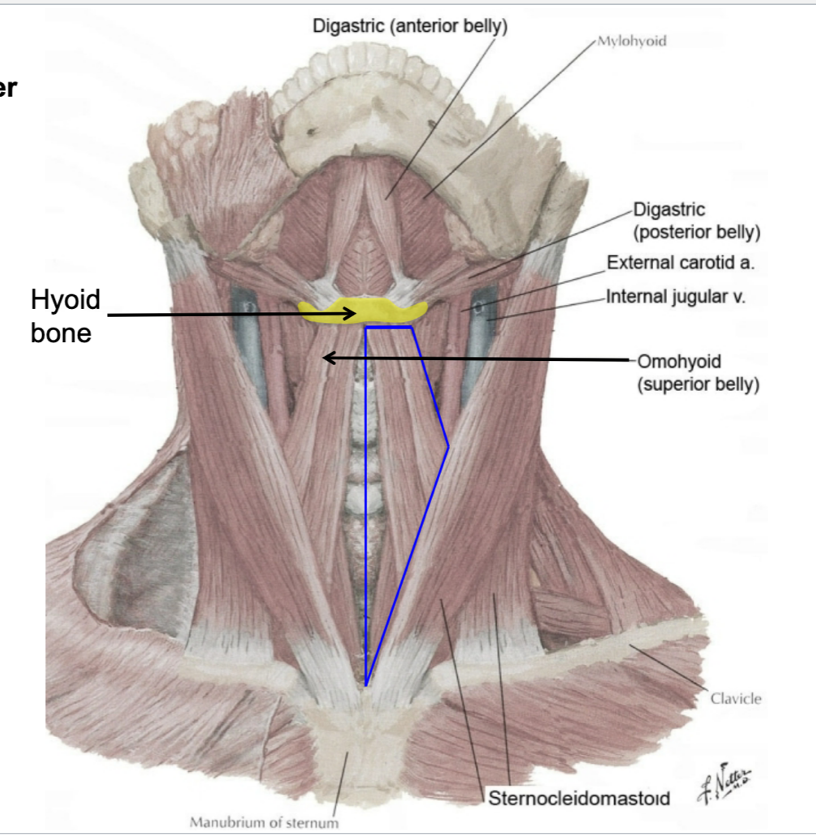
name the boundaries of the carotid triangle
superior belly of omohyoid
posterior belly of digastric
anterior border of SCM
name the contents of the carotid triangle
bifurcation of the common carotid into external/internal carotid arteries
carotid sinus
carotid body
vagus nerve
hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
internal jugular vein
(not a Q) carotid triangle
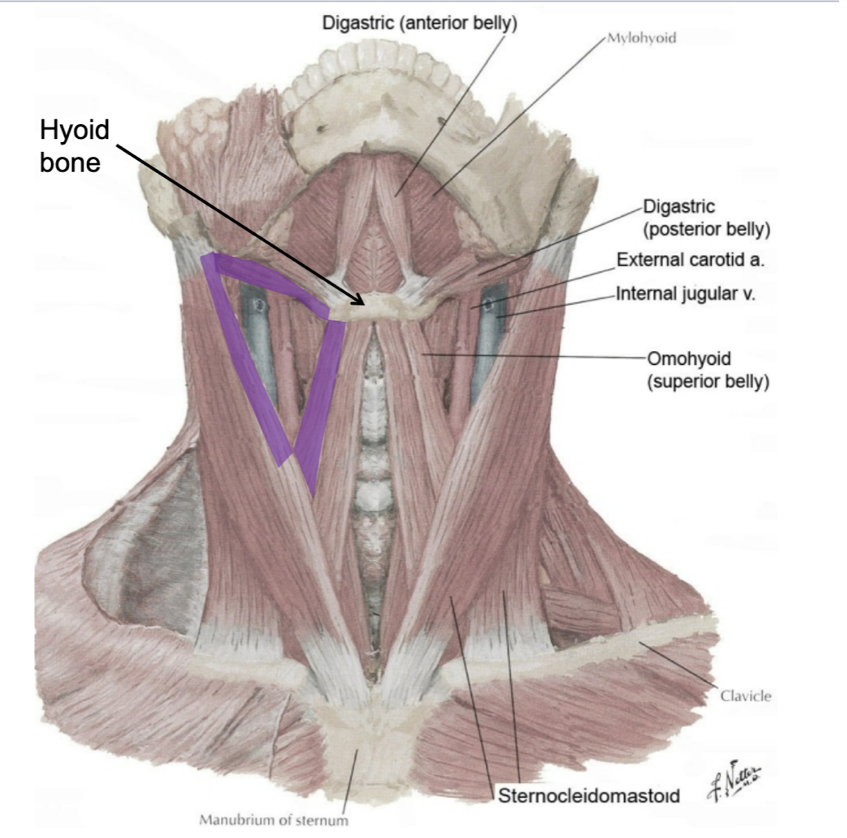
what bone do the suprahyoid muscles have a relationship with?
the suprahyoid muscles are attached or related to the superior aspect of the hyoid bone
true or false: the suprahyoid muscles are paired muscles
true
name the suprahyoid muscles
anterior belly of digastric
posterior belly of digastric
stylohyoid
mylohyoid
geniohyoid
which 2 suprahyoid muscles are continuous?
anterior and posterior bellies of digastric
what are the attachments of posterior belly of digastric?
mastoid process
hyoid bone
what is the innervation of posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid?
CN VII
(facial nerve)
what are the actions of posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid?
elevate, retract, and fix in place the hyoid
what is the innervation of anterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid?
CN V₃
(3rd division of trigeminal nerve)
what are the actions of anterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid?
depress (poorly) the mandible
elevate and fix in place the hyoid
geniohyoid is located deep to which muscle?
mylohyoid
(if you put a pin through mylohyoid, geniohyoid is the 2nd structure pierced)
true or false: geniohyoid is a suprahyoid muscle in the submental triangle
geniohyoid is a suprahyoid muscle
it is not in the submental triangle
what is the innervation of geniohyoid?
a branch of C1
(cervical nerve 1, NOT CN I)
(not a Q) suprahyoid muscles
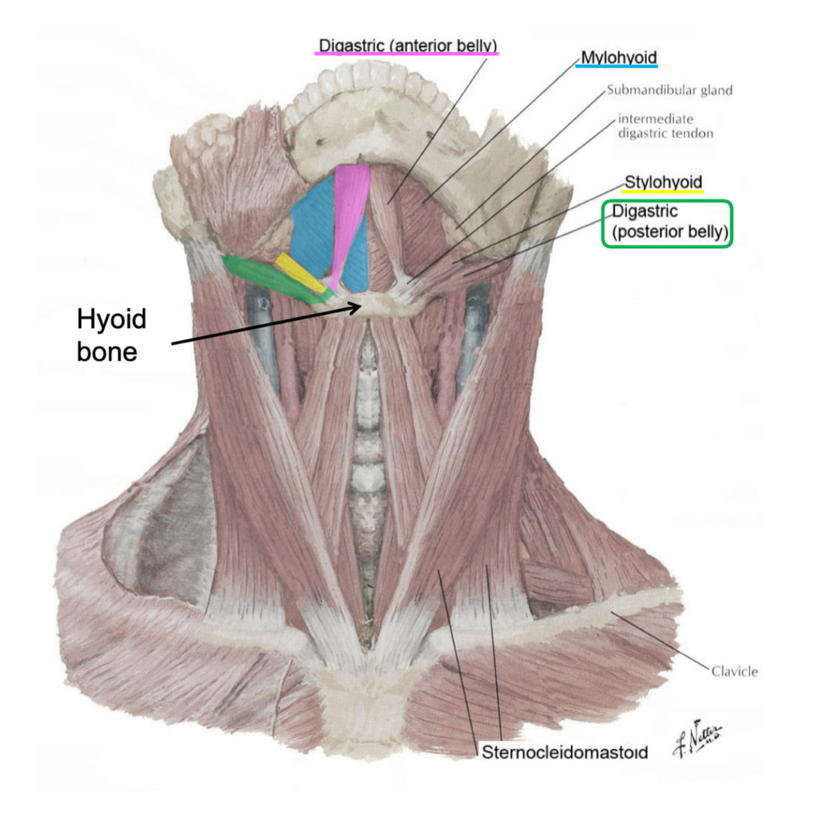
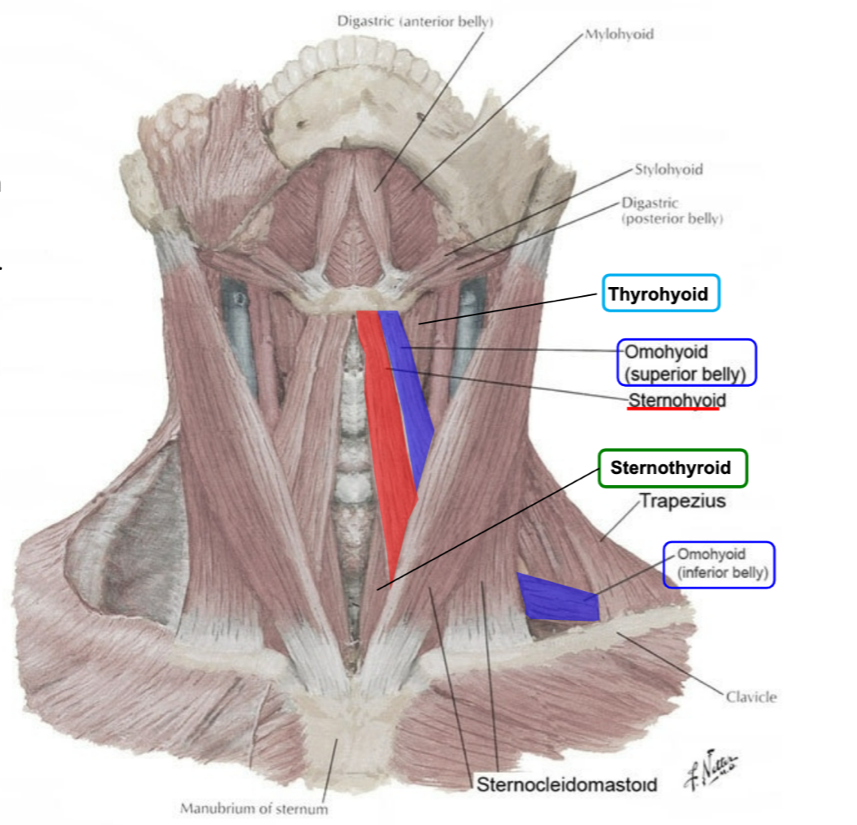
where do the infrahyoid muscles attach?
inferior side of hyoid bone
what are the infrahyoid muscles collectively known as?
strap muscles
name the infrahyoid muscles
omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies)
sternohyoid
sternothyroid
thyrohyoid
what are the actions of the infrahyoid muscles?
act on the hyoid to either depress it or fix it in place during swallowing
what is the innervation of the infrahyoid muscles?
ansa cervicalis innervates all the infrahyoid muscles except the thyrohyoid (which is innervated by a branch of C1)
(not a Q) infrahyoid muscles
(not a Q) arterial supply of the head and neck
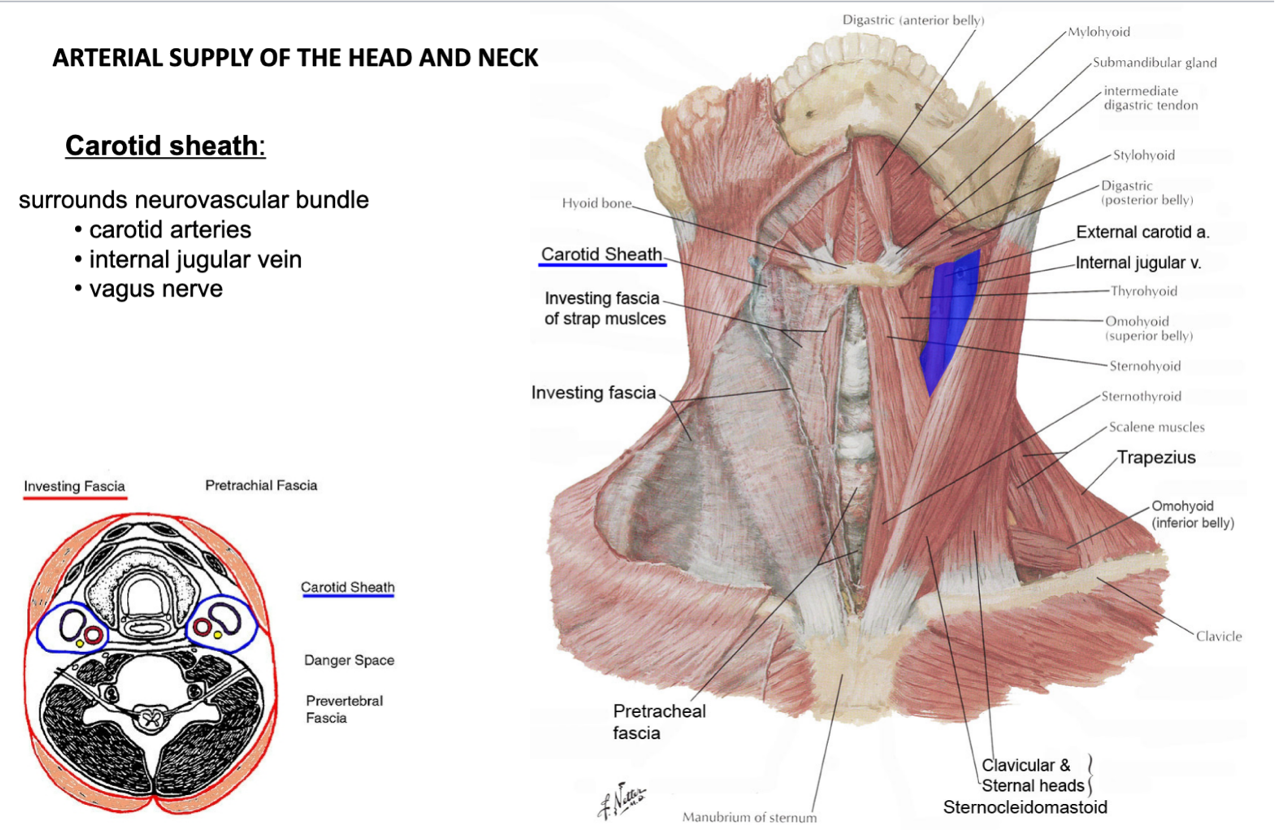
what fascia does the common carotid artery travel in?
carotid sheath
what does the external carotid artery supply?
primary supply of blood to neck and face
what does the internal carotid artery supply?
primary supply of blood to brain and orbit
what is the carotid sinus and where is it located?
the swelling that occurs at the branching of the internal carotid artery from the common carotid artery
it is a baroreceptor that regulates the blood pressure of the cerebral arteries
what is the carotid body and where is it located?
a small mass of tissue located at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery (lies in close relation with the carotid sinus)
it is a chemoreceptor responding to changes in blood CO₂ levels
(not a Q) arterial supply of the head and neck
*can’t really see carotid sinus and body in lab, but must know their approximate locations
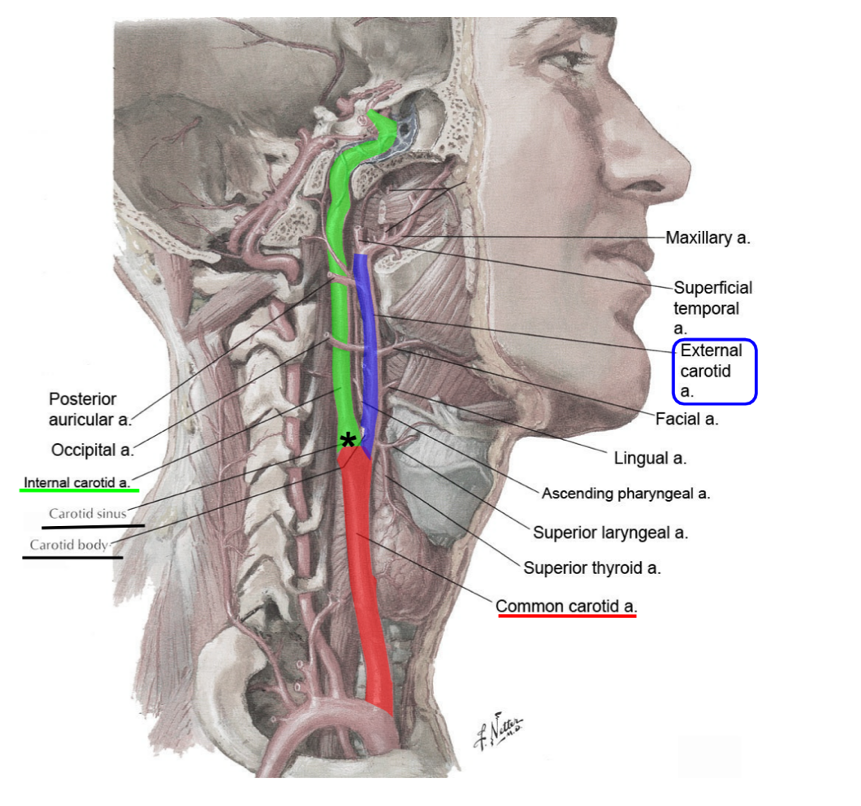
name the branches of the external carotid artery
superior thyroid artery
lingual artery
facial artery
maxillary artery
superficial temporal artery
ascending pharyngeal artery
occipital artery
posterior auricular artery
name the 3 branches of the external carotid artery that are generally easy to find in the neck
superior thyroid artery
lingual artery
facial artery
what does the superior thyroid artery supply?
it is one of the arteries to the thyroid gland
what branches off of the superior thyroid artery?
superior laryngeal artery
what does the superior laryngeal artery supply?
larynx
what structure does the superior laryngeal artery pierce through?
thyrohyoid membrane
what does the lingual artery supply?
tongue
parts of oral cavity
what does the facial artery supply?
passes deep to the submandibular gland to supply the external face and oral cavity
(may arise in common with lingual artery)
name the branches of the facial artery
inferior labial artery
superior labial artery
(supplies upper and lower lips)
what is the terminal branch of the facial artery?
angular artery
(this is a renaming of the facial artery by the nose)
(not a Q) branches of the external carotid artery
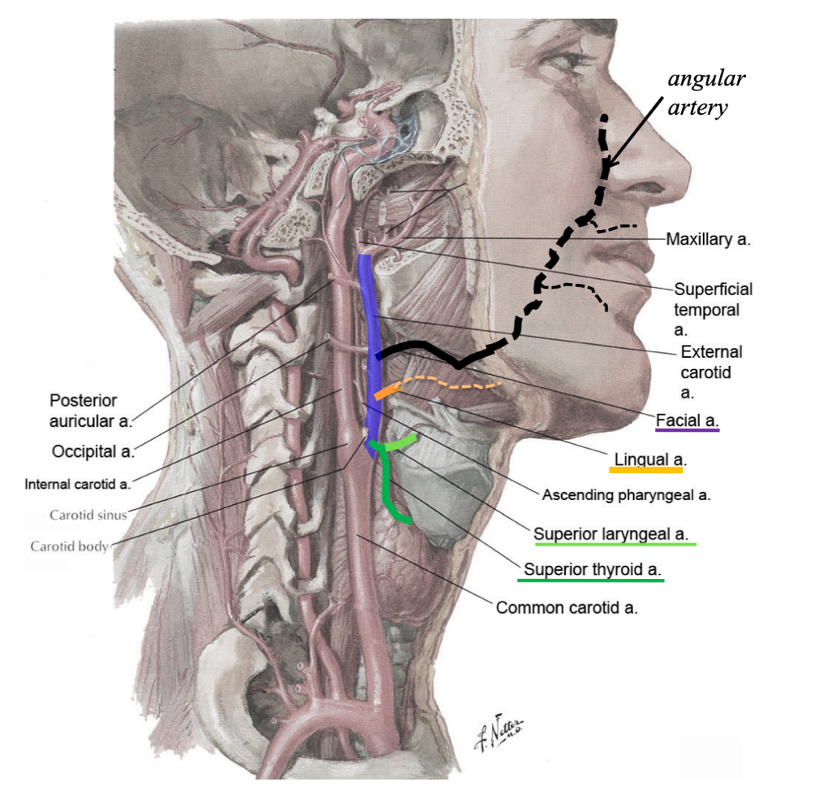
what does the maxillary artery supply?
infratemporal fossa
nasal cavity
teeth
what does the superficial temporal artery supply?
temporal region of the scalp
side of the head