Chapter 3 - Atoms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:50 PM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
Democritus
Argued that if you cut a substance in half, what results is two pieces of the same substance and that, eventually, you would reach a point where you could no longer divide it and still have the same substance.
2
New cards
Antoine Lavoisier
Created the Law of Conservation of Mass
3
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
In chemical reactions, matter is neither created or destroyed.
4
New cards
John Dalton
Created the Modern Atomic Theory
5
New cards
Unchanged Atomic Theory
\-Elements are made of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms
\-The atoms of each element are unique
\-Atoms can join together in whole number ratios to form compounds
\-Atoms are unchanged in chemical reactions
\-The atoms of each element are unique
\-Atoms can join together in whole number ratios to form compounds
\-Atoms are unchanged in chemical reactions
6
New cards
Three Foundational Ideas of Chemistry
1. All matter is composed of atoms
2. The atoms of each element have unique characteristics and properties
1. In chemical reactions, atoms are not changed, but combine in whole - number ratios to form compounds
7
New cards
How are we able to visualize atoms on a metal surface?
Through scanning tunneling microscopy
8
New cards
How can we visualize the arrangement of atoms?
X - Ray Crystallography
9
New cards
How does X - Ray Crystallography work?
A solid is bombarded with X - Rays, and based on the patterns the X - Rays form as they pass through the material, and scientists are able to visualize the arrangement of atoms in the solid
10
New cards
Dmitri Mendeleev
Father of the Periodic Table
11
New cards
The periodic table has rows that are called periods, and columns that have _____ _____, and they are called groups or families
Similar properties
12
New cards
The blocks of elements on the left and right sides of the periodic table are the _____________
Main group elements
13
New cards
The elements in the middle block are called the _________
Transition elements
14
New cards
At the bottom of the periodic table are two additional rows, called the ___________________
inner transition elements
15
New cards
On the left hand side of the periodic table, usually solid at room temperature, can be molded into different shapes, and they conduct heat and electricity
Metals
16
New cards
In the columns 2 - 13 and are harder and less reactive than the metals of the columns 1 - 2
Transition Elements
17
New cards
Has heavier, naturally occurring metals called rare earth metals
The first row of the inner transition metals, lanthanide series
18
New cards
The first few are mostly man made, although trace amounts have been found in nature
The second row of the inner transition metals, the actinide series
19
New cards
The primary atomic building blocks for all plant and animal life; are found on the upper - right side of the periodic
Nonmetals
20
New cards
Has a stair step pattern between the metals and nonmetals, they conduct electricity but not as efficiently as metals do (semi conductors) and are essentially the components of modern electronics
Metalloids
21
New cards
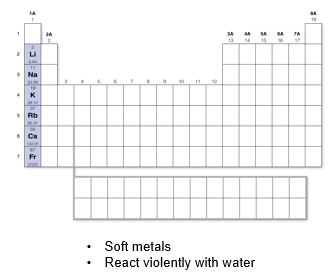
Group 1A: Alkaline Metals
Soft metals that react violently with water or even with moisture in the air
22
New cards
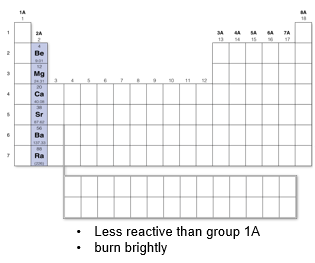
Group 2A: Alkaline Earth Metals
Less reactive than group 1A and burn brightly when combined with oxygen
23
New cards
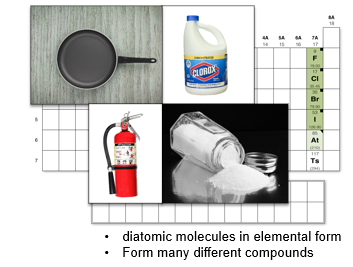
Group 7A: Halogens
Have diatomic molecules in elemental form and form many different compounds that make substances such as bleach, Teflon, fire retardants, antiseptics, and table salt
24
New cards
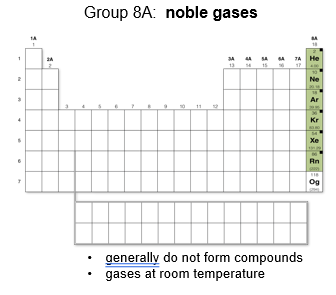
Group 8A: Noble Gases
Generally do not form compounds because they do not react with other elements and are gases at room temperature.
25
New cards
Which part of Dalton’s Atomic Theory turned out to not be true?
Atoms could not be broken into smaller peices
26
New cards
Subatomic particles
Small components that make up atoms
27
New cards
What properties do we use to make up atoms and subatomic particles?
Their mass and their charge
28
New cards
What is electricity and electrical energy?
A form of energy that involves the motion of charged particles
29
New cards
Alessandro Volta
Built the first electrochemical cell (battery)
30
New cards
What was the result of Volta’s device?
An electrical current, the flow of charged particles from one side of the battery to another
31
New cards
Using this controlled electrical energy of the battery, scientists later discovered that you can use electrical energy to
separate some compounds, such as water, into their elements and to discover elements in a few short years
32
New cards
Plum Pudding Model
Created by Thomson and other scientists; small, negative electrons were spread throughout the muffin
33
New cards
Alpha Particles
Positively charged particles
34
New cards
Rutherford knew that the Plum Pudding Model was incorrect when
some of the alpha particles reflected off of the film and back toward the alpha particle source, instead of passing straight through
35
New cards
What was Rutherford’s conclusion?
Most of the atom was empty space, with a very dense nucleus at the center of each atom
36
New cards
Although the nucleus contains almost all of the mass of the atom, it is ______________
incredibly dense, packing the mass into a very tiny volume
37
New cards
Atomic number
integer value normally seen above the atomic symbol of the periodic table and also tells us the number of electrons in the neutral atom
38
New cards
Mass number
the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom
39
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms that have the same atomic number, but a different mass number
40
New cards
If we want to show the atomic number, we place the atomic numbers at the ______________________
lower left - hand side of the atomic symbol
41
New cards
If we want to show the atomic mass of an atom, we plan the atomic mass number at the ______________
upper left - hand side of the atomic symbol
42
New cards
The mass number on the periodic table is the ____________
average mass number
43
New cards
Average atomic mass
A weight average of the different isotopes of an element
44
New cards
What is the equation for the average atomic mass?

45
New cards
Bohr Model
Electrons orbit the nucleus like planets orbit the sun
46
New cards
Quantum Model
Electrons behave as both particles and as waves
47
New cards
Atoms gain or lose electrons to form
ions