Steve Power Notes: MRI Physics and Sequence Review: T1, T2, Artifacts, and Parameters
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
What are the intrinsic tissue characteristics in MRI?
T1 and T2 relaxation times and Proton Density.
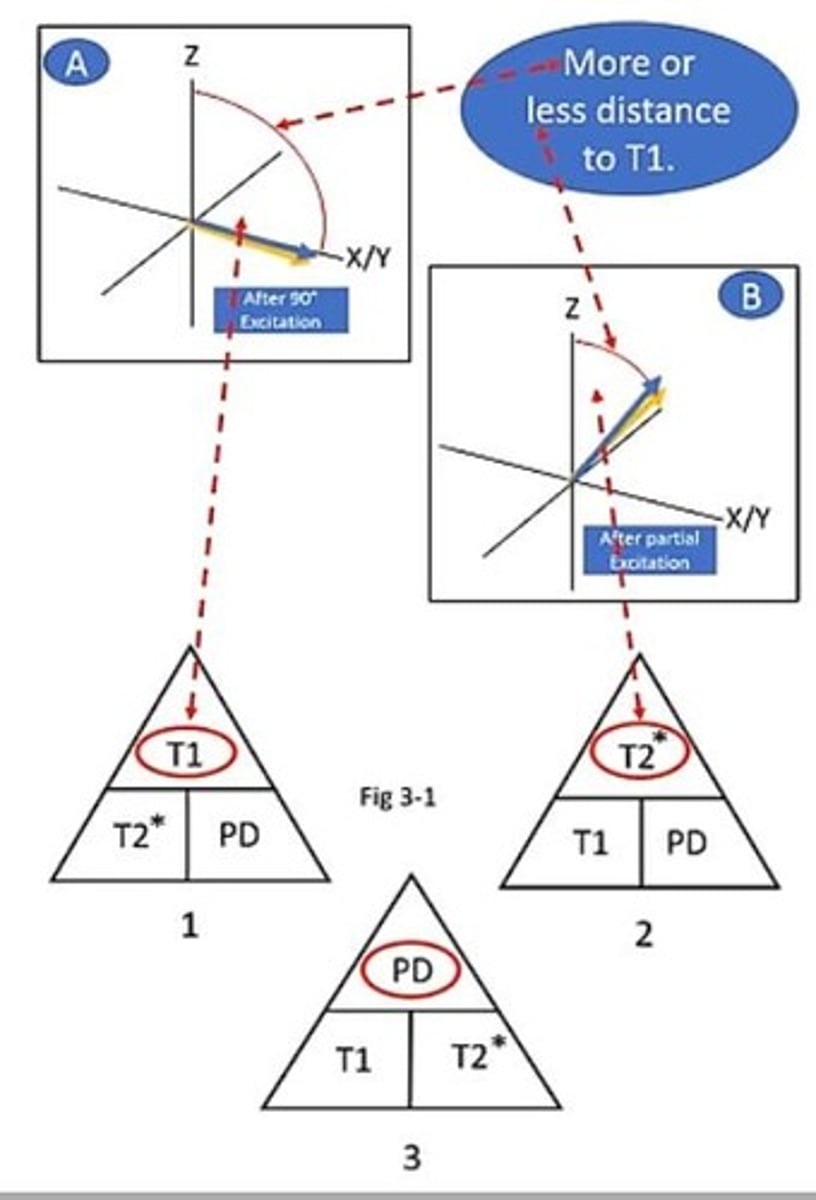
What is the definition of T1 relaxation?
The time it takes for 63% of the Net Magnetization Vector (NMV) to recover with B0.
What is T1 relaxation also known as?
T1 Recovery and Spin Lattice relaxation.
What is the T2 relaxation time?
The time for the NMV in the transverse plane to decay to 37% of its original value.
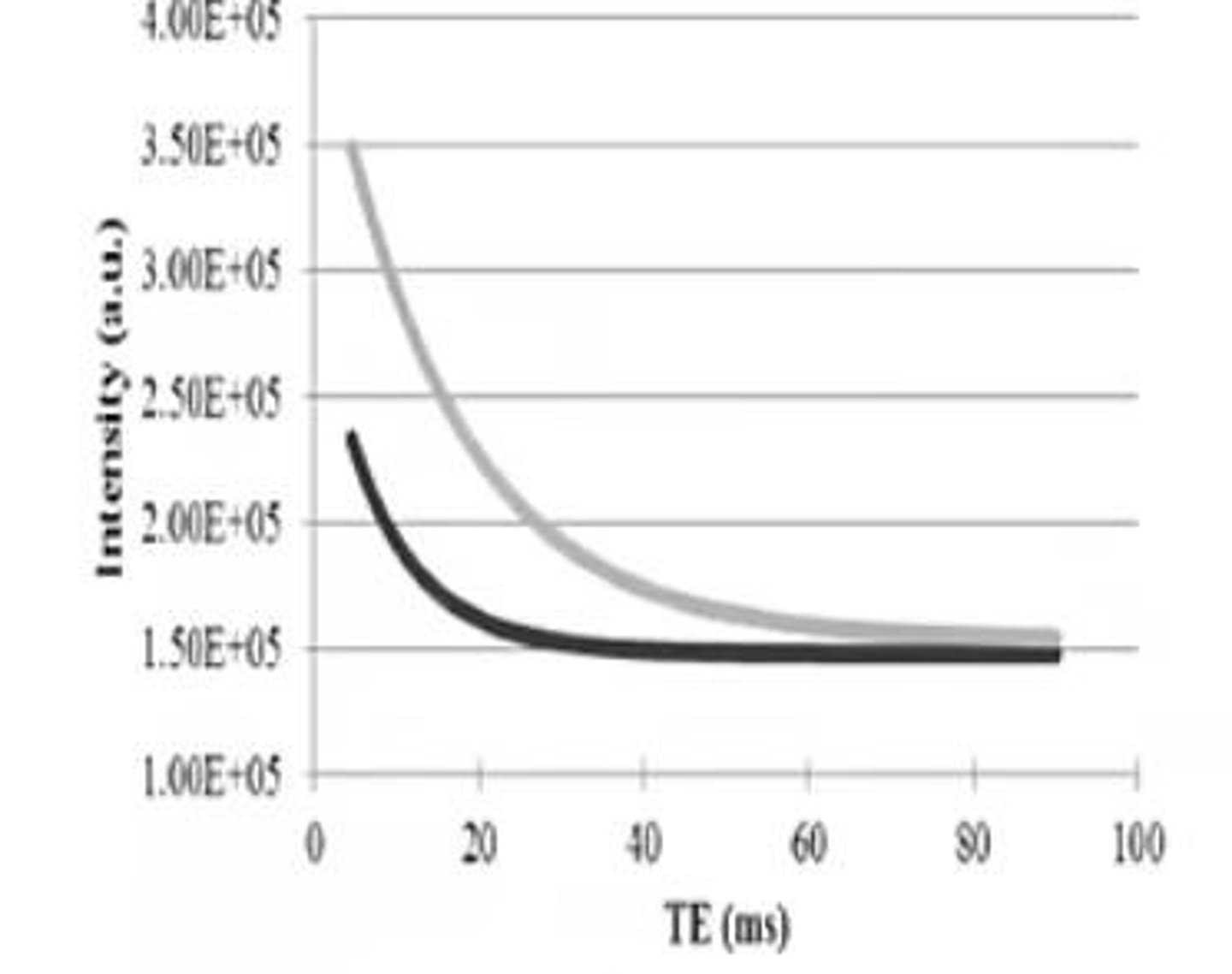
What is T2 relaxation also referred to as?
Spin-Spin relaxation or True T2.
How do T1 and T2 relaxation times compare?
T2 time is always several times shorter than T1 time.
What is Proton Density (PD) in MRI?
A tissue characteristic that indicates the amount of protons, often related to water content.
What are the three major image weightings produced by MRI?
T1, T2, and Proton Density (PD).
What does TR stand for in MRI?
Time of Repetition, the time from one 90-degree RF pulse to the next for the same slice.
How does TR affect T1 contrast?
Longer TRs allow both long and short relaxing protons to contribute to the signal, while shorter TRs favor short relaxing protons.
What is the relationship between TE and T2 contrast?
TE controls T2 contrast; longer TE allows more signal from long T2 tissues.
What happens during T1 relaxation?
Protons return to alignment with B0, releasing energy (heat) imparted during excitation.
What is the significance of T1 contrast?
It indicates the difference in T1 recovery rates between different tissues.
What is the significance of T2 contrast?
It indicates the difference in T2 decay rates between different tissues.
What is the effect of a long TR on image brightness?
Both long and short relaxing protons will contribute to the signal, resulting in a brighter image.
What is the effect of a short TR on image brightness?
Only short relaxing protons contribute to the signal, resulting in a brighter image for those tissues.
What is the definition of TE?
Time of Echo, the time from the center of the excitation pulse to the center of the echo.
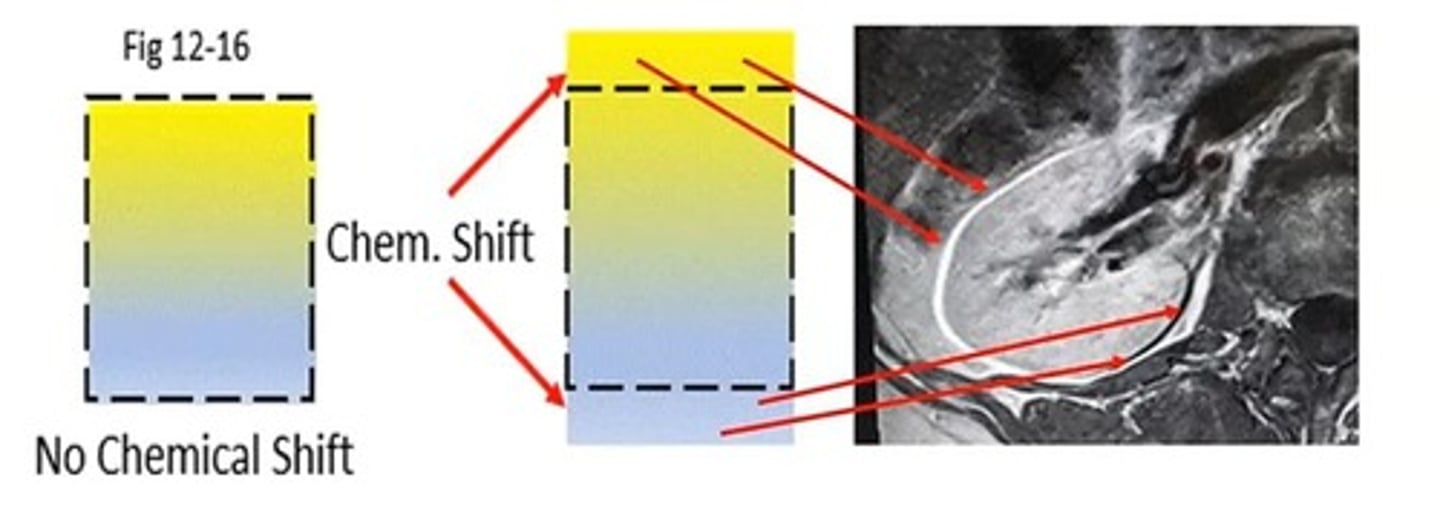
What happens to fat and water signals at long TE?
Fat signals decrease while water signals increase, making water appear brighter.
What is the purpose of the Larmor Equation in MRI?
It relates the frequency of precession of protons to the strength of the magnetic field.
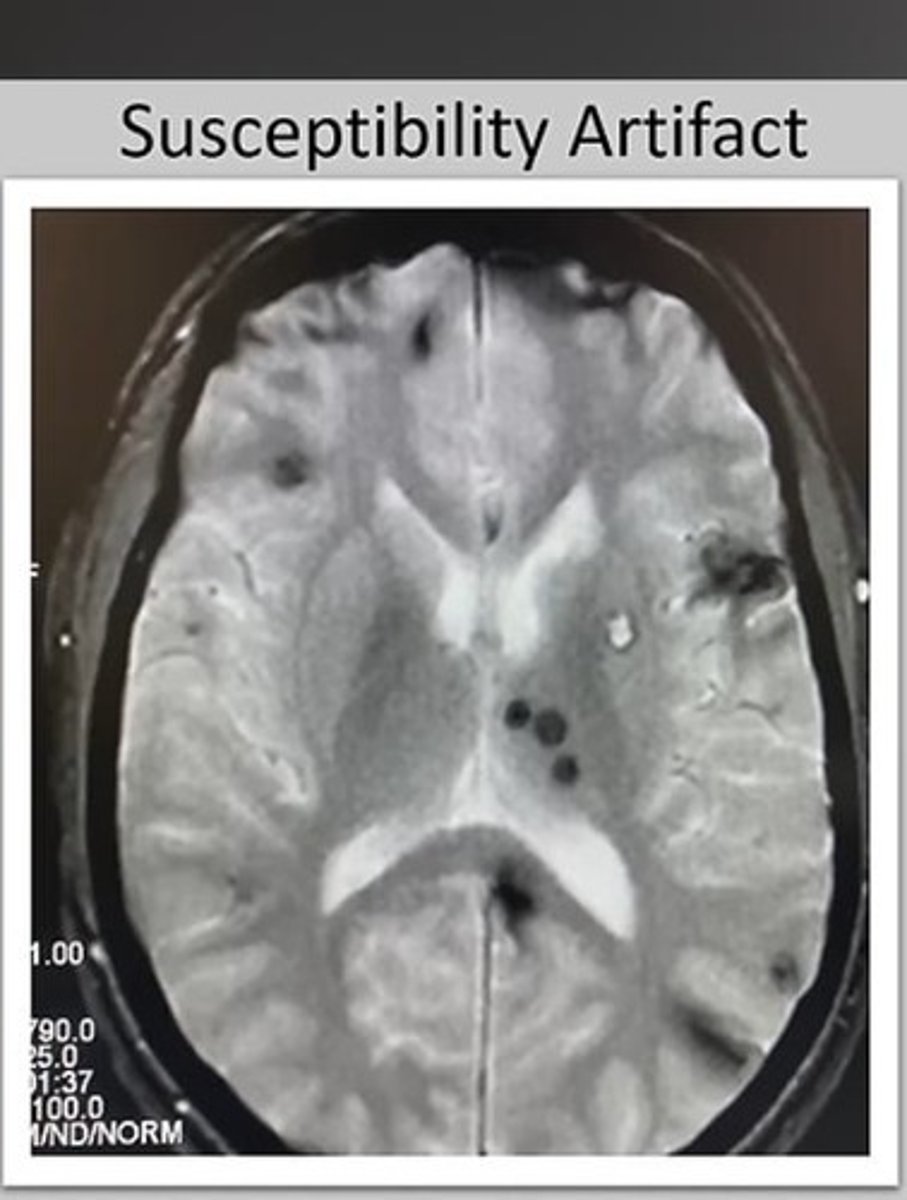
What types of artifacts can occur in MRI?
Motion, RF, Wrap, Chemical Shift, Cross-talk, Grad Warp, Metal susceptibility, Herring Bone, and Annefact.
What is the role of the Flip Angle in MRI?
It influences the amount of signal generated and the contrast of the image.
What is the effect of increasing TE on T2 contrast?
As TE increases, T2 contrast increases, allowing more signal from long T2 tissues.
What is the relationship between TR and SNR?
As TR shortens, T1 contrast increases while SNR decreases, and vice versa.
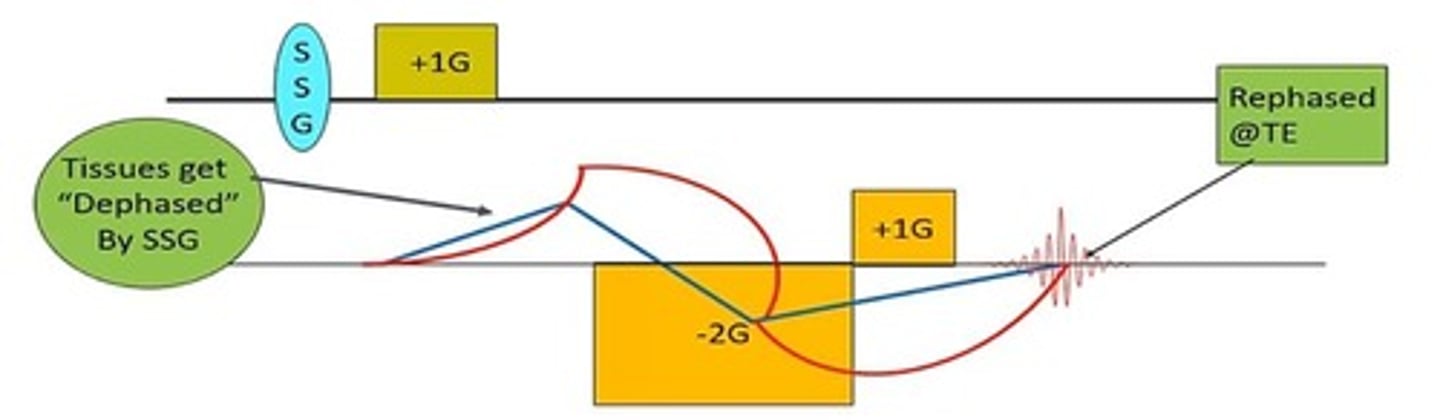
What does the term 'de-phase' refer to in MRI?
The spreading out of protons in the transverse plane after the RF pulse is turned off.
What is the significance of the T1 and T2 relaxation curves?
They illustrate the recovery and decay processes of different tissues over time.
What happens to T2 relaxation vectors as TE lengthens?
More T2 relaxation occurs, allowing longer T2 vectors to be reflected in the echo.
How does water appear compared to fat in MRI imaging?
Water appears brighter than fat due to its larger net magnetization vector (NMV) at TE.
What is the effect of long TE on fast relaxing protons?
Fast relaxing protons (like fat and proteins) have mostly left the X/Y plane, resulting in less signal.
What is an Echo Train Length (ETL) in MRI?
ETL refers to having multiple 180-degree refocusing pulses for each slice per TR, resulting in multiple echoes.
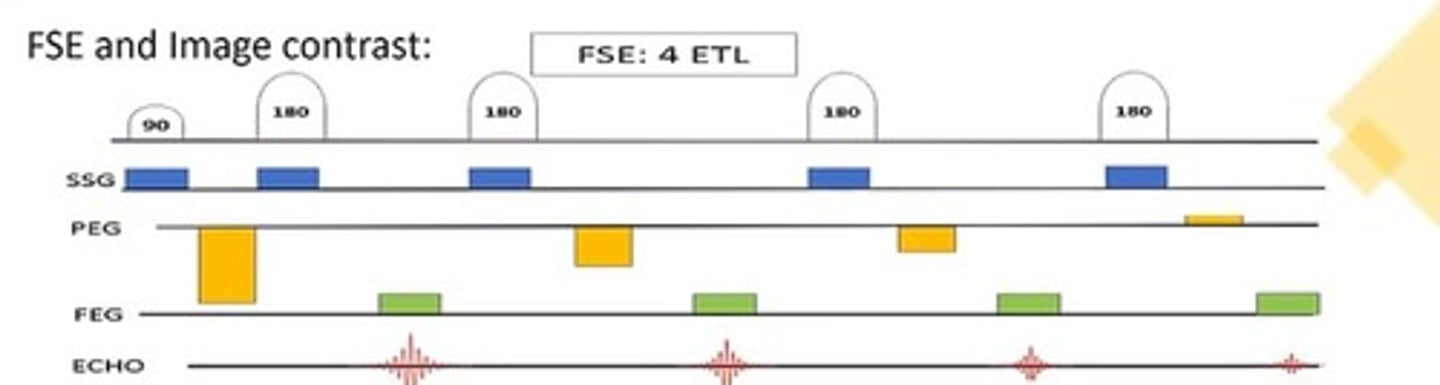
How does ETL affect scan time in FSE/TSE sequences?
Scan time is reduced by a factor of the ETL.
What is the relationship between echo train length and T2 weighting?
As ETL increases, echoes become progressively more T2 weighted.
What is the purpose of the Inversion Time (TI) in Inversion Recovery sequences?
TI determines which tissue will be suppressed, either fat or CSF.
How does a short TI affect T1 tissues?
A short TI suppresses short T1 tissues.
What is the significance of the 'Null Point' during TI?
If a tissue's vector is at the Null Point at the end of TI, that tissue will be suppressed.
What is the role of Flip Angle (F/A) in Gradient Echo (GRE) sequences?
F/A affects image contrast by determining how far the NMV is pushed into the X/Y plane.
What is the effect of a large Flip Angle in GRE?
A large F/A (60-70 degrees) increases T1 contrast in the images.
How does TE influence fluid brightness in GRE?
Longer TE results in brighter fluid, similar to T2 weighting in Spin-Echo.
What does weighting in MRI refer to?
Weighting indicates the dominance of one type of contrast (T1, T2, or PD) over the others in an image.
What is MR contrast?
MR contrast is the difference in signal intensities between tissues, creating a bright and dark appearance.
How does TR affect T1 contrast in MRI?
Short TR maximizes T1 contrast by allowing less time for long T1 tissues to relax.
What are the three usable TR/TE combinations for MRI weighting?
1. Short TR + Short TE for T1; 2. Long TR + Long TE for T2; 3. Long TR + Short TE for PD.
What is the effect of a long TR and short TE on image contrast?
It minimizes T1 and T2 contributions, allowing proton density to dominate.
What are the three aspects of image quality in MRI?
Contrast, Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), and Resolution.
What is the importance of contrast in MRI sequences?
Contrast is crucial for distinguishing between different tissues in an image.
What happens to SNR as ETL lengthens?
SNR decreases as ETL lengthens.
What is the effect of using a shallow Flip Angle in GRE? what degrees?
A shallow F/A (10-20 degrees) results in less T1 contrast and makes T2 contrast more visible.
What is the significance of the effective TE (ETE) in MRI?
ETE is critical for achieving the desired image contrast in the center lines of k-space.
How do T1 and T2 tissues differ in terms of relaxation?
T1 tissues (like fat) relax quickly, while T2 tissues (like CSF) relax slowly.
What is the impact of TR on tissue saturation in MRI?
Short TR can lead to saturation of long T1 tissues, resulting in low signal.
What is the relationship between TR, TE, and image quality?
TR and TE combinations are used to optimize contrast, SNR, and resolution in MRI images.
What is the definition of TE in MRI?
TE stands for Echo Time, the time from the center of the excitation pulse to the center of the echo.
How does TR affect image contrast?
TR controls T1 contrast, while TE controls T2 contrast.
What effect does increasing the Flip Angle (F/A) have on T1 contrast?
Increasing the Flip Angle maximizes T1 contrast.
What is the role of TI in Inversion Recovery?
TI is used to suppress tissues with different T1 relaxations.
What happens to T1 relaxing tissues with short and long TI?
Short TI suppresses long T1 relaxing tissues, while long TI suppresses long T1 relaxing tissues such as fluids.
What is ETL in MRI?
ETL stands for Echo Train Length, a series of 180-degree refocusing pulses each causing an echo.
How does increasing ETL affect image quality?
As ETL increases, the contrast becomes more T2 weighted, RF exposure increases, and blurring can adversely affect image quality.
What is SNR in MRI?
SNR stands for Signal to Noise Ratio, which compares the amount of signal generated with the sequence to the amount of noise in the system.
How does Field of View (FOV) affect SNR?
FOV is a huge contributor to SNR; doubling the FOV increases SNR by a factor of 4, while halving the FOV lowers SNR to 1/4th.
What is the relationship between FOV and pixel size?
Pixel size is calculated as FOV divided by the scan matrix.
What happens to resolution when the FOV is enlarged with no change in scan matrix?
Enlarging the FOV increases pixel size, which decreases resolution.
What are isotropic and anisotropic pixels?
Isotropic pixels have equal dimensions (2D), while anisotropic pixels do not have equal dimensions.
What is the effect of slice thickness on SNR and resolution?
A thicker slice increases SNR but decreases resolution, while a thinner slice decreases SNR but increases resolution.
How does the Slice Select Gradient (SSG) affect slice thickness?
The amplitude of the SSG controls slice thickness; a steeper SSG results in a thinner slice.
What is the impact of a higher scan matrix on pixel size and SNR?
A higher scan matrix results in smaller pixels, leading to lower SNR but higher resolution.
What does the term 'partial volume effect' mean?
Partial volume effect refers to the signal intensity of a pixel being an average of all tissues contained within it.
What is the formula for calculating scan time in MRI?
Scan time is calculated as TR x Phase x NEX.
What is the significance of the frequency encoding gradient (FEG) in determining FOV?
The amplitude of the FEG controls the size of the FOV; a lower amplitude FEG results in a larger FOV.
What is the relationship between slice thickness and RF bandwidth?
To achieve a thicker slice at constant SSG amplitude, a wider transmitted bandwidth is needed, which requires a longer RF pulse.
What happens to image contrast when changing the FOV?
Image contrast does not change with a change in the FOV.
How does the number of phase encodes affect scan time?
More phase encodes result in a longer scan time as more TRs are needed to fill k-space.
What is the impact of decreasing the phase matrix on SNR, resolution, and scan time?
Decreasing the phase matrix increases scan time, decreases resolution, and decreases SNR.
What is a voxel?
A voxel is a three-dimensional unit of volume in imaging, representing the smallest distinguishable box-shaped part of a three-dimensional space.
What is the effect on SNR, resolution, and scan time when the phase matrix is decreased?
SNR increases, resolution decreases, scan time decreases.
What are voxels and how do they relate to 2D sequences?
Voxels represent 3D volume elements; 2D sequences also have voxels with thickness as the third dimension.
How do you calculate voxel dimensions for a 180 FOV and a 256x256 matrix with 4mm thick slices?
Voxel dimensions are calculated as 180/256 = 0.70mm for both width and height, with a thickness of 4mm.
What is the voxel volume for dimensions 0.70x0.70x4mm?
The voxel volume is 0.70 x 0.70 x 4mm = 1.96mm³.
What are isotropic voxels and why are they ideal for reformatting?
Isotropic voxels have the same dimensions in all directions, making them ideal for accurate multiplanar reconstructions.
Which scan factors yield the most isotropic voxel?
A 320mm FOV, 224 x 320 matrix, and a 1mm thick slice.
What does the frequency matrix indicate in MRI?
It tells the receiver how many times to sample the echo, affecting the minimum TE.
What is receiver bandwidth (Rec. B/W) in MRI?
Rec. B/W is the sampling rate of frequencies across the FOV, impacting noise and SNR.
How does a wide receiver bandwidth affect SNR?
A wide bandwidth decreases SNR because it samples more noise earlier in echo formation.
What are the trade-offs between wide and narrow receiver bandwidth?
A wide bandwidth allows for shorter TE but results in lower SNR; a narrow bandwidth captures more signal but may require longer TE.
What do NEX, Acq, and NSA represent in MRI?
They refer to the number of excitations (NEX), acquisitions (Acq), and number of signal averages (NSA), affecting SNR and scan time.
What is the relationship between SNR and the number of signal averages?
SNR changes with the square root of the number of samples; it does not have a 1:1 ratio.
What is concatenation in MRI?
Concatenation links slices together in a series to achieve desired image contrast, often used for large stacks of slices.
What are the two main types of pulse sequences in MRI?
Spin-Echo (SE) and Gradient Echo (GRE); all other sequences are variations of these.
What characterizes a Spin-Echo sequence?
It includes a 90-degree excitation pulse followed by a 180-degree refocusing pulse.
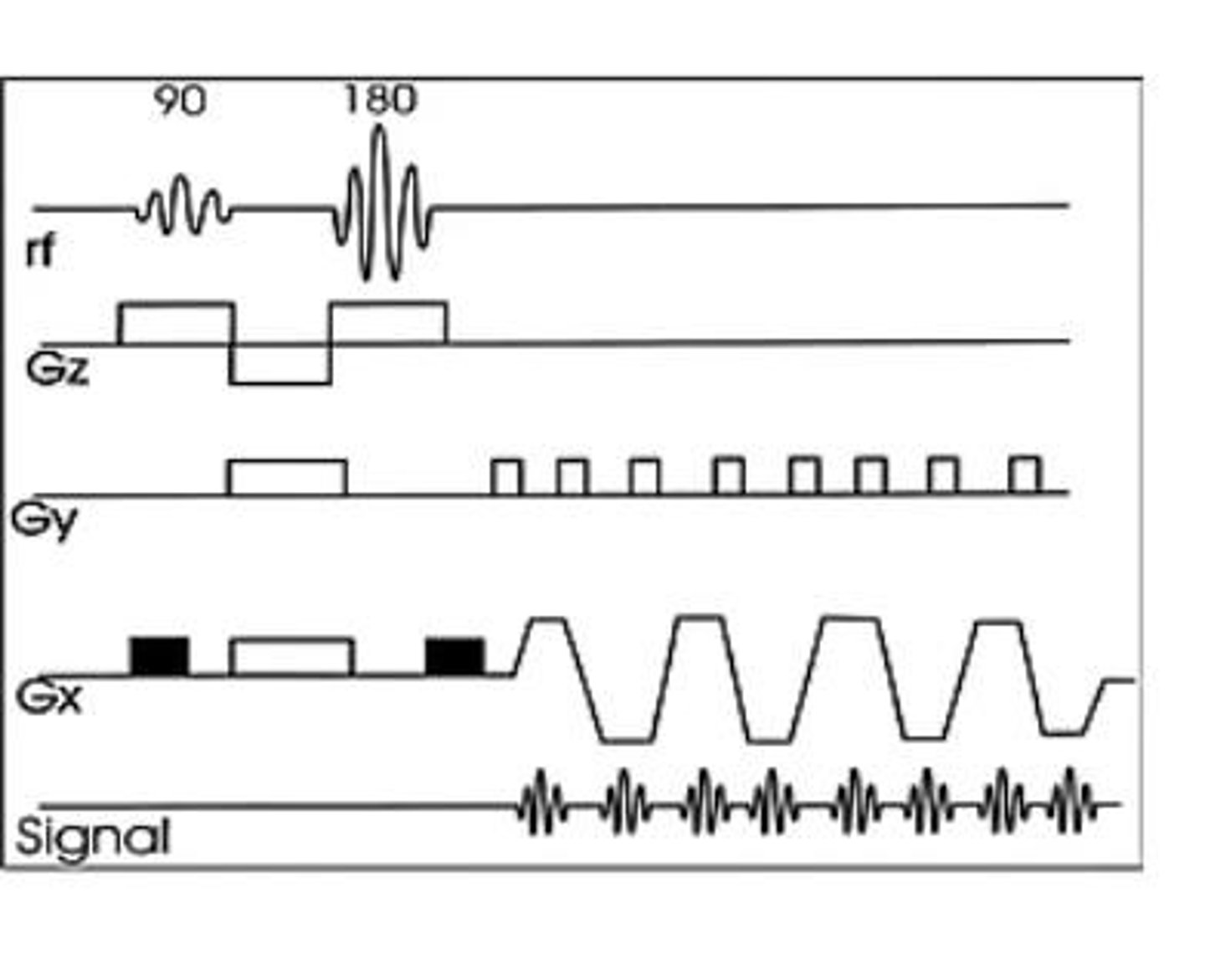
What is a key difference between Spin-Echo and Gradient Echo sequences?
Gradient Echo sequences do not include a 180-degree RF pulse, allowing for shorter minimum TR and TE.
What are the 'Big 3' factors that GRE sequences are sensitive to?
Main magnetic field inhomogeneities, local magnetic field inhomogeneities, and magnetic susceptibility differences.
What causes main magnetic field inhomogeneities in MRI?
The presence of the patient, which introduces variations in the magnetic field.
What is the purpose of a 180-degree refocusing pulse in Spin-Echo sequences?
It corrects for dephasing caused by magnetic field inhomogeneities and boosts SNR.
What is the significance of slice thickness in voxel dimensions?
Slice thickness is the third dimension in voxel calculations, affecting overall voxel volume.
How does the sampling rate affect the minimum TE in MRI?
A higher sampling rate (wide bandwidth) results in a shorter minimum TE but may lower SNR.
What is the minimum TE in relation to receiver bandwidth?
A narrow receiver bandwidth typically allows for a longer minimum TE, capturing more signal.
What is the effect of using fat suppression techniques in MRI?
Fat suppression sequences are often signal-starved and require careful consideration of SNR.
What is the purpose of using multiple TRs in k-space filling?
Using multiple TRs helps control motion artifacts by filling lines of k-space in succession.
What are local magnetic field inhomogeneities?
Small variations in the magnetic field within the field of view (FOV) being scanned, affected by factors like dental work or surgical clips.
What is magnetic susceptibility?
The tendency of some tissues to either attract or repel the magnetic field, leading to differences in signal.
What happens when brain tissue and blood are adjacent in an MRI?
Differences in magnetic susceptibility occur, causing variations in the signal due to the contrasting properties of the tissues.