MedChem
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is type of enzyme is AChE and what are the important parts of the catalytic site?
serine hydrolase
ACh bind and undergoes hydrolysis mediated by serine to form choline and acetic acid (rapid 1-2 min)
catalytic triad
glutamic acid
histidine
serine - covalently binds with the carboxylic acid
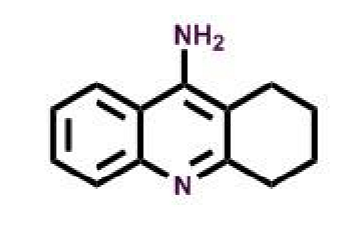
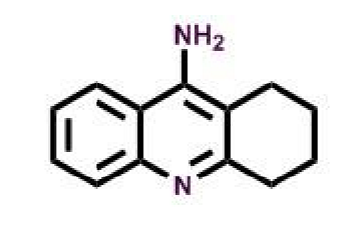
Tacrine
What allows tacrine to act as AChEI?
potent and reversible inhibitor
synthetic amino-acridine derivative
first gen
discontinues → hepatotoxic due to quinone metabolite
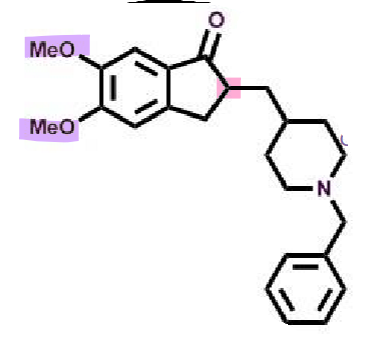
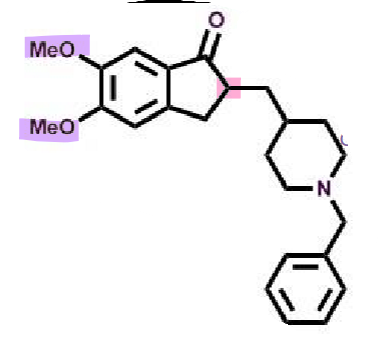
Donepezil
What makes donepezil an AChEI?
pharmacophore: indenone (fused rings)
lipophilic → longer half-life
piperidine → good oral bioavailability
2x methoxy → improved binding
racemic → both similar activity
potent and reversible
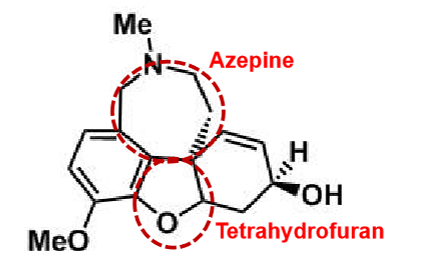
Galantamine
What makes galantamine a AChEI?
pharmacophores: azepine and tetrahydrofuran → enhance binding affinity
diasteromer (3 centers)
potent and reversible (less potent than donepezil)
alkaloid derived from plants
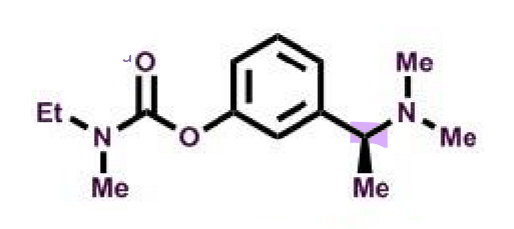
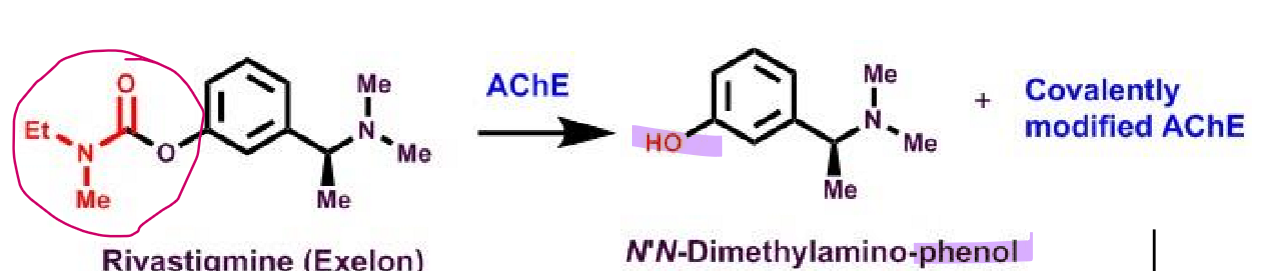
Rivastigmine
What makes rivastigmine a AChEI?
carbamate derivative (oxygen + amide)
important is what covalently binds
potent and covalent inhibitor
S-enantiomer has activity
metabolite also some activity
N’N-dimethylamino-phenol
What is the relative selectivity of AChE vs BuChE?
BuChE is isoform of AChE
as AD progresses AChE decreases and BuChE increases
donepezil > galantamine > rivastigmine
What causes the off target ADEs of AChEIs?
bind to muscarinic receptors in GI tract → N/V
bind to nicotinic receptors in skeletal muscle → muscle fatigue
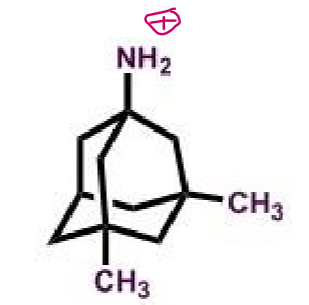
memantine
What makes memantine a NDMA antagonist?
pharmacophore: adamantane
lipophilic → gets drug into brain
primary amine protonated for ionic interactions with receptor
if change to secondary or tertiary amine decrease activity
reversible
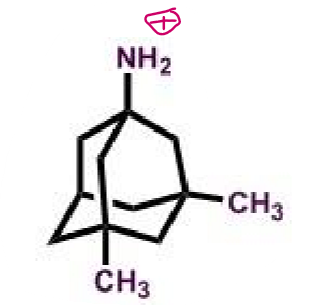
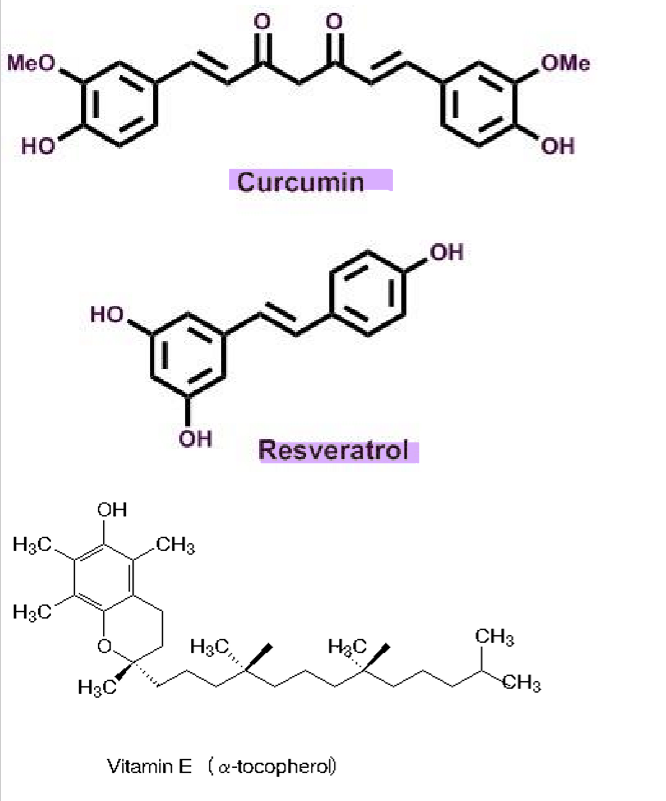
Curcumin
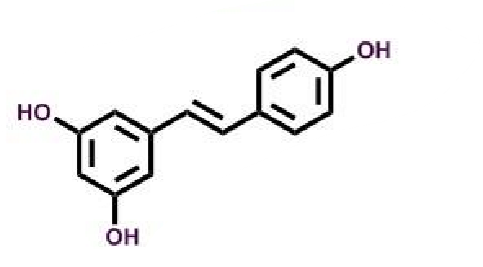
Resveratrol
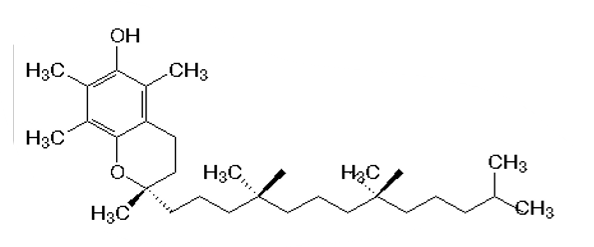
Vitamin E
What makes antioxidants effective in AD?
contain phenolic rings → which interact/quench reactive oxygen species
can chelate metal ions (iron, zinc and copper) which can promote reactive oxygen species